Dynamic Effect of NaCl Concentration on Intramuscular Lipid Hydrolysis and Oxidation in Pork
-
摘要: 为探究猪肉加工中不同食盐含量对肌内脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的影响,以猪背最长肌为原料,分别加入1%、2%、3%、4%和5%的食盐,经不同温度(15~30 ℃)处理后,研究肌内甘油三酯和磷脂水解的动力学规律及游离脂肪酸和脂肪氧化的动力学变化。结果表明,磷脂水解、甘油三酯水解和脂肪氧化均符合一级动力学模型,游离脂肪酸变化符合零级动力学模型;脂肪水解或游离脂肪酸生成平均速率常数均随处理温度或食盐浓度的增加而增加,磷脂脂解速率常数高于甘油三酯;脂肪氧化速率常数随温度的增加而增加,但随食盐浓度增加先增加,在3%时达到最大值,然后逐渐降低。Arrhenius方程分析表明脂肪水解活化能随食盐含量增加而减小,食盐含量对磷脂脂解的影响大于甘油三酯;在3%食盐浓度时脂肪氧化有最低活化能值。因此,食盐含量对猪肉中脂肪水解和脂肪氧化影响的规律不同,对脂肪氧化速率常数的影响远大于脂肪水解。Abstract: To investigate the effects of different NaCl concentration on intramuscular lipid hydrolysis and lipid oxidation in pork processing, 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, and 5% of NaCl were added to the longsissimus muscles, respectively. Then kinetic changes of triglyceride, phospholipid, free fatty acid, and lipid oxidation were described after treatment at different temperature range of 15~30 ℃. The results showed that the hydrolysis of triglyceride and phosphollipid, and the lipid oxidation accorded with first-order kinetic model, and the change of free fatty acid could be fitted by zero-order kinetic model. The average rate constants of both lipid hydrolysis and free fatty acid formation increased with the increasing temperature or NaCl content, and phospholipid had bigger lipolysis rate constants than triglyceride. At a fixed NaCl content, the rate constants of lipid oxidation increased with the increasing temperature, and at a fixed temperature, lipid oxidation rate constants first increased and then decreased with the salt concentration, reaching a maximum at 3% salt concentration. The Arrhenius equation analysis showed that the activation energy of lipid hydrolysis decreased with the increasing NaCl content, and NaCl had a more significant effect on phospholipid than on triglyceride. Lipid oxidation had smallest activation energy at 3% NaCl. So, NaCl concentration had a different effect on lipid hydrolysis and lipid oxidation in pork, and its role on rate constant of lipid oxidation was much bigger than that of lipid hydrolysis.
-
Keywords:
- pork /
- NaCl /
- lipid oxidation /
- lipid hydrolysis
-
食盐是肉食品加工中最常用的调味品之一,特别是对干腌肉制品的色、香、味、形和货架期均有重要影响[1-3]。但随着生活节奏的加快,人们食用越来越多加工食品的同时也食入了更多的食盐,使体内钠钾比增加[4],过量摄入钠盐会引起高血压,并增加心血管疾病和中风甚至死亡的风险[5-6]。因此,很多学者都在研究减少加工食品中食盐添加量,或寻找一些替代品,如钾盐、镁盐、钙盐等[7-8],特别是氯化钾,因其和氯化钠性质最接近[9]。但一些传统干腌肉制品的加工工艺是经成千上百年传承下来的,一味的减少食盐添加量或加入替代品可能会影响其传统特色与安全性,因此必须开展充分的理论研究。
