Study on Extraction Process Optimization, Structure Identification and Functional Activity of Polysaccharide from Sweet Potato Residue
-
摘要: 本研究采用超声波辅助热水浸提法提取甘薯渣粗多糖,经单因素实验和响应面优化提取工艺参数,并通过酶法脱蛋白、H2O2法脱色和Superose 12 10/300 GL凝胶柱对多糖进行分离纯化,得到甘薯渣多糖。采用紫外光谱法、红外光谱法和高效液相色谱法对甘薯渣多糖进行结构鉴定,在此基础上进一步对甘薯渣多糖进行抗氧化活性测定以及体外降血糖能力测定。结果表明,甘薯渣多糖的最佳提取工艺条件为提取温度70 ℃、超声功率264 W、提取时间56 min、料液比1:17 g/mL,在此条件下多糖得率为5.053%。经红外鉴定表明该多糖为α-吡喃葡萄糖,高效液相测定表明其由9.46%甘露糖、4.28%鼠李糖、11.72%葡萄糖醛酸、62.37%葡萄糖和10.58%木糖组成。测定其体外抗氧化活性发现,甘薯渣多糖清除DPPH·、·OH、超氧阴离子的IC50值分别为3.089、4.879、5.832 mg/mL,对其体外降血糖测定发现,甘薯渣多糖抑制α-淀粉酶以及α-葡萄糖苷酶的IC50值分别为7.674、18.961 mg/mL。综上,甘薯渣多糖具有良好的抗氧化、降血糖等功能活性。上述研究结果为甘薯渣多糖的纯化、功能活性分析及其综合利用提供了数据参考。Abstract: In this study, ultrasonic assisted hot water extraction was used to extract crude polysaccharides from sweet potato residue. Single factor experiments and response surface optimization were used to extract the technological parameters. The polysaccharides from sweet potato residue were obtained by enzymatic deproteinization, H2O2 decolorization and Superose 12 10/300 GL gel column. The structure of sweet potato residue polysaccharide was identified by ultraviolet spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy and HPLC. On this basis, the antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic ability of sweet potato residue polysaccharide were determined in vitro. The experimental results showed that the optimum extraction conditions of polysaccharide from sweet potato residue were extraction temperature 70 ℃, ultrasonic power 264 W, extraction time 56 min and solid-liquid ratio 1:17 g/mL. under these conditions, the yield of polysaccharide was 5.053%. Infrared identification showed that the polysaccharide was α-glucopyranose was determined by HPLC. It was composed of 9.46% mannose, 4.28% rhamnose, 11.72% glucuronic acid, 62.37% glucose and 10.58% xylose. The IC50 values of DPPH·, ·OH and superoxide anion scavenged by sweet potato residue polysaccharide were 3.089, 4.879, 5.832 mg/mL respectively, the IC50 values of α-amylase and α-glucosidase were 7.674 and 18.961 mg/mL, respectively. In summary, the sweet potato residue polysaccharide had good antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities. The above results would provide data reference for the purification, functional activity analysis and comprehensive utilization of sweet potato residue polysaccharide.
-
甘薯是我国淀粉加工产业重要的原材料。近年来,甘薯加工业在我国发展迅速,甘薯淀粉产出的同时,也产生了大量不易处理的甘薯渣,甘薯渣约占甘薯鲜重的45%~60%,其含有多种可溶性膳食纤维等多糖类物质[1-3]。大量的甘薯渣堆积,不仅处理费时费力而且容易腐败发臭[4-6],导致资源浪费以及环境污染。因此,甘薯废渣的综合利用是目前亟待解决的重要问题。
