Effects of Different Treatments on Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Rice Buckwheat
-
摘要: 为研究不同处理方式对米荞营养组成和生物活性的影响,以西盟米荞为原料,分析发芽、发酵、蒸制和蒸制后发酵四种处理方式对米荞的还原糖、蛋白质、游离氨基酸、γ-氨基丁酸、总酚、总黄酮等营养成分及抗氧化活性的影响。结果表明,米荞经发芽、发酵、蒸制和蒸制后发酵四种方式处理后,总酚、总黄酮含量及清除1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)自由基能力和铁离子还原能力均高于未处理米荞,且由相关性分析得知,总酚和总黄酮含量与DPPH自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力具有极显著相关性(P<0.01);而蒸制处理后,还原糖、γ-氨基丁酸和芦丁含量相比于未处理的米荞均有所下降。在四种处理方式中,相比于未处理的米荞,经乳酸菌发酵处理的生米荞最佳,其还原糖、γ-氨基丁酸、总酚、总黄酮、芦丁含量最高,分别为3.62%、4.84 mg/g、13.63 mg/g、4.63%、39.80 mg/g,且DPPH自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力最强。因此,发酵处理是较好的加工方式,可进一步改善米荞的营养组成及生物活性,可为米荞精深加工和高值化利用提供借鉴。Abstract: In order to study the influence of different treatment methods on the nutritional composition and biological activity of rice buckwheat, germination, fermentation, steaming and fermentation after steaming on the reducing sugar, protein, free amino acids, γ-aminobutyric acid, total phenol, total flavonoids and antioxidant activity. The results showed that after four treatments the content of total polyphenols, total flavonoids, scavenging DPPH free radicals and iron ion reduction ability of rice buckwheat were higher than that of untreated rice buckwheat, while after steamed processing the content of reducing sugar, γ-aminobutyric acid and rutin decreased compared with untreated rice buckwheat. By correlation analysis, the contents of total phenols and total flavonoids were significantly correlated with DPPH free radical scavenging ability and iron ion reducing ability (P<0.01). Among then, the raw rice buckwheat was the best treated by fermentation of lactic acid bacteria, with the highest content of reducing sugar, γ-aminobutyric acid, total phenol, total flavonoids, rutin, respectively, 3.62%, 4.84 mg/g, 13.63 mg/g, 4.63%, 39.80 mg/g and DPPH radical scavenging ability andiron ion reduction ability were the strongest. Therefore, fermentation treatment is a good processing method, which can further improve the nutritional composition and biological activity of rice buckwheat, and can provide a reference for the deep processing and high-value utilization of rice buckwheat.
-
Keywords:
- rice buckwheat /
- germination /
- fermentation /
- steaming /
- nutritional ingredient /
- antioxidant activity
-
荞麦主要有4种栽培种,分别为米荞、苦荞、翅荞和甜荞。米荞,是一种长得像米又似荞且可食用的作物,主要分布于我国云南省普洱、临沧、西双版纳等地。“西盟米荞”是米荞中的精品,在云南西盟县广泛分布,种植历史悠久。西盟米荞具有较高的营养价值,籽粒中无机物的含量约为小麦和精白米的2~3倍,还含有其他谷物中没有的叶绿素和芦丁,具有降低胆固醇和人体血脂的功效[1]。据云南省农业科学院研究表明,西盟米荞含有丰富的芦丁、微量元素及人体必需氨基酸,其中,芦丁、铁、钙、蛋白质含量高于其他同类荞食品,有“荞中之王”的美誉,是集营养、保健为一体的优质粮食作物[2]。