脂肪氧化对干腌肉制品风味形成有重要影响,一方面,肉品大多数挥发性风味物质都源自脂肪氧化,特别是肌内脂肪;另一方面,如脂肪氧化过度,会使产品引起哈败味等质量问题[10-11]。干腌肉制品加工中脂肪氧化受很多因素影响,如温度、原料、辅料、加工时间等,其中食盐添加量也是重要因素之一。关于肉制品中食盐对脂肪氧化的影响很多学者进行了报道,大都认为食盐在一定浓度范围内会促进脂肪氧化[12],超过一定范围则会逐步抑制脂肪氧化,食盐浓度对脂肪氧化的影响呈现二次曲线规律[1,11],如Rhee等[1]研究鸡肉和牛肉时发现2.5%的食盐有最大促氧化效果;他们[13]同时报道猪肉中氯化钠在2%左右促氧化作用最强,此后,随浓度增加,促氧化作用将逐渐减小。总的来说食盐添加量在5%[14]甚至7%[15-16]范围内都会促进肉中脂肪氧化。
干腌肉制品加工中,首先是脂肪在脂肪酶的作用下水解,形成游离脂肪酸,然后部分游离脂肪酸氧化形成部分小分子特征风味物质。关于脂肪水解与脂肪氧化的关系,Coutron-Gambotti等[17]和杨红菊[18]认为脂肪水解可促进脂肪氧化,而Jin等[19]和Gandemer等[20]认为两者关系不大,Huang等[21]发现在腊肉加工中,磷脂水解可促进脂肪氧化,而甘油三酯水解与脂肪氧化关系不大。关于食盐对肉中脂肪的影响,尽管很多学者研究了食盐对脂肪氧化的影响,但仅有少数学者研究过食盐对脂肪水解的影响,且大都只从游离脂肪酸变化的角度探讨了食盐对脂肪水解的影响[16,22],但因游离酸存在一个生成与分解的动态平衡,其变化并不能真正地反映脂肪水解;Andres等[23]研究了火腿加工中食盐对肌内甘三酯、磷脂水解的影响,但仅对比了3%和6%的食盐含量,且火腿加工中可能受很多其它因素的影响,如加工温度和时间、及加入的各种辅料等,因此到目前食盐对脂肪水解的确切影响规律仍不明确,也没有关于食盐作用下脂肪水解与脂肪氧化关系的报道。因此,为进一步探讨食盐对肉制品加工中脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的影响,本研究拟在肉制品加工常用的食盐添加范围内(1%~5%),以猪背最长肌为材料,探究脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的变化规律,并从动力学角度探讨脂肪水解与脂肪氧化、及磷脂与甘油三酯水解的关系,以期为降低肉制品中钠盐含量奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
猪背最长肌 购于当地永辉超市,为当天新宰杀的猪,冷藏条件下运回实验室后,去掉表面可见脂肪、筋膜和结缔组织,真空包装后于−18 ℃保藏待用;NaCl 重庆金锦乐化工有限公司;14%三氟化硼甲醇溶液、Amberlyst-26阴离子交换树脂、十七烷酸甲酯 Sigma公司;三氯甲烷、甲醇、丙酮、三氯乙酸、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、硫代巴比妥酸、1, 1, 3, 3-四乙氧基丙烷等 均为分析纯,成都科龙化工试剂厂。
FSH-2A匀浆机 上海梅香仪器有限公司;BSC-259恒温恒湿箱 上海博迅实业有限公司;U-3900H分光光度计 日本Hitachi公司;JYS-A800绞肉机 山东九阳电器有限公司;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;L-128型氮吹仪 北京来亨公司;Sep-Pack硅胶固相萃取小柱 美国Waters公司;QP-2010型气相色谱仪 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
a.样品于4 ℃解冻24 h,绞碎并混匀,然后平分为5组,分别加入1%、2%、3%、4%和5%的NaCl并拌匀;b.然后各组平均分成60份,每份20 g左右,分别用铝箔袋包装,不封口;c.每组的60份平均分成4组,分别于15、20、25、30 ℃恒温箱中保温,每个温度条件下分别于5个时间点取样,每次取样3份,作为3个重复,具体每个处理的5个时间点根据预备试验确定,温度高的处理时间相对较短,反之时间较长,以使每个温度条件下能够观察到明显的脂肪氧化和脂肪水解,如15 ℃的保温时间分别为0、20、40、60、80 h,20 ℃的保温时间分别为0、15、30、45、60 h,25 ℃的保温时间分别为0、8、16、24、32 h,而30 ℃的保温时间分别为0、5、10、15、20 h;d.处理结束后,马上分析各样品的甘油三酯、磷脂、游离脂肪酸含量和TBARS值(硫代巴比妥酸反应物质,Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance)。
1.2.2 脂肪含量测定
各样品中肌内磷脂、甘油三酯和游离脂肪酸的含量根据He等[24]的方法进行测定。
1.2.3 脂肪氧化测定
脂肪氧化程度用TBARS值来衡量,其测定根据GB5009. 181—2016的分光光度法。
1.2.4 动力学变化规律研究
磷脂、甘油三酯、游离脂肪酸、脂肪氧化的动力学变化规律分别用零阶式(1)与一阶反应动力学方程式(2)进行拟合。
