Effect of Helium Plasma Modified Technology on the Structure and Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Materials
-
摘要: 考虑到微生物污染引起的相关安全性问题,为了改善壳聚糖材料的抗菌性能,提高壳聚糖基抗菌材料的进一步应用,本文利用等离子体技术,在氦气氛围下对壳聚糖材料进行改性处理,设计得到改性壳聚糖抗菌材料,并通过抗菌实验、游离蛋白/核酸等的测定,探讨改性壳聚糖材料的抗菌性能与作用机制。通过改性壳聚糖结构分析,壳聚糖材料经氦气等离子体改性后,光斑区和非光斑区表面均变得粗糙,但光斑区的粗糙程度更加明显,材料表面的-NH2比例下降(83.32%下降到72.10%),而-CONH2的比例上升(16.68%上升到27.90%),这与改性过程中带电粒子的碰撞及壳聚糖材料中化学键的断裂有关。抗菌实验结果表明,相比于未改性材料,等离子体改性壳聚糖材料显著提高大肠杆菌的抗菌性能(P<0.05),而对于金黄色葡萄球菌,改性前后并没有显著性差异(P>0.05)。改性壳聚糖材料表面的化学基团变化,其与细菌接触时,能明显改变细菌细胞膜通透性,并局部形成不利于细菌生长的环境,从而达到抗菌的效果。Abstract: Considering the relevant safety problems caused by microbial pollution, in order to improve the antibacterial properties of chitosan materials and its further application, this study modified chitosan (CS) materials with plasma under helium atmosphere to design CS-based antibacterial materials. In order to discuss the antibacterial properties and action mechanism of modified CS materials, which through antibacterial experiments, free protein/nucleic acid determination and so on. The microstructure of modified CS materials were characterized, and the results showed that after the CS materials were modified by helium plasma, the surface became rough, and the roughness was more obvious, The results also showed the -NH2 of CS-based materials decreased from 83.32% to 72.10% and the -CONH2 increased from 16.68% to 27.90%, related to the collision of charged particles during plasma modification. Moreover, in the antibacterial experiment, these CS-based materials showed excellent antibacterial properties to Escherichia coli (P<0.05) but for Staphylococcus aureus, there was no significant difference before and after modification (P>0.05). With the changes of chemical linkages, the cell membrane permeability of bacterium was significantly changed when contacted with the CS-based materials. There was also locally formed a negative environment to bacterium growth, which contributed to the antibacterial effect of materials.
-
近年来,由于微生物污染导致的食源性疾病问题日益严重[1],学者们通过研发抗菌材料,以限制和抵御微生物带来的不良影响。抗菌材料根据化学组成的不同,可分为有机抗菌材料、无机抗菌材料和天然抗菌材料三大类[2]。壳聚糖是一种生物相容性好、可降解、绿色无毒的天然抗菌材料[3],具有良好的抗菌性能,能够有效地抑制细菌的生长和繁殖[4-6]。壳聚糖基抗菌材料是当前的一个研究热点,改性手段丰富,等离子体改性手段因其绿色高效的特点更易受到学者们的青睐[7]。等离子体是由部分电离或电离气体产生的,包括带电粒子、自由基、原子等[8]。利用等离子体,可对材料表面进行改性,通过蚀刻[9]、交联[10]、聚合[11]等在材料表面形成新的化学结构,从而改变其抗菌性、生物相容性等[12-13]。
KAWAKAMI等[14]采用空气等离子体射流对聚丙烯(PP)薄膜表面进行处理,空气等离子体可产生大量高浓度氧基功能极性基团,大大提高了PP薄膜表面的亲水性,同时也改善了PP薄膜的抗菌性。PANERUR等[15]采用氩气等离子体对聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖(PVA/CS)薄膜进行了表面改性,等离子体处理后,引入了新的含氧亲水性基团,膜的表面粗糙度明显提高。结果表明:经等离子体处理后,PVA/CS膜对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌效率显著提高,分别达到了98%和96%。LIN等[16]采用冷氮等离子体对β-环糊精包合物进行处理。对大肠杆菌的抗菌试验结果表明,经过冷氮等离子体处理过的β-环糊精包合物具有更好的抗菌活性。此外,也对其在蔬菜汁中的抗菌活性进行了研究,发现经过冷氮等离子体处理过的β-环糊精包合物对蔬菜汁具有良好的抗菌作用。等离子体改性技术在组织工程、生物医药领域应用广泛,其通过改变材料的表面性能、调控材料的亲疏水性等,提高材料的生物相容性[17]。
