Optimization of Fermentation Process of Grape Medicine Mulberry Wine and Its Antioxidant and Bile Acid Binding Capacity in Vitro
-
摘要: 本研究以提高总酚和黄酮保存率为目的,探究药桑葡萄发酵工艺并研究药桑葡萄酒的抗氧化活性与结合胆酸盐能力。以药桑和葡萄为原料,通过单因素(接种量、温度、时间、原料质量比)结合响应面试验来确定药桑葡萄酒的最佳发酵工艺,并通过三种抗氧化体系(DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH)来评价药桑葡萄酒的抗氧化活性,不同浓度的药桑葡萄酒与甘氨胆酸盐和牛磺胆酸盐的结合能力来评价药桑葡萄酒体外降血脂效果。结果表明, 药桑葡萄发酵的最优工艺参数为: 接种量0.3%、主发酵时间8 d、发酵温度26 ℃、葡萄药桑原料质量比是1:3。该工艺发酵出的药桑葡萄酒体积浓度为1.0 mL/mL时,对DPPH、ABTS和羟基自由基清除率分别为98.83%、98.38%、99.24%;表明与同类果酒相比有更强的抗氧化活性。当药桑葡萄酒样品体积浓度达到1.0 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒与甘氨胆酸盐、牛磺胆酸盐的结合率分别达到69.36%、73.28%,初步证实药桑葡萄酒具有较好的体外降血脂活性。Abstract: In order to improve the preservation rate of total phenols and flavonoids, the fermentation technology of grape medicine mulberry wine was explored, and the antioxidant activity and bile acid binding capacity of grape medicine mulberry wine were studied. Using grape and medicine mulberry as raw materials, the optimal fermentation process of grape medicine mulberry wine was determined by single factor (inoculation amount, temperature, time, mass ratio) combined with response test. Three antioxidant systems (DPPH·, ABTS+·, ·OH) were used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of grape medicine mulberry wine, and the binding ability of different concentrations of grape medicine mulberry wine with glycocholic acid and taurocholate was used to evaluate the effect of reducing blood lipid in vitro. The results showed that the optimum technological parameters of grape medicine mulberry fermentation were: Inoculation amount 0.3%, main fermentation time 8 d, fermentation temperature 26 ℃, raw material ratio 1:3. When the volume concentration of grape medicine mulberry wine fermented by this process was 1.0 mL/mL, the scavenging rates for DPPH, ABTS and hydroxyl radicals were 98.83%, 98.38%, and 99.24%, respectively. It showed that it had stronger antioxidant activity compared with similar fruit wines. When the concentration of grape medicine mulberry wine reached 1.0 mL/mL, the binding rate of grape medicine mulberry wine with glycocholic acid and taurocholate reached 69.36% and 73.28% respectively. It was preliminarily confirmed that the grape medicine mulberry wine had better lipid lowering activity in vitro.
-
Keywords:
- compound fruit wine /
- medicine mulberry /
- fermentation /
- antioxidant activity /
- cholate /
- hypolipidemic activity
-
新疆药桑具有多年的种植历史[1]。药桑因含有多种氨基酸和丰富的药用活性成分,在民间作为药材,常被用于消炎、补血和镇静[1-2]。随着科技的发展,药桑果实和叶中的活性成分陆续被开发及利用,尤其是多酚和黄酮类物质的抗氧化作用备受关注[3]。已有研究表明,药桑比其它桑品种具有更高的营养价值、药用价值和果用价值[4],可作为药用果用专用桑品种加以推广[5]。虽然对药桑的研究越来越多,但总体来说其利用率并不高,原料浪费问题依然严重[6]。药桑的化学成分和药理研究还不完善,使药桑没有得到充分的利用[7]。将易腐败变质、易损坏、易霉变的药桑椹制成果酒,可长久保藏且避免浪费,又能延长果桑的产业链[8],提高果桑附加值,还可丰富市面上果酒的种类[9]。
葡萄是全球种植面积最广的水果之一[10],随着世界葡萄产量与葡萄酒产业的快速发展,我国的葡萄种植及葡萄酒产量整体呈现稳步上升的发展趋势[11]。葡萄酒中含有糖、氨基酸、维生素、矿物质等多种物质[12]。葡萄酒能够提高食欲,促进消化,对结肠炎有一定的疗效,因此深受人们的喜爱[13]。