$$ \mathrm{A}=\mathrm{A}_0\pm \mathrm{k}\mathrm{t} $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{A}/\mathrm{A}_0)=\pm \mathrm{k}\mathrm{t} $$ (2) 式中:A、A0分别为处理时间为t和0时的脂肪含量或TBARS值;t为保温时间,h;k为脂肪水解或脂肪氧化速率常数,h−1。
因此,利用SPSS的线性回归程序,可利用式(1)或式(2)拟合得到某一特定盐含量、温度条件下的脂肪水解或脂肪氧化速率常数k。
Arrhenius式(3)经常用来评价温度对反应速率常数k的影响,因此在本试验中也用来评定温度对脂肪水解或脂肪氧化速率常数的影响,具体影响程度用反应活化Ea(kJ/mol)来衡量。
$$\rm {ln}\left(k\right)={\ln}({\rm k}_{0})-\dfrac{{\rm E}_{\rm a}}{\rm{RT}} $$ (3) 式中:R为通用气体常数,8.314 J/(mol.K);T为温度,K;k0为指前因子。
同样,利用SPSS的线性回归程序,在不同盐含量条件下,以ln(k)为因变量,−1/RT为自变量作线性回归分析,所得斜率即为不同食盐含量下脂肪水解或脂肪氧化的Ea。
1.3 数据处理
实验重复测定3次,采用SPSS软件对数据进行处理,实验结果表示为平均值±标准差。进行显著差异分析时采用Duncan法,显著水平设为0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 食盐含量对肌内磷脂水解的影响
2.1.1 磷脂脂解速率常数
在食品加工或贮藏中,大多与质量有关的品质变化都遵循零级或一级反应动力学规律[25],本研究中同时用零级与一级模型拟合脂肪水解和脂肪氧化速率常数。在某一特定食盐含量和温度条件下,测得各样品不同时间肌内磷脂的含量后,同时用式(1)和式(2)对磷脂脂解速率常数进行拟合(其中30 ℃时不同食盐浓度对磷脂含量的影响如图1所示),发现用一级动力学模型进行拟合效果更好,各速率常数如表1所示(各速率常数均极显著)。
表 1 猪肉中磷脂在不同食盐含量下脂解速率常数及活化能Table 1. Phospholipid lipolysis rate constant and activation energy in pork at different NaCl concentration食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 5.78±0.43 6.37±0.83 7.84±0.83 9.98±0.64 26.74±2.51a 2 6.84±0.50 7.55±1.02 8.97±0.75 10.90±0.87 22.76±2.67ab 3 9.70±0.42 10.74±0.27 12.19±1.07 14.34±1.10 18.84±1.74bc 4 11.97±0.78 12.58±0.75 15.07±0.90 16.71±1.09 17.13±0.92c 5 12.01±0.81 13.20±0.66 14.69±0.35 16.87±0.39 16.34±1.56c 注:不同小写字母代表显著差异(P<0.05);表2~表4同。 从表1可以看出,食盐含量固定时,磷脂脂解速率常数随温度的增加而增加,说明温度的升高能促进磷脂水解;本团队在另一个研究中探究温压结合处理对猪肉肌内脂肪氧化的影响时,也发现温度的增加能促进肌内磷脂的水解[26]。在固定温度不变时,除了25 ℃时添加5%食盐的样品外,脂解速率常数均随食盐含量的增加而增加,但5%与4%食盐浓度差异不大,因此,至少可以推断在1%~4%食盐浓度范围内,食盐含量的增加可以促进猪肉中磷脂水解。根据可查阅的资料,到目前为止还没有关于肉中磷脂水解速率常数方面的报道。
2.1.2 食盐含量对磷脂脂解速率常数的影响
从前述可知,在NaCl含量固定时,磷脂水解速率常数均随温度的增加而增加,具体增加规律可用Arrhenius方程进行评价。利用SPSS的线性回归程序(方程3)可求得各食盐含量条件下磷脂水解的活化能,如表1所示,利用方程(3)求出的各活化能均显著(P<0.05)。随着食盐浓度的增加,活化能值逐渐减少,但当食盐浓度在3%以上时差异不显著(P>0.05),而1%食盐浓度时活化能值显著(P<0.05)高于含盐量3%及以上的样品,2%食盐浓度显著(P<0.05)高于4%和5%的样品。因此,随着食盐浓度的增加,磷脂脂解所需要克服的能量障碍降低,从而促进磷脂水解。这与上面研究脂解速率常数时得到的结论基本一致。Andres等[23]研究火腿加工时,发现高盐(6%)相比于低盐(3%)更能促进肌内磷脂水解,与本研究的结论基本一致。
2.2 食盐含量对肌内甘油三酯水解的影响
2.2.1 甘油三酯脂解速率常数
同样,一级动力学模型能更好地拟合猪肉中甘油三酯的水解,各样品脂解速率常数如表2所示,同磷脂脂解一样,甘油三酯的脂解速率常数随温度增加或食盐含量的增加而增加,说明食盐含量和温度对甘油三酯和磷脂水解的影响规律是相似的。但可以看出,在其它条件相同时,甘油三酯的脂解速率常数小于磷脂,这说明猪肉中更多的磷脂发生了脂解。这可能是由于磷脂中含有更多的多不饱和脂肪酸,因此更容易水解。这与一些报道的结果是一致的[27-29],大都认为肉制品中大部分游离脂肪酸都来自于磷脂的水解。本研究中使用的猪肉原料由于肌内脂肪含量高(5%左右),且肌内脂肪中75%左右都为甘油三酯,因此从总量上来讲甘油三酯仍发生了较明显的水解,脂解速率常数在磷脂的1/3到1/2之间,这与一些学者的研究结果是一致的[20-21]。
