Optimization of Fermentation Process for Water-soluble Polysaccharides and Antioxidant Activity of Polygonatum odoratum Fermentated by Bacillus subtilis LY-05
-
摘要: 为了考察益生菌发酵玉竹产水溶性多糖的最佳工艺条件并比较发酵与未发酵多糖的抗氧化活性。本文以枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05为发酵菌株,水溶性多糖含量提高率为指标,研究了玉竹添加量、氮源种类、无机盐种类、接种量、培养温度、摇床转速及发酵时间等发酵条件对发酵玉竹产水溶性多糖的影响。在单因实验结果的基础上,选择对多糖含量提高率影响较大的因素,采用响应面试验法对发酵条件进行了优化;并通过检测DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS自由基清除率,OH自由基清除率及总还原能力,评价发酵与未发酵的玉竹多糖抗氧化活性的变化。结果表明:最佳的发酵工艺参数为:玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取粉3%,NaCl 1%,接种量3%,温度35 ℃,转速160 r/min,发酵时间48 h。在此条件下,多糖含量达到7.83 mg/mL,较未发酵(4.56 mg/mL)提高了71.78%。抗氧化试验表明,在一定浓度下,发酵后玉竹多糖的DPPH、ABTS、OH由基清除率及总还原力均有所提高,且呈现多糖浓度依赖性。发酵后多糖POP2对ABTS自由基清除的半抑制浓度(IC50)2.21 mg/mL,对OH自由基清除的IC50为0.49 mg/mL。此项研究表明,利用枯草芽孢杆菌发酵玉竹可以明显提高玉竹多糖的提取效率。通过发酵产生的玉竹多糖,具有更强的抗氧化能力。
-
关键词:
- 玉竹多糖 /
- 枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05 /
- 发酵工艺 /
- 水溶性多糖 /
- 抗氧化活性
Abstract: To investigate the optimal process conditions for the production of water-soluble polysaccharides from Polygonatum odoratum by aprobiotics and compare the change of antioxidant activities of polysaccharides fermented and unfermented. In this study, Bacillus subtilis LY-05 was used as fermentation strain, and increasing rate of water-soluble polysaccharides was index. Seven factors including Polygonatum odoratum addition, nitrogen source, inorganic salt, inoculation amount, temperature, stirring speed and fermentation time were studied with the increasing rate of water-soluble polysaccharides. On the basis of single-factor experiment, the fermentation conditions were optimized with response surface method; and evaluating the changes of the DPPH·scavenging rate, ABTS+·scavenging rate, OH· scavenging rate and total reducing power in the antioxidant activity of Polygonatum odoratum polysaccharides fermented and unfermented. The results