随着果酒行业的快速发展,复合果酒已经成为了研究的热点,越来越受到消费者的青睐[14]。果酒的营养成分丰富,在发酵过程中,水果中的维生素、矿物质、氨基酸、多酚等营养物质得到了很大程度的保留,且发酵后果酒中会产生各种醇类、酯类、有机酸等物质[15]。有研究表明,果酒富含酚类化合物,能够在体内显示抗氧化特性,显著降低心血管疾病的风险[16],长期适量饮用果酒能抗衰老,预防动脉硬化、高血压、心脑血管等疾病,还能调节情绪[14]。根据每种水果的不同营养成分及保健价值[17],可以将不同水果按一定比例进行复合发酵,从而得到口感更好、营养更全面且具有更好的保健价值的复合果酒[18-19]。
本研究以新疆地产酿酒赤霞珠葡萄和药食两用植物药桑为原料,以药桑葡萄酒的总酚和黄酮含量为考察指标,采用单因素结合响应面法筛选药桑葡萄酒的最佳发酵工艺参数,通过测定最佳工艺条件下发酵的药桑葡萄酒对DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH的清除率和与甘胺胆酸钠和牛磺胆酸钠的结合率来评价药桑葡萄酒的抗氧化活性和体外降血脂效果。本实验目的是充分有效利用新疆药食两用植物资源,降低药桑损失率,保留更多药桑葡萄功能性成分,开发特色复合酒类新产品。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
药桑 果桑品种为黑桑种,紫黑果,2020年6月采自新疆阿克苏市,在新疆农业大学628食品生物发酵与质量安全实验室冷冻保存;葡萄 赤霞珠葡萄2020年9月采自乌鲁木齐安宁渠新疆农业科学院综合试验场果园;果胶酶(酶活力4000 U/g)、焦亚硫酸钾、白砂糖 均为食品级,宁夏和氏璧生物技术有限公司;干酵母D254 安琪酵母股份有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2'-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS) 均为分析纯,麦克林生化科技有限公司;没食子酸、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钠、抗坏血酸、过硫酸钾、双氧水、硫酸亚铁、水杨酸 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甘氨胆酸钠(SGC) 日本TCI公司;牛磺胆酸钠(STC) Sigma公司;胰酶(胰蛋白酶4000 U/g,胰淀粉酶7000 U/g,胰脂肪酶4000 U/g) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
LE2002E/02电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;OK1310B料理机 欧科股份有限公司;FE20 PLUS pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;MJX-160-Z霉菌培养箱 上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂;TU-1810 紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限公司; B-220恒温水浴锅 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;H1750台式高速离心机 湘仪仪器(长沙)有限公司;PAL-1型手持糖度计 北京阳光亿事达科技有限公司;SXKW数显控温电热套 北京市永光明医疗仪器厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺
1.2.1.1 工艺流程
鲜葡萄、冷冻药桑→解冻→2种水果破碎打浆混合均匀→酶解→调糖→添加偏重亚硫酸钾→接种酵母→发酵→过滤分离→药桑葡萄酒
1.2.1.2 操作要点
药桑、葡萄:新鲜采摘的药桑果经过挑选之后放入−18 ℃冰箱冷冻保存,解冻后进行破碎打浆,得到药桑果浆,跟葡萄果浆混合进行全果汁与果肉发酵。
酶解、调糖:用白砂糖调节果浆的初始糖度为24 °Bx,在葡萄和药桑果浆自然pH条件下,加入0.1%的果胶酶,提高果浆的出汁率,搅拌均匀,静置2 h。
添加偏重亚硫酸钾:果浆中添加偏重亚硫酸钾使得SO2的质量浓度为80 mg/L,可起到杀菌、抗氧化和护色的作用[20]。
接种、发酵:称取干酵母D254于5%糖水中37 ℃活化30 min备用。将调整好成分、添加了偏重亚硫酸钾和酵母的药桑和葡萄混合浆装入消毒后的发酵瓶中置于不同的温度条件下发酵。每天测定残糖量变化情况,以确保发酵正常进行,残糖量不再变化时结束发酵[21]。
过滤:发酵结束后,将药桑葡萄发酵液进行皮渣分离,压榨过滤。
1.2.2 发酵工艺优化单因素实验
1.2.2.1 酵母接种量的确定
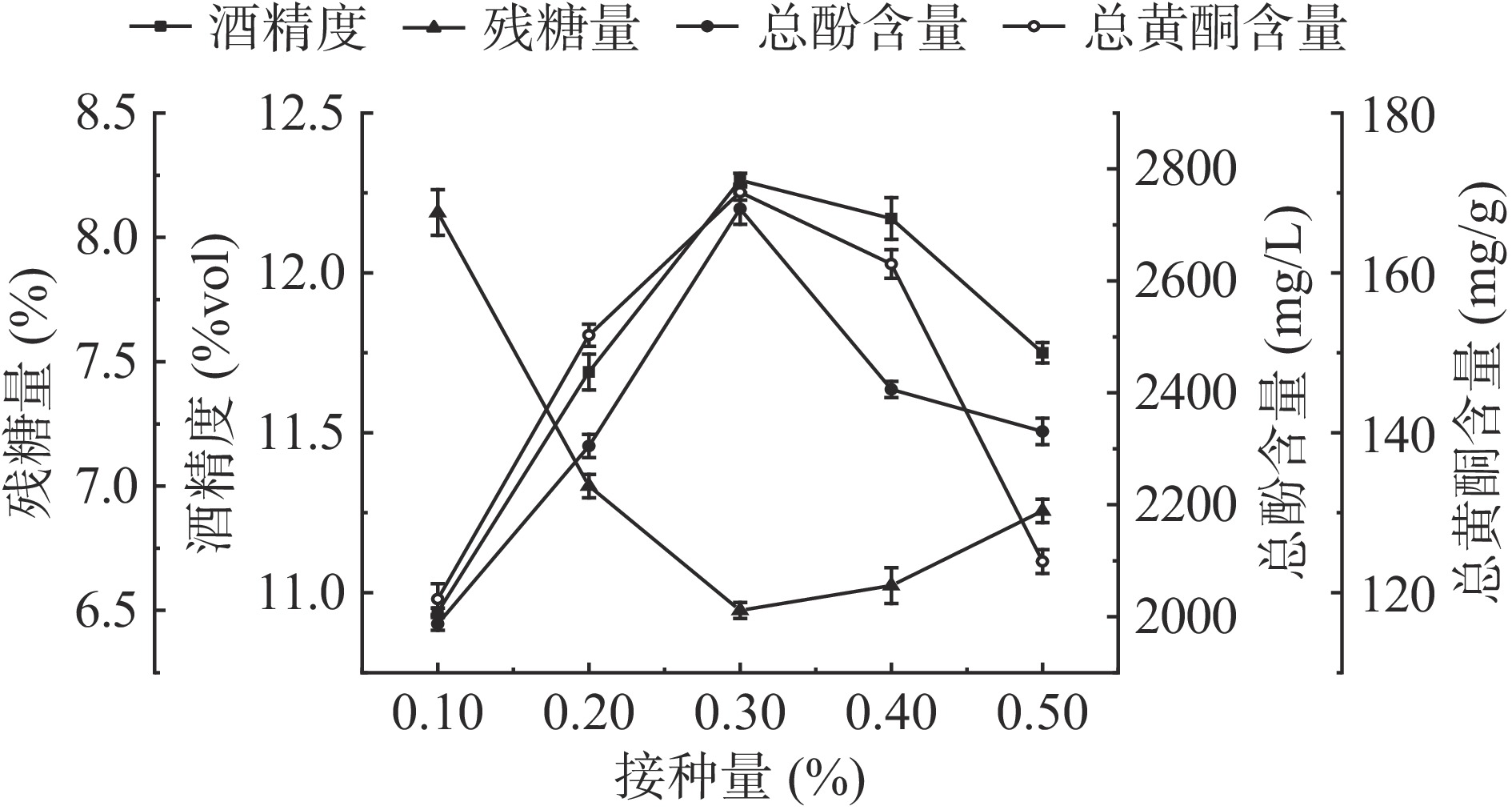
取一定量的药桑葡萄果浆于洁净的锥形瓶中,控制发酵温度为25 ℃,葡萄与药桑的果浆质量比为1:3,分别接种0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%酵母进行发酵,发酵时间为7 d。发酵结束后测定酒精度、残糖量以及总酚、总黄酮含量,确定最适的酵母菌接种量。
1.2.2.2 发酵温度的确定
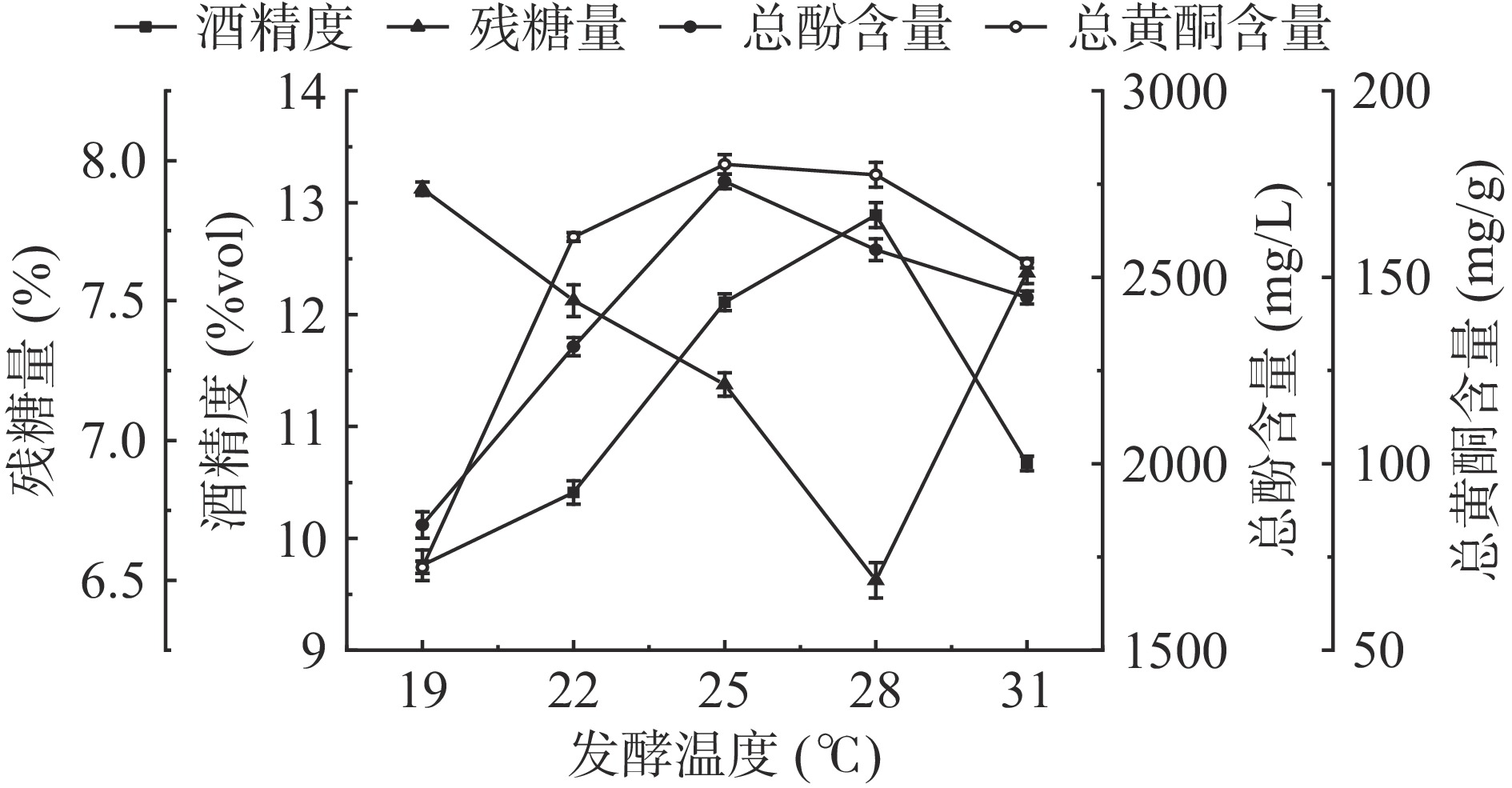
取一定量的药桑葡萄果浆于洁净的锥形瓶中,酵母接种量为0.3%,葡萄与药桑的果浆质量比为1:3,温度分别控制在19、22、25、28、31 ℃条件下进行发酵,发酵时间为7 d。发酵结束后测定酒精度、残糖量以及总酚、总黄酮含量,确定最适的发酵温度。
1.2.2.3 发酵时间的确定
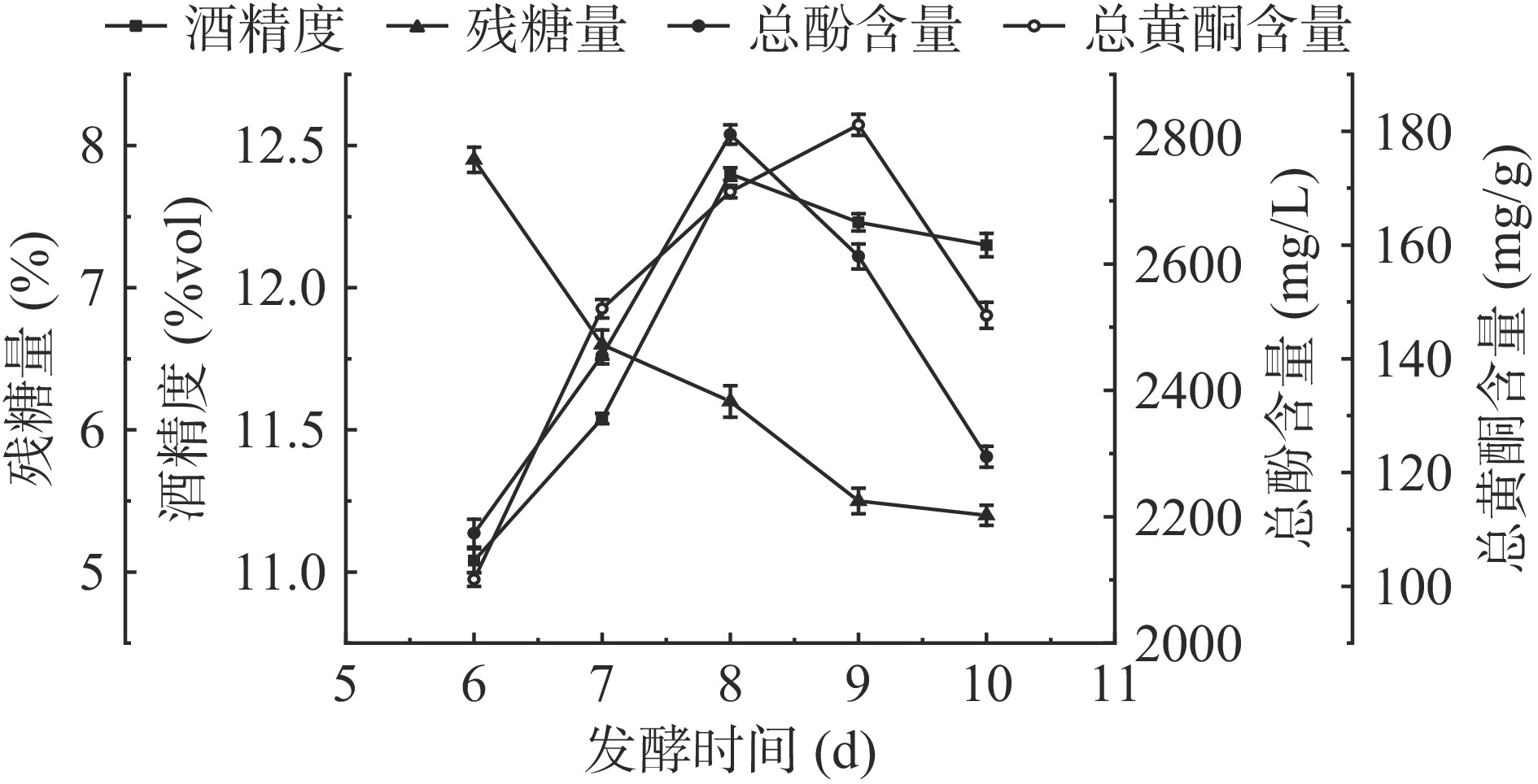
取一定量的药桑葡萄果浆于洁净的锥形瓶中,控制发酵温度为25 ℃,酵母接种量为0.3%,葡萄与药桑的果浆质量比为1:3,发酵时间分别设置为6、7、8、9、10 d,发酵结束后测定测定酒精度、残糖量以及总酚、总黄酮含量,确定最适的发酵时间。
1.2.2.4 原料质量比的确定
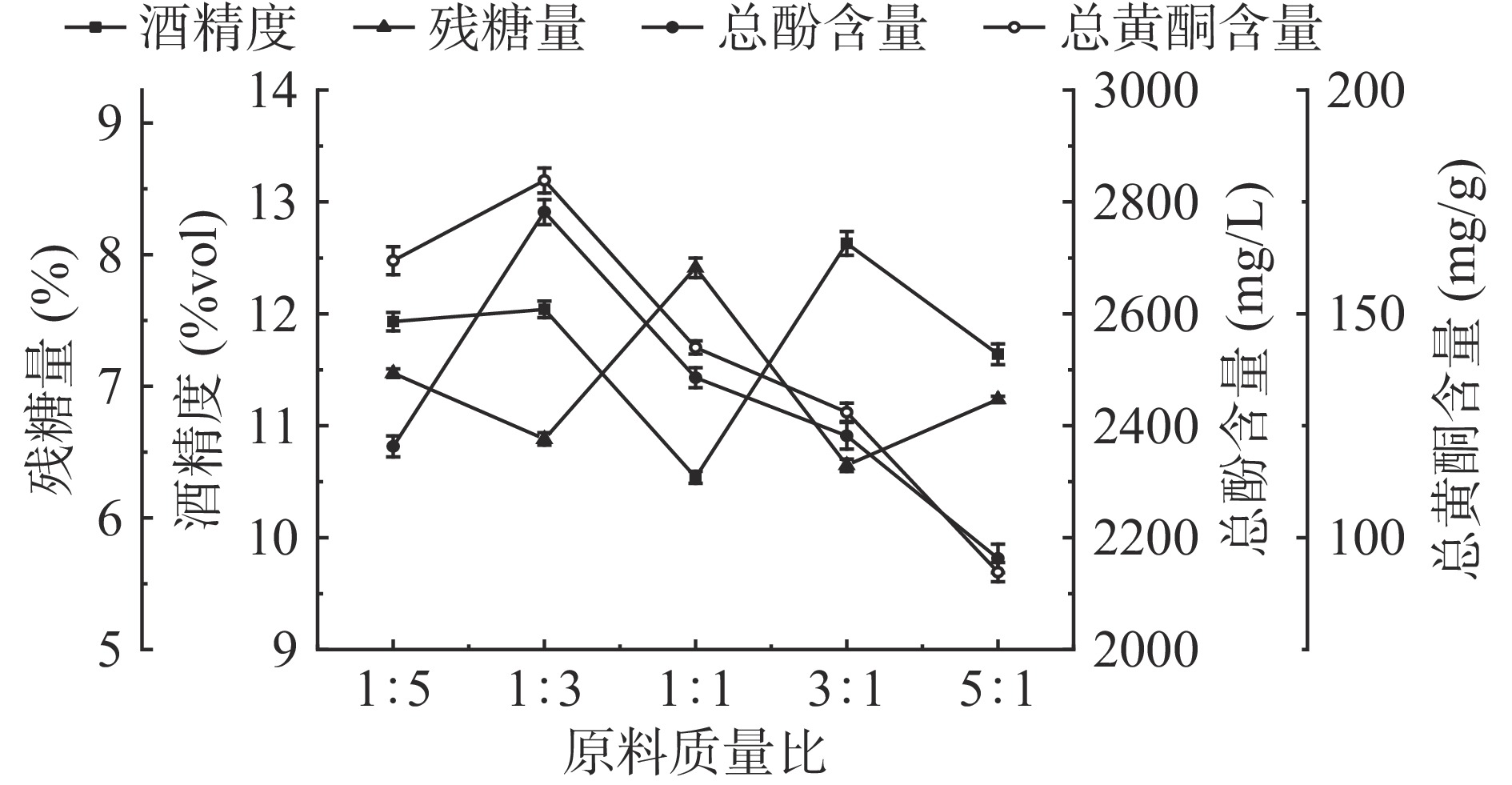
取一定量的药桑葡萄果浆于洁净的锥形瓶中,控制发酵温度为25 ℃,酵母接种量为0.3%,发酵时间为7 d,葡萄与药桑的果浆质量比分别设为1:5、1:3、1:1、3:1、5:1。发酵结束后测定酒精度、残糖量以及总酚、总黄酮含量,确定最佳的果浆原料质量比。
1.2.3 响应面优化试验
为优化药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺,在单因素实验基础上,以接种量(A)、发酵温度(B)、葡萄药桑原料质量比(C)和发酵时间(D)为影响因素,以总酚含量(Y1)和黄酮含量(Y2)为响应值,采用四因素三水平Box-Behnken设计进行优化试验,探究不同因素和水平对药桑葡萄酒的影响,利用优化工艺进行验证试验。Box-Behnken试验的因素与水平见表1。