荞麦是一种假谷物,具有与谷物类似的栽培方法和利用方式[3]。虽然荞麦的营养价值较高,但由于其籽粒中含有高活性的蛋白酶抑制剂、抗性淀粉等营养物质,使人体对其的吸收消化率较低,过量食用还会导致胃胀气等不良症状[4]。而发芽、发酵和蒸煮等处理方式,能使荞麦的营养价值和利用率提高。董晓萌等[5]的研究表明萌发处理能使苦荞茶的总黄酮、γ-氨基丁酸含量提高并改变其感官品质,使营养价值大幅提升。陈江[6]以黑曲霉为菌种对苦荞叶进行固态发酵,结果表明发酵处理能使苦荞叶抗氧化活性提高,且苦荞叶中的总多酚、总黄酮、芦丁和槲皮素的含量与抗氧化能力之间存在相关性。马艺超[7]研究蒸制、煮制、烤制等不同热加工方式对苦荞制品营养成分的影响,结果表明蒸制比烤制和煮制处理更能保留苦荞制品的营养成分且黄酮释放量较高,体外消化后的抗氧化能力更强。现今,对荞麦的研究主要聚焦在苦荞上,而对荞麦中具有较高营养价值的其他栽培种如西盟米荞鲜有研究。
发芽、发酵、热处理等是荞麦的重要加工方式,在荞麦深加工方面展现出巨大的潜力。发芽、发酵等处理可以降低荞麦内的抗营养因子水平,改善其营养成分及感官品质,进一步提高荞麦的生物活性。而发芽、发酵、热处理等加工方式对西盟米荞营养价值的影响暂未见研究。因此,该文对西盟米荞进行发芽、乳酸菌发酵、蒸制和蒸制后发酵4种处理,研究不同处理方式对米荞营养成分和抗氧化活性的影响。乳酸芽孢杆菌(Bacillus sp.)DU-106分离于传统的发酵奶酪,具有良好的发酵性能,本实验室相关研究已表明该菌株具有调节肠道菌群、增强免疫和降血脂等功效[8-9]。而植物乳杆菌有较强的发酵能力,与其他益生菌有协同作用,故采用乳酸芽孢杆菌和植物乳杆菌进行复配作为米荞发酵的菌种。研究不同处理方式对米荞营养成分及生理活性的影响,旨在提高米荞的营养价值及功能特性,为米荞的深加工及功能性产品研发提供一定的理论基础,以促进米荞的高值化利用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
米荞 云南省普洱市西盟县;DU-106乳酸芽孢杆菌(Bacillus sp.)、植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum) 现由华南农业大学新资源食品及功能性原料评价及研究中心鉴定及保藏,并委托广州市微生物所制成1×1012 CFU/g的菌粉,将二者菌粉按12:1进行复配得实验所用的菌粉;芦丁、槲皮素 标准品,中国食品药品检定研究院;葡萄糖、福林-酚、碳酸钠、3,5-二硝基水杨酸、硝酸铝、亚硝酸钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、重蒸苯酚 美国Sigma公司;没食子酸 标准品,上海化科实验器材有限公司;5-磺基水杨酸 烟台健硕化工有限公司。
UV759型紫外分光光度计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;ANKE TDL-5-A型离心机 上海安亭分析仪器有限责任公司;Labserv K3型酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;L-8900型全自动氨基酸分析仪 日本日立公司;Agilent 1260型高效液相色谱 安捷伦科技有限公司;JDS-BA型恒温水浴振荡器 精达仪器有限公司;Elementar rapid N exceed型杜马斯定氮仪 Elementara公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 常州市华普达数字仪器有限公司;DHP-600型恒温培养箱 北京市永光明医疗仪器厂;FD-1型真空冷冻干燥机 郑州科创仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
生米荞粉:挑选没有破损,颗粒大小基本一致,成熟饱满的米荞,用清水洗净后,低温冷冻干燥,粉碎,过80目筛。
生米荞发芽:参考周一鸣等[10]的方法,略有修改。取一定量的米荞清洗后,用体积分数5%的次氯酸钠浸泡15 min后用清水洗净,室温下浸泡12 h,置于铺有两层滤纸的培养皿中,于温度20 ℃、相对湿度75%的环境中萌发3 d,每d三次向培养皿内喷水,使滤纸保持湿润状态。米荞长出小芽时,视为萌发成功。挑选萌发成功的米荞于-20 ℃冰箱保存,低温冷冻干燥,粉碎,过80目筛。
生米荞发酵:称量0.5 g Bacillus sp. DU-106和植物乳杆菌复配菌粉,于0.9%生理盐水中活化。取60 g米荞于锥形瓶中,料水比1:3(g/mL),白砂糖添加量为2%。复合菌粉按2%接种,置于28 ℃恒温培养箱中培养3 d,发酵结束后冻干、粉碎,过80目筛,备用。
熟米荞:在蒸锅中加入去离子水,水沸腾后,将装有60 g米荞的蒸笼置于蒸锅内,蒸制20 min,蒸煮结束后于−20 ℃冰箱冻存,低温冷冻干燥,粉碎,过80目筛。
熟米荞发酵:蒸制结束后,进行发酵处理,处理方法同“生米荞发酵”。
1.2.2 还原糖的测定
采用3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS)法测定。以葡萄糖为标准物质,分别吸取0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4、1.6 mL葡萄糖标准溶液(1 mg/mL)于25 mL比色管中,补水至2 mL,加1.5 mL DNS溶液,混匀,于沸水浴中加热5 min,取出,冷却至室温后用水定容至25 mL,在540 nm处测定吸光度。标准曲线回归方程为y=0.3593x−0.0102,决定系数R2=0.9988。
样品中还原糖的提取:取1 g样品放入50 mL锥形瓶中,用少量蒸馏水搅拌至糊状,再加入25 mL蒸馏水,搅拌均匀,于50 ℃水浴浸提20 min。抽滤,用蒸馏水清洗滤渣,收集滤液,加水定容至50 mL。
还原糖含量的测定:取待测液1 mL置于25 mL比色管中,加1 mL蒸馏水和1.5 mL DNS溶液,摇匀后在沸水浴加热5 min,冷却至室温后加水定容至25 mL,于波长540 nm下测定吸光度,根据下式计算样品的还原糖含量。
还原糖含量(%)=C×V1m×V2×100 式中:C表示查标准曲线所得水解后还原糖含量,mg;V1表示提取液总体积,mL;V2表示测定时取用液体积,mL;m表示样品质量,mg。
