Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation on the Active Components, Antioxidant Activity and Enzymes on Hypoglycemic Activity in Vitro of Acanthopanax senticosus Leaves
-
摘要: 为了对刺五加叶在益生菌发酵保健品领域的应用提供理论基础,以刺五加叶为原料,采用嗜酸乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌、植物乳杆菌3种乳酸菌进行发酵,对发酵前后刺五加叶中活性成分含量变化进行研究,并评价刺五加叶乳酸菌发酵物的体外抗氧化作用与对降血糖相关酶的影响。结果表明:不同菌种的发酵能力存在差异,植物乳杆菌、嗜酸乳杆菌发酵显著增加了刺五加叶总黄酮的含量(P<0.05),较对照组增加2.02倍与1.45倍。3种乳酸菌发酵都显著增加了刺五加叶多糖、皂苷和异嗪皮啶的含量(P<0.05),其中多糖含量干酪乳杆菌发酵组最高,可达12.7 mg/g;皂苷含量植物乳杆菌发酵组最高,是对照组的1.9倍;异嗪皮啶含量干酪乳杆菌发酵组最高,是对照组的3.2倍。体外功能性评价实验显示,3种乳酸菌发酵都提高了刺五加叶1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)自由基清除能力、羟基自由基清除能力、超氧阴离子自由基清除能力和α-淀粉酶与α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制能力,且随发酵产物的浓度增加而增强。综合上述,乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶可以富集活性成分,增强抗氧化作用与降血相关酶的抑制能力,可作为刺五加叶功能食品加工重要手段。Abstract: In order to provide a theoretical basis for the application of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves in probiotic fermented health products, the Acanthopanax senticosus leaves were used as raw materials, and the three kinds of lactic acid bacteria were used for fermentation, namely Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus plantarum. After that, the changes in the content of bioactive compounds in Acanthopanax senticosus leaves fermented by lactic acid bacteria were studied, and the effect on antioxidant and inhibitory activity of hypoglycemic related enzymes in vitro were evaluated. The results showed that the fermentation abilities of the 3 strains were different. The fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus significantly increased the content of total flavonoids in Acanthopanax senticosus leaves (P<0.05), 2.02 times and 1.45 times higher than that in the control group. The content of polysaccharides, saponins and isoperidine in Acanthopanax senticosus leaves were significantly increased by fermentation of three strains of lactic acid bacteria (P<0.05), and the polysaccharide content of Lactobacillus casei fermentation group was the highest, reaching 12.7 mg/g. The saponin content of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation group was the highest, which was 1.9 times as high as that of the control. The content of isoperidine in Lactobacillus casei fermentation group was the highest, which was 