等离子体改性技术也常用于壳聚糖改性,以制备支架材料、水凝胶等,等离子体改性与其气体氛围有关,前人关于等离子体改性的研究中较少采用氦气。氦气是一种惰性气体,性质较为稳定,利用其进行等离子体改性,所得的壳聚糖分子结构、抗菌性能等将如何变化仍有待探讨。为此,本文采用氦气等离子体改性技术处理壳聚糖材料,探讨在氦气氛围下等离体子对壳聚糖材料表面结构的作用机理,并以大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌为模型,比较改性前后壳聚糖材料抗菌性能的变化,进一步探究改性壳聚糖材料的抑制机制。本研究为壳聚糖基抗菌材料的精准设计提供了一定的参考价值,拓宽了等离体子改性技术的使用方式,为氦气等离子体的作用机理研究及后续使用提供了理论支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
壳聚糖 分子量400000 g/mol,脱乙酰度>90%,上海楷洋生物技术有限公司;乙酸 分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂;氦气 纯度99.99%,佛山三水德力梅塞尔气体有限公司;大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli,E.coli):O78、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus,S.aureus):ATCC 10071 广州艾基生物技术有限公司;碘化丙啶染液:BH-S1010 广州赛国生物科技有限公司;琼脂粉 AR,广州市齐云生物技术有限公司;氯化钠 AR,国药集团试剂有限公司;胰蛋白胨、酵母提取粉 AR,广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;甘露醇氯化钠琼脂 AR,杭州百思生物技术有限公司。
UV-6100S紫外分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;ESCALAB 250X射线光电子能谱仪 美国Thermo Fisher Scientifics公司;H/T16MM台式高速离心机 湖南赫西仪器装备有限公司;Vertex 70傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 德国布鲁克公司;Verious 460场发射扫描电子显微镜 美国FEI公司;BX 63全自动智能荧光显微镜 日本Olympus公司;DW-P353-6ACE5高压直流电源 天津市东文高压电源厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料的制备
根据参考文献提及的方法[18],精确称取1.0000 g分子量为400 kDa的壳聚糖,溶于100 mL 1%(V/V)的乙酸溶液中,磁力搅拌24 h,温度为25 ℃,转速为1000 r/min。倒入15 mm×15 mm的聚四氟乙烯塑料盒中,45 ℃烘干,裁剪成10 mm×10 mm×0.1 mm的长条状薄膜,备用。
将裁剪好的长条状薄膜放进等离子体设备正下方有针头和没有针头的两个区域。固定好壳聚糖材料,用真空泵对设备进行抽真空处理,通入氦气,为等离子体设备接入高压直流电源。在温度为25~30 ℃、湿度为70%~75%、功率为3 W的条件下改性40 min,得到400 kDa的He等离子体改性壳聚糖材料。由于本实验所采用的等离子体是通过高压放电产生的,在等离子体作用过程中,放电针尖附近存在明显的蓝光,此处的壳聚糖薄膜经改性后可形成直径为0.5 cm大小的光斑。考虑到等离子体带电粒子浓度、刻蚀作用强弱等差异,将改性材料分作光斑区和非光斑区,后续对材料的结构、性能差异做进一步探讨。因此,对于本实验所使用的壳聚糖材料做如下命名:C400为未改性的400 kDa壳聚糖材料,C400-He-G为氦气等离子体改性400 kDa壳聚糖材料光斑区,C400-He-F为氦气等离子体改性400 kDa壳聚糖材料非光斑区。
1.2.2 衰减全反射傅立叶红外光谱(ATR-FTIR)
将壳聚糖材料样品置于ATR附件上,调节压头使晶体表面压紧壳聚糖材料的被测表面。以空气为背景,扫描400~4000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描16次,对所得谱图进行基线校正处理。
1.2.3 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)
采用X射线光电子能谱仪对制备的壳聚糖材料进行元素组成和化学价态分析,并根据元素结合能峰位化学位移研究元素化学键、价的变化情况。样品的测试条件为:荷电校正是以表面污染C1s(284.8 eV)为标准,单色化的Al Ka源(Mono Al Ka),真空度2×10−9 mbar;能量为1486.6 eV,15 kV,150 W;定性、定量分析采用Wagner(Al靶)Library。
1.2.4 表面形貌与元素分布
将薄膜样品裁剪成0.5 cm×0.5 cm的片状,并将待测样品表面向上固定在导电胶上,然后进行喷金处理。最后将样品置于扫描电子显微镜中,加速电压20 kV,观察并拍摄壳聚糖材料的表面形貌以及表面元素的分布情况。
1.2.5 壳聚糖材料的抗菌性能