showed that optimal fermentation condition was as follows: Polygonatum odoratum addition 4%, yeast extract powder 3%, NaCl 1%, inoculation amount 3%, fermention temperature 35 ℃, stirrig speed 160 r/min, fermentation time 48 h. Under these conditions, the polysaccharide content reached 7.83 mg/mL, which was 71.78% higher than that before fermentation(4.56 mg/mL). The antioxidant experiment showed that the DPPH·, ABTS+·, OH· scavenging rate and total reducing power of the fermented polysaccharide increased at certain concentrations and showed polysaccharide concentration dependence. The semi-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of the fermented polysaccharide POP2 on ABTS+·radical scavenging was 2.21 mg/mL, and the semi-inhibitory concentration on OH·radical scavenging was 0.49 mg/mL. These results implied that fermentation with Bacillus subtilis could significantly improve the extraction efficiency of Polygonatum odoratum polysaccharides, and polysaccharides in fermentated Polygonatum odoratum had better antioxidant capacity. -
玉竹(Polygonatum odoratum(Mill.)Druce)为百合科(Liliaceae)黄精属(Polygonatum)植物[1],又名萎蕤,最早出现于《神农本草经》,具有悠久的药用历史[2]。其化学成分复杂,主要包括多糖类、黄酮类、甾体皂苷、生物碱及其挥发性油等[3],具有降血糖、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、调节机体免疫等多种药理作用[4-6],其主要活性成分为多糖类化合物。研究发现,玉竹多糖可用于治疗免疫低下[7]、肥胖[8-9]、非酒精性脂肪肝[9]、糖尿病[10]等疾病。
利用益生菌发酵中草药可提高有效成分的提取率,提高药效的特点。众多研究表明,芽孢杆菌发酵可产多种酶类物质,能降解植物细胞壁成分,释放多糖[11]。郭云霞等[12]利用筛选的芽孢杆菌N-14发酵黄芪,经发酵优化后多糖得率为发酵前的1.57倍。武洪志等[13]利用枯草芽孢杆菌发酵复方中药(苍术、白术、黄柏、板蓝根、甘草、山楂),优化发酵工艺后多糖含量显著提高。近年来有研究指出,中草药经微生物发酵具有更高的抗氧化活性。WANG等[14]用四株益生菌混合发酵白芷根,发现发酵白芷根具有更强的抗酪氨酸酶活性和抗氧化活性。李暄[15]利用酿酒酵母菌和枯草芽孢杆菌混合发酵麸皮,其抗氧化活性显著性增强。CAO等[16]的研究中发现,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 SN-1发酵产生胞外多糖具有良好的抗氧化活性。近年来,益生菌发酵中草药的研究屡见不鲜,利用玉竹进行发酵却鲜有报道。玉竹多糖含量高,利用率低。利用微生物发酵可降解植物细胞壁,释放胞内活性物质,课题组前期利用不同的益生菌对玉竹进行发酵产多糖筛选,发现一株枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹后产水溶性多糖含量最高,可作为微生态与中草药发酵等研究领域的潜在菌株,因此对其发酵工艺进行优化研究具有一定的价值。