当今对植物多糖的研究越来越受到专家学者们的关注[7-8],其中可溶性多糖具有抗氧化[9]、抗肿瘤[10]、抗癌[11]、降血糖[12]、降血压[13]以及提高人体免疫力等生物功能活性[14-15]。甘薯渣多糖是一类由糖苷键链接而成的高分子聚合物,分为活性多糖、膳食纤维和糖蛋白等,目前甘薯多糖通过水提醇沉法、超声波辅助热水浸提法、微波辅助法以及酶解提取法等方法进行提取。抗氧化活性以及降血糖活性是甘薯渣多糖最主要的功能活性,甘薯渣多糖通过抗氧化作用减少自由基对胰岛功能损伤,使胰岛B细胞释放和合成胰岛素增加,或使胰岛素活性增加,从而降低血糖浓度[16]。Wu等[6] 采用水提醇沉法从紫甘薯中提取的一种甘薯多糖SPP3-1,其得率5.42%,由鼠李糖、木糖、葡萄糖和半乳糖组成,具有良好的抗氧化活性。
本试验采用超声波辅助热水浸提法提取甘薯渣多糖,相比于水提醇沉法[17]和微波辅助法[18]而言,超声波辅助热水浸提法具有提取时间短、操作简单以及成本低廉等优点,酶解提取法[19]同样技术成熟、价格低廉但是提取杂质较多,不益于后期分离纯化。本文采用响应面优化超声波辅助热水浸提工艺,并对其进行分离纯化及结构鉴定,同时测定其抗氧化活性以及体外降血糖能力等功能活性,为甘薯渣多糖的提取工艺、甘薯渣多糖对血糖的调节作用以及甘薯渣的综合利用提供研究依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
甘薯 河南省新乡市世纪华联超市;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、溴化钾、3,5-二硝基水杨酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;甲醇 天津科茂化学试剂有限公司;标准单糖系列标准品、α-淀粉酶(3000 U/g)、α-葡萄糖苷酶(100000 U/g)、对硝基苯-β-D-吡喃半乳糖苷(PNPG) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
SB-4000型超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;XL-30C型超微粉碎机 山东博科再生医学有限公司;RC-5C型台式高速冷冻离心机、Thermo Scientific型多功能酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;TU-1810PC型紫外分光光度计 麦科仪(北京)科技有限公司;SY-2000型旋转蒸发仪 上海艾革仪器有限公司;WIGGENS WH-410D型磁力搅拌器 山东桑泽仪器仪表有限公司;Alpha-1-2LD型真空冻干机 上海甄明科学仪器有限公司;Waters e2695高效液相色谱仪 沃特世科技(上海)有限公司;AKTA Purifier 10型蛋白纯化仪 美国Cytiva公司;TENSOR 27型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 北京海科思锐光电仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 甘薯渣多糖的提取
新鲜甘薯洗净,榨汁机榨汁2~3次,甘薯渣洗去淀粉,在65 ℃烘箱中烘10 h得到干燥的甘薯渣。经超微粉碎机粉碎后,过100目筛,得甘薯渣粉末。称取适量甘薯渣粉末,在适当条件下,采用超声波辅助热水浸提,经4000 r/min离心15 min后取上清液备用。
1.2.2 酶法-Sevag法联用除蛋白
将离心得到的甘薯渣多糖粗提液,经旋转蒸发仪浓缩,加入3%的木瓜蛋白酶溶液,调pH6.0,50 ℃水浴2 h后,加入1/3体积三氯甲烷-正丁醇溶液(三氯甲烷:正丁醇=4:1),磁力搅拌器搅拌1 h,8000 r/min离心20 min取上清液浓缩冻干备用[20]。
1.2.3 甘薯渣多糖得率测定
标准曲线制作:准确称取标准葡聚糖20 mg于500 mL容量瓶中,加水至刻度,分别吸取0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4、1.6及1.8 mL,各以蒸馏水补至2 mL,然后加入6%苯酚1.0 mL及浓硫酸5 mL,摇匀冷却,沸水浴显色15 min以后于490 nm测吸光值,以2 mL水按同样显色操作为空白对照,横坐标为浓度,纵坐标为光密度值,得标准曲线y=34.43x−0.0283,R2=0.9949。
将稀释后的样品取2 mL至试管中,加入1 mL 6%苯酚及5 mL浓硫酸,摇匀后沸水浴15 min显色,然后在490 nm处测吸光值。根据公式计算甘薯渣多糖得率:
甘薯渣多糖得率(%)=(m1/m)×100 式中:m1为甘薯渣多糖质量,mg;m为样品质量,mg。
1.2.4 单因素实验
以甘薯渣干粉为原料,固定提取温度65 ℃,提取时间50 min,超声功率60%(288 W),料液比1:15 g/mL其中一个因素,分别考察提取温度(55、60、65、70、75 ℃)、超声功率(192、240、288、336、384 W)、提取时间(30、40、50、60、70 min)和料液比(1:10、1:15、1:20、1:25、1:30 g/mL)对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响。
1.2.5 响应面试验设计
