Mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum on Prevention and Treatment of Obesity Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
-
摘要: 目的:通过网络药理学及分子对接技术揭示绞股蓝防治肥胖的物质基础及潜在作用机制。方法:使用TCMSP数据库结合文献补充筛选绞股蓝活性成分;使用Pubchem、Swiss target prediction数据库收集绞股蓝活性成分作用靶点;使用GeneCards、OMIM、DurgBank数据库获取肥胖疾病靶点。取绞股蓝作用靶点与疾病靶点交集为绞股蓝防治肥胖作用靶点,并使用Cytoscape3.7.2软件构建药物-化合物-靶点网络;使用STRING数据库构建靶蛋白互作PPI网络筛选核心靶点,Discovery Studio 3.5对筛选出的核心靶点与活性成分分子对接,DAVID数据库对交集靶点进行GO富集和KEGG通路注释分析,通过上述结果构建成分-靶点-通路相互作用网络模型。结果:共筛选出槲皮素、3-甲基鼠李素、人参皂苷f2、绞股蓝皂苷XXVIII等16个化合物为绞股蓝防治肥胖物质基础,107个绞股蓝治疗肥胖靶点,其中包括STAT3、AKT1、VEGFA、SRC、EGFR、MAPK3等38个关键靶点;分子对接结果显示,PPI中度值前6位核心靶点与相对应化合物3-甲基柔二醇、3-甲基鼠李素、黄夹次甙丙、a-菠菜甾醇、胆甾醇、槲皮素、人参皂苷f2、绞股蓝皂苷XXVIII有较好的结合活性,推测这些化合物可能为主要药效成分;GO分析得绞股蓝防治肥胖主要涉及细胞生长增殖过程、代谢过程等生物过程,酶结合、蛋白结合等分子功能,细胞核、细胞质等细胞组成。KEGG通路富集结果显示,绞股蓝防治肥胖通路涉及癌症信号通路、癌症中的蛋白多糖通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、HIF-1信号通路等。结论:本研究初步揭示了绞股蓝可通过多成分、多靶点、多通路影响机体脂肪细胞增殖分化、糖脂代谢及维持机体稳态等多方面实现肥胖防治作用,为进一步研究其有效成分及分子机制提供依据。Abstract: Objective: The study revealed the material basis and potential mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum for preventing obesity through network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Methods: Using TCMSP database combined with literatures to supplement the screening of active ingredients. Using Pubchem and Swiss target prediction databases to collect the targets of active ingredients of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Using GeneCards, OMIM and DurgBank databases to obtain obesity targets. Taking the intersection of Gynostemma pentaphyllum action targets and disease targets as Gynostemma pentaphyllum prevention and treatment targets for obesity, and using Cytoscape 3.7.2 software to construct a drug-compound-target network. The STRING database was used to construct a target protein interaction PPI network to screen core targets, Discovery Studio 3.5 was used to docks the selected core targets with the active ingredient molecules, DAVID database performs GO enrichment and KEGG pathway annotation analysised on intersection targets, and built a component-target-pathway interaction network model based on the above results. Results: A total of 16 compounds including quercetin, 3'-methyleriodictyol, ginsenoside f2, and gypenoside XXVIII were selected as the material basis for the prevention and treatment of obesity in Gynostemma pentaphyllum, and 107 targets for the treatment of obesity, including STAT3, AKT1, VEGFA , SRC, EGFR, MAPK3 and other 38 key targets. The results of molecular docking showed that the top 6 core targets of PPI had good binding activities with the corresponding compounds 3'-methyleriodictyol, Rhamnazin, Ruvoside, Spinasterol, ginsenoside f2, CLR, quercetin, Gypenoside XXVIII, speculate on these components may be the main pharmacodynamic components. GO analysis showed that the prevention and treatment of obesity by Gynostemma pentaphyllum mainly involved biological processes such as cell growth, proliferation and metabolic processes, molecular functions such as enzyme binding, protein binding, cellular components such as nucleus and cytoplasm. KEGG pathway enrichment results showed that pathway involving cancer signaling pathways, proteoglycan pathways in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, and HIF-1 signaling pathways. Conclusion: This study initially revealed that Gynostemma pentaphyllum could affect the proliferation and differentiation of adipocytes, glucose and lipid metabolism, and maintain body homeostasis through multiple components, multiple targets, and multiple pathways to achieve obesity prevention and treatment, would provide a basis for further research on the effective ingredients and molecular mechanisms.
-
Keywords:
- obesity /
- Gynostemma pentaphyllum /