根据参考文献提及的方法[19],抑菌性能测试采用稀释平板计数法。实验过程中,取培养好的菌液1000 μL滴加到灭菌过的试管中,再滴加灭菌后的生理盐水9000 μL,充分摇匀,即菌液稀释了10倍,标记为10−1。以此类推,继续稀释到10−2、10−3、10−4、10−5。取100 μL稀释度为10−5大肠杆菌菌液滴加到装有裁剪好的壳聚糖材料的培养皿,培养24 h后取出培养皿,然后滴加1900 μL生理盐水洗脱,摇匀、静置。取100 μL滴加到LB培养基上涂布培养8 h,之后取出平板后计数、拍照。壳聚糖材料对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌性能测试与大肠杆菌一致,区别在于滴加的浓度为10−4,在甘露醇氯化钠琼脂培养基上培养。抑菌率的计算公式为:
R=(N0−Nk)/N0×100 式中,R表示抑菌率,%;N0代表菌液滴加到玻璃片上的空白组长出细菌数量,个;Nk代表菌液滴加到壳聚糖材料上长出的细菌数量,个。
1.2.6 细菌蛋白质、核酸及细菌形态
将稀释度为10−5大肠杆菌菌液分别滴加100 μL到装有玻璃片和壳聚糖材料的培养皿上。用1900 μL生理盐水洗脱装有玻璃片和壳聚糖材料的菌液,然后将菌液装入灭菌离心管中,在16000 r/min下离心10 min。用紫外分光光度计测定在260和280 nm波长处的OD值。之后每隔4 h测定一次OD值。滴加稀释度为10−4的金黄色葡萄球菌也是同样的操作。
使用碘化丙啶(Propidium Iodide,PI)对细胞染色[20],将稀释度为10−5大肠杆菌菌液滴加100 μL到装有玻璃片和壳聚糖薄膜的培养皿上,培养24 h,然后用1900 μL生理盐水洗脱玻璃片和壳聚糖薄膜的菌液。直接滴加6.25 μL浓度为1 mg/mL的PI染液到125 μL的菌液中,使得最终浓度为25 μg/mL,于37 ℃下避光孵育5 min,在倒置荧光显微镜下可以观察到激发出来的橙红色荧光。
1.3 数据统计
实验平行重复3次,数据以
ˉx ±s形式表示,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异,采用Origin 2017软件进行绘图,采用SPSS 21.0软件(美国IBM公司),分析实验数据,数据差异性采用单因素方差分析处理。其他数据处理软件有:Excle 2013(美国Micrical公司)、XPS peak4.1(中国香港)、PhotoShop CS6(美国Adobe公司)、SPSS(美国IBM公司)。2. 结果与分析
2.1 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料的表面结构分析
2.1.1 ATR-FTIR分析
图1为氦气等离子体改性400 kDa壳聚糖材料的红外光谱图。未改性材料在3268 cm−1处出现-OH和N-H的伸缩振动吸收峰,在1645 cm−1附近为酰胺Ⅱ型中的C-N伸缩振动和N-H-CONH的变形振动峰,1400 cm−1处为=CH2和-CH3的振动峰,1068 cm−1处为C-OH的吸收峰[21]。与未改性材料相比,改性壳聚糖材料在3268 cm−1处的吸收峰峰型从平滑有一定宽度变为平缓,这一带强度的降低是因为氧自由基引起-NH2发生氧化,使氧分子解离成活性自由基[22]。对于光斑区和非光斑区的改性材料,其在1550~1645、1400和1068 cm−1处的吸收峰峰强均发生减弱,说明改性壳聚糖材料中的C-N伸缩振动和N-H-CONH的变形振动减弱、-CH2和-CH3减少、C-OH基团中的C-O键拉伸。通过ATR-FTIR结果可以看出,在氦气等离子体改性过程中,受带电粒子冲击,壳聚糖材料表面有大量基团发生断裂,产生活性基团,断裂的基团间又相互作用,从而改变了壳聚糖材料的表面分子结构。
可见应用红外光谱分析技术,不仅可以得到淀粉样品的分子基团信息,还可以利用其分析淀粉的短程有序结构。常规的压片法是给出样品的整体信息,而衰减全反射技术的出现,实现了对淀粉样品表层一定深度(μ)的分子信息分析,且不受影响并能分析含水样品,这将有利于对等离子体对淀粉分子结构的影响进行深层次的探讨。
2.1.2 XPS分析
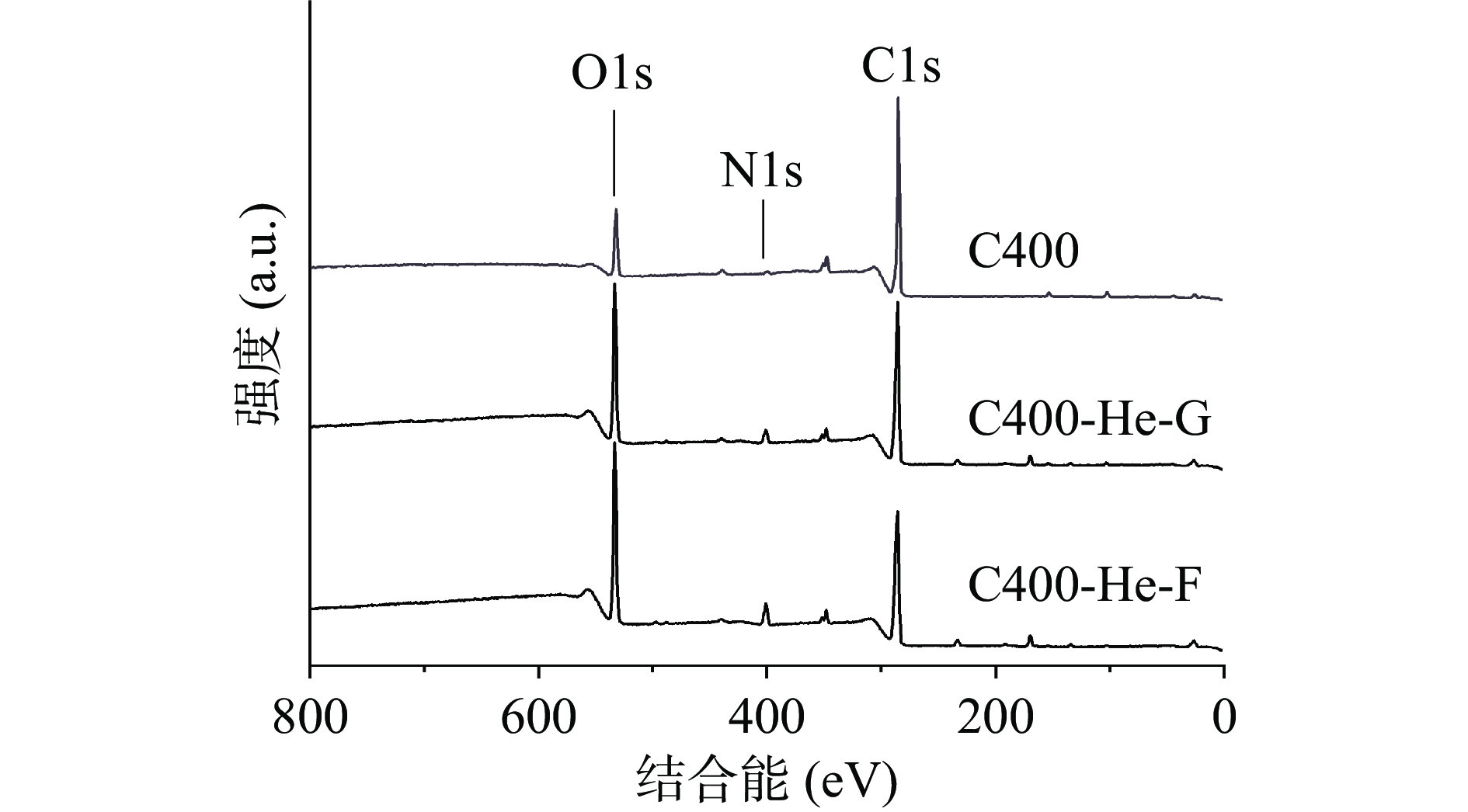
图2为氦气等离子体改性后壳聚糖材料表面光斑区和非光斑区的全谱图,图3是样品表面各元素分峰拟合后的XPS谱图。从全谱图可以看出,在氦气氛围改性下,壳聚糖材料表面的氧元素和氮元素含量明显增加,而碳元素含量减少。
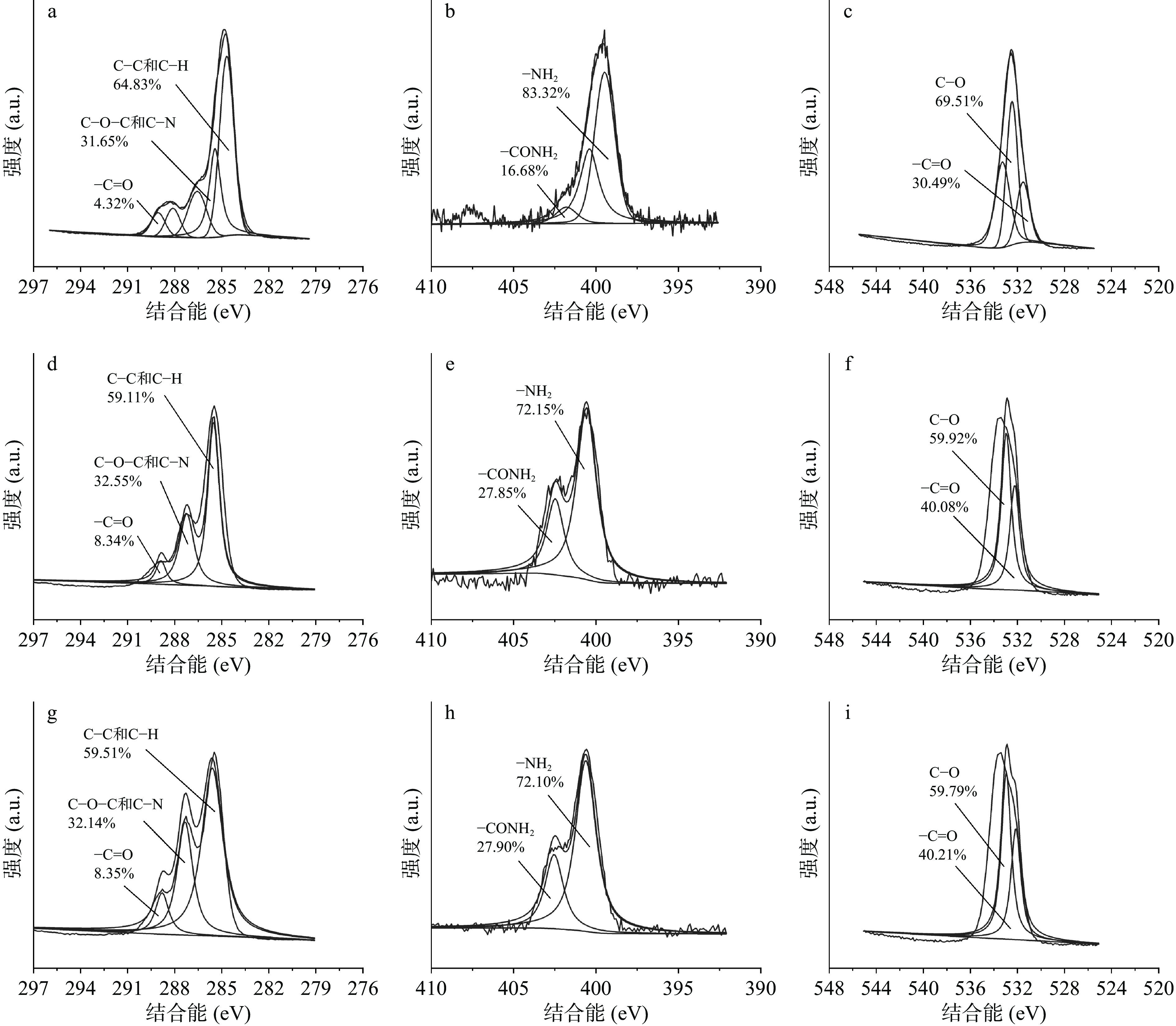
为探讨改性壳聚糖材料表面各化学基团的变化,对各元素不同化学价态进行分析。其中,壳聚糖材料表面的C1s轨道的XPS谱图分为C-C和C-H、C-O-C和C-N、-C=O。C-C和C-H单键的特征峰出现在284.6 eV(图3),在未改性材料中,C-C和C-H的含量降低,改性后,其占比从64.03%下降到59.11%,但光斑区壳聚糖材料与非光斑区壳聚糖材料之间的区别不大。与之相比,C-O-C、C-N和-C=O占比升高,C-O-C和C-N占比从31.65%上升到32.55%,且-C=O占比从4.32%上升到8.34%。同时,O1s轨道的XPS谱图主要分为-C=O和C-O两种特征峰。C-O的峰位在532.95 eV,改性后,C-O的含量从69.51%降低到59.79%,而-C=O的含量从30.49%上升到40.21%。改性壳聚糖材料表面氧元素的价态、基团的变化来源于两方面,一是等离子体中带电粒子的碰撞使原有的含氧基团断裂并与材料表面其余裂解基团相结合,从而转化成新基团;另外则是来源于裂解后的含氧基团与反应器中残留的O2反应生成的新基团。对于氮元素,壳聚糖材料表面的N1s轨道的XPS谱图主要分为-NH2和-CONH2。-NH2的特征峰出现在399.32 eV处,而-CONH2的特征峰则在401.6 eV处[23]。改性后,-NH2的比例从83.32%下降到72.10%。相反,-CONH2的比例从16.68%上升到27.90%。改性后,光斑区和非光斑区壳聚糖材料的化学结构相近,表明改性均匀,在分子结构区域差别小。
