Optimization of Flocculation Process of Yellow Serofluid by Response Surface Methodology and Its Metabolomics Analysis
-
摘要: 为了提高黄浆水的附加值和利用率,缓解排放黄浆水带来的环境污染,本文对黄浆水中的可溶性固形物进行絮凝处理。在单因素实验基础上结合响应面法对黄浆水中可溶性固形物的絮凝工艺进行优化,并且对絮凝前后黄浆水进行了蛋白质和总糖含量测定、生化需氧量和化学需氧量测定以及代谢组学测定。实验结果表明,絮凝沉降黄浆水可溶性固形物最佳工艺参数为:壳聚糖添加量为0.54 mg/mL,海藻酸钠添加量为0.24 mg/mL,pH为4.4,温度为47 ℃,此时黄浆水可溶性固形物沉降率为(46.26%±0.38%);蛋白质含量下降40.68%、总糖含量下降8.41%;生化需氧量和化学需氧量去除率分别为43%、40.95%。代谢组学实验结果表明:黄浆水絮凝前后有66种化合物含量存在显著变化。本研究结果表明絮凝能有效的降低黄浆水中可溶性固形物的含量,为黄浆水的进一步开发利用提供一定的参考。Abstract: In order to improve the added value and utilization rate of yellow serofluid and alleviate the environmental pollution caused by the discharge of yellow serofluid, the soluble solids in yellow serofluid were flocculated. On the basis of single factor experiment, the flocculation process of soluble solids in yellow serofluid was optimized with response surface methodology. The contents of protein and total sugar, BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), COD (chemical oxygen demand) and metabolomics of yellow serofluid before and after flocculation were determined. The experimental results showed that the optimal technological parameters of flocculation sedimentation of soluble solids in yellow serofluid were as follows: Chitosan content was 0.54 mg/mL, sodium alginate content was 0.24 mg/mL, pH was 4.4, temperature was 47 ℃, and the sedimentation rate of soluble solids in yellow serofluid was (46.26%±0.38%). Protein content decreased by 40.68% and total sugar content decreased by 8.41%. The removal rates of BOD and COD were 43% and 40.95%, respectively. Metabolomics experiment results showed that 66 compounds in yellow serofluid were significantly changed before and after flocculation. The results showed that flocculation could effectively reduce the content of soluble solids in yellow serofluid, which provides a certain reference for further development and utilization of yellow serofluid.
-
黄浆水是在豆制品(如豆干、千张和豆腐等)生产过程中排放的富含蛋白质、低聚糖、异黄酮等营养物质的乳黄色不透明废水[1],据不完全统计,每加工1 t大豆约排放2~5 t黄浆水[2]。长期以来,大部分黄浆水被直接排放,其中蛋白质等有机物也一起大量流失,造成了严重的环境污染[3]。因此充分回收黄浆蛋白、低聚糖和异黄酮等营养物质,提高其利用效率,不仅具有一定的经济价值,同时还可以缓解排放黄浆水带来的环境污染问题[4]。