- network pharmacology /
- molecular docking /
- mechanism
-
肥胖症(Obesity,OB)是指机体生理生化机能改变引起体内脂肪沉积量过多,体重增加,并伴随一系列病理变化的慢性代谢疾病。肥胖的诱因有多种,如家族遗传、环境因素、内分泌异常导致的低代谢率、一些药物副作用及能量摄入与消耗的不平衡等[1]。随着人民生活水平的提高,高能量、高脂肪的饮食习惯使得肥胖发病率呈现明显上升趋势,而且研究显示肥胖会显著提高患心脑血管疾病、2型糖尿病、高血压及癌症等疾病的风险[2],肥胖症已成为一个主要健康问题。由于脂肪组织是人体极其复杂且高度活跃的内分泌组织,脂肪形成期间受多种激素、基因表达和信号通路的调控,涉及糖脂代谢异常、慢性炎症以及诱发氧化等[3]病理机制,故有必要探究治疗肥胖多靶点药物。而中药有着“多成分、多靶点”作用特点,并且市场上出现的降脂中药如葛根,荷叶等[4]在肥胖治疗中显示出的良好疗效大大提高了人们对中药减肥的认可度,使得中药减肥药及减肥功能食品的开发正逐渐成为一个重点发展方向。
绞股蓝(Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino),又名七叶胆、五叶参等,是葫芦科绞股蓝属的多年生草质藤本植物。据《本草纲目》记载,绞股蓝有清热解毒、益气健脾、生津止渴和化浊降脂等之效[5]。现代药理研究证明绞股蓝具有抗疲劳、降血脂、降血压、增强免疫等作用,在药品、保健食品、畜牧业饲料添加及防疫中被广泛应用,是一种具有较大开发价值的药食两用植物资源[6]。在临床症状中,肥胖病人多数有浮肿肢沉、神疲乏力、胸闷气短、痰多喘促等症状,故中医学认为脾失健运、湿痰、气虚,是引起肥胖的主要因素[7]。而绞股蓝有益气、健脾、化浊功效,符合治疗肥胖特点。并且现代研究表明绞股蓝中多种成分有降脂活性,如绞股蓝皂苷可通过改变胆固醇胶束结构降低肠道对胆固醇的吸收[8],减少脂肪酶与脂质底物的亲和力,促进胆汁酸的合成与分泌促进脂质代谢[9];绞股蓝黄酮可通过抑制脂肪前体细胞和肝细胞等的成脂过程[10],调节慢性炎症引起的脂肪代谢紊乱[11],促进胆固醇的外排及胆固醇向胆汁酸转化[12]等;绞股蓝多糖可调节脂肪代谢相关基因表达,降低胰岛素抵抗作用[13]等达到调节脂肪代谢。故利用绞股蓝化学成分及作用途径多样特点,可将其作为潜在抑制肥胖多靶点药物。但另一方面,在绞股蓝降脂机制探究中,上述活性成分药理研究多依赖于某一降脂指标、单一通路或靶点进行探究,缺乏对绞股蓝多靶点、多通路防治肥胖的整体认识和各机制间协同作用系统性分析,而且使用传统实验方法系统全面检测出绞股蓝的减肥降脂机制过程漫长且复杂,因此有必要探索新方法来阐明绞股蓝降脂作用机制。
网络药理学是融合生物信息学、计算机技术、网络科学和系统药理学为一体的新兴学科[14]。其疾病与化合药物靶点网络全局化、系统化思路与中医的整体观念一脉相通,已成为中药研究的一种有效技术手段,如:利用网络药理学分析丹参治疗微循环障碍[15],利用网络药理学预测黄芪治疗糖尿病肾病[16]等诸多报道对中药治疗疾病提供了方向。因此,为针对性研究绞股蓝防治肥胖主要药效成分及作用机制间关系,本研究利用网络药理学构建“中药活性成分-靶点”、蛋白互作(PPI)网络、靶基因功能通路等多层次生物信息网络,并结合分子对接技术系统分析绞股蓝抑制肥胖的物质基础、潜在降脂靶点及作用机制,为绞股蓝防治肥胖方向的基础研究及后续应用提供新思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
TCMSP数据库(http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php);Pubchem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov);GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org);OMIM数据库(https://www.omim.org/);DrugBank数据库(https://www.drugbank.com);STRING11.0数据库(https://www.string-db.org);David数据库(https://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov);Cytoscape3.7.2软件。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 绞股蓝活性成分的筛选
通过TCMSP数据库(http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php)检索关键词“绞股蓝”,得到其活性成分信息。根据药动学参数中的口服生物利用度(oral bioavailability,OB)和类药性(drug-likeness,DL),筛选出同时满足OB≥20%和DL≥0.1的化学成分[17],并结合文献[18-20]报道的成分,整理得到绞股蓝活性成分。
1.2.2 活性成分与肥胖交集靶点筛选及成分-交集靶点网络构建
通过Pubchem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)下载每个活性成分的Smiles化学式,上传到Swiss Target Prediction(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/index.php)平台,以“人类”为研究物种收集靶点,整理得绞股蓝活性成分作用靶点。
在GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org)、OMIM数据库(https://www.omim.org/)、DrugBank数据库(https://www.drugbank.com),输入关键词“obesity”,可得与肥胖相关靶点,合并3大数据库肥胖靶点,去除重复基因和假阳性基因得肥胖靶点。将收集到的肥胖靶点与绞股蓝活性成分靶点匹配,其中共同靶点即为绞股蓝潜在抑制肥胖作用靶点。将交集靶点导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件进行可视化,构建绞股蓝活性成分-肥胖作用靶点网络。
1.2.3 PPI网络构建
将绞股蓝的蛋白靶点导入STRING11.0数据库(https://www.string-db.org),参考文献方法参数设置[21-22],并以P<0.01为显著临界值得蛋白相互作用关系。将筛选后分析文件导入Cytoscape3.7.2,将蛋白相互作用网络图(proteinprotein interaction,PPI)可视化。
1.2.4 分子对接验证
从PDB数据库下载上述PPI网络中度值靠前的靶点蛋白3D结构,通过加氢准备、赋予CHARMm力场后,定义原激酶域的ATP活性位点为对接口袋。选取有核心靶点化合物进入3D模式运行能量最小化计算,之后导入Discovery studio 3.5的CDocker模块进行柔性分子对接。运行结束后分析化合物与蛋白的对接模式。评价绞股蓝活性成分与靶点之间的结合活性,并且筛选出潜在主要药效化合物。
1.2.5 生物过程与通路分析
通过David数据库(https://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov)对绞股蓝抑制肥胖靶点进行GO(Gene Ontology,基因本体)分析和KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,京都基因与基因组百科全书)通路分析,按关联靶点数目由高到低排序,并以P<0.01作为明显功能与通路的界定值,选取排名前10通路。
1.2.6 绞股蓝防治肥胖成分-靶点-通路网络及靶点间相互作用网络构建
为进一步研究成分、靶点与信号通路之间的相互作用关系,利用Cytoscape3.7.2软件进行可视化,构建绞股蓝降脂成分-靶点-通路网络图及靶点间相互作用网络图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 绞股蓝活性成分筛选
根据TCMSP数据库中OB≥20%和DL≥0.10的标准筛选后,共有59种活性化合物,连同文献报道的活性成分5种,共64种,具体信息见表1。