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of Box-Behnken tests design水平 因素 A接种量(%) B发酵温度(℃) C质量比 D发酵时间(d) −1 0.2 22 1:1 7 0 0.3 25 1:3 8 1 0.4 28 1:5 9 1.2.4 指标测定方法
1.2.4.1 残糖量和酒精度的测定
糖度:参照NY/T2637-2014折射仪法进行测定。酒精度的测定:参照国标GB/T 15038-2006《葡萄酒、果酒通用分析方法》中规定的方法进行测定。
1.2.4.2 总酚含量的测定
总酚含量采用Y15全自动葡萄酒检测仪(Biosystems Barcelona Spain)测定,采用双试剂终点法在波长670 nm进行全自动操作。原理是样品中的总酚与福林酚试剂在碱性介质中发生反应,颜色的增加与样品的总酚浓度成正比。
1.2.4.3 总黄酮含量的测定
总黄酮含量的测定参照文献NaNO2-Al(NO3)3显色法[21-22]进行测定,准确称取芦丁5 mg,使用60%无水乙醇溶解,转移至25 mL容量瓶中,定容至刻度线。分别量取0、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、3.5 mL芦丁溶液置于10 mL容量瓶中,放入5% 0.3 mL的NaNO2溶液,摇匀,静置,加入10% Al(NO3)3溶液 0.3 mL,摇匀,静置,加入4%的NaOH 溶液4 mL,摇匀,用少量60%无水乙醇定容,静置,在505 nm处测定其吸光值。以芦丁浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,得到回归方程y=0.2575x+0.002,R2=0.999。
总黄酮含量(mg/g)=(Y×V)W 式中:Y为药桑总黄酮的质量浓度(mg/mL);V为原浸提液体积(mL); W为用的样品质量(g)。
1.2.5 药桑葡萄酒体外抗氧化试验
1.2.5.1 药桑葡萄酒对DPPH自由基的清除作用
对DPPH·的清除能力测定参照吴均等[23]方法略调整。吸取2.0 mL,样液体积浓度为(0.01、0.025、0.04、0.05、0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00 mL/mL)的药桑葡萄酒于试管中,加入0.2 mmoL/L的DPPH溶液2 mL混匀,避光反应30 min,无水乙醇为参比,517 nm 测吸光值(A1)。测相同体积无水乙醇、DPPH溶液混匀的吸光值(A0)及2 mL样品溶液和2 mL无水乙醇混匀的吸光值(A2)。以0.20 mg/mL的VC作对照,计算DPPH·清除率。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0表示空白组的吸光度;A1表示样品溶液的吸光度;A2表示用无水乙醇代替 DPPH 时测得的对应浓度的吸光度。
1.2.5.2 药桑葡萄酒中ABTS+·清除能力的测定
对ABTS+·的清除能力测定参照李湘利等[24]方法略调整,吸取2.0 mL,样液体积浓度为(0.01、0.025、0.04、0.05、0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00 mL/mL)的药桑葡萄酒于试管中,加入3.8 mL ABTS+·测试液,混匀静置5 min后于734 nm 处测吸光值(A1);测定同体积蒸馏水加3.8 mL ABTS+·测试液的吸光值(A0)及同体积果酒加3.8 mL蒸馏水的吸光值(A2),以0.2 mg/mL的VC溶液作对照,计算ABTS+·清除率。
ABTS+⋅清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0表示空白对照液的吸光度;A1表示样品测定管的吸光度;A2表示样品本底管的吸光度。
1.2.5.3 药桑葡萄酒中·OH清除能力的测定
对·OH的清除能力测定参照程宏桢等[25]方法略调整,吸取2.0 mL,样液体积浓度为(0.01、0.025、0.04、0.05、0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00 mL/mL)的药桑葡萄酒于试管中,和2 mL FeSO4(6 mmol/L)、2 mL水杨酸(6 mmol/L)混匀后,加入2 mL H2O2(6 mmol/L)引发反应。37 ℃下反应30 min后在波长510 nm处测定吸光度值A1;以蒸馏水替代样品为空白对照(A0);以蒸馏水替代水杨酸(A2);以0.2 mg/mL的VC溶液作对照,计算·OH清除率。
⋅OH清除率(%)=A0−A1+A2A0×100 1.2.6 药桑葡萄酒与胆酸盐的结合能力模拟体内试验
参照刘淑敏等[26-28]文献的方法,略作修改。取1 mL,样液体积浓度为0.05、0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00 mL/mL药桑葡萄酒溶液,与1 mL 0.01 mol/L盐酸溶液混匀,在37 ℃条件下消化1 h 并且恒温振荡(模拟胃消化环境),以0.10 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液调节pH为6.30,随后加入4 mL 10 mg/mL胰酶(以pH6.30的0.10 mol/L磷酸缓冲液配制),在37 ℃恒温振荡消化1 h(模拟肠道环境)。每个样品中加入4 mL胆酸盐溶液(牛黄胆酸钠、甘氨胆酸钠0.30 mmol/L,pH6.30的0.10 mol/L磷酸缓冲液),37 ℃条件下振荡1 h。将制得的混合物重新转入到离心管中,4500 r/min下离心20 min,取上清液,用比色法于387 nm处测定吸光度值,每个样品平行测定3次,按照标准曲线计算剩余甘氨胆酸盐和牛磺胆酸盐含量,所加入甘氨胆酸盐或牛磺胆酸盐总量减去剩余量所得差值与总量的比值即为结合率,以百分比表示。计算公式如下:
甘氨胆酸钠结合率(%)=C0−C1C0×100 式中:C0为甘氨胆酸钠加入量,μmol;C1为甘氨胆酸钠剩余量,μmol。
牛磺胆酸钠结合率(%)=C2−C3C2×100 式中:C2为牛磺胆酸钠加入量,μmol;C3为牛磺胆酸钠剩余量,μmol。
1.3 数据分析
每次实验均进行3组平行实验,实验数据采用Origin 9.0、SPSS 25.0和Design-Expert 8.0.6 进行处理和分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺优化单因素实验
2.1.1 酵母接种量对药桑葡萄酒发酵的影响