3.2 times higher than that in control group. In vitro functional evaluation experiments showed that the fermentation by 3 lactic acid bacteria improved DPPH free radical scavenging ability, hydroxyl free radical scavenging ability, superoxide anion free radical scavenging ability, and α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition ability of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves, which increased with the increase of the concentration of fermentation products. To sum up, the fermentation of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves by lactic acid bacteria could enrich the bioactive compounds, enhance the ability of antioxidant and inhibition of hypoglycemic related enzymes, which could be used as an important way for processing functional food from Acanthopanax senticosus leaves.
-
Keywords:
- Acanthopanax senticosus leaves /
- Lactobacillus /
- fermentation /
- active ingredients /
- hypoglycemia /
- antioxidant
-
糖尿病是以高血糖为主要特征的慢性代谢性紊乱综合征,长期的高血糖会导致眼部、血管、神经等组织的慢性损害并引发功能障碍[1]。糖尿病已经成为重要的健康问题,全球糖尿病患病率从1980年的4.7%增加到了2014年的8.5%[2],而我国成年人中的患病率从2007年的9.7%上升到2017年的11.2%[3]。2型糖尿病是糖尿病的主要类型,临床治疗上主要应用胰岛素类注射剂与口服降血糖药物[4],其中二甲双胍、拜糖平(α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制)、西格列汀(DPP-IV抑制剂)等西药与甘露消渴丸[5]、降糖舒片[6]等中成药较为常见,口服降血糖药物通常会引起胃肠道不适等不良反应。
刺五加(Acanthopanax senticosus)是东北道地药材,根茎入药,具有益气健脾、补肾安神的功效[7],是治疗糖尿病中成药降糖舒的主要成分。刺五加叶属于保健食品的原料[8],一直以来作为山野菜与代用茶被人们食用,随着现代人对于健康的关注,近年来刺五加叶的功效研究与产品研发已成为食品学科的研究热点。活性物质及功效研究表明其主要活性成分包含刺五加多糖PES、刺五加苷、紫丁香苷、金丝桃苷等皂苷和黄酮类物质,具有保护心脑血管系统,降血糖,抗肿瘤等药理作用[9-11]。食品研发主要集中在刺五加叶微生物发酵方面,其目的在于增加食品的保健功效,扩大刺五加的应用范围,使农产品资源得到更有效利用,增加附加值。微生物发酵中草药过程中,其分泌的活性酶能破坏物细胞壁以提高活性成分释放量与提取率,同时通过生物转化形成新的活性成分,展现出更强的疾病预防与保健作用[12-13]。曲霉、酵母等真菌对刺五加鲜叶进行固态发酵,黄酮含量较发酵前可提高30%以上,体外抗氧化试验显示出良好的抗氧化活性[14]。具有益生作用的乳酸菌发酵刺五加可以提高异嗪皮啶含量与总皂苷水平并降解紫丁香苷生成新物质[15];可以提高刺五加发酵液总皂苷水平,表现出降胆固醇的益生特性[16]。但乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶的抗氧化作用等活性研究方面鲜有报道。
本论文以刺五加叶为原料,以3种植物乳杆菌为发酵菌种,研究发酵前后刺五加叶中活性成分含量变化,考察乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶的体外抗氧化作用与对降血糖相关酶活性的影响,以期为刺五加叶在益生菌发酵保健品领域的应用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
