Comparison and Analysis of the Quality of Fermented Garlic Liquid with Different Strains
-
摘要: 为研究不同菌种对发酵大蒜液品质的影响,对大蒜发酵过程中总酚、可滴定酸、甲醇、乙醇等理化指标和羟基自由基清除能力进行监测,利用高效液相色谱法分析其有机酸种类及其含量,采用电子舌分析不同发酵时间发酵大蒜的味感变化。结果表明,不同菌种(酿酒酵母或植物乳杆菌)发酵制备的大蒜液,在其发酵过程中,总酚、可滴定酸均呈现上升的趋势,发酵大蒜中共检测到六种有机酸(酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸),其中苹果酸和乳酸的含量较高;植物乳杆菌制备的发酵大蒜液在发酵前期,各滋味响应值变化趋势较大,其中酸味响应值在发酵4 d时迅速增加到9.21±0.03,咸味响应值在发酵4 d时迅速降低到−21.11±0.01。羟基自由基清除能力、甲醇和乙醇呈现出先升高后趋于平稳的趋势,植物乳杆菌组发酵至80 d时,羟基自由基清除能力为99.88%±0.05%;酿酒酵母发酵产生的乙醇含量较高,植物乳杆菌发酵产生的甲醇含量较高,甲醇含量均在安全范围内。综合评价菌种发酵对发酵大蒜液的品质影响为:植物乳杆菌优于酿酒酵母,该研究为菌种发酵大蒜液产品的研究开发提供了理论依据。Abstract: In order to compare the change trend of fermented garlic broth by different strains in the fermentation process, the chemical and physical index of total phenol, titratable acid, methanol, ethanol, and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity during the fermentation process were determined, then the types and content of organic acid was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography. The taste of fermented garlic broth at different fermentation time was analyzed by electronic tongue. The results showed that the total phenols and titratable acids of fermented garlic broth prepared by different strains (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarum) showed an upward trend during the fermentation process. The content of six organic acids (tartaric acid, malic acid, lactic acid, acetic acid, citric acid, succinic acid) was measured in fermented garlic broth, among which the content of malic acid and lactic acid was relatively high. The taste response value of fermented garlic broth prepared by Lactobacillus plantarum had a large change in the early stage of fermentation. The value of sourness response rapidly increased to 9.21±0.03 after 4 days of fermentation, and the value of saltiness response rapidly decreased to −21.11±0.01 after 4 days of fermentation. The scavenging capacity hydroxyl radicals and the content of