表 1 绞股蓝活性成分信息Table 1. Active ingredient information of Gynostemma pentaphyllum序号 分子ID 分子名称 分子量 OB (%) DL 1 MOL000338 3'-methyleriodictyol 302.3 51.61 0.27 2 MOL000351 Rhamnazin 330.31 47.14 0.34 3 MOL000359 sitosterol 414.79 36.91 0.75 4 MOL004350 Ruvoside 390.57 36.12 0.76 5 MOL004355 Spinasterol 412.77 42.98 0.76 6 MOL005438 campesterol 400.76 37.58 0.71 7 MOL005440 Isofucosterol 412.77 43.78 0.76 8 MOL007475 ginsenoside f2 785.14 36.43 0.25 9 MOL000953 CLR 386.73 37.87 0.68 10 MOL000098 quercetin 302.25 46.43 0.28 11 MOL009973 Gypenoside XXVIII 416.71 32.08 0.74 12 MOL009855 (24S)-Ethylcholesta-5,22,25-trans-3beta-o 410.75 46.91 0.76 13 MOL009867 4α,14α-dimethyl-5α-ergosta-7,9(11),24(28)-trien-3β-ol 424.78 46.29 0.76 14 MOL009877 cucurbita-5,24-dienol 426.8 44.02 0.74 15 MOL009878 Cyclobuxine 386.69 84.48 0.70 16 MOL009888 Gypenoside XXXVI 458.8 37.85 0.78 17 MOL009928 Gypenoside LXXIV 801.14 34.21 0.24 18 MOL009929 Gypenoside LXXIX 785.14 37.75 0.25 19 MOL009938 Gypenoside XII 785.14 36.43 0.25 20 MOL009943 Gypenoside XL 799.12 30.89 0.21 21 MOL009969 Gypenoside XXXV 444.77 37.73 0.78 22 MOL009971 Gypenoside XXVII 418.73 30.21 0.74 23 MOL009976 Gypenoside XXXII 787.11 34.24 0.25 24 MOL009986 Gypentonoside A 472.78 36.13 0.80 25 MOL000131 EIC 280.5 41.9 0.14 26 MOL001746 ELD 281.54 31.2 0.14 27 MOL005284 (3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-
methylhept-5-en-2-yl]
-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6,12-triol476.82 20.13 0.78 28 MOL005327 Gypnoside V 460.82 29.69 0.77 29 MOL005334 (3S,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-
methylhept-5-en-2-yl]
-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol460.82 29.69 0.77 30 MOL005364 Malonylginsenoside Rd 460.82 29.69 0.77 31 MOL006728 Gypenoside XIV 460.82 29.69 0.77 32 MOL006734 Gypenoside I 460.82 29.69 0.77 33 MOL000675 oleic acid 282.52 33.13 0.14 34 MOL006754 ginsenoside Rb3 460.82 29.65 0.81 35 MOL000086 (24S)-5beta-Stigmastan-3beta-ol 416.81 25.32 0.75 36 MOL009860 2α-hydroxypanaxadiol 476.82 21.44 0.8 37 MOL009871 6'-malonylgypenoside V 460.82 29.69 0.77 38 MOL009873 7-(6-O-Malony-beta-D-glucopyransyloxy)-3-(4-hydroxphenyl)-4H-
1-benzopyran-4-one504.48 29.25 0.84 39 MOL009882 gynosaponin TN-1 476.82 20.13 0.79 40 MOL009884 gynsenoside Rd 460.82 29.69 0.77 41 MOL009894 Gypenoside L 446.79 29.61 0.78 42 MOL009896 Gypenoside LI 476.82 20.13 0.79 43 MOL009899 Gypenoside LIII 769.09 22.94 0.22 44 MOL009900 Gypenoside XL 474.8 29.29 0.79 45 MOL009910 Gypenoside LVIII 474.85 29.69 0.79 46 MOL009912 Gypenoside LX 476.82 20.13 0.79 47 MOL009920 Gypenoside LXVIII 462.79 20.59 0.8 48 MOL009924 Gypenoside LXXI 460.82 29.16 0.78 49 MOL009927 Gypenoside LXXIII 460.82 29.69 0.78 50 MOL009945 Gypenoside XLI 460.82 29.65 0.78 51 MOL009958 Gypenoside XVIII 446.79 29.4 0.77 52 MOL009962 Gypenoside XXX 446.79 29.4 0.78 53 MOL009964 Gypenoside XXIX 444.77 23.9 0.78 54 MOL009967 Gypenoside XXV 474.8 28.89 0.8 55 MOL009980 Gypenoside XXXIX 801.14 20.46 0.21 56 MOL009981 Gypenoside XXXIX 476.82 20.13 0.79 57 MOL009989 Gypinoside LXVII 476.82 20.18 0.79 58 MOL009992 Gypsogenin 470.76 26.77 0.75 59 MOL009998 Toddaculin 274.34 47.85 0.17 60 MOL009949 Gypenoside XLIX 1093.41 17.74 0.06 61 MOL009891 Gypenoside IV 1079.43 7.81 0.04 62 MOL009935 Gypenoside VⅢ 769.09 8.08 0.22 63 MOL009995 Ombuoside 638.63 14.86 0.63 64 MOL000415 Rutin 610.57 3.20 0.68 2.2 绞股蓝抑制肥胖潜在作用靶点预测及绞股蓝活性成分-靶点网络构建
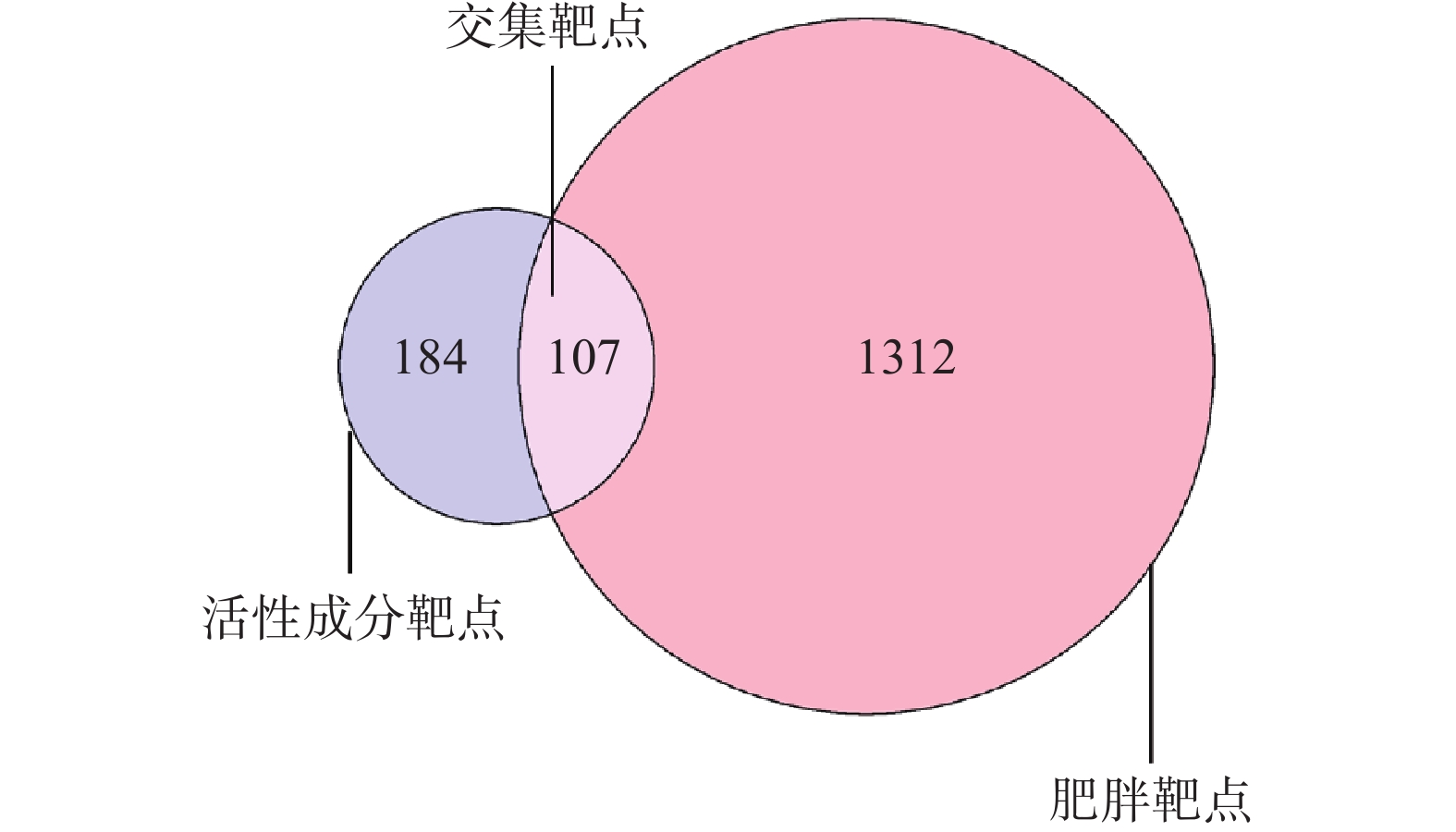
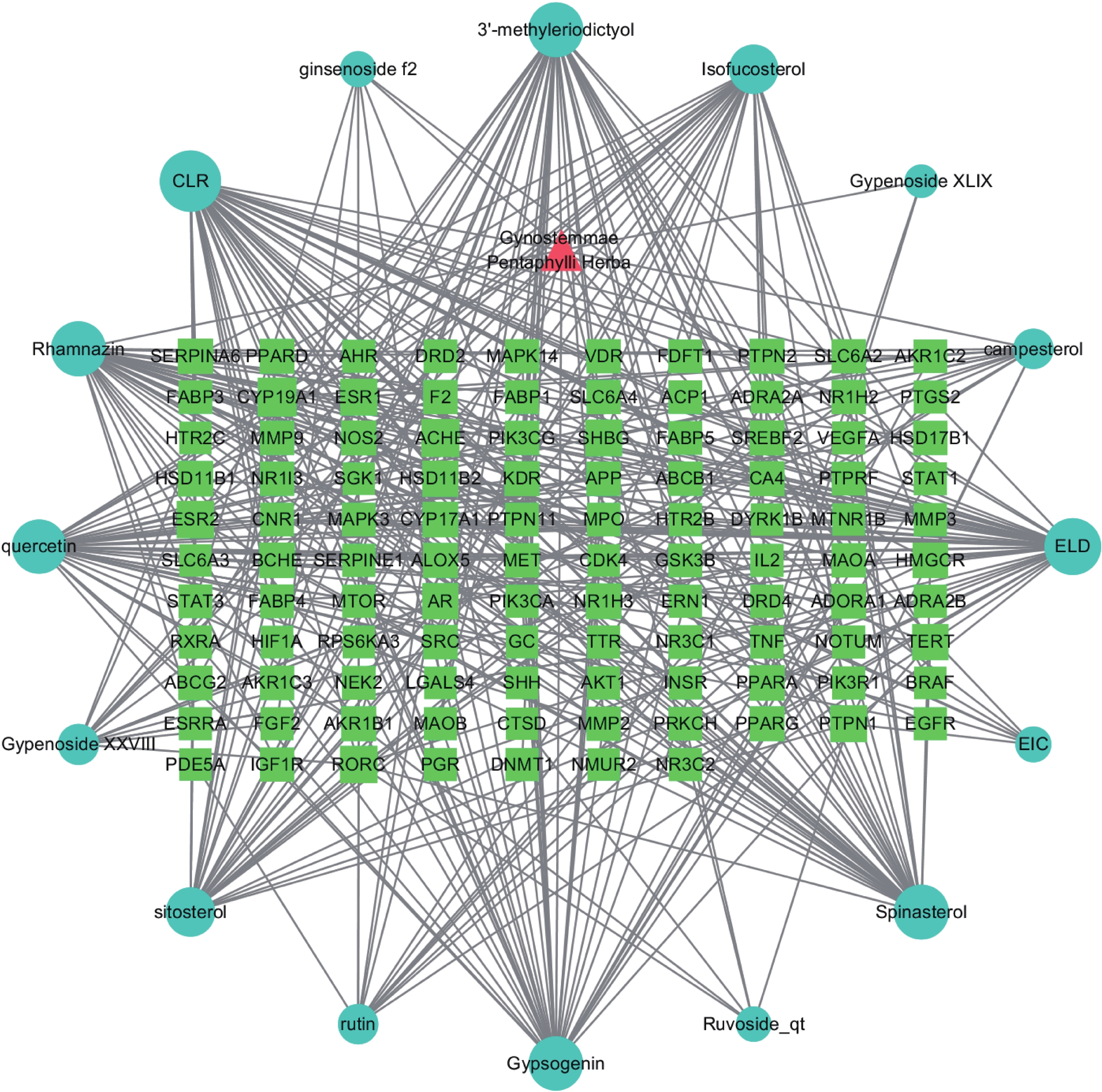
将上述64个绞股蓝活性成分在Swiss Target Prediction平台中检索得到的作用靶点整合,得到作用靶点291个。从GeneCards、OMIM、DrugBank数据库检索整合得到肥胖靶点1419个,绞股蓝活性成分作用靶点与肥胖靶点交集共有107个,如图1所示。将活性成分与肥胖交集靶点导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件进行可视化后,得绞股蓝-活性成分-作用靶点网络图,如图2所示。图中矩形表示活性成分与疾病交集靶点,圆形表示绞股蓝活性成分,图形面积越大代表其潜在活性靶点越多。由图2可以看出绞股蓝抑制肥胖活性成分共16种,有槲皮素(quercetin)、芦丁(rutin)、人参皂苷f2(ginsenoside f2)、绞股蓝皂苷XXVIII(Gypenoside XXVIII)、3'-甲基柔二醇(3'-methyleriodictyol)、3-甲基鼠李素(Rhamnazin)、谷甾醇(sitosterol)、黄夹次甙丙(Ruvoside)、a-菠菜甾醇(Spinasterol)、菜油甾醇(campesterol)、异氟固醇(Isofucosterol)、胆甾醇(CLR)、绞股蓝皂苷XLIX(Gypenoside XLIX)、脂凝素(Gypsogenin)、亚油酸(EIC)、油酰胺(ELD)。
