Optimization and Characterization of Microwave-assisted Enzymatic Extraction of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Anli Fruit Pomace
-
摘要: 为提高安梨资源的综合利用价值,本文以安梨食品加工的副产物果渣为原料,探究安梨果渣中可溶性膳食纤维的提取工艺。在单因素实验的基础上,通过响应面法优化安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维(ALDF)的微波辅助复合酶法最佳提取工艺,并通过扫描电镜、红外光谱和高效液相色谱对制备得到的膳食纤维进行结构表征。工艺优化结果表明:在微波功率370 W、液料比为14.4:1 mL/g、酶添加量为1.6%、pH7.0时,安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维的得率最高,达到8.07%。扫描电镜图显示安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维呈长约5 μm的纺锤型。红外光谱显示其具有多糖的特征峰,分子量在5~2.076×104 kDa之间。研究结果表明微波辅助酶法对安梨果渣SDF有较好的提取效果,具有一定工业的应用前景,因此该方法能够为安梨果渣的高值化开发利用提供理论基础。Abstract: In order to improve the comprehensive utilization value of Anli resources, the extraction technology of soluble dietary fiber from Anli pomace was studied with a by-product of food processing in this work. On the basis of single factor test, response surface methodology was used to optimize the microwave-assisted composite enzymatic extraction process of soluble dietary fiber from Anli fruit pomace (ALDF). The structure of the prepared dietary fiber was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The optimization results showed that when the microwave power was 370 W, the liquid-to-material ratio was 14.4:1 mL/g, the added amount of enzyme was 1.6%, and the pH was 7.0, the yield of ALDF was the highest level of 8.07%. The SEM showed that the ALDF had a spindle shape of about 5 μm in length, FT-IR showed that it had the characteristic peak of polysaccharide, and the molecular weight ranged from 5 to 2.076×104 kDa. The results showed that the microwave-assisted enzymatic method had a good extraction effect on the ALDF with a certain industrial application prospect. Therefore, this method could provide a theoretical basis for the high-value development and utilization of Anli fruit pomace.
-
膳食纤维(dietary fiber, DF)通常是指存在于植物中被食用且不被人体消化道消化吸收的碳水化合物,按溶解性可分为可溶性膳食纤维(soluble dietary fiber, SDF)和不溶性膳食纤维(insoluble dietary fiber, IDF)[1]。SDF的主要成分为葡聚糖、果聚糖、果胶和可溶性半纤维素,主要分布于水果[2]、蔬菜[3]和燕麦[4]中。IDF的成分主要为纤维素、不溶性半纤维素和木质素[5]等,在植物种皮[6]、坚果中含量丰富。作为一种低热量功能性成分,膳食纤维可以调节体内血糖[7-8]和降低血脂[9],提高药物耐受性[10],降低总胆固醇和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[11],维持肠道健康及降低患包括癌症在内的慢性疾病的风险[12-13]。成年男性和女性膳食纤维每日推荐摄入量分别为38和25 g/d[14],其中可溶性膳食纤维占有20%~30%。目前膳食纤维的人均日常摄入量为15 g/d,远低于推荐量[15],因此在食品加工中添加适量的膳食纤维不仅可以提高食物的口感,并且能够间接改善和提高人们的身体健康水平。安梨(Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim)是中国燕山地区特有的果品,为蔷薇科植物梨属秋子梨的重要品种之一,其果实富含多酚类[16]、多糖和三萜类[17]等活性物质,兼具食用和药用价值。目前,燕山地区安梨年产量达60余万吨,除部分鲜食外,其余用于果汁和安梨酒的生产[18],这也伴随着大量的果渣废弃物的产生。由于研究技术的欠缺和果汁生产的季节性,每到生产旺季,只有30%左右的安梨果渣可作为肥料被利用,极大地影响了安梨加工工业的可持续发展[19]。研究发现安梨果实中石细胞含量可达1.51%[20-21],主要成分是木质素和纤维素,因此安梨果渣是一种膳食纤维生产的潜在优质原料。
目前提取膳食纤维的方法主要有酸碱浸提、物理提取、酶法[22]提取和发酵提取[23]等。酶法是通过化学方法将样品中的淀粉、蛋白质等分解成葡萄糖、氨基酸等小分子,从而得到纯度较高的膳食纤维[24]。酶法提取可以与微波[25]、超声等物理方法相结合,在不破坏原料活性的基础上进一步提高产率,这类方法条件温和,耗能低,操作较为简单,近年来在原料处理方面得到了广泛地运用[26-27]。