目前,黄浆水营养成分回收利用方式有:富集与提取[5-8]、二次加工[9-10]、发酵处理[11-13]、单室微生物燃料电池处理[14]以及香蒲植物修复[15]等。此外,絮凝工艺[16-17]也是沉降黄浆中蛋白质等营养成分的一种重要方法,可以有效降低黄浆水中可溶性固形物的含量,回收其中的营养物质[16],降低黄浆水生化需氧量(biochemical oxygen demand,BOD)和化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand,COD),从而减少环境污染。
目前关于黄浆水絮凝工艺的研究主要集中在絮凝剂的选择以及对黄浆水中单个组分的回收利用方面,而对于复配絮凝剂、絮凝工艺的优化及多种成分同时絮凝回收利用的研究相对较少[1,16-17]。本实验在单因素的基础上,采用响应面法优化了复配絮凝剂对絮凝黄浆水中可溶性固形物的工艺参数,通过代谢组学分析探究黄浆水中小分子物质在絮凝前后的变化,同时测定分析絮凝前后黄浆水的蛋白质含量、总糖含量发现其中营养物质变化的规律,为有效控制黄浆水污染,开发利用其营养成分,提供一定的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黄浆水 南京市鸿味豆制品厂;壳聚糖 生物试剂,国药集团化学试剂有限公司(脱乙酰度 80~95,粘度50~800 mPa·s);海藻酸钠 化学纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;氢氧化钠、冰乙酸 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;盐酸 分析纯,南京化学试剂股份有限公司;试验用水为去离子水,除说明外其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
JY-502电子天平 上海浦春计量仪器有限公司;PHS-3C pH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;HH-2数显恒温水浴锅 上海江星仪器有限公司;NANOSTAR7.5digital悬臂搅拌器 艾卡仪器设备有限公司;CSY-G2可溶性固形物含量检测仪 深圳市芬析仪器制造有限公司(测定范围:0.01%~100%,可读性:0.01%);L3-5K台式低速离心机 湖南可成仪器设备有限公司;LC-QTOF-MS为高效液相色谱(安捷伦1260)串联飞行时间质谱(AB SCIEX QTOF 5600+) 安捷伦。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 絮凝工艺
取黄浆水原液(yellow serofluid)100 mL,添加壳聚糖和海藻酸钠(壳聚糖和海藻酸钠分别使用3%的冰乙酸和去离子水配置成3%的溶液使用),调节pH(1 mol/L HCl或1 mol/L NaOH)和温度,在恒温水浴锅中用机械搅拌器对其进行搅拌,搅拌时间为20 min,搅拌速度为120 r/min,取出絮凝后的黄浆水进行离心,4000 r/min离心10 min,将絮凝后的上清液收集,称为絮凝液(supernatant),使用可溶性固形物含量检测仪测定原液及絮凝液中可溶性固形物含量。
1.2.2 单因素实验
按照1.2.1中的提取方法,实验基本条件为:壳聚糖0.5 mg/mL,海藻酸钠0.2 mg/mL,pH4.5,温度35 ℃。单因素实验条件为壳聚糖添加量为0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 mg/mL;海藻酸钠添加量为0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mg/mL;pH为2.5、3.5、4.5、5.5、6.5;温度设定为15、25、35、45、55 ℃,分别考察壳聚糖添加量、海藻酸钠添加量、pH和温度对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面优化试验设计
在单因素实验结果的基础上采用Box-Benhnken的组合设计对絮凝工艺沉降黄浆水可溶性固形物工艺进行优化,以可溶性固形物沉降率为响应值,响应面优化试验因素和水平表见表1。根据响应面优化设计试验结果进行验证实验,并比较预测可溶性固形物沉降率与实际可溶性固形物沉降率。
表 1 响应面分析实验因素及水平Table 1. Independent variable and their levels of response surface methodology因素 实验水平 −1 0 1 A壳聚糖添加量(mg/mL) 0.4 0.5 0.6 B海藻酸钠添加量(mg/mL) 0.1 0.2 0.3 CpH 3.5 4.5 5.5 D温度(℃) 35 45 55 1.2.4 可溶性固形物沉降率的计算
按照公式(1)计算:
SR(%)=F1−F2F1×100 (1) 式(1)中:可溶性固形物沉降率简称为沉降率,SR(sedimentation rate)表示沉降率,%,F1为黄浆水原液中可溶性固形物含量,%,F2为絮凝液中可溶性固形物含量,%。
1.2.5 蛋白质及总糖含量的测定