刺五加叶 采摘自黑龙江省七台河市岚棒山刺五加种植基地;嗜酸乳杆菌(Lactobacillus acidophilus,LA)、干酪乳杆菌(Lactobacillus casei,LC)、植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum,LP) 购于科汉森公司;芦丁、葡萄糖、紫丁香苷、异嗪皮啶等标品 纯度均≥98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;色谱级甲醇、乙腈和分析级氯化钾、氯化钠、磷酸二氢钾、磷酸二氢钠、碳酸钠、磷酸、无水乙醇、硝酸铝 天津市光复科技有限公司;甘氨酸-辅氨酸-对硝基苯胺盐酸盐、DPPH试剂(批号:MKBS3069V)、4-硝基苯-α-D-吡喃葡糖苷(PNPG)、α-葡萄糖苷酶(批号:R03A6Y2118,100 U/mg) 美国Sigma公司;α-淀粉酶(批号:20140122, 3700 U/g) 北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司;MRS培养基 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;其余试剂均为分析纯。
SW-CJ-1F超净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;DK-98IIA型电热恒温水浴锅 天津泰斯特仪器有限公司;KQ-400KDE型高功率超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;LDZX-50KB立式压力蒸汽灭菌锅 上海申安医疗器械厂;HJ-3恒温磁力搅拌器 常州国华电器有限公司;DHG-9240A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;RLPHR1-4 LSC型真空冷冻干燥机 德国Martin Christ公司;XS204型分析天平 瑞士METTLER TOLEDO公司;3-18K型冷冻离心机 德国SIGMA公司;PHS-3C pH计 上海精科有限公司;CARY100型紫外分光光度计 美国VARIAN公司;U3000型高效液相色谱仪 美国Thermo Fisher公司;680型全自动酶标仪 美国BIO-RAD公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌悬液制备
首先将乳酸菌活化,接入MRS液体培养基,在37 ℃下培养24 h,然后在4000 r/min下离心10 min,用无菌生理盐水清洗沉淀菌落,进而将其溶于蒸馏水中,配制成活菌数为3.0×109 CFU/mL的菌悬液。
1.2.2 刺五加叶发酵工艺
参照文献[15]的方法,略有改动。挑选无腐败的新鲜的刺五加叶按料液比1:1加水匀浆3 min,121 ℃高压蒸汽灭菌15 min,即为刺五加叶发酵底物。分别接种2%嗜酸乳杆菌(LA)、干酪乳杆菌(LC)、植物乳杆菌(LP),于37 ℃条件下发酵15 d,不接种乳酸菌的刺五加浆底物作为对照(Ct),每组3个重复。发酵结束后将样品冻干、粉碎,用于后续分析。
1.2.3 总黄酮含量测定
称取待测样品10 mg置于25 mL量瓶中,加适量60%乙醇并超声提取5 min,用60%乙醇稀释至刻度待测。采用Al(NO3)3-NaNO2比色法测定总黄酮含量[17]。准确吸取0.28 mg/mL的芦丁标准溶液0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 mL于25 mL容量瓶中,加入5%的NaNO2溶液0.75 mL,放置6 min再加入10%的Al(NO3)3溶液0.75 mL,放置6 min后再加入4% NaOH溶液10 mL,60%乙醇定容,静置10~15 min后于510 nm处测定吸光度A并绘制标准曲线,并根据回归方程(Y=0.1165X−0.0257,R2=0.9909)计算刺五加叶总黄酮。
1.2.4 多糖含量的测定
采用苯酚-硫酸比色法测定总多糖含量[18],略作修改。吸取不同浓度葡萄糖标准溶液3 mL,加入5%苯酚溶液1 mL,迅速加入5 mL浓硫酸,37 ℃水浴20 min,测定在490 nm处测定吸光值,并绘制标准曲线。称取10 g处理后的刺五加干品,以1:20的料液比加入蒸馏水,在60 ℃、200 W功率条件下超声波提60 min,离心弃去残渣,取上清液2 mL,加入5%苯酚溶液1 mL、浓硫酸5 mL充分混匀,在490 nm波长处测其吸光度值,根据标准曲线回归方程(Y=0.0121X−0.1376,R2=0.9944)计算总糖含量。
1.2.5 总皂苷含量测定
称取样品0.5 g于5 mL甲醇中,在60 ℃、200 W功率条件下超声提取60 min,经0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤后待测。参考文献[19],取1 mL待测提取液挥干,加入0.5 mL 8%香草醛乙醇溶液和5 mL 72%硫酸,混匀后于60 ℃孵育10 min,水浴冷却15 min后测定542 nm处吸光值。相同操作条件下,测定不同浓度齐墩果酸的吸光度并绘制标准曲线,根据回归方程(Y=0.0061X+0.1222,R2=0.9940)计算刺五加叶总皂苷含量。
1.2.6 紫丁香苷和异嗪皮啶含量的测定