表 2 猪肉中甘油三酯在不同食盐含量下脂解速率常数及活化能Table 2. Triglyceride lipolysis rate constant and activation energy in pork at different NaCl concentration食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 2.68±0.30 2.99±0.19 3.45±0.22 4.10±0.52 20.57±2.24a 2 3.19±0.21 3.49±0.22 3.97±0.35 4.65±0.71 18.26±1.37ab 3 3.91±0.43 4.28±0.41 4.95±0.20 5.59±0.35 17.67±1.89abc 4 4.65±0.29 4.92±0.17 5.73±0.36 6.46±0.24 16.51±0.93bc 5 5.18±0.30 5.50±0.54 6.24±0.16 6.90±0.38 14.31±1.75c 表 3 猪肉中游离脂肪酸在不同食盐含量下变化速率常数及活化能Table 3. Change rate constant and activation energy of free fatty acid in pork at different NaCl concentration食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 3.57±0.27 3.80±0.25 4.33±0.50 5.28±0.61 18.88±2.98a 2 4.66±0.60 5.03±0.19 5.74±0.71 6.52±0.54 16.53±1.94a 3 5.36±0.41 5.56±0.32 6.11±1.03 7.08±0.38 13.44±3.22a 4 5.90±0.32 6.43±0.49 7.42±0.47 8.08±0.74 15.78±2.83a 5 6.09±0.30 6.37±0.56 7.09±0.51 8.46±0.48 15.81±2.66a 表 4 不同含量食盐对脂肪氧化(以TBARS衡量)速率常数及活化能的影响Table 4. Estimated reaction rate constant and activation energy of lipid oxidation measured by TBARS value at different NaCl concentration食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 9.73±0.84 12.54±1.05 17.86±1.19 27.93±1.67 50.98±2.67a 2 11.54±0.77 15.33±1.13 21.09±1.15 30.12±2.32 46.39±2.37abc 3 13.27±0.94 17.60±0.82 24.56±1.12 32.38±1.97 43.71±1.55c 4 12.09±0.54 15.31±0.94 20.89±0.85 31.19±2.08 45.72±1.42bc 5 10.67±0.93 12.95±0.68 21.21±1.43 28.20±0.95 49.39±2.45ab 2.2.2 食盐含量对甘油三酯脂解速率常数的影响
同样,根据方程(3),利用SPSS的线性回归程序,可求出各食盐含量条件下甘油三酯脂解活化能,变化规律与磷脂脂解活化能相似,但数值上略小于后者,说明相同条件下磷脂脂解所需要克服的能量障碍略高,这可能是脂膜对磷脂的保护作用。食盐对甘油三酯水解的促进作用可能与食盐对脂肪酶的激活有关,Motilva等[30]研究发现在8%的食盐浓度范围内,随食盐浓度增加,酸性脂肪酶活性在2%食盐浓度后逐渐增加,最大可达初始活性的3倍,而酸性脂肪酶被认为是促进甘油三酯水解的主要酶[19,30-31]。虽然食盐对脂肪水解的确切影响机制还没有阐明,但根据本研究的结论,在5%的食盐含量内,盐含量的增加能同时促进甘油三酯和磷脂的水解,Motilva等[30]与Vestegaard等[31]也报道了食盐可以促进脂肪水解,但Coutron-gambotti等[32]却认为食盐对脂肪水解没有显著影响。
2.3 食盐含量对肌内游离脂肪酸的影响
2.3.1 游离脂肪酸变化速率常数
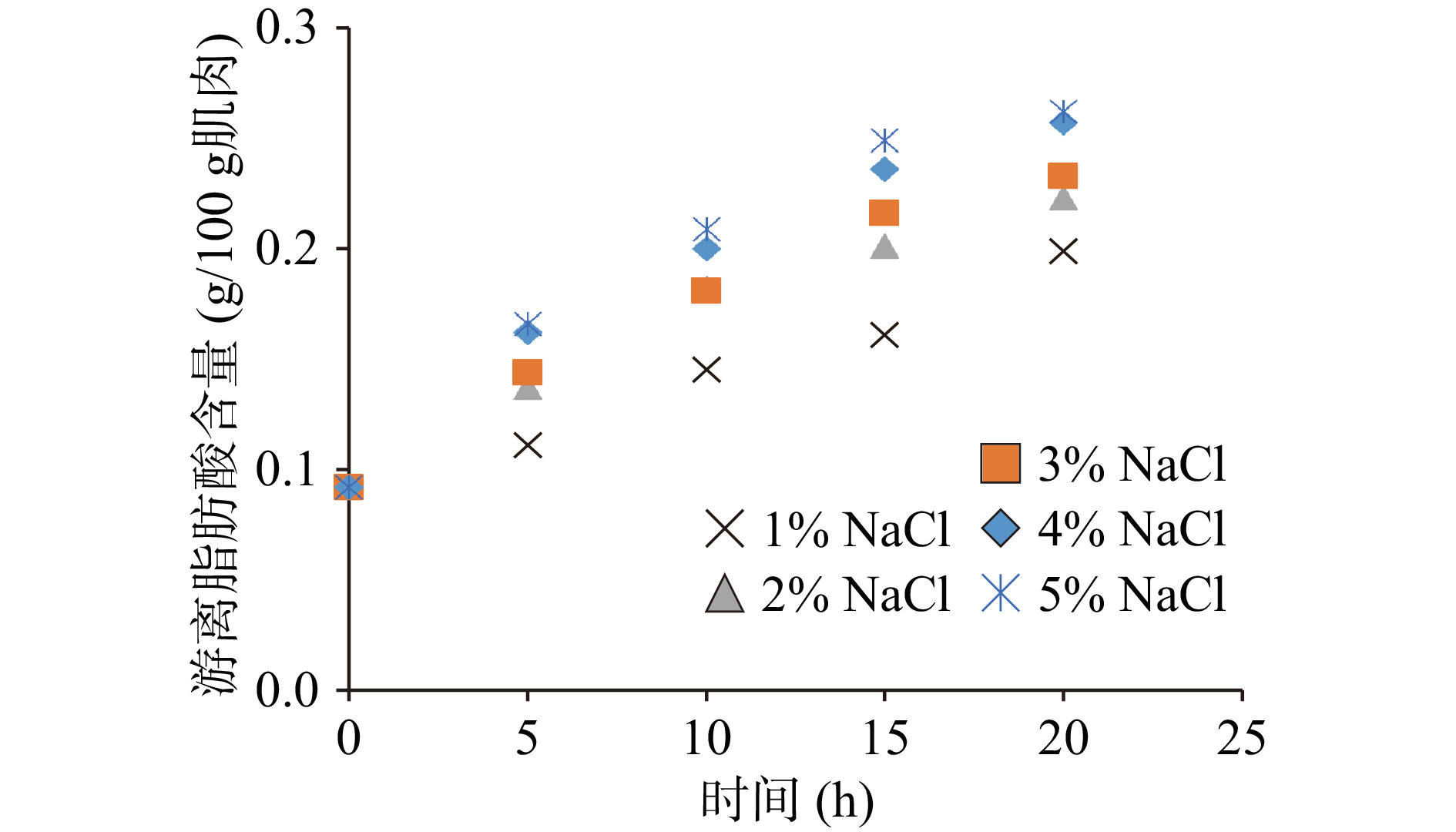
对游离脂肪酸含量变化进行拟合时,发现零级动力学方程(方程1)拟合效果更好,其中30 ℃时不同食盐浓度对游离脂肪酸含量的影响如图2所示。拟合的各速率常数如表3所示。可以看出,游离脂肪酸的变化速率常数也随温度的增加而增加,在1%~4%食盐范围内随食盐浓度的增加而增加。游离脂肪酸的变化存在一个动态平衡,一方面,磷脂和甘三酯的水解会产生游离脂肪酸,但同时一部分游离脂肪酸会氧化,特别是其中的多不饱和脂肪酸。在本研究的条件范围内,游离脂肪酸均是生成大于氧化分解,因此其变化速率常数的符号都相同,均大于0。
2.3.2 食盐含量对游离脂肪酸变化速率常数的影响
同样,根据方程(3)可求出游离脂肪酸生成的活化能,如表3所示。可以看出,除甘油三酯5%盐含量外,游离脂肪酸生成的活化能低于其他所有条件下磷脂和甘三酯脂解的活化能,这可能是由于游离脂肪酸主要来自于甘三酯和磷脂的水解,因此当两者的水解发生后,游离脂肪酸的生成便自然而然发生,不需要克服更多的能量障碍。当食盐含量从1%升到5%时,游离脂肪酸的生成活化能间没有显著差异(P>0.05),这可能是由于游离脂肪酸的变化是生成和分解的一个动态平衡,相对波动幅度较大。