2.3 PPI网络构建与分析
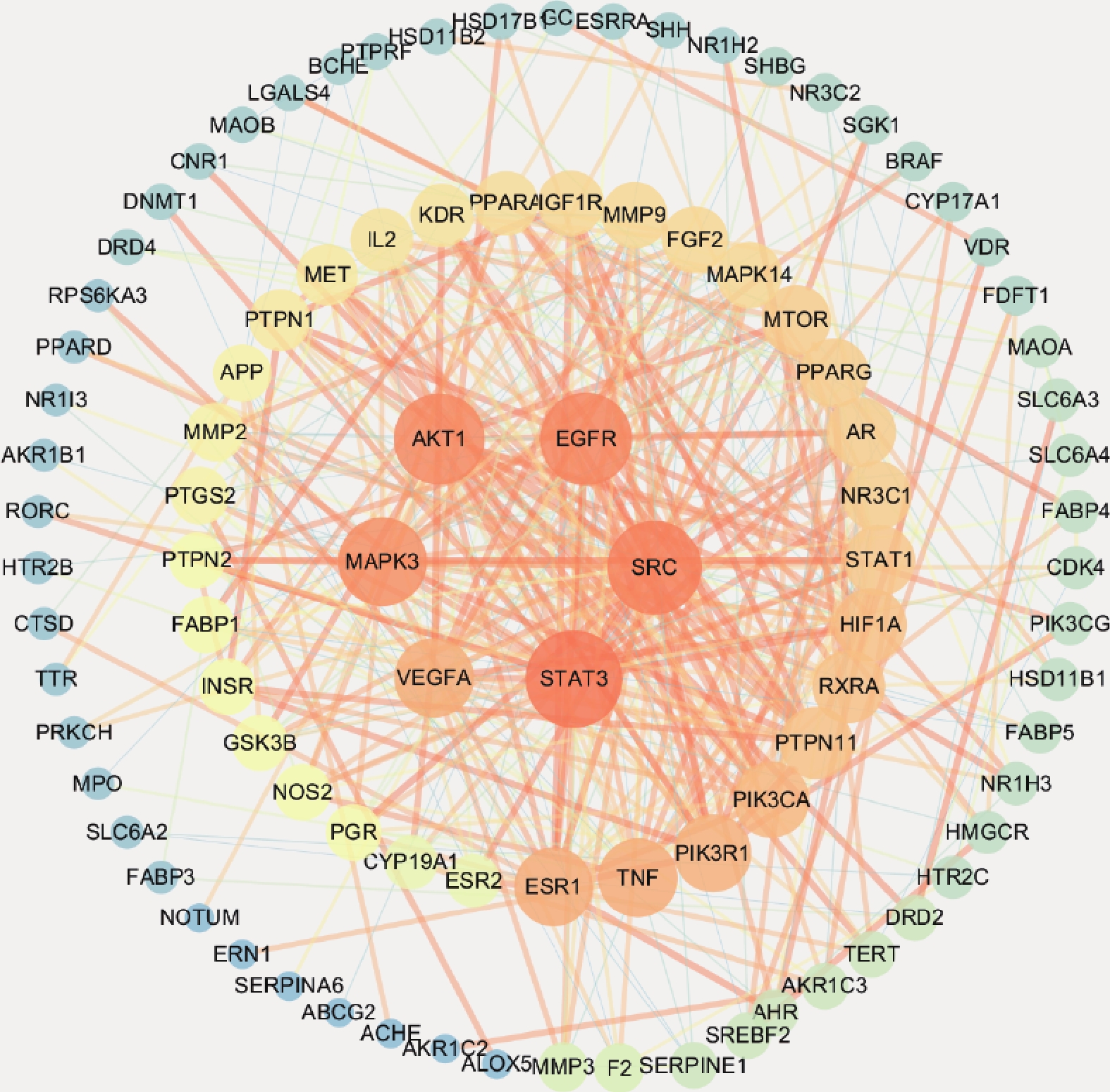
将107个共同靶点上传至STRING11.0,经规范后得到靶蛋白相互作用网络(PPI),详细见图3。图中圆圈代表该基因度值,圆圈越小Degree值越小,连线越粗Combined score值越大。根据网络拓扑学性质将靶点按照度值由高到低排序,结果显示共有107个节点,419条边,平均度值是7.83,其中超过平均度值的靶点有38个,推测这38个靶点为绞股蓝作用于肥胖的关键靶点。由这38个靶点可知绞股蓝在防治肥胖过程中有转录因子、信号分子、受体、蛋白(转移/载体蛋白)、酶(激酶、转移酶、蛋白酶)等多种物质的参与。其中STAT3、SRC、EGFR、AKT1、MAPK3、VEGFA的节点度值排名前六位,推测这些靶点可能是治疗肥胖的核心靶点。
2.4 分子对接验证结果
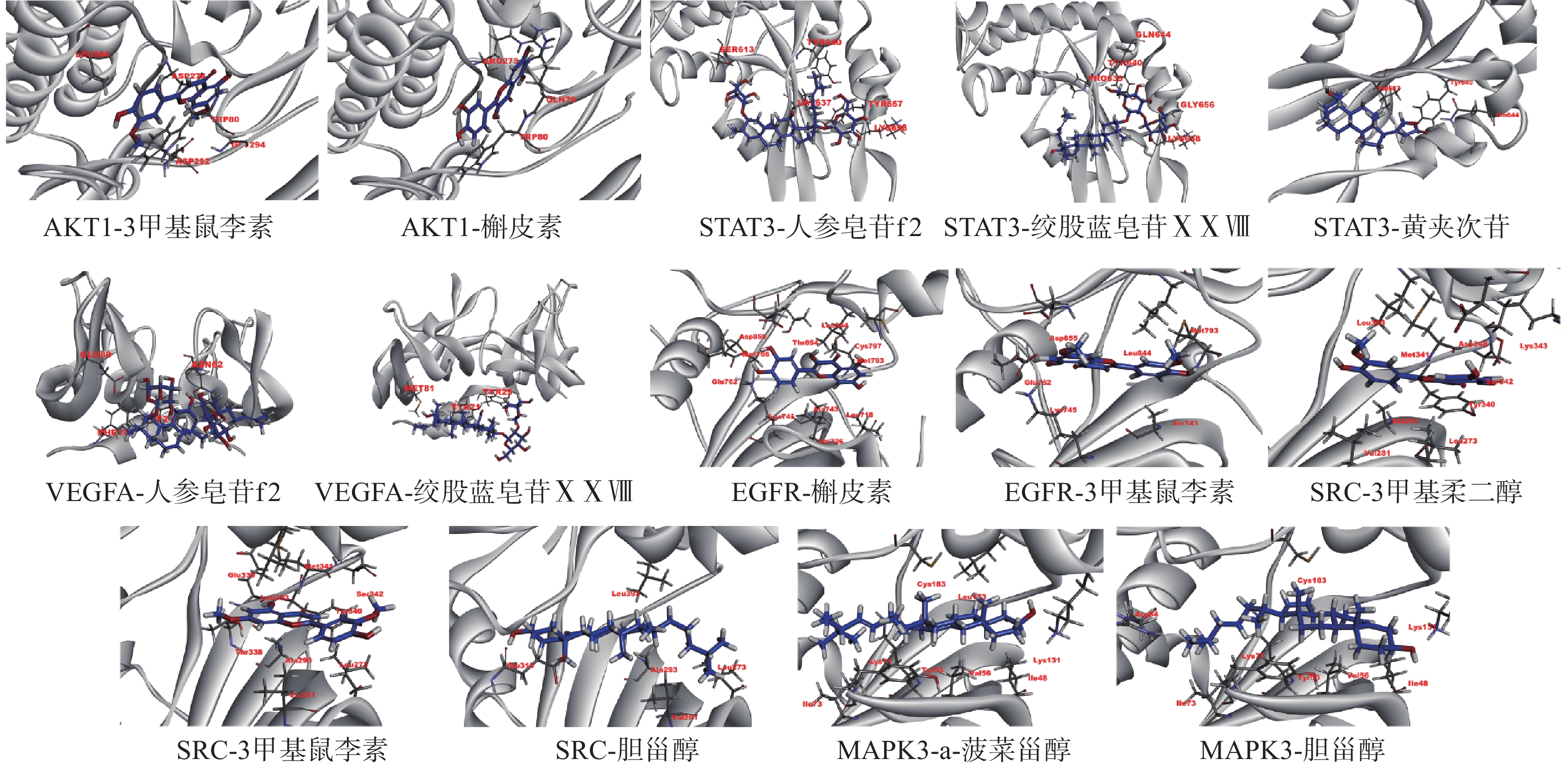
选取PPI中度值前6位靶点与有这6个靶点的化合物进行分子对接验证。表2为活性成分与相对应关键靶点信息,由表可知3'-甲基柔二醇(3'-methyleriodictyol)、3-甲基鼠李素(Rhamnazin)、黄夹次甙丙(Ruvoside)、槲皮素(quercetin)、人参皂苷f2(ginsenoside f2)、绞股蓝皂苷XXVIII(Gypenoside XXVIII)、a-菠菜甾醇(Spinastero)、胆甾醇(CLR)8个化合物有对应核心靶点,推测这8个化合物可能是绞股蓝抑制肥胖关键药效成分。在对接中,小分子与靶点蛋白相互作用能量打分<0表示有一定结合作用,相互作用能量打分<−30表示有较强结合作用[23]。由表3可知蛋白与化合物对接相互作用能量分数在−22.8832~−49.6606,表明这8个化合物与对应核心靶点蛋白结合普遍较好,提示本实验的数据与结果较为可靠,具有较高的参考价值。图4为8个化合物与肥胖核心靶点的分子对接模式图。
表 2 各活性成分对应防治肥胖关键靶点基因Table 2. Corresponding gene of each active ingredient分子ID 名称 关键靶点 MOL000338 3'-methyleriodictyol SRC、GSK3B、MMP2、KDR、MET、MAPK14、RXRA、APP、SERPINE1、PIK3CA MOL000351 Rhamnazin SRC、EGFR、MMP2、MET、KDR、GSK3B、F2、DRD4、AKT1、APP、INSR MOL000359 sitosterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG MOL004350 Ruvoside STAT3、PTPN1 MOL004355 Spinasterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG、MAPK3、PTPN11 MOL005438 campesterol AR、PTPN1 MOL005440 Isofucosterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG MOL007475 ginsenoside f2 STAT3、VEGFA、FGF2、KDR MOL000953 CLR AR、PTPN1、PPARG、PGR、MAPK3、PTPN11、DRD2、HIF1A MOL000098 quercetin EGFR、F2、DRD4、GSK3B、SRC、KDR、MMP2、MET、AKT1、INSR、APP MOL009973 Gypenoside XXVIII HTR2C、IL2、AR、VEGFA、FGF2、STAT3、DRD2、F2 MOL000415 rutin PTGS2、TNF、IL2 MOL009900 Gypenoside XLIX PPARA、TNF MOL009992 Gypsogenin ESR1、AR、CYP19A1、ESR2、FABP1、NOS2、NR3C1、PGR、PPARA、PPARG、PTGS2、PTPN1、PTPN11、PTPN2 MOL000131 EIC AR、CYP19A1、ESR1、ESR2、FABP1、MAPK14、NOS2、NR3C1
PGR、PPARA、PPARG、PTGS2、PTPN1、PTPN11、PTPN2MOL001746 ELD CYP19A1、MAPK14 注:加黑靶点为PPI中度值前六位核心靶点。 表 3 绞股蓝关键成分与对应核心靶点相互作用能量打分表Table 3. Key components and the corresponding core target interaction energy score table序号 成分 AKT1 STAT3 VEGFA EGFR SRC MAPK3 1 3'-methyleriodictyol − − − − −34.3333 − 2 Rhamnazin −38.7675 − − −34.8522 −37.7041 − 3 Ruvoside − −23.7509 − − − − 4 Spinasterol − − − − − −47.6866 5 ginsenoside f2 − −39.1435 −22.8832 − − − 6 CLR − − − − −38.7851 −49.6606 7 quercetin −39.6114 − − −38.8686 − − 8 Gypenoside XXVIII − −44.2180 −28.0355 − − − 注:“−”表示化合物筛选中无该核心作用靶点。 2.5 GO和KEGG富集分析
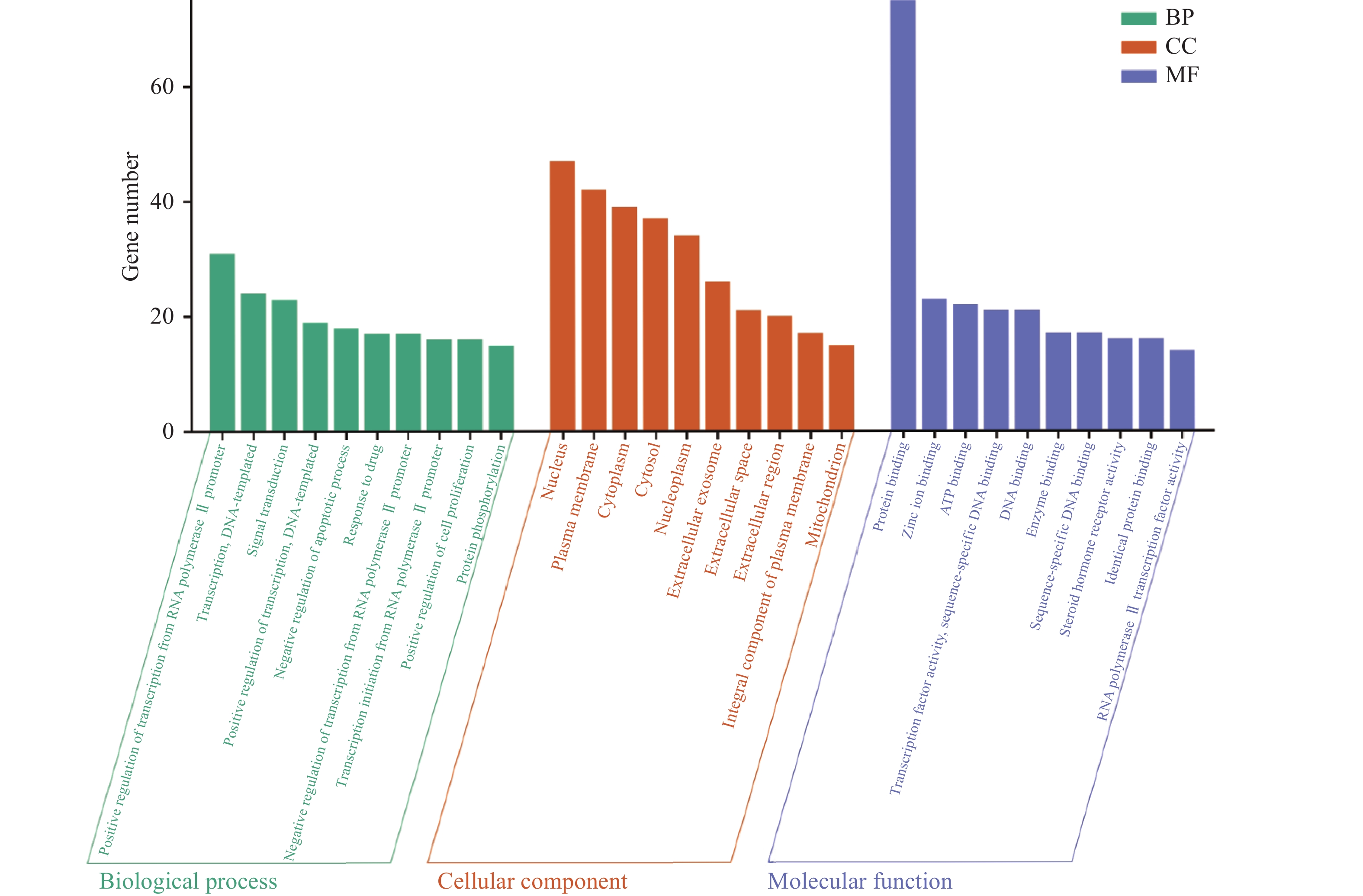
通过DAVID数据库对交集靶点进行GO富集分析,各过程富集排名前10位分析结果详细见图5(P<0.01),图中X轴代表靶基因中属于该过程的基因数量,Y轴3种颜色代表生物过程(Biological process,BP)、细胞组分(Cellular components,CC)、分子功能(Molecular function,MF)。图5结果显示绞股蓝抑制肥胖靶点参与的生物过程包括细胞生长增殖过程、代谢过程、激素调节过程等,如RNA聚合酶Ⅱ启动子转录的正/负调控(positive/negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter)、DNA模板转录调控(transcription, DNA-templated)、信号传导(signal transduction)、凋亡过程的正/负调控(positive/negative regulation of apoptotic process)、蛋白质磷酸化(protein phosphorylation)、氧化还原过程(oxidation-reduction process)、类固醇激素介导的信号通路(steroid hormone mediated signaling pathway)等;参与的细胞组成主要包括核(nucleus)、质膜(plasma membrane)、细胞质(cytoplasm)、胞质溶胶(cytosol)、核质(nucleoplasm)、细胞外泌体(extracellular exosome)、线粒体(mitochondrion)等;分子功能主要富集于蛋白质结合(protein binding)、锌离子结合(zinc ion binding)、ATP结合(ATP binding)、转录因子活性序列特异性DNA结合(transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding)、DNA结合(DNA binding)、酶结合(enzyme binding)、类固醇激素受体活性(steroid hormone receptor activity)等。
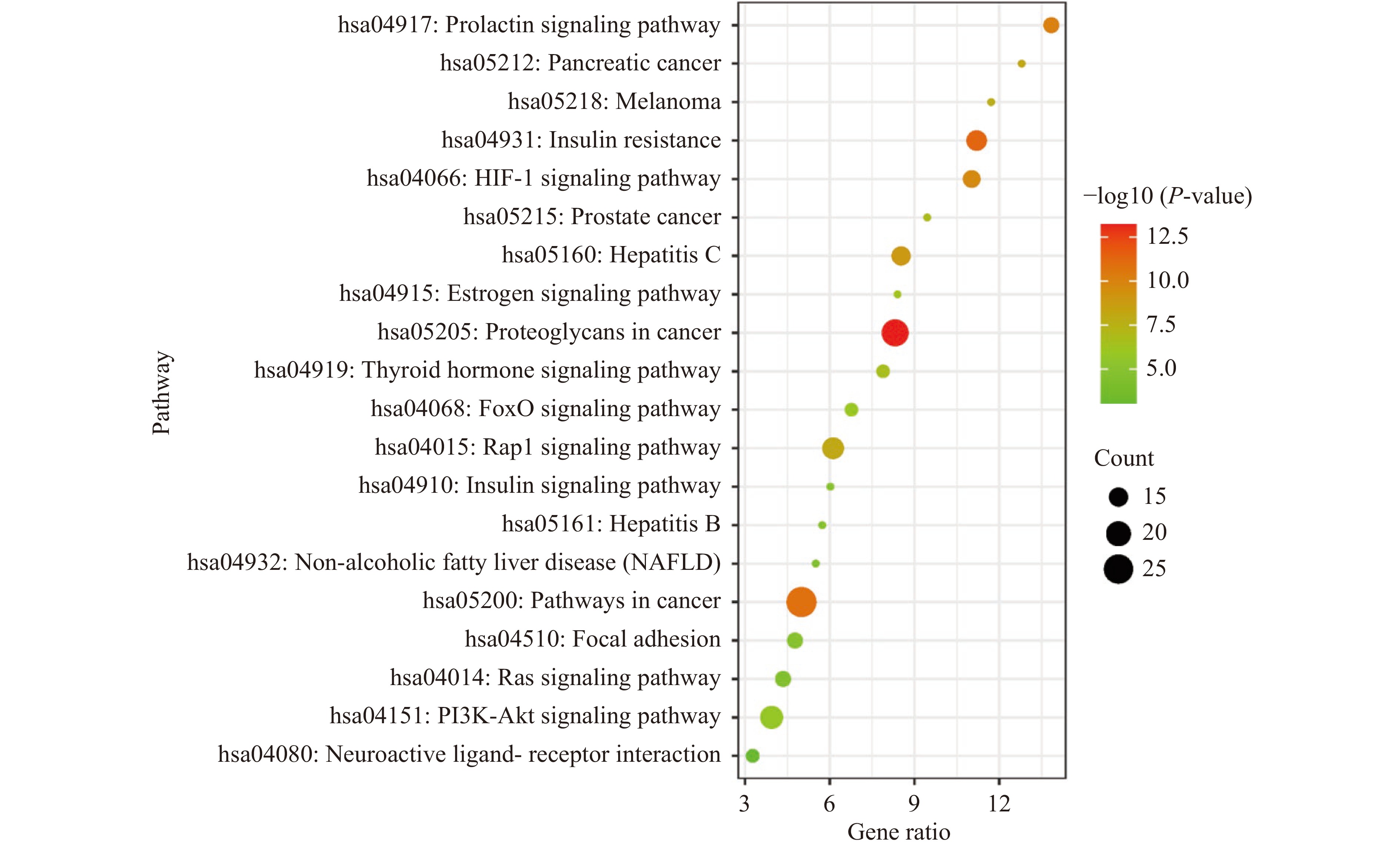