以文献[16]的方法为基础进行优化实现紫丁香苷和异嗪皮啶的同时测定。分别称取未发酵与经乳酸菌发酵后冻干样品各0.5 g,加入5 mL甲醇,在60 ℃、200 W功率条件下超声提取60 min,经0.45 μm微孔滤膜过滤后待测。精密称取紫丁香苷标准品5.7 mg、异嗪皮啶对照品3.7 mg,置100 mL容量瓶中,用色谱甲醇溶解,定容至刻度并混匀,配制0.57 mg/mL紫丁香苷和0.37 mg/mL异嗪皮啶混合标准品储备液。HPLC色谱条件:色谱柱为Waters Symmetry C18柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相采用乙腈(A)−0.1%磷酸溶液(B)梯度洗脱,0~20 min 90%~80%B,20~30 min 80%~75%B,30~40 min 60%B,40~50 min 30%B;流速1 mL/min;进样体积10 μL;柱温25 ℃;检测波长265 nm。绘制标准曲线,紫丁香苷回归方程为Y=565.31X−1.0183,R2=0.9925;异嗪皮啶回归方程为Y=560.3X−0.7504,R2=0.9911,线性关系良好。
1.2.7 DPPH自由基的清除能力
参照文献[20]的方法,按照1.2.6的方法制备供试样液。取供试样液1 mL,用去离子水稀释2、4、8、16、32倍,然后分别取不同浓度稀释液2 mL与2 mL 0.025 mg/mL DPPH标准溶液混合摇匀,室温下避光反应30 min,以50%乙醇作空白,在517 nm波长处测定吸光度A,按下列公式(1)计算对DPPH自由基的清除率,其中,A0为用蒸馏水代替样品提取液的吸光度;A1为样品溶液本身的吸光度,以无水乙醇代替DPPH;A2为样品组吸光度。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A2−A1A0)×100 (1) 1.2.8 羟基自由基(·OH)清除能力
采用芬顿(Fenton)体系邻二氮菲-Fe2+氧化法[21]进行测定,按照1.2.6的方法制备供试样液。向稀释2、4、8、16、32倍的供试样液中加入1 mmol/L的邻二氮菲溶液1.50 mL,100 mmol/L的pH7.4磷酸缓冲液4.50 mL,1 mmol/L的FeSO4 溶液1.00 mL,混匀后加入1.00 mL 0.1% H2O2启动反应,37 ℃恒温水浴1 h后测定509 nm处吸光值。另设损伤和未损伤组,损伤组加入1.00 mL蒸馏水代替样品试液,1.00 mL的0.1% H2O2溶液启动反应,未损伤组加入2.00 mL蒸馏水代替样品供试液,以磷酸缓冲液为空白对照,按公式(2)计算羟基自由基的清除率。
羟基自由基清除率(%)=(1−A样品−A损伤A未损−A损伤)×100 (2) 1.2.9 超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)清除能力
采用邻苯三酚自氧化法[21]进行测定,按照1.2.6的方法制备供试样液。取1.00 mL供试样液,稀释2、4、8、16、32倍,加入pH8.2的Tris-HCl缓冲溶液4.50 mL,25 mmol/L的邻苯三酚溶液0.40 mL,混匀并于25 ℃恒温水浴5 min,加入8 mol/L的HCL溶液1.00 mL终止反应,测定325 nm处吸光度,按下列公式(3)计算超氧阴离子的清除率,其中A0为用蒸馏水代替样品提取液的吸光度;A为样品组的吸光度;A1为样品溶液本身的吸光度,以蒸馏水代替邻苯三酚。
超氧阴离子清除率(%)=(1−A−A1A0)×100 (3) 1.2.10 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率的测定
按照文献[22]的方法,略作修改。待测样品、PNPG溶液与α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液使用0.1 mol/L pH6.86的PB缓冲液配制。分别移取60 μL不同浓度的待测样品于96孔微量滴定板,各加入20 μL 5 mmol/L PNPG溶液于37 ℃孵育10 min,再加入40 μL 1 U/mL的α-葡萄糖苷酶于37 ℃反应15 min,最后加入0.2 mol/L Na2CO3溶液60 μL终止反应,使用酶标仪检测反应溶液405 nm处吸光值,同时测定相同体系条件下的对照组(不加样品)、样品空白组(不加酶)、空白组(不加样品和酶)。计算公式(4)如下:
α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率(%)=(1−A样品−A样品空白A对照−A空白)×100 (4) 1.2.11 α-淀粉酶抑制活性的测定
参照DNS(3,5-二硝基水杨酸)比色法[23],稍作修改。称取1 g待测样品按料液比1:15加入15 mL去离子水,超声萃取30 min,收集滤液并在5000 r/min条件下离心15 min,取上清液定容至50 mL,即为供试样液。取样品溶液0.5 mL并加入0.5 mL α-淀粉酶溶液(1 U/mL,pH6.8)在25 ℃水浴中孵育10 min,加入0.5 mL的1%的淀粉溶液开始反应10 min后,加入1 mL DNS并于沸水浴中反应5 min,取出冷却定容至10 mL,于540 nm处测定吸光值。按下式(5)计算对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制率,其中A0为样品组吸光度;A1为用缓冲液代替α-淀粉酶的吸光度;A2为缓冲液代替样品溶液的吸光度。
α-淀粉酶抑制率(%)=(1−A0−A1A2)×100 (5) 1.3 数据处理
实验均重复3次,利用Excel 2016软件对实验数据进行统计分析,使用Origin2019进行图表绘制。数据采用SPSS软件应用单因素方差分析进行组间比较,P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