蛋白质含量参照GB5009.5-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定》进行测定;总糖含量测定参照苯酚-硫酸法[18],移取1 mg/mL葡萄糖标准溶液0.00、0.50、1.00、1.50、2.00、2.50、3.00、3.50 mL,分别置于8个100 mL的容量瓶中,蒸馏水稀释至刻度,制成不同浓度的标准溶液。然后从各瓶中分别移取2.00 mL标准溶液置于试管中,加入1 mL 6%的苯酚溶液,迅速加入5 mL浓硫酸,于室温静置20 min,后在490 nm处测吸光度。绘制得葡萄糖标准曲线为Y=4.65x−0.0016(其中Y为吸光度,A;x为葡萄糖浓度,g/L),R2=0.9995。移取2.00 mL样品稀释液,加入到25 mL试管中,加入1 mL 6%苯酚溶液,迅速加入5 mL浓硫酸,于室温静置20 min,后在490 nm处测吸光值,带入标准曲线,计算含量。
1.2.6 生化需氧量(BOD)和化学需氧量(COD)的测定
BOD的测定参照HJ 505-2009水质 五日生化需氧量(BOD5)的测定 稀释与接种法进行;COD的测定参照HJ828-2017水质 化学需氧量的测定 重铬酸盐法进行。
1.2.7 黄浆水代谢组学测定
将黄浆水原液和絮凝液进行LC-QTOF-MS检测,分析其中的化学组成[19]。LC-QTOF-MS的色谱柱条件为X Select HSS T3(4.6 mm×150.0 mm,3.5 μm),正电离模式流动相为0.1%甲酸/水(A)和乙腈(B),负电离模式流动相为0.005 mol/L乙酸铵(A)和乙腈(B)。流动相梯度洗脱程序为:0~3.00 min,10% B;3.00~21.00 min,10%~95% B;21.00~28.00 min,95% B;28.00~28.10 min,95%~10% B;28.10~34. 00 min,10% B。
LC-QTOF-MS的质谱条件选择QTOF-MS全扫描模式和信息相关分析(IDA),质量扫描范围为m/z 50~1000,正、负电离模式的源电压分别为5500 V和4500 V,帘气、雾化器(gas1)和加热气体(gas2)的流动压力分别为25、50和50 psi。碰撞能量(CE)分别为30 V和−30 V。利用MS-DIAL软件对LC-QTOF-MS数据进行分析,通过分析保留时间、质量精度和同位素比值以及与公共数据库(包括MassBank、LipidBlast、GNPS、Metabo BASE)进行MS/MS相似性匹配来进行化合物鉴定。
1.3 数据处理
单因素实验数据分析及显著性检验采用Origin9.6软件进行分析,响应面优化试验采用Design-Expert8.0.6软件进行设计及结果与方差分析,显著水平P<0.05。所有试验均重复3次。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 壳聚糖添加量对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响
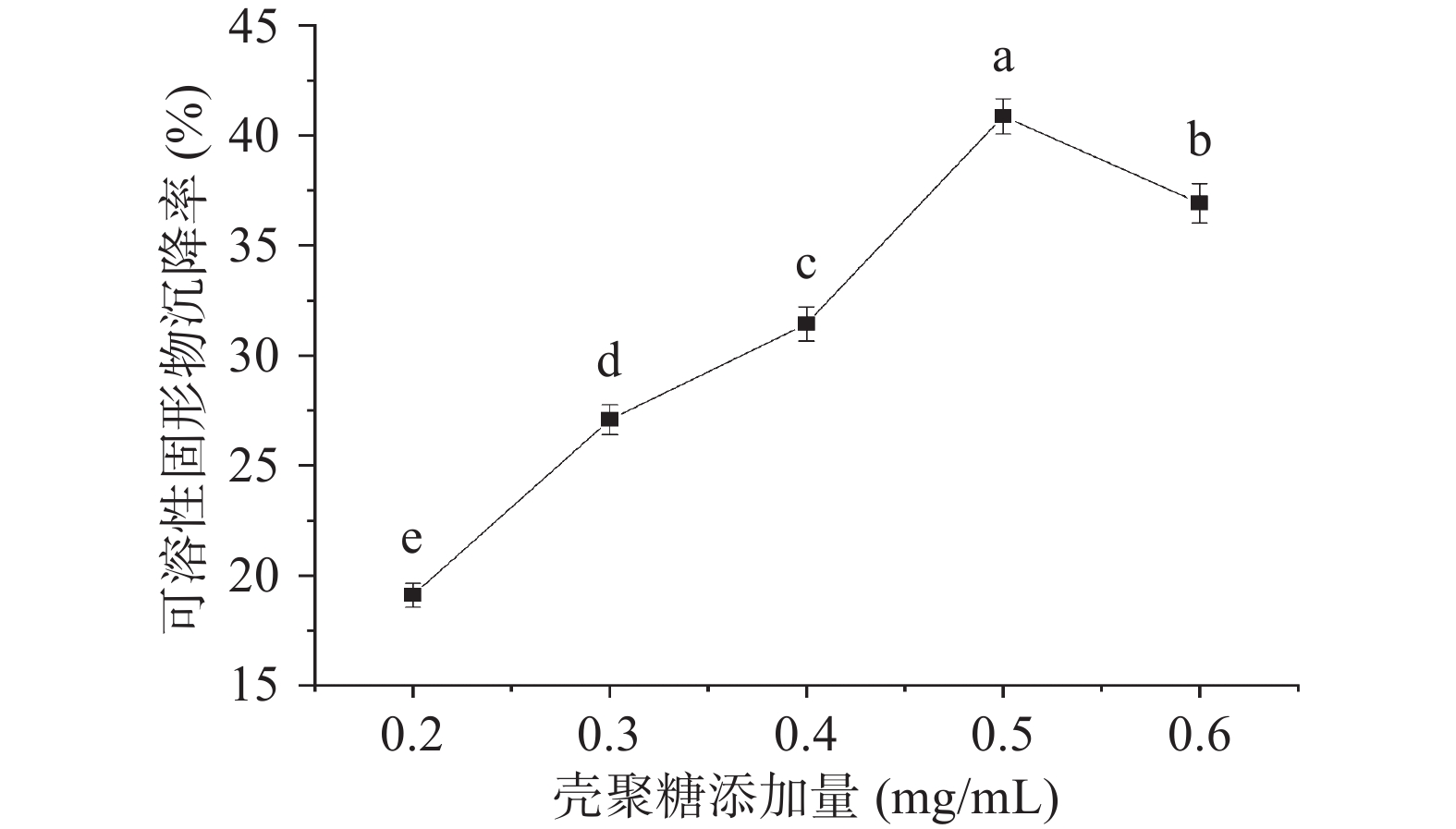
由图1可知,随着壳聚糖添加量的增加,沉降率明显上升,壳聚糖在絮凝过程中起着主要作用,当壳聚糖添加量为0.5 mg/mL时,此时沉降率最高为40.86%,可溶性固形物与壳聚糖充分结合达到平衡,可溶性固形物-壳聚糖二元复合物的浓度趋于饱和且形成稳定的絮体。当添加量超过0.5 mg/mL时,沉降率下降的主要原因是随着壳聚糖添加量的增加,溶液逐渐形成胶状悬浮体,其粘度也随之增大,可溶性固形物析出困难,导致沉降率降低[16,20]。因此,最优的壳聚糖添加量为0.5 mg/mL。
2.1.2 海藻酸钠添加量对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响
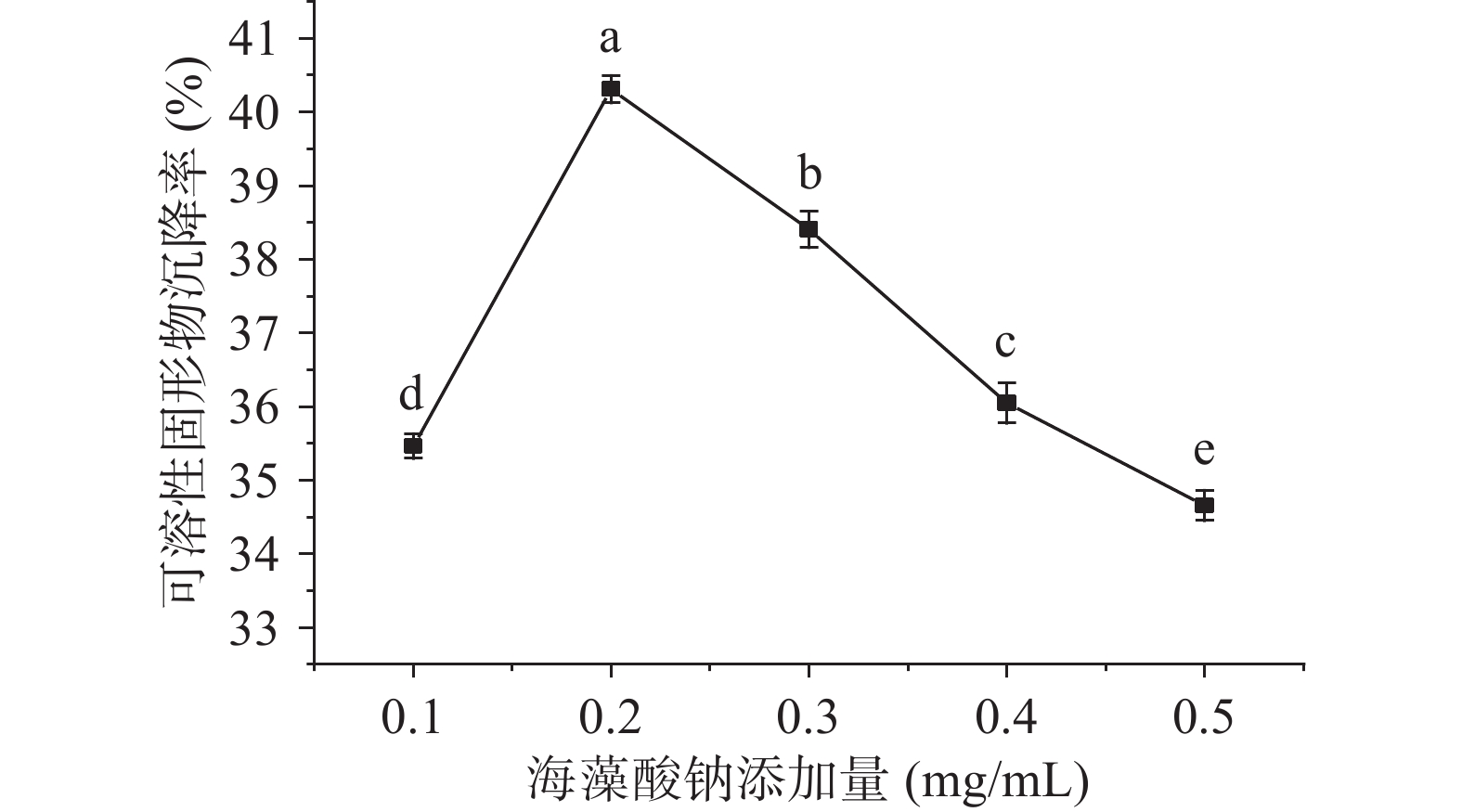
由图2可知,当海藻酸钠添加量为0.2 mg/mL时,沉降率最高为39.97%,随着海藻酸钠添加量逐渐增高,沉降率呈现下降趋势。这是因为壳聚糖是带正电的碱基多糖,在黄浆水中通过静电吸附作用进行絮凝形成絮体。海藻酸钠是一种阴离子多糖,壳聚糖和海藻酸钠通过静电作用吸附可溶性固形物,当海藻酸钠添加量超过0.2 mg/mL时,使复合絮凝剂的平衡状态破坏导致黄浆水中的絮体不稳定[16,21]。因此,最优的海藻酸钠添加量为0.2 mg/mL。
2.1.3 pH对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响
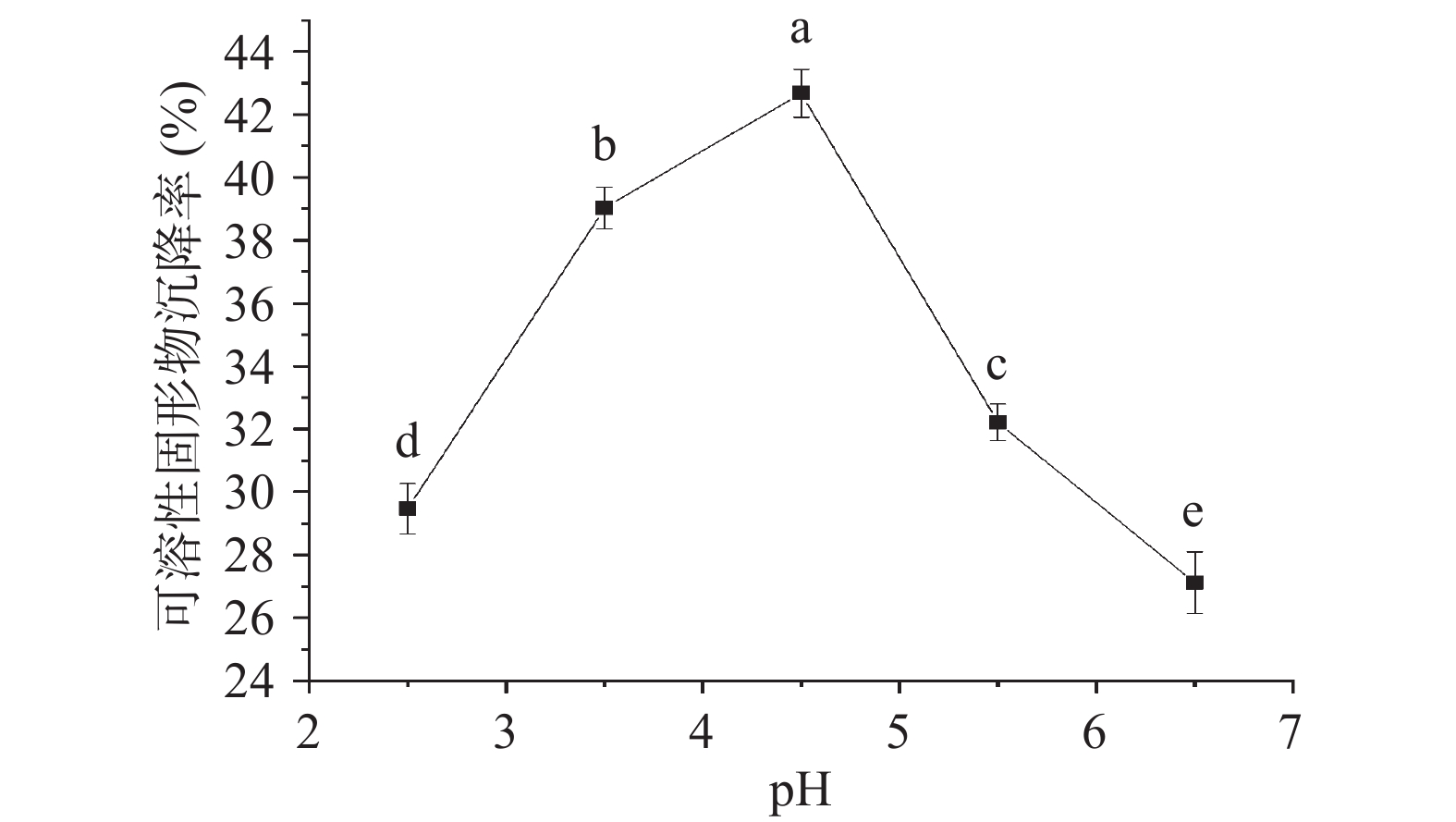
由图3可知,随着pH的增加,沉降率逐渐增加,在pH为4.5时沉降率达到最高,此时可溶性固形物的沉降率为42.67%,随着pH的继续增大,沉降率呈现下降趋势。当pH为4.5时接近大豆乳清蛋白的等电点,溶解度降低,导致蛋白质析出。同时在酸性条件下,壳聚糖的NH3+基团和海藻酸盐的COO−基团在静电力的作用下相互反应形成复合物,复合物对蛋白质和糖等可溶性固形物有较高的吸附性,可溶性固形物析出增多后导致可溶性固形物含量明显下降[19]。因此,最优的絮凝pH为4.5。
2.1.4 温度对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响