methanol, ethanol showed a trend that firstly increasing and then keeping in a steady state. The hydroxyl radical scavenging ability for fermented garlic solution was 99.88%±0.05% after 80 days of fementation by Lactobacillus plantarum. The ethanol content produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation was higher, while the content of methanol produced by fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum was higher. Considering the comprehensive evaluation of the effects of strains on the quality of fermented garlic broth, Lactobacillus plantarum was more suitable for garlic fermentation than Saccharomyces cerevisiae, methanol content was within the safe range. This research would provide a theoretical study for the research and development of garlic fermentation products.
-
Keywords:
- garlic /
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae /
- Lactobacillus plantarum /
- fermentation /
- organic acid /
- taste /
- antioxidant activity
-
大蒜(Allium sativum L.)为百合科葱属植物的地下鳞茎,具有强烈辛辣味,蒜头、蒜苗和蒜苔不仅可作蔬菜、调料味食用,而且可入药,是著名的药食两用植物[1]。大蒜富含蛋白质、糖类、含硫化合物、生物活性酶等物质,具有多种药理价值,如抗氧化、清除自由基[2]、降血脂[3]、抗肿瘤[4]、抗病原微生物[5]、改善血液循环、缓解疲劳等作用,长期食用可起到防病保健作用[6]。
目前,大蒜的初级加工产品种类较少,主要有糖醋蒜、黑蒜、蒜粉、蒜片等。现有的大蒜产品中,大蒜特有的辛辣气味和刺激性气味限制了其作为食品和食品配料的广泛应用[7]。利用微生物菌种对大蒜进行发酵,能够富集营养成分,降低辛辣和刺激性气味,以制备发酵大蒜产品,也是未来大蒜加工的一个重要方向[8]。侯进慧等[9]采用植物乳杆菌、嗜酸乳杆菌和鼠李糖乳杆菌复合发酵大蒜30 d之后,大蒜蒜味逐渐消失,并产生香味,口感显著改善。
酿酒酵母是对人体有益的一类微生物,常被用来酿酒,具有产酒精浓度高和发酵速度快等优点,使之成为常用的一类菌种[10];植物乳杆菌属于同型发酵乳酸菌,广泛应用于食品发酵过程中,如酸奶、面包和泡菜[11];在繁殖过程中产出的乳酸杆菌素,是一种生物型防腐剂[12];能发酵乳糖或葡萄糖酸盐,产生大量的乳酸[13]。目前,利用酿酒酵母和植物乳杆菌进行果蔬的发酵,已经有诸多研究报道和应用研究[14-16],利用菌种对大蒜进行发酵的研究报道较少,因此本文通过研究不同发酵菌种发酵制备发酵大蒜液,为大蒜深加工产品的进一步开发提供科学指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大蒜 购买于江苏邳州;酿酒酵母(菌种编号:CICC 1012)、植物乳酸菌(菌种编号:CICC 21786) 中国工业微生物菌种保藏管理中心(CICC);低聚异麦芽糖 保龄宝生物股份有限公司;甲醇(色谱纯) 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;乙醇(优级纯),叔丁醇、磷酸二氢钾、抗坏血酸、醋酸、乳酸(色谱纯) 上海阿拉丁化学试剂有限公司;草酸、苹果酸、柠檬酸(均为标准品) 中国药品生物制品鉴定所;其余试剂 均为国产分析纯。