从图1可知,葡萄与药桑原料质量比1:3时,残糖量随着接种量的增加出现先下降后上升的趋势,在接种量为0.1%~0.3%时,残糖量随接种量增加出现下降,酒精度出现上升。当接种量增加至0.4%时,残糖量出现缓慢上升,酒精度也开始下降,这可能是因接种密度过大,造成溶氧降低,从而抑制了酵母的生长[29]。随着酵母接种量的增加,药桑葡萄酒中总黄酮含量呈先上升后大幅下降的趋势,当接种量为0.3%,此时药桑葡萄酒的总黄酮含量处于最大值,达170.1 mg/g。多酚含量在接种量0.3%时达到最高,为2729 mg/L,当接种量进一步升高,多酚含量出现下降趋势。总黄酮含量与总酚含量的变化趋势一致,在0.3%时含量最高,接种量进一步升高会导致含量下降。由此可知,0.3%接种量为最适水平,此时不仅酵母代谢旺盛,同时也有利于发酵液中酚类化合物的溶出[30]。根据指标结果,选择接种量范围为0.2%、0.3%、0.4%。
2.1.2 发酵温度对药桑葡萄酒发酵的影响
发酵温度会影响酵母的活性,随着温度的升高,酵母的生长代谢不断增强。如图2所示,葡萄与药桑原料质量比1:3时,随着温度的升高,药桑葡萄酒残糖量呈现先降低后增高的趋势,酒精度呈现先增高后降低的趋势。在发酵温度为28 ℃时,酒精度最高,为12.89%vol,此时残糖量也较低。而在31 ℃时,高温抑制酵母活性,加快衰亡速度,发酵周期缩短,发酵底物利用率降低,使得发酵液残糖量偏高,酒精度偏低。
发酵温度会直接影响酵母的生长代谢能力以及黄酮和多酚的溶解度,进而造成发酵后的药桑葡萄酒中总黄酮和总酚含量的不同[31]。随着发酵温度的提高,药桑葡萄酒中总黄酮含量呈先增大后降低趋势,25 ℃时达到最大值180.3 mg/g。不同温度之间的总酚含量也有一定差异,随着温度的升高,总酚含量也呈快速上升态势,当温度为25 ℃时,药桑葡萄酒总酚含量最高,达2757 mg/L,在25 ℃后总酚含量逐渐下降。根据指标结果,采用22、25、28 ℃为适宜发酵温度。
2.1.3 发酵时间对药桑葡萄酒发酵的影响
如图3所示,葡萄与药桑原料质量比1:3时,随发酵时间梯度的增加,发酵过程中酒精度呈先升高后明显接近于平稳的态势,残糖量呈降低趋势并逐渐趋于平稳。药桑葡萄酒发酵前7 d,酒精度急剧上升,从0升高至11.59%vol,到发酵第8 d时,酒精度达到最高的12.35%vol,此后,发酵液酒精度呈缓慢平稳的态势,到发酵结束时为12.15%vol。随着发酵时间的延长,药桑葡萄酒中总酚和总黄酮含量呈先升高后降低的趋势。在发酵第8 d时总酚含量达到最大值2805 mg/L,在发酵第9 d时总黄酮含量达到最大值181.14 mg/g。在第9 d后总酚和总黄酮含量都逐渐下降。这可能是因为随着发酵时间的增加,酵母菌体开始大量死亡[32],单宁类等物质发生聚合以及在发酵过程中多酚发生自然氧化和微生物所产生的酶使黄酮发生降解,使得含量下降[33],且不同品种原料的内在因素和理化性质也影响着在发酵过程中的变化[34]。根据指标结果,建议采用7、8、9 d为适宜发酵时间。
2.1.4 原料质量比对药桑葡萄酒发酵的影响
由图4可知,不同原料质量比的药桑葡萄发酵后总酚和总黄酮含量存在不同程度的变化,不同原料合适的配比可以最大限度地保留药桑和葡萄中的总酚和总黄酮含量。葡萄与药桑的原料质量比在1:3时,总酚和总黄酮含量达到最大值,分别为2782 mg/L、179.8 mg/g,随着葡萄果浆添加量的增加,总酚和总黄酮含量呈下降趋势。葡萄与药桑的原料质量比为3:1时,酒精度为12.63%vol,总酚和总黄酮含量较低。因此考虑各方因素,选择原料质量比范围为葡萄比药桑为1:1、1:3、1:5用于后续响应面试验。
2.2 响应面试验优化发酵参数
2.2.1 数学模型的建立及分析
在单因素实验基础上结合Box-Behnken 设计,以接种量(A)、发酵温度(B)、葡萄药桑原料质量比(C)和发酵时间(D)为影响因子,以总酚含量(Y1)和总黄酮含量(Y2)为响应值,设计四因素三水平响应面试验,以优化药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺参数,响应面试验结果见表2,采用Design-Expert.V8.0.6.1软件对表2试验数据进行回归模型方差分析,结果如表3和表4所示。用Design-Expert.V8.0.6.1软件对表2试验结果进行多元回归方程拟合,获得以总酚和总黄酮为目标函数的二次回归拟合方程:
表 2 Box-Behnken设计试验方案及结果Table 2. Design and results of Box-Behnken experiments试验号 A B C D Y1总酚含量
(mg/L)Y2总黄酮含量
(mg/g)1 −1 −1 0 0 2427 137.38 2 1 −1 0 0 2570 152.41 3 −1 1 0 0 2592 149.7 4 1 1 0 0 2670 165.8 5 0 0 −1 −1 2318 134.57 6 0 0 1 −1 2412 151.2 7 0 0 −1 1 2453 145.5 8 0 0 1 1 2497 158.43 9 −1 0 0 −1 2232 131.93 10 1 0 0 −1 2370 148.58 11 −1 0 0 1 2407 145.55 12 1 0 0 1 2526 159.73 13 0 −1 −1 0 2423 131.99 14 0 1 −1 0 2479 156.5 15 0 −1 1 0 2404 149.09 16 0 1 1 0 2686 160.3 17 −1 0 −1 0 2340 132.52 18 1 0 −1 0 2384 150.09 19 −1 0 1 0 2412 145.2 20 1 0 1 0 2570 154.14 21 0 −1 0 −1 2312 136.75 22 0 1 0 −1 2352 147.1 23 0 −1 0 1 2432 141.07 24 0 1 0 1 2742 169.83 25 0 0 0 0 2863 172.95 26 0 0 0 0 2840 168.64 27 0 0 0 0 2855 170.68 28 0 0 0 0 2872 174.91 29 0 0 0 0 2756 173.82 表 3 以药桑葡萄酒总酚含量为评价指标响应面试验结果的方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance for response surface test results based on total polyphenols content of medicine mulberry and grape wine as evaluation indexes来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P>F 显著性 模型 9.35E+05 14 66807.52 25.73 <0.0001 ** A 38533.33 1 38533.33 14.84 0.0018 ** B 75684.08 1 75684.08 29.15 <0.0001 ** C 28421.33 1 28421.33 10.95 0.0052 * D 93810.08 1 93810.08 36.13 <0.0001 ** AB 1056.25 1 1056.25 0.41 0.5339 AC 3249 1 3249 1.25 0.2821 AD 90.25 1 90.25 0.035 0.8548 BC 12769 1 12769 4.92 0.0436 * BD 18225 1 18225 7.02 0.0191 * CD 625 1 625 0.24 0.6313 A2 2.34E+05 1 2.34E+05 90.04 <0.0001 ** B2 87621.09 1 87621.09 33.75 <0.0001 ** C2 2.73E+05 1 2.73E+05 105.09 <0.0001 ** D2 3.92E+05 1 3.92E+05 150.84 <0.0001 ** 残差 36350.72 14 2596.48 失拟 27555.92 10 2755.59 1.25 0.4468 纯误差 8794.8 4 2198.7 总和 9.72E+05 28 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 总酚含量Y1=2837.20+56.67A+79.42B+48.67C+88.42D−16.25AB+28.50AC−4.75AD+56.50BC+67.50BD−12.50CD−189.85A2−116.22B2−205.10C2−245.72D2
总黄酮含量Y2=172.20+7.37A+8.38B+5.60C+5.83D+0.27AB−2.16AC−0.62AD−3.32BC+4.60BD−0.92CD−12.61A2−9.50B2−13.05C2−12.96D2
结果表明,总酚含量(Y1)和总黄酮含量(Y2)的回归模型显著性结果显示P<0.001,为极显著,总酚含量(Y1)失拟项为P=0.4468,总黄酮含量(Y2)失拟项为P=0.4411,失拟项结果为不显著(P>0.05),两个模型的拟合系数为R2(Y1)=0.9626,R2(Y2)= 0.9787,校正系数为RAdj2(Y1)=0.9252,RAdj2(Y2)=0.9574,说明两个模型的回归拟合度较好,更接近实际试验,说明药桑葡萄酒总酚和总黄酮含量的实测值与预测值之间具有较好的拟合度,所得的回归方程能够较准确地对药桑葡萄酒总酚和总黄酮含量进行分析和预测。
根据回归方程系数显著性检验可知:对于总酚含量(Y1),一次项A、B、D的影响极显著(P<0.01),C的影响显著(P<0.05);交互项BC和BD的影响显著(P<0.05);二次项A2、B2、C2、D2的影响极显著(P<0.01);此外,通过F值大小可判断各因素对药桑葡萄酒总多酚的影响程度依次为:发酵时间(D)>发酵温度(B)>接种量(A)>原料质量比(C),即发酵时间的影响最大,原料质量比的影响最小。对于总黄酮含量(Y2),一次项A、B、C、D的影响极显著(P<0.01);交互项BC影响显著(P<0.05),BD的影响极显著(P<0.01);二次项A2、B2、C2、D2的影响极显著(P<0.01);由交互项F值可以判断各响应面因素对药桑葡萄酒总黄酮的影响排序为:发酵温度(B)>接种量(A)>发酵时间(D)>原料质量比(C),即发酵温度的影响最大,原料质量比的影响最小。
表 4 以药桑葡萄酒总黄酮含量为评价指标响应面试验结果的方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance for response surface test results based on total flavonoids content of medicine mulberry and grape wine as evaluation indexes来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P>F 显著性 模型 4896.23 14 349.73 45.97 <0.0001 ** A 652.25 1 652.25 85.74 <0.0001 ** B 842.36 1 842.36 110.73 <0.0001 ** C 376.21 1 376.21 49.45 <0.0001 ** D 408.1 1 408.1 53.64 <0.0001 ** AB 0.29 1 0.29 0.038 0.849 AC 18.62 1 18.62 2.45 0.14 AD 1.53 1 1.53 0.2 0.6612 BC 44.22 1 44.22 5.81 0.0302 * BD 84.73 1 84.73 11.14 0.0049 ** CD 3.42 1 3.42 0.45 0.5133 A2 1031.63 1 1031.63 135.61 <0.0001 ** B2 585.41 1 585.41 76.95 <0.0001 ** C2 1104.45 1 1104.45 145.18 <0.0001 ** D2 1089.48 1 1089.48 143.21 <0.0001 ** 残差 106.51 14 7.61 失拟 80.99 10 8.1 1.27 0.4411 纯误差 25.52 4 6.38 总和 5002.74 28 2.2.2 因素交互作用对药桑葡萄发酵后总酚和总黄酮含量的响应面分析
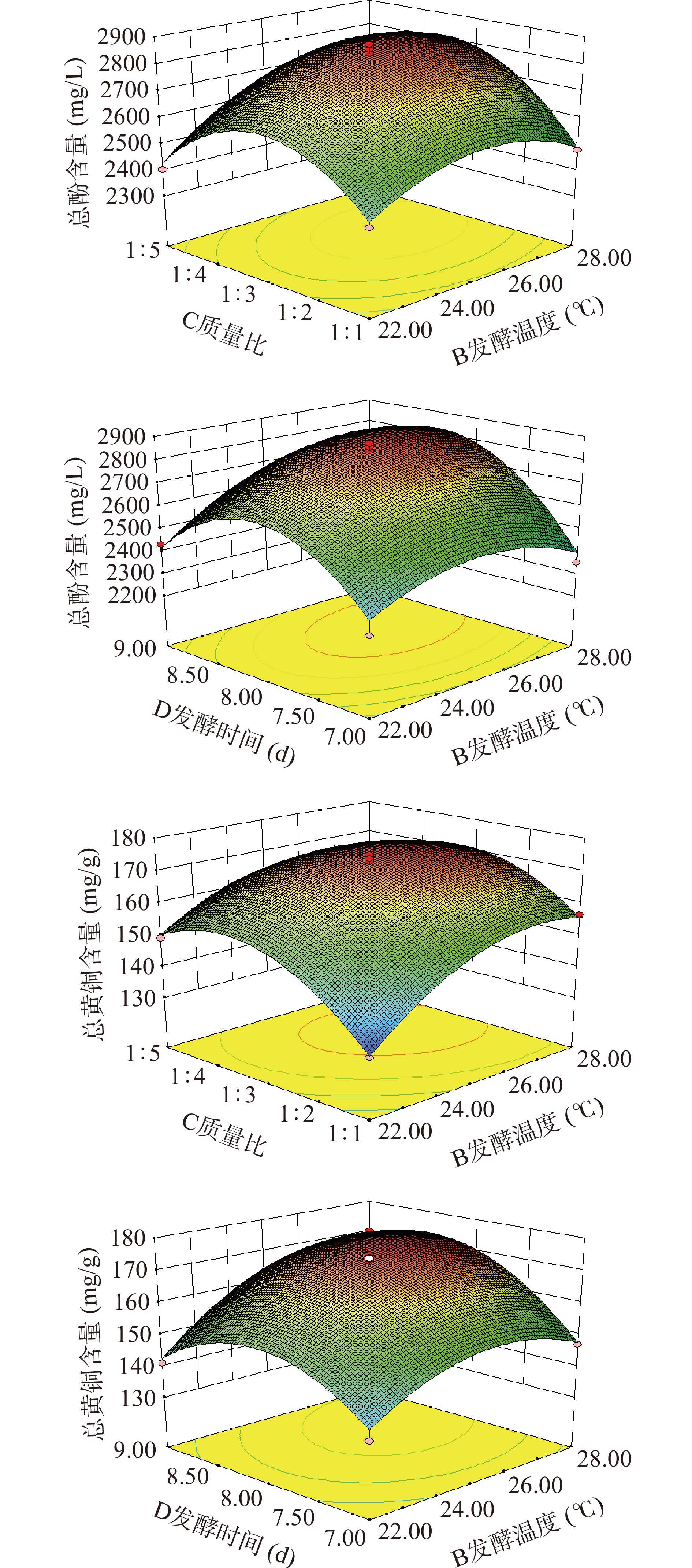
通过Design Expert V8.0.6软件分析,得出图5所示的响应曲面图,从图中可以看出各因素对响应值的影响和因素间的交互作用。根据药桑葡萄发酵液的总酚和总黄酮含量回归方程得出不同因子的响应面分析图,由图可知,在Y1模型中BC、BD和Y2模型中BC所形成的响应面曲面坡度在两因素交互作用响应面图中较陡峭,等高线呈椭圆形,表明交互作用达到显著效果,在Y2模型中BD的交互作用对黄酮含量的影响大,达到极显著效果。结果与回归分析的结果吻合。
2.2.3 响应面模型验证试验
根据响应面软件分析得出4个响应因素对总酚和总黄酮影响所得工艺参数分别为接种量0.32%、主发酵时间8.26 d、发酵温度26.39 ℃、原料质量比是1:2.9,此时所酿造出来的药桑葡萄酒总酚含量可达2872.48 mg/L,总黄酮含量可达176.42 mg/g。为检验该模型的准确性以及可操作性,将药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺条件调整为接种量0.3%、发酵时间8 d、发酵温度26 ℃、葡萄药桑原料质量比是1:3。验证分析得到,3组平行试验的总酚和总黄酮含量分别为2872.48 mg/L、176.42 mg/g,与理论值差异不显著(P>0.05),说明响应面试验和回归方程预测值基本吻合。因此,响应面法优化药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺条件具有良好的可靠性与实用性。