由图4可知,当温度逐渐升高时,沉降率逐渐上升,当温度升高至45 ℃时,此时沉降率最高为46.71%,超过45 ℃时,沉降的效果反而下降,此时絮体因为温度过高不稳定,导致可溶性固形物含量下降的效果不好。这可能是因为温度过高导致黄浆水中的蛋白质发生变性,使其与絮凝剂结合部位的结构发生改变,从而从絮凝剂解析下来,导致可溶性固形物沉降率的下降[22]。因此最优的絮凝温度为45 ℃。
2.2 响应面试验优化
2.2.1 实验设计方案与实验结果
在单因素实验结果的基础上,根据 Box-Behnken的中心组合原理设计了29组试验,试验结果见表2。试验结果使用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件进行拟合分析。
表 2 响应面实验设计及结果Table 2. RSM design and test results实验号 A壳聚糖
添加量B海藻酸钠
添加量CpH D温度 Y可溶性固
形物沉降率(%)1 1 0 −1 0 40.91 2 −1 1 0 0 31.28 3 0 0 0 0 44.65 4 0 −1 0 −1 35.56 5 1 −1 0 0 35.83 6 0 1 1 0 39.84 7 0 −1 0 1 33.69 8 0 1 0 − 1 38.50 9 0 0 −1 −1 39.30 10 0 0 1 −1 31.82 11 0 0 0 0 44.92 12 0 −1 1 0 32.09 13 0 1 −1 0 41.71 14 −1 −1 0 0 31.55 15 −1 0 1 0 28.88 16 −1 0 −1 0 35.29 17 −1 0 0 −1 27.81 18 1 0 1 0 39.57 19 1 0 0 −1 37.17 20 0 0 1 1 38.50 21 0 0 0 0 45.45 22 1 0 0 1 41.18 23 0 0 0 0 45.72 24 0 −1 −1 0 42.78 25 0 0 0 0 49.20 26 1 1 0 0 43.85 27 0 1 0 1 41.71 28 −1 0 0 1 29.14 29 0 0 −1 1 38.24 2.2.2 回归方程拟合及方差分析
对可溶性固形物沉降率的响应面实验结果进行回归分析,结果见表3。对四个因素进行回归拟合后得到回归方程Y(可溶性固形物沉降率)=45.99+4.55A+2.12B−2.29C+1.03D+2.07AB+1.27AC+0.67AD+2.21BC+1.27BD+1.93CD−6.69A2−3.45B2−3.39C2−5.42D2,由方差分析可知回归方程模型极显著(P<0.0001),失拟项不显著(P>0.05),R2=0.9690,Radj2=0.9380,说明此模型与实际拟合较好,实验方法可靠,所得方程与实际拟合中非正常误差所占比例较小,因此可以用此回归方程代替真实实验点分析实验结果。结果表明,壳聚糖添加量(A)、海藻酸钠添加量(B)、pH(C)、温度(D)、壳聚糖添加量与海藻酸钠添加量交互项(AB)、pH与海藻酸钠添加量交互项(BC)、壳聚糖添加量与温度交互项(CD)和各因素二次项对响应值影响显著(P<0.05),各个因素对响应值的影响显著性排序为A>C>B>D。
表 3 回归模型及方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of regression equation项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 877.91 14 62.71 31.25 <0.0001 ** A-壳聚糖 248.07 1 248.07 123.64 <0.0001 ** B-海藻酸钠 53.72 1 53.72 26.78 0.0001 ** C-pH 63.16 1 63.16 31.48 <0.0001 ** D-温度 12.61 1 12.61 6.28 0.0251 * AB 17.18 1 17.18 8.56 0.0111 * AC 6.43 1 6.43 3.20 0.0952 AD 1.8 1 1.80 0.89 0.3602 BC 19.45 1 19.45 9.69 0.0076 ** BD 6.45 1 6.45 3.22 0.0946 CD 14.98 1 14.98 7.46 0.0162 * A2 290.73 1 290.73 144.90 <0.0001 ** B2 77.37 1 77.37 38.56 <0.0001 ** C2 74.37 1 74.37 37.07 <0.0001 ** D2 190.89 1 190.89 95.14 <0.0001 ** 残差 28.09 14 2.01 失拟项 14.48 10 1.45 0.43 0.8754 不显著 误差 13.61 4 3.40 总和 906 28 注: *表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 两因素之间的交互作用响应面图见图5。通过响应曲面立体图可以清晰地看出各因素之间的相互作用对可溶性固形物沉降率的影响作用。壳聚糖添加量(A)与海藻酸钠添加量(B)的等高线图以及pH(C)与温度(D)的等高线图形状呈椭圆,三维图曲面陡峭,表明壳聚糖添加量与海藻酸钠添加量之间交互作用以及pH与温度交互作用明显且对可溶性固形物沉降率影响显著。壳聚糖添加量(A)和pH(C)的等高线图、壳聚糖添加量(A)与温度(D)的等高线图以及海藻酸钠添加量(B)与温度(D)等高线图形状接近圆形,表明壳聚糖添加量与pH之间交互作用、壳聚糖添加量与温度之间交互作用以及海藻酸钠添加量与温度之间的交互作用不显著。海藻酸钠添加量(B)和pH(C)等高线图形状呈椭圆,三维图曲面陡峭,表明海藻酸钠添加量与pH之间交互作用明显,且对可溶性固形物沉降率影响极显著。与表3中的分析结果一致。