结合单因素的实验结果,以提取温度、超声功率、提取时间、料液比为因素,甘薯渣多糖得率为实验指标,根据Box-Behnken设计原理,采用四因素三水平响应面进行试验,优化超声波辅助热水浸提甘薯渣多糖工艺,因素水平设计见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平Table 1. Experimental factors and levels of response surface水平 A 提取温度
(℃)B 超声功率
(W)C 提取时间
(min)D 料液比
(g/mL)−1 60 192 50 1:10 0 65 240 60 1:15 1 70 288 70 1:20 1.2.6 分离纯化
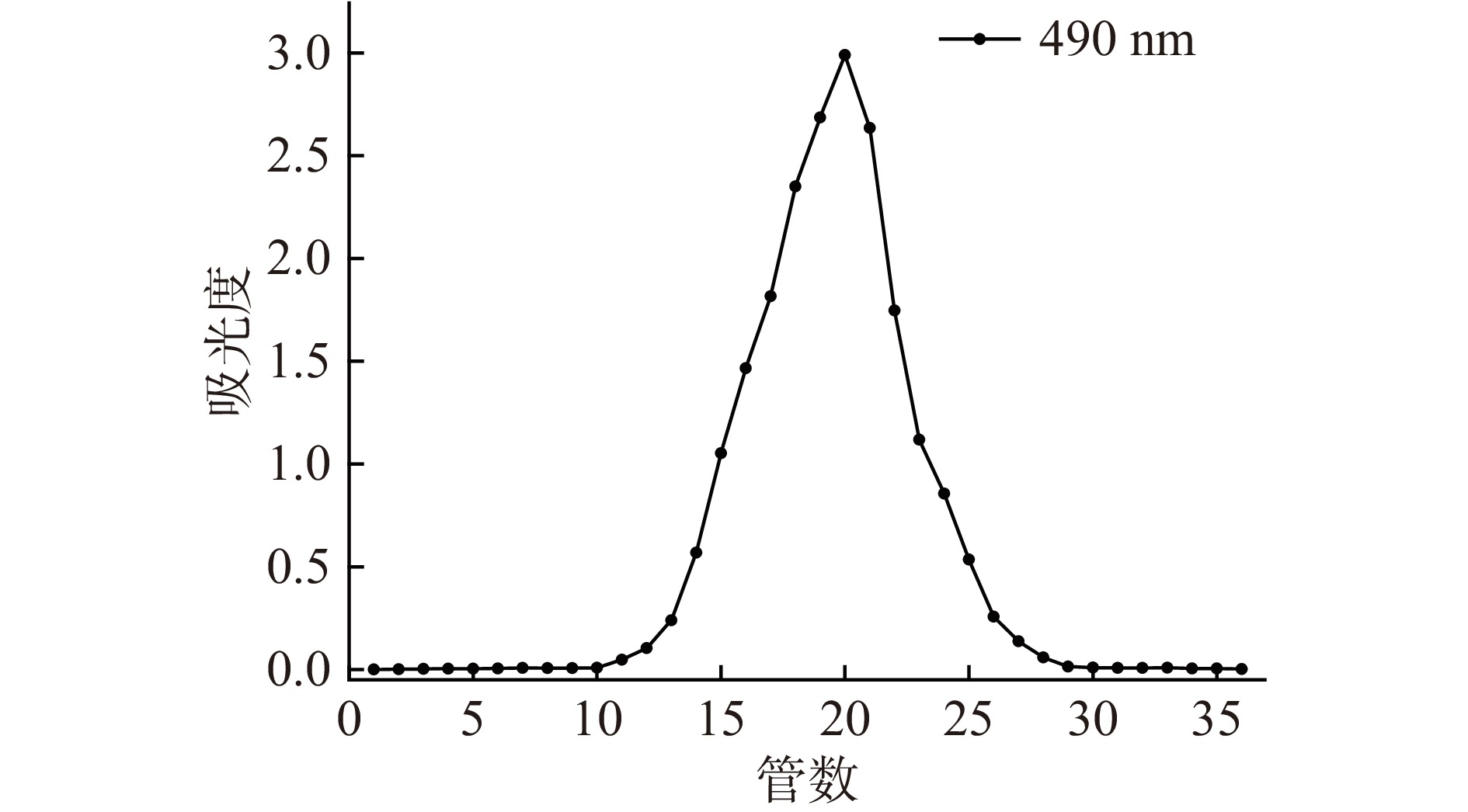
将制备得到的甘薯渣多糖粗提液经凝胶过滤层析柱Superose 12 10/300 GL进行纯化,超纯水进行洗脱[21]。条件设定为:进样量1 mL,流速1 mL/min,收集1 mL/管,检测波长205 nm。苯酚-硫酸法进行跟踪检测[22],收集单一对称峰所对应管中多糖,浓缩后冷冻干燥备用。
1.2.7 纯度及结构鉴定
1.2.7.1 紫外吸收光谱法
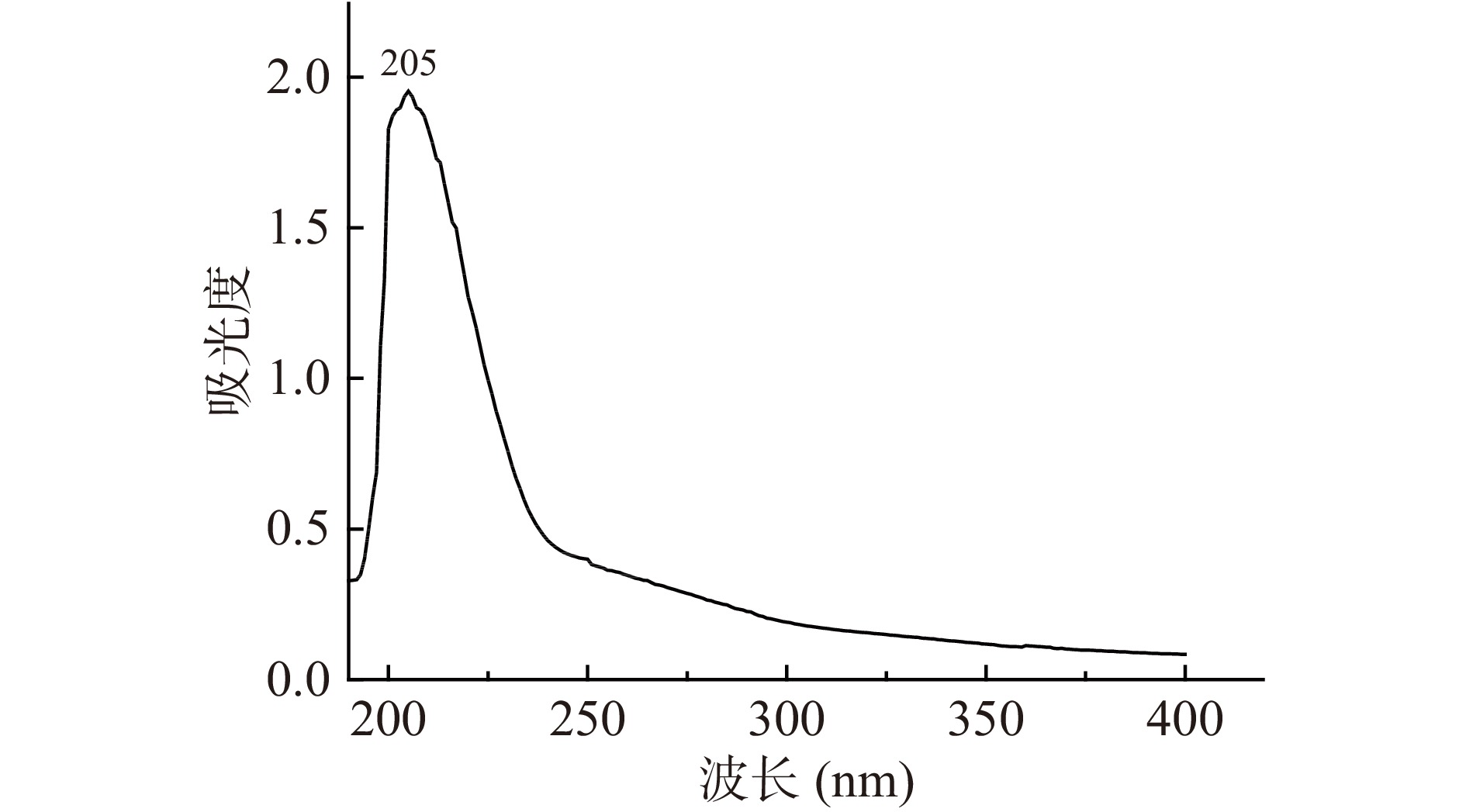
配制1 mg/mL多糖溶液在190~400 nm范围内全波长扫描,观察其在波长260、280 nm附近的吸收峰[23]。
1.2.7.2 红外光谱法
将2 mg多糖样品和100 mg KBr置于玛瑙研钵内,在烤灯下研磨混合均匀后,取少许在模具中压片,在400~4000 nm扫描[24]。
1.2.7.3 单糖组成分析
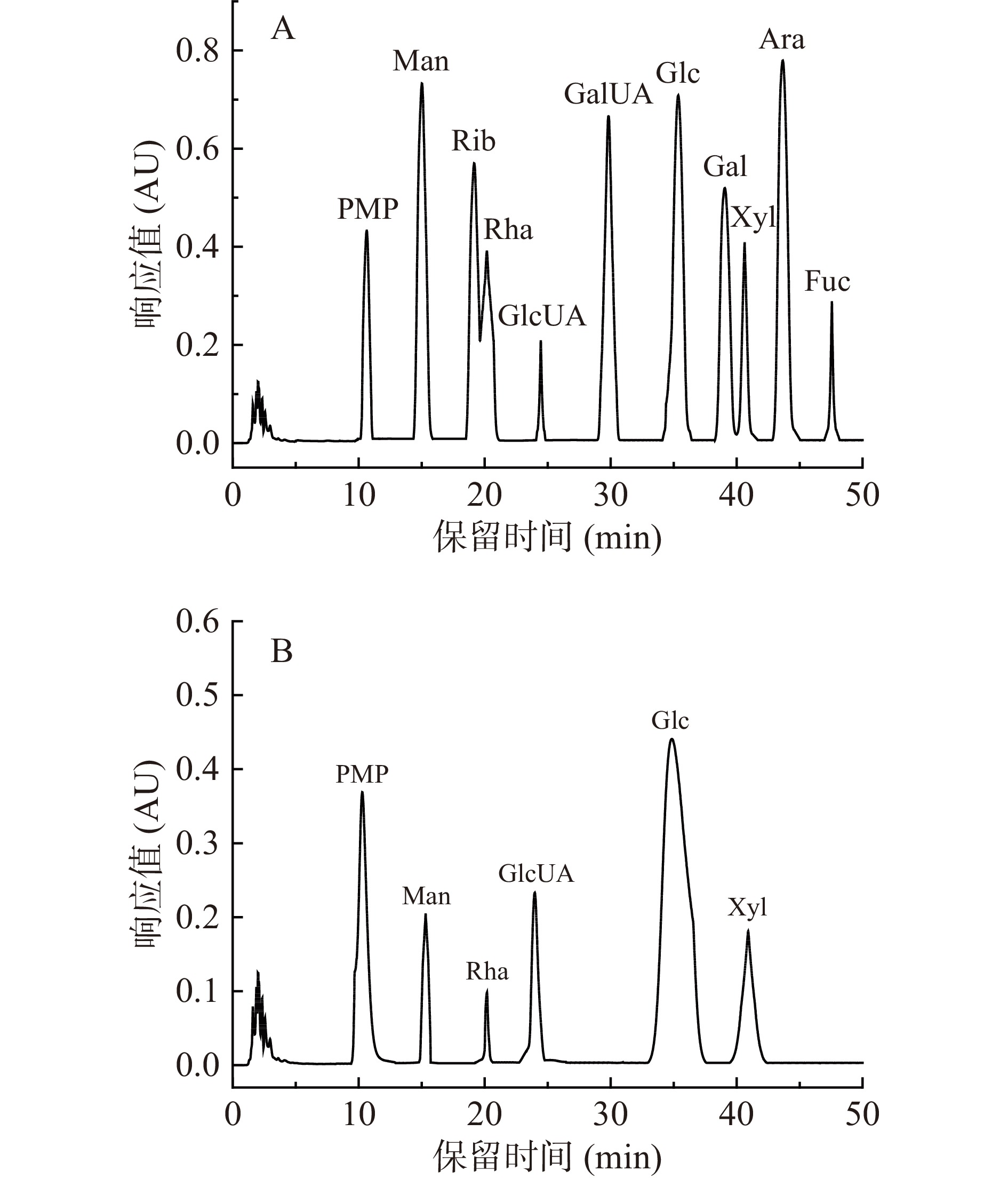
单糖组成分析采用PMP柱前衍生法进行测定[25]。酸水解:取20 mg/mL甘薯渣多糖溶液1 mL于安瓿瓶中,加入1 mL 4 mol/L三氟乙酸溶液,酒精喷灯封口后,置于120 ℃烘箱中水解2 h,水解完成后,冷却至室温,加入1 mL甲醇,50 ℃旋蒸至干,重复3次;PMP衍生化过程:加入1 mL 0.5 mol/L PMP甲醇溶液,溶解蒸干残渣,加入0.5 mL 0.3 mol/L NaOH溶液,70 ℃水浴100 min,冷却至室温后,加入0.5 mL 0.3 mol/L HCl溶液中和反应液,然后加入1 mL氯仿,混匀后静置20 min,除去下层氯仿溶液,重复萃取3次,而后过0.22 μm滤膜上机检测;检测条件:Waters e2695高效液相色谱仪;Sunfire C18色谱柱(4.6 mm×150 mm,5 μm,USA);流动相:体积比为83:17的PBS(0.1 mol/L,pH6.7)和乙腈混合液;流速1 mL/min;柱温30 ℃;检测波长245 nm。
1.2.8 抗氧化活性测定
1.2.8.1 甘薯渣多糖清除(DPPH·)能力测定
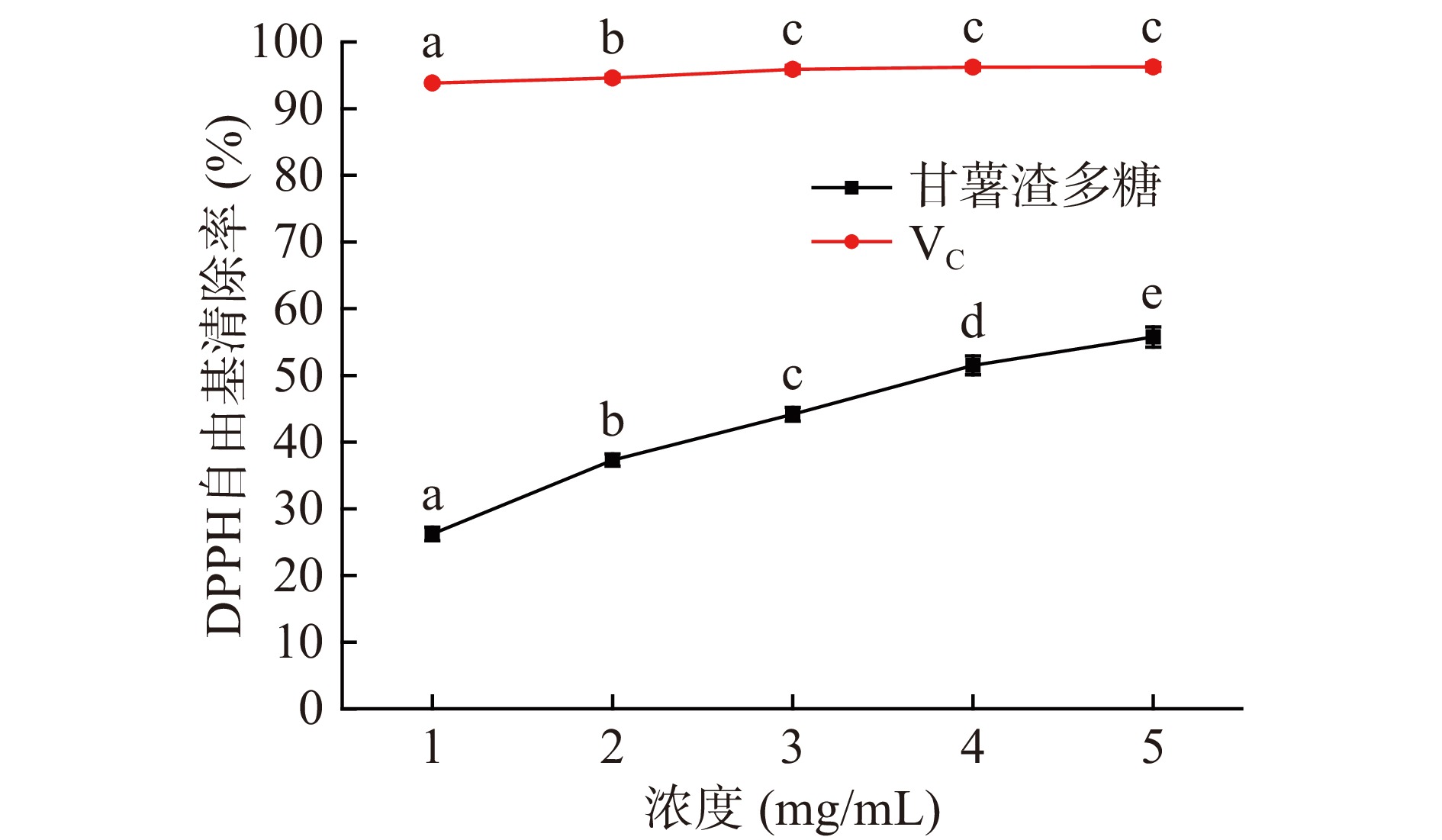
分别将2 mL不同浓度的甘薯渣多糖溶液与2 mL 0.2 mmol/L DPPH溶液旋涡混匀,置于暗处反应30 min后,在517 nm处测定吸光值ASample,用等体积的无水乙醇代替样品测定吸光度ABlank,以及用等体积的无水乙醇代替DPPH溶液,测定吸光值AControl,根据公式计算DPPH·清除率[26]:
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=[1−(ASample−AControl)/ABlank]×100 1.2.8.2 甘薯渣多糖羟基自由基(·OH)清除能力测定
向试管中依次加入2 mL 6 mmol/L的FeSO4溶液、2 mL甘薯渣多糖溶液以及2 mL 6 mmol/L的H2O2溶液,旋涡混匀,静置10 min后加入2 mL 6 mmol/L的水杨酸溶液,旋涡混匀,静置40 min,在510 nm处测定吸光值ASample。测定不加样品溶液的吸光值ABlank以及不加水杨酸是多糖溶液的吸光值AControl,根据公式计算羟基自由基清除率[27]:
⋅OH清除率(%)=[ABlank−(ASample−AControl)/ABlank]×100 1.2.8.3 甘薯渣多糖超氧阴离子清除能力测定
按照田春宇[28]的方法并加以改进将Tris-HCl(pH8.2、50 mmol/L)溶液37 ℃预热,取4.5 mL Tris-HCl溶液,加4 mL蒸馏水37 ℃水浴20 min,加入0.5 mL 3 mmol/L邻苯三酚溶液37 ℃水浴20 min,旋涡混匀计时1 min,立刻在325 nm处测定吸光值,每30 s测定一次。做出吸光值随时间变化的曲线,做回归方程,邻苯三酚的自氧化速率V为回归方程的斜率。用10 mmol/L HCl溶液作对照,计算邻苯三酚自氧化速率VControl。取不同浓度甘薯渣多糖溶液4 mL代替蒸馏水,计算邻苯三酚自氧化速率VSample,根据公式计算超氧阴离子清除率:
超氧阴离子清除率(%)=[(VControl−VSample)/VControl]×100 1.2.9 降血糖能力测定
1.2.9.1 甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶活性抑制
甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制实验参照陈树俊等[29]的方法进行。实验所用样品溶液、α-淀粉酶溶液(10 U/mL)及1%可溶性淀粉溶液均由磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH6.9,20 mmol/L)配制。取300 μL甘薯渣多糖溶液以及300 μL α-淀粉酶溶液,37 ℃水浴15 min后,加300 μL 1%可溶性淀粉溶液继续37 ℃水浴15 min,加500 μL DNS试剂显色,沸水浴10 min终止反应。向混合溶液中加入10 mL蒸馏水,540 nm处测吸光值ASample;以蒸馏水代替甘薯渣多糖溶液测定吸光值ABlank;以等体积缓冲溶液代替酶溶液测定吸光值AControl-1;以蒸馏水和缓冲溶液分别代替样品溶液和酶溶液测定吸光值AControl-2。根据公式计算甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶的抑制率:
α−淀粉酶抑制率(%)=[1−(ASample−AControl−1)/(ABlank−AControl−2)]×100 1.2.9.2 甘薯渣多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制
甘薯渣多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制试验参照韩芬霞等[30]方法并加以改进。用磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.1 mol/L,pH6.9)配制0.5 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液以及5 mmol/L pNPG溶液。分别吸取100μL不同浓度样品溶液和α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液于试管中,37 ℃孵育10 min,然后加入100 μL pNPG溶液开始反应,37 ℃继续孵育20 min,最后加入1 mL无水乙醇溶液使α-葡萄糖苷酶失活,在405 nm处测定吸光值ASample;以蒸馏水代替甘薯渣多糖溶液测定吸光值ABlank;以等体积缓冲溶液代替酶溶液测定吸光值AControl-1;以蒸馏水和缓冲溶液分别代替样品溶液和酶溶液测定吸光值AControl-2。根据公式计算甘薯渣多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率:
α−葡萄糖苷酶抑制率(%)=[1−(ASample−AControl−1)/(ABlank−AControl−2)]×100 1.3 数据处理
运用SPSS 23软件Duncan进行单因素方差分析(ANOVA)(P<0.05)、Desgn-Expert 8软件进行Box-Behnken试验设计以及Oringin 9软件进行结果图绘制,试验结果以X±SD表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 多糖提取工艺的单因素实验
2.1.1 提取温度对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响
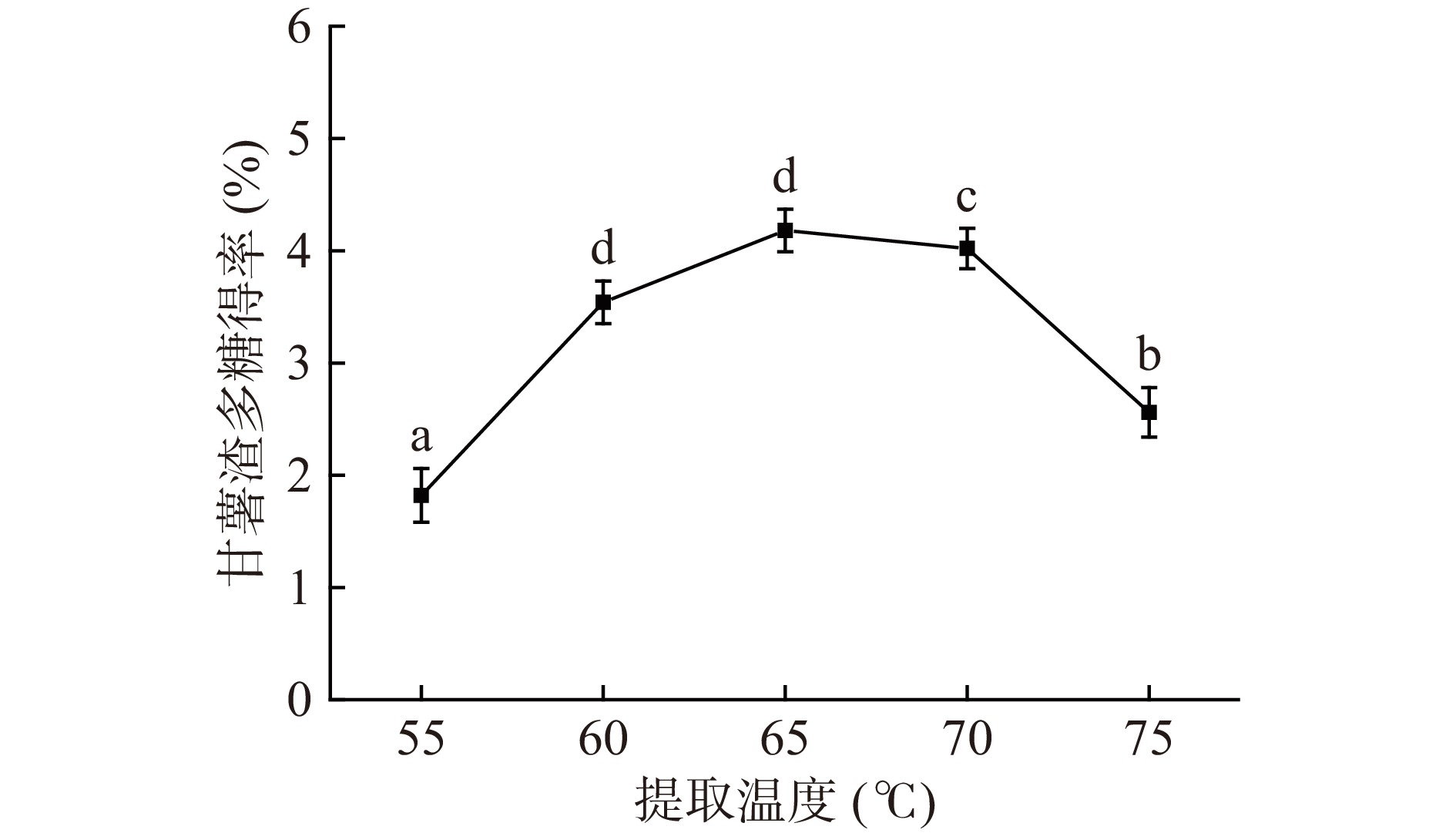
固定其他条件,在55、60、65、70、75 ℃下提取甘薯渣多糖的结果如图1所示。当提取温度到达65 ℃时,多糖得率最高,为4.18%±0.07%。当温度超过65 ℃时,多糖得率开始逐渐降低,可能是由于温度升高的原因,导致甘薯渣多糖的结构和活性受到影响,甘薯渣多糖不易溶出,从而导致甘薯渣多糖得率下降[31]。所以提取温度应控制在65 ℃最佳。
2.1.2 超声功率对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响
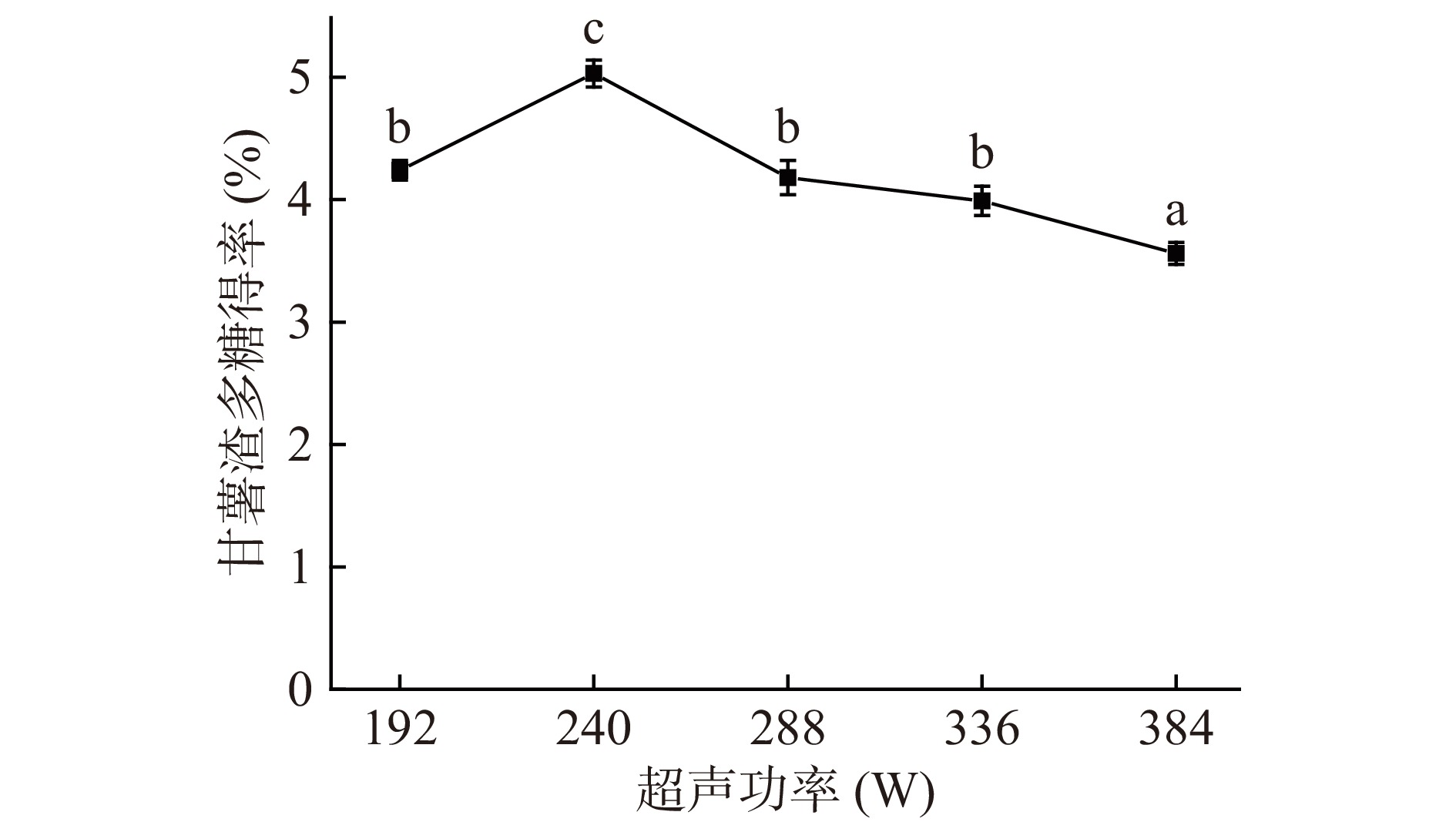
固定其他条件,在超声功率40%、50%、60%、70%、80%(总功率480 W)条件下对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响由图2所示。在超声功率为240 W时甘薯渣多糖得率达到最大值5.03%±0.2%,而后随着超声功率的增大,多糖得率逐渐降低。其原因可能是由于超声功率过大,水循环速度加快,传质过程加强,多糖结构遭到破坏,导致甘薯渣多糖的得率降低[32]。所以超声功率控制在240 W时最佳。
2.1.3 提取时间对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响
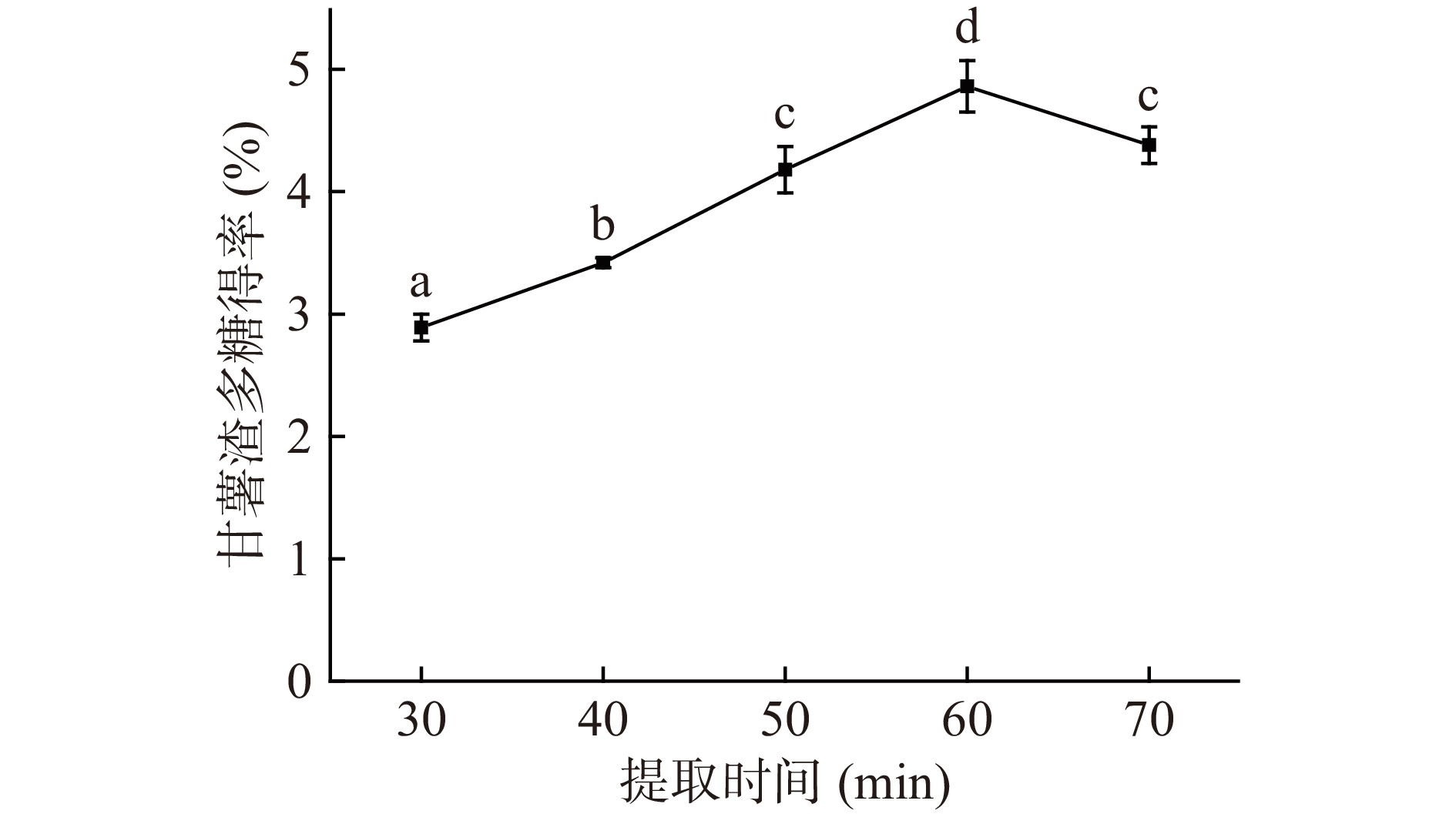
固定其他条件,在时间30、40、50、60、70 min条件下对甘薯渣多糖的得率如图3所示。在30~60 min的时间范围内,甘薯渣多糖得率逐渐上升,其原因是随着时间的增长,甘薯渣多糖的溶出越来越完全,在60 min时甘薯渣多糖得率到达最大值4.86%±0.19%。当时间超过60 min时,甘薯渣多糖得率下降,其原因是由于超声波作用时间过长,导致大分子多糖糖苷键断裂,多糖结构遭到破坏,从而导致甘薯渣多糖得率降低[33]。所以提取时间控制在60 min时最佳。
2.1.4 不同料液比对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响
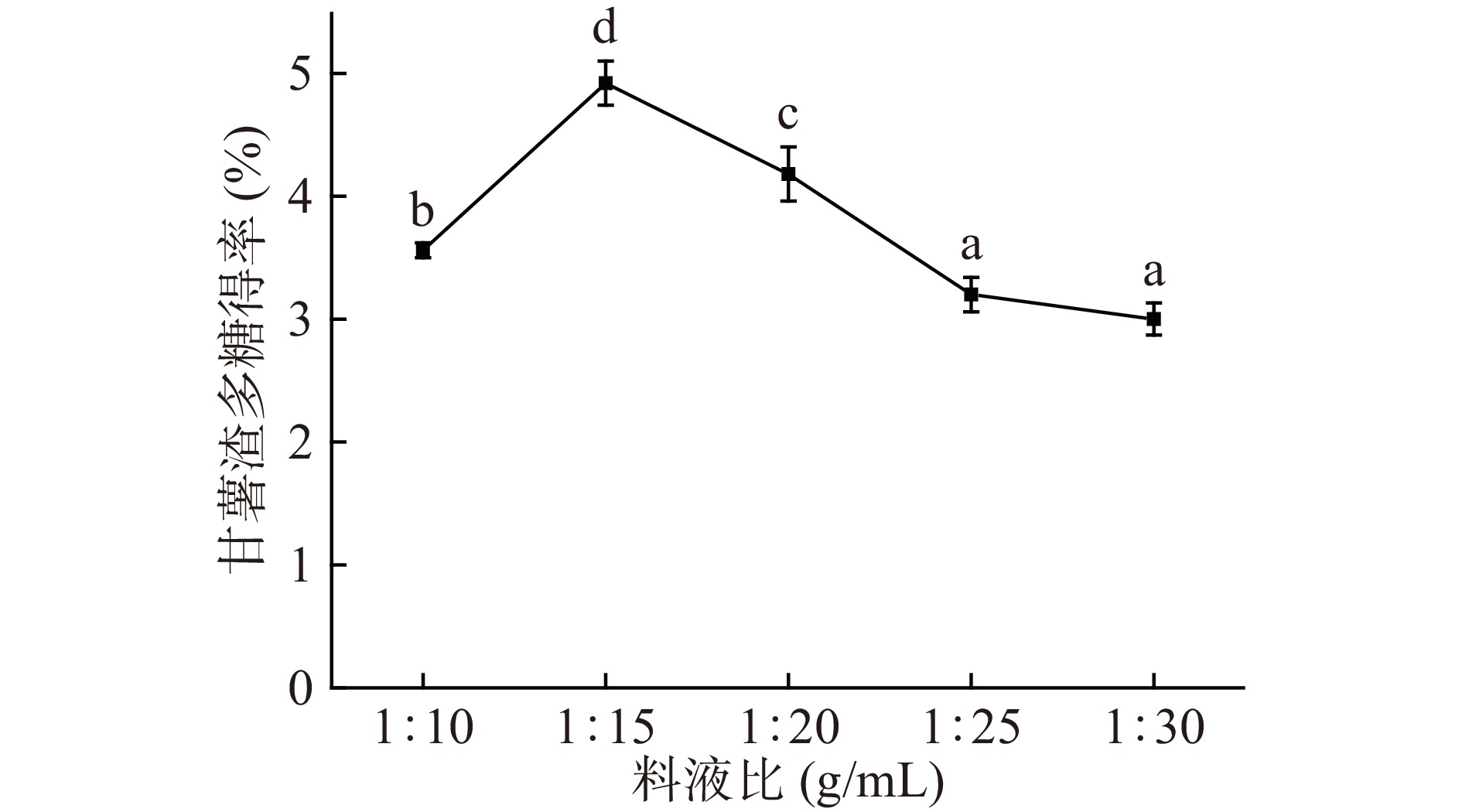
固定其他条件,在料液比1:10、1:15、1:20、1:25、1:30 g/mL条件下对甘薯渣多糖提取的影响如图4所示。在料液比为1:15 g/mL时,甘薯渣多糖得率到达最大值4.92%±0.29%,总体呈现先升高后降低的趋势。其原因是由于溶剂太少,甘薯渣多糖在溶液中的浓度差小,多糖溶出的速度慢,导致甘薯渣多糖得率低。随着溶剂的增加,固液相中的浓度差增大,溶质溶出速度增大,甘薯渣多糖得率增加。当溶剂量过大时,甘薯渣多糖溶出比较完全,其他物质也会随之溶出,从而影响甘薯渣多糖溶出,导致甘薯渣多糖得率下降[34]。所以料液比控制在1:15 g/mL时最佳。
