Ameliorative Effect and Mechanism of Probiotics Combined with Resveratrol on Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice
-
摘要: 利用C57BL/6J小鼠构建慢性酒精性肝损伤模型,探究益生菌联合白藜芦醇对慢性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用及可能机制。小鼠被随机分为空白对照组(Con组)和酒精模型组(Mod组),三组益生菌分别联合白藜芦醇(Resveratrol,Res)干预组(Lactobacillus paracasei J5+Res(J5+Res)、Lactobacillus casei YRL577+Res(YRL577+Res)、Bifidobacterium animalis F1-7+Res(F1-7+Res))和阳性药物硫普罗宁组(LP组)。实验结束后,通过分析小鼠肝脏脂质含量、酒精代谢酶活性、氧化应激水平等指标,对益生菌联合白藜芦醇的作用效果进行评价。为了进一步探究联合作用机制,对肝脏中氧化应激相关基因CYP2E1、核因子 E2 相关因子 2(Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2, Nrf2)、血红素加氧酶1(Heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)的mRNA表达进行分析。结果表明,相较于Mod组,益生菌联合白藜芦醇能够显著降低小鼠肝脏中甘油三脂、总胆固醇含量、血清谷草转氨酶和谷丙转氨酶活力(P<0.05),提高肝脏乙醇脱氢酶、乙醛脱氢酶活性并抑制肝脏CYP2E1活性及其mRNA表达,显著提高肝脏还原型谷胱甘肽含量和超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶活性(P<0.05),并能有效激活Nrf2/HO-1通路,其中,Nrf2 mRNA表达量在J5+Res、YRL577+Res、F1-7+Res三组益生菌联合干预组中分别被上调了2.6、3.7和2.7倍,HO-1 mRNA表达量被上调了2.0、6.2和4.0倍。因此,益生菌联合白藜芦醇可能通过激活Nrf2/HO-1途径预防慢性酒精性肝损伤。Abstract: To explore the protective effect and possible mechanism of probiotics combined with resveratrol on chronic alcoholic liver injury, C57BL/6J mice were used to construct chronic alcoholic liver injury model. Mice were randomly divided into the control group (Con group), themodel group (Mod group), three intervention groups of probiotics combined with resveratrol (Res) (Lactobacillus paracasei J5+Res (J5+Res), Lactobacillus casei YRL577+Res (YRL577+Res), Bifidobacterium animalis F1-7+Res (F1-7+Res)) groups, and the positive drug tiopronin group (LP group). After the experiment, the liver