1.2.3 蛋白质含量的测定
参考王钦权等[11]的方法,略有修改。将一定量的米荞样品装入锡箔纸中,包好并压走空气,记录重量。将样品放入杜马斯定氮仪的样品盘中,自动进样检测,仪器软件根据内置的校准曲线,从测得的峰面积及样品重量,得出每个样品的氮含量(%)。再用蛋白质换算因子(6.25)将氮含量(%)换算成蛋白质含量,以百分比(%)表示。
1.2.4 游离氨基酸含量的测定
取0.1 g样品于离心管中,加入3 mL 5%磺基水杨酸溶液,振荡混匀后静置1 h,于室温下12000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液用0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,滤液采用全自动氨基酸分析仪进行测定。
1.2.5 γ-氨基丁酸含量的测定
参考范霞等[12]的方法,略有修改。标准曲线回归方程为y=1.9963x+0.0623,R2=0.9992。取0.25 g米荞样品,用蒸馏水溶解后定容至25 mL,60 ℃超声浸提1 h,4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液后经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,待测。取0.5 mL待测液,加入0.5 mL硼酸盐缓冲液和1 mL重蒸苯酚,充分摇匀,2~3 min后加入1 mL次氯酸钠溶液,混匀后沸水浴10 min,取出立即冰浴20 min,不断振荡,出现蓝绿色化合物,加入60%乙醇溶液2 mL,再次振荡均匀,静置后于645 nm波长处的吸光度。
GABA含量(mg/g)=C×V×Nm 式中:C表示GABA浓度,mg/mL;V表示提取液体积,mL;N表示稀释倍数;m表示样品质量,g。
1.2.6 总黄酮含量的测定
参照国标NY/T 1295-2007《荞麦及其制品中总黄酮含量的测定》进行测定。
1.2.7 芦丁和槲皮素含量的测定
参考迟明艳等[13]的实验方法,略有修改。混合对照品溶液的制备:称取槲皮素对照品2 mg,置于10 mL容量瓶中,用甲醇定容,得槲皮素对照品溶液;称取芦丁对照品8 mg,置于10 mL容量瓶中,加槲皮素对照品溶液1 mL,用甲醇定容,制成芦丁、槲皮素质量浓度分别为0.8018、0.0198 mg/mL的混合对照品溶液。
供试品溶液的制备:称量0.5 g米荞样品置于三角瓶中,加入70%乙醇25 mL,称定质量,超声处理30 min,放至室温,加70%乙醇补足减失的质量,摇匀,抽滤,10000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,即得供试品溶液。
色谱条件:色谱柱为Agilent Zorbaxsb-C18(150 mm×4.6 m,5μm);流动相:甲醇(A)-0.4%磷酸(B),梯度洗脱(0~7 min,20%→40% A;7~14 min,40%→60% A;14~18 min,60%→90% A;18~20 min,90%→20% A),后运行时间8 min;柱温:40 ℃;检测波长:360 nm。槲皮素的出峰时间为10.13 min,芦丁出峰时间为13.72 min。
芦丁/槲皮素含量(mg/g)=C×V×Nm 式中:C表示由标准曲线中芦丁、槲皮素的质量浓度,mg/mL;V表示提取液总体积,mL;N表示稀释倍数;m表示样品质量,g。
1.2.8 总酚含量的测定
称量没食子酸标准品25 mg,用水溶解后定容于250 mL容量瓶中,得到0.1 mg/mL的标准贮备溶液。分别移取没食子酸标准储备溶液0.00、0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00、1.25、1.50 mL置于10 mL具塞试管中,分别加入1 mL福林-酚试剂,摇匀后再分别加入2 mL 12% Na2CO3溶液,用水定容至10 mL,摇匀。室温下避光反应1 h后,在765 nm波长下测定吸光度。以没食子酸标准溶液的浓度为横坐标,以吸光度为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线y=76.705x+0.1026,R2=0.9989。
称取0.5 g样品于25 mL锥形瓶中,加入10 mL 60%乙醇溶液,混匀,在75 ℃下超声50 min。提取液以3000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液,量取提取液体积。吸取1 mL稀释了5倍的总多酚提取液于10 mL具塞试管中,分别加入1 mL福林-酚试剂及2 mL 12%碳酸钠溶液并用60%乙醇定容至刻度,在室温下避光反应1 h,在765 nm波长处测定样品的吸光度。
总酚(mg/g)=C×V×Nm 式中:C表示由标准曲线得出样品中总酚的质量浓度,mg/mL;V表示提取液总体积,mL;N表示稀释倍数;m表示样品质量,g。
1.2.9 不同处理方式对米荞抗氧化能力的影响
1.2.9.1 米荞提取液的制备
参考杨红叶等[14]的方法,略有修改。称取0.5 g米荞样品,按料液比1:25加入50%丙酮,于55 ℃下超声25 min,离心,收集上清液。反复提取两次,合并滤液,用50%丙酮定容至50 mL,置于冰箱冷藏,备用。
1.2.9.2 DPPH自由基清除率的测定
参考赵武等[15]的实验方法,略有修改。称取19.7 mg DPPH用50%丙酮溶解并定容至50 mL,于4 ℃下避光保存,即得DPPH储备液,备用。使用前,量取5 mL DPPH储备液用50%丙酮定容至50 mL,制成浓度为0.1 mol/L的工作液。吸取2 mL不同浓度的样液,加入2 mL DPPH溶液,涡旋摇匀,避光30 min后于510 nm处测定吸光度A1。清除率公式为:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A3A2)×100 式中:
A1 表示样品测定的吸光值;A2 为50%丙酮代替样品的吸光值;A3 为50%丙酮代替DPPH溶液的吸光值。1.2.9.3 Fe3+还原能力的测定