2.2 响应面优化试验结果
在单因素实验结果的基础上,对影响甘薯渣多糖得率的主要因素进行组合优化,以提取温度(A)、超声功率(B)、提取时间(C)、料液比(D)为自变量,甘薯渣多糖得率(Y)为因变量,进行四因素三水平的中心组合试验,试验设计及结果见表2。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计与结果Table 2. Box-Behnken experimental design and results实验号 A提取温度 B超声功率 C提取时间 D料液比 Y多糖得率(%) 1 0 1 0 1 4.46 2 0 0 0 0 5.09 3 1 0 0 −1 4.26 4 −1 1 0 0 3.85 5 0 0 0 0 4.89 6 0 −1 0 1 4.27 7 0 0 1 1 4.11 8 0 1 −1 0 4.34 9 0 0 0 0 4.69 10 1 −1 0 0 4.03 11 −1 −1 0 0 3.72 12 0 0 −1 1 4.25 13 0 0 −1 −1 3.10 14 −1 0 −1 0 3.38 15 −1 0 0 1 4.05 16 −1 0 1 0 4.57 17 −1 0 0 −1 3.98 18 1 0 1 0 4.34 19 0 −1 1 0 3.96 20 1 1 0 0 4.71 21 0 −1 −1 0 3.08 22 0 0 0 0 4.76 23 0 0 1 −1 3.92 24 0 1 0 −1 4.16 25 0 −1 0 −1 3.43 26 0 0 0 0 4.99 27 1 0 −1 0 4.75 28 0 1 1 0 4.11 29 1 0 0 1 4.49 由表2建立二次元线性回归方程,Y=4.88+0.25A+0.26B+0.18C+0.23D+0.14AB−0.40AC+0.040AD−0.28BC−0.13BD−0.24CD−0.23A2−0.48B2−0.51C2−0.44D2。
由表3可知,模型中F值为13.67差异性极显著(P<0.001),失拟项为0.3539,差异性不显著,R2=0.9318,R2adj=0.8637,说明该回归模型预测值与实际值有高度相关性,可以反映93.18%的响应面值变化,可用该模型对甘薯渣多糖的提取做初步分析和预测。
表 3 Box-Behnken试验结果与方差分析Table 3. Box-Behnken experimental results and analysis of variance差异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 7.16 14 0.51 13.67 < 0.0001 *** A-提取温度 0.77 1 0.77 20.45 0.0005 *** B-超声功率 0.82 1 0.82 21.96 0.0003 *** C-提取时间 0.37 1 0.37 9.92 0.0071 ** D-料液比 0.64 1 0.64 17.22 0.001 ** AB 0.076 1 0.076 2.02 0.177 AC 0.64 1 0.64 17.11 0.001 ** AD 0.0064 1 0.0064 0.17 0.6854 BC 0.31 1 0.31 8.23 0.0124 * BD 0.073 1 0.073 1.95 0.1845 CD 0.23 1 0.23 6.16 0.0264 * A2 0.35 1 0.35 9.23 0.0088 ** B2 1.51 1 1.51 40.29 < 0.0001 *** C2 1.68 1 1.68 44.79 < 0.0001 *** D2 1.24 1 1.24 33.11 < 0.0001 *** 残差 0.52 14 0.037 失拟项 0.42 10 0.042 1.56 0.3539 不显著 误差 0.11 4 0.027 总和 7.68 28 注:表中***表示差异性极显著(P<0.001);**表示差异高度显著(P<0.01);
*表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。2.3 响应曲面各因素交互作用分析
由图5A可知,提取温度和超声功率对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响呈抛物线趋势。当固定提取温度时,甘薯渣多糖得率随超声功率的增加呈现出先增后降趋势;而固定超声功率时,其多糖得率的变化较小,说明超声功率对多糖得率变化的影响大于提取温度;由图5B可知,在提取时间不变的条件下,甘薯渣多糖得率随提取温度的升高也表现出先升后降的趋势,而固定提取温度,甘薯渣多糖得率随着提取时间的增加,则表现出先平稳上升,后急速下降,这表明提取时间对甘薯渣多糖得率的影响较为显著(P<0.01)。由图5D可知,提取时间和超声功率交互的响应曲面坡度比较接近拱形,说明两者交互作用对响应值影响显著。经过Design-Expert 8.0分析得甘薯渣多糖最优提取工艺条件为提取温度70 ℃、超声功率263.5 W、提取时间55.6 min、料液比1:16.5,在此条件下甘薯渣多糖得率的最优预测值为5.101%。为验证响应面模型方法的可靠性,考虑实际情况的条件下,最终确定提取温度70 ℃、超声功率264 W、提取时间56 min、料液比1:17 g/mL。验证试验进行了三次,最终甘薯渣多糖得率的平均值为5.053%,该值与预测结果相差不大,说明经过响应面优化后的超声波辅助热水浸提甘薯渣多糖的提取工艺条件合理可行。
2.4 甘薯渣多糖的分离纯化
由图6可知,甘薯渣粗多糖经AKTA蛋白纯化仪Superose 12TM 10/300 GL凝胶柱纯化,用苯酚-硫酸法对收集的样品进行跟踪检测,出现了一个单一对称峰,说明甘薯渣多糖可以被较好的分离出来。集中收集12~28管中的甘薯渣多糖经冷冻干燥后备用。