2.2.3 验证实验
经Design-Expert8.0.6预测模型极值点,结果显示最佳提取条件为:壳聚糖添加量为0.54 mg/mL,海藻酸钠添加量为0.24 mg/mL,pH为4.42,温度为46.57 ℃,此时可溶性固形物沉降率45.46%。根据实际操作设计验证实验,其实验条件设置为壳聚糖添加量0.54 mg/mL,海藻酸钠添加量0.24 mg/mL,pH4.4,温度47 ℃,按此提取条件进行3次平行实验,在此条件下的固形物沉降率为(46.26%±0.38%),验证实验结果与预测值接近,表明该模型拟合度良好,对工艺优化合理、有效。
2.3 絮凝对蛋白质含量及总糖含量的影响
黄浆水中蛋白质和糖类是其主要的组成成分[4]。在响应面最佳优化条件下,壳聚糖添加量为0.54 mg/mL,海藻酸钠添加量为0.24 mg/mL,pH调节为4.4,温度为47 ℃,测定絮凝前后蛋白质含量和总糖含量,结果见表4。使用最佳絮凝工艺处理后原液与絮凝液蛋白含量差异显著,下降幅度为40.68%,絮凝过程中吸附蛋白效果较好,絮凝剂与蛋白质形成稳定的絮体在黄浆水中沉降析出。絮凝前后黄浆水中总糖浓度两者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05),总糖含量下降率为8.41%,表明絮凝对黄浆水中糖类的吸附作用不明显,糖类析出较少,主要存在于絮凝液中。对絮凝沉降得到的物质进行真空冷冻干燥,测得其中蛋白质纯度为(63.21%±0.48%),蛋白纯度较高,可以看出蛋白质是絮凝沉降物质中主要成分。此技术工艺简单易行,条件温和,可用于工业生产回收黄浆水中的蛋白质,也可与其他工艺结合起来使用,例如膜分离超滤工艺处理黄浆水,可以实现大分子蛋白质和小分子糖类的体系化的分离回收。
表 4 蛋白质含量及总糖含量的变化Table 4. Changes in protein and total sugar contents指标 黄浆水 黄浆水絮凝液 蛋白质(g/L) 10.03±0.33a 5.92±0.24b 总糖(g/L) 18.54±0.23a 16.98±0.07a 注:结果以“平均值±标准差”表示,同行不同字母表示显著差异,P<0.05,表5同。 2.4 絮凝对BOD及COD的影响
在响应面最佳优化条件下,测量絮凝前后黄浆水的BOD与COD,结果见表5。使用最佳絮凝工艺处理后,黄浆水的BOD去除率为43%,COD去除率为40.95%,二者降低幅度较大,絮凝工艺对降低BOD与COD具有显著效果(P<0.05)。这是因为絮凝物质中蛋白质等有机物析出,使得BOD和COD降低,所以絮凝工艺可以有效的降低黄浆水对环境的污染,同时回收黄浆水中的蛋白质。絮凝工艺简洁省时,可用于工业化生产,对保护环境及大豆产业链的发展具有重要的意义。
表 5 BOD及COD的变化Table 5. Changes of BOD and COD指标 黄浆水 黄浆水絮凝液 BOD(mg/L) 7245±88a 4130±83b COD(mg/L) 18317±125a 10817±137b 2.5 代谢组学分析
对黄浆水原液和絮凝液进行LC-QTOF-MS鉴定其中的小分子化合物,采用主成分分析法(PCA)和层次聚类分析(热图)对LC-QTOF-MS数据进行判别分析[23-25]。如图6所示,在PCA得分图中黄浆水原液和絮凝液出现明显的离散型,表明黄浆水原液和絮凝液在化学组成方面存在显著差异。在热图图7中,LC-QTOF-MS分析鉴定出原液和絮凝液中66种化合物具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。其中4-香豆酸、异亮氨酸、烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸、5’-单磷酸腺苷、9-羟基-10,12-十八二烯酸、苹果酸、去氢大豆皂甙I、大豆皂苷Ba、山柰素-4’-甲醚、刺芒柄花素等56种物质在黄浆水原液中相对含量显著高于絮凝液。麦芽糖、香豆酸、可铁林、胆碱磷酸、5’-S-甲硫腺苷、七叶苷、2’-O-甲基腺苷、2-羟基戊酸、苯并咪唑磺酸、3-(4-羟基苯基)乳酸等10种物质在絮凝液中的相对含量显著高于原液。絮凝时小分子化合物随着大分子蛋白质等有机物被絮凝剂絮凝析出,鉴定出85%的化合物含量显著降低,随着絮凝物质析出后,部分化合物絮凝前后的相对含量发生了变化,所以出现了一小部分化合物在絮凝液中的含量大于黄浆水原液中的含量。鉴定出的物质中富含多种营养物质,其中大豆皂苷可以减少机体胆固醇,增强免疫力,抵抗癌细胞以及降血糖血脂等功效[26]。刺芒柄花素在改善妇女更年期症状和改善骨质疏松等方面具有一定的作用,还具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌等生物活性[27-28]。香豆酸具有抑制肥胖以及降血糖、降血脂等生物活性[29-30]。通过絮凝对黄浆水中小分子物质进行富集,有利于黄浆水中小分子物质进一步被利用,黄浆水中小分子营养物质非常丰富,营养物质的回收对于提高黄浆水的附加值具有重要的意义。