本文选用枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05,采用液体深层发酵技术和单因素实验法研究玉竹发酵产水溶性多糖的工艺条件。在单因素实验结果的基础上,利用 Box-Behnken试验法设计三因素三水平试验对玉竹发酵工艺条件进行优化,以期提高玉竹多糖的得率。并对发酵与未发酵的玉竹多糖进行抗氧化活性比较,为玉竹多糖的工业化生产及其功能性产品开发奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05(Bacillus subtilis) 保存于湖南农业大学生物科学技术学院微生物研究室;玉竹(Polygonatum odoratum) 采摘于湖南省娄底市;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2 ,2’-联氨-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;
TYSP-400高速多功能粉碎机 浙江省永康市红太阳机电有限公司;PL303电子分析天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;TGL18W台式高速离心机 长沙英泰仪器有限公司;UV1802G紫外分光光度计 天津冠泽科技有限公司;Epoch酶标仪 BioTek Instruments,Inc。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 培养基配制
斜面培养基:胰蛋白胨1%,酵母提取粉0.5%,氯化钠1%,琼脂2%,蒸馏水1000 mL,pH7.2~7.5。
液体种子培养基:成分同斜面培养基,但不加琼脂粉。
基础发酵培养基:玉竹5%,胰蛋白胨3%,氯化钠1%,蒸馏水1000 mL,pH7.2~7.5。
上述培养基均在115 ℃条件下灭菌30 min。
1.2.2 菌种活化与培养
1.2.2.1 菌种活化
将甘油保存的枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05接种到液体种子培养基中,37 ℃,180 r/min培养24 h后,转接到斜面培养基,37 ℃恒温培养24 h,重复活化2次,备用。
1.2.2.2 种子液培养
将活化的斜面菌种接种于液体种子培养基中,37 ℃,180 r/min培养24 h,备用。
1.2.2.3 发酵培养
将培养成熟的液体种子按2%(V/V)接种量接种至基础发酵培养基中,37 ℃,180 r/min恒温振荡培养48 h。
1.2.3 单因素实验
1.2.3.1 玉竹粉添加量
分别改变基础发酵培基中玉竹添加量为2%、3%、4%、5%、6% ,胰蛋白胨3%,NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量2%,37 ℃,180 r/min摇床发酵48 h,另设置添加相同含量玉竹粉且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.2 氮源种类
玉竹添加量4%,分别改变氮源的种类为氯化铵、硫酸铵、胰蛋白胨、酵母提取物、牛肉膏、豆粕,添加量均为3%,NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量2%,37 ℃,180 r/min摇床发酵48 h,另设置添加不同氮源且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.3 盐离子种类
玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取物3%,分别改变无机盐种类为NaCl、 KCl、MgSO4、CaCl2、FeCl3、MnSO4,添加量均为1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量2%,37 ℃,180 r/min摇床发酵48 h,另设置添加不同盐离子且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.4 接种量
玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取物3%,NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,分别改变接种量为1%、2%、3%、4%、5%,37 ℃,180 r/min摇床发酵48 h,另设置不接种的无菌培养基为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.5 培养温度
玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取物3%, NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量4%,分别改变培养温度为31、33、35、37、39 ℃,180 r/min摇床发酵48 h,另设置不同培养温度且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.6 转速
玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取物3%,NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量4%,温度35 ℃,分别改变摇床转速为140、160、180、200、220 r/min,发酵48 h,另设置不同转速且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.3.7 发酵时间
玉竹添加量4%,酵母提取物3%,NaCl 1%,蒸馏水100 mL,接种量4%,温度35 ℃,摇床转速160 r/min,分别改变发酵时间为12、24、36、48、60、72 h,另设置不同发酵时间且不接种的处理为对照组,发酵结束后测定发酵液中多糖含量。
1.2.4 响应面优化试验
在单因素优化结果的基础上,采用Box-Behnken(BBD)设计原理,选择接种量、培养温度、发酵时间为自变量,以多糖含量提高率为响应值,设计三因素三水平响应面优化试验。因素水平设计表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface experiment
因素水平 −1 0 1 接种量(%) A 2 3 4 温度(℃) B 33 35 37 发酵时间(h) C 36 48 60 1.2.5 水溶性多糖含量测定
水溶性多糖提取及多糖含量测定:参照文献[17]提供的方法稍作改动。水溶性多糖含量提高率计算公式如下:
提高率(%)=发酵后多糖含量−未发酵多糖含量未发酵多糖含量×100 式中:水溶性多糖含量提高率为发酵处理组相对对照组的多糖含量提高得率,全文统一为提高率。
1.2.6 玉竹多糖提取物的制备
根据前期优化工艺进行发酵,分别将未发酵组(未添加发酵菌,其余处理步骤与发酵组相同)与发酵组离心(10000 r/min,10 min)收集上清液,减压浓缩至200 mL,以4:1的体积比加入Sevage(氯仿:正丁醇=4:1)试剂,振荡30 min,离心(4000 r/min,10 min),收集上清液,重复两次。脱蛋白后的多糖溶液加入经预处理的AB-8大孔树脂进行脱色处理,振荡2 h,抽滤,收集样液。样液浓缩至一定体积后加入3倍无水乙醇,放于4 ℃冰箱过夜,离心(10000 r/min,10 min),沉淀复溶于去离子水。使用8000~14000 Da透析袋透析48 h,期间多次换水,透析液冷冻干燥得未发酵玉竹多糖( POP1)、发酵后玉竹多糖(POP2)。
1.2.7 玉竹多糖抗氧化活性测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除率
参照LIANG等[18]的方法并稍作改进。吸取100 μL不同浓度的POP1、POP2水溶液及VC溶液(0.125、0.25、0.5、1.0、2.0、4.0 mg/mL)于96孔板,分别加入0.4 mmol/L的无水乙醇-DPPH溶液15 μL,充分混匀,避光反应30 min,517 nm处检测样品吸光值。去离子水代替样品为样品空白对照,VC为阳性对照,无水乙醇代替DPPH溶液为背景对照。
按下列公式计算:
清除率=[1−A1−A2A0]×100 (1) 式中:A0:空白组在517 nm的吸光值;A1:样品组在517 nm的吸光值;A2:背景组在517 nm的吸光值。
1.2.7.2 ABTS自由基清除率