2.5 甘薯渣多糖纯度及结构鉴定
2.5.1 紫外光谱扫描
将制得的甘薯渣多糖,配制浓度为1 mg/mL的甘薯渣多糖溶液,在紫外光谱190~400 nm进行全波长扫描,扫描结果如图7所示,在260和280 nm处无吸收峰,在205 nm处有单一吸收峰,说明甘薯渣多糖中核酸和蛋白质已除尽。
2.5.2 傅里叶红外光谱扫描
采用傅里叶红外光谱仪对经过Superose 12 10/300 GL凝胶柱纯化冻干后的甘薯渣多糖在400~4000 cm−1区间范围内进行扫描测定。如图8所示,甘薯渣多糖在波数3358 cm−1处的信号代表着O-H伸缩振动吸收峰[35];在波数2980 cm−1处的信号表示为C-H伸缩振动吸收峰[36];1637 cm−1处的吸收峰为C=O特征峰[37];1292 cm−1处的吸收峰为C-H的变角振动信号,是糖类的特征吸收峰[38]。880 cm−1处有一吸收峰,是吡喃-β型C-H弯曲振动的特征吸收峰[39],840 cm−1处具有吸收峰,证明了甘薯渣多糖具有α-糖苷键,是一种α-吡喃葡萄糖。
2.5.3 单糖组成分析
甘薯渣多糖的单糖组成分析结果如图9所示,甘薯渣多糖分别由甘露糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖醛酸、葡萄糖和木糖组成,其摩尔百分比含量分别为9.46%、4.28%、11.72%、62.37%、10.58%。
2.6 甘薯渣多糖的抗氧化活性评价
2.6.1 甘薯渣多糖清除DPPH·自由基的能力测定
DPPH·乙醇溶液呈深紫红色,在波长517 nm处有一较强吸收峰,甘薯渣多糖提供的氢原子与DPPH·发生反应使溶液褪色,在波长517 nm处的吸光度减小,可作为甘薯渣多糖抗氧化能力强弱的判断依据。实验结果如图10可知,甘薯渣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除率随着其浓度的增大而逐渐升高。当甘薯渣多糖浓度为5 mg/mL时,对DPPH自由基的清除率为55.76%±1.52 %,该值明显弱于阳性对照组Vc。上述结果表明,甘薯渣多糖具有一定清除DPPH自由基的能力。经计算得知甘薯渣多糖清除DPPH自由基活性的IC50值为3.809 mg/mL。
2.6.2 甘薯渣多糖清除OH自由基的能力测定
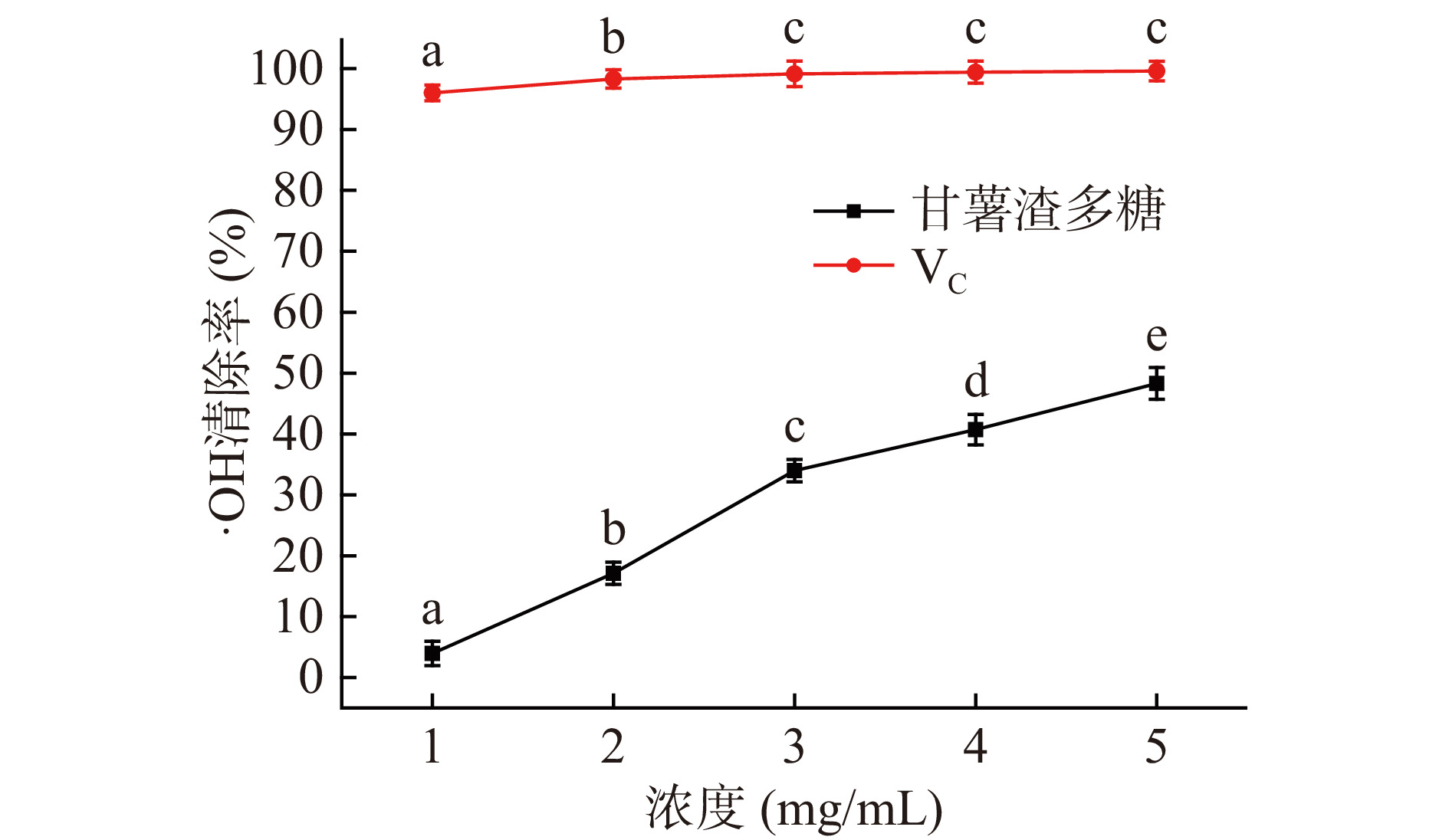
氢氧根失去一个电子形成·OH,OH自由基是一种氧化能力极强的氧化剂,几乎可以和细胞内所有分子发生氧化反应,将之氧化。由图11可知,甘薯渣多糖对羟基自由基的清除率随着其浓度的升高而增强,当甘薯渣多糖浓度为5 mg/mL时,其对OH自由基清除率达到48.3%±2.60%,弱于阳性对照组VC。上述结果表明,甘薯渣多糖具有一定的清除OH自由基的能力。经过计算得知,甘薯渣多糖清除OH自由基活性的IC50值为4.879 mg/mL。
2.6.3 甘薯渣多糖清除超氧阴离子自由基的能力测定
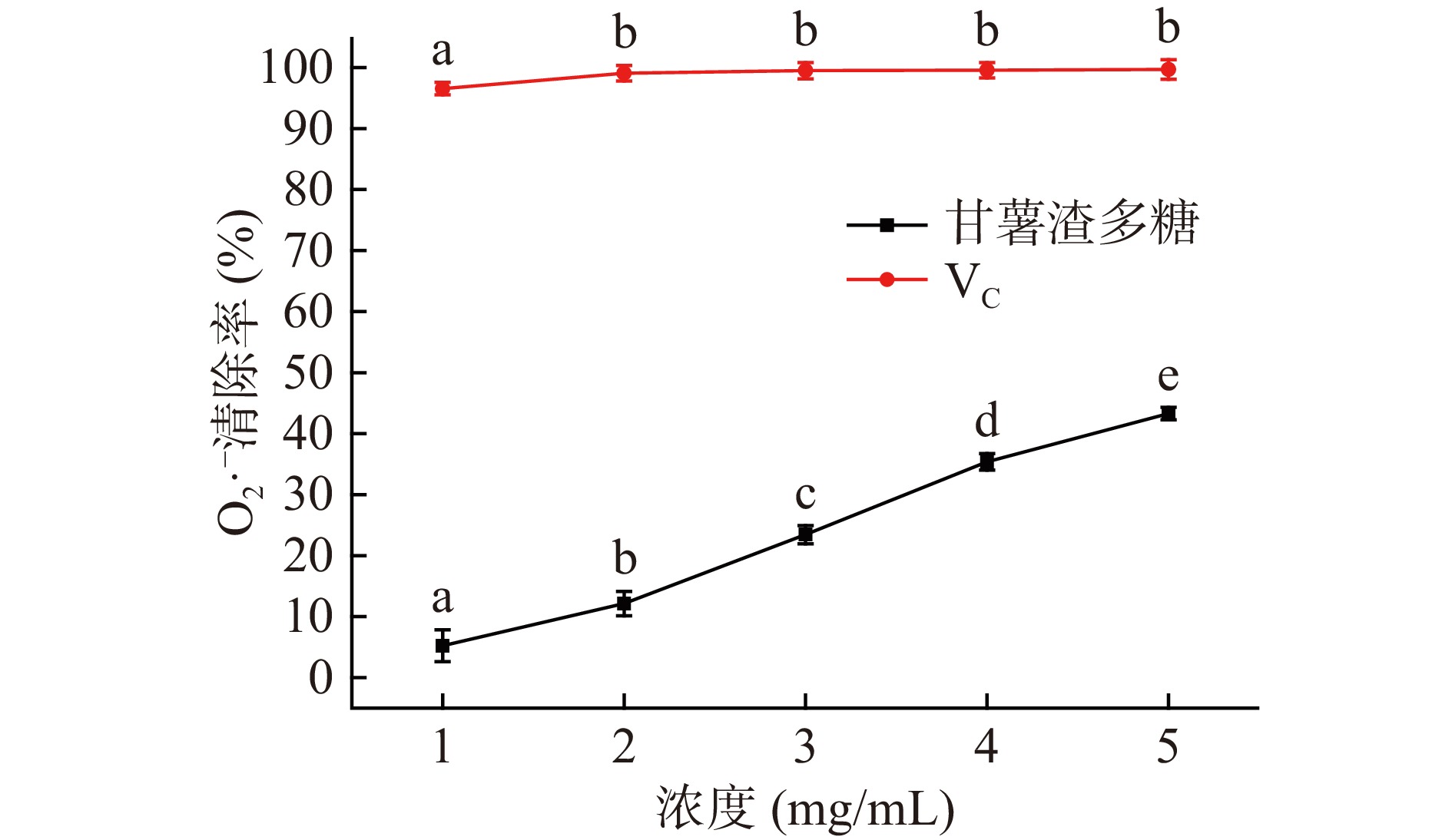
超氧阴离子自由基具有很强的氧化性,大量的超氧阴离子存在于体内会造成体内细胞组织受损。图12为甘薯渣多糖清除超氧阴离子的实验结果,由图12可知,甘薯渣多糖对超氧阴离子清除率随着其浓度的升高而升高,当甘薯渣多糖浓度为5 mg/mL时,其对超氧阴离子的清除率达到43.28%±1.03%,弱于阳性对照组VC。上述结果表明甘薯渣多糖具有良好的清除超氧阴离子能力。经过计算得知,甘薯渣多糖清除超氧阴离子活性的IC50值为5.832 mg/mL。
2.7 甘薯渣多糖体外降血糖能力评价
人体内消化淀粉的能力强弱主要在于α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性强弱,α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶可以水解碳水化合物中的α-1,4糖苷键,水解产物为糊精、低聚糖和单糖,使人体更易吸收,导致血糖浓度升高。因此,抑制α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性,可以降低碳水化合物转化成葡萄糖的速度,降低餐后血糖峰值,提高胰岛素敏感性,从而预防糖尿病及其并发症[40]。抑制α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的实验结果如图13所示。由图13可知,甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用随着甘薯渣多糖浓度的升高逐渐增强,当多糖浓度为25 mg/mL时,甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率分别为91.76%±0.69%、65.0%±1.4%。经过计算得知,甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶活性抑制的IC50值为7.674 mg/mL,明显低于桑葚多糖[41](19.31 mg/mL);对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制的IC50值为18.961 mg/mL,明显低于藜麦多糖[42](48.47 mg/mL)。上述结果表明,相比于桑葚多糖和藜麦多糖,甘薯渣多糖对α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用更强,说明其具有较好的降血糖活性。
3. 结论