2.4 食盐含量对脂肪氧化的影响
2.4.1 脂肪氧化速率常数
通过分别对式(1)和式(2)进行拟合,发现用一级动力学方程对脂肪氧化速率常数的拟合效果更好,不同条件下速率常数如表4所示。可以看出,在食盐含量固定的条件下,脂肪氧化速率常数随温度的增加而增加;在温度不变时,脂肪氧化速率常数先随食盐浓度的增加而增加,在3%食盐浓度时达到最大值,然后逐渐降低。这说明食盐浓度在3%以内时其含量的增加会促进脂肪氧化,而超过3%时对脂肪氧化的促进作用会降低。这与一些报道的结果是一致的,如张东等[33]发现腊肉加工中2%与3%的盐会促进脂肪氧化,而4%以上时脂肪氧化明显减弱;Rhee等[13]报道氯化钠在2%左右时促氧化作用最强,此后促氧化作用逐渐减小;Rhee等[1]和靳国锋[11]发现食盐含量对肉中脂肪氧化具有二次效应,脂肪氧化指标先随食盐浓度的增加逐渐增加,达到最大值后逐渐降低;但总的来说食盐添加量在5%[1,11,14]甚至7%[15-16]范围内都会促进肉中脂肪氧化。
2.4.2 食盐含量对脂肪氧化速率常数的影响
利用方程(3)求出的脂肪氧化活化能如表4所示,可以看出,活化能值先随食盐浓度的增加显著降低(P<0.05),在3%达到最小值,然后显著增加(P<0.05),这也进一步说明3%的食盐能最大程度的促进猪肉中脂肪氧化。对比表1~表4,可以看出,无论磷脂还是甘油三酯水解的活化能均远低于脂肪氧化的活化能,这说明脂肪水解虽然能促进脂肪氧化[17-18],且脂肪水解是脂肪氧化的必要条件,因为结合脂肪酸的直接氧化很困难,甘油三酯或磷脂大都要水解成游离脂肪酸后才能氧化[17];但脂肪水解并不是脂肪氧化的充分条件,脂肪氧化需要克服的能量障碍远高于脂肪水解。这可能与两者发生的机制不同有关,脂肪水解主要是在脂酶的作用下发生,而脂肪氧化是金属离子或脂肪氧化酶等的作用下发生的。关于肉制品加工中脂肪水解与脂肪氧化的关系,一些学者进行了研究,其中Coutron-Gambotti[17]和杨红菊[18]认为脂肪水解可促进脂肪氧化,而Jin等[19]和Gandemer[20]认为两者关系不大,Huang等[21]发现在腊肉加工中,磷脂水解可促进脂肪氧化,而甘油三酯水解与脂肪氧化关系不大。本研究在前述研究的基础上进一步提出脂肪水解是脂肪氧化的必要条件但不是充分条件的观点,但这一规律仍需要在其他肉类中验证。
另外,在1%~5%食盐浓度范围内,盐含量越高,脂肪水解越容易发生,而脂肪氧化在3%盐浓度时最显著,这也说明了食盐对猪肉中脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的影响规律并不一致。Zhao等[34]研究了不同食盐含量对中式香肠脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的影响,发现4%食盐相比2%的食盐含量能更促进脂肪水解和氧化,这与本研究的结论基本一致。
3. 结论
本文从动力学的角度研究了食盐含量对猪肉肌内脂肪水解和氧化的影响,发现在1%~5%食盐浓度和15~30 ℃条件下,猪肉中磷脂脂解、甘油三酯脂解、脂肪氧化都遵从一级动力学变化规律,而游离脂肪酸变化更符合零级动力学模型。磷脂脂解的速率常数和活化能均大于相应的甘三酯水解;食盐浓度的增加可促进磷脂和甘三酯水解。脂肪氧化速率常数先随食盐浓度增加而增加,在食盐浓度3%达到最大值后逐渐降低。因此,食盐对猪肉中脂肪水解和脂肪氧化影响的规律不一致,脂肪氧化的活化能远大于脂肪水解。本研究首次从动力学角度对肉中脂肪水解和脂肪氧化的关系度进行了有益的探索,也为进一步降低肉制品中食盐的使用量奠定了一定的理论基础。
-
表 1 猪肉中磷脂在不同食盐含量下脂解速率常数及活化能
Table 1 Phospholipid lipolysis rate constant and activation energy in pork at different NaCl concentration
食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 5.78±0.43 6.37±0.83 7.84±0.83 9.98±0.64 26.74±2.51a 2 6.84±0.50 7.55±1.02 8.97±0.75 10.90±0.87 22.76±2.67ab 3 9.70±0.42 10.74±0.27 12.19±1.07 14.34±1.10 18.84±1.74bc 4 11.97±0.78 12.58±0.75 15.07±0.90 16.71±1.09 17.13±0.92c 5 12.01±0.81 13.20±0.66 14.69±0.35 16.87±0.39 16.34±1.56c 注:不同小写字母代表显著差异(P<0.05);表2~表4同。 表 2 猪肉中甘油三酯在不同食盐含量下脂解速率常数及活化能
Table 2 Triglyceride lipolysis rate constant and activation energy in pork at different NaCl concentration
食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 2.68±0.30 2.99±0.19 3.45±0.22 4.10±0.52 20.57±2.24a 2 3.19±0.21 3.49±0.22 3.97±0.35 4.65±0.71 18.26±1.37ab 3 3.91±0.43 4.28±0.41 4.95±0.20 5.59±0.35 17.67±1.89abc 4 4.65±0.29 4.92±0.17 5.73±0.36 6.46±0.24 16.51±0.93bc 5 5.18±0.30 5.50±0.54 6.24±0.16 6.90±0.38 14.31±1.75c 表 3 猪肉中游离脂肪酸在不同食盐含量下变化速率常数及活化能