参考赵武等[15]的实验方法,略有修改。移取2.5 mL不同浓度的样品溶液于试管中,加入2.5 mL 10%铁氰化钾和2.5 mL pH6.6的磷酸缓冲液,混匀后于50 ℃水浴锅中水浴20 min,水浴结束后立马转移到冰水中冷却至室温。加入2.5 mL 10%三氯乙酸,摇匀后离心10 min,再取5 mL上清液于另一支试管中,加入1 mL 1%三氯化铁混匀后静置1 min,于700 nm测定吸光值,吸光值代表抗氧化能力。
1.3 数据处理
试验均进行3次重复操作,所有数据用平均值±标准差表示。采用Origin 8.0等软件对数据进行处理与分析。
2. 结果与分析
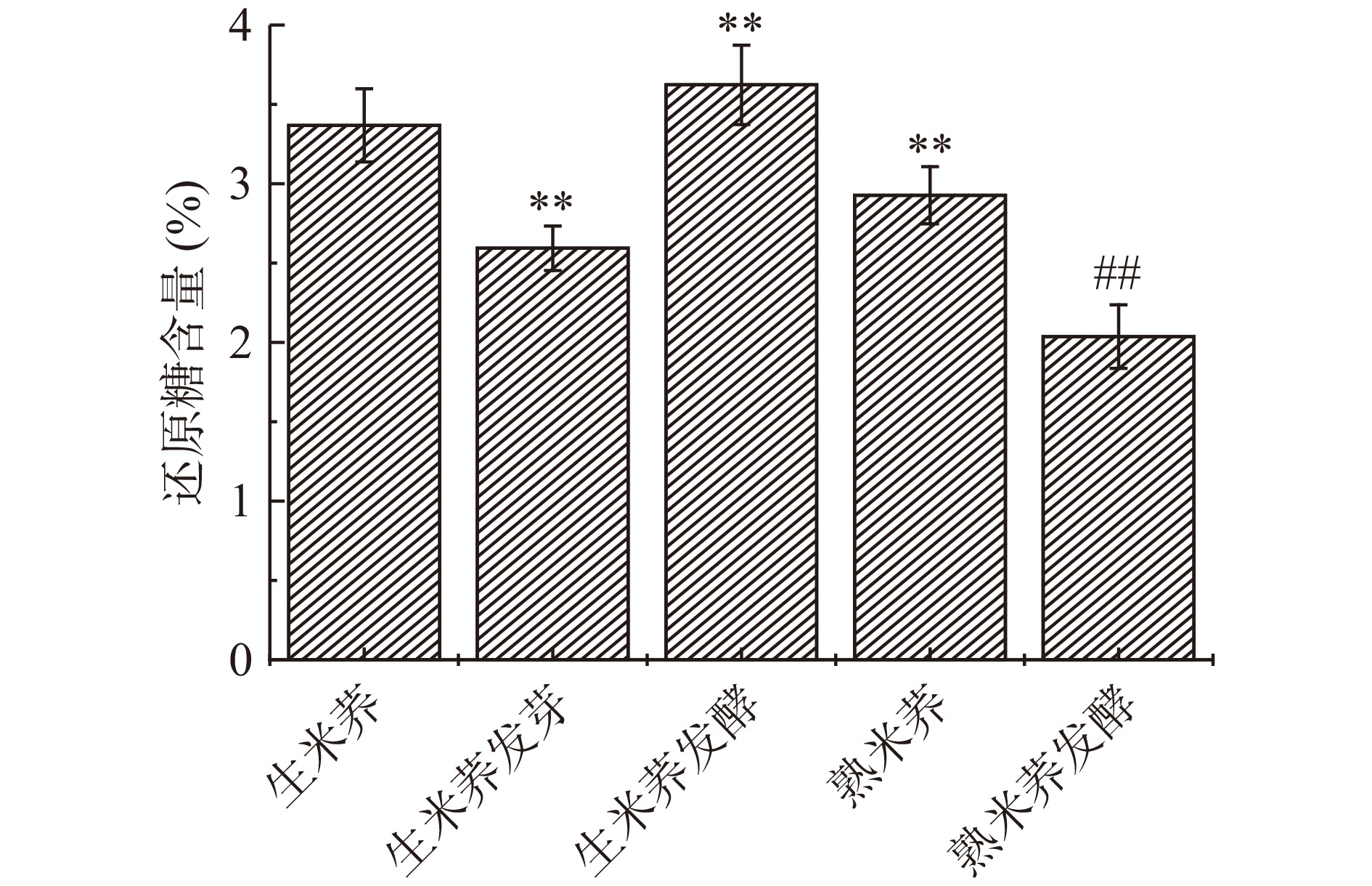
2.1 不同处理方式对米荞还原糖含量的影响
不同处理方式对米荞还原糖含量的影响如图1所示。米荞发芽过程中存在复杂的生理反应,如蛋白质、脂类和糖类的转化,发芽米荞的还原糖含量极显著降低,由3.36%下降至2.59%(P<0.01),相比于生米荞下降了22.92%,与郑丽娜等[16]的研究结果一致。而经发酵处理后的生米荞还原糖含量增加至3.62%,主要是因为乳酸菌发酵可利用自身酶系降解米荞中的淀粉等组分生成果糖、葡萄糖和半乳糖等还原糖,使还原糖含量增加[17],为米荞提供发酵所需能量和其他需求。蒸制过程中还原糖与α-氨基酸会发生美拉德反应[18],消耗还原糖,故蒸煮处理使米荞还原糖含量极显著下降(P<0.01)。而对蒸制后的米荞进行发酵处理会进一步导致还原糖含量下降至2.03%(P<0.01),这可能与乳酸菌在发酵过程中可将糖类物质转化为有机酸使还原糖含量下降有关。
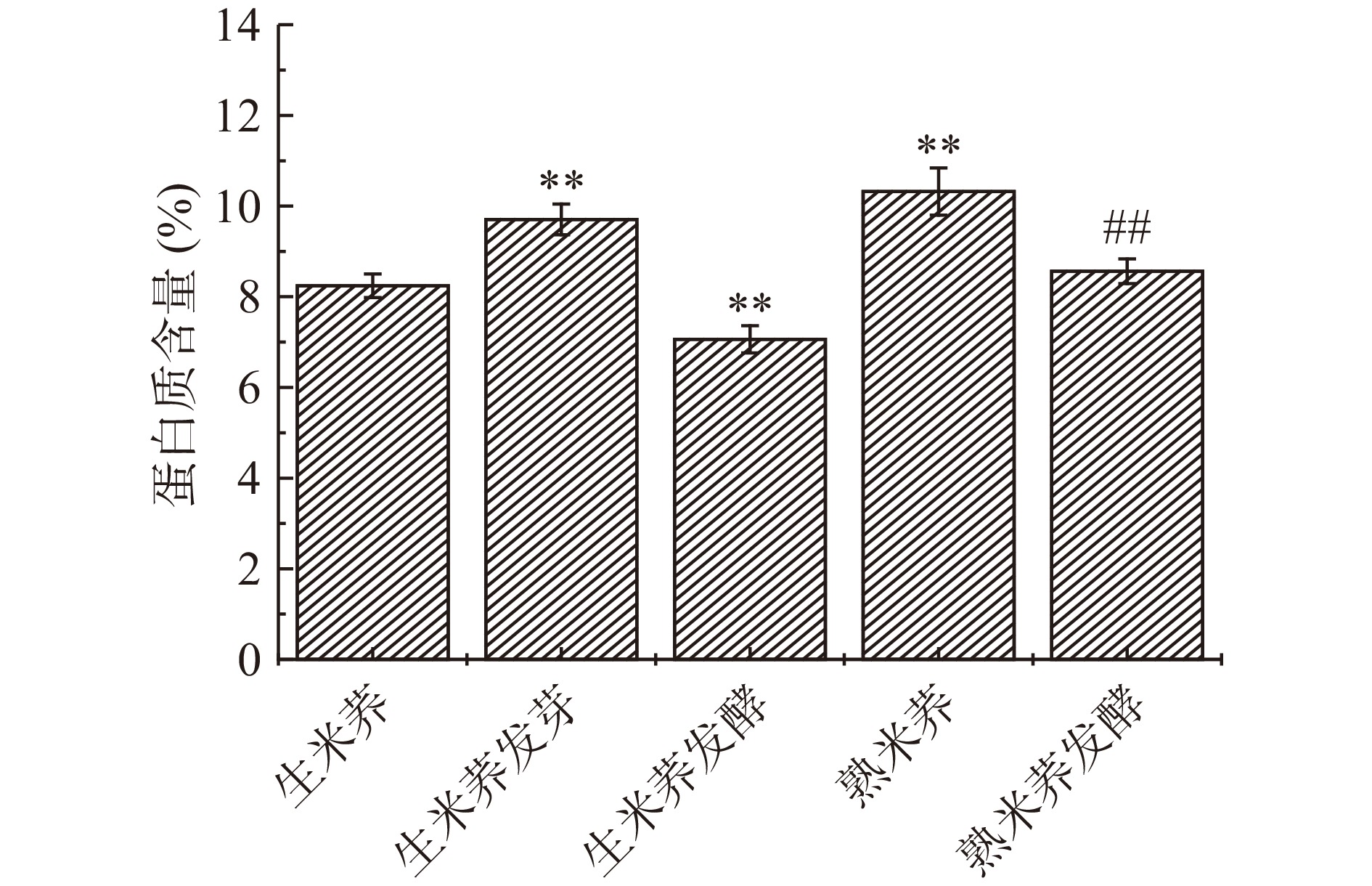
2.2 不同处理方式对米荞蛋白质含量的影响
不同处理方式对米荞蛋白质含量的影响如图2所示。由图2可得,经发芽处理后,米荞的蛋白质含量相比于未发芽的米荞增加约17.75%,主要是因为萌发过程中,需要消耗大量的供能物质,使总干基质量减少,导致蛋白质含量相对增加[19]。LEE等[20]的研究表明对大豆进行发芽处理也有利于蛋白质的合成,与本文的研究结果相类似。适当的蒸制处理能使米荞蛋白质含量由8.24%增加至10.32%。而对生米荞和熟米荞进行乳酸菌发酵处理时,蛋白质含量均有不同程度的降低,分别下降了14.34%和20.53%,该结果主要是因为发酵处理会使蛋白质发生水解,产生更多的短肽、多肽和游离氨基酸等非蛋白肽[21],从而导致蛋白质含量降低。
2.3 不同处理方式对米荞游离氨基酸含量的影响
不同处理方式对米荞游离氨基酸含量的影响如表1所示。米荞发芽前的游离氨基酸含量为(2026.77±16.52)μg/g,发芽3 d后游离氨基酸含量显著降低(P<0.05)。米荞在萌发过程中,细胞不断分裂,合成较多的核酸或含氮物质,需要米荞储存蛋白质提供氮源,从而导致游离氨基酸总量降低[22]。但经发芽处理后,米荞的必需氨基酸占比由21.26%增加至42.58%,这与靳颖[22]研究的大豆发芽过程中必需氨基酸的变化趋势相一致。发芽米荞中的甲硫氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸和赖氨酸等必需氨基酸含量均有不同程度的增加,说明发芽处理能使米荞蛋白质营养价值提高。
表 1 不同处理方式对米荞游离氨基酸含量的影响(μg/g )Table 1. Effects of different treatments on free amino acid content of rice buckwheat(μg/g)游离氨基酸含量 生米荞 生米荞发芽 生米荞发酵 熟米荞 熟米荞发酵 苯丙氨酸* 53.34±0.10b 37.29±0.54c 173.07±1.53a 34.89±0.91c 0.24±0.06d 甲硫氨酸* 8.82±0.15c 21.16±0.52b 39.15±1.10a 4.13±0.23d 0.159±0.10e 异亮氨酸* 22.55±0.88b 28.05±0.64b 68.70±0.24a 22.91±0.42b 0.4305±0.02c 亮氨酸* 47.60±1.22b 54.75±0.63b 233.22±0.12a 26.12±0.61c 8.64±0.25d 赖氨酸* 50.61±1.52c 54.98±0.54c 79.44±0.65a 65.87±1.51b 8.55±0.22d 苏氨酸* 26.58±0.48a 22.28±0.37a 31.16±0.12a 28.04±0.23a 1.03±0.22b 缬氨酸* 221.43±1.39b 50.61±0.57d 120.12±0.63c 273.41±2.02a 33.05±1.29d 丝氨酸 64.65±1.43a 26.87±0.71b 7.10±0.02c 76.62±1.64a 0.65±0.02d 甘氨酸 104.85±1.38a 51.44±0.44b 49.85±0.53b 116.40±1.35a 20.48±1.12c 谷氨酸 246.41±1.02a 91.43±1.41b 271.58±1.03a 279.24±1.04a 5.64±0.21c 组氨酸 39.15±0.81b 17.43±0.52c 18.59±0.08c 65.88±0.89a 10.43±0.43d 丙氨酸 92.66±1.46a 26.37±0.70b 87.26±0.24a 100.89±1.67a 16.69±0.64c 精氨酸 789.66±2.39b 72.29±0.83e 240.62±2.98c 1175.82±1.99a 199.91±1.89d 脯氨酸 15.41±0.63b 9.24±0.24c 44.39±0.36a 10.59±0.52c 10.49±0.83c 半胱氨酸 85.71±1.26b 1.65±0.21c 13.52±0.03c 117.36±1.46a 19.59±0.47c 酪氨酸 35.40±0.12b 39.20±1.13b 115.31±0.25a 38.52±0.74b 0.45±0.01c 天冬氨酸 121.97±0.28b 27.06±1.12c 119.01±0.34b 138.03±1.93a 5.415±0.83d 氨基酸总量 2026.77±16.52b 632.1±11.12d 1734.66±11.28c 2574.71±19.09a 342.10±13.20e 必需氨基酸总量 430.93±5.74b 269.15±3.81c 744.85±5.36a 455.36±5.82b 52.09±4.26d 必需氨基酸总量/氨基酸总量 21.26% 42.58% 43.94% 17.68% 15.20% 注:*为必需氨基酸;同行不同字母代表显著性差异(P<0.05)。 