lipid content, alcohol metabolism enzyme activities, oxidative stress level and other indexes of mice were investigated. In order to further explore the mechanism of the combined action, the mRNA expressions of oxidative stress related genes CYP2E1, nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in liver were analyzed. The results showed that compared with Mod group, probiotics combined with resveratrol could significantly reduce the contents of triglyceride, total cholesterol, serum aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase activites in liver of mice (P<0.05), increase the activities of alcohol metabolism enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase in liver, inhibit the activity of CYP2E1 and its mRNA expression in liver. In addition, the contents of glutathione as well as the activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase in liver significantly increased (P<0.05), the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway was effectively activated compared with Mod group (P<0.05). Nrf2 mRNA expression was up-regulated by 2.6, 3.7 and 2.7 times in J5+Res, YRL577+Res and F1-7+Res groups, and HO-1 was up-regulated by 2.0, 6.2 and 4.0 times, respectively. Therefore, probiotics combined with resveratrol mayprevente chronic alcoholic liver injury through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
-
Keywords:
- probiotics /
- resveratrol /
- alcoholic liver injury /
- oxidative stress
-
机体摄入的酒精超过90%在肝脏代谢,若长期酒精摄入产生的有害代谢产物超过肝脏的解毒能力,势必对肝脏造成严重损伤[1]。研究表明,酒精及其代谢物乙醛被认为是酒精性肝损伤的病因[2],氧化应激在急性或慢性酒精性肝损伤的发病机制中也起着重要作用[3-4]。因此,加速肝脏酒精代谢排出和预防氧化应激是延缓酒精性肝损伤发病的有效途径。