Table 3 Change rate constant and activation energy of free fatty acid in pork at different NaCl concentration
食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 3.57±0.27 3.80±0.25 4.33±0.50 5.28±0.61 18.88±2.98a 2 4.66±0.60 5.03±0.19 5.74±0.71 6.52±0.54 16.53±1.94a 3 5.36±0.41 5.56±0.32 6.11±1.03 7.08±0.38 13.44±3.22a 4 5.90±0.32 6.43±0.49 7.42±0.47 8.08±0.74 15.78±2.83a 5 6.09±0.30 6.37±0.56 7.09±0.51 8.46±0.48 15.81±2.66a 表 4 不同含量食盐对脂肪氧化(以TBARS衡量)速率常数及活化能的影响
Table 4 Estimated reaction rate constant and activation energy of lipid oxidation measured by TBARS value at different NaCl concentration
食盐含量
(%)速率常数(10−3 h−1) Ea(kJ/mol) 15 ℃ 20 ℃ 25 ℃ 30 ℃ 1 9.73±0.84 12.54±1.05 17.86±1.19 27.93±1.67 50.98±2.67a 2 11.54±0.77 15.33±1.13 21.09±1.15 30.12±2.32 46.39±2.37abc 3 13.27±0.94 17.60±0.82 24.56±1.12 32.38±1.97 43.71±1.55c 4 12.09±0.54 15.31±0.94 20.89±0.85 31.19±2.08 45.72±1.42bc 5 10.67±0.93 12.95±0.68 21.21±1.43 28.20±0.95 49.39±2.45ab -
[1] RHEE K S, ZIPRIN Y A. Pro-oxidative effects of NaCl in microbial growth-controlled and uncontrolled beef and chicken[J]. Meat Science,2001,57(1):105−112. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(00)00083-8
[2] 马晓丽, 黄雅萍, 张龙涛, 等. 肉制品加工中的低钠策略研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,54(14):256−262. [MA X L, HUANG Y P, ZHANG L T, et al. Strategies for sodium reduction in meat products: A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,54(14):256−262. [3] INGUGLIA E S, ZHANG Z, TIWARII B K, et al. Salt reduction strategies in processed meat products-A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,59:70−78.
[4] MESIAS M, HOLGADO F, MARQUEZ-RUIZ G, et al. Effect of sodium replacement in cookies on the formation of process contaminants and lipid oxidation[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,62(1):633−639. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014.11.028
[5] OH Y S, APPEL, L J, GALIS Z S, et al. National heart, lung, and blood institute working group report on salt in human health and sickness building on the current scientific evidence[J]. Hypertension,2016,68(2):681−688.