同样,对生米荞进行发酵处理后,游离氨基酸总量下降,但必需氨基酸占比明显增加。在7种必需氨基酸中,除了缬氨酸的含量由(221.43±1.39)μg/g下降至(120.12±0.63)μg/g,其余必需氨基酸的含量均增加,其中,苯丙氨酸和亮氨酸的含量增加最显著(P<0.05),其他谷物中缺乏的赖氨酸和豆类中缺乏的甲硫氨酸含量分别增加至(79.44±0.65)μg/g和(39.15±1.10)μg/g,说明发酵处理能提高米荞的营养利用率。生米荞发酵过程中乳酸菌自身分泌的蛋白酶可促使米荞蛋白分解成氨基酸,且乳酸菌的自身代谢也可促进氨基酸含量的增加,这均能使米荞的必需氨基酸含量增加[23]。刘磊等[24]研究发现5种乳酸菌复合发酵使脱脂米糠提取物的必需氨基酸含量提高了21.23%,与本文研究结果相一致。对米荞进行蒸制处理时游离氨基酸含量最高,为(2574.71±19.09)μg/g,但必需氨基酸占比相比于生米荞下降至17.68%。而对熟米荞进行乳酸菌发酵处理时,游离氨基酸总量显著下降(P<0.05),仅为(342.10±13.20)μg/g,必需氨基酸占比也下降至15.20%。
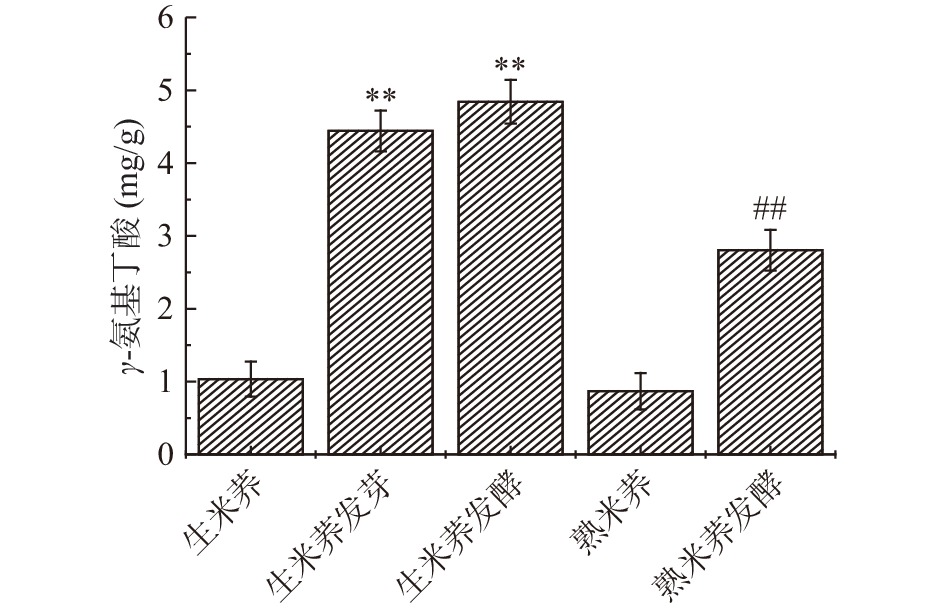
2.4 不同处理方式对米荞的γ-氨基丁酸含量的影响
γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)是一种非蛋白氨基酸,是中央神经系统的一种抑制性神经递质,是谷氨酸在谷氨酸脱氢酶作用下形成的,具有降压、改善肝功能等作用[25]。由图3可知,发芽处理能使米荞中的γ-氨基丁酸含量极显著增加(P<0.01),相比于未发芽的米荞γ-氨基丁酸含量增加了约4倍,可能与米荞在发芽处理过程中内部的谷氨酸脱氢酶被激活后利用米荞本身所含的谷氨酸作为底物从而生成γ-氨基丁酸有关[26-27]。蒸煮处理会使米荞中γ-氨基丁酸含量下降,主要是因为γ-氨基丁酸在高温环境中易被破坏。而乳酸菌发酵处理均能使生米荞和熟米荞的γ-氨基丁酸含量极显著增加(P<0.01),分别增加至4.84和2.81 mg/g,其中生米荞发酵的γ-氨基丁酸含量最高,约为生米荞的5倍。增加的γ-氨基丁酸可能是由两种途径生成的,一种是在发酵过程中随着乳酸菌的生长代谢,蛋白酶活性会积累,从而水解蛋白质生成一定量的谷氨酸;另一种是乳酸菌在发酵过程中直接激活了潜在的谷氨酸脱氢酶,催化谷氨酸脱去α-羧基生成γ-氨基丁酸[28]。由此可得,发芽、发酵处理均能使米荞的γ-氨基丁酸含量增加,且对生米荞进行发酵处理γ-氨基丁酸的含量最高。
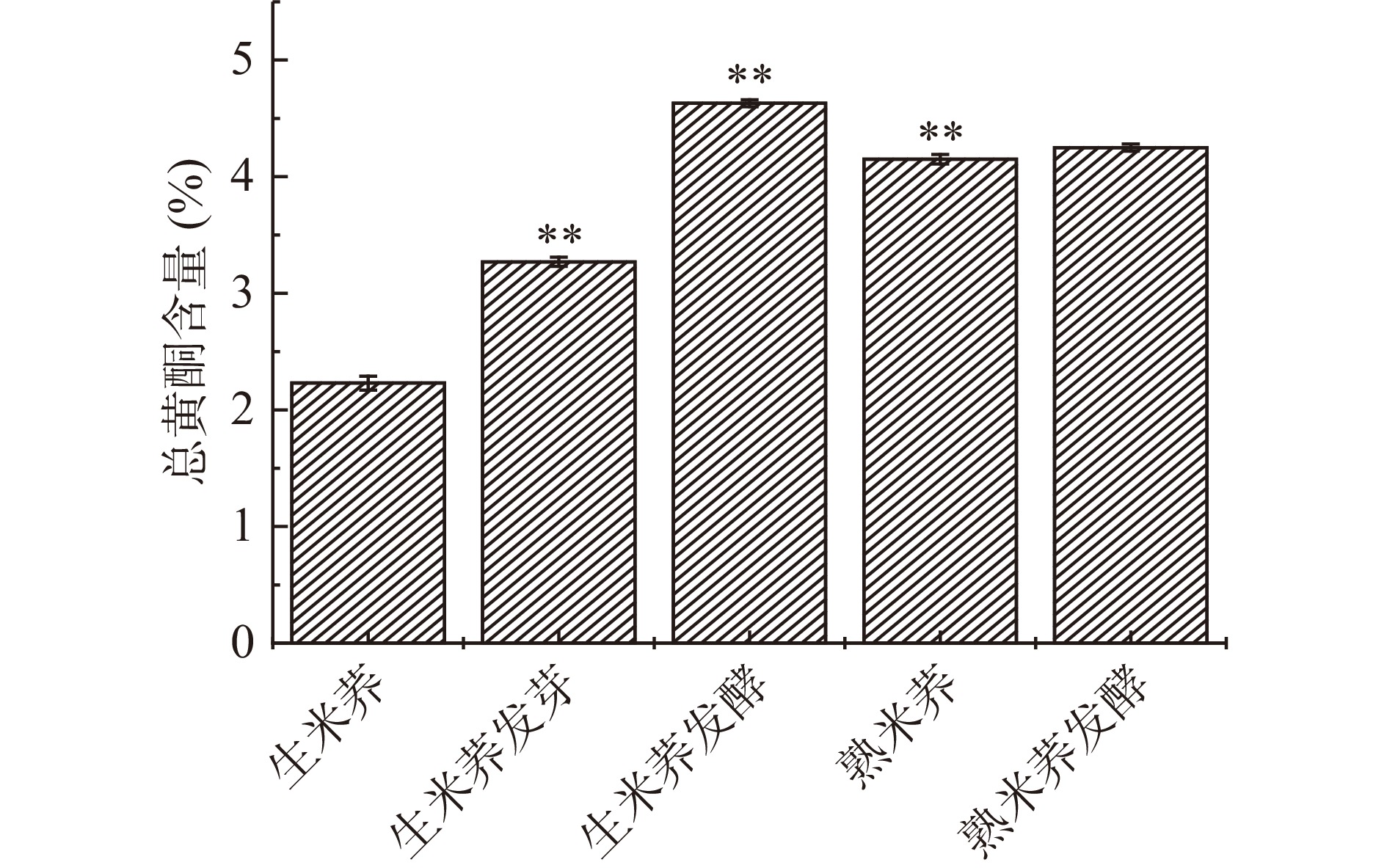
2.5 不同处理方式对米荞总黄酮含量的影响
不同处理方式对米荞总黄酮含量影响如图4所示。对米荞进行发芽处理总黄酮含量极显著增加(P<0.01),主要因为在浸泡发芽过程中,大量结合态的黄酮类化合物被酶水解而释放,使黄酮含量增加[29]。黄酮类物质的合成受查尔酮异构酶(CHI)和苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)等关键酶共同作用,在特定酶的作用下,植物会向着某一特定黄酮类化合物方向进行合成[30]。相关研究表明,在发芽的苦荞中CHI和PAL的活性与总黄酮含量呈正相关[31]。经乳酸菌发酵后,生米荞的总黄酮含量显著增加(P<0.01),由2.23%增加至4.63%,乳酸菌发酵过程中会产生多种活性较强的酶系,而细胞壁的纤维等物质会被这些酶系代谢,从而促进黄酮类物质的释放[32]。蒸制处理后,米荞的总黄酮含量由2.23%极显著增加至4.15%(P<0.01)。在蒸制过程中,米荞内部结构会遭到破坏,蛋白质发生变性,淀粉糊化,与大分子物质结合的结合黄酮类化合物释放,导致总黄酮含量上升[7]。对熟米荞再进行发酵处理时,也能增加总黄酮含量,但无显著性差(P>0.05)。由上可得,不同处理方式均能使米荞的黄酮含量增加,且对生米荞进行发酵处理时黄酮含量增加最显著(P<0.01)。
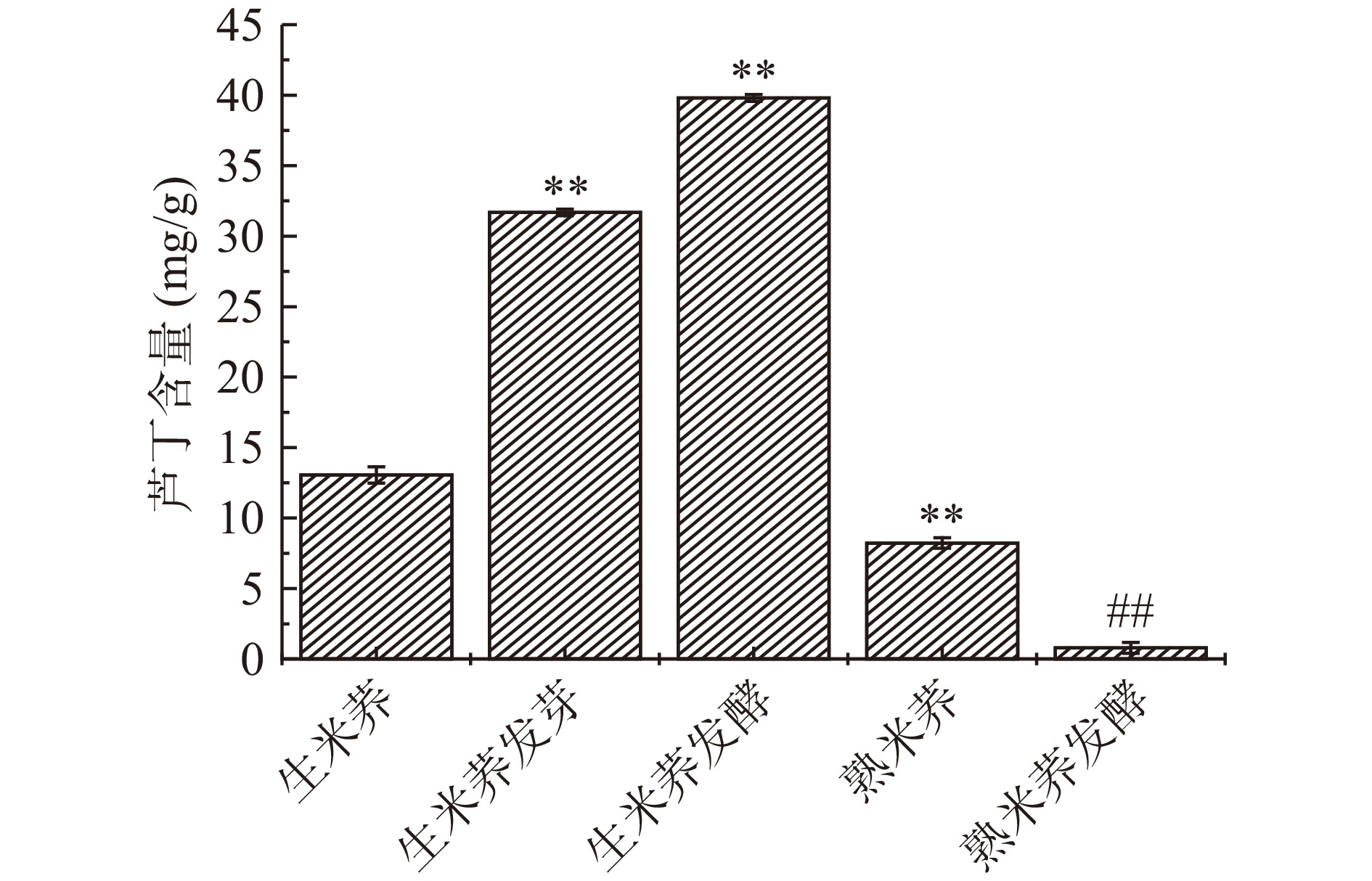
2.6 不同处理方式对米荞芦丁和槲皮素的含量
不同处理方式对米荞的芦丁和槲皮素含量的影响如图5和图6所示。生米荞的芦丁含量为13.05 mg/g,槲皮素含量为1.65 mg/g;蒸煮后芦丁含量下降至8.23 mg/g,槲皮素的含量增加至5.64 mg/g。研究表明,蒸煮过程会使米荞内的芦丁降解酶活性增加,从而迅速分解芦丁产生芸香糖和槲皮素,加快芦丁向槲皮素转化,导致芦丁含量下降,槲皮素含量增加[7]。对生米荞进行发芽、发酵处理均能使芦丁含量有不同程度的增加,其中,生米荞发酵的芦丁含量最高为39.80 mg/g;而经发芽、发酵处理的生米荞槲皮素含量较低,均低于1 mg/g,表明芦丁和槲皮素含量的变化趋势基本相反。芦丁广泛存在于植物中,但其在可食用部分相对罕见,而发芽、发酵处理能使芦丁含量极显著增加(P<0.01),说明对原料进行发芽和发酵处理是积累生物活性黄酮的好方法。
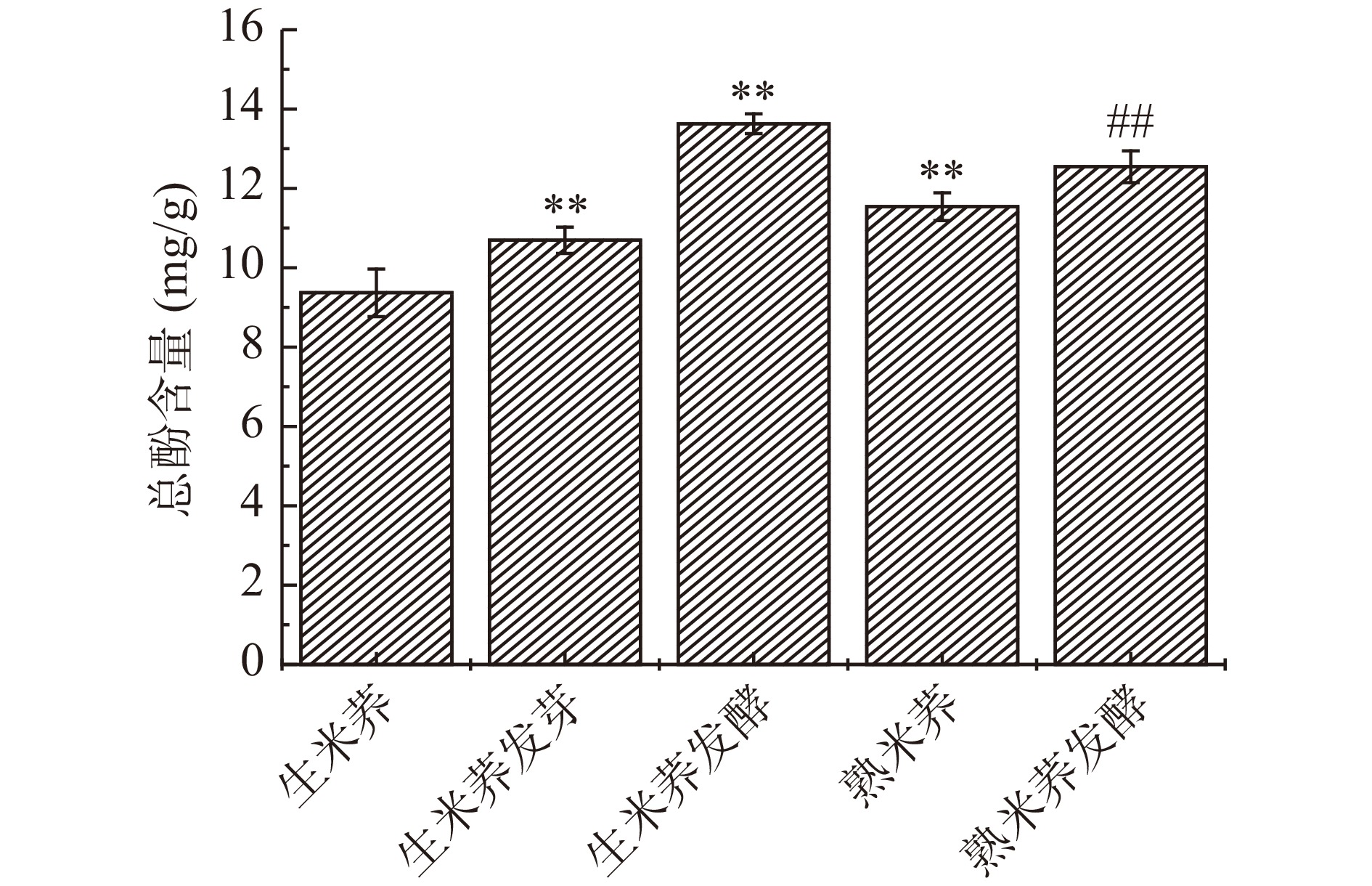
2.7 不同处理方式对米荞总酚含量的影响
酚类物质是重要的抗氧化物质,可抑制组织和膜内自由基链式反应,起到抗氧化的作用。一般认为谷物中的大部分酚类物质都是与多糖、脂质、蛋白质等大分子物质以共价键形成聚合物,不易被提取出来[33]。由图7可知,发芽处理能使米荞的总酚含量极显著增加(P<0.01),发芽过程中酚类合成酶如苯丙氨酸解氨酶的活性显著增加,而大分子物质如淀粉、蛋白质会发生溶解,使酚类物质溶出,故发芽过程中酚类物质增加[34]。