在反应器中,在高压电流下,发生等离子体作用,产生带电的粒子,通过刻蚀,使材料表面的化学键发生断裂,从而增加材料的亲水性[24],但材料表面的元素改变只能来源材料内部。结合图3可知,等离子体改性后,壳聚糖材料自身结构发生明显变化,原有结构中的N-H-CONH、C-N、=CH2、-CH3、C-OH等基团数量下降,这是由于等离子体中带电粒子的刻蚀作用,使基团中的化学键发生断裂,壳聚糖材料表面形成自由基[25]。由于氦气是一种惰性气体,化学性质稳定,较难电离,壳聚糖材料表面受带电粒子冲击形成的自由基无法从环境中与其他粒子结合,继而向材料深层处未断裂的壳聚糖分子链段进行结合,逐渐破坏壳聚糖材料深层结构,生成-C=O、-CONH2等基团[26]。
2.2 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖薄膜的形貌及表面元素分析
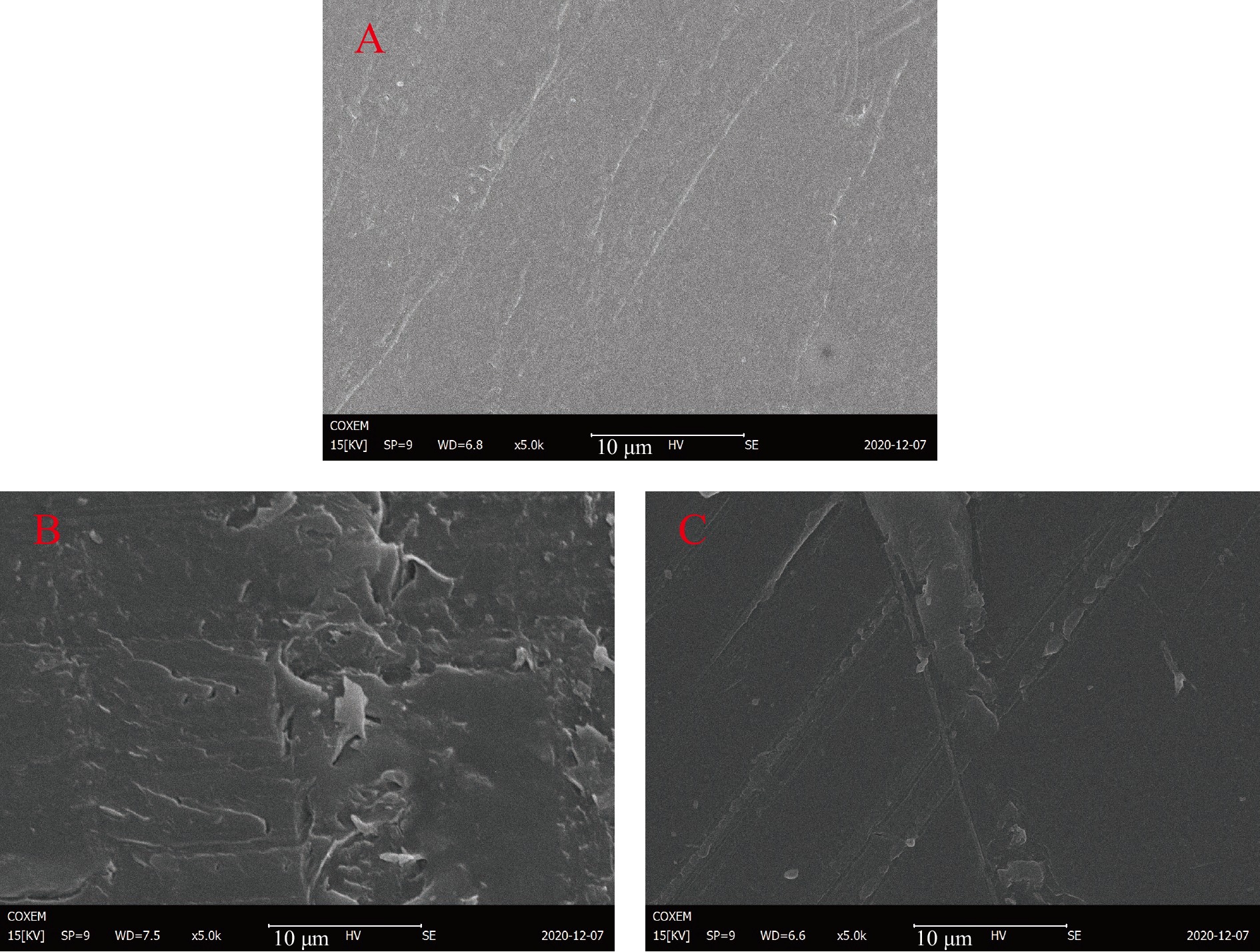
图4为氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料各元素的SEM图,图4A中未改性材料表面形貌平整,改性后,光斑区壳聚糖材料表面变得粗糙(图4B),非光斑区壳聚糖材料表面虽然粗糙,但其粗糙程度不及光斑区(图4C)。这与等离子体改性过程中带电离子在壳聚糖材料表面产生刻蚀反应并引入自由基进行反应有关,由于光斑区处于放电针尖下端,带电粒子的密度较高,因此,此处的反应程度比非光斑区更加剧烈,从而导致壳聚糖材料表面粗糙度更加明显。
2.3 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料的抗菌性分析
如表1所示,未改性材料对大肠杆菌的抗菌率为(82.86%±0.76%),对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率达到(98.52%±0.55%)。经过氦气等离子体改性之后,改性壳聚糖材料对大肠杆菌的抗菌率有所提升,其中,光斑区的抗菌率为(93.89%±6.21%),非光斑区的抗菌率为(94.48%±7.20%)。但是,改性壳聚糖材料对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率反而下降,光斑区的抗菌率为(98.09%±0.96%),非光斑区的抗菌率为(98.23%±0.69%)。对抗菌性数据进行显著性分析,对于大肠杆菌来说,改性后壳聚糖材料的抗菌性跟改性前相比存在显著性差异(P<0.05),表明通过等离子体改性后,增加了材料表面极性基团的形成,使等离子体处理膜的润湿性得到明显改善,从而使材料与菌体之间有良好的接触,这使得壳聚糖材料对大肠杆菌抗菌性能会有一定的增强[27]。并且,相比于光斑区壳聚糖材料,非光斑区壳聚糖材料对大肠杆菌有更好的抗菌性能,这与光斑区材料刻蚀作用严重,材料破损有关。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌,改性前后并没有显著性差异(P>0.05),氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌性能没有改变。后续,将结合细菌菌液的核酸、蛋白质含量变化等结果,对氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料对两种细菌的抗菌性能差异和抑菌机制做探讨。
表 1 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料对不同细菌的抗菌性能Table 1. Antibacterial properties of helium plasma modified chitosan materials to different bacteria材料 抗菌性(%) 大肠杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 C400 82.86±0.76a 98.52±0.55a C400-He-G 93.89±6.21b 98.09±0.96a C400-He-F 94.48±7.20c 98.23±0.69a 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 2.4 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖薄膜的抑菌机制探讨
2.4.1 细菌蛋白质、核酸分析
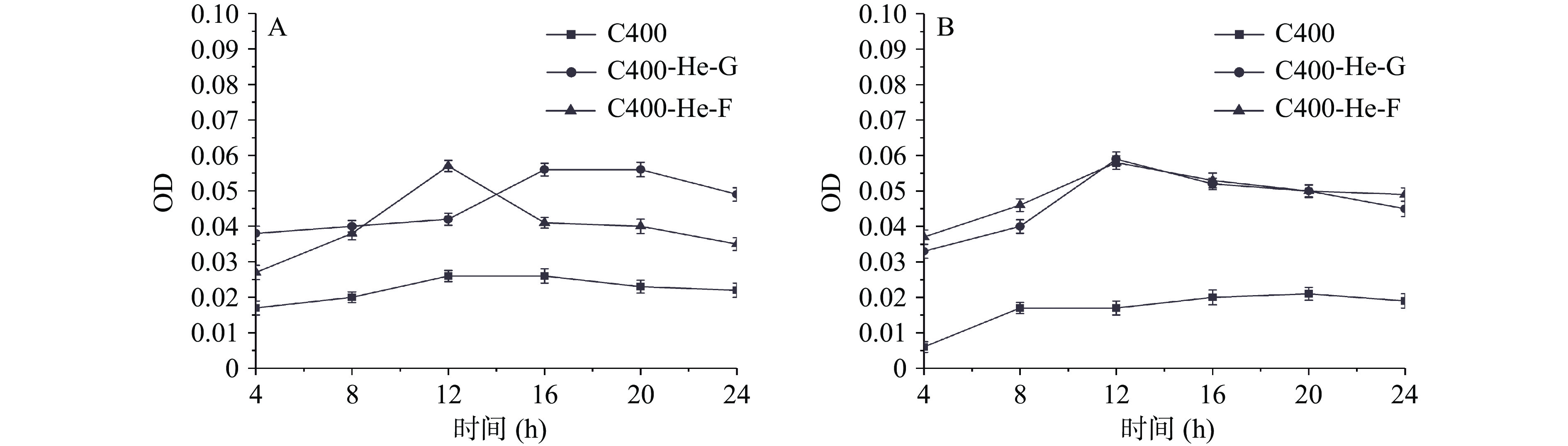
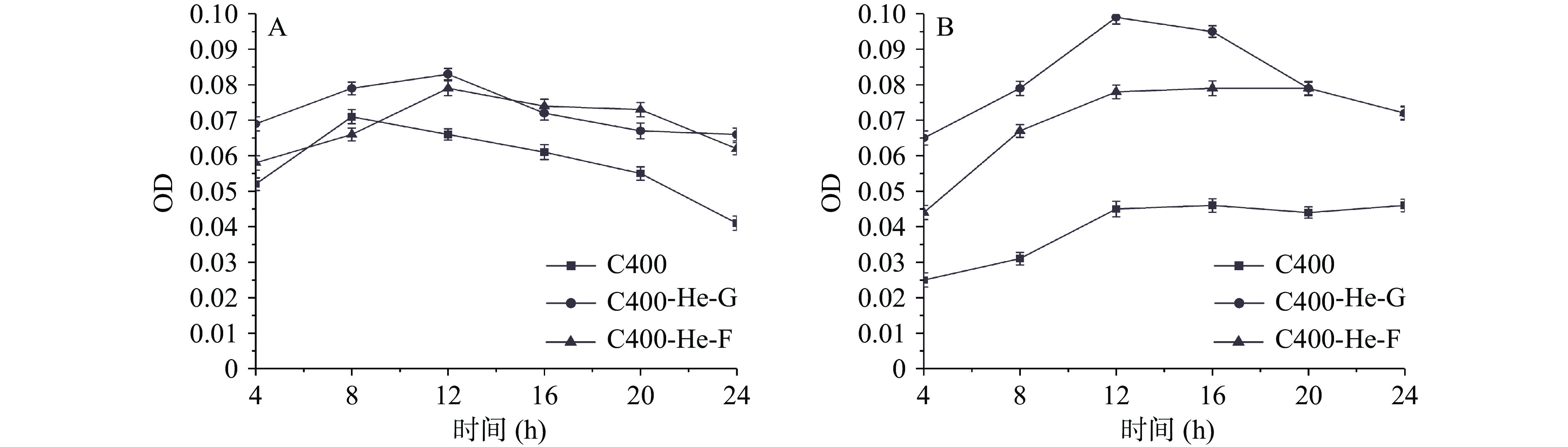
大肠杆菌在氦气等离子体改性后壳聚糖材料表面接触后,其菌悬液中核酸及蛋白质OD值变化,如图5所示。其中,与改性壳聚糖材料接触后,大肠杆菌菌悬液中游离的核酸OD值要高于未改性材料。而改性壳聚糖材料的光斑区处理的大肠杆菌,其菌悬液中游离核酸OD值基本比非光斑区的要高。这说明在氦气等离子体改性条件下,改性壳聚糖材料表面分子结构的变化对大肠杆菌细胞膜有明显作用,壳聚糖材料与大肠杆菌接触后,细胞膜通透性改变,泄露了小分子物质。同样的,对菌悬液中蛋白质吸光值进行测定,与改性壳聚糖材料接触后,大肠杆菌菌悬液中蛋白OD值要明显高于未改性材料。这说明氦气等离子体改性的壳聚糖材料可破坏大肠杆菌细胞膜的完整性,使得菌液中小分子物质核酸、大分子物质蛋白质泄露。
从图6A中可以看到,对于改性后的材料,无论光斑区还是非光斑区,菌悬液中金黄色葡萄球菌核酸OD值均高于未改性的壳聚糖材料,并且光斑区材料的核酸OD值要高于非光斑区的。同样的,菌悬液中的蛋白质的变化情况和核酸的OD值一致。这说明等离子体材料与金黄色葡萄球菌接触,破坏金黄色葡萄球菌细胞膜的完整性,使其泄露核酸、蛋白质等,进而改变金黄色葡萄球菌的生长状况。
2.4.2 细菌形态分析
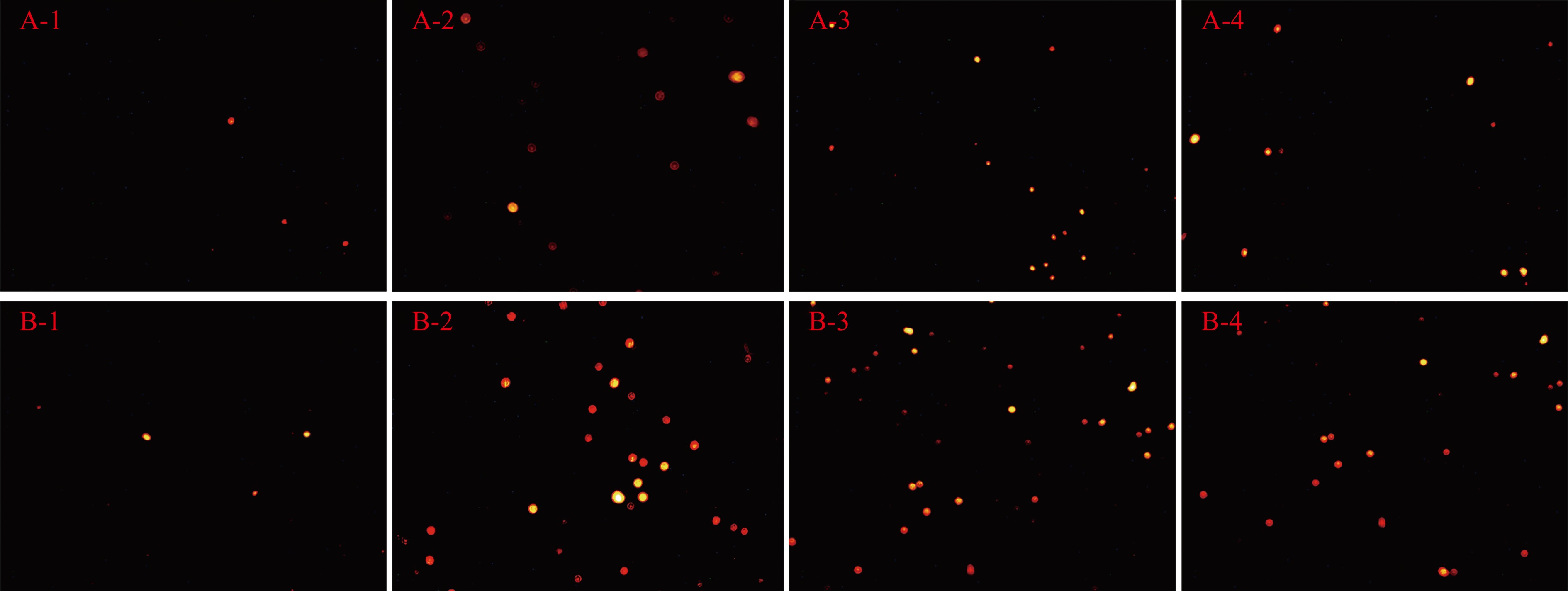