3. 结论
本文在单因素实验的基础上,利用响应面优化絮凝工艺中黄浆水可溶性固形物沉降率的最佳条件,确定了最佳工艺参数:壳聚糖添加量为0.54 mg/mL,海藻酸钠添加量为0.24 mg/mL,pH为4.4,温度为47 ℃,在此条件下的可溶性固形物沉降率为(46.26%±0.38%),得到的絮凝物质冷冻干燥后蛋白质纯度为(63.21%±0.48%),沉降析出的蛋白质占比黄浆水原液中的40.68%,BOD和COD去除率分别43%、40.95%。絮凝对黄浆水中的可溶性固形物具有较好的沉降作用,可以有效降低黄浆水环境污染。经过絮凝后,黄浆水原液与絮凝液基于LC-QTOF-MS方法分析,鉴定出其中的66种化合物的含量发生了显著变化,代谢组学实验结果表明黄浆水在絮凝过程中,不仅使蛋白质及糖类等大分子物质絮凝出来,同时对黄浆水中的一些具有生物活性功能的小分子物质起到一定的富集作用,为黄浆水中活性小分子物质的回收利用提供一定的参考。本研究对黄浆水的絮凝工艺进行了探索,研究结果对黄浆水的处理及工业化应用提供了科学依据和数据参考。
-
表 1 响应面分析实验因素及水平
Table 1 Independent variable and their levels of response surface methodology
因素 实验水平 −1 0 1 A壳聚糖添加量(mg/mL) 0.4 0.5 0.6 B海藻酸钠添加量(mg/mL) 0.1 0.2 0.3 CpH 3.5 4.5 5.5 D温度(℃) 35 45 55 表 2 响应面实验设计及结果
Table 2 RSM design and test results
实验号 A壳聚糖
添加量B海藻酸钠
添加量CpH D温度 Y可溶性固
形物沉降率(%)1 1 0 −1 0 40.91 2 −1 1 0 0 31.28 3 0 0 0 0 44.65 4 0 −1 0 −1 35.56 5 1 −1 0 0 35.83 6 0 1 1 0 39.84 7 0 −1 0 1 33.69 8 0 1 0 − 1 38.50 9 0 0 −1 −1 39.30 10 0 0 1 −1 31.82 11 0 0 0 0 44.92 12 0 −1 1 0 32.09 13 0 1 −1 0 41.71 14 −1 −1 0 0 31.55 15 −1 0 1 0 28.88 16 −1 0 −1 0 35.29 17 −1 0 0 −1 27.81 18 1 0 1 0 39.57 19 1 0 0 −1 37.17 20 0 0 1 1 38.50 21 0 0 0 0 45.45 22 1 0 0 1 41.18 23 0 0 0 0 45.72 24 0 −1 −1 0 42.78 25 0 0 0 0 49.20 26 1 1 0 0 43.85 27 0 1 0 1 41.71 28 −1 0 0 1 29.14 29 0 0 −1 1 38.24 表 3 回归模型及方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of regression equation
项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 877.91 14 62.71 31.25 <0.0001 ** A-壳聚糖 248.07 1 248.07 123.64 <0.0001 ** B-海藻酸钠 53.72 1 53.72 26.78 0.0001 ** C-pH 63.16 1 63.16 31.48 <0.0001 ** D-温度 12.61 1 12.61 6.28 0.0251 * AB 17.18 1 17.18 8.56 0.0111 * AC 6.43 1 6.43 3.20 0.0952 AD 1.8 1 1.80 0.89 0.3602 BC 19.45 1 19.45 9.69 0.0076 ** BD 6.45 1 6.45 3.22 0.0946 CD 14.98 1 14.98 7.46 0.0162 * A2 290.73 1 290.73 144.90 <0.0001 ** B2 77.37 1 77.37 38.56 <0.0001 ** C2 74.37 1 74.37 37.07 <0.0001 ** D2 190.89 1 190.89 95.14 <0.0001 ** 残差 28.09 14 2.01 失拟项 14.48 10 1.45 0.43 0.8754 不显著 误差 13.61 4 3.40 总和 906 28 注: *表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 表 4 蛋白质含量及总糖含量的变化