目前,药物干预仍是预防和治疗酒精性肝损伤的主要方法,然而,药物具有的严重副作用及不能为所有人所耐受的缺点使得探索天然成分的安全有效干预手段迫在眉睫[5]。益生菌对人体具有良好的生理生化功能,研究表明鼠李糖乳杆菌CCFM1107(Lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM1107)能通过提高肝脏抗氧化酶活性、抑制脂质过氧化发挥对慢性酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用[6]。白藜芦醇(Resveratrol,Res)作为存在于红酒、葡萄、花生和其他各种植物中的一种多酚类物质,可抑制大鼠肝脏脂质过氧化,提高肝脏抗氧化酶活性,通过增强抗氧化防御体系预防慢性酒精干预造成的肝损伤[7]。然而,益生菌与白藜芦醇通过降低机体氧化应激途径预防酒精性肝损伤的研究均已有报道[8-9],但两者联合作用是否具有更好的预防效果及可能机制还需进一步探明。
因此,本研究基于具有抗氧化及降脂活性的益生菌副干酪乳杆菌J5(Lactobacillus paracasei J5、L. paracasei J5)、干酪乳杆菌YRL577(Lactobacillus casei YRL577、L. casei YRL577)、动物双歧杆菌F1-7(Bifidobacterium animalis F1-7,Bif. animals F1-7)[10-12],探讨其分别联合白藜芦醇对慢性酒精性肝损伤的可能保护作用及潜在机制,以期为后续解酒护肝功能性产品的开发利用提供参考和借鉴。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
C57BL/6J雄性小鼠(17~19 g) 济南朋悦生物技术有限公司(许可证号SCXK(鲁)20190003);L. paracasei J5、L. casei YRL577、Bif. animals F1-7 中国海洋大学功能乳品与益生菌工程实验室保藏菌株;白藜芦醇 纯度98%,阿拉丁试剂;95%食品级酒精 河南鑫河阳酒精有限公司;MRS液体培养基 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;无菌磷酸缓冲盐溶液(Phosphate buffer saline,PBS) 北京Solarbio科技有限公司;甘油三脂(Triglyceride,TG)、总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、谷草转氨酶(Aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、谷丙转氨酶(Alanine aminotransferase,ALT)、乙醇脱氢酶(Alcohol dehydrogenase,ADH)、乙醛脱氢酶(Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase,ALDH)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)、还原型谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)检测试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;细胞色素酶CYP2E1(CYP2E1)ELISA试剂盒 艾莱萨生物科技(上海)有限公司;Trizol裂解液 美国Invertrogen;异丙醇、氯仿 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix、逆转录试剂盒 东洋纺生物科技有限公司;DEPC去离子水、BCA蛋白浓度试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司。