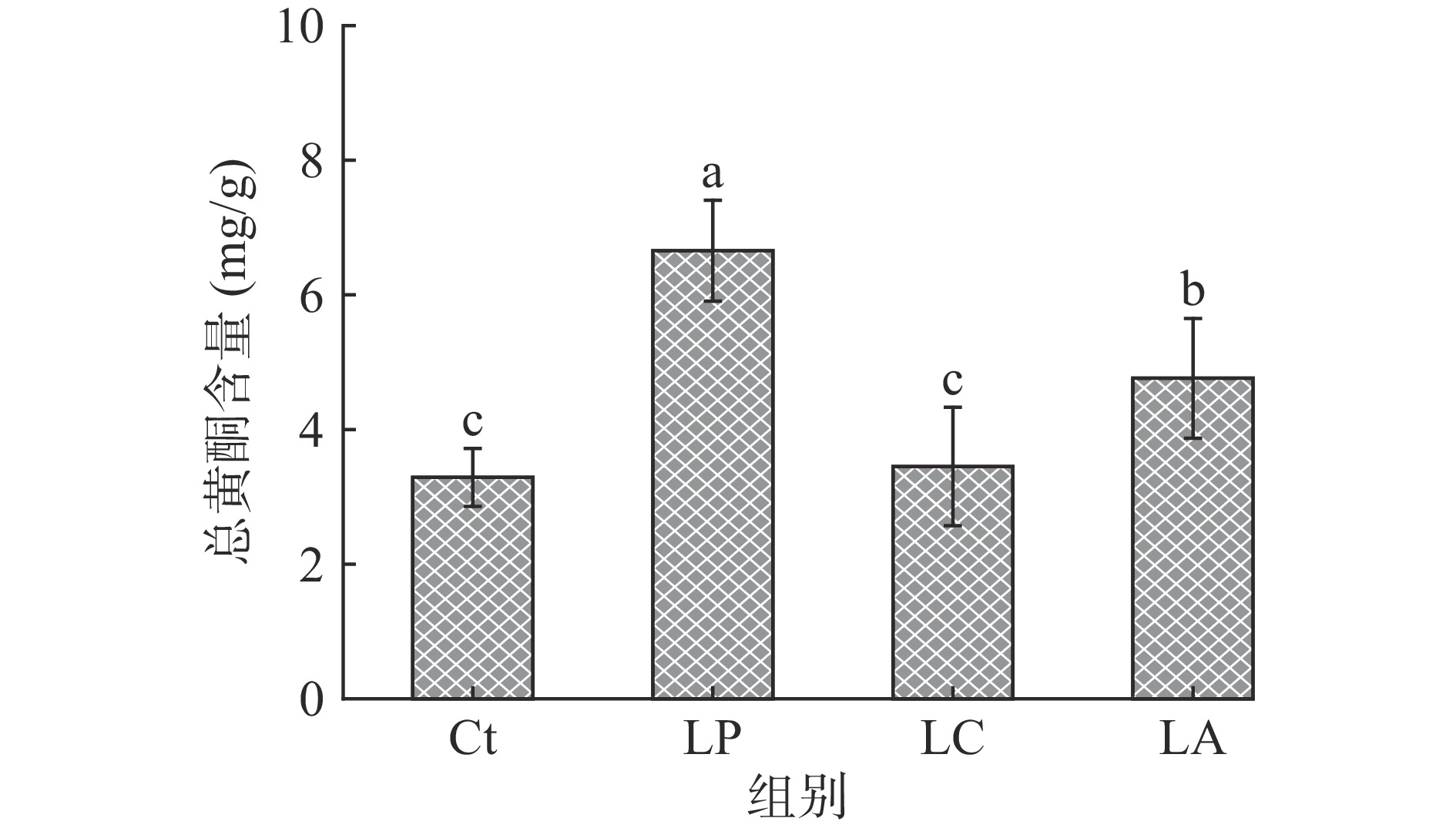
2.1 乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶中总黄酮含量的影响
刺五加叶中含有金丝桃苷、槲皮苷、槲皮素、芦丁等黄酮类化合物,由图1可知,经3种乳酸菌发酵后刺五加叶中的总黄酮含量均有所增加,其中干酪乳杆菌LC实验组无显著差异(P>0.05),植物乳杆菌LP与嗜酸乳杆菌LA实验组的含量较对照组Ct增加2.02倍与1.45倍,植物乳杆菌LP与嗜酸乳杆菌LA发酵对于刺五加叶总黄酮的影响显著大于干酪乳杆菌LC发酵处理(P<0.05)。黄酮类化合物是中草药中的重要的活性成分,微生物发酵可以实现总黄酮含量的增加。白术经乳酸菌发酵后,总黄酮含量分别提高了1.87倍[24];黑曲霉发酵蒲公英可使总黄酮含量提高2~3倍[25];以植物乳杆菌与保加利亚乳杆菌经混合发酵铁皮石斛后,总黄酮含量提高了31.87%[26]。对于刺五加的微生物发酵,红曲霉、米曲霉和产朊假丝酵母的固态发酵可使刺五加黄酮含量较未发酵前提高32.37%[14]。本文首次探索了乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶对于黄酮含量的影响,不同菌种的发酵性能不同,在所选取的3种乳酸杆菌中植物乳杆菌LP提高黄酮含量能力最强。
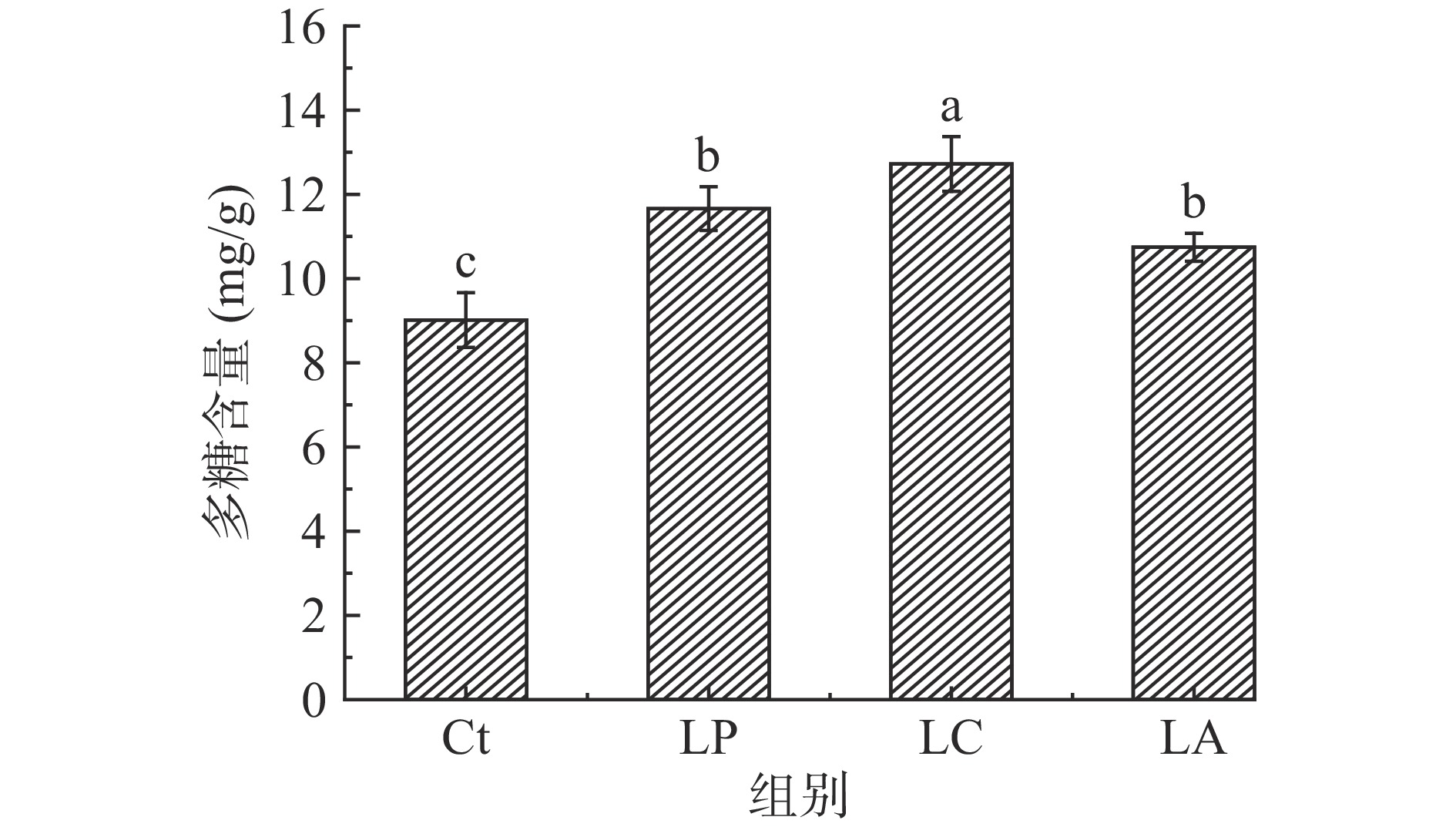
2.2 乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶中多糖含量的影响
多糖广泛存在于植物中,研究表明中草药中的多糖具有调节血糖、改善肥胖等功效[27]。为了明确乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶多糖含量的影响,本研究对刺五加叶及其乳酸菌发酵产物的多糖含量进行分析。由图2可知,经3种乳酸菌发酵后刺五加叶中的多糖含量均显著增加(P<0.05),其中干酪乳杆菌LC发酵处理自含量最高为12.7 mg/g,较未发酵对照组(9.0 mg/g)提高41.1%。植物乳杆菌LP与嗜酸乳杆菌LA组间无显著差异(P>0.05)。中药玉屏风由防风、黄芪、白术(炒)三味中药组成,经少孢根霉菌发酵后玉屏风多糖含量减少,单糖吡喃葡萄糖苷含量增加,表现出了更强的双向免疫调节功能[28]。白术经酵母菌发酵后总多糖含量降低47.89%,经双歧杆菌发酵后总多糖含量提高36.41%,乳酸菌发酵后总多糖含量提高14.73%,总多糖含量变化显著[24]。结合本研究与以上报道,可以推测不同微生物发酵对中草药多糖含量影响不同,酵母与霉菌有降低多糖含量的效果,而乳酸菌有强化多糖的效果,可能与乳酸菌分泌胞外多糖有关。
2.3 乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶中皂苷含量的影响
皂苷是刺五加的主要活性成分之一,刺五加叶含有皂苷类化合物主要为三萜类皂苷[29]。由图3可知,经3种乳酸菌发酵后刺五加叶中的皂苷含量均显著增加(P<0.05),较未发酵对照组提高1.3~1.9倍。其中,植物乳杆菌LP>干酪乳杆菌LC>嗜酸乳杆菌LA,且3个实验组间差异显著(P<0.05)。酸面团源菌株短乳杆菌HUCM105振荡培养可明显提高总皂苷水平,较未发酵组提高了79.0%[16],与本研究中对乳酸菌发酵富集刺五加叶皂苷含量的结果一致。人参皂苷的生物转化研究较为深入,微生物发酵不仅可以提高人参皂苷含量,还可以产生新的皂苷组分[30]。本文后续研究将探讨乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶对皂苷组分变化的影响。
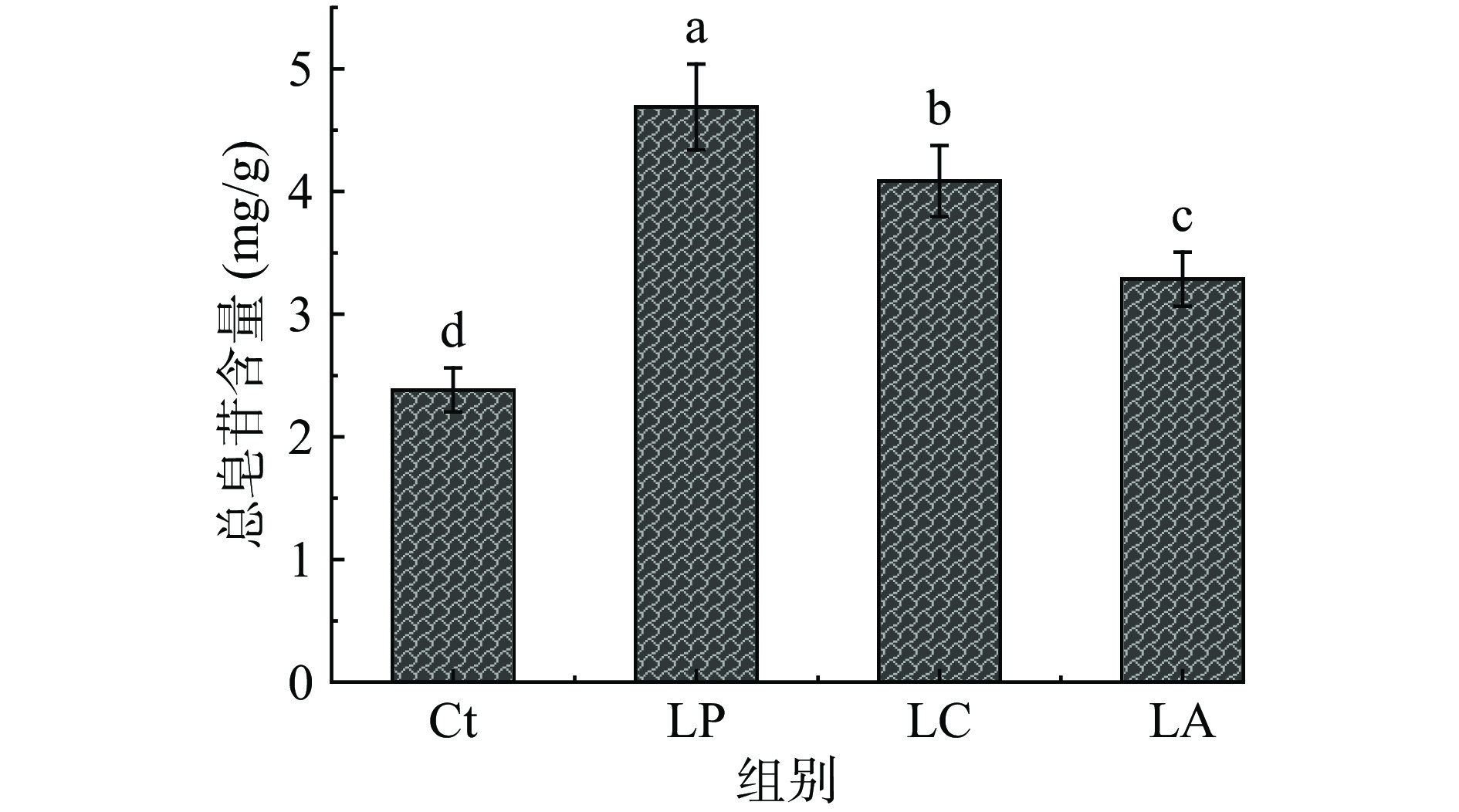
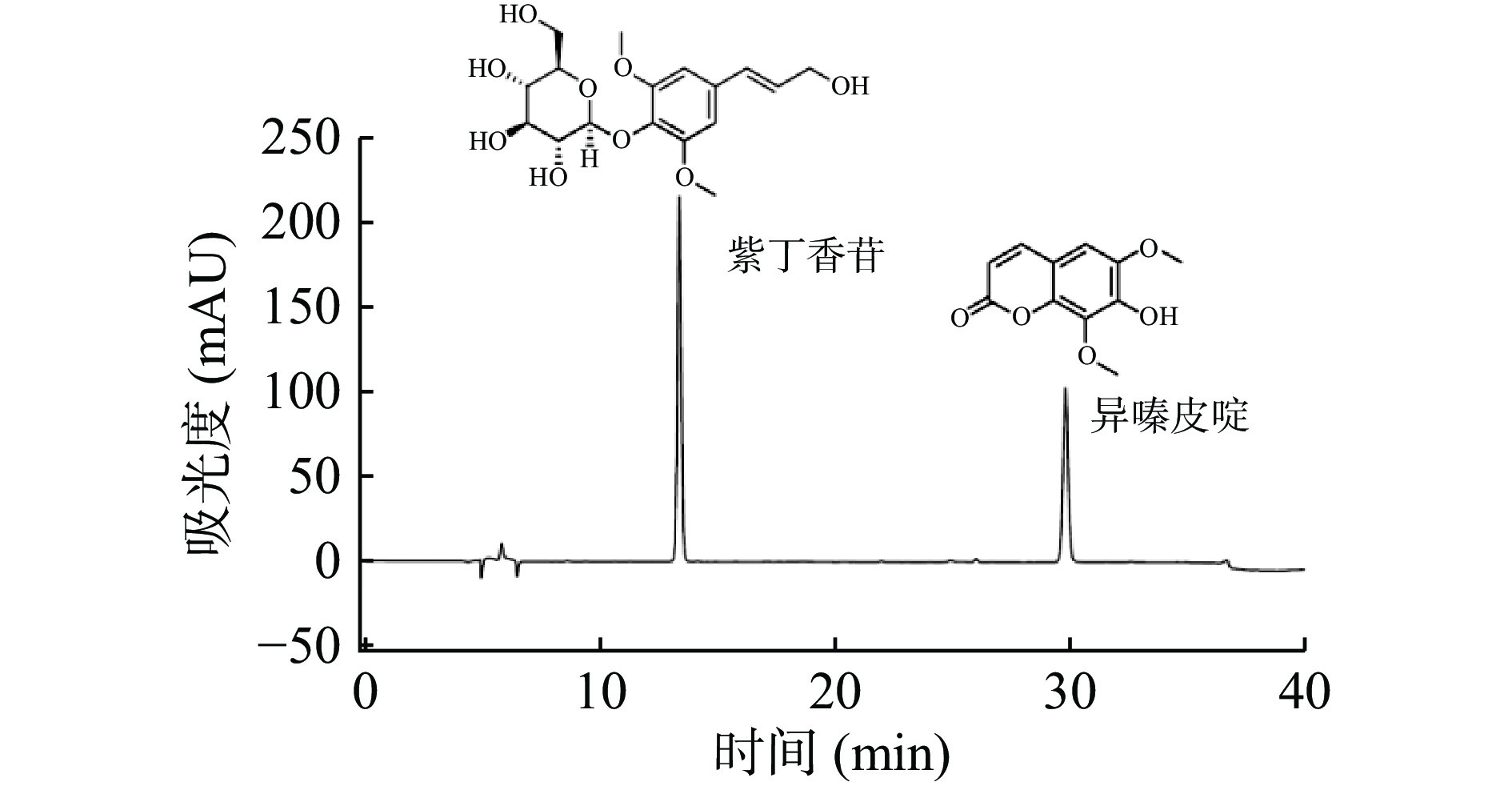
2.4 乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶中紫丁香苷和异嗪皮啶含量的影响
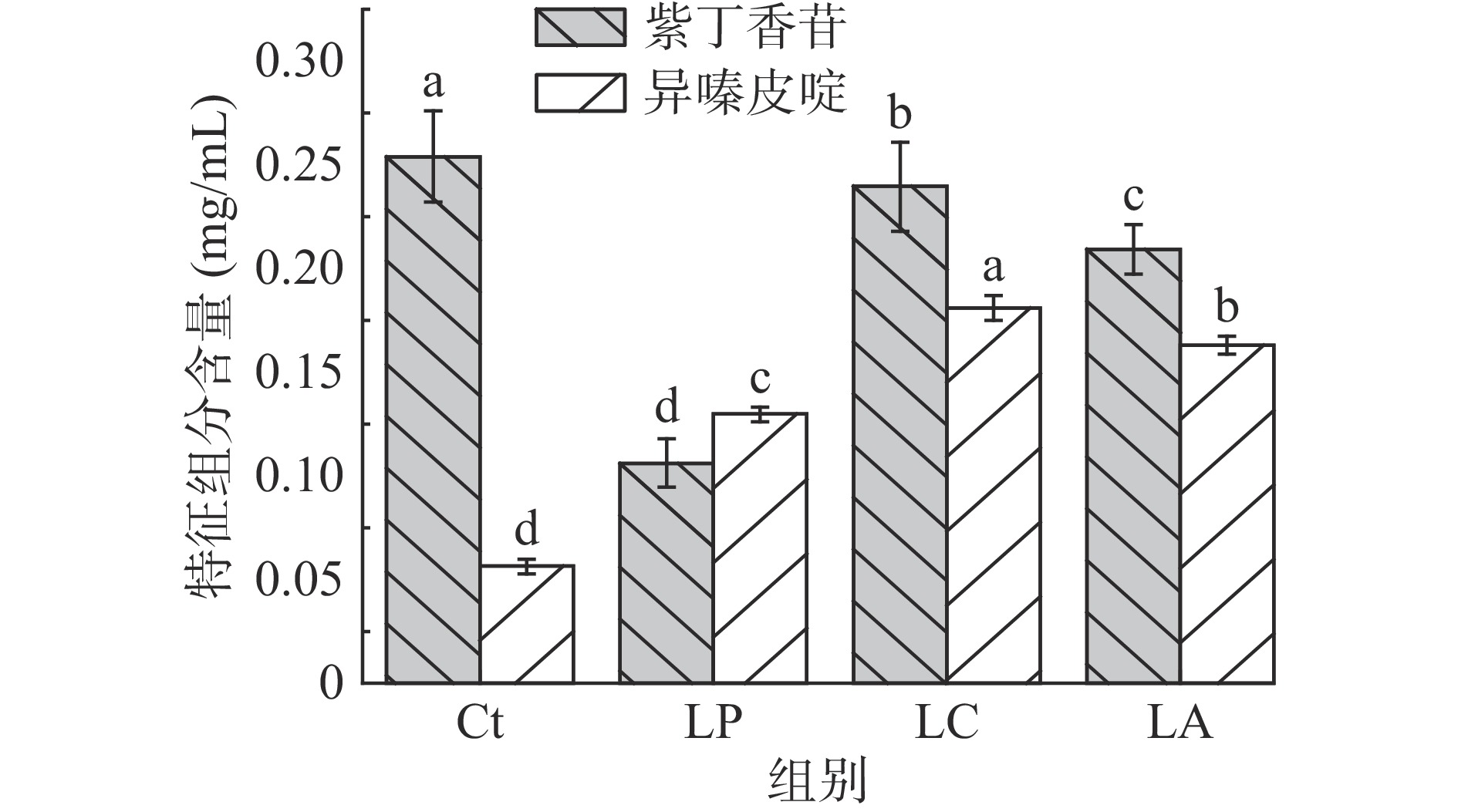
紫丁香苷及异嗪皮啶是刺五加的主要活性成分[15],具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降血糖等功效[7-9]。在优化的HPLC检测方法下,实现了紫丁香苷和异嗪皮啶的同时检测(图4)。如图5所示,乳酸菌发酵后紫丁香苷的含量均显著下降(P<0.05),植物乳杆菌LP发酵组仅为对照组的42.4%,这与文献[15]报道的结果相似,表明紫丁香苷在为微生物发酵作用下降解或转化为其他物质[15,31]。相反,异嗪皮啶在乳酸菌发酵的作用下含量明显增加,植物乳杆菌LP发酵组、干酪乳杆菌LC发酵组、嗜酸乳杆菌LA发酵组分别为对照组的2.3倍、3.2倍、2.9倍,也与文献[15]呈现相同趋势。郑春英[15]研究团队近期从刺五加中分理出一株内生真菌AJ14,可定向提高异嗪皮啶的含量,为强化刺五加的功能性提供了新的技术支撑。
2.5 乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶体外抗氧化活性