SpectraMax iD5多功能酶标仪 美国Molecular Devices公司;GC-2010气相色谱 日本岛津公司;HSS86.50顶空进样器 意大利DANI公司;SA402B型味觉感应系统 日本Insent公司;Waters e2695型高效液相色谱 美国Waters公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌种的培养
酿酒酵母:YEPD液体培养基,接种后在30 ℃培养36~48 h;植物乳杆菌:MRS液体培养基,接种后在30 ℃培养24~48 h。
酿酒酵母发酵种子液:向灭菌的纯水中加入5%的酿酒酵母菌液体培养基(107 CFU/mL)。
植物乳杆菌发酵种子液:向灭菌的纯水中加入5%的植物乳杆菌液体培养基(107 CFU/mL)。
1.2.2 发酵大蒜液的制备
将大蒜去皮,用无菌水冲洗无霉变、无腐烂、无机械损伤的大蒜,自然沥干,打浆粉碎后用紫外照射灯辐射处理30 min后备用[9]。将低聚异麦芽糖用紫外灯辐射30 min,将大蒜、低聚异麦芽糖和发酵种子液(酿酒酵母、植物乳杆菌)以质量比为1:1:3加入经高压蒸汽灭菌后的20 L不锈钢发酵罐中,于20±5 ℃下避光发酵,定期取大蒜发酵液样品50 mL,发酵前16 d,每隔4 d取一次样,发酵16至80 d,每隔8 d取一次样,将所取样品液于6000 r/min条件下离心15 min,将上清液保存于−80 ℃超低温冰箱中,待测。
1.2.3 总酚含量测定
参考薛淑龙等[17]方法并作修改,测定样品中总酚含量。分别取原液100 μL,加入10%福林酚溶液500 μL,振荡混匀,静止3 min,加入7.5% Na2CO3溶液400 μL,振荡混匀,避光反应1 h,取150 μL加入到96孔板,于765 nm处测定吸光度,空白水为对照组。
1.2.4 可滴定酸含量测定
参照GB/T 12456-2021《食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定》[18],使用电位滴定仪测定样品中的可滴定酸含量,测定结果以乳酸质量分数(g/100 mL)计。
1.2.5 甲醇、乙醇含量的测定
参照范昊安等[19]方法并作修改,测定样品中甲醇、乙醇的含量。
混合标准溶液配制:以终质量浓度为10 g/L的叔丁醇作为内标,配制质量浓度为0.1、0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5、5 g/L和0.5、1、5、10、15、20、25、50 g/L的甲醇、乙醇混合标准溶液,待测。样品配制:将样品稀释10倍,加入终质量浓度为10 g/L的叔丁醇作为内标,待测。自动顶空条件:炉温85 ℃,平衡时间40 min;进样阀温度105 ℃;传输线温度110 ℃。气相色谱条件:RTX-5毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);柱温40 ℃,平衡时间3 min,10 ℃/min升温至180 ℃,保温5 min;进样口温度200 ℃;分流比30:1;检测器温度250 ℃。
1.2.6 有机酸的测定
采用高效液相色谱法测定样品中有机酸含量[20]。液相色谱分析条件,色谱柱:AtiantisR T3柱(250 mm×4.6 mm i.d,5 μm),检测波长为210 nm,V(甲醇):V(0.01 mol/L KH2PO4,用磷酸调pH2.7)=2:98,柱温20 ℃,流速为1 mL/min,进样量为10 μL。配制酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、柠檬酸和琥珀酸浓度分别为0.1、0.5、1、1、1、1 mg/mL的混合标准溶液,上机检测。将样品用0.01 mol/L的KH2PO4溶液(pH2.7)稀释10倍,过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,上机检测。
1.2.7 电子舌滋味分析
采用电子舌[21]分析不同发酵时间样品的味感变化。取1 mL样品,用超纯水定容至100 mL容量瓶中,装入电子舌专用烧杯中。每秒采集1次数据,共采集120 s,清洗330 s。使用CTO、CAO、C00、AE1传感器分别对样品的咸味、酸味、苦味(及其回味)和涩味(及其回味)进行检测,每个样品重复测定4次;使用GL1传感器检测样品的甜味,每个样品重复测定5次,均选取最后3次的稳定数据纳入分析。
1.2.8 羟自由基清除能力的测定
参照赵优萍等[22]方法并作修改,进行样品测定。取200 μL样品,加入140 μL 6mmol/L H2O2溶液,60 μL 20 mmol/L水杨酸钠和200 μL 1.5 mmol/L硫酸亚铁,振荡混匀,37 ℃下恒温水浴1 h,取150 μL加入到96孔板,于510 nm处测定吸光度,空白水为对照组。羟基自由基清除能力计算公式:
羟基自由基清除率(%)=(A0−A1+A2)/A0×100 式中:A0为空白对照液的吸光度;A1为样品测定的吸光度;A2为样品本底的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验均重复三次,采用Origin 8.6软件绘制图,结果以平均值±标准差(SD)表示。利用SPSS 22软件进行相关性分析,利用HemL 1.0软件进行相关性热图分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同菌种发酵过程中总酚含量的变化
酚类物质存在于大蒜原料中,研究发酵大蒜液中的酚类物质,对开发高活性大蒜发酵液产品具有重要的研究价值和意义,大蒜发酵液中的酚类物质含量直接影响产品的口感及抗氧化性等[23]。对分别接种酿酒酵母和植物乳杆菌的大蒜发酵液中总酚含量进行跟踪检测,结果见图1,由图1可知,大蒜发酵液制备过程中,总酚含量在发酵4 d内明显下降,4 d后均呈现出近乎直线上升的趋势,与发酵第4 d的大蒜发酵液相比,其余发酵时间点的总酚含量均有明显提高,大蒜发酵液前期总酚含量明显下降的原因可能是部分酸性酚类物质在中性环境下降解生成其它物质[24],在整个发酵过程中,植物乳杆菌发酵组的总酚含量高于酿酒酵母发酵组。
2.2 不同菌种发酵过程中可滴定酸的变化
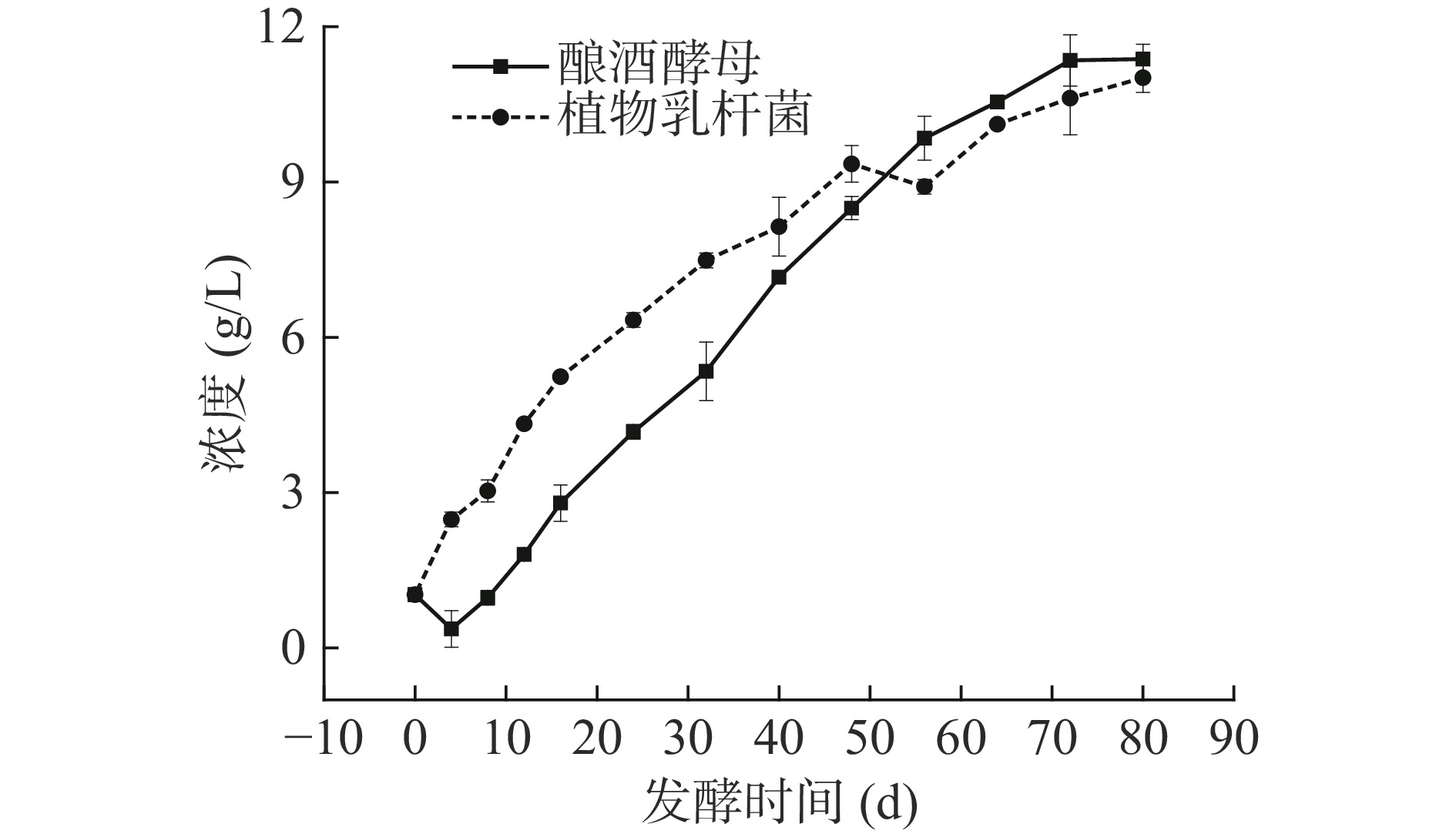
可滴定酸是衡量发酵大蒜液品质的重要理化指标之一,也是衡量大蒜发酵液成熟度的重要指标。由图2可知,在整个发酵过程中,可滴定酸含量均呈现出上升的趋势。酿酒酵母是一种单细胞真菌,属于兼性厌氧菌,在有氧和无氧的条件下均能生存,酿酒酵母在有氧的条件下可以大量繁殖,因为大蒜中的抑菌物质存在可以抑制酵母菌的代谢,产生二氧化碳和水,只有部分二氧化碳溶于水,在发酵后期则进行无氧呼吸产生酒精和二氧化碳[25],因此前期酿酒酵母组的可滴定酸含量较低。植物乳杆菌产生乳酸,乳酸可以被氧化成醋酸[26]。在发酵后期,酿酒酵母组中可滴定酸含量高于植物乳杆菌组,可能主要与菌种发酵制得的大蒜发酵液中形成的有机酸有关。
2.3 不同菌种发酵过程中有机酸的变化
将质量浓度在0.001~1.0 mg/mL范围内的系列有机酸混标溶液进行HPLC分析,以各标准有机酸质量浓度(x)对峰面积(y)进行线性回归,结果见表1。由表1可知,各有机酸标准曲线决定系数R2均≥0.998,表明在既定的浓度单位内,峰面积和有机酸质量浓度之间的线性关系较好。
表 1 6种有机酸标准品标准曲线回归分析Table 1. Regression analysis of standard curves of six organic acid standards有机酸 回归方程 决定系数R2 酒石酸 y=76833x−52754 0.9989 苹果酸 y=623653x−18419 0.9999 乳酸 y=315558x−8713.1 0.9999 醋酸 y=365687x−10441 0.9999 柠檬酸 y=674270x−10747 0.9999 琥珀酸 y=325924x−11192 0.9998 大蒜发酵液中的有机酸,除部分来源于大蒜原料固有的有机酸溶出外,还有一部分是通过产酸微生物的代谢而形成[27]。有研究报道表明[18],果蔬自然发酵过程中的优势菌种主要为酵母菌、醋酸菌和乳酸菌等。酵母菌主要通过糖酵解和三羧酸循环途径,在其生长期内可产生大量的有机酸;而植物乳杆菌通过一系列复杂的代谢过程可以产生乳酸等有机酸[28]。由图3可知,大蒜发酵液中的有机酸种类丰富,且因发酵菌种生长和代谢而发生改变,主要的有机酸为苹果酸和乳酸,酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、柠檬酸和琥珀酸是发酵大蒜的重要组成部分。叶秀娟等[29]相关研究报道表明,使用高效液相色谱法检测到泡蒜中6种有机酸,其中柠檬酸含量最高,为2.62 mg/g,这主要可能是因大蒜产品品种差异所致。大蒜发酵液中高含量的有机酸,也是造成其发酵过程中可滴定酸含量不断增加的重要原因。
2.4 不同菌种发酵过程中的滋味分析
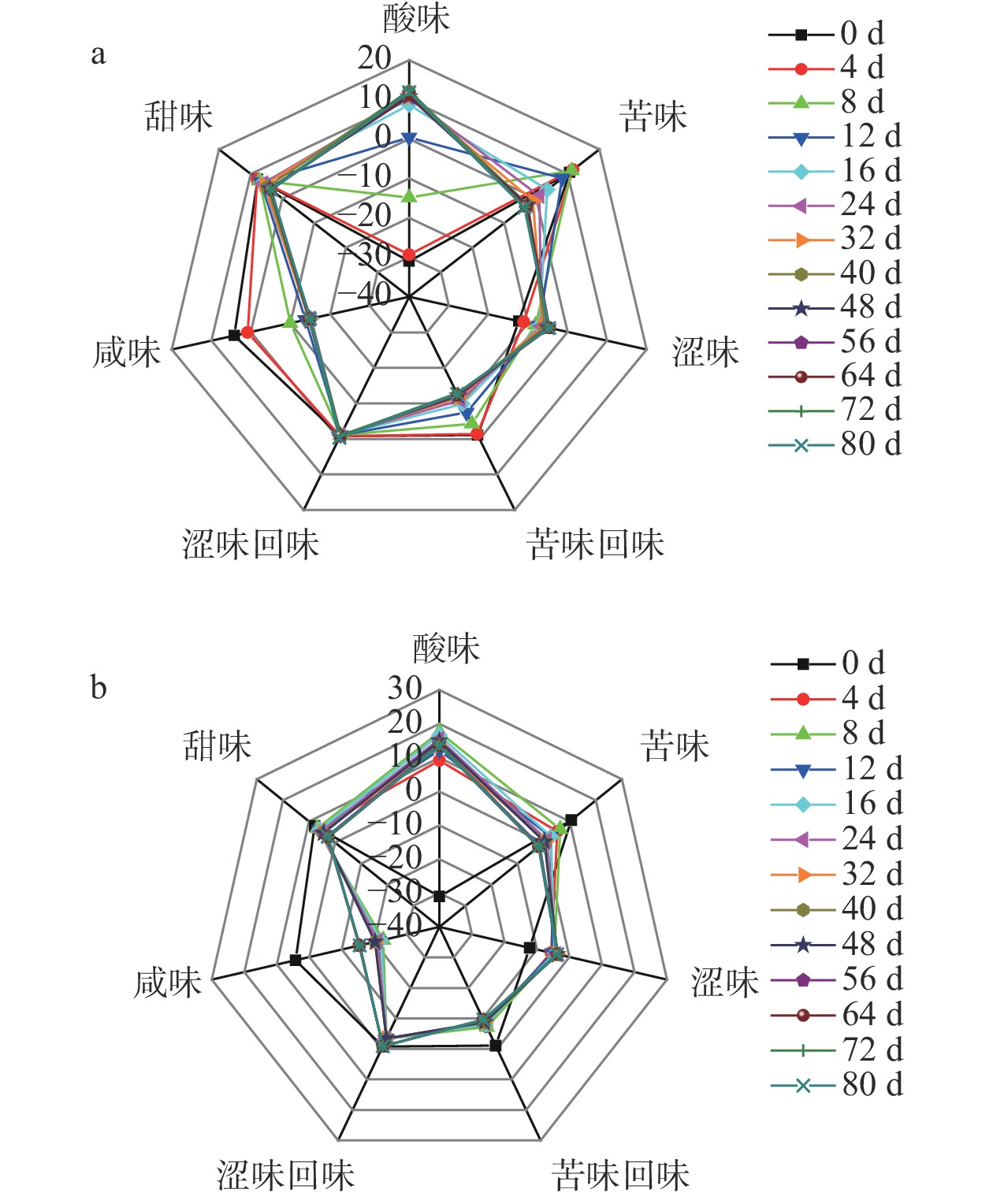