微波辅助酶法具有操作简便,能耗低,提取时间短等优点,在多糖[28]和酚类[29]提取上得到广泛运用。安梨是燕山地区特有经济植物,近年来在果品培育和果汁加工等[30]方面研究较多,但有关安梨果渣及膳食纤维的提取鲜有报道。本研究拟采用微波辅助复合酶法[31]提取安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维,通过葡萄糖苷淀粉酶、高峰α-淀粉酶和中性蛋白酶对安梨果渣进行提取纯化,结合微波萃取进一步提高产量,通过工艺优化确定最佳提取工艺参数。运用扫描电镜、红外光谱及高效液相色谱等手段对制得的膳食纤维进行结构鉴定和表征,探究安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维潜在的应用价值,以期为安梨的高值化开发利用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
安梨 河北省秦皇岛市售当季成熟果实;葡萄糖苷淀粉酶(100 U/mg)、高峰α-淀粉酶(4000 U/g) 源叶生物有限公司;中性蛋白酶(50 U/mg) 上海瑞永生物科技有限公司;盐酸、氢氧化钠 分析纯,天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司;无水乙醇 分析纯,上海泰坦化学有限公司。
JSP-200金穗高速多功能粉碎机 浙江省永康市金穗机制造厂;lME204E分析天平 梅特勒-托利多(上海)有限公司;HH-6数显恒温水浴锅 江苏金坛荣华仪器制造有限公司;ST-20 pH计 奥豪斯国际贸易(上海)有限公司;微波化学反应合成仪 济南蓝迈仪器有限公司;GM-200刀式研磨粉碎机 德国莱驰公司;EYELAN-1100旋转蒸发仪 日本东京理化公司;Alpha2-4L Dplus冷冻干燥机 德国CHRIST公司;3-18KS冷冻离心机 德国SIGMA公司;U-4100型紫外-可见-近红外光谱仪 德国布鲁克公司;HPLC1100高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦公司;SU-8010扫描电子显微镜 日本日立公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 安梨果渣的制备
选择新鲜成熟安梨,洗净、切成大小相同的小块,用刀式研磨仪将其打碎,将果渣与果汁分离,果渣于恒温干燥箱干燥48 h,放入粉碎机充分粉碎均匀,用60目筛过滤,得到安梨果渣粉末样品,于−80 ℃冰箱冷冻储存。
1.2.2 安梨果渣SDF的提取
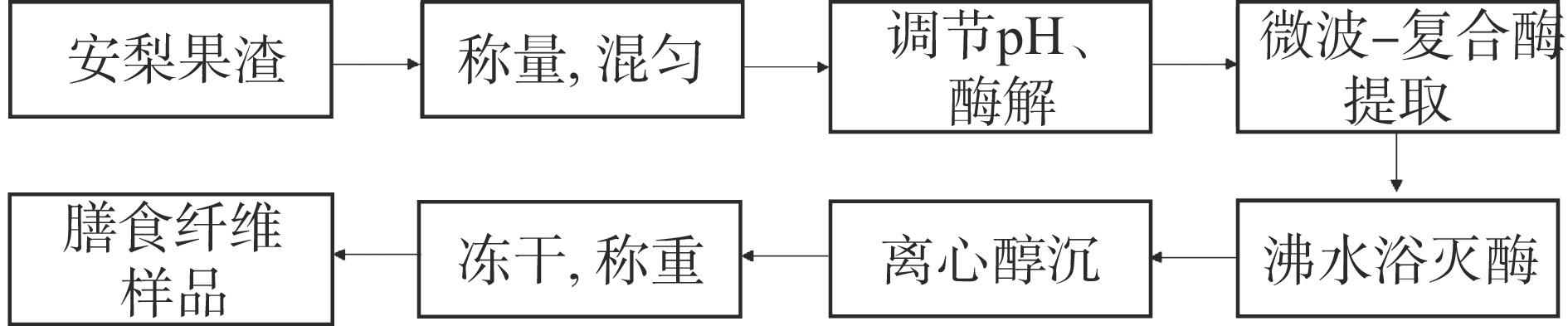
1.2.2.1 工艺流程图
安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维提取工艺流程如图1所示。
1.2.2.2 操作要点
a.称量、混匀:准确称取安梨果渣粉(2.0000±0.0003)g,置于250 mL锥形瓶中,加入液料比分别为20:1 mL/g的蒸馏水,不断搅拌使样品形成均匀悬浊液。
b.调节pH、酶解:用质量浓度为1 mol/L NaOH和HCl调节溶液pH至6.5,依次加入1.5%(w/w)高峰α-淀粉酶、葡萄糖苷淀粉酶。
c.微波-复合酶提取:用微波化学合成仪进行微波提取,控制微波功率为500 W,提取时间为60 s(每提取20 s后间隔2 min,一共提取三次),再次调节pH为7.0,加入1.5%(w/w)的中性蛋白酶,于相同的微波提取条件下提取。
d.灭酶:于水浴锅中95 ℃水浴15 min,使酶失活。
e.收集:待悬浊液降至室温后,将混合液转移至50 mL离心管,在转速为7000 r/min的条件下并于4 ℃离心15 min,取出上清液并转移至另外一个干净的烧杯中,加入4倍体积的无水乙醇,于4 ℃冰箱中过夜醇沉,抽滤收集沉淀,于−80 ℃冷冻干燥48 h,称重即得安梨果渣SDF样品[31]。
1.2.2.3 单因素实验
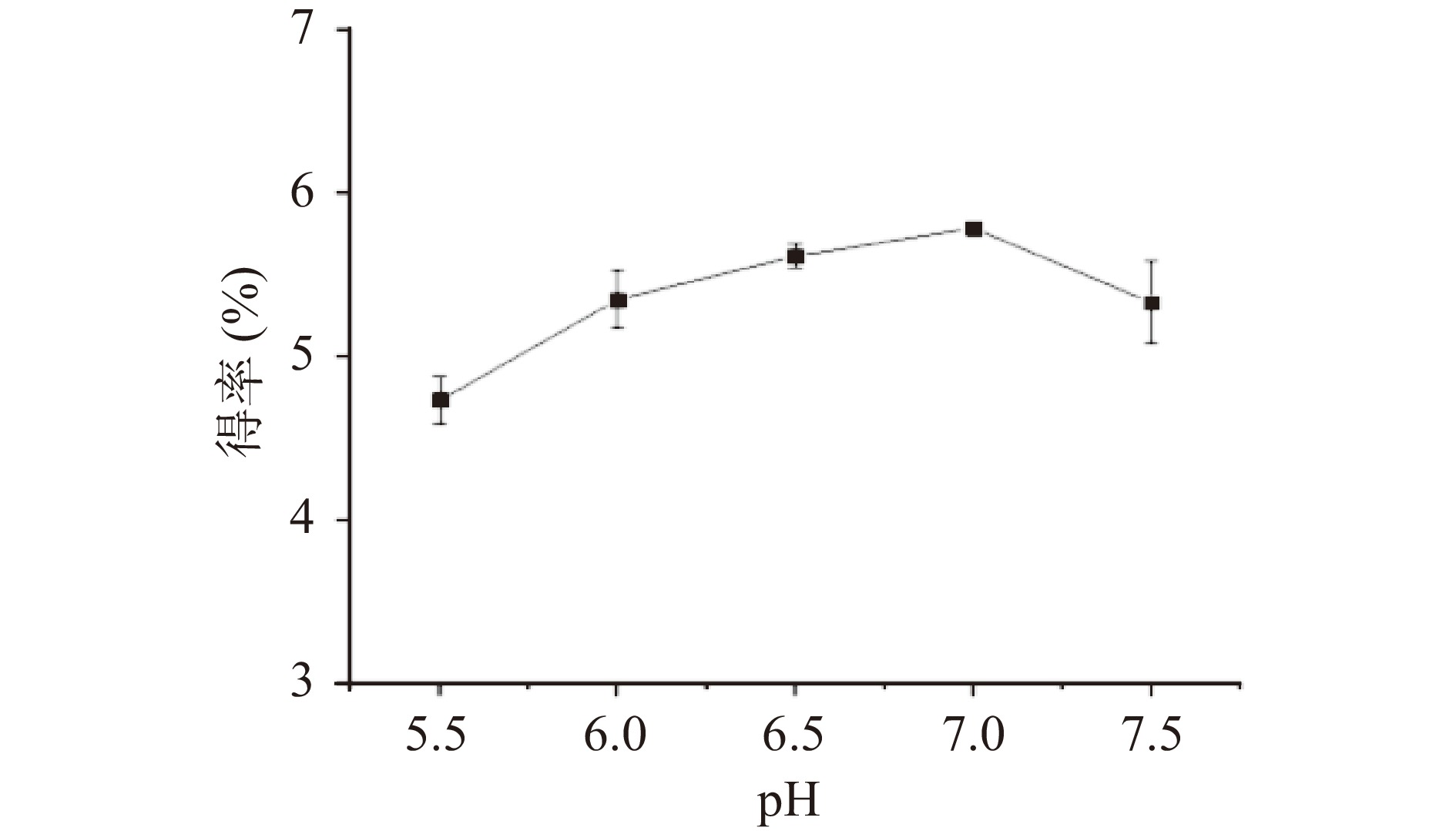
准确称取安梨果渣粉(2.0000±0.0003)g,置于250 mL锥形瓶中,固定液料比为20:1 mL/g,微波时间60 s,微波功率300 W,中性蛋白酶pH7.0,酶添加量为1.5%不变,考察高峰α-淀粉酶、葡萄糖苷淀粉酶的pH为5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0、7.5时对安梨果渣SDF的得率的影响。
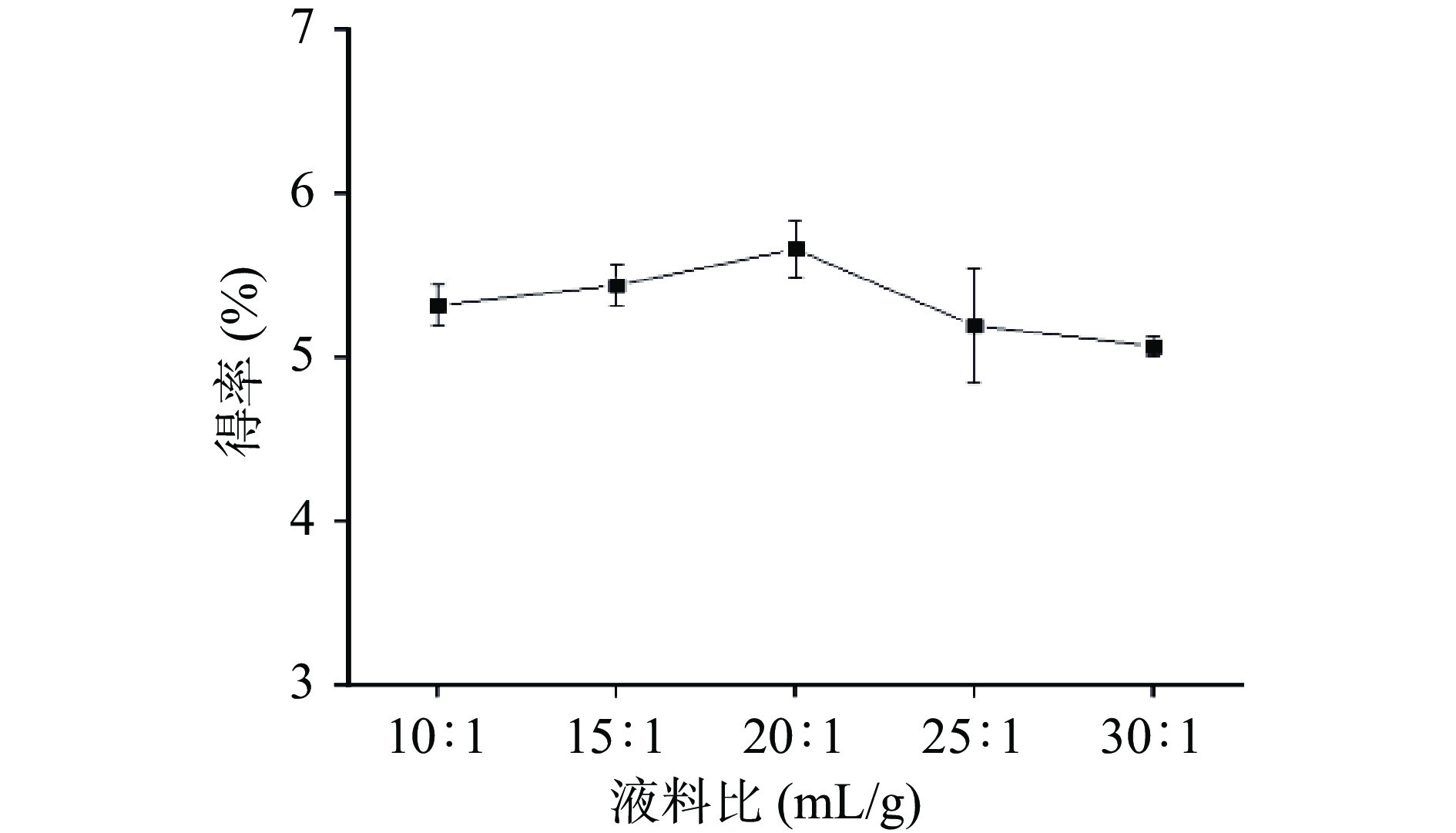
准确称取安梨果渣粉(2.0000±0.0003)g,置于250 mL锥形瓶中,固定微波时间60 s,微波功率300 W,高峰α-淀粉酶、葡萄糖苷淀粉酶pH6.5,中性蛋白酶的pH7.0,酶添加量为1.5%不变,考察液料比为10:1、15:1、20:1、25:1、30:1 mL/g时对安梨果渣SDF得率的影响。
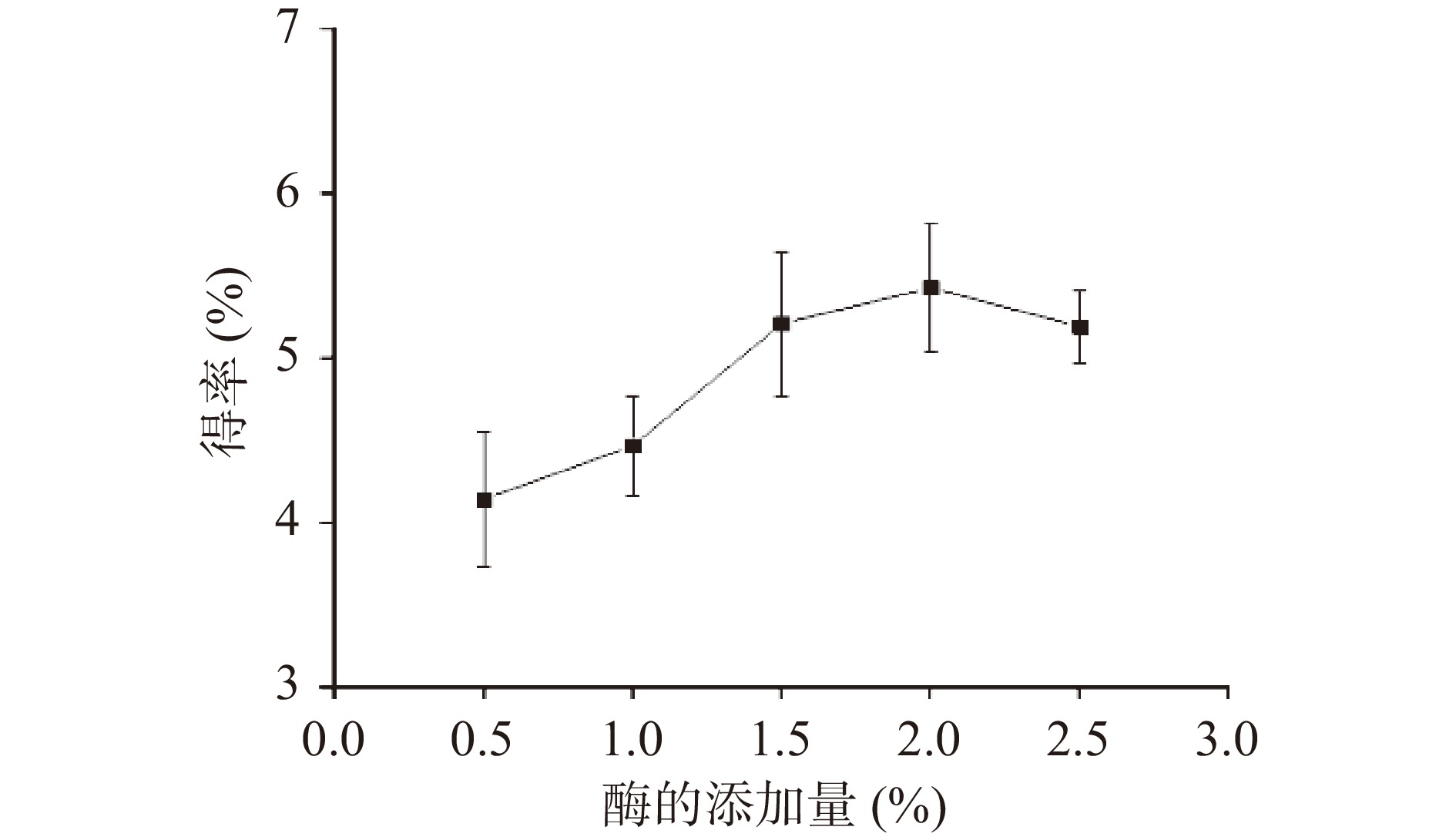
准确称取安梨果渣粉(2.0000±0.0003)g,置于250 mL锥形瓶中,固定液料比为20:1 mL/g,微波时间60 s,微波功率300 W,高峰α-淀粉酶、葡萄糖苷淀粉酶pH6.5,中性蛋白酶pH7.0不变,考察酶添加量为0.5%、1.0%、1.5%、2.0%、2.5%时对安梨果渣SDF得率的影响。
准确称取安梨果渣粉(2.0000±0.0003)g,置于250 mL锥形瓶中,固定液料比为20:1 mL/g,微波时间60 s,高峰α-淀粉酶、葡萄糖苷淀粉酶pH6.5,中性蛋白酶pH7.0,酶添加量为1.5%不变,考察微波功率为100、200、300、400、500 W时对安梨果渣SDF得率的影响。
1.2.3 安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维提取的工艺优化
以单因素实验结果为基础,利用Box-Behnken响应面法进行实验设计,选取自变量为:微波功率(A)、液料比(B)、酶的添加量(C)、pH(D)的四因素,响应值为安梨果渣SDF的得率,采用4因素3水平的响应面法求取安梨果渣SDF最佳提取工艺参数(表1)。