如图6所示,乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶可以增加其体外抗氧化能力,与发酵刺五加茶结果一致[14]。在质量浓度1~20 mg/mL的范围内,DPPH自由基清除能力、羟基自由基(·OH)清除能力和超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)清除能力均随质量浓度的增加而增加,不同菌种对刺五加叶抗氧化能力提高程度不同,植物乳杆菌LP发酵组的体外抗氧化能力较强。发酵组与对照组的DPPH自由基清除能力在质量浓度1~5 mg/mL的范围内呈现相同的增加趋势,在质量浓度5~10 mg/mL的范围内发酵组的DPPH自由基清除能力增加幅度大于对照组,大于10 mg/mL后均趋于平缓。在质量浓度1~10 mg/mL的范围内,乳酸菌发酵组的羟基自由基(·OH)清除能力随质量浓度增加的幅度明显大于对照组,与DPPH自由基清除能力相似,大于10 mg/mL后均趋于平缓。在超氧阴离子自由基清除活性方面,嗜酸乳杆菌LA发酵组略高于未发酵对照组,差异不显著(P>0.05) ,植物乳杆菌LP发酵组、干酪乳杆菌LC发酵组显著高于嗜酸乳杆菌LA发酵组(P<0.05),在质量浓度1~10 mg/mL的范围内浓度依存性较强。
2.6 乳酸菌发酵对刺五加叶中α-淀粉酶及α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用
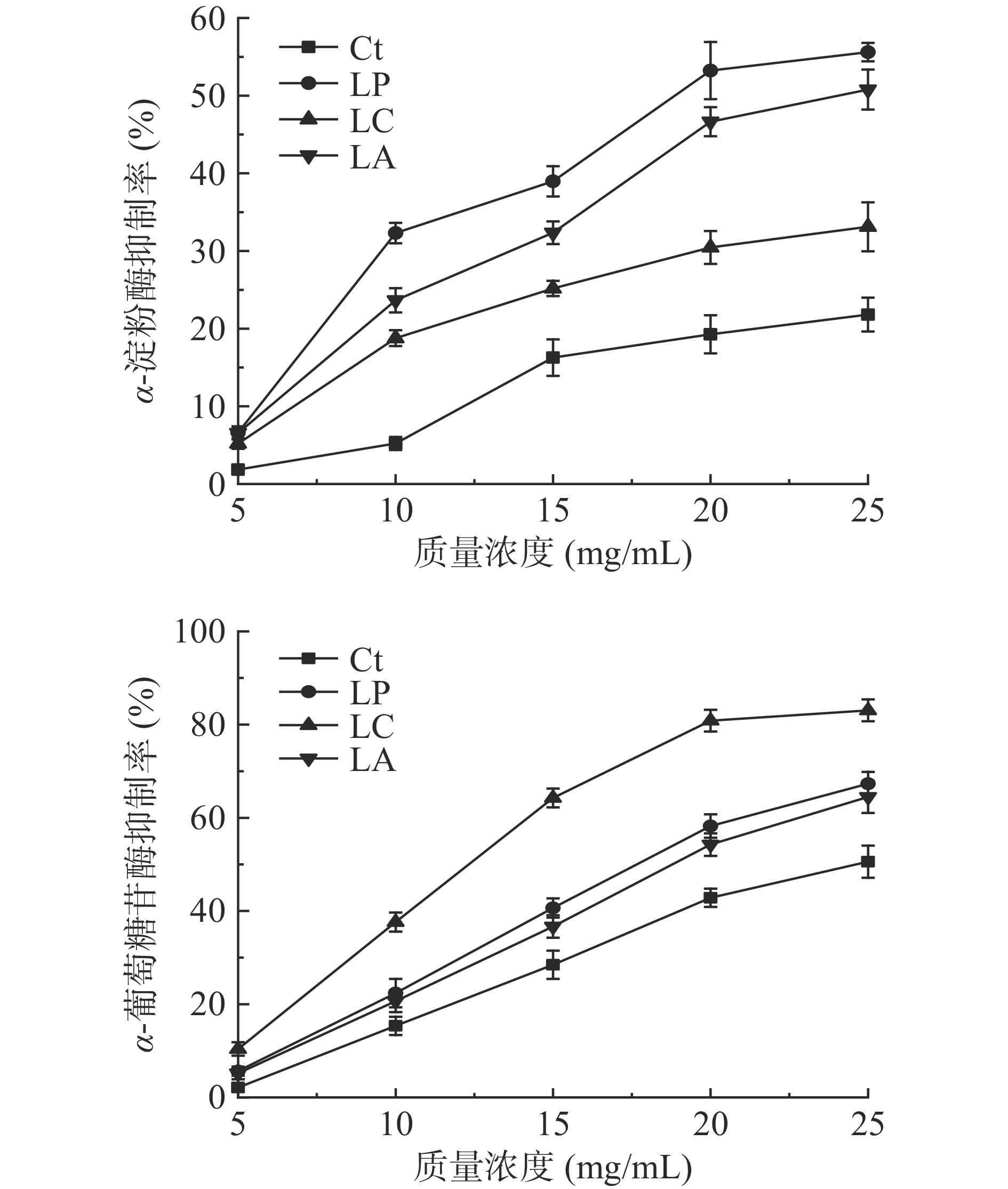
α-淀粉酶与α-葡萄糖苷酶是参与碳水化合物分解的关键酶,抑制这两种酶的活性可以降低淀粉等多糖向单糖的转化,改善血糖水平[32]。由图7可知,未发酵刺五加叶对照组具有α-淀粉酶与α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性,与文献报道一致[20],在质量浓度25 mg/mL时抑制率分别为21.82%与50.59%,且α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率高于α-淀粉酶抑制率。3种乳酸菌发酵均提高了刺五加叶的α-淀粉酶及α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制能力,抑制能力随质量浓度的增加而增强,表现出了浓度依存性。与对照组一样,各发酵组α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率更高,在质量浓度25 mg/mL时抑制率均超过了50%,干酪乳杆菌LC发酵组达到83.06%,表现出了最强的抑制作用(P<0.05)。3组发酵组中植物乳杆菌LP发酵组与嗜酸乳杆菌LA发酵组α-淀粉酶抑制率显著高于对照组(P<0.05),但只有植物乳杆菌LP发酵组在质量浓度25 mg/mL时α-淀粉酶抑制率超过50%。在本研究中,发酵刺五加叶的α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制能力并不是很强,IC50值均大于10 mg/mL,而通常被作为阳性对照的阿卡波糖的α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性的IC50值分别为0.238 mg/mL和2.83 mg/mL[32]。但发酵刺五加叶具有与银耳多糖[33]、孔石莼多糖[34]、山药多糖[35]等相近的α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制能力。
3. 结论
以刺五加叶为原料,利用乳酸菌发酵技术,对发酵前后刺五加叶中活性成分含量变化、体外抗氧化和降糖能力进行了研究。刺五加叶经乳酸菌发酵后多糖、总黄酮、皂苷、异嗪皮啶含量增加,紫丁香苷含量降低,总体而言,活性物质得到富集。不同菌种富集能力存在差异,植物乳杆菌LP富集能力优于干酪乳杆菌LC与嗜酸乳杆菌LA。乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶对DPPH自由基清除能力、羟基自由基清除能力、超氧阴离子自由基清除能力和α-淀粉酶与α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制能力都强于未发酵对照组,说明发酵可以提高刺五加叶的抗氧化与降血糖能力,在药品、食品和保健品领域具有很好的开发潜力。今后还需要运用代谢组学等手段进一步全面解析乳酸菌发酵刺五加叶产物中活性成分组成与含量,探讨不同菌种发酵特异性,结合细胞实验与动物实验阐明活性成分富集与功能强化相关性以及可能存在的协同增效作用。
-
-
[1] TARGHER G, LONARDO A, BYRNE C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus[J]. Nature Reviews Endocrinology,2018,14(2):99−114. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.173
[2] PANDEY S K, SHARMA V. World diabetes day 2018: Battling the emerging epidemic of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology,2018,66(11):1652−1653. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1681_18