图7是不同改性壳聚糖材料作用于大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌菌悬液后的PI染色图。正常的细菌由于细胞膜完整,PI染料无法穿透,而凋亡的细菌,由于细胞膜完整性、通透性发生改变,PI染料可以进入细菌内部,并对其细胞核进行染色,在荧光下呈橙红色。对比图7发现,未改性壳聚糖材料对大肠杆菌有一定的抑菌效果,材料表面的菌体成较暗的红斑,但在改性壳聚糖材料上,PI染色的细菌所呈现的光斑颜色明亮、集中,说明细菌细胞膜破损更为严重。而对于金黄色葡萄球菌,在未改性壳聚糖材料和改性壳聚糖材料表面,均能观察到橙红色的亮斑,且数量、颜色深浅差异不大,说明材料改性前后对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用差异不明显。这也与前文关于壳聚糖材料在等离子体改性前后对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用没有显著性差异的结论一致。而两种细菌在光斑区材料上所呈现的亮斑,数量与颜色明亮程度要高于非光斑区材料,说明细菌细胞膜通透性改变更明显,细胞内物质更容易游离。这一结果也与图5、图6中细菌菌悬液中游离核酸、蛋白的结果一致。
2.5 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料的抗菌作用机理
在氦气氛围下,经高压电源作用,放电产生等离子体(图8所示),反应器中充满带电粒子,对壳聚糖材料表面N-H-CONH、C-N、=CH2、-CH3、C-OH等基团进行裂解,同时,由于氦气化学性质稳定,较难电离,断裂后的化学基团无法与氦气结合,继而从壳聚糖材料表面向内,与深层的壳聚糖分子链段进行反应,结合,从ATR-FTIR和XPS的分析结果也表明有基团数目及含量的变化。
另外,本实验通过放电针,采用高压放电产生等离子体,受电子流的冲击,处于放电针尖下的改性壳聚糖材料(光斑区)的微观形貌粗糙,材料不平整,有明显沟壑。光斑区材料内部也明显受到等离子体的刻蚀作用。而非光斑区材料受等离子体作用,其化学基团、表面分子结构等发生了变化,但材料微观形貌相对平整,未见破损,材料内部也没有暴露。在XPS分峰拟合结果中,光斑区与非光斑区材料表面的化学基团比例差别不大,但粗糙的光斑区可充分与细菌菌体接触,从而对抗菌性能造成影响。
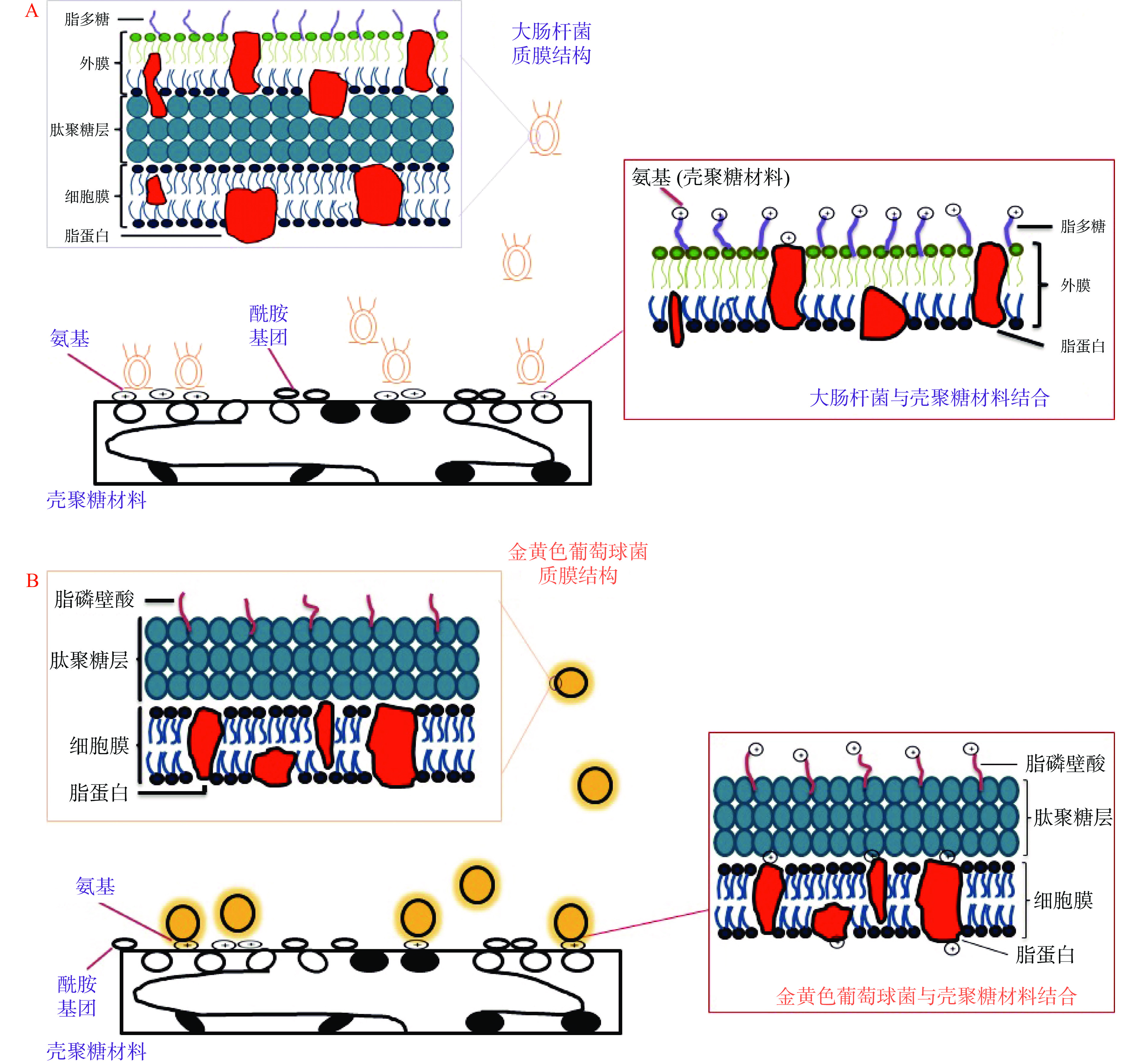
壳聚糖材料中的-NH2基团能够在酸性条件下发生质子化生成-NH3+,-NH3+会跟细菌细胞表面的负电荷分子发生静电相互作用,进而改变细胞膜通透性,细胞内容物流出,最终导致细菌细胞死亡[28-29]。如图9A所示,大肠杆菌细胞膜表面有脂蛋白和脂多糖,当壳聚糖材料与大肠杆菌接触时,壳聚糖上的-NH3+会与外膜上带负电荷的脂蛋白和脂多糖发生静电相互作用,从而改变大肠杆菌的细胞膜通透性,因此大肠杆菌细胞内核酸、蛋白质等物质可游离出细胞外,进而对大肠杆菌生长造成抑制作用[30-31]。
与大肠杆菌不同,金黄色葡萄球菌属于革兰氏阳性菌,其细胞膜上主要由肽聚糖和脂蛋白组成,肽聚糖层有带负电荷的磷壁酸(图9B),当壳聚糖材料与金黄色葡萄球菌接触时,-NH3+会与磷壁酸发生相互作用,再穿过肽聚糖层与细胞膜上的脂蛋白发生作用,破坏金黄色葡萄球菌的细胞膜完整性,使细胞内物质泄露,从而导致细菌死亡[32-33]。金黄色葡萄球菌的质膜结构组成相对简单,而-NH3+可直接与金黄色葡萄球菌细胞膜内部的成分相结合,进而改变细胞膜完整性,因此,在金黄色葡萄球菌抗菌过程中,未改性壳聚糖材料具有较高的抗菌率。改性后,虽然材料表面的-NH2基团比例有所下降,但材料表面的-CONH2基团比例增加,酰胺键为亲水的带负电基团[34],在接触过程中,材料表面的酰胺键与细菌细胞膜表面带负电的成分相互排斥,局部地形成不利于细菌生长的环境,进而抑制细菌的生长。此外,光斑区材料由于处于放电针下方,等离子体的刻蚀作用,增加材料表面的粗糙度,粗糙的表面容易使细菌粘附,对抑菌造成一定阻碍[35],而非光斑区材料则相对平整,所以在抗菌率上,非光斑区材料的抗菌率稍高于光斑区的。
3. 结论
本实验针对目前较少采用的氦气等离子进行研究,在化学性质稳定的氦气氛围下,运用等离子体技术对壳聚糖材料进行改性处理,结构表征好抗菌实验均表明,通过带电粒子的冲击,使壳聚糖材料表面化学基团和内部结构发生变化,影响细菌的细胞膜通透性,从而达到抗菌的目的。论文阐明了氦气等离子体技术对壳聚糖材料的作用机制,氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料的抗菌机理也进行了探讨,可为氦气等离子体改性技术的深入提供参考。此外,实验所改用的等离子体改性条件会破坏材料深层结构,后续需要对此进行改进,同时本实验仅对有代表性的大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌进行研究,尚未对其他不同类型的微生物作探讨,材料的抗菌作用机理是否具有适用性,仍有待进一步探讨。
-
表 1 氦气等离子体改性壳聚糖材料对不同细菌的抗菌性能
Table 1 Antibacterial properties of helium plasma modified chitosan materials to different bacteria
材料 抗菌性(%) 大肠杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 C400 82.86±0.76a 98.52±0.55a C400-He-G 93.89±6.21b 98.09±0.96a C400-He-F 94.48±7.20c 98.23±0.69a 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] ONUR P, AGNETA R, DAHLFORS P. Bacterial sensing and biofilm monitoring for infection diagnostics[J]. Macromolecular Bio-science,2020,20(11):2000129. doi: 10.1002/mabi.202000129