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素及水平Table 1. Design factors and levels of the Box-Behnken test试验水平 A
微波功率
(W)B
液料比
(mL/g)C
酶添加量
(%)D
pH−1 200 15:1 1.5 6 0 300 20:1 2 6.5 1 400 25:1 2.5 7 1.2.4 安梨果渣SDF得率的计算
安梨果渣得率(%)=mM×100 式中:m表示干燥后安梨果渣SDF重量,g;M表示安梨果渣粉重量,g。
1.2.5 结构及表征
1.2.5.1 扫描电镜分析
在样品台上用双面导电胶将样品均匀分散,将沾有样品的样品台放入离子溅射仪进行喷金处理300 s,设定扫描电镜加速电压为10 kV,通过操控台将视野调整到合适的观测区域,观察安梨果渣SDF在一定倍率下的形貌及结构。
1.2.5.2 红外光谱分析
将干燥SDF样品与干燥后的KBr按一定比例混合均匀,在红外灯照射下于研钵中充分研磨混匀,然后将混合粉末制成厚度均匀无明显裂纹的样品薄片,以KBr为空白对照,扣除背景,在波数为500~4000 cm−1进行红外光谱分析。
1.2.5.3 分子量的测定
安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维分子量的测定方法采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)进行测定。测试条件为:安捷伦HPLC1100高效液相色谱仪;G1362A示差折光检测器(RID);Agilent PL aquagel-OH MIXED-H(300 mm×7.5 mm, 8 μm)凝胶色谱柱;流动相为蒸馏水;流速为0.8 mL/min、柱温为35 ℃;检测波长为245 nm;标准品及样品质量浓度均为2 mg/mL−1,进样量20 μL。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验均平行进行3组,取平均值作为安梨果渣SDF的响应值,通过方差分析来确定不同因素对安梨果渣SDF提取的显著性影响。单因素实验图表选用Origin 2018pro软件绘制,响应面分析采用Design-Expert.8.0.6软件并选取Box-Behnken试验设计,分析不同实验因素对安梨果渣SDF得率的影响。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 pH对得率的影响
由图2可知,在其他因素固定不变的情况下,当溶液pH从5.5~7.0时,安梨果渣SDF的得率逐渐增加,当溶液pH从7.0~7.5时,SDF的得率逐渐减小。这可能是因为较高的pH使SDF降解[32]。蒋纬等[33]分析了5种不同提取方法对野木瓜膳食纤维提取及其抗氧化特性的影响,发现pH较高或较低都会在一定程度上降低膳食纤维活性。单因素结果表明pH7.0时,安梨果渣SDF得率最高。本文选取的中性蛋白酶和高峰α-淀粉酶最适pH为6.0~7.5,安梨果渣样品pH为3~4,本身为弱酸性,考虑到降低降成本和绿色环保的理念,因此选取pH为6.0~7.0进行工艺优化。
2.1.2 液料比对得率的影响
由图3可知,在其他因素固定不变的情况下,当液料比从10:1到20:1 mL/g时,SDF得率有较小的提高,当液料比从20:1增至30:1 mL/g时,SDF的得率逐渐趋于平稳。实验结果显示液料比最佳提取条件为20:1 mL/g。丁政宇等[34]在提取黄精渣不溶性膳食纤维过程中发现随液料比增加,膳食纤维得率先上升后下降,水与原料接触面积足够充分,可以有效提高产率,这与本实验结果相吻合,因此可以选取液料比为15:1至25:1 mL/g进行工艺优化。
2.1.3 酶添加量对得率的影响
由图4可知,在其他因素固定不变的情况下,当酶添加量从0.5%~1.5%时,SDF的得率明显增加,在2.0%~2.5%时不再提高。随着酶添加量的增大,酶与原料接触几率增加,从而使得率提高;王凌翌等[35]在提取豆渣蛋白肽和可溶性膳食纤维发现酶添加量在一定比例后反应趋于饱和,得率不再提高。单因素结果表明安梨果渣SDF最优酶添加量为2.0%,因此可以选择酶添加量为1.5%~2.5%进行工艺优化。
2.1.4 微波功率对得率的影响
由图5可知,在其他因素固定不变的情况下,微波功率从100~300 W时,随着微波功率的提高,SDF得率也随之提高;当微波功率大于300 W后,SDF得率明显下降。这可能是由于微波功率过高减少了酶和原料的充分接触,并且产生过多的热量,造成SDF得率的降低。陈法志等[36]在提取牡丹果壳膳食纤维也得到相似的结论。实验结果显示安梨果渣SDF最佳提取功率为300 W,因此本实验选取微波功率为200~400 W进行工艺优化。
2.2 安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维提取工艺优化分析
以安梨果渣SDF的得率为优化指标,采用4因素3水平的响应面法得到安梨果渣SDF最佳提取工艺参数,响应面设计结果见表2,方差分析结果见表3。
表 2 Box-Behnken 试验设计及其结果Table 2. Box-Behnken experimental design and results实验号 A B C D SDF得率
(%)1 1 0 0 −1 5.44 2 1 0 1 0 5.86 3 0 0 1 1 7.00 4 1 1 0 0 7.93 5 0 1 1 0 7.32 6 0 −1 1 0 5.85 7 0 0 1 −1 5.93 8 −1 0 −1 0 5.71 9 −1 0 0 −1 5.07 10 0 −1 −1 0 6.47 11 0 0 −1 −1 5.04 12 0 −1 0 −1 6.33 13 0 0 0 0 6.69 14 0 0 −1 1 8.11 15 0 1 0 1 7.60 16 1 −1 0 0 7.32 17 0 0 0 0 6.60 18 −1 0 0 1 7.62 19 −1 −1 0 0 5.85 20 −1 0 1 0 7.45 21 0 1 −1 0 5.57 22 −1 1 0 0 5.62 23 1 0 0 1 7.66 24 0 0 0 0 6.78 25 0 0 0 0 6.58 26 1 0 −1 0 6.97 27 0 0 0 0 6.76 28 0 −1 0 1 6.05 29 0 0 0 −1 5.22 2.2.1 回归方程的建立
使用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件并通过Box-Behnken实验设计分析得到的数据如表2所示,以安梨果渣SDF得率为工艺参数建立二次回归模型。得到回归方程为:
Y=6.56+0.32A+0.12B+0.13C+0.92D+0.21AB−0.71AC−0.083AD+0.59BC+0.67BD−0.50CD+0.074A2−0.097B2−0.077C2−0.10D2
由表3可知,回归模型P<0.05,说明模型显著。显著性分析表明,D对响应值的影响高度显著(P<0.001),AC、BC、BD对响应值影响显著(P<0.05),这表明建立的二次回归模型具有一定的拟合性。四个因素显著性影响大小分别为pH>微波功率>酶添加量>液料比。
表 3 响应面方差分析结果Table 3. Response surface analysis of variance results方差来源 平法和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 18.33 14 1.31 4.33 0.0048 ** A 1.24 1 1.24 4.11 0.0622 B 0.16 1 0.16 0.53 0.4776 C 0.20 1 0.20 0.66 0.4294 D 10.12 1 10.12 33.47 <0.0001 *** AB 0.18 1 0.18 0.58 0.4577 AC 2.03 1 2.03 6.72 0.0213 * AD 0.027 1 0.027 0.090 0.7685 BC 1.40 1 1.40 4.64 0.0491 * BD 1.77 1 1.77 5.85 0.0298 * CD 0.99 1 0.99 3.27 0.0919 残差 4.23 14 0.30 失拟项 3.86 10 0.39 4.11 0.0929 不显著 纯误差 0.38 4 0.094 总和 22.57 28 注:***表示差异高度显著(P<0.001);**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.2.2 双因素交互的响应面分析结果
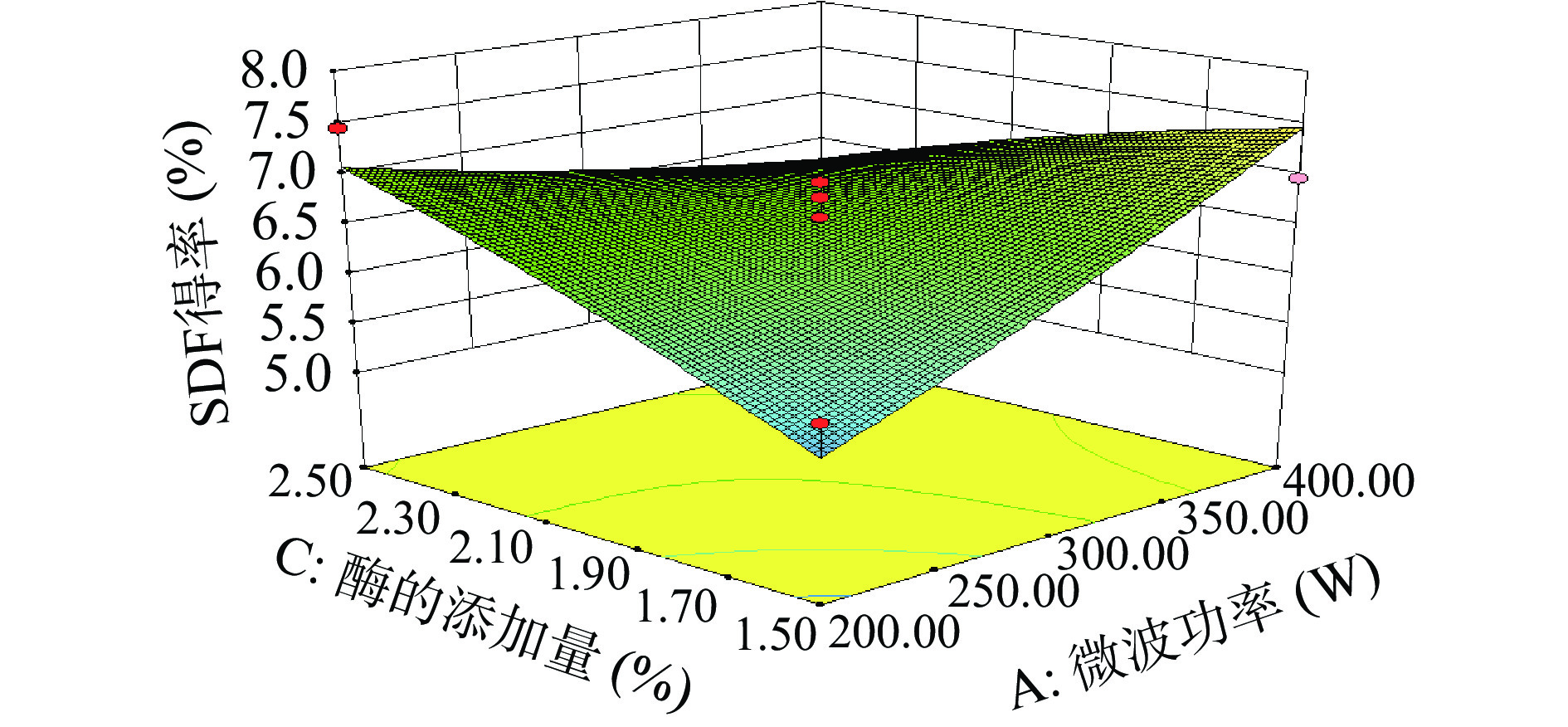
响应面分析广泛运用于食品加工和药物开发条件优化中,用于研究不同因素组合对响应值的作用。从图6可以看到,当酶添加量和微波功率处于较低水平(1.5%,200 W)时,响应值较低,随着微波功率和酶添加量逐渐增加,响应值提升显著。这说明微波在一定条件下可以增加酶和安梨果渣的接触机率,从而使SDF得率提高。
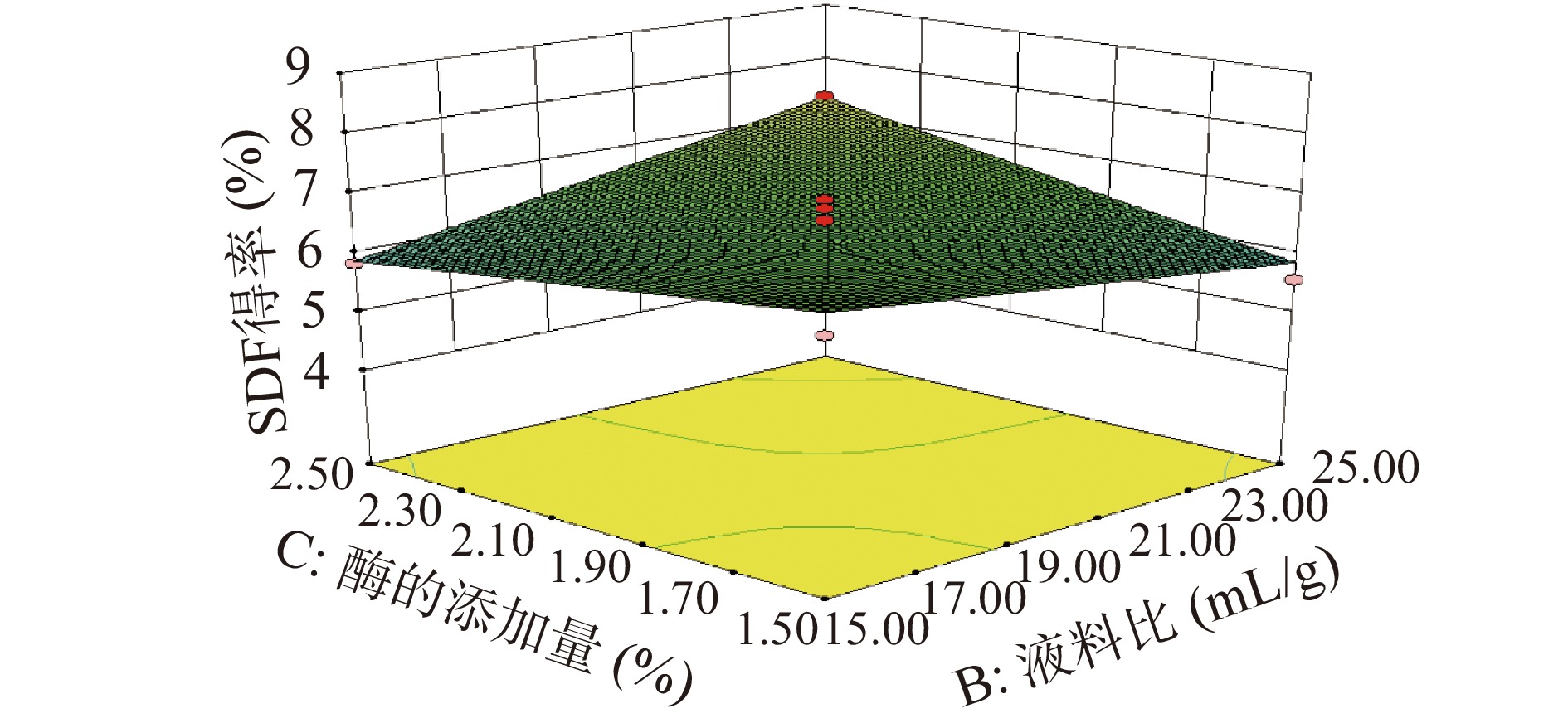
从图7可以看到,当酶添加量和液料比处于高水平(2.5%,20:1 mL/g)时,响应值很低,随着pH和酶添加量从高水平降低到适中水平后,响应值得到了较为明显的提高,说明酶添加量和料液比对SDF的得率影响显著。
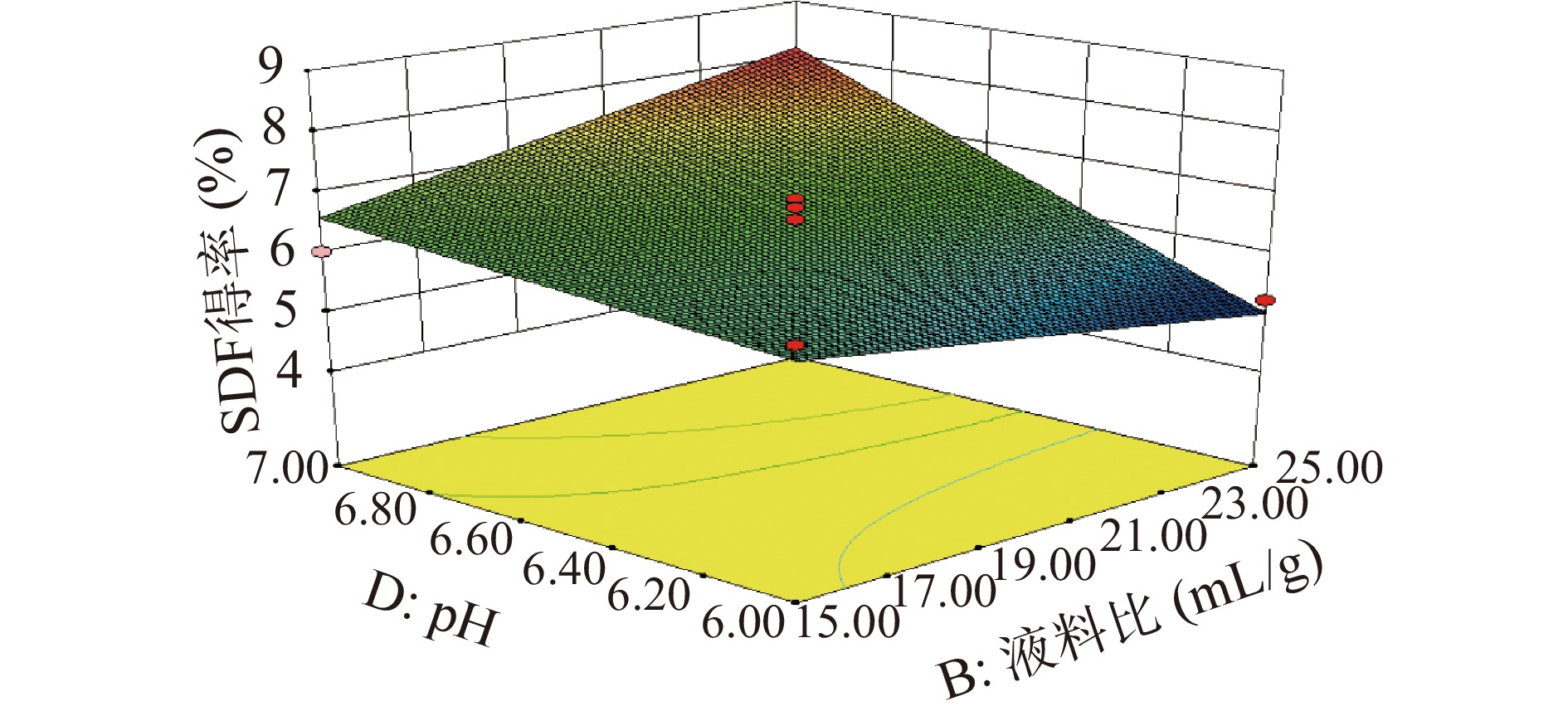
从图8可以发现,随着pH和液料比的逐渐增加,响应值有较为显著的提高,且等高线相对密集,说明pH和液料比的交互对SDF的提取影响显著。这可能是由于液料比增加,加大了酶与安梨果渣的接触机会,并且在合适的pH下可以有较好的酶解效果。
2.2.3 最佳工艺条件的确定及验证试验
以安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维的得率为评价标准,使用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件并通过Box-Behnken实验设计分析得到安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维微波辅助酶法提取的最佳工艺条件为微波功率373 W、液料比为14.39:1 mL/g、酶添加量为1.59%、pH6.95,在该条件优化下的得率预测值为8.12%。为方便实验的操作简便和可行性,将最佳工艺优化条件调整为微波功率370 W、液料比为14.4:1 mL/g、酶添加量为1.6%、pH为7.0。在该实验条件下平行进行三组实验验证,得到安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维的得率为(8.07%±0.66%),该实验验证结果与预测值接近,表明该实验优化模型具有重现性,方案可行。
2.3 结构表征
2.3.1 扫描电镜结果分析
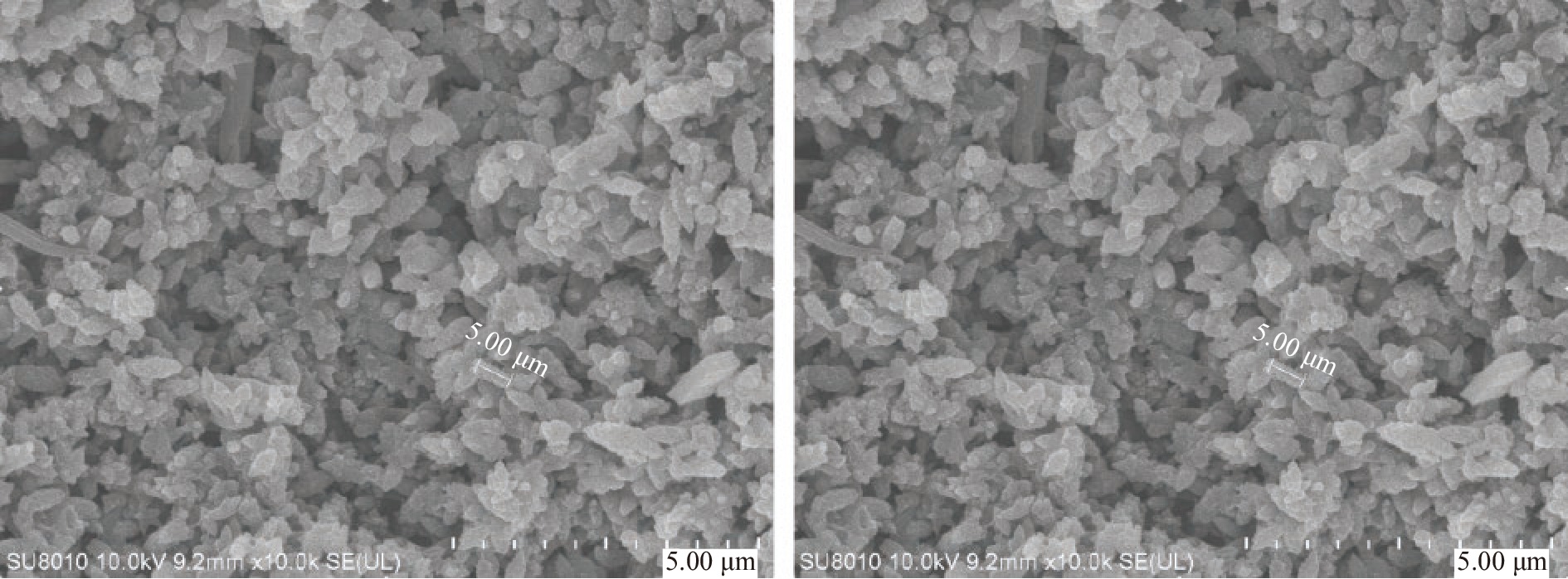
从图9可知,安梨果渣SDF的扫描电镜结果显示SDF由长度约为5 μm的纺锤型颗粒组成,这一形貌可能是提取过程中酶和微波的协同分解使得SDF的粒度变小[37]。在样品的表面还存在较多的孔洞,这可能是提取过程中微波的空化效应和孔洞效应[38]造成的,较多的孔洞和松散的结构可能会使得SDF具有较强的吸附能力,因此安梨果渣SDF能作为一种潜在的吸附剂和药物载体。
2.3.2 红外光谱结果分析
红外分析结果如图10所示,在3393 cm−1处有宽而强的吸收峰,这是由于分子内部或分子间的-OH发生伸缩振动所引起的,说明安梨果渣SDF具有较多缔合状态的氢键;在2943 cm−1处有一个弱而小的吸收峰,这是糖类的甲基或亚甲基上C-H伸缩振动引起的,这一结果表明该样品具有多糖类化合物的典型结构特征;1749和1605 cm−1的吸收峰是由羰基伸缩振动引起的,这是羧基或醛基的特征吸收峰,说明安梨果渣SDF中含有糖醛酸;QU等[39]指出植物多糖的保肝活性与高糖醛酸含量有关。1416 cm−1可能是C-H的弯曲振动引起的;在1016 cm−1和1105 cm−1处有窄而强吸收峰可能属于吡喃糖苷的C-O-C键伸缩振动[40]。
2.3.3 分子量分布
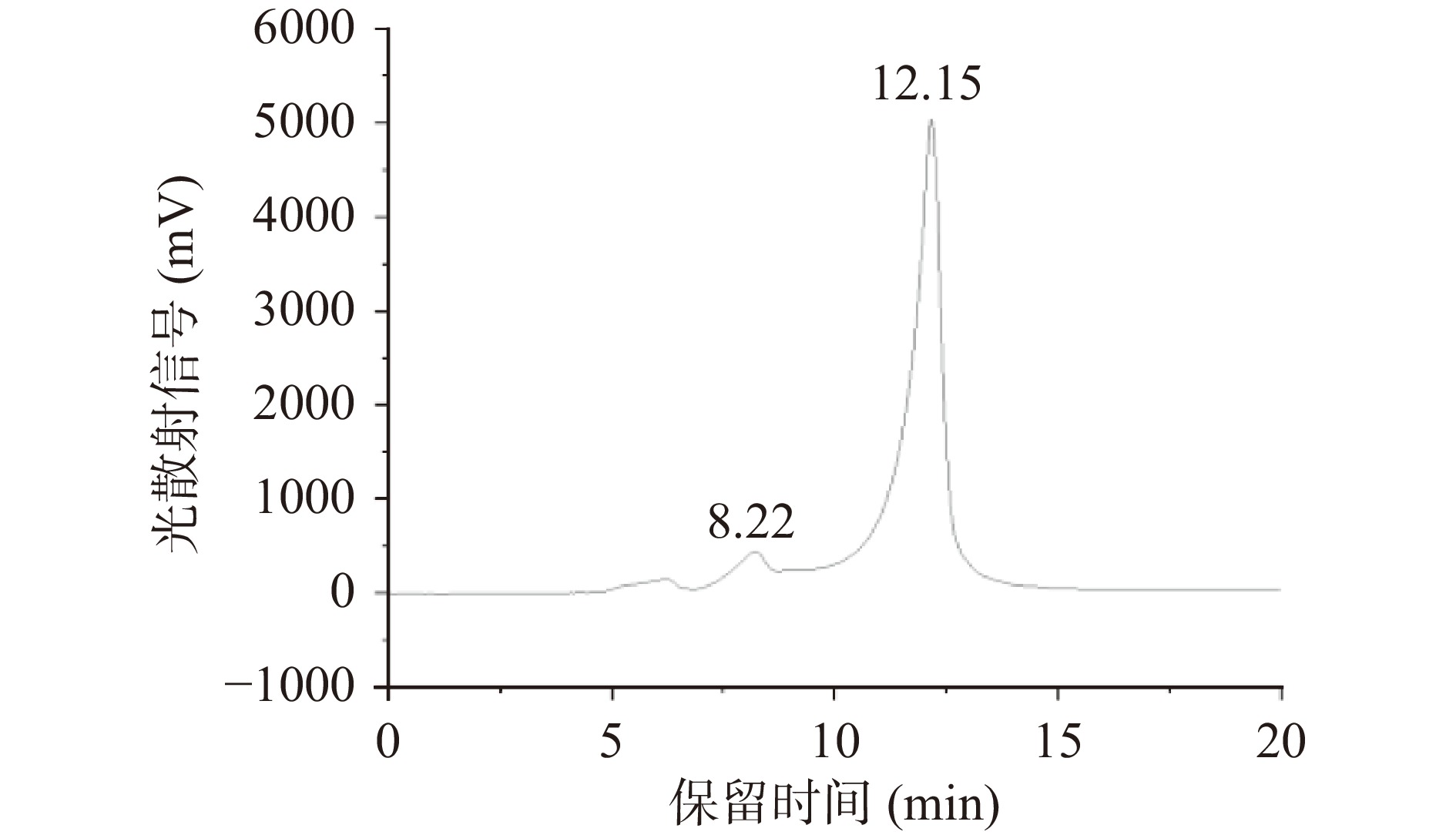
从图11和表4中可以看出,安梨果渣SDF主要分布在5~2.076×104 kDa之间的不均一多糖,其中主要为小分子多糖,数均分子量Mn为0.584 kDa,重均分子量为Mw为5.423 kDa。分布系数为9.28,另外还有部分为大分子多糖,数均分子量Mn为1.2×104 kDa,重均分子量为Mw为2.076×104 kDa,分布系数为1.72。研究发现低分子量的多糖具有更好的降血糖等生理活性[41],因此安梨果渣SDF有望成为一种药物载体或食品添加剂,在预防和控制糖尿病等慢性疾病中具有潜在的应用价值。