[6] 张东, 李洪军, 吴练军, 等. 减少肉制品中氯化钠含量的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,43(11):238−243. [ZHANG D, LI H G, WU L J, et al. Research progress on reducing sodium chloride in meat products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,43(11):238−243. [7] 丁习林, 王桂瑛, 王雪峰, 等. 肉制品加工中镁盐部分替代氯化钠的应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(17):327−332, 339. [DING X L, WANG G Y, WANG X F, et al. Application research progress of the partial replacement of sodium chloride by magnesium salt in meat processing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(17):327−332, 339. [8] HWANG J W, JIN S K, HUR S J, et al. Quality changes in fat-reduced sausages by partial replacing sodium chloride with other chloride salts during five weeks of refrigeration[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,97:818−824. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.08.004
[9] PIETRASIK Z, GAUDETTE N J, JOHNSTON S P. The use of high pressure processing to enhance the quality and shelf life of reduced sodium naturally cured restructured cooked hams[J]. Meat Science,2016,116(6):102−109.
[10] MOTTRAM D S. Flavour formation in meat and meat products: A review[J]. Food Chemistry,1998,62(4):415−424. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00076-4
[11] 靳国锋. 干腌培根加工过程中脂肪氧化调控机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. JIN G F. Regulation and mechanism of lipid oxidation during processing of dry cured bacon[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2011.
[12] MARIUTTI L R B , BRAGAGNOLO N. Influence of salt on lipid oxidation in meat and seafood products: A review[J]. Food Research International,2017,94:90−100. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.02.003
[13] RHEE K S, SMITH G C, TERRELL R N. Effect of reduction and replacement of sodium chloride on rancidity development in raw and cooked ground pork[J]. Journal of Food Protection,1983,46(7):578−581. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-46.7.578
[14] BELTRAN E, PLA R, YUSTE J, et al. Lipid oxidation of pressurized and cooked chicken: Role of sodiumchloride and mechanical processing on TBARS and hexanal values[J]. Meat Science,2003,64(1):19−25. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00132-8
[15] 何翠. 低钠腊肉加工过程中脂肪氧化特性的研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2017: 13−21. HE C. Study on characteristics of lipid oxidation of low sodium bacon during processing[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017: 13−21.