Table 4 Changes in protein and total sugar contents
指标 黄浆水 黄浆水絮凝液 蛋白质(g/L) 10.03±0.33a 5.92±0.24b 总糖(g/L) 18.54±0.23a 16.98±0.07a 注:结果以“平均值±标准差”表示,同行不同字母表示显著差异,P<0.05,表5同。 表 5 BOD及COD的变化
Table 5 Changes of BOD and COD
指标 黄浆水 黄浆水絮凝液 BOD(mg/L) 7245±88a 4130±83b COD(mg/L) 18317±125a 10817±137b -
[1] 张焕焕, 徐雅芫, 李婷婷, 等. 豆制品黄浆水综合利用研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 农产品加工,2021,520(2):79−83,86. [ZHANG H H, XU Y W, LI T T, et al. Research status and development trend of comprehensive utilization of soybean yellow pulp water[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021,520(2):79−83,86. [2] 孔彦卓, 尹乐斌, 雷志明, 等. 豆清液综合利用研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技,2017(1):247−249. [KONG Y Z, YIN L B, LEI Z M, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of soybean processing wastewater[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2017(1):247−249. [3] 李云捷, 周哲, 刘志, 等. 大豆黄浆水综合利用研究进展[J]. 科技与创新,2016,53(5):9−10. [LI Y J, ZHOU Z, LIU Z, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of soybean yellow pulp water[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation,2016,53(5):9−10. [4] 郑玉玺. 大豆黄浆水回收利用研究进展[J]. 广州城市职业学院学报,2015,9(2):58−61. [ZHENG Y X. Research and progress on recycling of soybean yellow slurry water[J]. Journal of Guangzhou City Polytechnic,2015,9(2):58−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0408.2015.02.010 [5] 刘峥, 蒋毅民. 微波法提取大豆中低聚糖的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2002(2):24−26. [LIU Z, JIANG Y M. Study on microwave extraction of oligosaccharides from soybean[J]. Food Research and Development,2002(2):24−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2002.02.011 [6] 顾建明, 潘春云. 混合活性炭吸附柱法回收黄浆水中大豆异黄酮[J]. 食品研究与开发,2007,135(2):68−71. [GU J M, PAN C Y. The recovery soybean isoflavone by the method of arsrption column packed with compounded activated carbon[J]. Food Research and Development,2007,135(2):68−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2007.02.021 [7] COURIOL C, QUELLEC S L, GUIHARD L, et al. Separation of acid whey proteins on the preparative scale by hyperdiffusive anion exchange chromatography[J]. Chromatographia,2000,52(7-8):465−472.