电子舌可以清晰地区分不同样品中的各味感指标的差异。由图4所示,两种菌发酵制备发酵大蒜过程中,不同发酵时间的样品之间咸味、甜味、酸味、苦味、涩味和苦味回味响应值存在明显差异,而涩味回味响应值则无明显变化。随着发酵时间的延长,两种菌发酵制备的大蒜发酵液中苦味响应值、苦味回味响应值、咸味响应值和甜味响应值均呈现出下降的趋势,酿酒酵母组咸味响应值在发酵4~8 d时下降较大,植物乳杆菌组苦味回味响应值和咸味响应值在发酵前4 d时下降较多;酿酒酵母组酸味响应值和涩味响应值呈现出匀速增长后趋于稳定的趋势,植物乳杆菌组酸味响应值和涩味响应值呈现出迅速增长后趋于稳定的趋势,其中植物乳杆菌组在第8 d时,酸味响应值达到最高为17.58±0.02。酸味响应值结果与有机酸测定结果一致,进一步说明了经微生物代谢以后产生的苹果酸和乳酸是酸味的主要来源[30];苦味物质大部分存在于植物中,可在食物加工、老化及变质过程中形成[31];咸味的产生与盐解离出的阳离子关系密切,添加少量的甜味剂对咸味有削弱作用[32],通过外源添加低聚异麦芽糖可降低大蒜发酵液中的咸味响应值;甜味由蔗糖、葡萄糖、果糖构成,酿酒酵母和植物乳杆菌发酵的大蒜在发酵过程中消耗大蒜和原料中的碳源,因此甜味响应值均呈现出下降的趋势。
2.5 不同菌种发酵过程中羟基自由基清除能力的变化
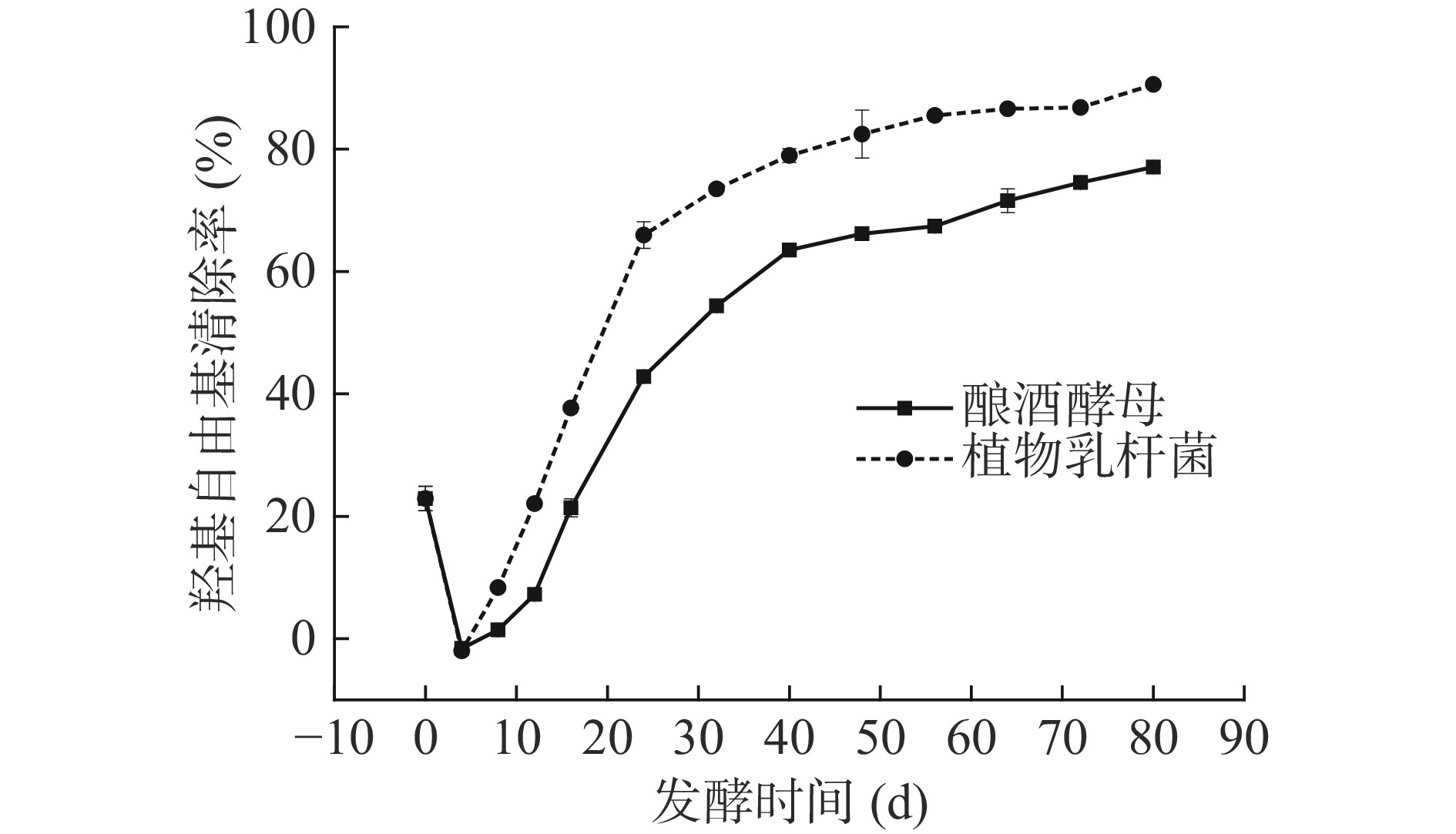
羟基自由基是氧自由基中最为活泼的自由基,过量的羟基自由基会引起邻近生物分子的严重损伤[18]。大蒜发酵液在制备过程中羟基自由基清除能力的变化如图5所示,由图5可知,在大蒜发酵过程中,两种单菌种发酵制备得到的大蒜发酵液,羟基自由基清除能力呈现出迅速降低后上升的趋势,且在发酵4 d时,羟基自由基清除能力最低,与总酚趋势一样。相关研究表明,羟基自由基的清除能力与果蔬中的总酚含量有一定关系[33],大蒜发酵液的羟基自由基清除能力在发酵4 d时趋近于零,表明大蒜发酵液中的促氧化与抗氧化作用基本达到平衡[34]。王征帆[35]相关研究表明,大蒜水提物对羟基自由基具有较强的清除作用,本文通过菌种发酵制备的大蒜发酵液,与发酵4 d相比均表现出具有较高的羟基自由基清除率,植物乳杆菌组发酵的大蒜提取液在第80 d时,羟基自由基清除能力为99.88%±0.05%,明显高于酿酒酵母组。
2.6 不同菌种发酵过程中甲醇、乙醇含量的变化
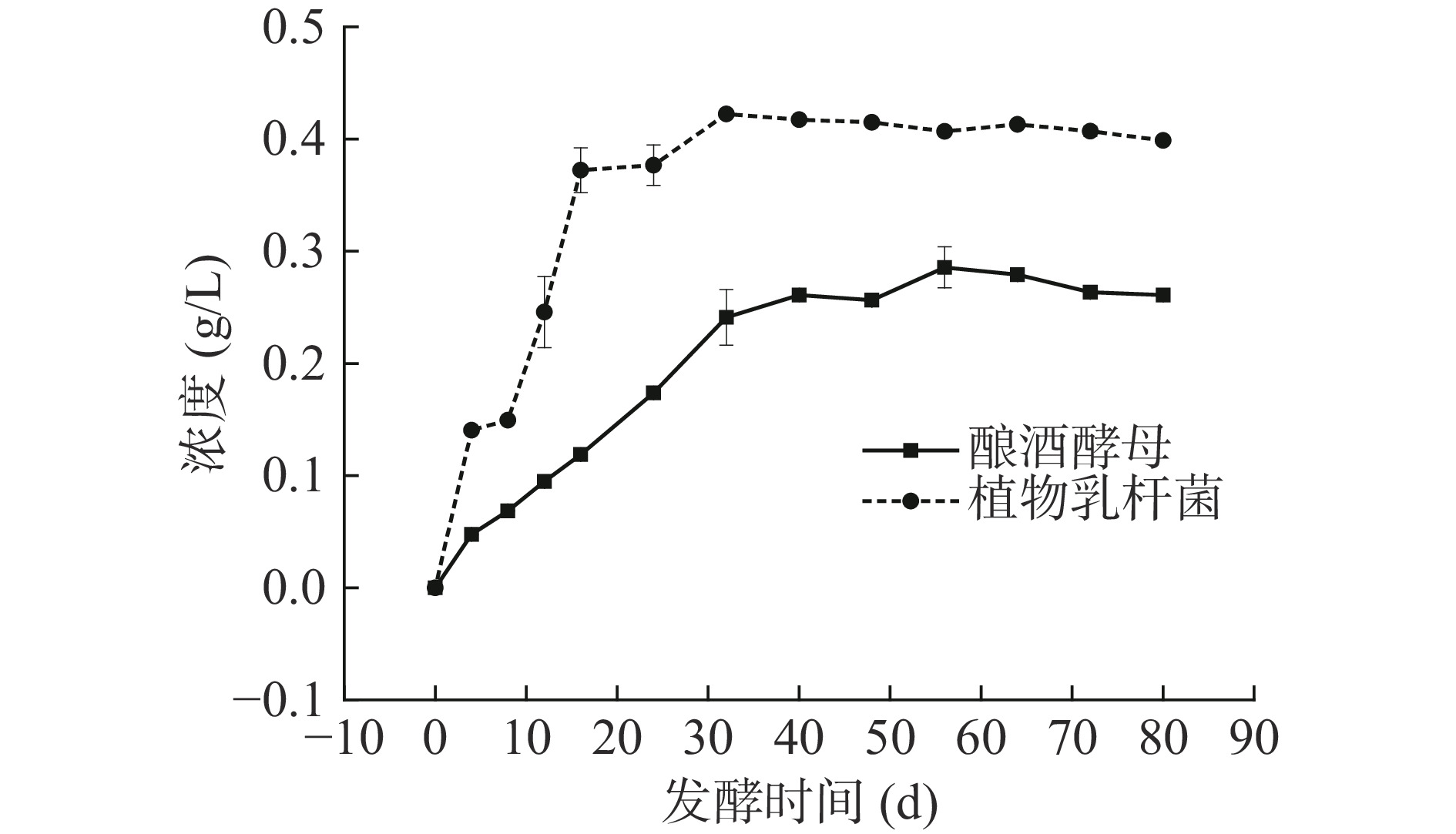
果蔬发酵产品中,甲醇和乙醇的含量是重要的安全性控制指标。甲醇是反映发酵制品质量控制的重要指标之一,大蒜发酵液在制备过程中甲醇含量的变化如图6所示。由图6可知,大蒜在发酵过程中甲醇的含量均呈现出先升高后趋于稳定的趋势,其中植物乳杆菌组产生的甲醇含量高于酿酒酵母组,但均低于0.5 g/L。甲醇对人体的健康的危害极大,尤其对视网膜、呼吸及神经系统具有明显的麻痹、毒害作用[36]。根据《食品安全国家标准 蒸馏酒及其配制酒》(GB 2757-2012)规定[37],蒸馏酒中的甲醇的最大限量值为2.0 g/L,按此规定,本研究制备的两种发酵大蒜液均符合食品安全相关标准。
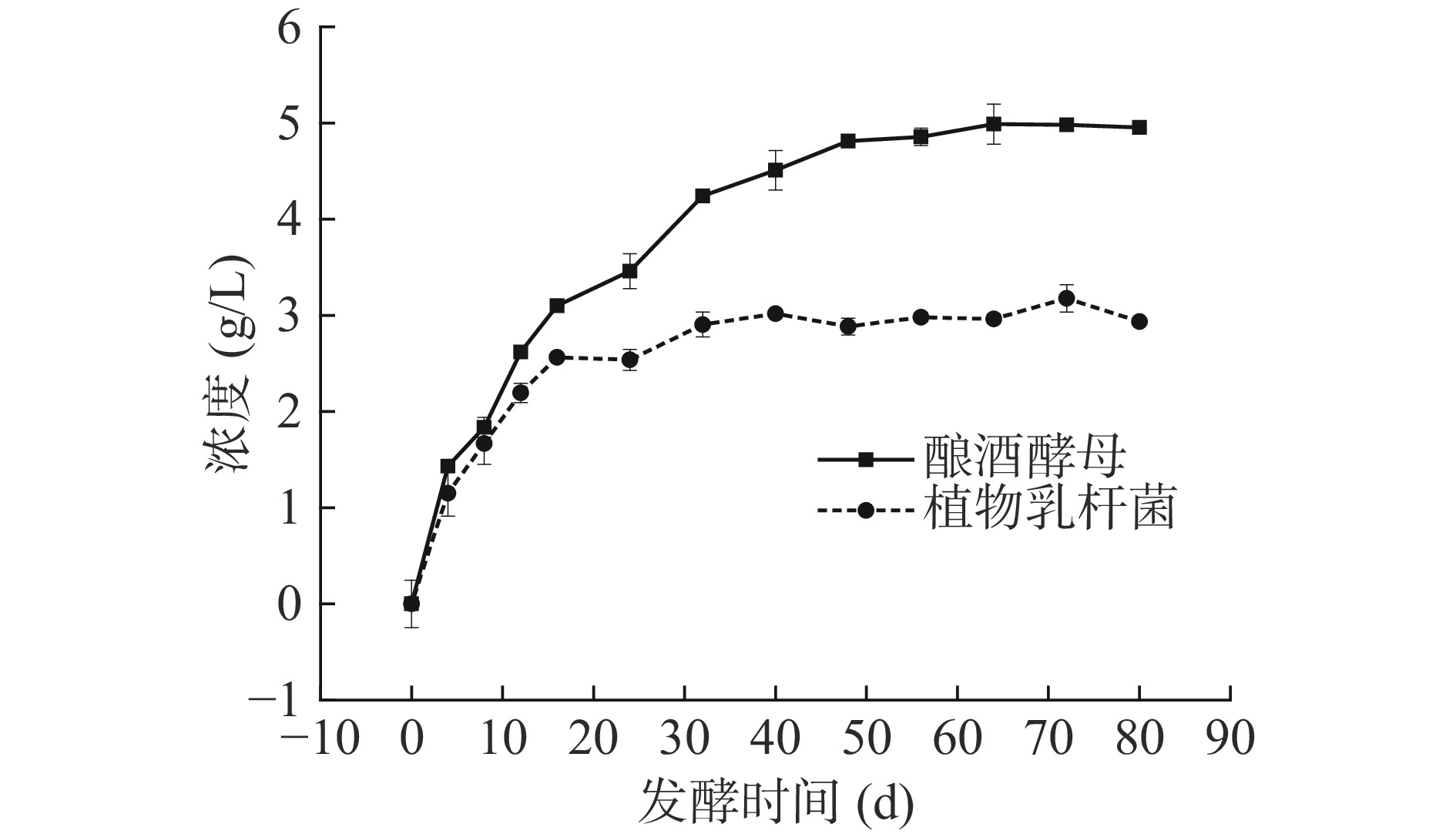
大蒜在发酵制备过程中乙醇含量的变化结果如图7所示。由图7可知,大蒜发酵过程中乙醇的含量均呈现出先升高后趋于稳定的趋势,其中酿酒酵母组产生的乙醇含量高于植物乳杆菌组,但均低于5 g/L。植物发酵产品中产生的乙醇含量最大限量一般为5 g/L,本文两种菌发酵制备得到的发酵大蒜提取液,乙醇含量均符合相关食品安全标准[38]。乙醇是酿酒酵母发酵后形成的主要产物,高浓度乙醇对酵母细胞会产生抑制作用,主要体现为降低酵母细胞存活率和细胞生长速率,进而导致发酵过程的终止[10]。
2.7 大蒜发酵液各理化指标与有机酸的相关性分析
利用不同菌种发酵制备大蒜发酵液,发酵大蒜中的各理化指标可能都影响其有机酸的代谢和转化。为了研究不同发酵大蒜提取液中不同理化指标与有机酸的关系,进一步对大蒜在发酵过程各理化指标(总酚、可滴定酸、甲醇、乙醇、羟基自由基清除能力)与有机酸(酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸)含量进行相关性分析,结果如图8所示。由图8可知,不同菌种制备的大蒜发酵提取液,其主要理化指标与有机酸含量之间均表现出显著的正相关性(P<0.05),表明各理化指标均对有机酸含量的增加有各自的贡献。经不同菌种发酵制备的大蒜发酵液中总酚、可滴定酸、甲醇、乙醇、羟自由基清除能力与酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、琥珀酸之间存在非常显著的相关性(P<0.01);不同菌种发酵制备的大蒜发酵液中的总酚、可滴定酸、甲醇、乙醇、羟自由基清除能力与柠檬酸之间存在显著的相关性(P<0.05)。通过相关性分析热图,进一步揭示了大蒜发酵提取液中的各理化指标与有机酸含量的增加有着密切的关联。