KEGG通路分析结果详见图6,图中气泡颜色代表富集显著性(P-value)的大小;气泡大小代表目标基因集中属于该pathway的基因数量。表4为KEGG富集排名前10通路信息表(P<0.01)。由图表可知绞股蓝治疗肥胖的靶点主要集中在癌症信号通路、癌症中蛋白多糖信号通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、Rap1信号通路、HIF-1信号通路等。
表 4 绞股蓝防治肥胖KEGG通路排名前10位富集分析Table 4. Enrichment analysis of the top 10 KEGG pathways序号 条目 KEGG通路 基因数 P值 1 hsa05200 癌症通路(Pathways in cancer) 26 1.47E-11 2 hsa05205 癌症中的蛋白多糖通路(Proteoglycans in cancer) 22 5.57E-14 3 hsa04151 PI3K-Akt信号通路(PI3K-AKT signaling pathway) 18 1.77E-06 4 hsa04015 小分子G蛋白Rap1介导的细胞信号转导通路(Rap1 signaling pathway) 17 9.38E-09 5 hsa04931 胰岛素抵抗(Insulin resistance) 16 5.57E-12 6 hsa05160 丙型肝炎(Hepatitis C) 15 1.33E-09 7 hsa04066 缺氧诱导因子1信号通路(HIF-1 signaling pathway) 14 2.26E-10 8 hsa04917 催乳素信号通路(Prolactin signaling pathway) 13 8.10E-11 9 hsa04510 局灶性粘连(Focal adhesion) 13 1.33E-05 10 hsa04014 Ras信号通路(Ras signaling pathway) 13 3.35E-05 2.6 绞股蓝降脂成分-靶点-通路网络构建
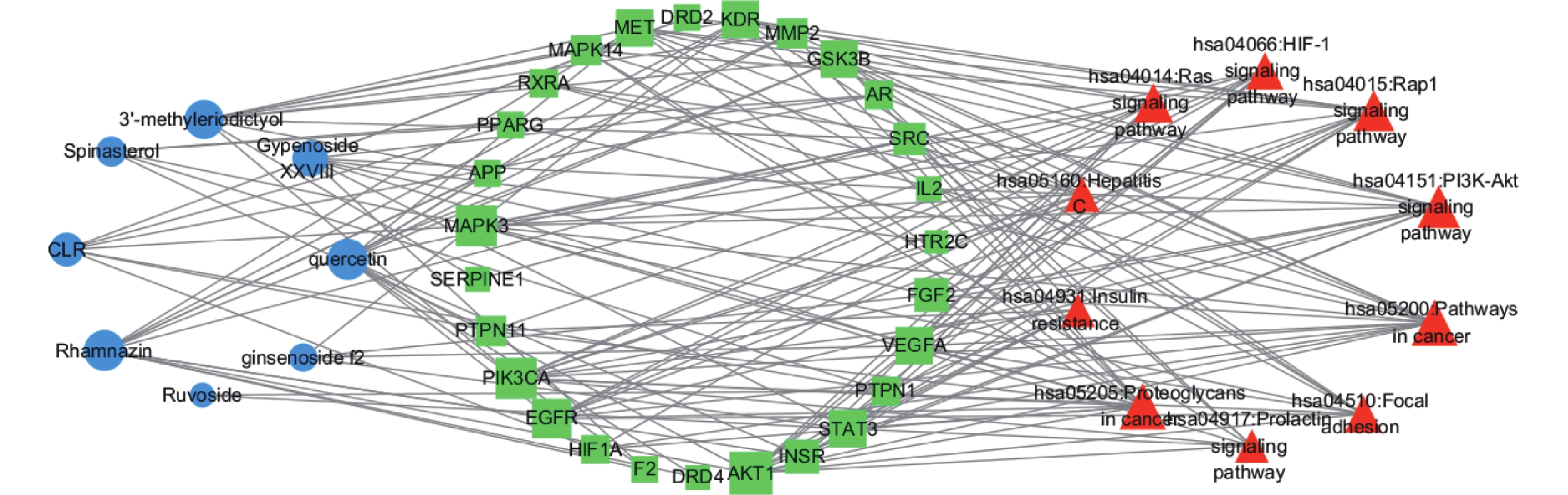
为进一步研究成分、靶点与信号通路之间的相互作用关系,将分子对接中筛选的8个潜在降脂关键药效成分、38个关键作用靶点及排名前10的作用通路采用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件构建“成分-靶标-通路”网络,详细见图7,图中蓝色圆形表示降脂成分,绿色矩形表示作用靶点,橙色三角形表示作用通路,图内连线表示各点之间的相互关系。由图7可得绞股蓝治疗肥胖有多个成分作用于同一靶点,同一靶点调节多个信号通路,体现出绞股蓝多成分、多靶点及多种作用通路协同防治肥胖。
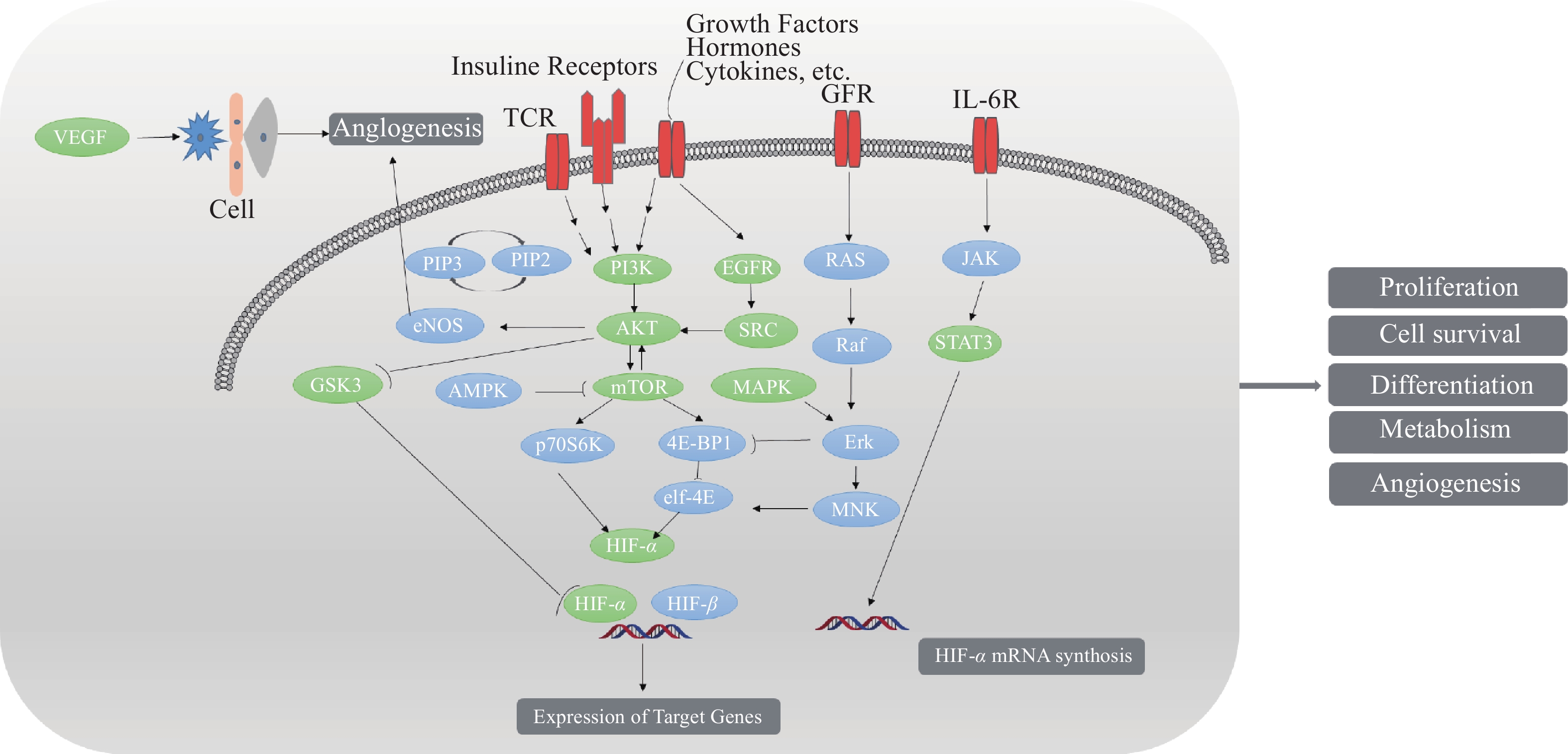
使用KEGG数据库搜索靠前信号通路,联合Cell Signaling数据库,得到关键靶点相互作用网络图,详细见图8。由图可知,绞股蓝可通过多个信号通路协同治疗肥胖,各通路间存在上下游关系,各靶点间存在相互作用关系。通过靶点与通路间网络,绞股蓝可调节细胞增殖、分化、存活、代谢等途径起到防治肥胖作用。如图中HIF-1通路受上游通路PI3K-Akt通路、STAT3通路调控,在这3条通路中绞股蓝防治肥胖靶点AKT1、STAT3、HIF-1处于关键节点,通过3条通路上靶点在细胞间、细胞质、细胞核内的相互作用,调控着细胞增殖、分化、代谢等过程。
3. 讨论
本研究筛选出绞股蓝中16个活性成分有对应肥胖靶标,这16个活性成分可能为绞股蓝防治肥胖物质基础。结合筛选出的核心靶点蛋白与对应化合物分子对接结合良好,分析出槲皮素、人参皂苷f2、绞股蓝皂苷XXVIII、3'-甲基柔二醇、黄夹次甙丙、3-甲基鼠李素、a-菠菜甾醇、胆甾醇8个化合物可能为防治肥胖关键药效成分。同时文献调研结果显示,如槲皮素可明显改善糖尿病肥胖大鼠体内的总胆固醇含量及体内的氧化应激反应[24],可调节MAPK信号转导中转导因子ERK1/2、JNK、P38MAPK、MCP-1及TNF-α表达量来抑制肥胖,还可提高脂肪组织中UCP1(内膜上解偶联蛋白1)水平来增加能量消耗,并在肥胖引起的炎症中,抑制炎症细胞因子IL-1、IL-6和刺激抗炎因子IL-10的分泌,达到防治肥胖目的[25]。人参皂苷f2可抑制脂肪生成标记物PPARγ表达进而阻止脂肪细胞分化起到降脂作用[26]。芦丁可抑制PPARγ和C/EBPα等成脂转录因子表达进而干扰脂肪前体细胞和肝细胞等的成脂过程[27],故本研究筛选结果有一定理论依据,可为绞股蓝治疗肥胖的药效成分研究提供方向。
药物靶点的预测揭示了药物与分子作用机制重要信息,对促进药物研发有着重要意义。在对绞股蓝降脂靶点筛选中,通过构建PPI网络图,筛选出节点相关性最强的靶点有AKT1、STAT3、VEGFA、SRC、EGFR、MAPK3。其中,AKT激酶是在脂肪细胞中具有关键体内功能的胰岛素效应器,可刺激葡萄糖摄取和糖原合成,以及蛋白质合成[28]。AKT1是AKT主要亚型之一,可介导胰岛素、IGF-1、IL-3以及其他生长因子的多种代谢、促有丝分裂和抗凋亡作用,是参与脂肪形成的重要致病因子[29]。相关实验已证明AKT1可增加CDK2(AKT磷酸化周期蛋白依赖性激酶)的活性使得3T3-L1细胞的生长周期变快影响其增殖和生长[30];STAT3是一种信号传导及转录激活蛋白,属于与DNA结合的STAT蛋白质家族。在机体内,白色脂肪组织向棕色脂肪组织转化对于改善肥胖具有重要意义[31],而STAT3作为减肥作用靶点时,STAT3能够进入线粒体,调节电子传递链,增加线粒体ATP生成,进而促进棕色脂肪生成,调节能量以维持正常能量稳态[32]。并且有研究报道STAT3可作为直接靶标通过调控脂肪酸代谢相关基因影响脂肪细胞增殖和分化[33]。VEGFA在脂肪发育和能量代谢中起重要调节作用。VEGFA属于VEGF家族,参与血管形成、调节血管通透性、维持血管生理功能等过程。而VEGFA与调节机体肥胖也有直接关系,脂肪组织会刺激内皮细胞的扩大产生VEGFA,进而促进新生毛细血管的形成,随后机体通过提高血清瘦素水平去控制血管生成,对抗脂肪细胞中脂质的积累[34]。在筛选的核心靶点中,SRC(非受体酪氨酸激酶)、EGFR(表皮生长因子受体)、MAPK3(丝裂原活化蛋白激酶3)这3个靶点可参与细胞增殖、分化、迁移和存活,且主要集中在癌症机制研究中[35]。文献显示癌细胞通常被大量脂肪细胞包围,这些脂肪细胞会产生富含脂肪酸的环境作为癌细胞生长的外部刺激,使得癌细胞对葡萄糖和谷氨酰胺异常高需求,继而表现出脂质代谢的改变即脂肪生成增加、脂肪酸摄取增加[36],因此筛选出这三个靶点有可能是其影响了癌细胞脂质代谢。通过上述文献调研可得绞股蓝的靶点筛选与目前大量药理学实验研究结果相吻合,后期可根据预测结果进一步探究药效成分与靶点作用关系。
在绞股蓝治疗肥胖的分子机制中,KEGG分析得富集靶点较多并且显著性较高的为癌症通路、癌症中的蛋白多糖通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、Rap1信号通路、HIF-1信号通路等。在肥胖发展过程中,细胞水平上表现为脂肪细胞数目增多、体积增大,这些变化导致脂质在脂肪组织中过量积累。而在肿瘤的发展过程中,机体同样发生增殖过度,期间肿瘤细胞增加促进生长的信号因子,改变对生长抑制提示的反应,下调保护性凋亡机制,增强肿瘤灌注和不受控制的复制遗传物质的能力等最终导致细胞无限制、无序增殖、组织侵袭和转移[37]。结合前面PPI筛选绞股蓝防治肥胖关键靶点,推测绞股蓝可能是通过调控如STAT3、AKT1、EGFR、VEGFA等靶点,参与细胞增殖和细胞凋亡的过程,达到抑制脂肪细胞不受控制分化、增殖目的。细胞外基质(ECM)是介导代谢和炎症信号转导,确保细胞功能完整性的中心枢纽。而蛋白多糖是胞外基质的重要组成部分,在胚胎发生、组织修复、炎症和癌症相关的信号通路中起到关键角色[38]。其中炎症与肥胖的相关性已得到广泛认可,尤其是中枢性肥胖,内脏脂肪的过度沉积与血清促炎细胞因子如IL-6、CRP、TNF水平升高有关[39]。故推测绞股蓝中活性成分可能通过癌症蛋白多糖通路影响由肥胖引起的慢性炎症的发展。PI3K-Akt信号通路在脂肪形成中影响脂肪细胞增殖,并且是调控血糖平衡的重要通路[40]。在该通路中PI3K激活后,在磷酸肌醇依赖性激酶的帮助下,导致Akt结合到细胞膜上,紧接着PI3K-Akt通过磷酸化糖原合酶激酶3β的N端丝氨酸来抑制糖原合酶激酶3β的活性增加细胞周期蛋白D1的积累,导致糖原的合成减少,增加糖酵解,促进葡萄糖摄入细胞,进而促进脂肪合成,故推断绞股蓝中活性成分可能通过抑制该通路影响机体糖脂代谢[41]。Rap1信号通路在PI3K-Akt通路上游,其中Rap1在各种代谢和信号通路中作为基因表达的分子决定因素,Rap1缺乏可导致多系统代谢紊乱,表现为葡萄糖不耐受、血脂异常、肝脏脂肪变性和过量脂肪堆积[42]。