NanoDrop2000超微量分光光度计 赛默飞世尔科技公司;BIO-RAD CFX96实时荧光定量PCR仪 美国BIO-RAD公司;TP600PCR 扩增仪 宝日医生物技术有限公司;Olympus CKX51倒置显微镜 奥林巴斯公司;UV-2550紫外分光光度计 苏州岛津仪器公司;NIKON/Ni-E电动荧光显微镜 日本尼康公司;TG20KR-D高速冷冻离心机 长沙东旺实验仪器有限公司;Multiskan FC酶标仪 美国Thermo Scientific公司;AB135-S分析天平 瑞士Mettler Toledo公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌株培养
菌株以2%(v/v)接种量分别接种于MRS液体培养基,37 ℃恒温培养24 h。将培养后的菌株发酵液在4 ℃条件下以8000 r/min离心5 min,弃去上清,菌体重悬于无菌PBS洗涤两次,通过平板计数法获得菌体浓度为109 CFU/mL的PBS菌悬液,使用前临时置于4 ℃冰箱中备用。
1.2.2 动物模型与分组
42只雄性C57BL/6J小鼠在清洁级、12 h光照/黑暗交替、(23±2)℃温度、(50%±10%)相对湿度的动物房适应性喂养7 d,随后被随机分成6组(n=7),分别为空白对照组(Con组)、酒精模型组(Mod组),三种益生菌分别联合白藜芦醇干预组(J5+Res、YRL577+Res、F1-7+Res组)、阳性药物硫普罗宁组(LP组),所有组别小鼠均喂食普通饲料。实验按照中国科学技术部动物管理条例,并经中国海洋大学食品科学与工程学院实验动物伦理委员会批准(批准号:SPXY20200717)。
适应性喂养1周后,从第2周开始每天上午除Con组外其余组别小鼠均灌胃酒精(酒精浓度从20%(v/v)每3 d提高5%到终浓度40%,保持酒精浓度40%至11周末),Con组灌胃无菌蒸馏水,灌胃剂量均为10 mL/kg body weight。同时每天下午对小鼠以10 mL/kg body weight进行益生菌联合白藜芦醇及阳性药物灌胃干预,白藜芦醇在菌悬液中混匀并使最终干预剂量为50 mg/kg body weight,阳性药物干预剂量为65 mg/kg/d,Con与Mod组以10 mL/kg body weight灌胃无菌PBS。灌胃至11周末处死小鼠。处死前12 h禁食,自由饮水。小鼠眼球静脉取血,室温放置30 min,3000 r/min离心15 min,小心吸取上层淡黄色血清分装保存,同时收集肝脏组织均置于−80 ℃冰箱待用。
1.2.3 肝脏组织病理学分析
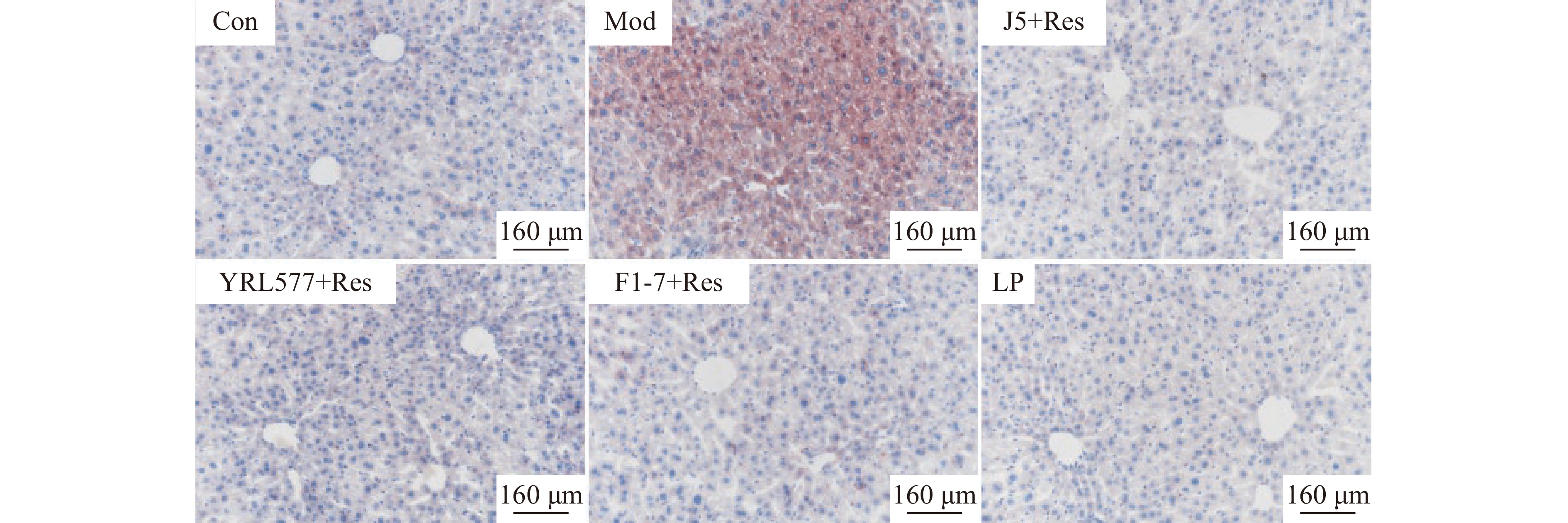
将小鼠肝左叶5 mm×5 mm固定在4%多聚甲醛中5~6 h,并常规进行石蜡包埋,从石蜡块上切下一片厚度约为4 μm的肝脏组织切片,进行油红O染色,并在显微镜下进行观察拍照。
1.2.4 其它指标测定
按照厂家提供的说明,采用谷草转氨酶和谷丙转氨酶测试盒检测小鼠血清中AST、ALT活性。使用甘油三脂、总胆固醇、丙二醛、还原型谷胱甘肽、乙醇脱氢酶、乙醛脱氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶商业试剂盒及细胞色素酶CYP2E1ELISA试剂盒测定小鼠肝脏组织匀浆液中TG、TC、MDA、GSH含量及ADH、ALDH、SOD、CAT、CYP2E1活性。
1.2.5 RT-PCR检测氧化应激相关基因的mRNA表达