相对于生米荞,蒸煮处理能使米荞的总酚含量从9.37 mg/g增加到11.54 mg/g,增加了23.16%。由于一定程度的蒸煮处理会加快米荞细胞的膨胀,使米荞细胞间隙变大或细胞壁结构破裂,从而释放更多的酚类化合物,使熟米荞的总酚含量增加[35]。PRADEE等[36]的研究表明对小米进行蒸制处理能显著提高总酚含量,与本文研究结果一致。乳酸菌发酵处理使生米荞和熟米荞的总酚含量分别增加至13.63 mg/g和12.55 mg/g。米荞多酚以结合态和游离态形式存在于米荞细胞中,乳酸菌在发酵过程中会代谢产生各种分解细胞壁的酶,从而促进酚类物质的释放,并且发酵过程中会产生大量的乳酸等有机酸,形成酸性的环境有利于酚类化合物的稳定[17]。综上所述,发芽、发酵和蒸制处理均能使米荞的总酚含量有不同程度的增加,且生米荞发酵的总酚含量最高。
2.8 不同处理方式对米荞抗氧化能力的影响
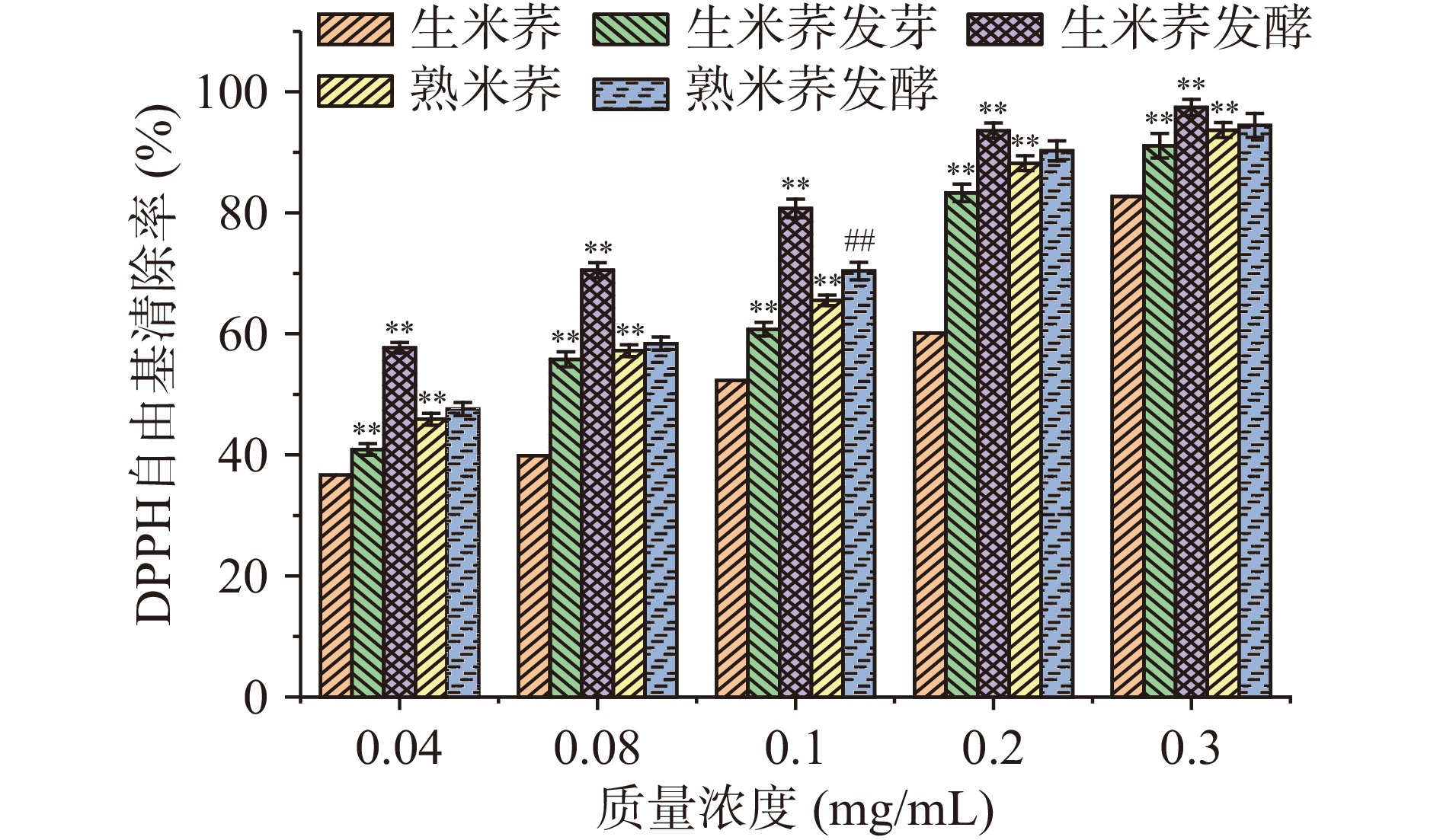
2.8.1 DPPH自由基清除率的测定
由图8可得,经不同处理的米荞对DPPH自由基均有较好的清除能力,并且在浓度0.04~0.3 mg/mL内呈现良好的量效关系。另外,对生米荞直接发酵处理清除DPPH自由基能力最强,而未做处理的生米荞清除DPPH自由基能力最弱。结果表明,经乳酸菌发酵处理的生米荞抗氧化活性最强,主要是因为乳酸菌本身就具有抗氧化活性,且当遇到较多的过氧自由基时会产生超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、NADH氧化酶、GSH-Px等过氧化物酶类等物质清除活性氧[37-38]。JIN等[39]对经乳酸菌发酵的豆浆进行体外抗氧化活性测定,发现与未发酵的豆浆相比DPPH自由基清除率显著增强,抗氧化能力明显提高,与本文的研究结果一致。
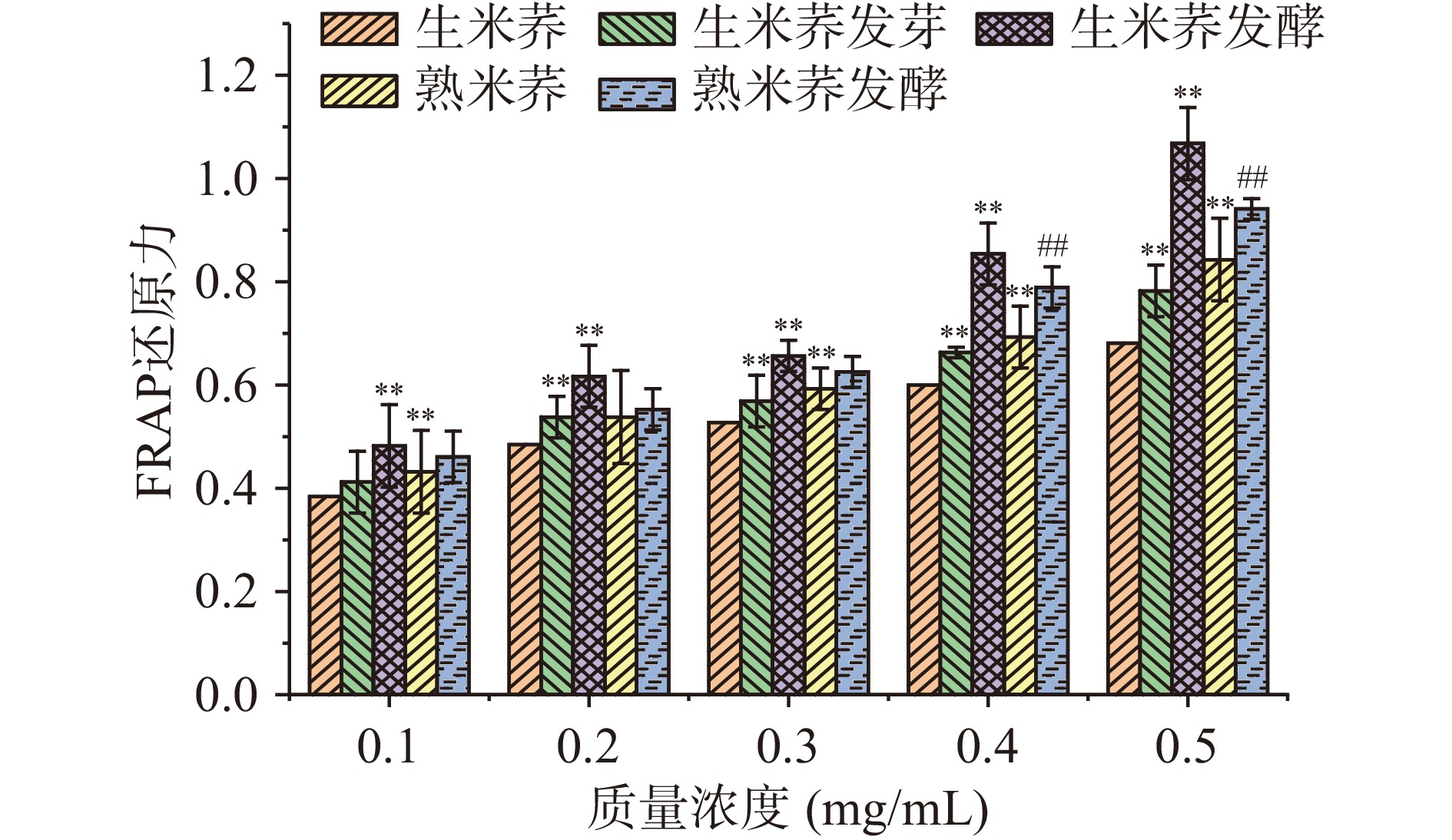
2.8.2 FRAP离子的还原能力的测定
各米荞样品在不同浓度下的铁离子还原能力如图9所示,与DPPH自由基清除能力的变化趋势相似,在0.1~0.5 mg/mL质量浓度之间,铁离子还原能力大小依次为生米荞发酵>熟米荞发酵>熟米荞>生米荞发芽>生米荞,且随着质量浓度的增大,其对应的吸光度值增大,还原能力增强。经发酵处理的生米荞铁离子还原能力最强,在浓度0.5 mg/mL时吸光值达1.07,而生米荞的铁离子还原能力最低。结合样品清除DPPH自由基的实验结果可以得出,发酵米荞是一种较好的天然抗氧化资源。
2.9 相关性分析
经不同处理的米荞清除DPPH自由基能力和铁离子还原能力的变化趋势与其总黄酮和总酚变化趋势相一致。因此,该文进一步分析了不同处理方式米荞对DPPH自由基的清除能力和铁离子还原能力与总黄酮和总酚之间的相关性。由表2可知,米荞的抗氧化能力(清除DPPH自由基能力和铁离子还原能力)与总黄酮含量(r=0.984;r=0.934,P<0.01)及总酚含量(r=0.950;r=0.994,P<0.01)具有极显著相关。说明米荞中的总酚和总黄酮是主要的抗氧化物质。
表 2 抗氧化成分与抗氧化活性斯皮尔曼相关性Table 2. Spearman correlation of antioxidant ingredients with antioxidant activity项目 总黄酮 总多酚 DPPH FRAP 总黄酮 1.00 0.962** 0.984** 0.934** 总多酚 1.00 0.950** 0.994** DPPH 1.00 0.926** FRAP 1.00 注:**代表在置信度(双侧)为0.01时,相关性极显著。 3. 结论
该文研究了不同处理方式对米荞的营养成分及抗氧化性的影响。结果表明,米荞经发芽、发酵、蒸制、蒸制后发酵处理后均能提高总酚、总黄酮含量以及抗氧化活性。由相关性分析可得,米荞抗氧化活性与总黄酮、总酚含量显著相关,说明总黄酮和总酚是米荞主要的抗氧化物质。经发芽和乳酸菌发酵处理的生米荞,芦丁含量显著增加,而槲皮素含量较低,均低于1 mg/g。而蒸制处理后米荞的还原糖、芦丁和γ-氨基丁酸含量均有所下降,说明蒸制处理会使部分营养物质被破坏。
总体来看,在这四种处理方式中,经乳酸菌发酵处理的生米荞最佳,其还原糖、总酚、总黄酮、γ-氨基丁酸和芦丁均最高以及DPPH自由基清除活性和铁离子还原能力最强。由此可得,发酵处理可以使米荞中的营养物质更好的释放出来,可进一步提高米荞的营养价值和生物活性。乳酸菌中含有丰富的酶系,能将米荞中的大分子物质分解成易被人体吸收的小分子物质;另外,乳酸菌在发酵过程中会产生新的代谢产物,从而使米荞的营养成分更加均衡和丰富。本研究为米荞的精加工提供了一定的参考,为后续开发具有保健功效的米荞制品提供理论依据和数据支撑。
-
表 1 不同处理方式对米荞游离氨基酸含量的影响(μg/g )
Table 1 Effects of different treatments on free amino acid content of rice buckwheat(μg/g)
游离氨基酸含量 生米荞 生米荞发芽 生米荞发酵 熟米荞 熟米荞发酵 苯丙氨酸* 53.34±0.10b 37.29±0.54c 173.07±1.53a 34.89±0.91c 0.24±0.06d 甲硫氨酸* 8.82±0.15c 21.16±0.52b 39.15±1.10a 4.13±0.23d 0.159±0.10e 异亮氨酸* 22.55±0.88b 28.05±0.64b 68.70±0.24a 22.91±0.42b 0.4305±0.02c 亮氨酸* 47.60±1.22b 54.75±0.63b 233.22±0.12a 26.12±0.61c 8.64±0.25d 赖氨酸* 50.61±1.52c 54.98±0.54c 79.44±0.65a 65.87±1.51b 8.55±0.22d 苏氨酸* 26.58±0.48a 22.28±0.37a 31.16±0.12a 28.04±0.23a 1.03±0.22b 缬氨酸* 221.43±1.39b 50.61±0.57d 