表 4 保留峰时间与分子量计算Table 4. Retention peak time and molecular weight calculation样品 峰 保留时间 Mn(Da) Mw(Da) D(Mw/Mn) SDF 1 8.22 12081875 20760280 1.72 2 12.15 584 5432 9.28 3. 结论与讨论
本实验采用微波辅助酶法对安梨果渣中可溶性膳食纤维进行提取,同时采用响应面法对工艺进行优化,结果表明在微波功率为370 W、液料比14.4:1 mL/g、酶添加量1.6%、pH7.0时安梨果渣可溶性膳食纤维的得率最优,在此工艺参数下验证实验得率为(8.07%±0.66%),与理论预测得率8.12%基本相吻合,证明了实验模型的可行性。响应面分析结果表明pH对安梨果渣SDF得率影响最大。红外谱图结果显示安梨果渣SDF具有多糖的特征峰,高效液相色谱分析得到其主要成分为分布在5~2.076×104 kDa之间的不均一多糖,在电镜下观察到安梨果渣SDF呈长度约为5 μm的纺锤型颗粒,具有较好的空间微孔结构。
李晗等[42]采用超声辅助酶法在纤维素酶添加量9%、超声时间40 min的条件下提取了无籽刺梨渣膳食纤维;徐新乐等[43]选取超声-微波辅助酶法并于酶解时间为75 min时制备猴头菇膳食纤维,得到SDF含量为(12.89%±0.12%)。相比于其他提取方法,本文选取的微波辅助酶法具有提取效率高,耗能低、条件温和的特点,在安梨废弃物生产加工处理上具有较好的应用前景。目前对安梨的研究主要集中在果品培育、储藏[44]和果汁加工[45]方面,在功能性成分和食品加工方面应用暂时空缺。该方法提取的安梨果渣SDF分子量较低,结构松散,具有一定的孔隙和较大的比表面积,可作为一种潜在的膳食纤维补充剂和食品添加剂,为安梨产品进一步的开发利用提供参考思路。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素及水平
Table 1 Design factors and levels of the Box-Behnken test
试验水平 A
微波功率
(W)B
液料比
(mL/g)C
酶添加量
(%)D
pH−1 200 15:1 1.5 6 0 300 20:1 2 6.5 1 400 25:1 2.5 7 表 2 Box-Behnken 试验设计及其结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken experimental design and results
实验号 A B C D SDF得率
(%)1 1 0 0 −1 5.44 2 1 0 1 0 5.86 3 0 0 1 1 7.00 4 1 1 0 0 7.93 5 0 1 1 0 7.32 6 0 −1 1 0 5.85 7 0 0 1 −1 5.93 8 −1 0 −1 0 5.71 9 −1 0 0 −1 5.07 10 0 −1 −1 0 6.47 11 0 0 −1 −1 5.04 12 0 −1 0 −1 6.33 13 0 0 0 0 6.69 14 0 0 −1 1 8.11 15 0 1 0 1 7.60 16 1 −1 0 0 7.32 17 0 0 0 0 6.60 18 −1 0 0 1 7.62 19 −1 −1 0 0 5.85 20 −1 0 1 0 7.45 21 0 1 −1 0 5.57 22 −1 1 0 0 5.62 23 1 0 0 1 7.66 24 0 0 0 0 6.78 25 0 0 0 0 6.58 26 1 0 −1 0 6.97 27 0 0 0 0 6.76 28 0 −1 0 1 6.05 29 0 0 0 −1 5.22 表 3 响应面方差分析结果
Table 3 Response surface analysis of variance results
方差来源 平法和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 18.33 14 1.31 4.33 0.0048 ** A 1.24 1 1.24 4.11 0.0622 B 0.16 1 0.16 0.53 0.4776 C 0.20 1 0.20 0.66 0.4294 D 10.12 1 10.12 33.47 <0.0001 *** AB 0.18 1 0.18 0.58 0.4577 AC 2.03 1 2.03 6.72 0.0213 * AD 0.027 1 0.027 0.090 0.7685 BC 1.40 1 1.40 4.64 0.0491 * BD 1.77 1 1.77 5.85 0.0298 * CD 0.99 1 0.99 3.27 0.0919 残差 4.23 14 0.30 失拟项 3.86 10 0.39 4.11 0.0929 不显著 纯误差 0.38 4 0.094 总和 22.57 28 注:***表示差异高度显著(P<0.001);**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 保留峰时间与分子量计算
Table 4 Retention peak time and molecular weight calculation
样品 峰 保留时间 Mn(Da) Mw(Da) D(Mw/Mn) SDF 1 8.22 12081875 20760280 1.72 2 12.15 584 5432 9.28 -
[1] THEUWISSEN E, MENSINK R P. Water-soluble dietary fibers and cardiovascular disease[J]. Physiology & Behavior,2008,94(2):285−292.
[2] 李娜. 番茄皮可溶性膳食纤维的改性与表征[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. LI N. The modification and characterization of soluble dietary fiber from tomato peels[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018.
[3] 廖樟华. 青稞嫩叶可溶性膳食纤维制备及生物活性研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019 LIAO Z H. Preparation and bioactivities of soluble dietary fiber from young huskless barley leaves[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019.