利用RT-PCR检测氧化应激相关基因CYP2E1、Nrf-2、HO-1的mRNA表达,引物序列如表1所示。根据试剂盒操作说明,称取适量的肝脏组织,并加入trizol裂解液从组织中提取总RNA。通过逆转录试剂盒合成cDNA单链后进行qPCR操作。每个靶基因的检测值与β-actin的比率代表每个靶基因的表达水平。ΔΔCt用于计算基因表达的倍数差异。
表 1 逆转录聚合酶链反应的引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction基因 正向 (5’-3’) 反向 (5’-3’) CYP2E1 AGGGGACATTCCTGTGTTCC TTACCCTGTTTCCCCATTCC Nrf-2 TTGGCAGAGACATTCCCATTTG AAACTTGCTCCATGTCCTGCTCTA HO-1 TGCAGGTGATGCTGACAGAGG GGGATGAGCTAGTGCTGATCTGG β-actin GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT 1.3 数据处理
数据表示为平均值±标准差,使用SPSS Statistics 26.0进行数据分析。使用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)并进行S-N-K检验,P<0.05被认为具有显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 益生菌联合干预对慢性酒精摄入导致的小鼠肝脏脂质积累的影响
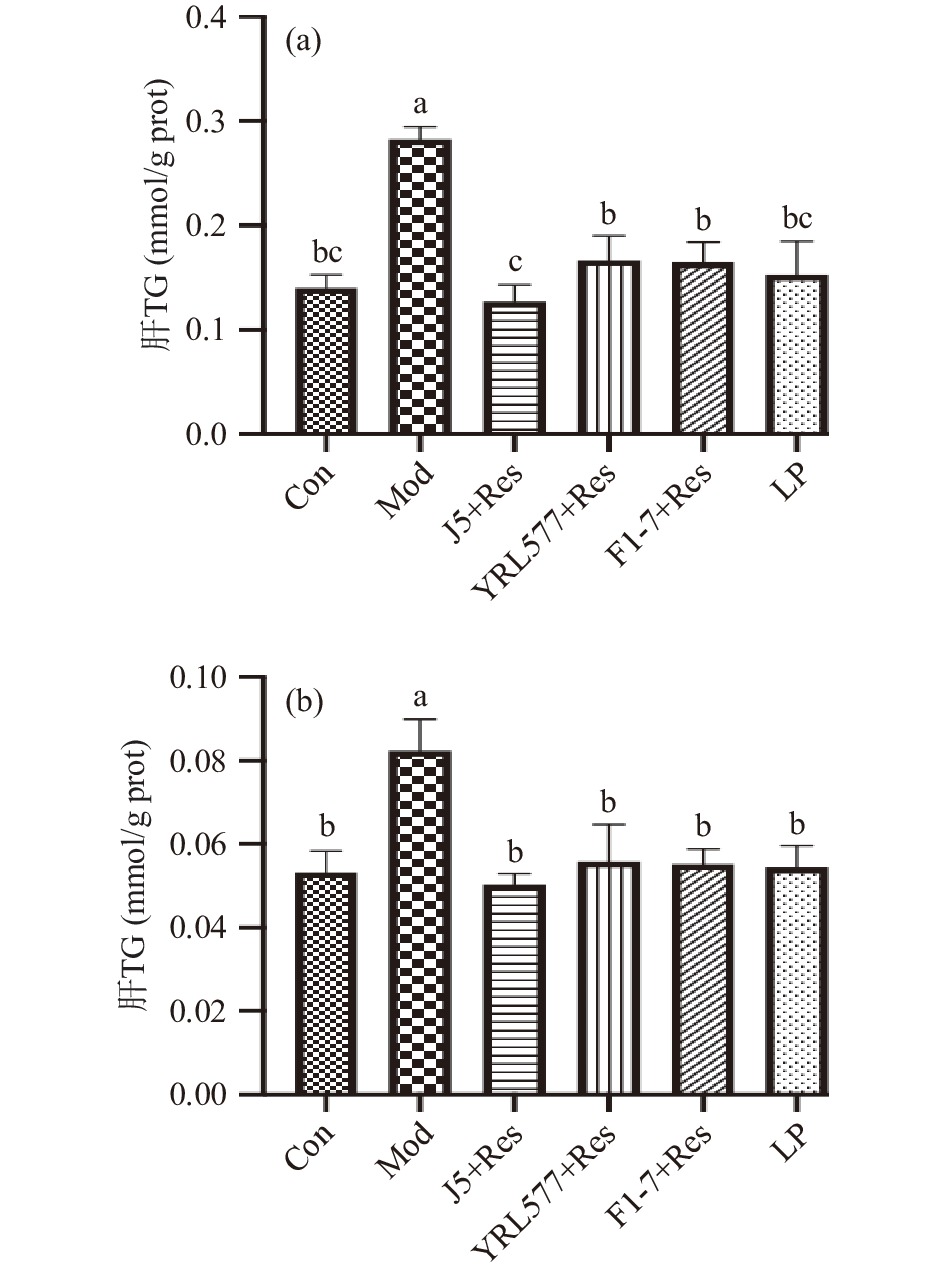
研究发现,长期过量饮酒会导致机体脂质代谢紊乱,使肝脏中TG、TC含量显著增加[13]。为了探讨益生菌与Res联合补充对慢性酒精喂养小鼠肝脏脂质积累的影响,采用组织学分析结合生化TG、TC测定来评价肝脂肪变性[14]。由图1可知,与Con相比,Mod组小鼠肝脏脂质积聚增加,而联合干预组脂质积累情况均得到改善。由图2可知,益生菌联合干预组及LP组的肝TG、TC含量均与Con组无显著性差异(P>0.05),表明益生菌联合干预组均能够有效抑制慢性酒精喂养小鼠的脂质增加,其表现出的较强降脂活性与益生菌和Res本身具有的降脂活性密不可分,且两者相互联合的预防效果与LP组无显著性差异(P>0.05),这对开发辅助降脂功能产品具有重要意义。
2.2 益生菌联合Res干预对慢性酒精摄入导致的小鼠肝损伤的影响
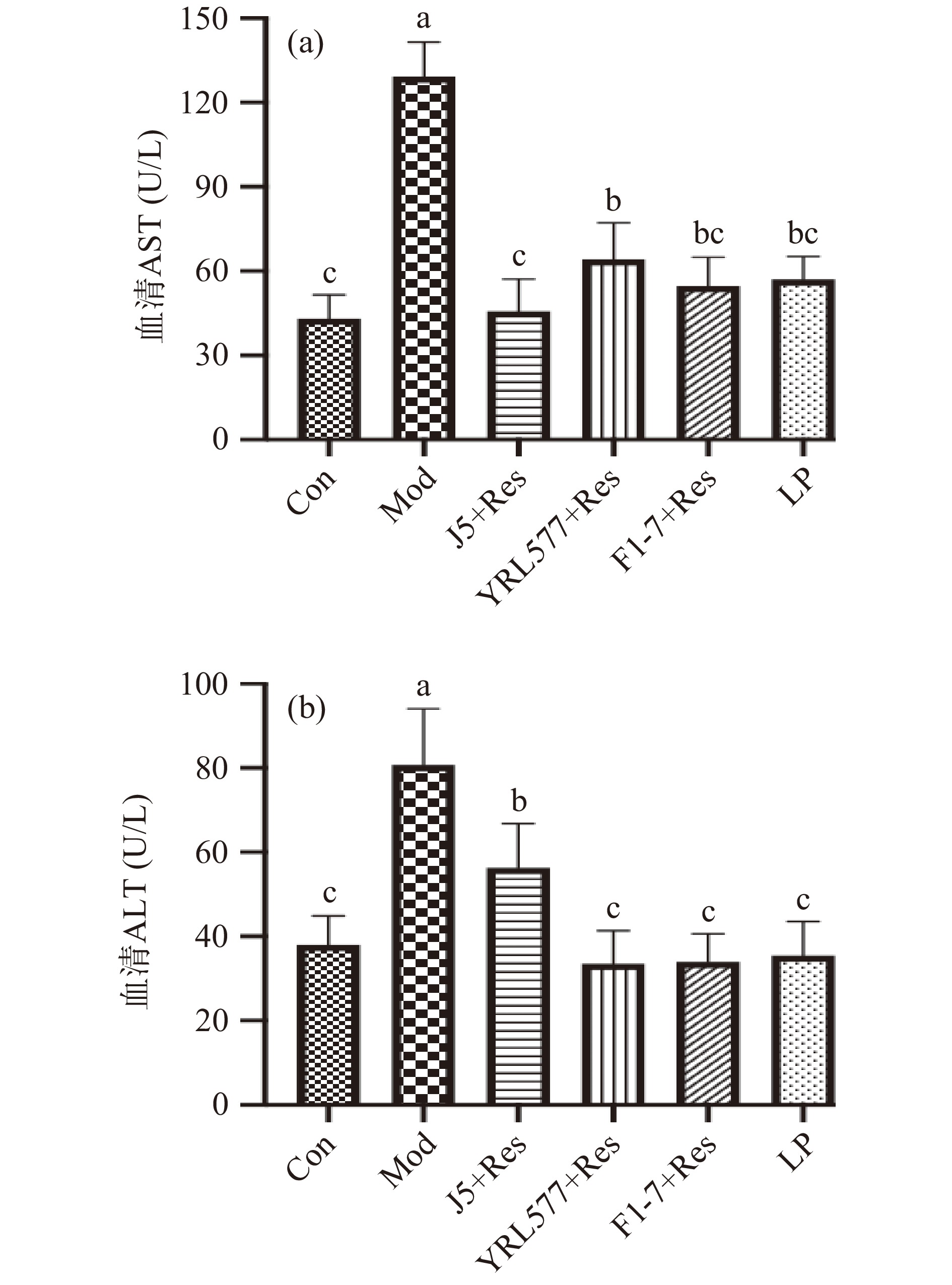
AST和ALT被用作评估肝损伤的敏感指标[15],酒精积累会破坏肝细胞膜的完整性和线粒体功能,促进AST和ALT的释放[16-17]。由图3可知,长期慢性饮酒导致Mod组小鼠血清AST和ALT活力较Con组小鼠显著升高(P<0.05),但这种情况在所有预防干预组中均得到明显改善;F1-7+Res和LP组小鼠血清AST和ALT水平均与Con组无显著性差异(P>0.05),YRL577+Res组的AST水平及J5+Res组的ALT水平虽未处于正常水平但较Mod组分别降低了50.38%和30.20%。这表明各预防组均具有较好的预防慢性酒精性肝损伤的效果。
2.3 益生菌干预对调节慢性酒精摄入小鼠酒精代谢酶活性的影响
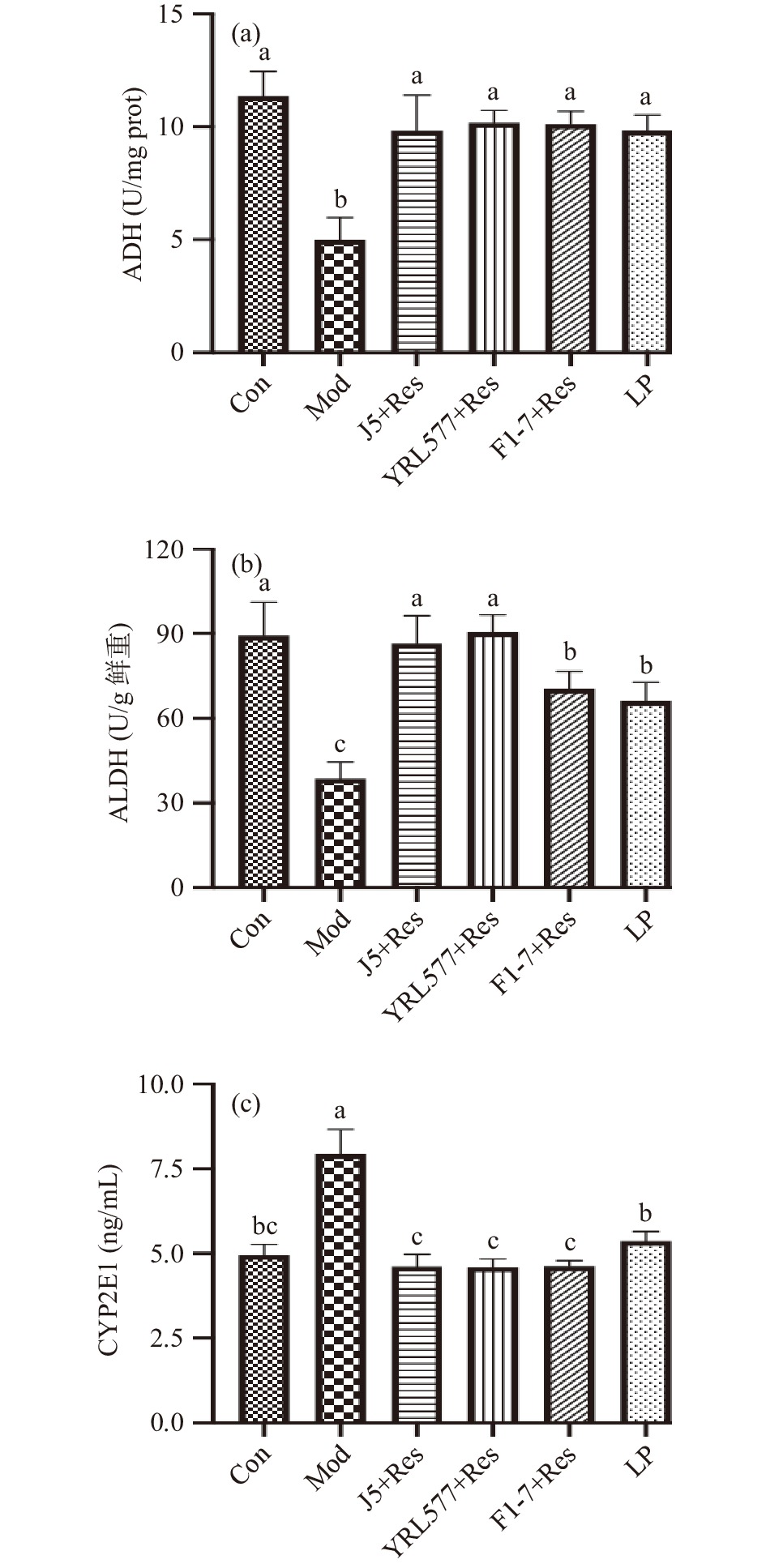
ADH、ALDH和CYP2E1是肝脏参与酒精代谢的酶,但大量酒精摄入会导致CYP2E1发挥主要作用[18-19],而CYP2E1被认为是诱导肝脂肪变性和氧化应激的重要因素[20]。从图4结果可知,Mod组小鼠肝脏中ADH和ALDH活性均显著降低,而CYP2E1活性却显著升高(P<0.05),但这一情况在四个预防干预组中得到改善,其中ADH活性在各干预组中不具有显著性差异且与Con组同一水平(P>0.05),四个预防干预组(J5+Res、YRL577+Res、F1-7+Re、LP)ALDH活性分别是Mod组的2.23、2.34、1.80和1.71倍,同时,三个益生菌联合干预组中CYP2E1活性与Con组不具有显著性差异(P>0.05)且显著优于LP组(P<0.05)。以上结果表明,益生菌联合干预组能够通过调控肝脏酒精代谢酶活力发挥对肝脏的保护作用。