[8] 佟献俊, 孙洋, 钱方. 大豆黄浆水中乳清蛋白和低聚糖制备研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2009,213(12):3−5. [TONG X J, SUN Y, QIAN F. Research progress on preparation of whey protein and oligosaccharides in soybean yellow pulp water[J]. China Brewing,2009,213(12):3−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2009.12.002 [9] 郑宋友, 段红梅, 吴淑清. 黄浆水苹果汁复合饮料的研制[J]. 江苏调味副食品,2018,154(3):9−12. [ZHENG S Y, DUAN H M, WU S Q. Development of yellow pulp apple juice compound beverage[J]. Jiangsu Condiment and Subsidiary Food,2018,154(3):9−12. [10] 李丽梅, 刘霞, 李喜宏, 等. 黄浆水红枣复合饮料的研制及其稳定性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(2):74−77. [LI L M, LIU X, LI X H, et al. The development of yellow slurry water and red jujube compound beverage and its stability study[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(2):74−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.02.016 [11] 乔明武, 何人可, 宋莲军, 等. 乳酸菌和酵母菌发酵黄浆水制备有机酸工艺优化[J]. 农产品加工,2018(17):19−21,28. [QIAO M W, HE R K, SONG L J, et al. Optimal preparation technology of organic acids by lactic acid bacteria and yeast fermentation of yellow pulp water[J]. Farm Products Processing,2018(17):19−21,28. [12] GAN L L, HUI L, YUN Y T, et al. Improved S-adenosyl-L-methionine production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using tofu yellow serofluid[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2020,309:100−106. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.01.004
[13] 李穗君, 费永涛, 李理. 乳酸菌发酵豆腐乳清的代谢作用研究[C]//第十四届益生菌与健康国际研讨会摘要集, 2019: 55−56. LI S J, FEI Y T, LI L. The high density fermentation factors affect a streptococcus the rmophilic strain isolated from dairy fan of lyophilization[C] // Summary of the Fourteenth International Symposium on Probiotics and Health, 2019: 55−56.
[14] PERMANA D, DJAENUDIN. Performance of single chamber microbial fuel cell (scmfc) for biological treatment of tofu wastewater[J]. Iop Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2019,277(1):8−12(9pp).
[15] PERTIWI A, BADRUS Z, ANGGIT O P. The ability of Typha angustifolia L. for degradation of bod and cod in wastewater of tofu industry using phytoremediation[J]. Advanced Science Letters,2017,23(3):2200−2203(4). doi: 10.1166/asl.2017.8713
[16] 褚绍霞. 大豆黄浆水的资源化利用[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2010. CHU S X. Beneficial utilization of tofu wastewater[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2010.
[17] 刘宇. 豆制品废水中功能性成分的分离与纯化[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2015. LIU Y. Separation and purification of function comptents in soybean wastewater[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2015.
[18] ROBYT J F, BEMIS S. Use of the autoanalyzer for determining the blue value of the amylose-iodine complex and total carbohydrate by phenol-sulfuric acid[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1967,19(1):56−60. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90133-9
[19] 刘启月, 李勇, 陈小龙, 等. 基于代谢组学分析桃胶中酚类化合物含量及抗氧化活性[J]. 江苏农业学报,2021,37(3):746−753. [LIU Q Y, LI Y, CHEN X L, et al. Analysis on phenolics contents and antioxidant activity in peach gum based on metabolomics[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2021,37(3):746−753. [20] 侯静宇, 赵佳启, 张金秀, 等. 壳聚糖絮凝蛹虫草菌丝体多糖工艺优化及其失活动力学分析[J]. 菌物学报,2020,39(12):2346−2354. [HOU J Y, ZHAO J Q, ZHANG J X, et al. Optimization of chitosan flocculation of cordyceps militaris polysaccharide and analysis of inactivation mechanics of chitosan[J]. Mycosystema,2020,39(12):2346−2354. [21] 黄立新, 王占全, 尹寿伟, 等. 海藻酸钠用于红糖溶液脱钙的试验研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(3):106−113. [HUANG L X, WANG Z Q, YIN S W, et al. Experimental study on decalcification of brown sugar solution by sodium alginat[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2021,49(3):106−113. [22] 刘淑集, 黄珊红, 陈晓婷, 等. 响应面法优化三氯化铁回收河鲀鱼糜漂洗液中蛋白质的研究[J]. 渔业研究,2021,43(3):268−274. [LIU S J, HUANG S H, CHEN X T, et al. Optimization of the recovery of protein from washing solution of the fugu surimi by FeCl3[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research,2021,43(3):268−274. [23] 田翔, 薄涛, 康瑜, 等. 基于GC-MS评估不同预处理对小米代谢物提取的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021:1−15. [TAIN X, BO T, KANG Y, et al. Effects of pretreatment methods on extraction of millet metabolites based on GC-MS analysis[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021:1−15. doi: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2864.TS.20210714.1051.006.html [24] ROSA M A S, CARLOS H, ALEJANDRO B, et al. Technological classification of basque cider apple cultivars according to their polyphenolic profiles by pattern recognition analysis[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2004(26):16−8006.
[25] 宋江峰, 李大婧, 刘春泉, 等. 甜糯玉米软罐头主要挥发性物质主成分分析和聚类分析[J]. 中国农业科学,2010,43(10):2122−2131. [SONG J F, LI D J, LIU C Q, et al. Principal components analysis and cluster analysis of flavor compositions in waxy corn soft can[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(10):2122−2131. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.10.019 [26] A E A, A B M, W S K. Inhibition of AKT signaling and enhanced ERK1/2 activity are involved in induction of macroautophagy by triterpenoid b-group soyasaponins in colon cancer cells.[J]. Carcinogenesis,2006,27(2):298−306. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi214
[27] JULIANA M D, P E P J, REJANE A B. Formononetin: Biological effects and uses-a review[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,359:129975. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129975
[28] WU J J. Formononetin relieves the facilitating effect of lncRNA AFAP1-AS1-miR-195/miR-545 axis on progression and chemo-resistance of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(undefined).
[29] PRAHADEESH N, SITHAMBARESAN M, MATHIVENTHAN U. A study on hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity and ferric reducing ability of simple coumarins[J]. Emerging Science Journal,2018,2(6):417−417. doi: 10.28991/esj-2018-01161
[30] ZHAO R S, BORA Y, SUMI O, et al. Aqueous extracts of hulled barley containing coumaric acid and ferulic acid inhibit adipogenesis in vitro and obesity in vivo[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2015,12:208−218. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.11.022
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陆健航,李瑞琳,陈凤美,刘宇,姜维. 东海区市售大黄鱼鲞的品质分析研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(11): 159-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗振玲,高海波,杨挺,付余. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定小黄花鱼中9种生物胺. 食品工业科技. 2023(05): 251-257 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王梅英,吴若玫,黄琳杉,陈慧斌. 黄鱼鲞加工中感官品质和挥发性风味成分分析. 闽南师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 79-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