参照柴美灵等[19]的方法并稍作改进。配制7 mmol/L的ABTS甲醇溶液和15 mmol/L过硫酸钾溶液,等体积混合后,室温避光保存12 h,用甲醇稀释ABTS+·溶液,直至732 nm处的吸光值为(0.70±0.02),制得ABTS+·溶液。吸取20 μL不同浓度的POP1、POP2溶液于96孔板,接着加入150 μL ABTS+·工作液,室温避光反应30 min,732 nm处检测样品吸光值。去离子水代替样品为空白对照,VC为阳性对照,甲醇代替ABTS+·溶液为背景对照。
按下列公式计算:
清除率=[1−A5−A4A3]×100 (2) 式中:A3:空白组在732 nm的吸光值;A4:样品组在732 nm的吸光值;A5:背景组在732 nm的吸光值。
1.2.7.3 OH·自由基清除率
参照宗鑫妍等[20]的方法并稍作改进。吸取50 μL不同浓度的POP1、POP2溶液至96孔板,分别加入等体积的硫酸亚铁溶液(6.0 mmol/L)、过氧化氢溶液(6.0 mmol/L)、水杨酸-醇溶液(9.0 mmol/L),37 ℃孵育1 h,于517 nm 测定吸光值。去离子水代替样品为空白对照,VC为阳性对照,甲醇代替水杨酸溶液为背景对照。
按下列公式计算:
清除率=[1−(A7−A8)A6]×100 (3) 式中:A6:空白组在517 nm的吸光值;A7:样品组在517 nm的吸光值;A8:背景组在517 nm的吸光值。
1.2.7.4 总还原力测定
参照ZONG等[21]的方法并稍作改进后进行测定。吸取250 μL POP1、POP2溶液和250 μL磷酸缓冲液(pH6.6,0.2 mol/L)与250 μL 1%铁氰化钾溶液混合均匀,放于50 ℃充分反应30 min,加入250 μL 10%三氯乙酸终止反应,离心,取上清液100 μL,加入100 μL蒸馏水和20 μL 0.1%氯化铁溶液,混合静置30 min,在700 nm处测定吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
上述试验均设置三次重复,试验结果采用SPSS25.0软件进行分析,测定结果均以“平均值±标准错误(SEM)”表示,统计学显著性差异为P<0.05。采用Design Expert 12.0软件进行响应面设计,GraphPad Prism 8绘图软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 玉竹粉添加量对多糖提高率的影响
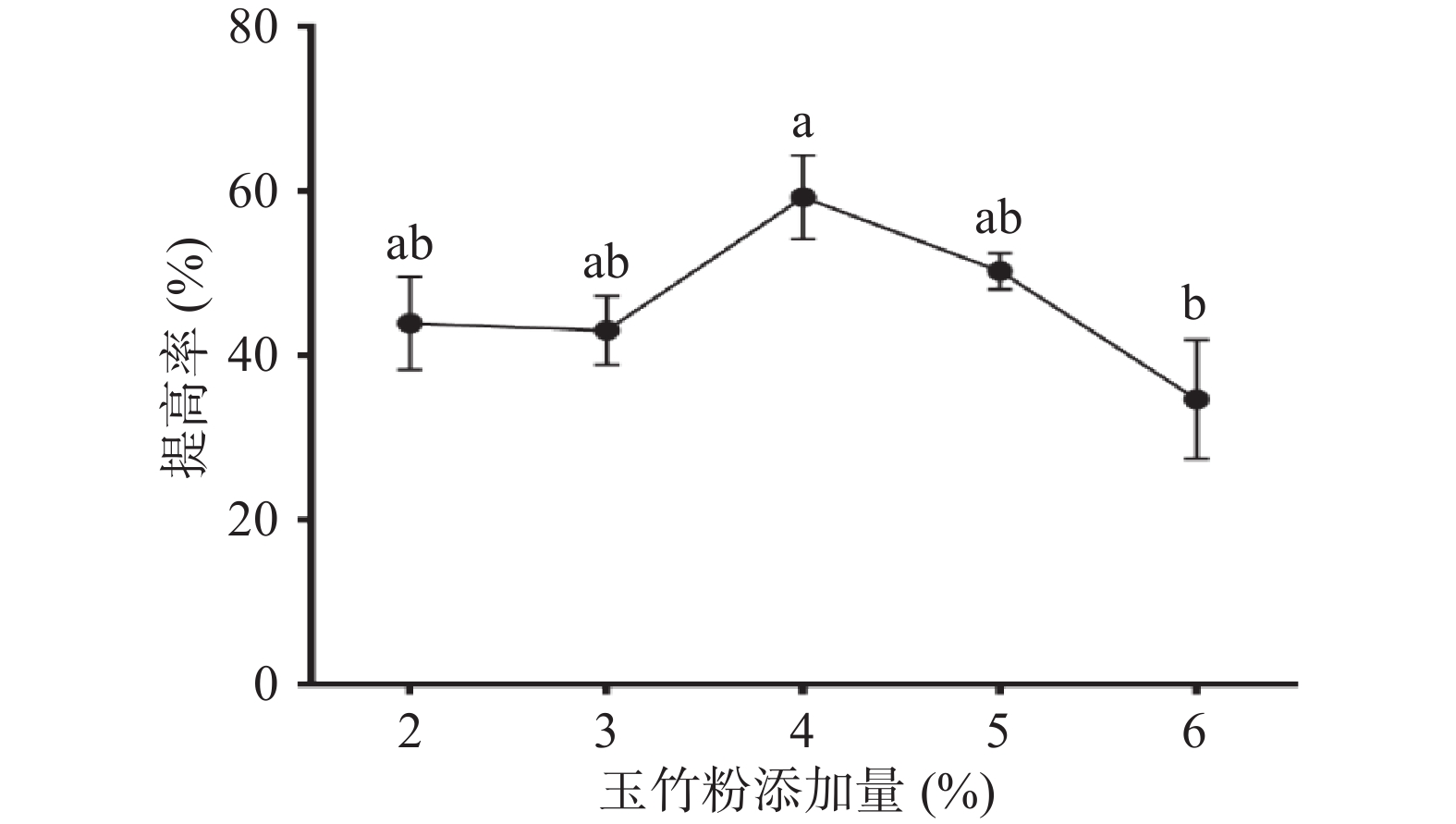
图1为玉竹粉添加量对益生菌发酵玉竹产水溶性多糖的影响,由图可知,在一定添加量范围内,随着玉竹粉添加量的增加,多糖提高率也随之增加。当玉竹添加量为4%时,提高率达到(59.23%±5.16%),但玉竹粉添加量超过4%,提高率明显下降。原因可能是玉竹粉添加量过大,枯草芽孢杆菌产出的纤维素酶、淀粉酶不足以酶解因增加玉竹粉带来的更多淀粉和纤维素。而且,由于玉竹化学成分黄酮类、生物碱等生物活性物质含量增高,减缓和抑制了枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05的生长和代谢。故选择玉竹粉添加量为4%进行后续试验。
![]() 图 1 玉竹添加量对多糖提高率的影响注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。Figure 1. Effects of Polygonatum odoratum addition on increasing rate of polysaccharides
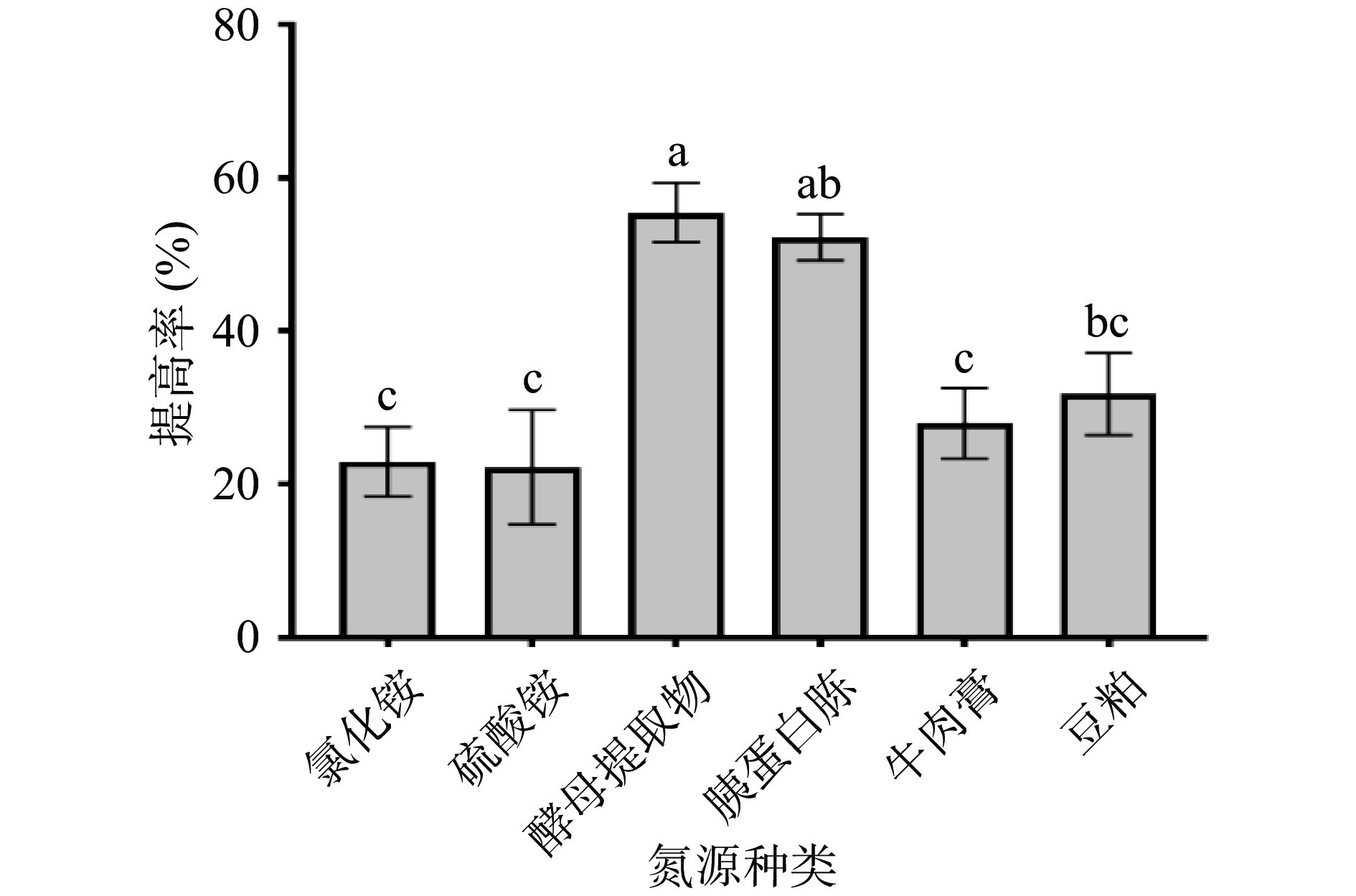
图 1 玉竹添加量对多糖提高率的影响注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。Figure 1. Effects of Polygonatum odoratum addition on increasing rate of polysaccharides2.1.2 氮源种类对多糖提高率的影响
等氮条件下,在基础发酵培养基中分别加入酵母提取物、胰蛋白胨、牛肉膏、豆粕、氯化铵,硫酸铵,考察不同氮源种类对多糖提高率的影响,结果见图2。图2结果表明,以酵母提取物为唯一氮源时,提高率达到(55.48%±3.86%),明显高于其他氮源处理组,同时也可以看出,以无机氮为唯一氮源时,多糖提高率均较低,说明无机氮不适合枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹产多糖。因此,选择酵母提取物进行后续研究。