2.4 益生菌联合Res干预对慢性酒精摄入小鼠肝脏氧化应激和脂质过氧化水平的影响
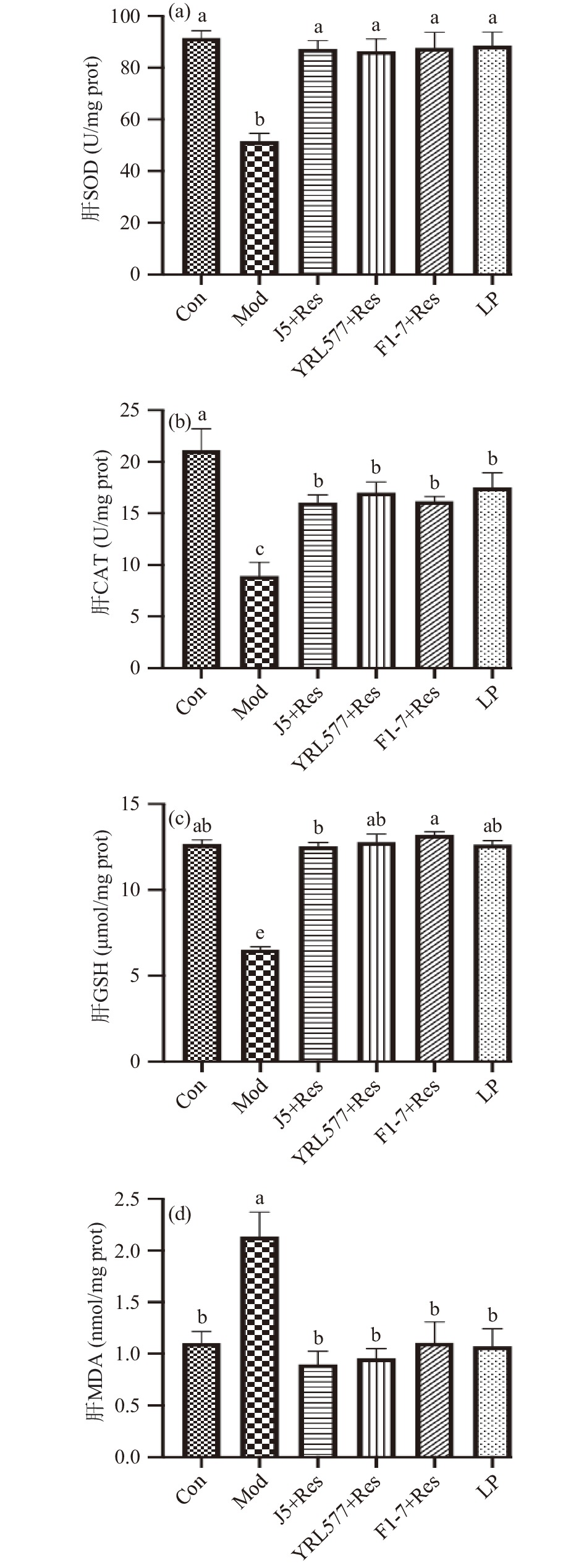
酒精摄入会导致酶(如SOD、CAT)和非酶抗氧化剂(如GSH)过度消耗,诱发肝脏氧化应激反应[21], 还会诱导肝细胞脂质自由基的形成和脂质的积累,从而导致脂质过氧化。MDA被用作氧化应激的生物标志物,以评估膜脂质过氧化的程度[22]。氧化应激和脂质过氧化均可增加酒精性肝损伤。图5(a~c)结果显示长期酒精摄入导致小鼠肝脏中SOD和CAT活性显著降低,GSH大量减少(P<0.05),但这一情况在四个预防干预组中的得到显著改善,其中,各干预组的SOD活性和GSH含量均与Con组无显著性差异(P>0.05),各干预组的CAT活性虽未恢复至正常水平但均显著高于Mod组(P<0.05)。同时为了评估脂质过氧化,测定了小鼠肝脏中的MDA含量。从图5d可知,小鼠肝脏中MDA水平在各干预组中均不具有显著性差异且与Con同一水平(P>0.05)。这些结果表明益生菌联合干预组具有较强的抗氧化活性,能够通过降低酒精导致的肝脏氧化应激和抑制脂质过氧化发挥对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用。
2.5 益生菌联合Res干预对小鼠肝脏氧化应激相关基因mRNA表达的影响
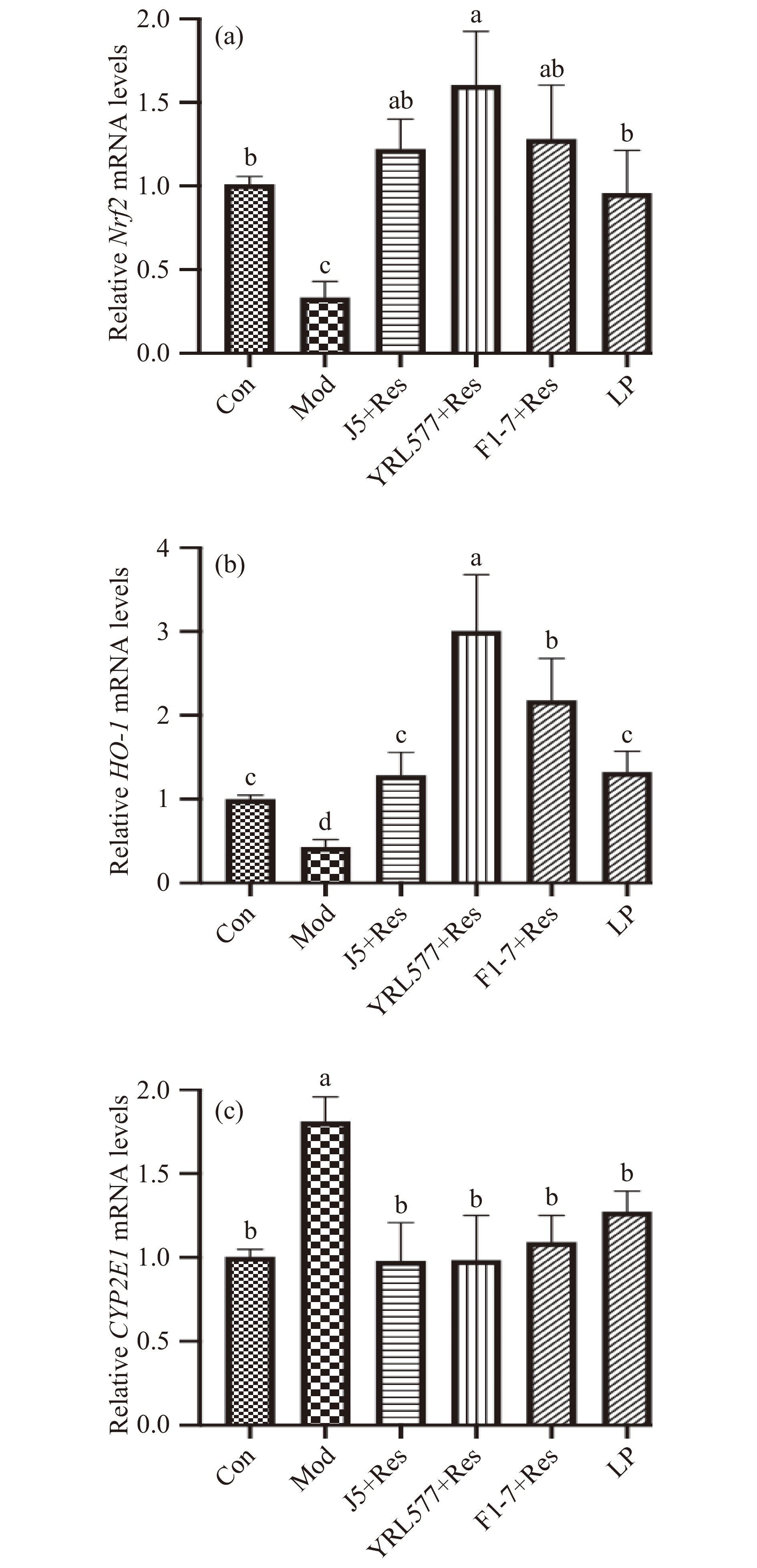
Nrf-2、HO-1、CYP2E1均是调控肝脏氧化应激反应的关键基因[23]。Nrf2是一种转录因子,对于抑制氧化应激和维持细胞内稳态非常重要[24-25],其在调节抗氧化基因表达方面起着关键作用,它的激活被认为是预防和治疗与氧化损伤有关疾病的一个有吸引力的策略,包括急性和慢性肝损伤[26]。HO-1是Nrf2调控的下游基因,一种防御蛋白,通过催化血红素降解保护细胞免受氧化应激损伤。从图6可知,长期酒精暴露显著抑制Nrf-2、HO-1基因并上调CYP2E1基因的表达(P<0.05);益生菌联合干预组及LP组均能显著上调基因Nrf2 、HO-1 mRNA表达,使之恢复正常,同时CYP2E1 mRNA表达量(J5+Res、YRL577+Res、F1-7+Re、LP)也较Mod组分别下调45.0%、39.8%、34.8%和29.8%。以上结果表明益生菌联合干预组可能通过调控Nrf-2、HO-1和CYP2E1基因的表达来改善机体的氧化应激状态。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究发现,益生菌联合白藜芦醇能够显著提高酒精喂养小鼠肝脏ADH、ALDH活性,并显著抑制CYP2E1活性及基因CYP2E1的mRNA表达(P<0.05),这对转变酒精氧化代谢途径进而减少自由基产生具有重要意义。前人研究报道,蓝莓联合益生菌对酒精性脂肪性肝病具有协同保护作用,这与两者联合后具有的强大抗氧化活性有关[27-28],但蓝莓汁成分复杂,难以明确解释其协同作用的分子机制。根据本团队前期对缓解酒精性肝损伤的活性物质筛选结果,最终选择白藜芦醇与三株潜在功能性益生菌联合作用。研究结果表明各益生菌联合干预组均能显著改善酒精导致的肝脏氧化和抗氧化失衡状态,提高肝脏的抗氧化防御体系,提高肝脏GSH含量和SOD、CAT活性,降低MDA水平,并使部分指标恢复至正常水平,因此,联合干预组表现出了强大的抗氧化能力,这对预防酒精导致的肝脏氧化应激具有重要作用。