[4] GAO H, SONG R, LI Y, et al. Effects of oat fiber intervention on cognitive behavior in ldlr/mice modeling atherosclerosis by targeting the microbiome-gut-brain axis[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(49):14480−14491. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05677
[5] RAZA G S, MAUKONEN J, MAKINEN M, et al. Hypocholesterolemic effect of the lignin-rich insoluble pomace of brewer’s spent grain in mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,67(4):1104−1114.
[6] YANG L, LIN Q, HAN L, et al. Soy hull dietary fiber alleviates inflammation in BALB/C mice by modulating the gut microbiota and suppressing the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(7):5965−5975.
[7] REYNOLDS A, MANN J, CUMMINGS J, et al. Carbohydrate quality and human health: A series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses[J]. The Lancet,2019,393(10170):434−445. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31809-9
[8] ZHAO L, ZHANG F, DING X, et al. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes[J]. Science,2018,359(6380):1151−1156. doi: 10.1126/science.aao5774
[9] LI Q, FANG X, CHEN H, et al. Retarding effect of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot (Phyllostachys edulis) in hyperlipidemic rats induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(10):4696−4706.
[10] BENITEZ V, REBOLLO-HERNANZ M, HERNANZ S, et al. Coffee parchment as a new dietary fiber ingredient: Functional and physiological characterization[J]. Food Research International,2019,122:105−113. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.002
[11] MUÑOZ-CABREJAS A, LACLAUSTRA M, GUALLAR-CASTILLÓN P, et al. High-quality intake of carbohydrates is associated with lower prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis in femoral arteries: The awhs study[J]. Clinical Nutrition,2021,40(6):3883−3889. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.049
[12] LEÓN-GONZÁLEZ A J, JARA-PALACIOS M J, ABBAS M, et al. Role of epigenetic regulation on the induction of apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia cells by white grape pomace rich in phenolic compounds[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(11):4062−4069.
[13] MACAGNA1N F T, DA SILVA L P, HECKTHEUER L H. Dietary fiber: The scientific search for an ideal definition and methodology of analysis, and its physiological importance as a carrier of bioactive compounds[J]. Food Research International,2016,85:144−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.04.032
[14] SLAVIN J L. Position of the American dietetic association: Health implications of dietary fiber[J]. Journal of the American Dietetic Association,2008,108(10):1716−1731. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2008.08.007