120.12±0.63c 273.41±2.02a 33.05±1.29d 丝氨酸 64.65±1.43a 26.87±0.71b 7.10±0.02c 76.62±1.64a 0.65±0.02d 甘氨酸 104.85±1.38a 51.44±0.44b 49.85±0.53b 116.40±1.35a 20.48±1.12c 谷氨酸 246.41±1.02a 91.43±1.41b 271.58±1.03a 279.24±1.04a 5.64±0.21c 组氨酸 39.15±0.81b 17.43±0.52c 18.59±0.08c 65.88±0.89a 10.43±0.43d 丙氨酸 92.66±1.46a 26.37±0.70b 87.26±0.24a 100.89±1.67a 16.69±0.64c 精氨酸 789.66±2.39b 72.29±0.83e 240.62±2.98c 1175.82±1.99a 199.91±1.89d 脯氨酸 15.41±0.63b 9.24±0.24c 44.39±0.36a 10.59±0.52c 10.49±0.83c 半胱氨酸 85.71±1.26b 1.65±0.21c 13.52±0.03c 117.36±1.46a 19.59±0.47c 酪氨酸 35.40±0.12b 39.20±1.13b 115.31±0.25a 38.52±0.74b 0.45±0.01c 天冬氨酸 121.97±0.28b 27.06±1.12c 119.01±0.34b 138.03±1.93a 5.415±0.83d 氨基酸总量 2026.77±16.52b 632.1±11.12d 1734.66±11.28c 2574.71±19.09a 342.10±13.20e 必需氨基酸总量 430.93±5.74b 269.15±3.81c 744.85±5.36a 455.36±5.82b 52.09±4.26d 必需氨基酸总量/氨基酸总量 21.26% 42.58% 43.94% 17.68% 15.20% 注:*为必需氨基酸;同行不同字母代表显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 抗氧化成分与抗氧化活性斯皮尔曼相关性
Table 2 Spearman correlation of antioxidant ingredients with antioxidant activity
项目 总黄酮 总多酚 DPPH FRAP 总黄酮 1.00 0.962** 0.984** 0.934** 总多酚 1.00 0.950** 0.994** DPPH 1.00 0.926** FRAP 1.00 注:**代表在置信度(双侧)为0.01时,相关性极显著。 -
[1] 王自芬. “西盟米荞”产业开发现状与市场前景[J]. 农民致富之友,2017(2):37−38. [WANG Z F. Present situation and market prospect of "Rice Buckwheat in Western League" industry[J]. Friends of Farmers,2017(2):37−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1650.2017.02.034 [2] 张林福. 西盟米荞生产发展及效益分析[J]. 云南农业,2009(4):20−21. [ZHANG L F. Development and benefit analysis of Ximeng rice buckwheat production[J]. Yunnan Agriculture,2009(4):20−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1627.2009.04.019 [3] ZHU F. Chemical composition and health effects of tartary buckwheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,203(15):231−245.
[4] SKRABANJA V, LAERKE H N, KERFT I. Effects of hydrothermal processing of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) groats on starch enzymatic availability in vitro and in vivo in rats[J]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1998, 28(2).
[5] 童晓萌, 柴春祥, 王永强. 萌发对苦荞籽粒品质的影响及工艺优化[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(4):176−183. [TONG X M, CAI C X, WANG Y Q. Effect of germination on grain quality and process optimization of rice buckwheat[J]. Food and Machinery,2021,37(4):176−183. [6] 陈江. 黑曲霉固态发酵对苦荞叶抗氧化活性及其化学成分的影响[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学, 2017. CHEN J. Effects of aspergillus niger solid state fermentation on antioxidant activity and chemical composition of tartary buckwheat leaves[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University, 2017.