2.3 药桑葡萄酒的体外抗氧化结果与分析
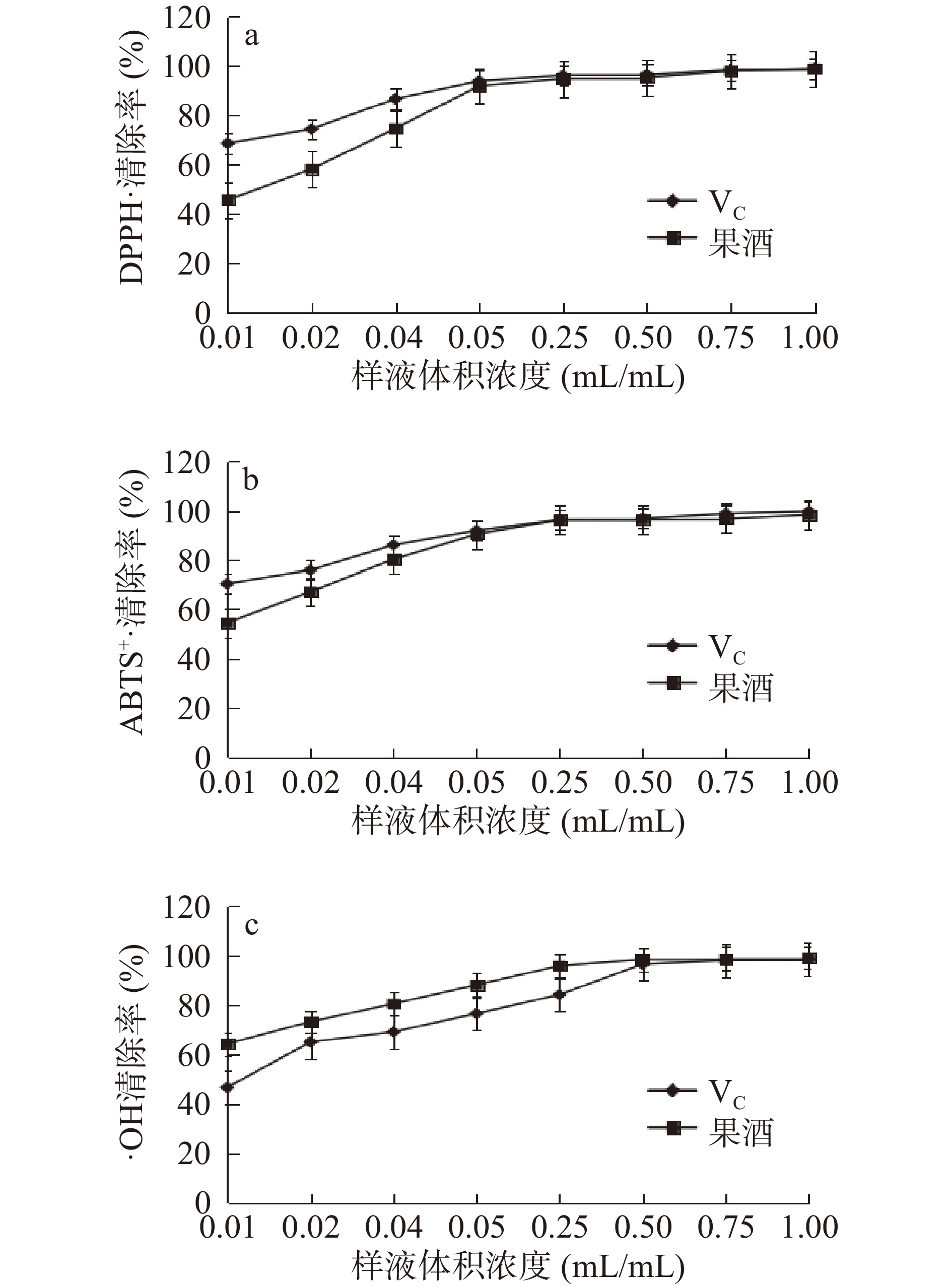
2.3.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定结果
由图6可知,药桑葡萄酒中含有大量的酚类物质及黄酮类化合物。由图6a可知,DPPH自由基清除率随样液体积浓度的增加而增强,呈现正相关关系。当样液体积浓度在0.01~0.25 mL/mL之间时,样品的DPPH自由基清除率呈持续上升态势,当样液体积浓度为0.05 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒的DPPH自由基清除率达到了91.94%,VC溶液的清除率是93.93%,样品体积浓度0.25 mL/mL时,均已达到较高的清除效果,样品体积>0.5 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒和VC溶液对DPPH自由基的清除率增长逐渐趋于平稳态势。在相同体积浓度下,VC溶液对DPPH自由基的清除率均高于药桑葡萄酒。
2.3.2 ABTS+·清除率测定结果
由图6b可知,当样液体积浓度为<0.25 mL/mL时,ABTS+·清除率随样品用量体积的增加而增强。当样液体积浓度为0.25 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒对ABTS+·清除率为96.28%,VC溶液的清除率为96.44%。样液体积浓度>0.25 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒和VC溶液对ABTS+·的清除率的增长趋于平稳态势,ABTS+·清除率与VC相近。相同体积的药桑葡萄酒的ABTS+·的清除能力低于VC溶液。
2.3.3 羟自由基清除率测定结果
由图6c可知,药桑葡萄酒在体积浓度为0.5 mL/mL时已达到较高的自由基清除效果,清除率为98.53%,此时VC的清除率为96.62%,此用量体积浓度后药桑葡萄酒对·OH清除率的增长缓慢。样品体积浓度在(0.01~0.5 mL/mL)时,药桑葡萄酒和VC溶液对·OH清除率在试验范围内呈持续上升的态势。随着样品用量体积的增加,药桑葡萄酒对·OH清除率显著高于VC。结果表明药桑葡萄酒对·OH清除能力很强。钟石等[1]对药桑体外抗氧化活性测试发现,药桑桑椹中含有的总酚和总多糖对羟自由基(·OH)的清除效率显著高于果桑品种大10,新疆药桑桑椹总多酚、总多糖的质量浓度在0.4 mg/mL时,对·OH的清除率分别高达91.48%和90.19%。药桑椹体外抗氧化能力与其含有丰富的生物活性物质有密切关系[35]。
2.4 药桑葡萄酒与胆酸盐的结合能力
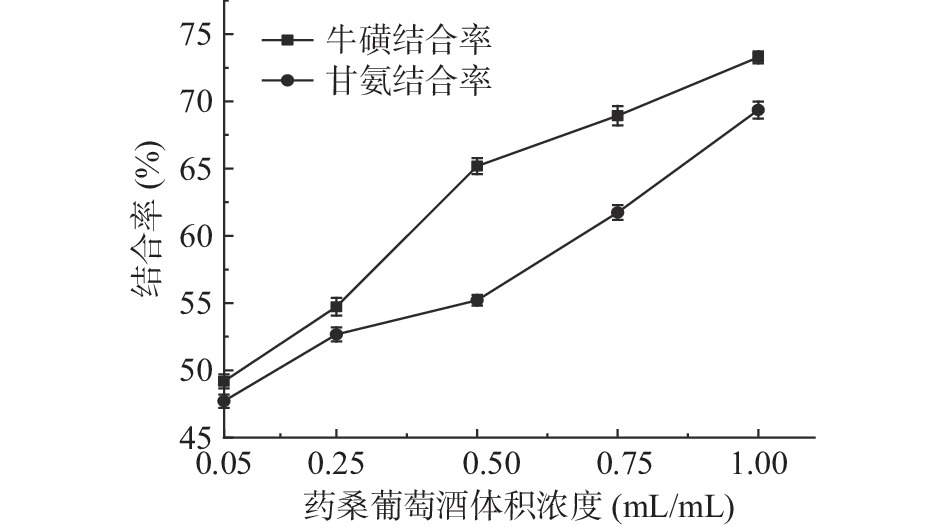
本试验模拟人胃和肠道的环境,选取甘氨胆酸钠和牛磺胆酸钠作为结合对象,分析药桑葡萄酒对二者的结合能力,评价其降血脂效果。
牛磺胆酸钠、甘氨胆酸钠的回归方程依次为:y=0.3201x+0.1277,R2=0.9989;y=0.3251x+0.068,R2=0.998。2个标准曲线线性关系良好,可计算胆酸盐浓度。
从图7可以看出,药桑葡萄酒对牛磺胆酸盐和甘氨胆酸盐均有一定的结合能力。药桑葡萄酒与牛磺胆酸钠的结合能力显著高于与甘氨胆酸钠的结合能力,即药桑葡萄酒与牛磺胆酸盐的结合能力更强,并且二者的结合量均随药桑葡萄酒样品用量体积的增加而升高,呈现出剂量效应关系。当药桑葡萄酒的样品用量体积浓度达到1.0 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒与甘氨胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠的结合率分别达到69.36%、73.28%。当药桑葡萄酒样品用量体积浓度达到0.75 mL/mL时,药桑葡萄酒与甘氨胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠的结合率分别达到61.74%和68.94%。仅是药桑葡萄酒样品用量体积浓度为1.0 mL/mL时结合率的0.89和0.94倍。初步证实药桑葡萄酒具有较好的体外降血脂活性。
3. 结论
本文在单因素实验基础上,选取接种量、发酵时间、发酵温度和原料质量比为影响因子,以药桑葡萄酒的总酚和总黄酮含量为响应值,采用响应面法优化药桑葡萄酒的发酵工艺。试验结果表明,最佳发酵工艺参数为接种量0.3%、发酵时间8 d、发酵温度26 ℃、葡萄药桑原料质量比是1:3。在此条件下所酿造的药桑葡萄酒具有较高的总酚和总黄酮活性成分,为保留药桑葡萄酒中较高的生物活性成分酿造提供良好的基础。
本研究通过测定药桑葡萄酒DPPH、ABTS、OH自由基清除率水平评价了其体外抗氧化活性,结果表明药桑葡萄酒具有较强的抗氧化活性,对·OH清除能力很强。与甘氨胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠的结合能力较强。随着药桑葡萄酒体积浓度的升高,药桑葡萄酒与甘氨胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠的结合能力逐渐增强,呈现出剂量效应关系。新疆药桑氨基酸组成比例较为合理,矿物质元素种类丰富,因此利用药桑复合发酵制备出的药桑葡萄酒具有较强的体外抗氧化与降血脂能力,为推广药桑深加工和综合利用提供了新思路。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of Box-Behnken tests design
水平 因素 A接种量(%) B发酵温度(℃) C质量比 D发酵时间(d) −1 0.2 22 1:1 7 0 0.3 25 1:3 8 1 0.4 28 1:5 9 表 2 Box-Behnken设计试验方案及结果
Table 2 Design and results of Box-Behnken experiments
试验号 A B C D Y1总酚含量
(mg/L)Y2总黄酮含量