2.1.3 无机盐对多糖提高率的影响
不同无机盐在培养基中的作用不同,如Na+调节细胞通透性,K+可作为某些酶的辅助因子,Mg2+可作为糖酵解(EMP)的酶激活剂。从图3可以看出,本实验中培养基添加NaCl多糖提高率达到(57.95%±4.13%),效果提升最明显,其次是MgSO4、KCl、MnSO4、FeCl3,添加CaCl2效果最差,提高率为(40.05%±6.38%),与添加NaCl的效果有显著差别(P<0.05)。在发酵的过程中会产生酸类物质,培养基中添加NaCl具有维持pH稳定,调节细胞通透性的功能,故培养基中添加NaCl作为盐离子是适宜的选择。
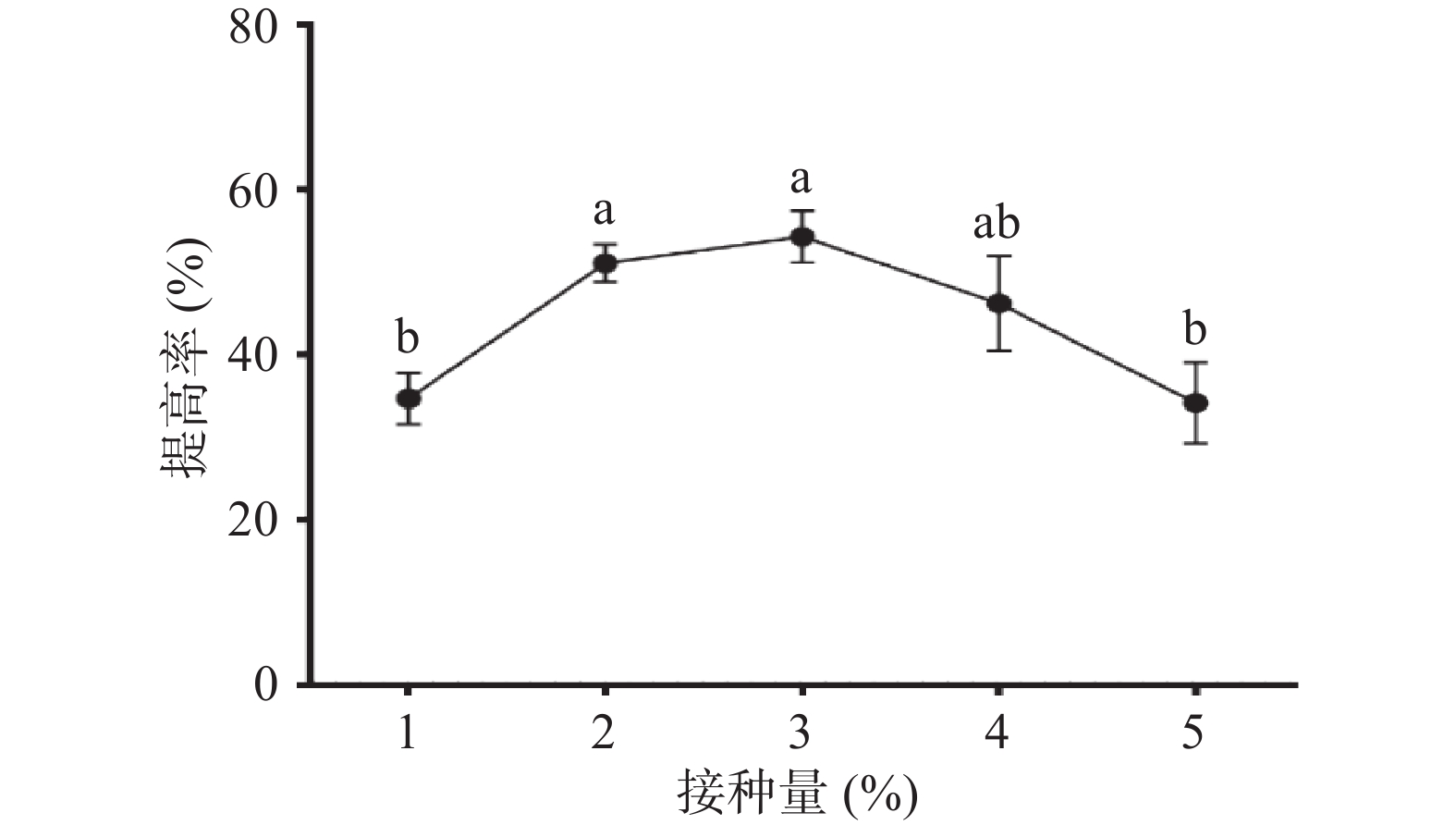
2.1.4 接种量对多糖提高率的影响
由图4可以看出,接种量在1%~3%范围内,多糖提高率随接种量的增加逐渐增大。当接种量3%时,提高率为(54.28%±3.15%),继续加大接种量,多糖提高率明显下降。原因是接种量过大,导致发酵前期培养基中营养物质消耗过快及菌体生物量增加,影响了发酵中后期营养物质的供应及培养基中的溶氧量,从而影响了枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05的生长和代谢。故选择3%的接种量进行后续研究。
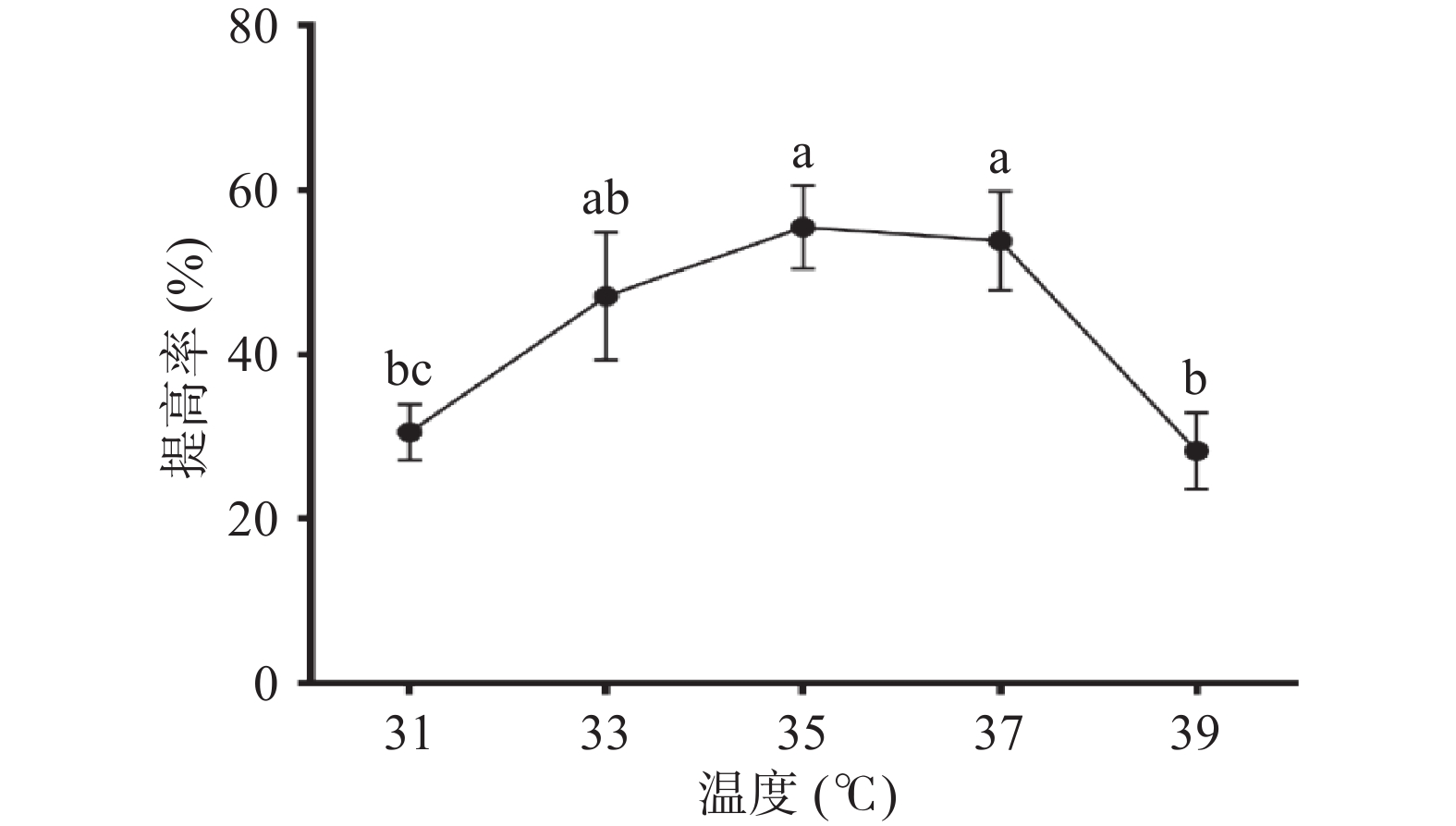
2.1.5 温度对多糖提高率的影响
菌体的生长需要一个适宜的温度,低于最适温度,部分菌体新陈代谢和产酶活力都处于低水平,温度过高时,释放的酶量和活力都受到影响,则菌体生长受到抑制。如图5,温度对玉竹多糖提高率的影响呈先上升后下降的趋势,当培养温度为35 ℃,提高率最大为(55.53%±5.10%),说明此温度有可能是枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05生长的最适温度。故选择35 ℃为后续实验的发酵温度。
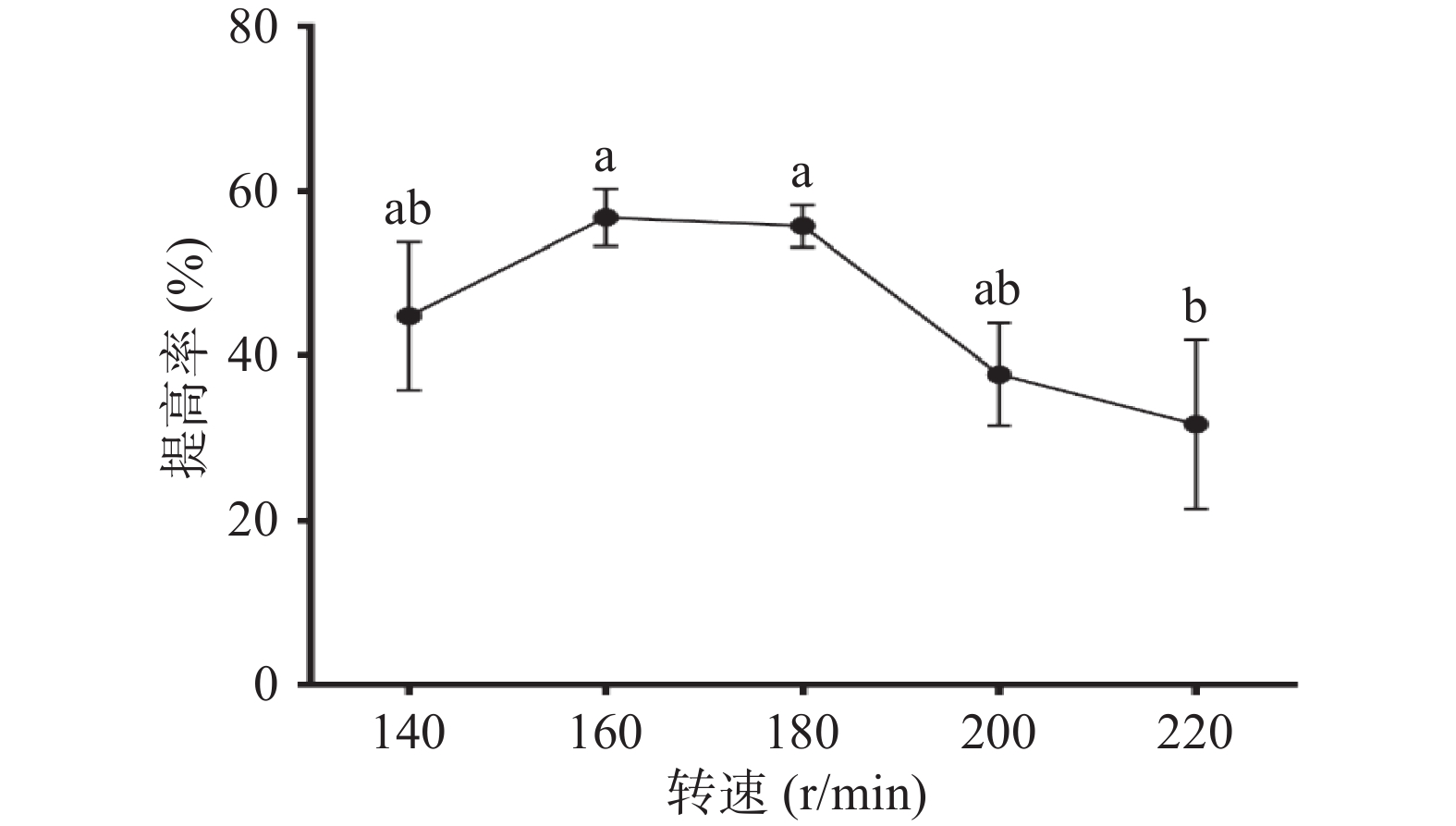
2.1.6 摇床转速对多糖提高率的影响
枯草芽孢杆菌为典型的好氧型细菌,培养基中溶解氧的量与菌体生殖存在密切关系。在摇瓶发酵培养中,摇床转速是溶解氧的调节方式之一。在装液量同样的条件下,转速过低,发酵瓶中溶解氧量低,菌体未能充分接触氧气,难以满足菌体的好氧呼吸。转速过高,代谢产物增加,产生泡沫,会抑制氧与液体的接触,也影响供养,因此转速过高过低都不利于菌体的增长。图6可以看出,转速为160 r/min时,体系中多糖提高率明显增高,达(56.72%±3.48%),当转速增加至180 r/min,提高率并无显著差异(P>0.05),随着转速继续增大,多糖提高率趋于降低。在生产过程中,出于成本考虑,应选择160 r/min进行发酵为宜。
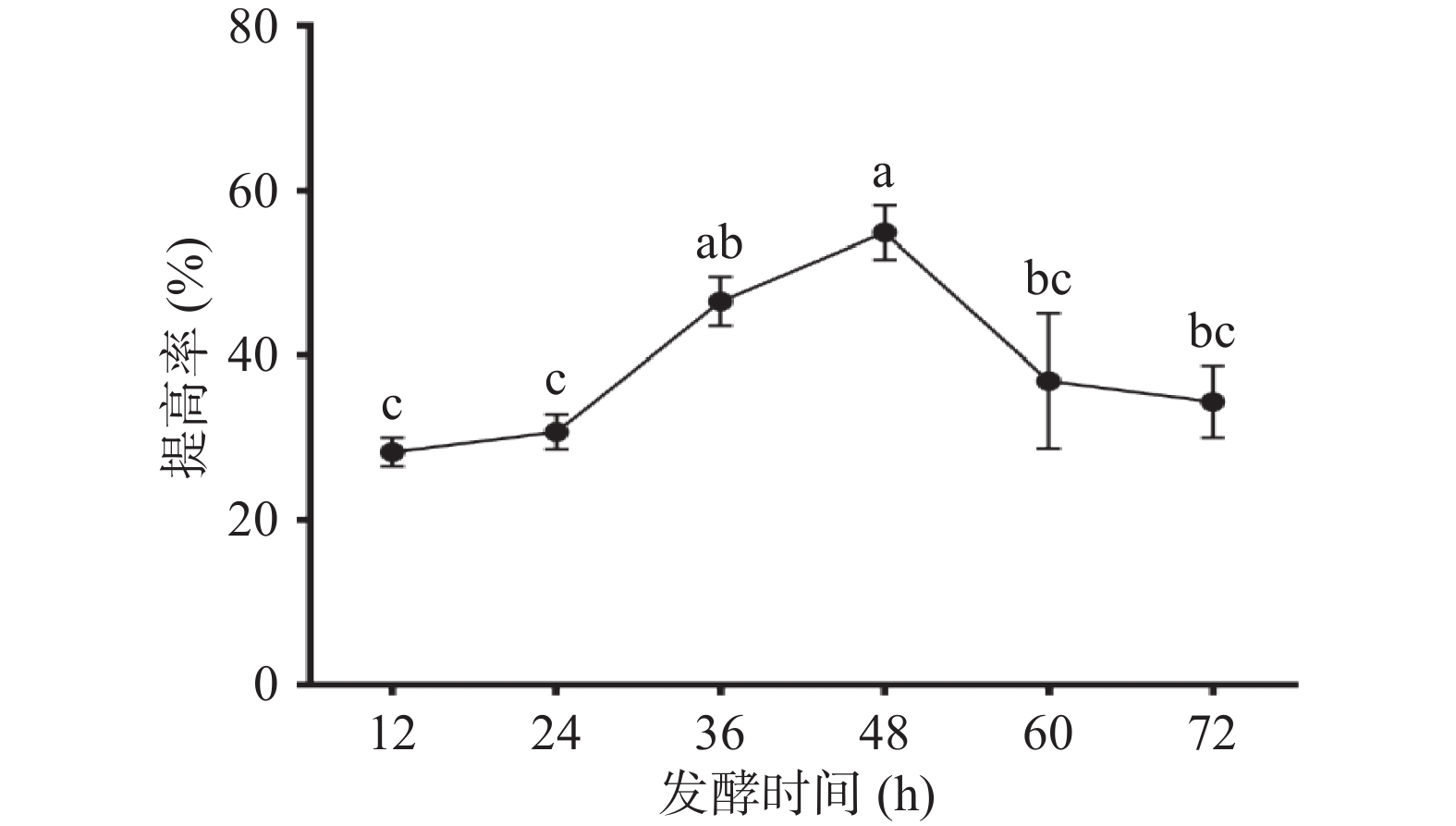
2.1.7 发酵时间对多糖提高率的影响
菌体的生长包括四个阶段,延滞期、对数期、稳定期及衰老期,一般来说,菌体生长达到稳定后便逐渐进入衰老阶段。如图7在接种量3%,温度35 ℃,转速160 r/min的条件下,发酵时间为48 h,多糖提高最多,随着发酵时间延长,多糖提高率下降,原因为多糖消耗速率大于生产速率,多糖产生其他代谢物,致使多糖产率降低。发酵48 h玉竹多糖提高率达到(54.87%±3.30%),说明48 h为枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵的最佳时间。
2.2 响应面试验结果
2.2.1 Box-Behnken试验设计及结果
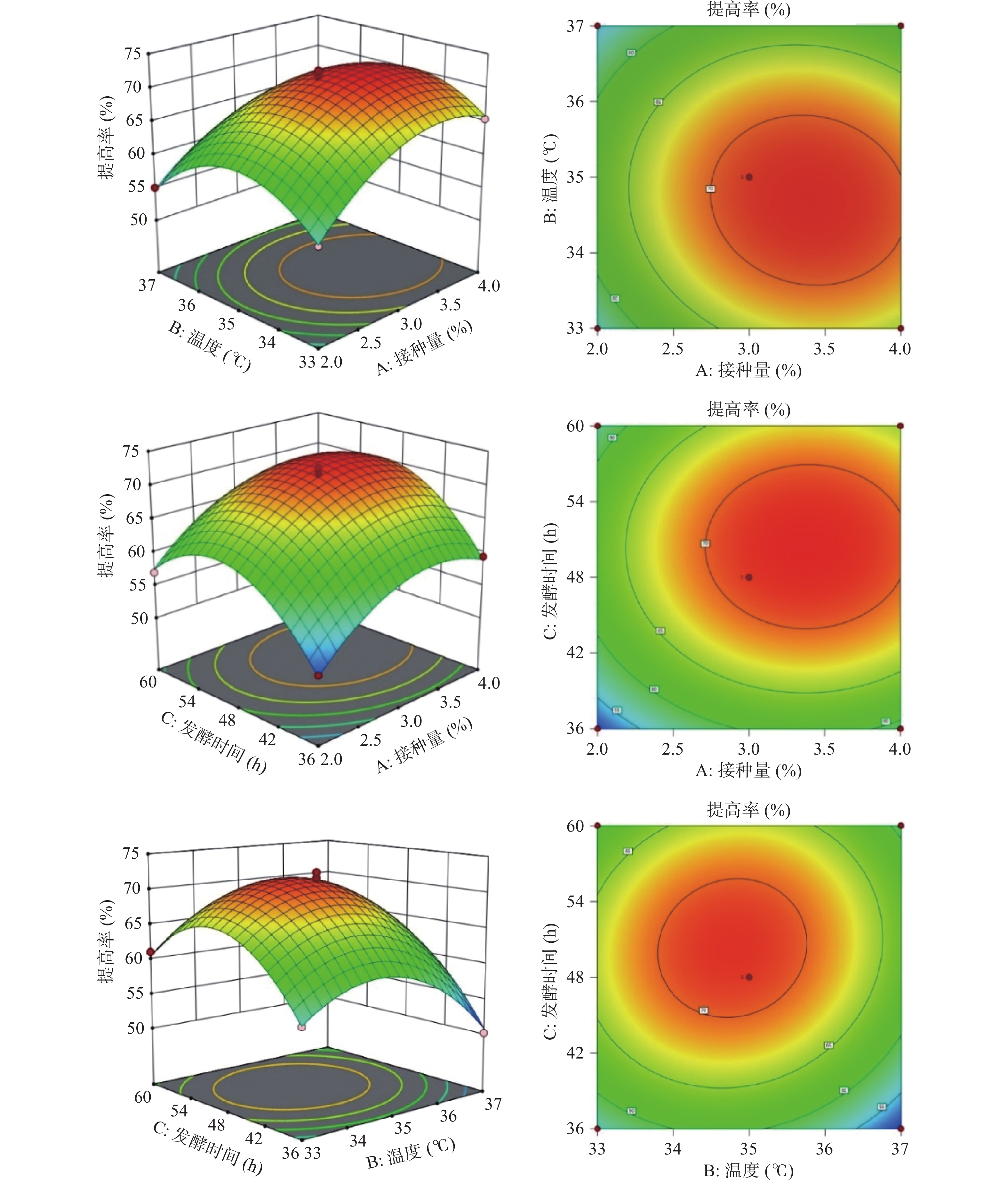