在PI3K-Akt通路下游mTOR靶向蛋白是细胞生长和增殖的关键调节分子,其通过PI3K-Akt或Ras-ERK信号通路接收生长因子、营养、能量等多种信号促进细胞生长增殖,而对mTOR信号通路的抑制可以使细胞停滞在G1期而触发细胞凋亡。在肥胖相关研究中,有文献报道药物可通过调节PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路,显著降低脂肪生成标记PPARγ、FASN和FABP4的表达水平,抑制前脂肪细胞增殖和分化[43]。由此结合KEGG分析推测绞股蓝活性成分很可能通过Rap1通路及PI3K-Akt-mTOR通路调控细胞增殖、生长及生成脂质基因发挥防治肥胖作用。在KEGG分析中胰岛素抵抗通路排第五位,病理研究显示肥胖会通过诱导胰岛素抵抗来增加2型糖尿病的风险,且由于机体能量代谢不平衡,脂肪细胞变大,增生,内质网应激和线粒体功能障碍等,使得炎性因子水平升高,机体呈现一种慢性炎性反应进而影响全身各器官[44]。由此推测绞股蓝活性成分可能通过胰岛素抵抗通路影响机体糖脂代谢及炎症因子分泌达到防治肥胖作用。在KEGG分析中HIF-1信号通路显著性也较高,其中绞股蓝降脂靶点HIF-α处在PI3K-Akt-mTOR通路和STAT3通路下游,其蛋白水平受PI3K-Akt-mTOR和STAT3调节[45],同时HIF-α也可调控众多下游基因,包括血管生成基因(VEGF),红细胞生成和能量代谢基因(GLUT1,ALDOA,ENO1,LDHA,PFK2,PGK1和HK),细胞增殖和分化基因(FGFs,TGF和IGF)。在肥胖状态下,脂肪细胞可通过增加HIF-α来控制线粒体的生物发生和糖酵解,增加胰岛素抵抗来控制脂肪细胞消耗氧气维持机体稳态[46]。因此如果绞股蓝中活性成分通过HIF-1通路激活HIF-α将是治疗肥胖和胰岛素抵抗的重要药物研发方向。
综上,本研究利用网络药理学方法及分子对接技术对绞股蓝防治肥胖的活性成分、潜在靶点和作用机制进行了初步预测分析,阐述了绞股蓝通过多成分、多靶点、多通路的协同作用,影响机体脂肪细胞增殖分化、脂质基因表达、糖脂代谢及机体炎症等发挥疗效,为后续更深层次的挖掘绞股蓝防治肥胖机制及绞股蓝药物的开发利用提供了新思路和方向。
-
表 1 绞股蓝活性成分信息
Table 1 Active ingredient information of Gynostemma pentaphyllum
序号 分子ID 分子名称 分子量 OB (%) DL 1 MOL000338 3'-methyleriodictyol 302.3 51.61 0.27 2 MOL000351 Rhamnazin 330.31 47.14 0.34 3 MOL000359 sitosterol 414.79 36.91 0.75 4 MOL004350 Ruvoside 390.57 36.12 0.76 5 MOL004355 Spinasterol 412.77 42.98 0.76 6 MOL005438 campesterol 400.76 37.58 0.71 7 MOL005440 Isofucosterol 412.77 43.78 0.76 8 MOL007475 ginsenoside f2 785.14 36.43 0.25 9 MOL000953 CLR 386.73 37.87 0.68 10 MOL000098 quercetin 302.25 46.43 0.28 11 MOL009973 Gypenoside XXVIII 416.71 32.08 0.74 12 MOL009855 (24S)-Ethylcholesta-5,22,25-trans-3beta-o 410.75 46.91 0.76 13 MOL009867 4α,14α-dimethyl-5α-ergosta-7,9(11),24(28)-trien-3β-ol 424.78 46.29 0.76 14 MOL009877 cucurbita-5,24-dienol 426.8 44.02 0.74 15 MOL009878 Cyclobuxine 386.69 84.48 0.70 16 MOL009888 Gypenoside XXXVI 458.8 37.85 0.78 17 MOL009928 Gypenoside LXXIV 801.14 34.21 0.24 18 MOL009929 Gypenoside LXXIX 785.14 37.75 0.25 19 MOL009938 Gypenoside XII 785.14 36.43 0.25 20 MOL009943 Gypenoside XL 799.12 30.89 0.21 21 MOL009969 Gypenoside XXXV 444.77 37.73 0.78 22 MOL009971 Gypenoside XXVII 418.73 30.21 0.74 23 MOL009976 Gypenoside XXXII 787.11 34.24 0.25 24 MOL009986 Gypentonoside A 472.78 36.13 0.80 25 MOL000131 EIC 280.5 41.9 0.14 26 MOL001746 ELD 281.54 31.2 0.14 27 MOL005284 (3S,5R,6S,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-
methylhept-5-en-2-yl]
-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6,12-triol476.82 20.13 0.78 28 MOL005327 Gypnoside V 460.82 29.69 0.77 29 MOL005334 (3S,5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R,17S)-17-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-6-
methylhept-5-en-2-yl]
-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-2,3,5,6,7,9,11,12,13,15,16,17
-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,12-diol460.82 29.69 0.77 30 MOL005364 Malonylginsenoside Rd 460.82 29.69 0.77 31 MOL006728 Gypenoside XIV 460.82 29.69 0.77 32 MOL006734 Gypenoside I 460.82 29.69 0.77 33 MOL000675 oleic acid 282.52 33.13 0.14 34 MOL006754 ginsenoside Rb3 460.82 29.65 0.81 35 MOL000086 (24S)-5beta-Stigmastan-3beta-ol 416.81 25.32 0.75 36 MOL009860 2α-hydroxypanaxadiol 476.82 21.44 0.8 37 MOL009871 6'-malonylgypenoside V 460.82 29.69 0.77 38 MOL009873 7-(6-O-Malony-beta-D-glucopyransyloxy)-3-(4-hydroxphenyl)-4H-
1-benzopyran-4-one504.48 29.25 0.84 39 MOL009882 gynosaponin TN-1 476.82 20.13 0.79 40 MOL009884 gynsenoside Rd 460.82 29.69 0.77 41 MOL009894 Gypenoside L 446.79 29.61 0.78 42 MOL009896 Gypenoside LI 476.82 20.13 0.79 43 MOL009899 Gypenoside LIII 769.09 22.94 0.22 44 MOL009900 Gypenoside XL 474.8 29.29 0.79 45 MOL009910 Gypenoside LVIII 474.85 29.69 0.79 46 MOL009912 Gypenoside LX 476.82 20.13 0.79 47 MOL009920 Gypenoside LXVIII 462.79 20.59 0.8 48 MOL009924 Gypenoside LXXI 460.82 29.16 0.78 49 MOL009927 Gypenoside LXXIII 460.82 29.69 0.78 50 MOL009945 Gypenoside XLI 460.82 29.65 0.78 51 MOL009958 Gypenoside XVIII 446.79 29.4 0.77 52 MOL009962 Gypenoside XXX 446.79 29.4 0.78 53 MOL009964 Gypenoside XXIX 444.77 23.9 0.78 54 MOL009967 Gypenoside XXV 474.8 28.89 0.8 55 MOL009980 Gypenoside XXXIX 801.14 20.46 0.21 56 MOL009981 Gypenoside XXXIX 476.82 20.13 0.79 57 MOL009989 Gypinoside LXVII 476.82 20.18 0.79 58 MOL009992 Gypsogenin 470.76 26.77 0.75 59 MOL009998 Toddaculin 274.34 47.85 0.17 60 MOL009949 Gypenoside XLIX 1093.41 17.74 0.06 61 MOL009891 Gypenoside IV 1079.43 7.81 0.04 62 MOL009935 Gypenoside VⅢ 769.09 8.08 0.22 63 MOL009995 Ombuoside 638.63 14.86 0.63 64 MOL000415 Rutin 610.57 3.20 0.68 表 2 各活性成分对应防治肥胖关键靶点基因
Table 2 Corresponding gene of each active ingredient
分子ID 名称 关键靶点 MOL000338 3'-methyleriodictyol SRC、GSK3B、MMP2、KDR、MET、MAPK14、RXRA、APP、SERPINE1、PIK3CA MOL000351 Rhamnazin SRC、EGFR、MMP2、MET、KDR、GSK3B、F2、DRD4、AKT1、APP、INSR MOL000359 sitosterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG MOL004350 Ruvoside STAT3、PTPN1 MOL004355 Spinasterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG、MAPK3、PTPN11 MOL005438 campesterol AR、PTPN1 MOL005440 Isofucosterol AR、PTPN1、PPARG MOL007475 ginsenoside f2 STAT3、VEGFA、FGF2、KDR MOL000953 CLR AR、PTPN1、PPARG、PGR、MAPK3、PTPN11、DRD2、HIF1A MOL000098 quercetin EGFR、F2、DRD4、GSK3B、SRC、KDR、MMP2、MET、AKT1、INSR、APP MOL009973 Gypenoside XXVIII HTR2C、IL2、AR、VEGFA、FGF2、STAT3、DRD2、F2 MOL000415 rutin PTGS2、TNF、IL2 MOL009900 Gypenoside XLIX PPARA、TNF MOL009992 Gypsogenin ESR1、AR、CYP19A1、ESR2、FABP1、NOS2、NR3C1、PGR、PPARA、PPARG、PTGS2、PTPN1、PTPN11、PTPN2 MOL000131 EIC AR、CYP19A1、ESR1、ESR2、FABP1、MAPK14、NOS2、NR3C1
PGR、PPARA、PPARG、PTGS2、PTPN1、PTPN11、PTPN2MOL001746 ELD CYP19A1、MAPK14 注:加黑靶点为PPI中度值前六位核心靶点。 表 3 绞股蓝关键成分与对应核心靶点相互作用能量打分表
Table 3 Key components and the corresponding core target interaction energy score table
序号 成分 AKT1 STAT3 VEGFA EGFR SRC MAPK3 1 3'-methyleriodictyol − − − − −34.3333 − 2 Rhamnazin −38.7675 − − −34.8522 −37.7041 − 3 Ruvoside − −23.7509 − − − − 4 Spinasterol − − − − − −47.6866 5 ginsenoside f2 − −39.1435 −22.8832 − − − 6 CLR − − − − −38.7851 −49.6606 7 quercetin −39.6114 − − −38.8686 − − 8 Gypenoside XXVIII − −44.2180 −28.0355 − − − 注:“−”表示化合物筛选中无该核心作用靶点。 表 4 绞股蓝防治肥胖KEGG通路排名前10位富集分析
Table 4 Enrichment analysis of the top 10 KEGG pathways
序号 条目 KEGG通路 基因数 P值 1 hsa05200 癌症通路(Pathways in cancer) 26 1.47E-11 2 hsa05205 癌症中的蛋白多糖通路(Proteoglycans in cancer) 22 5.57E-14 3 hsa04151 PI3K-Akt信号通路(PI3K-AKT signaling pathway) 18 1.77E-06 4 hsa04015 小分子G蛋白Rap1介导的细胞信号转导通路(Rap1 signaling pathway) 17 9.38E-09 5 hsa04931 胰岛素抵抗(Insulin resistance) 16 5.57E-12 6 hsa05160 丙型肝炎(Hepatitis C) 15 1.33E-09 7 hsa04066 缺氧诱导因子1信号通路(HIF-1 signaling pathway) 14 2.26E-10 8 hsa04917 催乳素信号通路(Prolactin signaling pathway) 13 8.10E-11 9 hsa04510 局灶性粘连(Focal adhesion) 13 1.33E-05 10 hsa04014 Ras信号通路(Ras signaling pathway) 13 3.35E-05 -
[1] JURA M, KOZAK L P. Obesity and related consequences to ageing[J]. Age (Dordr),2016,38(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s11357-016-9884-3
[2] ORTEGA F B, LAVIE C J, BLAIR S N. Obesity and cardiovascular disease[J]. Circ Res,2016,118(11):1752−1770. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306883
[3] TAHERGORABI Z, KHAZAEI M, MOODI M, et al. From obesity to cancer: A review on proposed mechanisms[J]. Cell Biochem Funct,2016,34(8):533−545. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3229
[4] 顾志敏. 降脂中药的研究进展[C]//天津: 第十三届中国科协年会论文集. 中国科协, 2011: 1−4. GU Z M. Research progress of lipid-lowering Chinese medicine[C]// Tianjin: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference of China Association for Science and Technology. China Association for Science and Technology, 2011: 1−4.
[5] 张欣怡, 夏明明. 绞股蓝化学成分的降血脂机制研究进展[J]. 光明中医,2020,345(8):161−164. [ZHANG X Y, XIA M M. Research progress on the mechanism of lowering blood lipids of the chemical constituents of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Guangming Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,345(8):161−164. [6] 沈子琳, 王振波, 侯会芳, 等. 绞股蓝的化学成分和药理作用及应用研究新进展[J]. 人参研究,2020,32(5):59−64. [SHEN Z L, WANG Z B, HOU H F, et al. The chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum and the new progress of application research[J]. Ginseng Research,2020,32(5):59−64. [7] 田梦菲, 陈涤平, 李文林, 等. 肥胖与中医体质类型相关性的研究进展[J]. 广东医学,2018,1(39):68−70. [TIAN M F, CHEN D P, LI W L, et al. Research progress on the correlation between obesity and traditional Chinese medical constitution[J]. Guangdong Medicine,2018,1(39):68−70. [8] JIAN H, SU H, WANG C, et al. Hypolipidemic mechanism of gypenosides via inhibition of pancreatic lipaseand reduction in cholesterol micellar solubility[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2016,242(3):305−312. doi: 10.1007/s00217-015-2540-9
[9] 汪巍. 胆汁酸通路介导的绞股蓝总皂苷调节糖脂代谢的作用机制研究[D]. 遵义: 遵义医学院, 2017. WANG W. Study on the mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum by bile acid pathway in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical College, 2017.
[10] CHOI I, PARK Y, CHOI H, et al. Anti-adipogenic activity of rutin in 3T3-L1 cells and mice fed with high-fat diet[J]. Biofactors,2006,26(4):273−281. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520260405
[11] KOJTA I, CHACIŃSKA M, BŁACHNIO-ZABIELSKA A. Obesity, bioactive lipids, and adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(5):1305. doi: 10.3390/nu12051305
[12] 张敏. 槲皮素调节胆固醇代谢作用的途径分析[D]. 北京: 解放军军事医学科学院, 2016. ZHANG M. Analysis of the pathways of quercetin regulating cholesterol metabolism[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Military Medical Sciences, 2016.
[13] 杨夏, 冯颖淑, 童珊珊, 等. 降血脂多糖活性机制及构效关系研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2018,43(20):4011−4018. [YANG X, FENG Y S, TONG S S, et al. Progress in research on the mechanism and structure-activity relationship of lipid-lowering polysaccharide activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2018,43(20):4011−4018. [14] ZHANG W, BAI Y, WANG Y, et al. Polypharmacology in drug discovery: A review from systems pharmacology perspective[J]. Curr Pharm Des,2016,22(21):3171−3181. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160224142812
[15] 王乐琪, 张云帆, 李莎莎, 等. 丹参治疗微循环障碍作用机制的“成分-靶点-通路”多层次互作网络模型研究[J]. 中草药,2020,51(2):439−450. [WANG L Q, ZHANG Y F, LI S S, et al. Research on the “component-target-pathway” multi-level interaction network model of the mechanism of action of Danshen in the treatment of microcirculation disorders[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2020,51(2):439−450. [16] 谈钰濛, 胡骏, 倪青. 黄芪防治糖尿病肾病的网络药理学研究[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2020,15(8):1480−1489. [TAN Y M, HU J, NI Q. A network pharmacology study on the prevention and treatment of diabetic nephropathy by Astragalus[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,2020,15(8):1480−1489. [17] LI Y, ZHANG J, CHEN X, et al. Systems pharmacology to decipher the combinational anti-migraine effects of Tianshu formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2015,174:45−56. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.043
[18] 鲍凤霞, 陶泠雪, 章海燕. 绞股蓝有效成分的药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志,2018,1(3):11−17. [BAO F X, TAO L X, ZHANG H Y. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of the active ingredients of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinics,2018,1(3):11−17. [19] 史琳, 王志成, 时圣明, 等. 绞股蓝皂苷水解产物化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究,2017,40(5):711−716. [SHI L, WANG Z C, SHI S M, et al. Research progress on the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of hydrolysates of gypenosides pentaphyllum[J]. Drug Evaluation Research,2017,40(5):711−716. [20] 王绍辉, 陈道金, 刘同祥. 绞股蓝化学成分, 药理作用及其体内代谢的研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术:中医药现代化,2015,11(11):2389−2393. [WANG S H, CHEN D J, LIU T X. Research progress on the chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and metabolism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. World Science and Technology: Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,11(11):2389−2393. [21] SZKLARCZYK D, MORRIS J H, COOK H, et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible[J]. Nucleic Acids Res,2017,45(1):362−368.
[22] 陈江锋, 林芝娴, 韩孙亚, 等. 基于网络药理学结合分子对接方法探讨绞股蓝治疗非小细胞肺癌的作用机制[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2020,37,183(3):121−129. [CHEN J F, LIN Z X, HAN S Y, et al. Explore the mechanism of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer based on network pharmacology combined with molecular docking methods[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,37,183(3):121−129. [23] YASUO N, SEKIJIMA M. Improved method of structure-based virtual screening via interaction-energy-based learning[J]. J Chem Inf Model,2019,59(3):1050−1061. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00673
[24] 郭艳芳, 张皓, 朱玲, 等. 槲皮素改善糖尿病肥胖大鼠糖脂代谢紊乱及总胆固醇的作用[J]. 解剖学研究,2018,40(6):49−53. [GUO Y F, ZHANG H, ZHU L, et al. Effects of quercetin on improving glucose and lipid metabolism disorder and total cholesterol in diabetic obese rats[J]. Anatomical Research,2018,40(6):49−53. [25] SATO S, MUKAI Y. Modulation of chronic inflammation by quercetin: The beneficial effects on obesity[J]. J Inflamm Res,2020,13:421−431. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S228361
[26] SIRAJ F M, SATHISHKUMAR N, KIM Y J, et al. Ginsenoside F2 possesses anti-obesity activity via binding with PPARγ and inhibiting adipocyte differentiation in the 3T3-L1 cell line[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem,2015,30(1):9−14. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2013.871006
[27] SANCHEZ-GURMACHES J, MARTINEZ CALEJMAN C, JUNG S M, et al. Brown fat organogenesis and maintenance requires AKT1 and AKT2[J]. Mol Metab,2019,23:60−74. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.02.004
[28] YUAN X, WEI G, YOU Y, et al. Rutin ameliorates obesity through brown fat activation[J]. Faseb J,2017,31(1):333−345. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600459rr
[29] JIA X, CHANG T, WILSON T W, et al. Methylglyoxal mediates adipocyte proliferation by increasing phosphorylation of Akt1[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(5): e36610.
[30] CLEMENTE-POSTIGO M, TINAHONES A, EL BEKAY R, et al. The role of autophagy in white adipose tissue function: Implications for metabolic health[J]. Metabolites,2020,10(5):179. doi: 10.3390/metabo10050179
[31] 徐梦, 马青, 范春兰, 等. STAT3与线粒体电子传递链[J]. 生理科学进展,2019,50(5):366−370. [XU M, MA Q, FAN C L, et al. STAT3 and the mitochondrial electron transport chain[J]. Advances in Physiological Sciences,2019,50(5):366−370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2019.05.011 [32] XU Y, DU J, ZHANG P, et al. MicroRNA-125a-5p mediates 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation[J]. Molecules,2018,23(2):317. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020317
[33] 芦小单. 血管内皮生长因子参与脂肪组织分化和能量代谢的调节机制[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2012. LU X D. The regulation mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor involved in adipose tissue differentiation and energy metabolism[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2012.
[34] JÁSZAI J, SCHMIDT M H H. Trends and challenges in tumor anti-angiogenic therapies[J]. Cells,2019,8(9):1102. doi: 10.3390/cells8091102
[35] MIYAKE T, PARSONS S J. Functional interactions between Choline kinase α, epidermal growth factor receptor and c-Src in breast cancer cell proliferation[J]. Oncogene,2012,31(11):1431−1441. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.332
[36] SONG L, LIU Z, HU H H, et al. Proto-oncogene Src links lipogenesis via lipin-1 to breast cancer malignancy[J]. Nat Commun,2020,11(1):5842. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19694-w
[37] PESSENTHEINER A R, DUCASA G M, GORDTS P L S M. Proteoglycans in obesity-associated metabolic dysfunction and meta-inflammation[J]. Front Immunol,2020,11:769. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00769
[38] AMIN M N, HUSSAIN M S, SARWAR M S, et al. How the association between obesity and inflammation may lead to insulin resistance and cancer[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr,2019,13(2):1213−1224. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.01.041
[39] CHUANG C C, YANG R S, TSAI K S, et al. Hyperglycemia enhances adipogenic induction of lipid accumulation: Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma signaling[J]. Endocrinology,2007,148(9):4267−4275. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0179
[40] XIE Y, SHI X, SHENG K, et al. PI3K/Akt signaling transduction pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia[J]. Mol Med Rep,2019,19(2):783−791.
[41] CAI R, SUN Y, QIMUGE N, et al. Adiponectin AS lncRNA inhibits adipogenesis by transferring from nucleus to cytoplasm and attenuating adiponectin mRNA translation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids,2018,1863(4):420−432.
[42] YEUNG F, RAMÍREZ C M, MATEOS-GOMEZ P A, et al. Nontelomeric role for Rap1 in regulating metabolism and protecting against obesity[J]. Cell Rep,2013,3(6):1847−1856. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.05.032
[43] CAI R, TANG G, ZHANG Q, et al. A novel lnc-RNA, named lnc-ORA, is identified by RNA-Seq analysis, and its knockdown inhibits adipogenesis by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Cells,2019,8(5):477. doi: 10.3390/cells8050477
[44] YE J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity[J]. Front Med,2013,7(1):14−24. doi: 10.1007/s11684-013-0262-6
[45] KASUNO K, TAKABUCHI S, FUKUDA K, et al. Nitric oxide induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation that is dependent on MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling[J]. Biol Chem,2004,279(4):2550−2558. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308197200
[46] CIFARELLI V, BEEMAN S C, SMITH G I, et al. Decreased adipose tissue oxygenation associates with insulin resistance in individuals with obesity[J]. J Clin Invest,2020,130(12):6688−6699. doi: 10.1172/JCI141828
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 冯博,邵毅,黄柳娟,禹建虎,龚新武,白冰. 不同处理方式对‘大泡’青皮核桃采后保鲜效果的影响. 上海农业学报. 2024(01): 103-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王盼盼,管维良,孙志栋,蔡路昀. 芥末精油复合1-甲基环丙烯保鲜处理对绿花菜贮藏期间品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(11): 270-279 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李金金,李春媛,罗铮,张鹏,张爱琳,吴迪,李江阔. 高值果蔬采后保鲜技术研究进展. 保鲜与加工. 2024(06): 109-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张玉萍,莫丽媛,丁惠敏,史君彦,王文亮,王延圣,乔丽萍. 双乙酰处理对鲜切西兰花贮藏品质及抗氧化能力的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(24): 114-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 钱井,郑鄢燕,李蔚,满杰,郑丽静,韦强,赵立群. 1-甲基环丙烯结合寡雄腐霉菌对番茄贮藏品质的影响. 食品科技. 2023(09): 23-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘培秀,赵美萱,杨梅,雷晓英,刘文强,杨敏,李玉鹏. 西兰花粉营养成分及理化性质研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(11): 326-333 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