[2] 麻晓霞, 马玉龙. 氧化锌型复合抗菌材料抗菌活性研究进展[J]. 功能材料,2018,49(9):9061−9066. [MA Xiaoxia, MA Yulong. Research progress on antibacterial activity of zinc oxide type composite anti-bacteria materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2018,49(9):9061−9066. [3] NAVEED M, PHIL L, SOHAIl M, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS): An overview[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,129:827−843. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.192
[4] PAL P, PAL A, NAKASHIMA K, et al. Applications of chi-tosan in environmental remediation: A review[J]. Chemosphere,2021,266:128934. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128934
[5] PELEGRINO M T, PIERETTI J C, NAKAZATO G, et al. Chitosan chemically modified to deliver nitric oxide with high antibacterial activity[J]. Nitric Oxide,2021,106:24−34. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2020.10.003
[6] AN Jing, JI Zhenxing, WANG Desong, et al. Preparation and characterization of uniform-sized chitosan/silver microspheres with antibacterial activities[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C,2014,36:33−41. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.11.037
[7] KHAN A, ALAMRY K A. Recent advances of emerging green chitosan-based biomaterials with potential biomedical applications: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2021,506:108368. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108368
[8] MILLAN S D, HAN L, MILOSAVLJEVIC V, et al. Assessing bacterial recovery and efficacy of cold atmospheric plasma treatments[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing,2015,96:154−160. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2015.07.011
[9] SHARMA S, SINGH R K. Cold plasma treatment of dairy proteins in relation to functionality enhancement[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,102:30−36.
[10] LIU P, WANG G, RUAN Q, et al. Plasma-activated interfaces for biomedical engineering[J]. Bioactive Materials,2021,6(7):2134−2143. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.001
[11] WAGHMARE R. Cold plasma technology for fruit based beverages: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,114:60−69.
[12] 曲培培, 张清, 丁树民, 等. 低温等离子体在材料表面改性中的应用[J]. 广东化工,2018:146−147. [QU Peipei, ZHANG Qing, DING Shumin, et al. Application of low temperature plasma in surface modification of materials[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2018:146−147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2018.11.062 [13] LI Yuan, WU Chunhua, BAI Yan, et al. Effect of glow discharge plasma on surface modification of chitosan film[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,138:340−348. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.039