以接种量(A)、温度(B)、发酵时间(C)三个因素为自变量,多糖提高率(Y)为响应值,采用Design-Expert 12.0软件进行多元回归分析,得到回归模型方程:Y=71.23+3.8A−1.71B+3.12C−0.89AB+0.14AC+1.03BC−5.07A2−6.78B2−7.81C2,试验结果见表2。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计和结果Table 2. Design and results of Box-Behnken experimental试验号 A接种量 B温度 C发酵时间 Y提高率(%) 1 0 0 0 71.78 2 1 −1 0 65.48 3 1 0 1 65.21 4 −1 0 1 56.99 5 0 0 0 72.61 6 1 1 0 60.83 7 0 −1 −1 56.17 8 0 1 1 59.18 9 −1 0 −1 51.79 10 0 1 −1 50.14 11 0 0 0 69.32 12 −1 −1 0 56.16 13 0 −1 1 61.10 14 −1 1 0 55.07 15 1 0 −1 59.45 由表3可以看出,此模型的P值为0.0003<0.0001,模型差异性极显著,失拟项的P值为0.8845>0.05,差异不显著,说明该模型拟合程度较好,能够充分解释响应值的变异。决定系数R2为0.9884,预测值R2为0.9363,调整后R2为0.9676,均达到0.9以上,说明模型的可信度高,真实值与预测值之间具有高相关性,可以对多糖提高率进行预测和分析。表中显示,A(接种量)、B(温度)、C(发酵时间)对枯草芽孢杆菌发酵玉竹产多糖均存在影响,大小顺序为A>C>B,交互项AB、AC、BC不显著(P>0.05),二次项A2、B2、C2的P值均小于0.001,说明其对多糖提高率的影响达到显著水平。
表 3 回归模型显著性及方差分析表Table 3. Significance and variance analysis of regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 显著性 模型 655.93 9 72.88 47.48 0.0003 ** A 119.81 1 119.81 78.05 0.0003 ** B 23.46 1 23.46 15.28 0.0113 * C 77.70 1 77.70 50.62 0.0009 ** AB 3.17 1 3.17 2.07 0.2101 AC 0.075 1 0.075 0.049 0.8337 BC 4.22 1 4.22 2.75 0.1581 A2 94.85 1 94.85 61.79 0.0005 ** B2 169.77 1 169.77 110.60 0.0001 ** C2 225.11 1 225.11 146.65 < 0.0001 *** 残差 7.67 5 1.53 失拟项 1.82 3 0.61 0.21 0.8845 纯误差 5.85 2 2.93 总和 663.61 14 R2 0.9884 R2adj 0.9676 R2pre 0.9363 注:*表示显著差异(P<0.05),**表示较显著(P<0.001),***表示极显著(P<0.0001)。 2.2.2 各因素之间的交互作用结果分析
图8为接种量、温度、发酵时间对多糖提高率的影响程度三维曲面图,存在最优值。随着温度升高与接种量的增加,提高率增大,当二者交互作用达到峰值时,提高率逐渐下降;随着发酵时间和接种量的增加,提高率不断增大,达到最佳后,开始出现下降趋势;随着发酵时间和温度的变化,多糖提高率先上升后下降。
2.2.3 响应面结果优化及模型验证
数学模型预测最佳结果:接种量3.40%、温度34.73 ℃、发酵时间50.33 h,此时的多糖提高率达到72.42%。考虑到试验操作的可行性,对发酵工艺参数做出修正,为了验证模型的可靠性,将修正后的发酵工艺:玉竹添加量4%、酵母提取物3%,氯化钠1%,接种量3%、温度35 ℃、摇床转速160 r/min,发酵时间48 h进行重复3次试验,取平均值,多糖提高率为71.78%。实际值与理论值无显著性差异,表明该模型可靠,可用于枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹产多糖的预测。
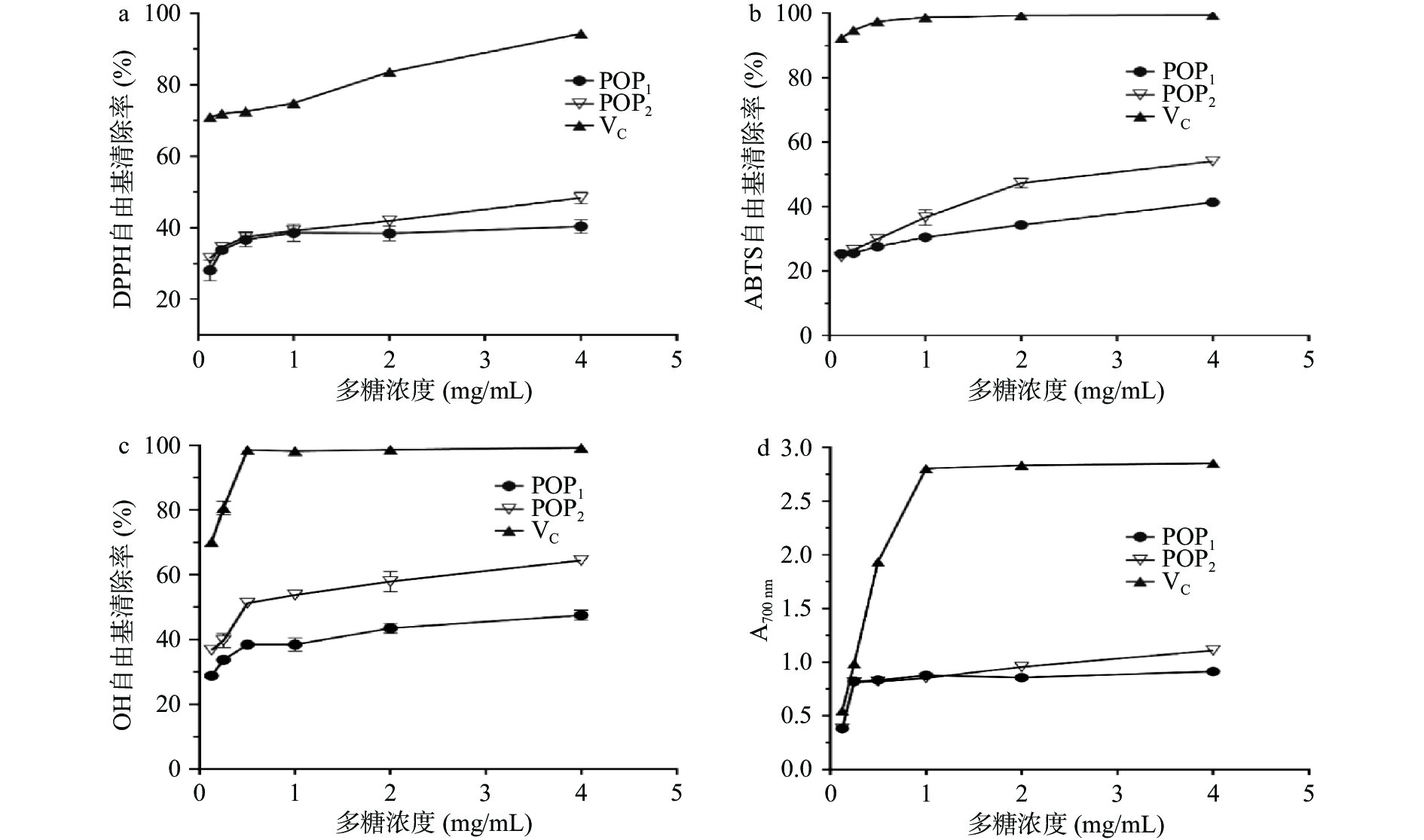
2.3 抗氧化测定