本研究采用超声波辅助热水浸提法提取甘薯渣多糖,经Superose 12 10/300 GL凝胶柱对甘薯渣多糖进行分离纯化,并对其进行结构鉴定、抗氧化能力测定以及降血糖能力测定。获得的最佳提取工艺条件为:提取温度70 ℃、超声功率264 W、提取时间56 min、料液比1:17 g/mL,在此提取条件下,甘薯渣多糖得率为5.053%。进一步对其结构进行鉴定可知,该多糖为一种α-吡喃葡萄糖,由甘露糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖醛酸、葡萄糖、木糖组成。对其进行抗氧化能力和降血糖能力测定表明甘薯渣多糖具有一定的抗氧化活性和降血糖活性。综上所述,本研究为甘薯渣多糖的提取工艺及其对血糖的调节作用和甘薯渣多糖的综合开发利用提供理论依据。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平
Table 1 Experimental factors and levels of response surface
水平 A 提取温度
(℃)B 超声功率
(W)C 提取时间
(min)D 料液比
(g/mL)−1 60 192 50 1:10 0 65 240 60 1:15 1 70 288 70 1:20 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计与结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken experimental design and results
实验号 A提取温度 B超声功率 C提取时间 D料液比 Y多糖得率(%) 1 0 1 0 1 4.46 2 0 0 0 0 5.09 3 1 0 0 −1 4.26 4 −1 1 0 0 3.85 5 0 0 0 0 4.89 6 0 −1 0 1 4.27 7 0 0 1 1 4.11 8 0 1 −1 0 4.34 9 0 0 0 0 4.69 10 1 −1 0 0 4.03 11 −1 −1 0 0 3.72 12 0 0 −1 1 4.25 13 0 0 −1 −1 3.10 14 −1 0 −1 0 3.38 15 −1 0 0 1 4.05 16 −1 0 1 0 4.57 17 −1 0 0 −1 3.98 18 1 0 1 0 4.34 19 0 −1 1 0 3.96 20 1 1 0 0 4.71 21 0 −1 −1 0 3.08 22 0 0 0 0 4.76 23 0 0 1 −1 3.92 24 0 1 0 −1 4.16 25 0 −1 0 −1 3.43 26 0 0 0 0 4.99 27 1 0 −1 0 4.75 28 0 1 1 0 4.11 29 1 0 0 1 4.49 表 3 Box-Behnken试验结果与方差分析
Table 3 Box-Behnken experimental results and analysis of variance
差异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 7.16 14 0.51 13.67 < 0.0001 *** A-提取温度 0.77 1 0.77 20.45 0.0005 *** B-超声功率 0.82 1 0.82 21.96 0.0003 *** C-提取时间 0.37 1 0.37 9.92 0.0071 ** D-料液比 0.64 1 0.64 17.22 0.001 ** AB 0.076 1 0.076 2.02 0.177 AC 0.64 1 0.64 17.11 0.001 ** AD 0.0064 1 0.0064 0.17 0.6854 BC 0.31 1 0.31 8.23 0.0124 * BD 0.073 1 0.073 1.95 0.1845 CD 0.23 1 0.23 6.16 0.0264 * A2 0.35 1 0.35 9.23 0.0088 ** B2 1.51 1 1.51 40.29 < 0.0001 *** C2 1.68 1 1.68 44.79 < 0.0001 *** D2 1.24 1 1.24 33.11 < 0.0001 *** 残差 0.52 14 0.037 失拟项 0.42 10 0.042 1.56 0.3539 不显著 误差 0.11 4 0.027 总和 7.68 28 注:表中***表示差异性极显著(P<0.001);**表示差异高度显著(P<0.01);
*表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 綦峥, 乐志威, 韩馥蕊, 等. 甘薯渣多糖的性质与开发利用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(10):3989−3993. [QI Z, LE Z W, HAN F R, et al. Properties, development and utilization of polysaccharide from sweet potato residue[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(10):3989−3993. [2] 徐梦瑶. 甘薯渣的资源化利用[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2017. XU M Y. Resource utilization of sweet potato residue [D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2017.