[15] SOLIMAN G A. Dietary fiber, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(5):1155. doi: 10.3390/nu11051155
[16] BRAHEM M, BORNARD I, RENARD C M G C, et al. Multiscale localization of procyanidins in ripe and overripe perry pears by light and transmission electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(33):8900−8906. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02036
[17] CHO J Y, KIM C M, LEE H J, et al. Caffeoyl triterpenes from pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) fruit peels and their antioxidative activities against oxidation of rat blood plasma[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(19):4563−4569. doi: 10.1021/jf400524b
[18] 孔明明. 安梨果酒的制备工艺优化[D]. 天津: 天津中医药大学, 2020 KONG M M. Optimization of preparation rechnology of Anli (Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim. ) liquo[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[19] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018 National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018.
[20] 赵纪伟. 不同安梨株系果实贮藏过程中品质变化研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2011 ZHAO J W. Studies on the change of fruit quality during storage in different lines of Pyrus ussuriensis ‘Anli’[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2011.
[21] MENG S, WANG W H, CAO L K. Soluble dietary fibers from black soybean hulls: Physical and enzymatic modification, structure, physical properties, and cholesterol binding capacity[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85:1668−1674. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15133
[22] LIU Y L, ZHANG H B, YI C P, et al. Chemical composition, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by cellulase treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,342:128352. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128352
[23] BAI Y, ZHAO J B, TAO S Y, et al. Effect of dietary fiber fermentation on short-chain fatty acid production and microbial composition in vitro [J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2020, 100: 4282−4291.
[24] 李艳. 不同酶法改性的马铃薯渣膳食纤维工艺条件及性能研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019 LI Y. Study on process conditions and properties of dietary fibers from potato pomace modified by different enzymatic method[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019.
[25] LE B, PHAM T N A, YANG S H. Prebiotic potential and anti-inflammatory activity of soluble polysaccharides obtained from soybean pomace[J]. Foods,2020,9:12.
[26] 林于洋. 酶-微波辅助协同提取心里美萝卜中有效成分研究[D]. 广州: 广东药科大学, 2020 LIN Y Y. Study on synergistic extraction of multiple effective constituents from purple-heart radish by enzyme and microwave co-assisted extraction[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2020.