[7] 马艺超. 不同热加工对苦荞制品功能成分、质构及体外消化的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. MA Y C. Effects of different heat processing on functional composition, structure and in vitro digestion of tartary buckwheat products[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019.
[8] TIAN W N, DAI L W, LU S M, et al. Effect of Bacillus sp. DU-106 fermentation on Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide: Structure and immunoregulatory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:1034−1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.203
[9] HUANG J Z, XIAO N, SUN Y Y, et al. Supplementation of Bacillus sp. DU-106 reduces hypercholesterolemia and ameliorates gut dysbiosis in high-fat diet rats[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2021,105(12):1−13.
[10] 周一鸣, 崔琳琳, 王宏, 等. 苦荞在萌发过程中营养物质的变化及其营养评价[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(13):208−212. [ZHOU Y M, CUI L L, WANG H, et al. Nutrient changes and nutritional evaluation of tartary buckwheat during germination[J]. Food Science,2014,35(13):208−212. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201413040 [11] 王钦权, 翁佳妍, 黄诚, 等. 凯氏定氮法和杜马斯燃烧法测定食品中蛋白质含量的比较研究[J]. 轻工科技,2014,30(3):13−14. [WANG Q Q, WENG J Y, HUANG C, et al. Comparative study on determination of protein content in food by nitrogen and Dumas combustion[J]. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry,2014,30(3):13−14. [12] 范霞, 徐廷, 刘程, 等. 藤茶γ-氨基丁酸含量测定方法研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2016,55(13):3453−3455. [FAN X, XU T, LIU C, et al. Determination of the γ-aminobutyric acid in Ampelopsis grossedentata[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2016,55(13):3453−3455. [13] 迟明艳, 李光芳, 刘丽娜. 黔产荞麦黄酮类成分的含量测定与分析[J]. 中国药房,2016,27(21):2969−2972. [CHI M Y, LI G F, LIU L N. Content determination and analysis of flavonoids in buckwheat from Guizhou province[J]. China Dispensary,2016,27(21):2969−2972. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2016.21.28 [14] 杨红叶, 柴岩, 黄忠民, 等. 溶剂与提取方式对苦荞提取液抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2011,11(1):28−33. [YANG H Y, CHAI Y, HUANG Z M. Effects of extraction solvents and methods on antioxidant activity of tartary buckwheat bran extracts[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2011,11(1):28−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2011.01.005 [15] 赵武, 邱明阳, 周东月, 等. 五味子糖蛋白的纯化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(1):241−246,322. [ZHAO W, QIU M Y, ZHOU D Y. Purification and antioxidant activity of glycoprotein from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(1):241−246,322. [16] 郑丽娜, 赵莹. 绿豆发芽过程中营养成分的变化[J]. 中国农学通报,2008,24(2):125−128. [ZHENG L N, ZHAO Y. The contents changes of nutritional composition during mung bean germination[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2008,24(2):125−128. [17] 王清爽. 乳酸菌发酵对薏米营养和理化性质的影响[D]. 淮安: 淮阴工学院, 2020. WANG Q S. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on nutrition and physicochemical properties of barley[D]. Huaian: Huaiyin Institute of Technology, 2020.
[18] 雷焕娜, 李彦, 曹忠娜, 等. 烹饪方式对甘薯营养成分的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(21):27−31,61. [LEI H N, LI Y, CAO Z N, et al. Effects of cooking methods on the nutritional content of sweet potato[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(21):27−31,61. [19] SMITH G N, EMMANUEL A, ELIJAH H K, et al. Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals and legumes through activation of endogenous enzymes[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2018,6(8):2446−2458.
[20] LEE C K, KARUNANITY R. Effects of germination on the chemical composition of glycine and Phaseolus beans[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2010,51(4):437−445.
[21] 延莎, 邢洁雯, 王晓闻. 不同菌种发酵对藜麦蛋白质特性及脂质构成的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2020,53(10):2045−2054. [YAN S, XING J W, WANG X W. Effects of different strain fermentation on protein hydrolysis and lipid profile of quinoa[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53(10):2045−2054. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.10.011 [22] 靳颖. 大豆在发芽过程中抗原蛋白和营养特性变化及应用[D]. 郑州: 郑州轻工业大学, 2020. JIN Y. Changes and application of antigenic protein and nutrition characteristics of soybean[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2020.
[23] IBEGBULEM C O, IGWE C U, OKWU G N, et al. Total amino acid profiles of heat-processed fresh Elaeis guineensis and Raphia hookeri wines[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,138(2-3):1616−1620. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.110
[24] 刘磊, 冉玉兵, 张名位, 等. 乳酸菌发酵对脱脂米糠营养成分的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(1):118−126. [LIU L, RAN Y B, ZHANG M W, et al. Effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on nutritional component of defatted rice bran[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(1):118−126. [25] LI L, DOU N, ZHANG H, et al. The versatile GABA in plants[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2021, 16(3).
[26] 范军, 栗尤祥, 郭小云, 等. 发芽糙米抗氧化活性在发芽及干燥过程中的变化研究[J]. 农产品加工(学刊),2012(9):34−36. [FAN J, LI Y X, GUO X Y, et al. The antioxidative activity of germinated brown rice during germination and drying[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing,2012(9):34−36. [27] 周玉龙, 贾富国, 张强, 等. 贮藏温湿度对糙米平衡含水率的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2011,26(12):78−82. [ZHOU Y L, JIA F G, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of storage temperature and humidity on equilibrium moisture content of brown rice[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2011,26(12):78−82. [28] 李志江, 关琛, 翟爱华, 等. 糙米酵素发酵工艺对γ-氨基丁酸和谷胱甘肽含量影响研究[J]. 农产品加工(学刊),2014(1):6−8,11. [LI Z J, GUAN C, HUO A H, et al. Effect of brown rice fermentation on γ-Content of aminobutyrate and glutathione[J]. Agricultural Products Processing (Journal Journal),2014(1):6−8,11. [29] 孙丹, 黄士淇, 蔡圣宝. 不同加工方式对苦荞中总酚、总黄酮及抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2016,42(1):141−147. [SUN D, HUANG S Q, CAI S B. Effects of different processing methods on total phenol, total flavonoids and antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2016,42(1):141−147. [30] SINGH K, KUMAR S, RANI A, et al. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) and catechins (flavan-3-ols) accumulation in tea[J]. Functional & Integrative Genomics,2009,9(1):125−134.
[31] WANG L, LI X, NIU M, et al. Effect of additives on flavonoids, D-chiro-Inositol and trypsin inhibitor during the germination of tartary buckwheat seeds[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2013,58(2):348−354. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2013.07.004
[32] 崔江明, 周海龙, 马利华. 发芽、发酵对燕麦营养性及抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):130−134. [CUI J M, ZHOU H L, MA L H. Effects of germination and fermentation on nutritional and antioxidant properties of oats[J]. Food Technology,2021,46(2):130−134. [33] 翟玮玮. 萌发谷物中多酚类物质与苯丙氨酸解氨酶的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(8):370−372,376. [CUI W W. Research progress of phenolic compounds and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in pre-germinated grains[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(8):370−372,376. [34] DANIELS D, MARTIN H F. Antioxidants in oats: Glyceryl esters of caffeic and ferulic acids[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,1968,19(12):710−712. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740191206
[35] DONA A M. Enhancing antioxidant activity and extractability of bioactive compounds of wheat bran using thermal treatments[D]. Manitoba: University of Manitoba, 2011
[36] PRADEE S R, MANISHA G. Effect of processing methods on the nutraceutical and antioxidant properties of little millet (Panicum sumatrense) extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,126(4):1643−1647. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.12.047
[37] 赵彤, 钟宜科, 荀一萍, 等. 乳酸菌抗氧化性及其作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2018(9):202−209. [ZHAO T, ZHONG Y K, XUN Y P, et al. Research progress on antioxidation and regulation mechanism of lactic acid bacteria[J]. China Food Additives,2018(9):202−209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.09.025 [38] 范昊安, 沙如意, 方晟, 等. 苹果梨酵素发酵过程中的褐变与抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(14):116−123. [FAN H A, SHA R Y, FANG S, et al. Browning and antioxidant activity of apple-pear Jiaosu during fermentation[J]. Food Science,2020,41(14):116−123. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190515-151 [39] JIN Y J, PYO Y H. Effect of monascus-fermented soybean extracts on antioxidant and skin aging-related enzymes inhibitory activities[J]. Preventive Nutrition & Food Science,2017,22(4):376−380.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 蒋美君,张启元,蒙扬辉,白科,张兴志,农珍珍,钟方杰,朱鹏,彭金霞,官俊良,严雪瑜. 香港牡蛎BMP7基因克隆与表达. 广东海洋大学学报. 2023(04): 129-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周晖,汤保贵,伍栩民,彭梓峰,钟培贵,于鸽,孔繁森. 香港牡蛎在综合养殖池塘育肥期间不同组织的碳、氮稳定同位素周转. 热带海洋学报. 2023(04): 125-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汤保贵,周晖,赵力强,伍栩民,彭梓峰,钟培贵,于鸽. 香港牡蛎在异地基围育肥时的生长、形态及体成分变化. 水生生物学报. 2023(11): 1762-1768 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)













 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