[14] KAWAKAMI R, YOSHITANI Y, MITANI K, et al. Effects of air-based nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment on characteristics of polypropylene film surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,509:144910. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144910
[15] PANERU R, KI S H, LAMICHHANE P, et al. Enhancement of antibacterial and wettability performances of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan film using non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,532:147339. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147339
[16] LIN Lin, LIAO Xue, LI Changzhu, et al. Cold nitrogen plasma modified cuminaldehyde/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex and its application in vegetable juices preservation[J]. Food Research International,2021,141:110132. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110132
[17] GRAVIS D, MOISAN S, PONCIN E F. Surface characterization of plasma-modified carbon fiber: Correlation between surface chemistry and morphology of the single strand[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces,2020,21:100731. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100731
[18] 李群, 周文琴, 李超群, 等. 流延法制备纳米纤维素/壳聚糖/聚乙烯醇复合膜及其在生物抗菌膜中的应用[J]. 天津造纸,2018,40(4):24−26. [LI Qun, ZHOU Wenqin, LI Chaoqun, et al. Preparation of nanofellulose/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol composite film and its application in biological antibacterial membrane[J]. Tianjin Paper,2018,40(4):24−26. [19] 高翔, 马鹏飞, 崔亚宁. 食品微生物检验菌落总数测定方法的效果探讨[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021(3):94−95, 97. [GAO Xiang, MA Pengfei, CUI Yaning. Effect of total method of food microbiology[J]. Food Safety Magazine,2021(3):94−95, 97. [20] 李妍, 王海, 张铎, 等. 碘化丙啶染色流式细胞术分析肿瘤细胞凋亡的方法学探讨[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2012,16(5):799−800. [LI Yan, WANG Hai, ZHANG Duo, et al. Pyridine iodide stained flow cytometry analyzed tumors methods of apoptosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis,2012,16(5):799−800. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2012.05.013 [21] 潘晴彦, 周闯, 杨子明, 等. 季铵盐修饰壳聚糖及其复合膜的制备与表征[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(12):136−144, 204. [PAN Qingyan, ZHOU Chuang, YANG Ziming, et al. Preparation and characterization of quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan and its composite film[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(12):136−144, 204. [22] LIM S H, HUDSON S M. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of a water-soluble chitosan derivative with a fiber-reactive group[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2004,339(3):313−319.