(mg/g)1 −1 −1 0 0 2427 137.38 2 1 −1 0 0 2570 152.41 3 −1 1 0 0 2592 149.7 4 1 1 0 0 2670 165.8 5 0 0 −1 −1 2318 134.57 6 0 0 1 −1 2412 151.2 7 0 0 −1 1 2453 145.5 8 0 0 1 1 2497 158.43 9 −1 0 0 −1 2232 131.93 10 1 0 0 −1 2370 148.58 11 −1 0 0 1 2407 145.55 12 1 0 0 1 2526 159.73 13 0 −1 −1 0 2423 131.99 14 0 1 −1 0 2479 156.5 15 0 −1 1 0 2404 149.09 16 0 1 1 0 2686 160.3 17 −1 0 −1 0 2340 132.52 18 1 0 −1 0 2384 150.09 19 −1 0 1 0 2412 145.2 20 1 0 1 0 2570 154.14 21 0 −1 0 −1 2312 136.75 22 0 1 0 −1 2352 147.1 23 0 −1 0 1 2432 141.07 24 0 1 0 1 2742 169.83 25 0 0 0 0 2863 172.95 26 0 0 0 0 2840 168.64 27 0 0 0 0 2855 170.68 28 0 0 0 0 2872 174.91 29 0 0 0 0 2756 173.82 表 3 以药桑葡萄酒总酚含量为评价指标响应面试验结果的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance for response surface test results based on total polyphenols content of medicine mulberry and grape wine as evaluation indexes
来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P>F 显著性 模型 9.35E+05 14 66807.52 25.73 <0.0001 ** A 38533.33 1 38533.33 14.84 0.0018 ** B 75684.08 1 75684.08 29.15 <0.0001 ** C 28421.33 1 28421.33 10.95 0.0052 * D 93810.08 1 93810.08 36.13 <0.0001 ** AB 1056.25 1 1056.25 0.41 0.5339 AC 3249 1 3249 1.25 0.2821 AD 90.25 1 90.25 0.035 0.8548 BC 12769 1 12769 4.92 0.0436 * BD 18225 1 18225 7.02 0.0191 * CD 625 1 625 0.24 0.6313 A2 2.34E+05 1 2.34E+05 90.04 <0.0001 ** B2 87621.09 1 87621.09 33.75 <0.0001 ** C2 2.73E+05 1 2.73E+05 105.09 <0.0001 ** D2 3.92E+05 1 3.92E+05 150.84 <0.0001 ** 残差 36350.72 14 2596.48 失拟 27555.92 10 2755.59 1.25 0.4468 纯误差 8794.8 4 2198.7 总和 9.72E+05 28 注:“**”表示差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 表 4 以药桑葡萄酒总黄酮含量为评价指标响应面试验结果的方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance for response surface test results based on total flavonoids content of medicine mulberry and grape wine as evaluation indexes
来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F值 P>F 显著性 模型 4896.23 14 349.73 45.97 <0.0001 ** A 652.25 1 652.25 85.74 <0.0001 ** B 842.36 1 842.36 110.73 <0.0001 ** C 376.21 1 376.21 49.45 <0.0001 ** D 408.1 1 408.1 53.64 <0.0001 ** AB 0.29 1 0.29 0.038 0.849 AC 18.62 1 18.62 2.45 0.14 AD 1.53 1 1.53 0.2 0.6612 BC 44.22 1 44.22 5.81 0.0302 * BD 84.73 1 84.73 11.14 0.0049 ** CD 3.42 1 3.42 0.45 0.5133 A2 1031.63 1 1031.63 135.61 <0.0001 ** B2 585.41 1 585.41 76.95 <0.0001 ** C2 1104.45 1 1104.45 145.18 <0.0001 ** D2 1089.48 1 1089.48 143.21 <0.0001 ** 残差 106.51 14 7.61 失拟 80.99 10 8.1 1.27 0.4411 纯误差 25.52 4 6.38 总和 5002.74 28 -
[1] 钟石, 丁天龙, 李有贵, 等. 新疆药桑桑椹中的主要营养活性成分检测分析[J]. 蚕业科学,2012,38(6):1067−1072. [ZHONG S, DING T L, LI Y G, et al. Determination and analysis of main nutritional ingredients in mulberry fruit of Morus nigra L[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica,2012,38(6):1067−1072. [2] 马慧, 李文慧, 李昱, 等. 新疆药桑化学成分抗氧化机理及药理作用研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2020(19):72−76. [MA H, LI W H, LI Y, et al. Advances in the study of chemical constituents antioxidation mechanism and pharmacological action of radix notoginseng in Xinjiang[J]. Farm Products Processing,2020(19):72−76. [3] MA X L, SONG F F, ZHANG H, al. Compositional monosaccharide analysis of Morus nigra Linn by HPLC and HPCE quantitative determination and comparison of polysaccharide from Morus nigra Linn by HPCE and HPLC[J]. Curr Pharm Anal,2017,13(5):433−437.