[3] 乔汉桢, 宋爽, 邵会敏, 等. 甘薯渣多糖的提取工艺、生理功能及应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):321−325. [QIAO H Z, SONG S, SHAO H M, et al. Research progress on extraction technology, physiological function and application of polysaccharide from sweet potato residue[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):321−325. [4] LIU M, LI X, ZHOU S, et al. Dietary fiber isolated from sweet potato residues promote healthy gut microbiome profile[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(4):689−699.
[5] 王鑫, 王峙力, 谢静南, 等. 甜玉米芯多糖对α-淀粉酶抑制作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(10):48−54. [WANG X, WANG S L, XIE J N, et al. Sweet corncob polysaccharide pair α- study on the inhibition of amylase[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(10):48−54. [6] WU Q, QU H, JIA J, et al. Characterization, antioxidant and antitumor activities of polysaccharides from purple sweet potato[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,132:31−40. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.045
[7] FENG S, CHENG H, FU L, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Camellia oleifera leaves[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,68:7−12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.04.026
[8] 屈红森, 吴琼英, 贾俊强. 超声协同淀粉酶法提取紫山芋多糖及其生物活性研究[J]. 食品工业,2014,35(11):47−52. [QU H S, WU Q Y, JIA J Q. Ultrasonic assisted amylase extraction of Purple Mountain taro polysaccharide and its biological activity[J]. Food Industry,2014,35(11):47−52. [9] WANG Z, WANG C, SU T, et al. Antioxidant and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Gentiana scabra Bunge roots[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,112:114−118. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.077
[10] ZHAO H, WANG Q, SUN Y, et al. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory effects of Plantago depressa polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,112:63−72. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.069
[11] WU X, MAO G, ZHAO T, et al. Isolation, purification and in vitro anti-tumor activity of polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba sarcotesta[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,86(2):1073−1076. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.069
[12] TANG C, SUN J, LIU J, et al. Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharides from purple sweet potato[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,123:923−930. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.187
[13] 赵泽文, 马雅静, 潘起涛, 等. 提取方式对茶树菇菌糠多糖提取效率及生物学活性的影响[J]. 核农学报,2021,35(9):2172−2181. [ZHAO Z W, MA Y J, PAN Q T, et al. Effects of extraction methods on extraction efficiency and biological activity of tea tree mushroom bran polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2021,35(9):2172−2181. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.09.2172 [14] 汲晨锋. 基于CR3受体研究甘薯渣多糖抗肿瘤作用及免疫应答机制[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨商业大学, 2019. JI C F. Study on antitumor effect and immune response mechanism of sweet potato residue polysaccharide based on CR3 receptor [D]. Harbin: Harbin Commercial University, 2019.
[15] GOU Y, SUN J, LIU J, et al. Structural characterization of a water-soluble purple sweet potato polysaccharide and its effect on intestinal inflammation in mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,61:103502. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103502
[16] WU G J, LIU D, WAN Y J, et al. Comparison of hypoglycemic effects of polysaccharides from four legume species[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,90:299−304. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.12.035
[17] 杨国伟, 王树翠, 杨树林. 茯苓多糖对小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 生物化工,2021,7(4):29−32. [YANG G W, WANG S C, YANG S L. Effect of Poria cocos polysaccharide on intestinal flora in mice[J]. Biochemistry,2021,7(4):29−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0387.2021.04.006 [18] 邓建梅, 余传波, 甘雨薇. 响应面法优化石榴皮果胶微波辅助提取工艺[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(9):127−131. [DENG J M, YU C B, GAN Y W. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction process of pomegranate peel pectin by response surface methodology[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(9):127−131. [19] Ji Li et al. Aqueous enzymatic process assisted by microwave extraction of oil from yellow horn (Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge.) seed kernels and its quality evaluation[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,138(4):2152−2158. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.12.011
[20] 郭慧静, 张伟达, 陈国刚. 蒲公英多糖脱色脱蛋白方法及其降血糖活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(3):24−28. [GUO H J, ZHANG W D, CHEN G G. Decolorization and deproteinization of dandelion polysaccharide and its hypoglycemic activity[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(3):24−28. [21] YUAN B, YANG X Q, KOU M, et al. Selenylation of polysaccharide from the sweet potato and evaluation of antioxidant, antitumor, and antidiabetic activities[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2017,65(3):605.
[22] 张妍, 刘太林. 苯酚-硫酸法与蒽酮-硫酸法测定麦冬中麦冬多糖含量的比较研究[J]. 现代食品,2018(18):95−102. [ZHANG Y, LIU T L. Comparative study on the determination of Ophiopogon japonicus polysaccharide in Ophiopogon japonicus by phenol sulfuric acid method and anthrone sulfuric acid method[J]. Modern Food,2018(18):95−102. [23] 陈树俊, 崔云. 甘薯渣多糖提取、分离纯化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(10):56−62. [CHEN S J, CUI Y. Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from sweet potato residue[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2020,35(10):56−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.10.010 [24] 沈佳琳. 黑果枸杞多糖的提取纯化、抗氧化活性及体外模拟消化和发酵研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017. SHEN J L. Study on extraction, purification, antioxidant activity, in vitro simulated digestion and fermentation of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
[25] BHAWAL SHALAKA, KUMARI ANKITA, KAPILA SUMAN, et al. Physicochemical characteristics of novel cell-bound exopolysaccharide from probiotic Limosilactobacillus fermentum (MTCC 5898) and its relation to antioxidative activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021(69):10338−10349.
[26] 于鹏. 富硒甘薯中性硒多糖的分离纯化和组成研究[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁大学, 2019. YU P. Isolation, purification and composition of neutral selenium polysaccharide from selenium rich sweet potato [D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University, 2019.
[27] 赵慧. 石花菜多糖的提取、分离纯化、理化性质及生物活性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018. ZHAO H. Extraction, purification, physicochemical properties and bioactivity of cauliflower polysaccharide [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018.
[28] 田春宇. 甘薯渣多糖分离纯化及生物活性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2011. TIAN C Y. Separation, purification and bioactivity of Polysaccharide from sweet potato residue [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2011.
[29] 陈树俊, 崔云. 甘薯渣多糖提取、结构鉴定及体外功能研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(9):1−11. [CHEN S J, CUI Y. Extraction, structure identification and in vitro function of polysaccharide from sweet potato residue[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2021,36(9):1−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2021.09.002 [30] 韩芬霞, 范新景, 耿升, 等. 异甘草素抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的分子机制[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(15):37−42. [HAN F X, FAN X J, GENG S, et al. Isoglycyrrhizin inhibition α- molecular mechanism of glucosidase[J]. Food Science,2019,40(15):37−42. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180830-337 [31] 张浩然, 魏晶晶, 王慧春. 超声法提取猴头菇多糖工艺优化研究[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(3):154−156. [ZHANG H R, WEI J J, WANG H C. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Condiments,2021,46(3):154−156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.03.031 [32] 吴金松, 王晓芳, 王建玲, 等. 超声波辅助提取铁棍山药皮水溶性多糖的工艺优化[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(7):110−114. [WU J S, WANG X F, WANG J L, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction of water-soluble polysaccharide from tiebang yam peel[J]. Grain and Oil,2021,34(7):110−114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2021.07.028 [33] XU C, LEI Q, YU G, et al. Preparation, characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides and proteins-capped selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,195:576−585. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.110
[34] 帅良, 廖玲燕, 段振华, 等. 百香果果皮多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(18):150−156. [SHUAI L, LIAO Y H, DUAN Z H, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of Polysaccharide from passion fruit peel[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2020,41(18):150−156. [35] LI S, GAO A, DONG S, et al. Purification, antitumor and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from soybean residue fermented with Morchella esculenta[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,96:26−34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.007
[36] MKADMINI, KHAOULA, HAMMAMI, et al. Optimization extraction of polysaccharide from Tunisian Zizyphus lotus fruit by response surface methodology: Composition and antioxidant activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,212(dec.1):476−484.
[37] BO, LI, NING, et al. The core structure characterization and of ginseng neutral polysaccharide with the immune-enhancing activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018(123):713−722.
[38] ZHANG L, HU Y, DUAN X, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from thirteen boletus mushrooms[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018(17):345−382.
[39] JIANG J Y, KONG F S, LI N S, et al. Purification, structural characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of a novel polysaccharide from Boshuzhi[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016:365−371.
[40] 汪磊. 刺梨多糖的分离纯化、降血糖作用及其对肠道微生态的影响[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. WANG L. Isolation, purification, hypoglycemic effect of Rosa roxburghii polysaccharide and its impact on intestinal microecology [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of technology, 2019.
[41] ZHANG J Q, LI C, HUANG Q, et al. Comparative study on the physicochemical properties and bioactivities of polysaccharide fractions extracted from Fructus Mori at different temperatures[J]. Food & Function,2019:584−588.
[42] 张亮, 张爱婧, 孙宇. 不同粒色藜麦多糖的超声辅助酶解提取工艺的优化及其体外活性比较[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(6):15−23. [ZHANG L, ZHANG A J, SUN Y. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted enzymatic hydrolysis and extraction process of quinoa polysaccharides with different grain colors and comparison of their in vitro activities[J]. China Food Additives,2021,32(6):15−23.






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:
