Establishment of Indirect Competitive ELISA Method for Detecting Amanitin in Mushroom
-
摘要: 目的:旨在建立一种检测蘑菇中鹅膏毒肽(Amanitin, AMA)的间接竞争酶联免疫吸附方法(Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ic-ELISA)。方法:通过EDC/NHS在α-鹅膏毒肽的羧基位置引入6-氨基己酸得到半抗原,并进一步与不同的载体蛋白偶联制备免疫原和包被原。之后,利用免疫原免疫Balb/c小鼠制备单克隆抗体。基于所获得的抗体,并通过对包被原和抗体工作浓度、包被条件、封闭条件、酶标二抗工作浓度和孵育时间等条件的优化,建立了蘑菇中鹅膏毒肽间接竞争ELISA检测方法,最后对所建立方法的灵敏度、添加回收率、批内及批间变异等参数进行了评价。结果:合成的半抗原分子量为1033.12,经MALDI-TOF鉴定免疫原的偶联比约为10.03。基于杂交瘤技术制备、筛选出鼠单克隆抗体13H4的IC50为1.91 μg/L。基于所获得单克隆抗体,所建立蘑菇中鹅膏毒肽间接竞争ELISA方法的检出限为0.88 μg/kg,添加回收率为85.66%~113.05%,批内变异系数为5.35%~9.54%,批间变异系数小于15%。结论:本研究所建立的ic-ELISA方法准确度、精密度、灵敏度较高、性能稳定,为突发毒蘑菇中毒事件的毒原分析提供了一种简便、可靠的快速检测方法。
-
关键词:
- 蘑菇 /
- 鹅膏毒肽 /
- 间接竞争酶联免疫吸附测定法
Abstract: Objective: This study aims to establish an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of amanitin (AMA) in mushroom. Methods: In this study, the hapten was obtained by introducing 6-aminocaproic acid into the carboxyl position of the α-amanotropin molecule through EDC/NHS, and further coupled with different carrier proteins to prepare immunogens and coating antigen. Afterwards, Balb/c mice were immunized with the immunogen to prepare monoclonal antibodies. Based on the obtained antibody, an indirect competitive ELISA method for the detection of amanitin in mushroom was established by optimizing the working concentrations of coating antigen and antibody, coating conditions, blocking conditions, working concentrations of enzyme labeled secondary antibody and incubation time. Finally, the sensitivity, recovery rate, intra batch and inter batch variation of the established method were evaluated. Results: The molecular weight of the synthesized hapten in this study was 1033.12, and the coupling ratio of the immunogen identified by MALDI-TOF was about 10.03. Based on hybridoma technology, the IC50 of the mouse monoclonal antibody 13H4 was 1.91 μg/L. Based on the obtained monoclonal antibody, the detection limit of the established ic-ELISA method for amanitin in mushroom was 0.88 μg/kg, the recovery rate was 85.66%~113.05%, the intra-assay coefficient of variation was 5.35%~9.54%, and the inter-assay coefficient of variation was less than 15%. Conclusion: The ic-ELISA method established in this study had high accuracy, precision, sensitivity, and stable performance. It provided a simple, reliable and rapid detection method for the analysis of the toxicogen of sudden mushroom poisoning. -
蘑菇引起的食物中毒一直是世界上许多国家重点关注的食品安全问题之一。近年来,我国因误食毒蘑菇而引起的中毒事件频发,且死亡率居高不下。我国蘑菇资源丰富,有记载的毒蘑菇多达480多种,其中,鹅膏菌属类蘑菇含有一种毒性环肽,即鹅膏毒肽[1]。鹅膏毒肽能与真核细胞RNA聚合酶Ⅱ、DNA模板及新合成的RNA形成稳定的四元复合物,进而阻碍蛋白质的合成,最终导致肝脏等组织细胞的坏死[2]。据报道,我国90%以上的蘑菇食物中毒死亡事件都是由鹅膏毒肽引起的[3]。鹅膏毒肽主要包括α-鹅膏毒肽、β-鹅膏毒肽和γ-鹅膏毒肽,对人的口服半数致死量(LD50)分别为0.3、0.5和0.2 mg/kg [4-5]。误食含有鹅膏毒肽的毒蘑菇后,一旦出现了中毒症状,抢救效果往往不好,死亡率较高[6]。因此,早期诊断对于鹅膏毒肽中毒的救治尤为重要。
目前,检测鹅膏毒肽的方法主要有液相色谱法[7-8]、超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法[9-11]、超高效液相色谱-四极杆飞行时间质谱[12-15]、基因扩增技术[16-17]、毛细管电泳法[18-19]、酶联免疫吸附法[20-23]等。仪器方法是近年来应用最为广泛的检测方法,具有灵敏度高、准确性好等优点,但是仪器方法操作繁琐,价格昂贵,不适用大批量样品的现场检测。超分支滚环扩增技术对人员的操作技术要求较高,很难实现广泛的推广使用。相比之下,酶联免疫分析方法作为一种操作简便、灵敏度高、检测时间短的快检方法,在蘑菇毒素检测项目中备受关注,许多国家已经批准了一系列商业ELISA试剂盒的应用,但国内对于α-鹅膏毒肽的免疫学检测方法的报道较少[24-25]。
因此,本研究欲建立一种快速、灵敏、准确的蘑菇中α-鹅膏毒肽间接竞争ELISA检测方法,为突发毒蘑菇中毒事件的快速诊断提供一种便捷可靠的检测技术手段,对保障人们的生命健康有着重要的现实意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
甲醇(CH3OH)、碳酸氢钠(NaHCO3)、硫酸铵((NH4)2SO4) 中国医药集团有限公司;1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐(EDC)、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF) 上海江莱生物科技有限公司;N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺(NHS) 北京中生瑞泰科技有限公司;牛血清蛋白(BSA)、卵清蛋白(OVA) 美国Amresco公司;辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)、弗氏完全佐剂(FCA)和弗氏不完全佐剂(FICA)等药物 Sigma公司;6~8周龄Balb/c雌鼠 北京实验动物研究中心,实验动物许可证号SYXK(京)2020-0038;α-鹅膏毒肽、β-鹅膏毒肽和γ-鹅膏毒肽等标准品(纯度≥95%) 上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;蘑菇样品,共计30份 美廉美超市、物美温泉品超市和前沙涧早市。
ES-A电子天平 天津德安特传感技术有限公司;Sorvall LYNX 6000超速离心机、MK3酶标仪 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific;KQ-100E超声波清洗仪 昆山市超声仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 溶液配制
鹅膏毒肽标准溶液:准确称取1.0 mg鹅膏毒肽标准品,用甲醇溶解并定容至10 mL,配制成100 ppm的标准品储备液,于−20 ℃避光保存,备用;洗液(PBST):取300 μL Tween-20加入到100 mL PBS(0.02 mol/L)中混匀,备用。
1.2.2 鹅膏毒肽抗原的制备
称取α-鹅膏毒肽标准品10 mg,10 mL DMF溶解,再加入6.25 mg EDC与3.75 mg NHS,室温反应3 h。然后,再加入1.42 mg 6-氨基己酸,室温反应过夜,采用薄层制备板纯化得半抗原(图1)。
称取2.29 mg α-鹅膏毒肽半抗原,用0.5 mL DMF溶解,200 r/min室温搅拌10 min,加入1 mg EDC溶解后再加入1 mg NHS,室温500 r/min搅拌活化2~3 h。将上述反应液逐滴加入到5 mL含有1% BSA(包被原:1% OVA)的碳酸氢钠缓冲溶液(0.1 mol/L)中,500 r/min室温搅拌反应24 h。用1 L0.01 mol/L PBS(pH7.2)透析3 d(4 ℃,100 r/min),每天换液3次(早中晚各一次),共计换液9次。将透析产物5000 r/min离心6 min,即得到鹅膏毒肽完整抗原,并通过MALDI-TOF/MS对所合成抗原的偶联比进行测定[26]。
1.2.3 单克隆抗体的制备
使用1.2.2制备的免疫原免疫6~8周龄的健康雌性BALB/c小鼠,共4只,免疫前需观察7 d。将100 μg免疫原用无菌生理盐水稀释至1 mg/mL,首次免疫加入等量的弗氏完全佐剂,完全乳化后,采用颈背部皮下、多点注射的方式免疫4只小鼠。共免疫6次,每次免疫间隔时间均为2周。具体免疫方案见表1。
表 1 单克隆抗体(小鼠)的免疫程序Table 1. Monoclonal antibody (mouse) immune program免疫次数 免疫原 剂量 免疫方式 首次免疫 免疫原+FCA 100 μg/只 颈背部皮下多点注射 二免 免疫原+FICA 同上 同上 三免 同上 同上 同上 四免 同上 同上 同上 五免 同上 同上 同上 六免(加强免疫) 免疫原 同上 腹腔注射 四免一周后,对小鼠眼眶进行采血,室温放置2 h,4000 r/min离心10 min。然后,采用间接ELISA方法对血清效价进行检测[27]。末次免疫后,将免疫小鼠的脾细胞与小鼠骨髓瘤细胞(SP2/0)混合,用50% PEG进行细胞融合,用HAT培养基悬浮均匀,再加入适量的饲养细胞,于96孔培养板中,37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养,5 d后用HAT培养基半换液,9 d后进行全换液。然后采用间接ELISA方法,选择和标记效价高、抑制率高的阳性杂交瘤细胞。将阳性杂交瘤细胞用半固体培养基培养法进行2~3次培养,将最终获得的阳性单克隆细胞株采用体内诱生法制备腹水,腹水采用Protein A亲和层析柱进行纯化,最终得到鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体。
1.2.4 特异性试验
选择与α-鹅膏毒肽具有类似结构的β-鹅膏毒肽,γ-鹅膏毒肽和鬼笔毒肽进行ELISA测定,通过标准曲线分别得到各自的IC50值,然后根据下式计算α-鹅膏毒肽结构类似物的交叉反应率(%):
式中:IC50(α-鹅膏毒肽)为引起50%抑制的α-鹅膏毒肽浓度(μg/L);IC50(结构类似物)为引起50%抑制的结构类似物浓度(μg/L)[28]。
1.2.5 ic-ELISA检测方法的建立
用包被液将包被抗原稀释至最适浓度,按照100 μL/孔加入酶标板,孵育一定时间。用PBST洗板3次后,每孔加入150 μL封闭液,封闭一段时间,弃去封闭液并拍干。竞争反应:加入鹅膏毒肽标准品或待测样品,50 μL/孔,再加入50 μL合适浓度的抗体工作液,37 ℃孵育竞争反应30 min。用PBST(300 μL/孔)洗板3次后,每孔加入100 μL的酶标二抗HRP-IgG,37 ℃孵育一段时间。用PBST(300 μL/孔)洗板3次后,加入新鲜配制的TMB溶液(100 μL/孔),37 ℃避光反应15 min。加入2 mol/L H2SO4(50 μL/孔),用酶标仪测定各孔的OD450 nm值。
1.2.6 ic-ELISA方法的优化
1.2.6.1 包被原和抗体工作浓度的优化
利用矩阵法对包被原和抗体的工作浓度进行优化。用包被液将抗原分别按1:500、1:1000、1:2000、1:4000、1:8000和1:16000进行稀释,鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体分别按1:750、1:1500、1:3000、1:6000、1:12000、1:24000和1:48000稀释,按照1.2.5步骤进行操作,确定吸光度值为2.0附近的组合作为最佳包被原和抗体工作浓度。
1.2.6.2 包被条件的筛选
分别用含0.05 mol/L的Tris-HCl(pH8.0)、0.05 mol/L的碳酸盐缓冲液(CB,pH9.6)、0.01 mol/L PBS作为包被液(pH7.4),分别置于37 ℃孵育1 h、2 h、4 ℃孵育过夜,然后按照1.2.5的方法进行检测。比较各组OD值,确定该方法中最佳包被条件。
1.2.6.3 封闭条件的筛选
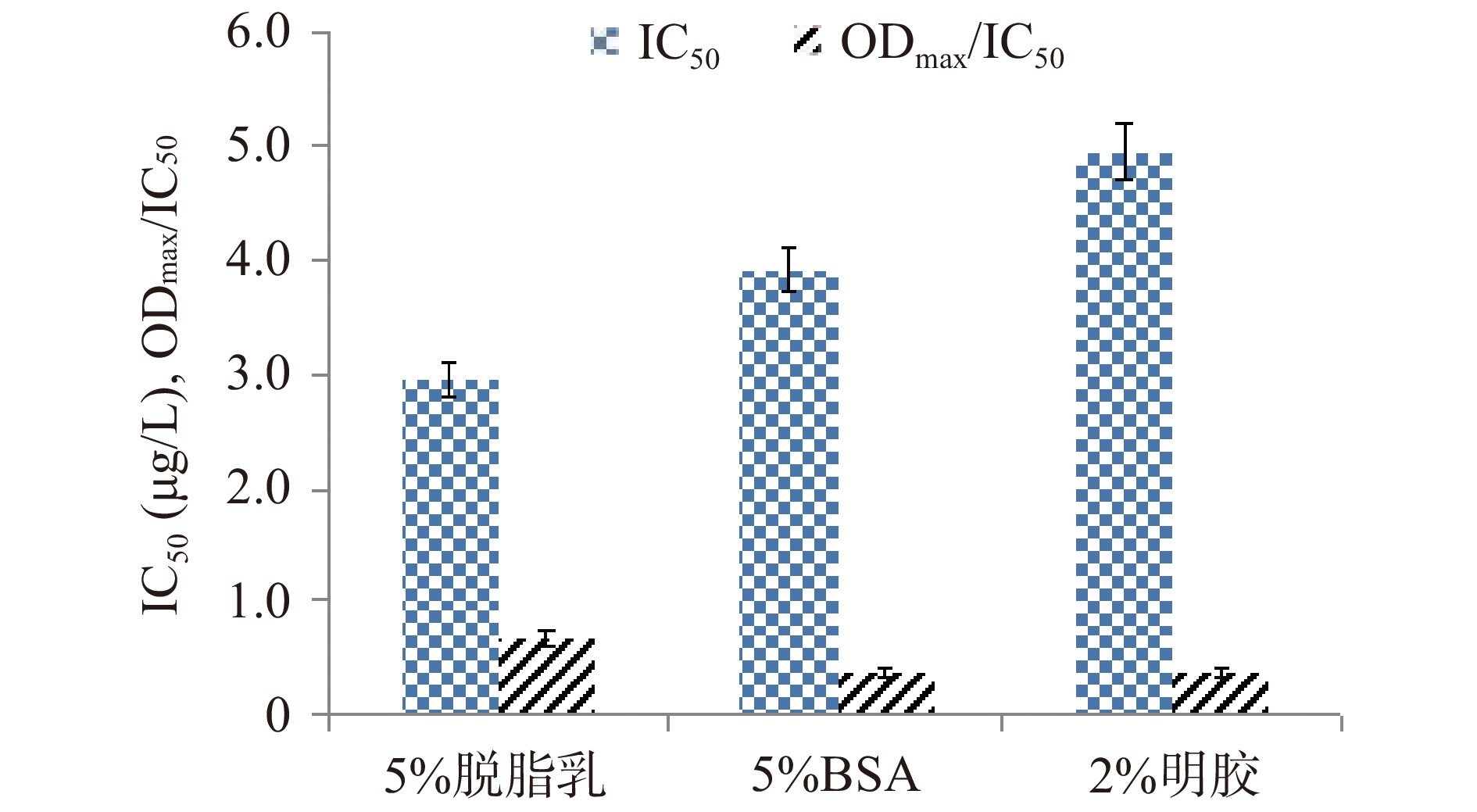
分别用5%脱脂乳、5%的BSA、2%明胶作为封闭液,分别置于37 ℃条件下封闭30、45、60、90 min。按照1.2.5步骤进行操作,根据IC50和ODmax/IC50确定最佳封闭条件。
1.2.6.4 酶标二抗工作条件的优化
在优化后的包被原和抗体工作浓度,包被及封闭条件下,羊抗鼠酶标二抗按照1:500、1:1000、1:2000、1:4000和1:8000进行稀释,分别以20、25、30和40 min孵育时间来进行反应,按照1.2.5步骤操作,根据IC50和ODmax/IC50确定最佳酶标二抗稀释浓度和孵育反应时间。
1.2.7 样品前处理
称取(2±0.05)g经烘干、均质后的蘑菇样品于50 mL离心管中,加入6 mL甲醇,充分涡动10 min;4000 r/min以上离心5 min,取4 mL上层有机相,于50~60 ℃水浴氮气吹干。加入1 mL正己烷,再加入0.5 mL样品稀释液(氯化钠0.4 g,十二水合磷酸氢二钠0.268 g,氯化钾0.01 g,磷酸二氢钾0.01 g,去离子水100 mL配制而成),充分涡动10 s;4000 r/min以上离心5 min,除去上层有机相,取下层进行检测。
1.2.8 标准曲线的建立
取6份处理后的蘑菇样品,向其中添加鹅膏毒肽的标准溶液,使其终浓度分别为0、0.5、1.0、2.0、4.0、8.0、16.0 μg/kg,充分混匀后,按照1.2.7节进行样本处理。采用所建立的ic-ELISA方法进行检测,每个添加量分别重复5次,取其OD450 nm平均值,并绘制标准曲线。
1.2.9 ic-ELISA检测方法的评价
1.2.9.1 检出限
选取α-鹅膏毒肽阴性的蘑菇样品20份,按照1.2.7、1.2.5进行样本的处理和检测,依据1.2.8建立的标准曲线,计算20份样本检测结果的均值和标准差。20份样本测定结果的均值加上3倍标准偏差即为本方法的检出限[29]。
1.2.9.2 准确度和精密度
分别采用添加回收率和变异系数(CV)来评价方法的准确度和精密度。将蘑菇空白样品中分别添加终浓度为2.0、4.0、8.0 μg/kg的α-鹅膏毒肽,每个浓度做3个平行,按照1.2.7中的方法进行样品前处理,采用1.2.5中ic-ELISA方法进行检测,计算添加回收率[30]。
在3个不连续的工作日内重复测定3次,按照下述公式计算批内和批间变异系数:
1.3 数据分析
在标准曲线制作过程中,以样本中添加的α-鹅膏毒肽质量浓度(μg/kg)的自然对数值为X轴,吸光度OD值为Y轴,采用Origin 8.0软件拟合四参数竞争标准曲线。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 鹅膏毒肽抗原的合成与鉴定
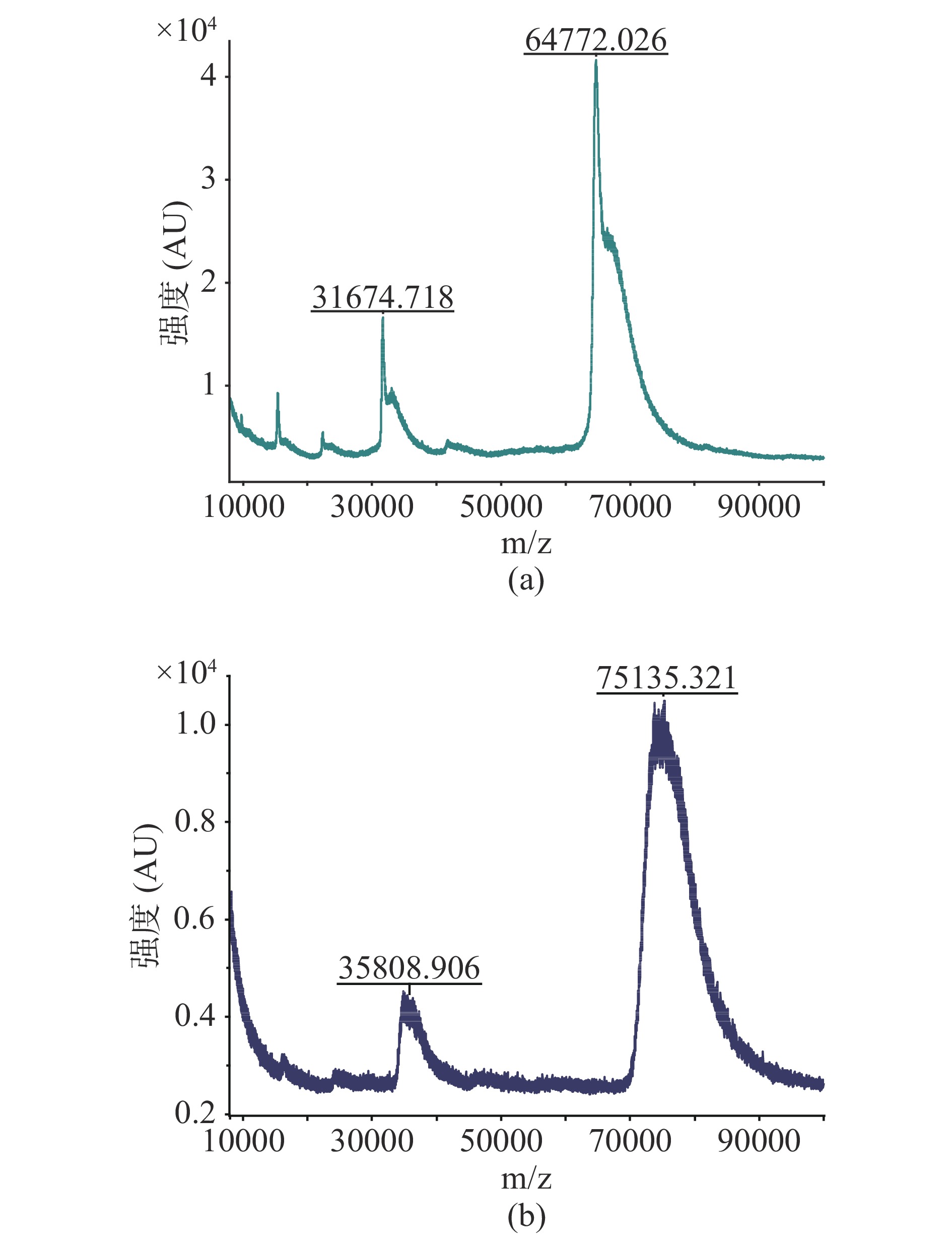
本研究在α-鹅膏毒肽分子的羧基位置引入6-氨基己酸,获得含有6碳间隔臂的半抗原(分子量为1033.12),有利于高特异性抗体的制备。据文献报道,其它类型的间隔臂也用于鹅膏毒肽半抗的合成,例如琥珀酸酐、混合酸酐和三聚氯氰等[22-23]。α-鹅膏毒肽是一种非免疫原性的低分子量半抗原,因此需要将其与载体蛋白偶联才能刺激动物反应并产生抗体[31]。本研究使用牛血清白蛋白(BSA)和卵清蛋白(OVA)作为载体蛋白,分别制备α-鹅膏毒肽免疫原和包被原,并使用基质辅助激光解吸电离飞行时间质谱法(MALDI-TOF)对免疫原的偶联比进行测定。结果如图2所示:载体蛋白BSA的分子质量为64772.026,免疫原的分子质量为75135.321,经计算可知,免疫原AMA-BSA的偶联比为10.03。
2.2 抗体的制备与特异性评价
2.2.1 鼠单克隆抗体的制备
小鼠四免一周后,对小鼠进行眼眶采血,采用间接ELISA方法测定其血清效价,数据见表2。从表中数据可以看出,3#小鼠的血清效价最高(1:12800,OD=2.016)。因此,选择3#小鼠进行下一步的脾细胞融合试验。
表 2 免疫Balb/c小鼠血清效价ELISA检测结果Table 2. The serum titer of immunized Balb/c mice by ELISA稀释倍数 800 1600 3200 6400 12800 25600 51200 空白 1# 3.011 2.745 2.157 1.846 1.048 0.639 0.412 0.215 2# 3.324 2.931 2.569 2.107 1.413 0.922 0.634 0.211 3# 3.756 3.215 2.864 2.352 2.016 1.312 0.743 0.198 4# 3.153 2.764 2.069 1.751 1.215 0.894 0.359 0.195 融合细胞后,经3次克隆后阳性率达100%,采用间接竞争ELISA方法筛选得到效价高、免疫抑制率的杂交瘤细胞13H4。然后,将筛选得到的杂交瘤细胞注射到小鼠腹腔,采用体内诱生法制备腹水。7 d后,观察小鼠产生抗体的情况,待腹部明显膨大时,收集腹水。采用Protein A亲和层析柱对收集的腹水进行纯化,最终得到纯化的α-鹅膏毒肽鼠单克隆抗体,其效价和IC50分别为1:32000和1.91 μg/L。
2.2.2 特异性试验结果
用间接竞争ELISA方法对α-鹅膏毒肽及其类似物进行检测,以测定所制备单克隆抗体的特异性(表3)。结果显示,α-鹅膏毒肽与β-鹅膏毒肽和γ-鹅膏毒肽的交叉反应率分别为84.14%和76.70%,而鬼笔毒肽的交叉反应率均小于0.50%,这种交叉反应率的差异是由其分子结构的不同造成的(表3)[32]。由此可见,本研究所制备的α-鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体具有良好的特异性,可应用于免疫学快检方法的开发。
表 3 鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体的特异性Table 3. The specificity of amanitin monoclonal antibody名称 分子结构 IC50(μg/L) 交叉反应率(%) α-鹅膏毒肽 
1.91 100.0 β-鹅膏毒肽 
2.27 84.14 γ-鹅膏毒肽 
2.49 76.70 鬼笔毒肽 
>400 <0.50 2.3 反应条件的优化
2.3.1 包被原和抗体工作浓度的确定
包被原、抗体的浓度直接影响方法的线性范围、灵敏度、最低检测限等,是建立免疫学检测方法的核心研究内容。本研究以OD值接近2.0时的包被原浓度和抗体稀释度作为最佳抗原包被浓度与最适抗体稀释度。结果如表4所示,随着包被原和抗体稀释度的增加,OD值呈现下降趋势。当单抗的稀释度为1:6000,包被原稀释度为1:1000时,OD值在2.0左右,因此选择1:6000为抗体稀释浓度,1:1000为包被抗原稀释浓度,进行后续试验。
表 4 包被原浓度和抗体稀释度的确定Table 4. Determination of the concentration of coating antigen and antibody抗体稀释度 包被原稀释度 1:500 1:1000 1:2000 1:4000 1:8000 1:16000 1:750 4.432 3.23 2.741 2.154 1.433 0.986 1:1500 3.431 2.689 2.221 1.897 1.262 0.894 1:3000 3.05 2.406 1.815 1.543 0.943 0.756 1:6000 2.524 2.012 1.491 1.014 0.678 0.541 1:12000 1.915 1.165 0.841 0.568 0.439 0.243 1:24000 1.431 0.613 0.438 0.307 0.231 0.127 1:48000 0.825 0.376 0.312 0.225 0.133 0.07 2.3.2 最佳包被条件的确定
通过建立ic-ELISA方法对包被条件进行优化,根据OD值确定最佳包被时间和包被液。结果如表5所示,0.05 mol/L碳酸盐缓冲液(pH9.6)作为抗原包被液,4 ℃孵育过夜时,OD值在2.0左右。因此选择0.05 mol/L碳酸盐缓冲液(pH9.6),4 ℃孵育过夜作为最佳包被条件。
表 5 包被条件的优化Table 5. Optimization of coating conditions包被液 37 ℃ 1 h 37 ℃ 2 h 4 ℃孵育过夜 Tris-HCl 1.304 1.551 1.430 CB 1.542 1.753 2.032 PBS 0.825 1.196 1.615 2.3.3 封闭条件的确定
封闭是影响ic-ELISA检测方法的重要因素之一,选择合适的封闭液不仅可以发挥稳定剂和保护剂的作用,还可以减少抗原或抗体的非特异性结合[33-34]。因此,本研究对其封闭条件进行优化,结果由图3、图4所示,不同种类的封闭液和封闭时间对其结果影响较大。当选择5%的脱脂乳作为封闭液,封闭60 min时,IC50最低,ODmax/IC50值最大。因此,本试验选择5%的脱脂乳作为封闭液,封闭时间为60 min。
2.3.4 酶标二抗工作浓度和孵育时间的确定
在ic-ELISA方法中,抗体与酶标二抗的结合受到二抗浓度以及反应时间的影响。稀释浓度大,可节约二抗的使用量,节省成本,但稀释倍数过大时会造成底物显色较弱,方法的线性范围窄。因此,需要对二抗工作浓度和孵育时间进行优化。结果由图5可知,当孵育时间为30 min时,IC50值最小,ODmax/IC50值最大,故选择孵育时间为30 min。酶标二抗不同稀释倍数的数据见图6,同理可得出酶标二抗浓度稀释倍数为1:1000时为最佳条件。
2.4 标准曲线
α-鹅膏毒肽拟合得到的四参数曲线如图7所示,其方程为Y=0.7458+3.53431/(1+(x/2.1966)1.8025),IC50为2.80 μg/kg,该标准曲线的线性区间(IC20~IC80)为1.18~15.00 μg/kg,R2=0.9989。
2.5 方法学评价
2.5.1 检出限测定结果
本研究利用ic-ELISA方法检测20份阴性的蘑菇,从表6中可以看出,20个样本检测结果的平均值为0.43 μg/kg,标准差为0.15 μg/kg,计算得到该方法蘑菇样本中α-鹅膏毒肽的检出限为0.88 μg/kg。
表 6 鹅膏毒肽空白样品测定结果(μg/kg)Table 6. The detection results of amanitin in free mushroom samples by the established ic-ELISA(μg/kg)样品 测定值(n=20) 平均值 标准差 检出限 蘑菇 0.54 0.61 0.64 0.39 0.54 0.28 0.16 0.41 0.32 0.53 0.43 0.15 0.88 0.38 0.42 0.38 0.53 0.73 0.35 0.38 0.31 0.17 0.47 2.5.2 准确度和精密度测定结果
回收率实验是通过计算分析方法的实验误差和操作过程的损失,来评价所建立方法的可靠性。本研究在蘑菇样本中依次添加α-鹅膏毒肽标准物质,使其终浓度分别为2.0、4.0和8.0 μg/kg,使用本研究所建立的ELISA方法检测得到的结果如表7所示。本方法对蘑菇中α-鹅膏毒肽添加回收率为85.66%~113.05%,批内变异系数为5.35%~9.54%,批间变异系数为小于15%。免疫检测方法的准确度和精密度受到多种因素的影响,包括样本基质差异、前处理方法的提取效率、检测操作的偏差等。在多数的国家标准或行业标准中,免疫学检测方法及仪器检测方法的准确度在80%~120%,精密度在15%以内。由此可见,本研究所建立的ic-ELISA方法具有较好的准确度和精密度,能够满足实际检测的需求。
表 7 ic-ELISA准确度和精密度Table 7. Accuracy and precision of the established ic-ELISA样品 添加浓度(μg/kg) 批次 批内 批间 平均值±标准偏差(μg/kg) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 平均值±标准偏差(μg/kg) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 蘑菇 2.0 第一批 2.17±0.16 108.34 7.15 1.95±0.24 97.71 12.27 第二批 1.71±0.11 85.66 6.19 第三批 1.98±0.19 99.13 9.54 4.0 第一批 3.66±0.28 91.44 7.75 3.94±0.50 98.41 12.78 第二批 4.52±0.24 113.05 5.35 第三批 3.63±0.32 90.74 8.83 8.0 第一批 6.89±0.55 86.12 7.98 8.15±1.07 101.82 13.33 第二批 8.66±0.54 108.27 6.20 第三批 8.89±0.74 111.08 8.30 3. 结论
本研究成功合成了α-鹅膏毒肽半抗原(分子量为1033.12),并制备了α-鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体。通过优化反应条件,建立了蘑菇中α-鹅膏毒肽的间接竞争酶联免疫吸附检测方法。该方法的IC50为2.80 μg/kg,线性范围为1.18~15.00 μg/kg,检测限为0.88 μg/kg。除β-鹅膏毒肽(84.14%)和γ-鹅膏毒肽(76.70%)以外,与其它类似物的交叉反应率均小于0.50%,表明该方法特异性良好。该方法对蘑菇中α-鹅膏毒肽的添加回收率为85.66%~113.05%,批内变异系数为5.35%~9.54%,批间变异系数小于15%。由此可见,本研究所建立的ic-ELISA方法准确度、精密度、灵敏度较高,且性能稳定,可用于蘑菇中α-鹅膏毒肽的残留检测,为突发毒蘑菇中毒事件的毒素分析提供了一种可靠的方法。
-
表 1 单克隆抗体(小鼠)的免疫程序
Table 1 Monoclonal antibody (mouse) immune program
免疫次数 免疫原 剂量 免疫方式 首次免疫 免疫原+FCA 100 μg/只 颈背部皮下多点注射 二免 免疫原+FICA 同上 同上 三免 同上 同上 同上 四免 同上 同上 同上 五免 同上 同上 同上 六免(加强免疫) 免疫原 同上 腹腔注射 表 2 免疫Balb/c小鼠血清效价ELISA检测结果
Table 2 The serum titer of immunized Balb/c mice by ELISA
稀释倍数 800 1600 3200 6400 12800 25600 51200 空白 1# 3.011 2.745 2.157 1.846 1.048 0.639 0.412 0.215 2# 3.324 2.931 2.569 2.107 1.413 0.922 0.634 0.211 3# 3.756 3.215 2.864 2.352 2.016 1.312 0.743 0.198 4# 3.153 2.764 2.069 1.751 1.215 0.894 0.359 0.195 表 3 鹅膏毒肽单克隆抗体的特异性
Table 3 The specificity of amanitin monoclonal antibody
名称 分子结构 IC50(μg/L) 交叉反应率(%) α-鹅膏毒肽 
1.91 100.0 β-鹅膏毒肽 
2.27 84.14 γ-鹅膏毒肽 
2.49 76.70 鬼笔毒肽 
>400 <0.50 表 4 包被原浓度和抗体稀释度的确定
Table 4 Determination of the concentration of coating antigen and antibody
抗体稀释度 包被原稀释度 1:500 1:1000 1:2000 1:4000 1:8000 1:16000 1:750 4.432 3.23 2.741 2.154 1.433 0.986 1:1500 3.431 2.689 2.221 1.897 1.262 0.894 1:3000 3.05 2.406 1.815 1.543 0.943 0.756 1:6000 2.524 2.012 1.491 1.014 0.678 0.541 1:12000 1.915 1.165 0.841 0.568 0.439 0.243 1:24000 1.431 0.613 0.438 0.307 0.231 0.127 1:48000 0.825 0.376 0.312 0.225 0.133 0.07 表 5 包被条件的优化
Table 5 Optimization of coating conditions
包被液 37 ℃ 1 h 37 ℃ 2 h 4 ℃孵育过夜 Tris-HCl 1.304 1.551 1.430 CB 1.542 1.753 2.032 PBS 0.825 1.196 1.615 表 6 鹅膏毒肽空白样品测定结果(μg/kg)
Table 6 The detection results of amanitin in free mushroom samples by the established ic-ELISA(μg/kg)
样品 测定值(n=20) 平均值 标准差 检出限 蘑菇 0.54 0.61 0.64 0.39 0.54 0.28 0.16 0.41 0.32 0.53 0.43 0.15 0.88 0.38 0.42 0.38 0.53 0.73 0.35 0.38 0.31 0.17 0.47 表 7 ic-ELISA准确度和精密度
Table 7 Accuracy and precision of the established ic-ELISA
样品 添加浓度(μg/kg) 批次 批内 批间 平均值±标准偏差(μg/kg) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 平均值±标准偏差(μg/kg) 回收率(%) 变异系数(%) 蘑菇 2.0 第一批 2.17±0.16 108.34 7.15 1.95±0.24 97.71 12.27 第二批 1.71±0.11 85.66 6.19 第三批 1.98±0.19 99.13 9.54 4.0 第一批 3.66±0.28 91.44 7.75 3.94±0.50 98.41 12.78 第二批 4.52±0.24 113.05 5.35 第三批 3.63±0.32 90.74 8.83 8.0 第一批 6.89±0.55 86.12 7.98 8.15±1.07 101.82 13.33 第二批 8.66±0.54 108.27 6.20 第三批 8.89±0.74 111.08 8.30 -
[1] WU F, ZHOU L W, YANG Z L, et al. Resource diversity of chinese macrofungi: Edible, medicinal and poisonous species[J]. Fungal Diversity,2019,98(1):1−76.
[2] LE D B, FERRON P J, GICQUEL T. Toxic effects of amanitins: Repurposing toxicities toward new therapeutics[J]. Toxins,2021,13(6):417. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060417
[3] CHEN Z H, ZHANG P, ZHANG Z, et al. Investigation and analysis of 102 mushroom poisoning cases in southern china from 1994 to 2012[J]. Fungal Diversity,2014,64(1):123−131. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0260-7
[4] DE O J, WANG J J, VILLENEUVE E, et al. Current fatality rate of suspected cyclopeptide mushroom poisoning in the united states[J]. Clinical Toxicology,2021,59(1):24−27. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2020.1747624
[5] 张晓萌, 秦鸣蔚, 赵新月, 等. 鹅膏毒肽类毒素检测方法的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(19):295−300. [ZHANG X M, QIN M W, ZHAO X Y, et al. Research progress on detection methods of amanita cyclopeptide toxins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(19):295−300. [6] YE Y, LIU Z. Management of amanita phalloides poisoning: A literature review and update[J]. Journal of Critical Care,2018,46:17−22. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.03.028
[7] 任荆蕾, 图力古尔, 包海鹰. 东北地区非鹅膏属真菌中鹅膏肽类毒素的分布[J]. 菌物学报,2016,35(9):1080−1098. [REN J L, BAU T, BAO H Y. Distribution characteristics of amatoxins in fungi excluding amanita[J]. Mycosystema,2016,35(9):1080−1098. [8] 胡劲松, 陈作红. 大孔吸附树脂联合葡聚糖凝胶Sephadex LH20分离制备鹅膏肽类毒素的研究[J]. 菌物学报,2014,33(3):549−559. [HU J S, CHEN Z H. Isolation and preparation of cyclopeptide toxins by macroporous adsorptive resins combined with sephadex LH20 column chromatography from amanita exitialis[J]. Mycosystema,2014,33(3):549−559. [9] 周贻兵, 李磊, 吴玉田, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定人血浆中蘑菇毒肽的含量[J]. 理化检验-化学分册,2019,55(12):1406−1411. [ZHOU Y B, LI L, WU Y T, et al. Determination of mushroom toxins in human blood plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis),2019,55(12):1406−1411. [10] 李帮锐, 冯家力, 曾栋, 等. 尿液和血浆中蘑菇毒肽测定的方法学研究[J]. 职业与健康,2016,32(20):2786−2791. [LI B R, FENG J L, ZENG D, et al. Methodology research on detection of phallotoxins in urine and plasma samples[J]. Occupation and Health,2016,32(20):2786−2791. [11] 肖绍震, 林锋, 傅武胜, 等. 血浆和尿液中6种鹅膏毒肽和鬼笔毒肽的超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(22):312−318. [XIAO S Z, LIN F, FU W S, et al. Determination of amatoxins and phallotoxins in plasma and urine by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2018,39(22):312−318. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822047 [12] 徐小民, 张京顺, 蔡增轩, 等. 在线液相色谱-二极管阵列检测器-串联质谱法检测野生菌中鹅膏毒肽和鬼笔毒肽[J]. 色谱,2017,35(6):613−619. [XU X M, ZHANG J S, CAI Z X, et al. Determination of amanitins and phallotoxins in wild mushrooms by online liquid chromatography-diodearray detector-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2017,35(6):613−619. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2017.02008 [13] XU X M, CAI Z X, ZHANG J S, et al. Screening of polypeptide toxins as adulteration markers in the food containing wild edible mushroom by liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Food Control,2017,71:393−402. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.07.024
[14] TOMKOVÁ, JANA, ONDRA P, et al. Simultaneous determination of mushroom toxins α-amanitin, β-amanitin and muscarine in human urine by solid-phase extraction and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with ultra-high-resolution tof mass spectrometry[J]. Foren Sicence International,2015,251:209−213. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2015.04.007
[15] 柳洁, 丁文婕, 何碧英, 等. 超高效液相色谱-电喷雾离子化-四级杆飞行时间串联质谱指纹图谱检测毒蕈中4种鹅膏肽类毒素[J]. 分析化学,2013,41(4):500−508. [LIU J, DING W J, HE B Y, et al. Identification of four toxin peptides from amanita in poisonous mushroom by mass spectrum fingerprint based on ultra performance liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole time of flight-mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2013,41(4):500−508. [16] HE Z M, LUO T, FAN F X, et al. Universal identification of lethal amanitas by using hyperbranched rolling circle amplification based on α-amanitin gene sequences[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,298(Nov.15):125031.1−125031.8.
[17] WOŁOSZYN A, KOTŁOWSKI R. A universal method for the identification of genes encoding amatoxins and phallotoxins in poisonous mushrooms[J]. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig,2017,b68(3):247−251.
[18] BRÜGGEMANN O, MEDER M, FREITAG R. Analysis of amatoxins alpha-amanitin and beta-amanitin in toadstool extracts and body fluids by capillary zone electrophoresis with photodiode array detection[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,1996,744(1-2):167. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(96)00173-2
[19] ROBINSON F V. A, JAIME S J L, GARCÍA A L, et al. Determination of α- and β-amanitin in clinical urine samples by capillary zone electrophoresis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biomedical Analysis,2008,47(4-5):913−917.
[20] BERGIS P, BETZ C, BOJUNGA J, et al. 911 effective treatment of amanita phalloides intoxication by fractioned plasma separation and adsorption (prometheus)[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2011,54:364−364. doi: 10.1002/hep.24219
[21] PARANT F, PELTIER L, LARDET G, et al. Phalloidin syndrome: Role of elisa-based assay for the detection of alpha- and gamma-amanitins in urine[J]. Acta clinica Belgica. Supplementum,2006,61:11−17. doi: 10.1179/acb.2006.063
[22] HE K, MAO Q W, ZANG X Y, et al. Production of a broad-specificity monoclonal antibody and application as a receptor to detection amatoxins in mushroom[J]. Biologicals,2017,49:57−61. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2017.06.008
[23] BEVER C S, HNASKO R M, CHENG L W, et al. A rapid extraction method combined with a monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for the detection of amatoxins[J]. Toxins,2019,11(12):724−734. doi: 10.3390/toxins11120724
[24] KIDO K, EDAKUNI K, MORINAGA O, et al. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for aconitine-type alkaloids using an anti-aconitine monoclonal antibody[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2008,616:109e14.
[25] 方力, 邱凤梅, 余新威. TurboFlow在线净化-液相色谱-串联质谱法快速检测人尿中鹅膏肽类毒素[J]. 色谱,2021,39(3):338−345. [FANG L, QIU F M, YU X W. Determination of amanita peptide toxins in human urine by TurboFlow online clean-up-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2021,39(3):338−345. [26] SINGH K V, KAUR J, VARSHNEY G C, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hapten-protein conjugates for antibody production against small molecules[J]. Bioconjug Chem,2004,15:168−173. doi: 10.1021/bc034158v
[27] KOHL T O, ASCOLI C A. Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols,2017,65(7):193−199.
[28] 赵维章, 崔乃元, 张汉青, 等. 时间分辨荧光免疫层析定量检测牦牛肉中喹诺酮类药物[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(18):239−243,251. [ZHAO W Z, CUI N Y, ZHANG H Q, et al. Quantitative detection of quinolone by time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatography in yak meat[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(18):239−243,251. [29] 丁亚芳, 贾良羲, 邢维维, 等. 基于免疫磁珠前处理的荧光免疫层析法定量检测牦牛肉中金刚烷胺[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(6):294−300. [DING Y F, JIA L X, XING W W, et al. Quantitative detection of amantadine in yak beef by fluorescence immunochromatography based on pretreatment of immunomagnetic beads[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(6):294−300. [30] 张正英, 崔乃元, 高海燕, 等. 牦牛肉中阿维菌素残留的时间分辨荧光免疫层析检测方法的建立[J]. 肉类研究,2020,34(8):57−62. [ZHANG Z Y, CUI N Y, GAO H Y, et al. Establishment of time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic method for detection of abamectin residues in yak meat[J]. Meat Research,2020,34(8):57−62. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-20200331-086 [31] BEVER C S, BARNYCH B, HNASKO R, et al. A new conjugation method used for the development of an immunoassay for the detection of amanitin, a deadly mushroom toxin[J]. Toxins (Basel),2018,10(7):265. doi: 10.3390/toxins10070265
[32] ABUKNESHA R A, MARAGKOU A. A highly sensitive and specific enzyme immunoassay for detection of β-amanitin in biological fluids[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem,2004,379:853−860.
[33] 张继忠. 酶联免疫吸附测定中封闭液的作用与选择[J]. 上海医药,2018,39(11):64−66. [ZHANG J Z. Role of blocking solution in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and its selection[J]. Shanghai Medical & Pharmaceutical Journal,2018,39(11):64−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1533.2018.11.020 [34] 杜改梅, 刘茂军, 甘源, 等. ELISA检测方法中最佳封闭液和样品稀释液的筛选研究[J]. 农业科学与技术:英文版,2013,14(6):816−819, 837. [DU G M, LIU M J, GAN Y, et al. Study on screening of optimal blocking buffer and sample diluent for ELISA[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology,2013,14(6):816−819, 837.






 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