[23] YIN Shiheng, REN Li, WANG Yingjun, et al. Plasma graft of poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEGMA) on RGP lens surface for reducing protein adsorption[J]. Plasma Science and Technology,2017,19(1):51−56.
[24] 张锋, 舒适, 齐永莲, 等. 表面处理对液晶显示阵列基板中黑矩阵残留的影响[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(6):915−919. [ZHANG Feng, SHU Shi, QI Yonglian, et al. Effect of surface treatment on BM residue in TFT-LCD array substrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays,2015,30(6):915−919. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153006.0915 [25] CEPEDA C M, TORREGROSA R, MARTIN J M. Surface modifications of EVA copolymers by using RF oxidizing and non-oxidizing plasmas, Lausanne, 2003[C]. Elsevier, 2003.
[26] 尹诗衡. 角膜修复材料表面等离子体改性与表面性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012: 162. YIN Shiheng. Surface modification and characterization of cornea repair materials by plasma[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012: 162.
[27] TURALIJA M, BISCHOF S, BUDIMIR A, et al. Antimicrobial PLA films from environment friendly additives[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering,2016,102:94−99. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.07.017
[28] 柯松, 王敏, 徐源, 等. 壳聚糖抑菌性能的研究进展[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2019,16(3):59−62. [KE Song, WANG min, XU Yuan, et al. Research progress on antibacterial activity of chitosan[J]. Orthopaedic Biomechanics Materials and Clinical Study,2019,16(3):59−62. [29] ABDEIHACK M E, EISAADONY M T, SHAFI M E, et al. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:2726−2744. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.153
[30] LI Jianhui, ZHUANG Shaoling. Antibacterial activity of chitosan and its derivatives and their interaction mechanism with bacteria: Current state and perspectives[J]. European Polymer Journal,2020,138:109984. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109984
[31] KHAN F, PHAM D T N, OLOKETUYI S F, et al. Chitosan and their derivatives: Antibiofilm drugs against pathogenic bacteria[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2020,185:110627. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110627
[32] RUBINI D, FARISA B S, VEDA H B N, et al. Chitosan extracted from marine biowaste mitigates staphyloxanthin production and biofilms of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2018,118:733−744. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.017
[33] ANDRADE L F D, APOLINARIO A C, RANGELYAGUI C O, et al. Chitosan nanoparticles for the delivery of a new compound active against multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology,2020,55:101363. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101363
[34] 孙仁凇, 张建斌, 房佳霓, 等. 壳聚糖纳米粒作为药物递送系统在癌症治疗中的应用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2021,26(1):65−75. [SUN Rensong, ZHANG Jianbin, FANG Jiami, et al. Application of chitosan nanoparticle served as drug delivery system for cancer therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics,2021,26(1):65−75. [35] CHATURONGKASUMRIT Y, TAKAHASHI H, KEERATIPIBUL S, et al. The effect of polyesterurethane belt surface roughness on Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation and its cleaning efficiency[J]. Food Control,2011,22(12):1893−1902. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.04.032
-
期刊类型引用(18)
1. 王若莹,李俊瑶,陈钰,孙晶. 三种多酚类物质协同L-精氨酸对冷藏鸡肉糜氧化稳定性和品质的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(01): 8-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 唐柏蛟,杨贤庆,潘创,魏涯,杨少玲,赵永强,陈胜军,许加超. 坛紫菜多糖对微冻南美白对虾仁肌原纤维蛋白氧化和结构特性的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(06): 144-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李海燕,尹盼盼,彭腾腾,马趣环,马中森,石晓峰. 甘草中20种无机元素的测定及对有害元素的健康风险评估. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(08): 281-291 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 芦慧勤,黄予豫,任晓镤,牛希跃,兰道亮,王雨祺,王琳琳. 腌制时间对复合低钠酱牦牛肉制品食用品质及氧化特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(15): 76-84 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 韩磊,贾娟,岳亚锋. 药食同源甘草的生物活性及其在食品中应用的研究. 粮食与食品工业. 2024(06): 53-55+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 马婉茹,徐凯丽,董琪,丁之恩. 模糊数学方法结合响应面优化新型鸡肉脯的工艺. 信阳农林学院学报. 2024(04): 89-94+99 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 常海军,伯朝英,周文斌,吴丽,吕佳珂. 阿魏酸对·OH诱导的肌原纤维蛋白氧化及凝胶特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2023(04): 32-40 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 常海军,周文斌,谢娜娜,冯敏,朱苓. 阿魏酸调控肉肌原纤维蛋白氧化及对乳化特性的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2023(08): 194-200 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 赵佳莹,唐善虎,李思宁,陈腊梅,李巧艳. 香蕉花提取物对牦牛肉自然发酵香肠蛋白质氧化的影响. 食品科学. 2023(10): 90-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈国宝,张家蓉. 甘草制品在食品中的应用. 食品安全导刊. 2023(16): 190-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 常海军,伯朝英,石源伟,熊杰,胡渝. 姜黄素对羟自由基诱导的肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响. 中国食品学报. 2023(11): 74-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 孙路,邹金浩,黄群,杨怀谷,唐道邦,王旭苹. 捶打时间对牛肉凝胶品质的影响研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(02): 27-34 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 熊杰,伯朝英,常海军,周文斌,朱建飞. 鼠曲草提取物对·OH诱导的肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(03): 72-80 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 李明杨,刘帅光,卢梦娇,任晓镤,彭增起. 不同抗氧化剂体外抗氧化活性及其对肉品氧化稳定性的影响. 食品科学. 2022(01): 67-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 刘梦竹,魏琦麟,向蓉,康桦华,彭新宇,徐志宏. 鸡肉低温储藏保鲜技术研究进展. 保鲜与加工. 2022(03): 104-110+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 李琼帅,唐善虎,李思宁,莫然,李锦锦,夏佳军,蔡寅川. 石榴皮提取物对贮藏期间牦牛肉糜蛋白质氧化及挥发性风味物质的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(10): 93-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 邹欣洋,计瑶,张晶,陈钰,孙晶. 复合香辛料提取物对冷藏猪肉糜氧化及品质特性的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2022(10): 23-31+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 伯朝英,熊杰,常海军,吴丽,彭荣. 马齿苋提取物抑制冷藏猪肉糜脂肪和蛋白氧化及对品质特性的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(22): 172-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)








 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