[4] 刘丹, 陈虎, 蒲俊松, 等. 药桑桑椹总多酚的提取工艺条件优化及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 蚕业科学,2016,42(6):1068−1076. [LIU D, CHEN H, PU J S, et al. Extraction process optimization and antioxidant activity analysis of total polyphenols from medicinal mulberry fruit[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica,2016,42(6):1068−1076. [5] 马春兰. 新疆药桑抗氧化性成分的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2011. MA C L. Isolation and identification of chemical constituent and antioxidant activity of extracts from Morus nigra Linn[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2011.
[6] 胡康, 周金虎, 颜雪辉, 等. 桑葚酒发酵工艺的研究[J]. 酿酒,2017,44(5):42−47. [HU K, ZHOU J H, YAN X H, et al. Research on the fermentation technology of mulberry wine[J]. Liquor Making,2017,44(5):42−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8110.2017.05.014 [7] 王贺, 刘健健, 杨俊玲, 等. 新疆药桑不同部位降血糖活性研究[J]. 广州化工,2014,42(14):76−78. [WANG H, LIU J J, YANG J L, et al. Study of Morus nigia L. mulberry hypoglycemic activity from fifferent active parts[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2014,42(14):76−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2014.14.027 [8] 张晶, 左勇, 谢光杰, 等. 桑椹果酒主发酵过程中主要理化指标的变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(14):18−22,28. [ZHANG J, ZUO Y, XIE G J, et al. Dynamic changes of main physical and chemical indexes during main fermentation process in mulberry wine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(14):18−22,28. [9] 杨新, 卢红梅, 杨双全, 等. 桑葚及桑葚果酒的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(4):257−262. [YANG X, LU H H, YANG S Q, et al. Research progress of mulberry and mulberry fruit wine[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(4):257−262. [10] ANDERSON K, NELGEN S. Internationalization, premiumization and diversity of the world’s winegrape varieties[J]. Wine Economics Research Centre Working Papers,2021,20(9):67−73.
[11] 冯玲霞, 熊作成. 酿酒葡萄皮渣综合利用研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2018,41(2):103−104,132. [FENG L X, XIONG Z C. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of wine grape skin pomace[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2018,41(2):103−104,132. [12] SHIMIZU H, AKAMATSU F, KAMADA A, et al. Variation in the mineral composition of wine produced using different winemaking techniques[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2020,130(2):166−172. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2020.03.012
[13] 杨帆, 卢灏泽, 贾福晨, 等. 葡萄酒中优良酵母菌的筛选研究[J]. 轻工科技,2021,37(5):30−31,36. [YANG F, LU H Z, JIA F C, et al. Study on the screening of fine yeasts in wine[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2021,37(5):30−31,36. [14] 赵家乐, 吴虹艳, 孔令姝, 等. 响应面法优化蓝靛果桑葚低糖饮料发酵工艺[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(8):76−80. [ZHAO J L, WU H Y, KONG L S, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of Lonicera eduils and mulberry low sugar beverage by response surface methodology[J]. The Food Industry,2019,40(8):76−80. [15] 杜恣闲, 郑建莉. 果酒的营养成分及其发展分析研究[J]. 江西化工,2011,102(2):23−26. [DU Z X, ZHENG J L. Analysis and research on the nutritional components and development of fruit wine[J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry,2011,102(2):23−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3103.2011.02.006 [16] 罗光琳. 复合型果酒产业化关键工艺技术优化研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. LUO G L. Research on optimization of key process technology for compound fruit wine industrialization[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018.
[17] KAUR C, KAPOOR H C. Anti-oxidant activity and total phenolic content of some asian vegetables[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2010,37(2):87−95.
[18] 欧燕. 桑葚—草莓酒的酿造及其抗氧化性的研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学, 2014. OU Y. Study on brewing and antioxidant activity of mulberry-strawberry wine[D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2014.
[19] PAN Y L, HUANG W P, YANG C P. Study on fermentation technology of compound fruit wine by mixed juice of tomato and passion fruit[J]. Journal of Guangxi Agriculture,2019,34(3):41−48.
[20] 吴均, 谢青松, 熊虎, 等. 响应面实验优化红肉蜜柚果酒发酵工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(3):238−243. [WU J, XIE Q S, XIONG H, et al. Optimization of fermentation of red pulp honey pomelo fruit wine by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(3):238−243. [21] 何倩, 苏比努尔, 李俊辉, 等. 新疆药桑总黄酮的富集纯化工艺研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2019,47(4):176−180. [HE Q, SUBINUER, LI J H, et al. Study on enrichment and purification process of total flavonoids from Xinjiang mulberry[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(4):176−180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.04.048 [22] 刘阿文. 桑葚果酒发酵工艺条件及生理活性研究[D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2019. LIU A W. Study on the fermentation technology and physiological activity of mulberry wine[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2019.
[23] 吴均, 黄传书, 赵珮, 等. 响应面试验优化桑葚果酒发酵工艺及其品质分析[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(1):98−104. [WU J, HUANG C S, ZHAO P, et al. Optimization of fermentation technology of mulberry wine by response surface methodology and quality analysis[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(1):98−104. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.01.019 [24] 李湘利, 刘静, 朱九滨, 等. 鸡枞菌饮料的体外抗氧化特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(3):87−96. [LI X L, LIU J, ZHU J B, et al. Study on the antioxidation in vitro of Termitornyces albuminosus beverages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(3):87−96. [25] 程宏桢, 蔡志鹏, 王静, 等. 百香果全果酒发酵工艺优化及体外抗氧化性比较分析[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(4):91−97. [CHENG H Z, CAI Z P, WANG J, et al. Optimization of fermentation process for whole passion fruit wine and comparative analysis of antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(4):91−97. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.04.019 [26] 刘淑敏. 不同茶类浸提液及茶多酚的生物活性和机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016. LIU S M. Study on the biological activities and functional mechanisms of different tea extracts and tea polyphenols[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016.
[27] 徐霞, 刘靖, 宋雨, 等. 基于胆酸盐吸附作用的藜麦蛋白质酶解工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(15):192−197. [XU X, LIU J, SONG Y, et al. Study on the enzymatic hydrolysis technology of quinoa protein based on cholate adsorption[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(15):192−197. [28] 胡凯, 黄惠华. 不同茶浸提液对胆酸盐的结合及其降血脂机理的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(8):105−111. [HU K, HUANG H H. Study on the ability of bile salt-binding among different tea extracts in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(8):105−111. [29] 叶学林, 程水明, 温露文, 等. 响应面法优化桑葚果酒发酵工艺[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(12):105−109. [YE X L, CHENG S M, WEN L W, et al. Optimization of fermentation technology for mulberry wine by response surface methodology[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(12):105−109. [30] 张敏. 酿造工艺对蜂蜜酒多酚类抗氧化活性成分的影响[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016. ZHANG M. Effect of brewing technology on the active antioxidant components of polyphenols of mead[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2016.
[31] 许亮, 师俊玲, 陈东方, 等. 枸杞果酒中总黄酮含量的发酵条件优化[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(7):188−193. [XU L, SHI J l, CHEN D F, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for production of chinese wolfberry fruit wine with higher total flavonoid content[J]. Food Science,2011,32(7):188−193. [32] 张晶, 左勇, 谢光杰, 等. 发酵条件对猕猴桃果酒中多酚含量的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(9):160−163,167. [ZHANG J, ZUO Y, XIE G J, et al. Influence of fermentation conditionson the yield of polyphenols in kiwi fruit wine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(9):160−163,167. [33] 冯彬. 桑葚蜜酒生产工艺优化、抗氧化活性研究及品质分析[D]. 太原: 山西农业大学, 2019. FENG B. Production technology optimization, antioxidant activity researchand quality analysis of mulberry honey wine[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2019.
[34] 黄佳. 猕猴桃酒发酵及陈酿过程中多酚及多糖的变化规律[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. HUANG J. Change of polyphenol and polysaccharides during kiwi wine fermentation and ageing[D]. Yangling: Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry, 2016.
[35] 江岩, 聂文静. 新疆药桑椹营养成分分析及其体外抗氧化作用[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(22):126−129. [JIANG Y, NIE W J. Nutritional composition and in vitro antioxidant capacity of black mulberry (Morus nigra L.) fruits from Xinjiang province[J]. Food Science,2014,35(22):126−129. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201422023 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 刘璐,李晶峰,兰梦,李冬冰,张凯月,王跃龙,申嘉明,李春楠,张辉,孙佳明. 牡蛎蛋白酶解肽制备工艺优化及其对小鼠睾丸间质细胞睾酮分泌和氧化应激的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(09): 168-176 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李冬冰,兰梦,王跃龙,刘璐,申嘉明,李晶峰,张辉,孙佳明. 珍珠母肽酶解工艺的优化及对人肝癌细胞HepG2能量代谢的影响. 现代食品科技. 2024(05): 92-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈灼娟,柯秀贤,黄霄. 姬松茸抗氧化酶解液的制备. 食品与机械. 2023(03): 183-187+232 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张书会,罗璐,孙雪言,马爱民. 虎奶菇菌丝体抗菌肽提取工艺优化及活性研究. 食品与机械. 2022(08): 158-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