[3] LI Y, TENG D, SHI X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National cross sectional study[J]. British Medical Journal,2020,369:m997.
[4] SANTWANA P, AMIT K N, ANINDITA B. Type II diabetes mellitus: A review on recent drug based therapeutics[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020(131):110708.
[5] 薄家璐, 朱长源, 李焰. 甘露消渴胶囊的实验研究[J]. 中成药研究,1985(10):41. [FU J L, ZHU C Y, LI Y. Experimental study on Ganlu Xiaoke capsule[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine Research,1985(10):41. [6] 李婉妮, 李洁. 降糖舒片联合瑞格列奈治疗2型糖尿病的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2019,34(12):3696−3699. [LI W N, LI J. Clinical study on Jiangtangshu tablets combined with repaglinide in treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Drugs & Clinic,2019,34(12):3696−3699. [7] 黄晓巍, 刘玥欣, 张啸环. 刺五加叶化学成分、药理作用及现代临床应用研究进展[J]. 吉林中医药,2017,37(6):611−613. [HUANG X W, LIU Y X, ZHANG X H. Advances in chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and modern clinical application of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves[J]. Jilin Journal of Chinese Medicine,2017,37(6):611−613. [8] 张天静, 李玲, 沈宝宇, 等. 刺五加特征特性及开发利用[J]. 园艺与种苗,2018(11):34−37. [ZHANG T J, LI L, SHEN B Y, et al. Characteristics, development and utilization of Acanthopanax senticosus[J]. Horticulture & Seed,2018(11):34−37. [9] 潘景芝, 金莎, 崔文玉, 等. 刺五加的化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(23):353−360. [PAN J Z, JIN S, CUI W Y, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Acanthopanax senticosus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(23):353−360. [10] 陈宏昌, 魏文峰, 霍金海, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS分析刺五加叶的化学成分[J]. 中药材,2016,39(7):1536−1540. [CHEN H C, WEI W F, HUO J H, et al. Identification of chemical constituents of the leaves from Acanthopanax senticosus by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2016,39(7):1536−1540. [11] WANG Y, WANG R, SHI L, et al. Systematic studies on the in vivo substance basis and the pharmacological mechanism of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms leaves by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS coupled with a target-network method[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(12):6555−6565.