Nrf2/HO-1通路是重要的内源性抗氧化应激通路,在维持机体抗氧化系统的生物学功能中起着不可或缺的作用[29]。酒精摄入会导致Nrf2/HO-1通路受到抑制[30],这种抑制作用在所有益生菌联合干预组中均得到显著改善,因此,推测其可能通过调控Nrf2/HO-1通路预防酒精性肝损伤。然而,本研究仅初步检测了Nrf2和HO-1的mRNA表达水平,接下来还需使用该信号通路的抑制剂或激活剂进行深入研究以验证推测。
本研究利用C57BL/6J小鼠构建慢性酒精性肝损伤模型探究益生菌联合白藜芦醇对慢性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用及可能机制,实验结果提示,益生菌联合白藜芦醇能够显著降低小鼠肝脏TG、TC含量和血清AST、ALT活性(P<0.05),提高肝脏酒精代谢酶ADH、ALDH活性并抑制肝脏CYP2E1活性及其mRNA表达,并增强肝脏抗氧化防御体系,使肝脏GSH含量和SOD、CAT活性显著提高(P<0.05),并能有效激活Nrf2/HO-1通路,推测益生菌联合白藜芦醇通过Nrf2/HO-1途径发挥对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用。综上所述,益生菌联合白藜芦醇对慢性酒精性肝损伤具有很好的预防作用,这为解酒护肝功能性产品的开发利用提供参考,未来具有广泛的应用前景。
-
表 1 逆转录聚合酶链反应的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
基因 正向 (5’-3’) 反向 (5’-3’) CYP2E1 AGGGGACATTCCTGTGTTCC TTACCCTGTTTCCCCATTCC Nrf-2 TTGGCAGAGACATTCCCATTTG AAACTTGCTCCATGTCCTGCTCTA HO-1 TGCAGGTGATGCTGACAGAGG GGGATGAGCTAGTGCTGATCTGG β-actin GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT -
[1] REHM J, MATHERS C, POPOVA S, et al. Alcohol and global health global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders[J]. Lancet,2009,373(9682):2223−2233. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60746-7
[2] LIEBER C S. Alcoholic fatty liver: Its pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Alcohol,2004,34(1):9−19. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2004.07.008
[3] CHENG C F, PAN T M. Protective effect of monascus-fermented red mold rice against alcoholic liver disease by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(18):9950−9957. doi: 10.1021/jf202577t
[4] LOUVET A, MATHURIN P. Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2015,12(4):231−242.