[27] 巫永华, 刘梦虎, 孙悦, 等. 超声微波辅助酶法提取黑豆皮水溶性膳食纤维及理化特性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(6):8−14. [WU Y H, LIU M H, SUN Y, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted enzymatic extraction of water-soluble dietary fiber from black soybean hull and its physicochemical properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(6):8−14. [28] 申红林, 王凤玲. 灰树花多糖复合酶协同微波辅助提取工艺及抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(22):124−131. [SHEN H L, WANG F L. Studies on compound enzymes synergistic microwave-assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of Grifola frondose polysaccharide[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(22):124−131. [29] 胡福田, 周红军, 徐华, 等. 微波预处理复合酶法浸提茶皂素工艺条件研究[J]. 广州化学,2018,43(5):18−23. [HU F T, ZHOU H J, XU H, et al. Study on extraction technology of tea saponin from microwave pretreatment camellia oleifera powder by complex enzyme[J]. Guangzhou Chemistry,2018,43(5):18−23. [30] 李晓颍, 张文静, 刘宝丽, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用法优化与‘安梨’花序挥发性成分分析[J]. 中国果树,2020(2):16−22. [LI X Y, ZHANG W J, LIU B L, et al. Optimization and analysis of aroma components in ‘Anli’ pear flower by headspace solid phase micro-extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. China Fruits,2020(2):16−22. [31] 梁文康, 苏平, 魏丹. 复合酶法提取黄秋葵可溶性膳食纤维的工艺优化及其理化特性、结构表征[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(17):199−205,218. [LIANG W K, SU P, WEI D. Optimization techniques for the extraction of soluble dietary fiber from okra with complex enzymes and its physicochemical properties and structure characterization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(17):199−205,218. [32] 李施瑶, 代玲敏, 范宜杰, 等. 化学法提取红树莓果渣可溶性膳食纤维的工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):180−186,193. [LI S Y, DAI L M, FAN Y J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of soluble dietary fiber from raspberry pomaces by chemical method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):180−186,193. [33] 蒋纬, 王嘉莹, 何鸿. 不同提取方法对野木瓜膳食纤维提取及其抗氧化特性的影响研究[J]. 农产品加工,2019(24):28−31. [JIANG W, WANG J Y, HE H. Effects of different extraction methods on dietary fiber extraction and antioxidant properties of wild papaya[J]. Farm Products Processing,2019(24):28−31. [34] 丁政宇, 张士凯, 何子杨, 等. 响应面优化黄精渣不溶性膳食纤维酶法提取工艺及其结构表征[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):157−163. [DING Z Y, ZHANG S K, HE Z Y, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction process of insoluble dietary fiber from Polygonatum sibiricum residue by response surface methodology and its characterization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):157−163. [35] 王凌翌, 周利琴, 刘志国, 等. 联合酶法提取豆渣蛋白肽和可溶性膳食纤维[J]. 中国油脂,2021,46(6):114−118. [WANG L Y, ZHOU L Q, LIU Z G, et al. Extraction of protein peptides and soluble dietary fiber from soybean dregs by combined enzymatic method[J]. China Oils and Fats,2021,46(6):114−118. [36] 陈法志, 翟敬华, 刘克华, 等. 响应面法优化微波提取牡丹果壳水溶性膳食纤维工艺[J]. 江汉大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(6):48−55. [CHEN F Z, ZHAI J H, LIU K H, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of water-soluble dietary fiber from peony husk by response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Jianghan University ( Nat. Sci. Ed. ),2020,48(6):48−55. [37] 王娟, 康子悦, 肖金玲, 等. 超声-微波辅助酶法对小米SDF提取和物理性质的影响[J]. 包装工程,2020,41(7):25−32. [WANG J, KANG Z Y, XIAO J L, et al. Influence of ultrasonic-microwave assisted enzymatic method on extraction and physical properties of water-soluble dietary fiber from millet[J]. Packaging Engineering,2020,41(7):25−32. [38] GAN J P, PENG G Y, LIU S, et al. Comparison of structural, functional and in vitro digestion properties of bread incorporated with grapefruit peel soluble dietary fibers prepared by three microwave-assisted modifications[J]. Food Function,2020,11:6458−6466. doi: 10.1039/D0FO00760A
[39] QU J L, HUANG P, ZHANG L, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of plant polysaccharides from natural resources: A review of the mechanisms and structure-activity relationship[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2020,161:24−34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.196
[40] HASHEMIFESHARAKI R, XANTHAKIS E, ALTINTAS Z, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from the marshmallow roots: Optimization, purification, structure, and bioactivity[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,240:116301. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116301
[41] ZENG A Q, YANGR J, YU S H, et al. Porphyra A novel hypoglycemic agent: Polysaccharides from laver (spp.)[J]. Food Function,2020,11:9048−9056. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01195A
[42] 李晗, 范方宇, 戚建华, 等. 超声辅助酶法提取无籽刺梨渣膳食纤维及理化性质评价[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(4):194−201. [LI H, FAN F Y, QI J H, et al. Ultrasonic assisted enzymatic extraction of dietary fiber from rosa sterilis pomace and its physicochemical properties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(4):194−201. [43] 徐新乐, 刘婷婷, 张闪闪, 等. 猴头菇高品质膳食纤维的制备及理化性质分析[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−12[2021-09-11] XU X L, LIU T T, ZHANG S S, et al. Preparation, physicochemical properties of high-quality dietary fiber from Hericium erinaceus[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−12[2021-09-11].
[44] 郑璞帆, 张梅, 庞志豪, 等. 京津冀地区主栽梨品种果实外观特征、营养特性及香气物质分析[J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版),2020,53(6):35−42. [ZHENG P F, ZHANG M, PANG Z H, et al. Analysis of fruit appearance, nutritional characteristics and aroma compounds of the main cultivars of pear (Pyrus L.) in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naiuralium Unirversitatis Nankaiensis,2020,53(6):35−42. [45] 孔明明. 安梨果酒的制备工艺优化[D]. 天津: 天津中医药大学, 2020 KONG M M. Optimization of preparation technology of anli (Pyrus ussuriensis Maxim.) liquor[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 孙细珍,熊亚青,倪兴婷,李强. 吡嗪类化合物对酱香型白酒香气特征的影响分析. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(01): 305-311 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王高伟,曹润洁,陈双,徐岩. 采用顶空固相微萃取结合全二维气相色谱飞行时间质谱解析不同等级中高温大曲的挥发性组分差异特征. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(02): 285-292 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王娜,沈毅,庄园,程伟,罗森,张亚东,刘子轩,刘冰,高红波. 气相色谱-串联质谱同时测定白酒中20种吡嗪类化合物. 食品科学. 2025(05): 30-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 蒋倩儿,梁会朋,李琳琳,钟俊辉,刘军峰. 芽孢杆菌在白酒酿造过程中的应用研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2025(08): 391-401 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 杨瑞政. 白酒及原料检验准确性的影响因素及控制策略探讨. 食品安全导刊. 2024(07): 149-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨沙,罗玉航,张季,侯睿. 高效液相色谱法同时测定不同年份酱香型白酒中12种吡嗪化合物含量. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(12): 220-229 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 缪坤辰,张梦梦,赵巧珍,吕志远,吕晓凤,任广花. 两种功能麸曲混合应用对芝麻香型白酒酿造的影响. 酿酒科技. 2024(07): 74-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王宏雨,翁梦婷,孔子浩,张迪. 发酵处理对广叶绣球菌挥发性成分及风味的影响. 菌物学报. 2024(08): 154-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈艳,王孝彦,刘冲,杨沙,张季. GC-MS/MS法同时测定年份酱香型白酒中19种吡嗪类和呋喃类化合物. 中国酿造. 2024(09): 241-248 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 何艳艳,刘俊男,李瑞杰,丁润月,杨阳,李姝,赵侨,钟小忠,王松涛,周嘉裕. 酱香型白酒风味及其关键物质分析技术研究进展. 中国酿造. 2024(11): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 薛锡佳,程伟,陈雪峰,兰伟,李娜,李瑞龙,潘天全,代森. 馥合香型白酒酿造过程中四甲基吡嗪的检测及其溯源分析. 中国酿造. 2024(12): 38-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吕晓凤,孟武,刘玉涛,张梦梦,卢春玲,李强,邱振清,石林,赵巧珍,缪坤辰. 功能菌添加对芝麻香原酒中吡嗪类化合物含量的影响研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(07): 155-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 陈荻,杨康卓,刘志鹏,赵东,郑佳. 包包曲风味萃取方式的对比及GC×GC-TOFMS在其风味化合物鉴定中的应用. 酿酒科技. 2023(06): 71-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 苏泽佳,卢斌,李志溥,熊若冰,白卫东,梁景龙,赵文红. 12种市售豉香型白酒挥发性风味物质的分析. 中国酿造. 2023(08): 234-241 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 秦炳伟,吕志远,张梦梦,刘阳晴雪,刘玉涛,王文洁,胥鑫钰,李小杰,崔新莹,商海林,王瑞明,高红波,宋妍妍. 顶空固相微萃取-全二维气相色谱-飞行时间质谱解析泉香型白酒的风味物质. 食品与发酵工业. 2023(18): 289-296 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 陈心雨,刘念,王超凯,张磊,李觅,常少健,蔡海燕,彭奎. 高温大曲中美拉德反应的研究进展. 食品与发酵科技. 2023(06): 109-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