[12] 艾素, 汤伟, 郭若琳, 等. 微生物发酵中草药及其活性物质的研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44(6):1110−1118. [AI S, TANG W, GUO R L, et al. Research progress on Chinese herbal medicine fermentation and profile of active substances derived[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,44(6):1110−1118. [13] 李秋月, 林连兵, 杨雪娇, 等. 微生物发酵中草药的研究现状[J]. 微生物学通报,2021,48(6):2232−2244. [LI Q Y, LIN L B, YANG X J, et al. Research status of microbial fermentation of Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Microbiology China,2021,48(6):2232−2244. [14] 化洪苓, 尹文哲, 张智, 等. 刺五加发酵茶工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2018,36(3):56−65. [HUA H L, YIN W Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Optimization of antimicrobial process of Acanthopanax senticosus fermented tea[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,36(3):56−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2018.03.008 [15] 郑春英, 石震华, 徐翠. 乳酸杆菌HD11发酵刺五加对紫丁香苷及异嗪皮啶含量的影响[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(23):189−192. [ZHENG C Y, SHI Z H, XU C. Effect of Lactobacillus brevis HD11 fermentation on syringin and isofraxidin contents of Radix Acanthopanacis senticosi[J]. Food Science,2012,33(23):189−192. [16] 国立东, 李秀萍, 张焕, 等. 一株酸面团源乳酸菌的益生特性及其对刺五加叶总皂苷的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):121−126. [GUO L D, LI X P, ZHANG H, et al. The probiotic properties of a strain of sourdough-derived lactic acid bacteria and its effect on the total saponins of Acanthopanax senticosus leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):121−126. [17] 王彦博, 石燕, 袁毅君. 麦积山野生刺五加多酚与黄酮的超声辅助提取与体外抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31(12):2153−2162. [WANG Y B, SHI Y, YUAN Y J. Ultrasonic assisted extraction of polyphenols and flavonoids from Maijishan wild Acanthopanax and their antioxidant activities in vitro[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019,31(12):2153−2162. [18] 李俊萍, 郭盛磊, 王谦博, 等. 不同产地刺五加中多糖含量测定、聚类分析及其超声提取工艺优化[J]. 中国药房,2019,30(18):2541−2545. [LI J P, GUO S L, WANG Q B, et al. Determination of polysaccharide content, cluster analysis in Acanthopanax senticosus from different producing areas and optimization of its ultrasonic extraction technology[J]. China Pharmacy,2019,30(18):2541−2545. [19] 金焱, 姚会敏. 刺五加口服液中刺五加总皂苷的含量测定[J]. 黑龙江医药,2011,24(1):25−26. [JIN Y, YAO H M. Determination of the content of the total saponins of Acanthopanax senticosus[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine Journal,2011,24(1):25−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2882.2011.01.015 [20] 郭丽丽, 张茜, 郭如洹, 等. 刺五加总苷的提取工艺优化及其抗氧化作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(18):152−159. [GUO L L, ZHANG Q, GUO R H, et al. Optimization of extraction process of the total glycosides from Acanthopanax senticosus and its antioxidant activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(18):152−159. [21] 于鑫欣, 赵多佳, 张钋, 等. 食品级刺五加叶黄酮微乳的制备及功能特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(19):8−16. [YU X X, ZHAO D J, ZHANG P, et al. Preparation and functional properties of food-grade flavonoid microemulsion from Acanthopanax senticosus leaves[J]. Food Science,2019,40(19):8−16. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181016-163 [22] WANG Z, JIANG H, XIA Y, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibitory constituents from Acanthopanax senticosus Harm leaves[J]. Molecules,2012,17(6):6269−6276. doi: 10.3390/molecules17066269
[23] DOU F, XI M, WANG J, et al. α-Glucosidase and -amylase inhibitory activities of saponins from traditional Chinese medicines in the treatment of diabetes mellitus[J]. An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2013,68(4):300−305.
[24] 叶思勇, 张宁, 朱荣刚. 不同益生菌发酵后白术总黄酮与总多糖含量测定研究[J]. 国际中医中药杂志,2020,42(12):1145−1148. [YE S Y, ZHANG N, ZHU R G. Research on the content of total flavonoids and total polysaccharids in Atractmlodis macrocephalae rhizoma after fermentation[J]. International Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,42(12):1145−1148. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115398-20200204-00024 [25] 宗凯, 刘国庆, 张黎利, 等. 蒲公英发酵及对其粗提物中黄酮类物质含量的影响[J]. 农产品加工(创新版),2010,25(2):38−41. [ZONG K, LIU G Q, ZHANG L L, et al. The effects of Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-mazz. fermentation on flavonoids content in their extracts[J]. Innovational Edition of Farm Products Processing,2010,25(2):38−41. [26] 黄振勇, 张娥珍, 淡明, 等. 乳酸菌发酵对铁皮石斛活性物质含量及其抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 热带作物学报,2020,41(3):572−578. [HUANG Z Y, ZHANG E Z, DAN M, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus fermentation on active substance and antioxidant activity of Dendrobium candidum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2020,41(3):572−578. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2020.03.021 [27] ZHENG Y, BAI L, ZHOU Y, et al. Polysaccharides from Chinese herbal medicine for anti-diabetes recent advances[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:1240−1253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.072
[28] SUN H, NI X, ZENG D, et al. Bidirectional immunomodulating activity of fermented polysaccharides from Yupingfeng[J]. Research in Veterinary Science,2017,110:22−28. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.10.015
[29] LI F, LI W, FU H, et al. Pancreatic lipase-inhibiting triterpenoid saponins from fruits of Acanthopanax senticosus[J]. Chem Pharm Bull(Tokyo),2007,55(7):1087−1089. doi: 10.1248/cpb.55.1087
[30] 陈旸, 王义, 孙亮, 等. 植物乳杆菌发酵转化人参皂苷的研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2014,39(8):1435. [CHEN Y, WANG Y, SUN L, et al. Fermentation transformed ginsenoside by Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2014,39(8):1435. [31] 陈丽艳, 金爽, 张迎, 等. 猴头菌发酵刺五加后多糖与紫丁香苷的含量变化研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(9):184−186. [CHEN Y L, JIN S, ZHANG Y, et al. The content analysis of the crude polysaccharides and syringin in Acanthopanax senticosus fermented by Hericium erinaceus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(9):184−186. [32] 李榕娣, 庄远杯, 魏爱红, 等. 不同蕨菜制品醇提物体外抗氧化及降血糖活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(19):56−63. [LI R, ZHUANG Y, WEI A H, et al. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of ethanol extracts from different products of Blechnum orientale L. in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(19):56−63. [33] 杜沁岭, 杨芳, 徐文, 等.银耳多糖对淀粉消化酶的抑制作用及其机理研究[J/OL].食品工业科技:1−8[2021-09-29].https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021060084. DU Q L, YANG F, XU W, et al. Inhibitory effect of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide on starch digestive enzymes and its action mechanism[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−8[2021-09-29].https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021060084.
[34] 汤陈鹏, 吕 峰, 王蓉琳. 孔石莼多糖锌结构表征与体外降血糖活性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(7):52−58. [TANG C P, LV F, WANG R L. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity in vitro of Ulva pertusa polysaccharides-Zinc complex[J]. Food Science,2020,41(7):52−58. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190320-263 [35] 朱娇娇, 周安婕, 丁怡, 等. 3种天然植物多糖的抗氧化与降血糖活性研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2018,31(8):96−100. [ZHU J J, ZHOU A J, DING Y, et al. Antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of three natural plant polysaccharides[J]. Cereals & Oils,2018,31(8):96−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2018.08.025 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 郭新颖. 柱前衍生-高效液相色谱法测定鱼类中组胺. 化学分析计量. 2024(01): 12-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王建凤,冯月超,王颖,刘艳,周阳,刘佳. 鱼露中章鱼胺含量分析及衍生化产物结构推断. 分析仪器. 2024(04): 64-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卢竹阳,邵彪,王琳琳,许晶晶,张霞,李玲玉,沈蕾. 冷藏时间对大黄鱼、鲳鱼中生物胺含量变化的影响. 肉类研究. 2024(11): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)










 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