![]() 图 8 不同菌种制备的大蒜发酵液各理化指标与有机酸的相关性分析热图注:a:酿酒酵母;b:植物乳杆菌;TPC:总酚;TTA:可滴定酸;MET:甲醇;ETH:乙醇;H:羟基自由基清除率;TAR:酒石酸;DL:苹果酸;PLA:乳酸;HAC:醋酸;LEM:柠檬酸;SUC:琥珀酸。Figure 8. Heat map of correlation analysis between various physical and chemical indexes of garlic fermentation broth prepared by different strains and organic acids
图 8 不同菌种制备的大蒜发酵液各理化指标与有机酸的相关性分析热图注:a:酿酒酵母;b:植物乳杆菌;TPC:总酚;TTA:可滴定酸;MET:甲醇;ETH:乙醇;H:羟基自由基清除率;TAR:酒石酸;DL:苹果酸;PLA:乳酸;HAC:醋酸;LEM:柠檬酸;SUC:琥珀酸。Figure 8. Heat map of correlation analysis between various physical and chemical indexes of garlic fermentation broth prepared by different strains and organic acids3. 结论
本研究利用不同菌种(酿酒酵母或植物乳杆菌)对大蒜进行发酵制备大蒜发酵液,并对其理化指标和有机酸种类及含量进行检测分析。结果表明,在发酵过程中,植物乳杆菌发酵制备的大蒜液总酚含量、可滴定酸含量、羟基自由基清除能力、甲醇含量均高于酿酒酵母,当植物乳杆菌组发酵至80 d时,羟基自由基清除能力为99.88%±0.05%;发酵大蒜中共检测到六种有机酸(酒石酸、苹果酸、乳酸、醋酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸),其中苹果酸和乳酸的含量较高;植物乳杆菌制备的发酵大蒜液酸味响应值最高为17.58±0.02,说明了经微生物代谢以后产生的苹果酸和乳酸是酸味的主要来源。综合评价两种菌种对发酵大蒜制备过程中的品质影响为:植物乳杆菌优于酿酒酵母,该研究为菌种发酵大蒜产品的研究开发提供了理论基础。
-
图 8 不同菌种制备的大蒜发酵液各理化指标与有机酸的相关性分析热图
注:a:酿酒酵母;b:植物乳杆菌;TPC:总酚;TTA:可滴定酸;MET:甲醇;ETH:乙醇;H:羟基自由基清除率;TAR:酒石酸;DL:苹果酸;PLA:乳酸;HAC:醋酸;LEM:柠檬酸;SUC:琥珀酸。
Figure 8. Heat map of correlation analysis between various physical and chemical indexes of garlic fermentation broth prepared by different strains and organic acids
表 1 6种有机酸标准品标准曲线回归分析
Table 1 Regression analysis of standard curves of six organic acid standards
有机酸 回归方程 决定系数R2 酒石酸 y=76833x−52754 0.9989 苹果酸 y=623653x−18419 0.9999 乳酸 y=315558x−8713.1 0.9999 醋酸 y=365687x−10441 0.9999 柠檬酸 y=674270x−10747 0.9999 琥珀酸 y=325924x−11192 0.9998 -
[1] 侯进慧, 刘春雷. 我国大蒜资源深加工与产业化研究进展[J]. 生物资源,2020,42(1):36−42. [HOU J H, LIU C L. Research progress on the deep processing and industrialization of garlic resources in my country[J]. Biological Resources,2020,42(1):36−42. HOU J H, LIU C L. Research progress on the deep processing and industrialization of garlic resources in my country[J]. Biological Resources, 2020, 42(1): 36-42.