[5] ZHU J J, REN T T, ZHOU M Y, et al. The combination of blueberry juice and probiotics reduces apoptosis of alcoholic fatty liver of mice by affecting SIRT1 pathway[J]. Drug Design Development and Therapy,2016,10:1649−1661.
[6] TIAN F W, CHI F F, WANG G, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM1107 treatment ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury in a mouse model of chronic alcohol feeding[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2015,53(12):856−863. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-5239-5
[7] KASDALLAH-GRISSA A, MORNAGUI B, AOUANI E, et al. Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rat liver[J]. Life Sciences,2007,80(11):1033−1039. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.11.044
[8] NAM Y, KIM J H, KONKIT M, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of Lactococcus chungangensis CAU 1447 in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2019,102(12):10737−10747. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16891
[9] PETRELLA C, CARITO V, CARERE C, et al. Oxidative stress inhibition by resveratrol in alcohol-dependent mice[J]. Nutrition,2020,79−80:110783. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.110783
[10] LIANG X, ZHANG Z, ZHOU X H, et al. Probiotics improved hyperlipidemia in mice induced by a high cholesterol diet via downregulating FXR[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(11):9903−9911.
[11] ZHANG Z, ZHOU H, GUAN M Y, et al. Lactobacillus casei YRL577 combined with plant extracts reduce markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2021,125(10):1081−1091. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520003013
[12] ZHANG Z, ZHOU H, ZHOU X H, et al. Lactobacillus casei YRL577 ameliorates markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver and alters expression of genes within the intestinal bile acid pathway[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2021,125(5):521−529. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520003001
[13] GU Z, WU Y, WANG Y, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosusgranules dose-dependently balance intestinal microbiome disorders and ameliorate chronic alcohol-induced liver injury[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2020,23(2):114−124. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4357
[14] ZHANG M, WANG C, WANG C, et al. Enhanced AMPK phosphorylation contributes to the beneficial effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG supernatant on chronic-alcohol-induced fatty liver disease[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2015,26(4):337−44. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.10.016
[15] YANG J L, ZHU A, XIAO S, et al. Anthraquinones in the aqueous extract of cassiae semen cause liver injury in rats through lipid metabolism disorder[J]. Phytomedicine,2019,64:153059. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153059
[16] GUO Q H, ZHANG M, ZHOU G Y, et al. Highly sensitive simultaneous electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and catechol with three-dimensional N-doping carbon nanotube film electrode[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2016,760:15−23. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.11.034
[17] SUN H N, MU T H, LIU X L, et al. Purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L. ) anthocyanins: Preventive effect on acute and subacute alcoholic liver damage and dealcoholic effect[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(11):2364−2373. doi: 10.1021/jf405032f
[18] LEE H I, MCGREGOR R A, CHOI M S, et al. Low doses of curcumin protect alcohol-induced liver damage by modulation of the alcohol metabolic pathway, CYP2E1 and AMPK[J]. Life Sciences,2013,93(18-19):693−699. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.09.014
[19] BAJAJ J S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2019,16(4):235−246.
[20] YANG L L, WU D F, WANG X D, et al. Cytochrome P4502E1, oxidative stress, JNK and autophagy in acute alcohol-induced fatty liver[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2012,53(5):1170−1180. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.06.029
[21] LEUNG T M, NIETO N. CYP2E1 and oxidant stress in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2013,58(2):395−398. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.08.018
[22] DAI C, LI D, GONG L, et al. Curcumin ameliorates furazolidone-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in human hepatocyte L02 Cells by inhibiting ROS production and mitochondrial pathway[J]. Molecules,2016,21(8):1061. doi: 10.3390/molecules21081061
[23] SUN X, WANG P, YAO L P, et al. Paeonol alleviated acute alcohol-induced liver injury via SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-B signaling pathway[J]. 2018, 60: 110−117.
[24] HE M, PAN H, CHANG R C, et al. Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway contributes to the protective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in the rodent retina after ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage[J]. PloS One,2014,9(1):e84800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084800
[25] NGUYEN T, NIOI P, PICKETT C B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2009,284(20):13291−13295. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R900010200
[26] CAO M, WANG H, GUO L, et al. Dibenzoylmethane protects against CCl4-induced acute liver injury by activating Nrf2 via JNK, AMPK, and calcium signaling[J]. AAPS Journal,2017,19(6):1703−1714. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0133-1
[27] 沈艳艳, 任婷婷. 蓝莓及蓝莓联合益生菌对酒精性脂肪性肝病的保护作用[J]. 贵阳医学院学报,2018,43(11):1241−1246,1251. [SHEN Y Y, REN T T. Effects of dietary blueberry and blueberry combined with probiotics on alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Journal of Guiyang Medical College,2018,43(11):1241−1246,1251. [28] CHENG M, ZHU J, REN T, et al. The combination of blueberry juice and probiotics reduces apoptosis of alcoholic fatty liver of mice by affecting SIRT1 pathway[J]. Drug Design Development & Therapy,2016,10:1649−1661.
[29] DAI W B, CHEN C, FENG H T, et al. Protection of ficus pandurata hance against acute alcohol-induced liver damage in mice via suppressing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,275:114140. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114140
[30] HONG S, KIM Y, SUNG J, et al. Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) protects hepatocytes against alcohol-induced damage through Nrf2 activation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2020,2020(2):1−8.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王玉净,都治香,张霞,王旭,王娜. 沙棘黄酮通过调控TLR4/NF-κB信号通路改善大鼠多囊卵巢综合征的作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(16): 340-347 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王杰,常晨城,杨彦达,郭丽丽,张景萍,付绍印,石彩霞,张文广. 黄酮在反刍动物生产中的应用研究进展. 饲料研究. 2023(12): 144-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈美庆,朱卫丰,管咏梅,冯育林,张艳丽,景秀村,彭万钱,欧阳辉,李琼. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术分析葛根配方颗粒的化学成分. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(19): 176-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