[16] 张平, 杨勇, 巩洋, 等. 食盐用量对四川腊肉加工及贮藏过程中肌内脂肪变化的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(13):327−331. [ZHANG P, YANG Y, GONG Y, et al. Effects of salt content on changes of intramuscular lipids in Sichuan bacon during processing and storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(13):327−331. [17] COUTRON-GAMBOTTI C, GANDEMER G. Lipolysis and oxidation in subcutaneous adipose tissue during dry-cured ham processing[J]. Food Chemistry,1999,64(1):95−101. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00079-X
[18] 杨红菊. 宣威火腿加工过程中肌内脂肪水解及磷脂水解酶的纯化鉴定[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2005. YANG H J. Lipolysis in intramuscular lipids during processing of xuanwei ham & purification and characterization of phospholipid hydrolases from porcine skeletal muscle[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2005.
[19] JIN G, ZHANG J, YU X, et al. Lipolysis and lipidoxidation in bacon during curing and drying-ripening[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,123(2):465−471. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.031
[20] GANDEMER G. Lipids in muscles and adipose tissues, changes during processing andsensory properties of meat products[J]. Meat Science,2002,62(3):309−321. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00128-6
[21] HUANG Y, LI H, HUANG T, et al. Lipolysis and lipid oxidation during processing of Chinese traditional smoke-cured bacon[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,149:31−39. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.081
[22] STAHNKE L H. Dried sausages fermented with Staphylococcus xylosus at different temperatures and with different ingredient levels-Part I. chemical and bacteriological data[J]. Meat Science,1995,41(2):179−191. doi: 10.1016/0309-1740(94)00070-N
[23] ANDRES A I, CAVA R, MARTIN D, et al. Lipolysis in dry-cured ham: Influence of salt content and processing conditions[J]. Food Chemistry,2005,90(4):523−533. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.05.013
[24] HE Z, HUANG Y, LI H, et al. Effect of high-pressure treatment on the fatty acid composition of intramuscular lipid in pork[J]. Meat Science,2012,90(1):170−175. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2011.06.022
[25] 王强. 香肠脂肪氧化动力学特性及温度对其影响研究[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(11):130−133. [WANG Q. Kinetic charateristics of lipid oxidation in sausages as affected by temperature[J]. Food Science,2013,34(11):130−133. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201311029 [26] HUANG Y, GAN Y, LI F, et al. Effects of high pressure in combination with thermal treatment on lipid hydrolysis and oxidation in pork[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,63(1):136−143. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.103
[27] MARTIN L, CORDOBA J J, VENTANAS J, et al. Changes in intramuscular lipids during ripening of Iberian dry-cured ham[J]. Meat Science,1999,51(2):129−134. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(98)00109-0
[28] YANG H, MA C, QIAO F, et al. Lipolysis in intramuscular lipids during processing of traditional Xuanwei ham[J]. Meat Science,2005,71(4):670−675. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.05.019
[29] XU W, XU X, ZHOU G, et al. Changes of intramuscular phospholipids and free fatty acids during the processing of Nanjing dry-cured duck[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,110(2):279−284. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.11.044
[30] MOTILVA M, TOLDRA F. Effect of curing agents and water activity on pork muscle and adipose subcutaneous tissue lipolytic activity[J]. Zeitschrift fur Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und-Forschung,1993,196(3):228−232. doi: 10.1007/BF01202737
[31] VESTEGAARD C S, SCHIVAZAPPA C, VIRGILI R. Lipolysis indry cured ham maturation[J]. Meat Science,2000,55(1):1−5. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(99)00095-9
[32] COUTRON-GAMBOTTI C, GANDEMER G, ROUSSET S, et al. Reducing salt content of dry cured ham: Effect on lipid composition and sensory attributes[J]. Food Chemistry,1999,64(1):13−19. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00111-3
[33] 张东, 李洪军, 王鑫月, 等. 食盐添加量对腊肉品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,43(11):159−164,171. [ZHANG D, LI H G, WANG X Y, et al. Effect of different amounts of salt on the quality of Chinese bacon[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,43(11):159−164,171. [34] ZHAO B, ZHOU H M, ZHANG S L, et al. Changes of protein oxidation, lipid oxidation and lipolysis in Chinese dry sausage with different sodium chloride curing salt content[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2020,9(4):328−337. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2020.04.013
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 徐浩宇,祝振杰,李军,杨会芳,李文山,毕艳兰. 几种市售鸡精脂肪组成及风味对比研究. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 30-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)









 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