[2] CHAI H, WO L, FU Y, et al. S-allyl-L-cysteine sulfoxide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced monocyte adhesion and intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J]. Anatomical Record Advances in Integrative Anatomy & Evolutionary Biology,2012,295(5):421−430.
[3] ELKAYAM A, PELEG E, GROSSMAN E, et al. Effects of allicin on cardiovascular risk factors in spontaneously hypertensive rats[J]. The Israel Medical Association Journal: IMAJ,2013,15(3):170−173.
[4] CHU Y L, HO C T, CHUNG J G, et al. Allicin induces anti-human liver cancer cells through the p53 gene modulating apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2013,61(41):9839−9848.
[5] SALAMA A A, ABOULAILA M, TERKAWI M A, et al. Inhibitory effect of allicin on the growth of Babesia and Theileria equi parasites[J]. Parasitology Research,2014,113(1):275−283. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3654-2
[6] 马丽娜, 李峰杰, 陈坚, 等. 大蒜主要活性成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报,2014,30(6):760−763. [MA L N, LI F J, CHEN J, et al. Research progress on the main active ingredients and pharmacological effects of garlic[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin,2014,30(6):760−763. MA L N, LI F J, CHEN J, et al. Research progress on the main active ingredients and pharmacological effects of garlic[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2014, 30(6): 760-763.
[7] SOHN C W, KIM H, YOU B R, et al. High temperature- and high pressure-processed garlic improves lipid profiles in rats fed high cholesterol diets[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2012,15(5):435−440. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2011.1922
[8] KIM E S. Effect of fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum and heat processing on the anti-oxidant activity and volatile composition of garlic[J]. Food Engineering Progress,2012,16(4):374−380.
[9] 侯进慧, 李勇, 唐梦笛, 等. 乳酸菌复合发酵大蒜风味、活性成分和微生物种群变化分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(21):92−95. [HOU J H, LI Y, TANG M D, et al. Analysis of the flavor, active ingredients and microbial population changes of garlic compound fermented by lactic acid bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(21):92−95. HOU J H, LI Y, TANG M D, et al. Analysis of the flavor, active ingredients and microbial population changes of garlic compound fermented by lactic acid bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(21): 92-95.
[10] 何迎粉, 何荣荣, 刘敦华, 等. 海藻糖与酿酒酵母乙醇耐受性相关性的研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(11):1−4. [HE Y F, HE R R, LIU D H, et al. Research progress on the correlation between trehalose and ethanol tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(11):1−4. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.11.001 HE Y F, HE R R, LIU D H, et al. Research progress on the correlation between trehalose and ethanol tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(11): 1-4. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.11.001
[11] 王水泉, 包艳, 董喜梅, 等. 植物乳杆菌的生理功能及应用[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2010(4):49−55. [WANG S Q, BAO Y, DONG X M, et al. Physiological function and application of Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. Review of China Agricultural Science and Technology,2010(4):49−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2010.04.10 WANG S Q, BAO Y, DONG X M, et al. Physiological function and application of Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. Review of China Agricultural Science and Technology, 2010(4): 49-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0864.2010.04.10
[12] KAUR G, MALIK R K, MISHRA S K, et al. Nisin and class IIa bacteriocin resistance among Listeria and other foodborne pathogens and spoilage bacteria[J]. Microbial Drug Resistance,2011,17(2):197−205. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0054
[13] 曲冬梅, 刘小杰. 植物乳杆菌及其在食品工业中的应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2008(C):219−222. [QU D M, LIU X J. Lactobacillus plantarum and its application in food industry[J]. China Food,2008(C):219−222. QU D M, LIU X J. Lactobacillus plantarum and its application in food industry[J]. China Food, 2008(C): 219-222.
[14] KWAW E, MA Y, TCHABO W, et al. Effect of Llactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,250(1):148−154.
[15] YANG X, ZHOU J, FAN L, et al. Antioxidant properties of a vegetable-fruit beverage fermented with two Lactobacillus plantarum strains[J]. Food Science & Biotechnology,2018:1−8.
[16] 王克明. 多菌种共固定化发酵果蔬米乳饮料的研究[J]. 发酵科技通讯,2005(3):9−11. [WANG K M. Research on the co-immobilization of fermented fruit and vegetable rice milk beverages with multiple strains[J]. Journal of Fermentation Science and Technology,2005(3):9−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2214.2005.03.004 WANG K M. Research on the co-immobilization of fermented fruit and vegetable rice milk beverages with multiple strains[J]. Journal of Fermentation Science and Technology, 2005(3): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2214.2005.03.004
[17] 薛淑龙, 范昊安, 陈小伟, 等. 竹叶酵素发酵过程中代谢产物及抗氧化活性的变化[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(5):228−235. [XUE S L, FAN H A, CHEN X W, et al. Changes in metabolites and antioxidant activity during bamboo leaf enzyme fermentation[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(5):228−235. XUE S L, FAN H A, CHEN X W, et al. Changes in metabolites and antioxidant activity during bamboo leaf enzyme fermentation[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(5): 228-235.
[18] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 12456-2021食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 12456-2021 National Food Safety standard. Determination of total acids in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2021.
[19] 范昊安, 沙如意, 杜柠, 等. 苹果梨酵素发酵过程中香气成分的变化[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):177−184. [FAN H A, SHA R Y, DU N, et al. Changes in aroma components during the fermentation of apple pear enzymes[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):177−184. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191106-077 FAN H A, SHA R Y, DU N, et al. Changes in aroma components during the fermentation of apple pear enzymes[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(2): 177-184. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191106-077
[20] 王珍珍, 沙如意, 王高坚, 等. HPLC法同时测定食用植物酵素中12种有机酸[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(19):279−285. [WANG Z Z, SHA R Y, WANG G J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 12 organic acids in edible plant enzymes by HPLC[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(19):279−285. WANG Z Z, SHA R Y, WANG G J, et al. Simultaneous determination of 12 organic acids in edible plant enzymes by HPLC[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(19): 279-285.
[21] 刘雨霞, 张玲, 张小军, 等. 基于电子舌技术分类评价核桃内种皮的口感品质[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(19):258−263. [LIU Y X, ZHANG L, ZHANG X J, et al. Evaluation of the taste quality of walnut inner seed coat based on electronic tongue technology classification[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(19):258−263. LIU Y X, ZHANG L, ZHANG X J, et al. Evaluation of the taste quality of walnut inner seed coat based on electronic tongue technology classification[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(19): 258-263.
[22] 赵优萍, 张沙沙, 张婷, 等. 不同提取方法对牡丹籽油品质与抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(1):11−16. [ZHAO Y P, ZHANG S S, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of different extraction methods on the quality and antioxidant properties of peony seed oil[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(1):11−16. ZHAO Y P, ZHANG S S, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of different extraction methods on the quality and antioxidant properties of peony seed oil[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(1): 11-16.
[23] MARQUEZ A, SERRATOSA M P, LOPEZ-TOLEDANO A, et al. Colour and phenolic compounds in sweet red wines from merlot and tempranillo grapes chamber-dried under controlled conditions[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,130(1):111−120. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.010
[24] 陈希苗, 李美英, 许秋莉, 等. 体外模拟胃肠消化中山楂多酚及抗氧化活性的变化[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(5):31−37. [CHEN X M, LI M Y, XU Q L, et al. Changes in hawthorn polyphenols and antioxidant activity in simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[J]. Food Science,2019,40(5):31−37. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20170930-447 CHEN X M, LI M Y, XU Q L, et al. Changes in hawthorn polyphenols and antioxidant activity in simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(5): 31-37. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20170930-447
[25] 张巧, 柯博芳, 唐小闲, 等. 不同发酵菌种对大果山楂酵素品质的影响[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(6):162−166. [ZHANG Q, KE B F, TANG X X, et al. The effect of different fermentation strains on the quality of enzymes in Crataegus hawthorn[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(6):162−166. ZHANG Q, KE B F, TANG X X, et al. The effect of different fermentation strains on the quality of enzymes in Crataegus hawthorn[J]. Food Industry, 2020, 41(6): 162-166.
[26] ZHAOG H, FANG Z, DZIUGAN P, et al. Development of organic acids and volatile compounds in cider during malo lactic fermentation[J]. Czech Journal of Food Sciences,2014,32(1):69−76. doi: 10.17221/127/2013-CJFS
[27] 雍炜, 刘健, 邢仕歌, 等. 醋蒜加工过程中有机酸和矿质元素的变化规律研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(24):6460−6464. [YONG W, LIU J, XING S G, et al. Study on the changes of organic acids and mineral elements during the processing of vinegar and garlic[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2018,9(24):6460−6464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.24.021 YONG W, LIU J, XING S G, et al. Study on the changes of organic acids and mineral elements during the processing of vinegar and garlic[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2018, 9(24): 6460-6464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.24.021
[28] 肖仔君, 钟瑞敏, 陈惠音, 等. 植物乳杆菌的生理功能与应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2005(2):87−89. [XIAO Z J, ZHONG R M, CHEN H Y, et al. Physiological function and application of Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. China Food Additives,2005(2):87−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2005.02.023 XIAO Z J, ZHONG R M, CHEN H Y, et al. Physiological function and application of Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. China Food Additives, 2005(2): 87-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2005.02.023
[29] 叶秀娟, 郑炯. 高效液相色谱法同时测定泡蒜中的有机酸[J]. 中国调味品,2014,39(11):100−104. [YE X J, ZHENG J. Simultaneous determination of organic acids in garlic by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Seasoning,2014,39(11):100−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2014.11.025 YE X J, ZHENG J. Simultaneous determination of organic acids in garlic by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chinese Seasoning, 2014, 39(11): 100-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2014.11.025
[30] 方晟, 陈犇, 沙如意, 等. 百合酵素自然发酵过程中有机酸及其体外抗氧化活性的变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(22):39−46. [FANG S, CHEN B, SHA R Y, et al. Changes in organic acids and their in vitro antioxidant activities during natural fermentation of lily enzymes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(22):39−46. FANG S, CHEN B, SHA R Y, et al. Changes in organic acids and their in vitro antioxidant activities during natural fermentation of lily enzymes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(22): 39-46.
[31] 代丽凤, 罗理勇, 罗江琼, 等. 植物苦味物质概况及其在食品工业的应用[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(11):305−318. [DAI L F, LUO L Y, LUO J Q, et al. General situation of plant bitter substances and their application in food industry[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2020,20(11):305−318. DAI L F, LUO L Y, LUO J Q, et al. General situation of plant bitter substances and their application in food industry[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2020, 20(11): 305-318.
[32] 梁莹, 崔炳群, 程航, 等. 高倍甜味剂在调味品中的应用[J]. 中国酿造,2009(12):75−78. [LIANG Y, CUI B Q, CHENG H, et al. Application of high-strength sweeteners in condiments[J]. China Brewing,2009(12):75−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2009.12.027 LIANG Y, CUI B Q, CHENG H, et al. Application of high-strength sweeteners in condiments[J]. China Brewing, 2009(12): 75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2009.12.027
[33] 王益莉, 欧雪莲, 李朝南, 等. 发酵时间对五种果蔬酵素抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2018(1):175−181. [WANG Y L, OU X L, LI C N, et al. The effect of fermentation time on the antioxidant activity of five fruit and vegetable enzymes[J]. China Food Additives,2018(1):175−181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.01.018 WANG Y L, OU X L, LI C N, et al. The effect of fermentation time on the antioxidant activity of five fruit and vegetable enzymes[J]. China Food Additives, 2018(1): 175-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.01.018
[34] 陈小伟, 程勇杰, 蒋立新, 等. 草莓酵素发酵过程中代谢产物及抗氧化性的变化研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(5):163−171. [CHEN X W, CHENG Y J, JIANG L X, et al. Study on the changes of metabolites and antioxidant activity during strawberry enzyme fermentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2020,20(5):163−171. CHEN X W, CHENG Y J, JIANG L X, et al. Study on the changes of metabolites and antioxidant activity during strawberry enzyme fermentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2020, 20(5): 163-171.
[35] 王征帆. 用清除羟基自由基法评价大蒜、生姜、洋葱水提物抗氧化能力[J]. 中国调味品,2012(1):89−90. [WANG Z F. Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of aqueous extracts of garlic, ginger and onion by scavenging hydroxyl free radicals[J]. Chinese Condiments,2012(1):89−90. WANG Z F. Evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of aqueous extracts of garlic, ginger and onion by scavenging hydroxyl free radicals[J]. Chinese Condiments, 2012(1): 89-90.
[36] SIU M T, SHAPIRO A M, WILEY M J, et al. A role for glutathione, independent of oxidative stress, in the developmental toxicity of methanol[J]. Toxicology & Applied Pharmacology,2013,273(3):508−515.
[37] 胡建锋. 《食品安全国家标准蒸馏酒及其配制酒》(GB 2757-2012)新标准的解读[J]. 酿酒科技,2013(2):119−121. [HU J F. Interpretation of the new standard of “National food safety standard for distilled liquor and its blended liquor” (GB 2757-2012)[J]. Wine Making Science and Technology,2013(2):119−121. HU J F. Interpretation of the new standard of “National food safety standard for distilled liquor and its blended liquor” (GB 2757—2012)[J]. Wine Making Science and Technology, 2013(2): 119-121.
[38] 全国食品工业标准化技术委员会(SAC/TC64). QB/T 5323-2018植物酵素[S]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2018. National Food Industry Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC64). QB/T 5323-2018 Plant enzyme[S]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2018.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 郭元新,郭宇,朱凤,张瑶,王东旭,叶华,俞玥. 微波联合金属离子对麦胚中肽的富集研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(01): 217-223 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





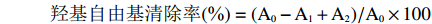

 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