抗坏血酸(VC)具有较强的抗氧化活性,一般被用作抗氧化活性检测的对照品。本文以VC为阳性对照,对发酵与未发酵的两种玉竹多糖提取物进行抗氧化活性指标检测,结果如图9所示。两类多糖对DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、OH自由基均具有清除能力,随着多糖浓度升高,自由基清除率增大,清除率与多糖浓度存在依赖性。在4 mg/mL的多糖浓度下,自由基清除率最大。在相同的多糖浓度下,VC的自由基清除率最强,其次是POP2,最差是POP1。由图9可知,4 mg/mL POP1对DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、OH自由基清除率分别为(40.35%±1.87%)、(41.38%±1.16%)、(47.52%±1.60%),POP2对DPPH自由基、ABTS自由基、OH自由基清除率分别为(48.34%±1.66%)、(54.07%±0.9%)、(64.26%±0.91%)。总还原力的研究结果呈现相同的趋势,4 mg/mL POP1的OD700值为(0.91±0.01),POP2的OD700值为(1.11±0.00)。POP2对ABTS自由基清除的半抑制浓度(IC50)2.21 mg/mL,对OH自由基清除的半抑制浓度为0.49 mg/mL。数据结果显示,POP2的抗氧化能力明显强于POP1,存在差异的原因可能是,经枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05 发酵后的多糖组分POP2的组成、分子量或结构发生了变化,具体原因需要进一步验证。
3. 讨论
发酵菌株的选择是中草药发酵的关键,不同的发酵菌剂会产生不同的发酵效果,对于富含多糖的中药材,多糖含量是评价中草药发酵工艺优化的一个重要检测指标。薛文娟[22]用嗜酸链球菌CIC20364及植物乳杆菌CICC794发酵佛手,发现发酵后粗多糖含量降低了60%。与本试验的发酵结果相反,可能的原因是,培养基中多糖被益生菌利用消耗。而李嘉懿等[23]利用植物乳杆菌植物和副干酪乳杆菌混合发酵中草药(黄芪、三七、甘草、鹰嘴豆),发现发酵后复方中药液的多糖得率是优化前的1.65倍,是未发酵的2.51倍。刘洋等[24]用产朊假丝酵母、干酪乳杆菌及粪肠球菌固态发酵复方中草药(王不留行、益母草),发现经发酵后粗多糖含量提高了55.42%。与本文选用枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹,水溶性多糖提高71.78%的结果相似。这是因为微生物在发酵过程中产生胞外酶[25],如纤维素酶、果胶酶,可破坏中草药植物的细胞壁,促进胞内活性物质溶出。
微生物发酵受多种因素影响,如温度、转速、接种量、发酵时间等,本文通过单因素与响应面法对此发酵工艺优化,发现发酵温度为35 ℃,摇床转速为160 r/min,接种量3%,发酵时间为48 h时,发酵效果最佳,多糖含量提高了71.71%。众多研究表明,适宜的发酵条件会促进多糖析出。解淀粉芽孢杆菌发酵当归,优化发酵工艺后,当归多糖含量达到了发酵前的149.70%[26]。过多的接种量,导致菌株竞争生长,达到一定量,培养基中营养供应不足,出现饥饿生长,均不利于发酵。窦富超[27]用地衣芽孢杆菌SN02004-01发酵蛹虫草超微粉,发现在3%的接种量,发酵液中多糖含量最高。发酵时间太长,代谢废物的积累对发酵带来负面影响。郭舒等[28]、武洪志等[29]均用枯草芽孢杆菌发酵中草药等研究中,发酵时间为48 h时,多糖含量均显著提高。发酵温度与转速也是影响发酵的重要因素,与发酵菌株的生长密切相连,孔利华等[30]在优化饲用枯草芽孢杆菌JY24发酵条件时,温度为35 ℃下,发酵效果最佳。可见,不同的发酵条件对多糖的提取率大不相同,适宜的发酵条件对微生物发酵至关重要。
多糖在免疫调节、抗炎、抗肿瘤和抗氧化、抗衰老等特性方面表现出广泛的生物活性[31]。自由基的清除能力对其抗氧化活性有着积极的影响[32],各类文献中报道了不同来源的多糖显示出不同的抗氧化能力,这可能与多糖的化学组成及分子结构特性有关[33-34]。薛燕[35]在探究发酵前后铁皮石斛多糖的抗氧化活性的研究中,发现发酵后总抗氧化能力、DPPH及ABTS自由基能力均有所提高,且发酵后多糖的分子量下降。罗游[36]研究了发酵前后番石榴叶,结果发现发酵后多糖得率提高,抗氧化性增强,但分子量从697.61 kDa 下降至 633.28 kDa。本文测定发酵与未发酵玉竹多糖的抗氧化活性,发现两类多糖均表现出一定的抗氧化能力,且POP2的抗氧化性强于POP1,与上述研究结果一致,由此可推测,益生菌发酵中草药促进胞内多种物质溶出,经发酵后多糖的分子量或组成结构发生改变。需后续进一步的研究来证明。
益生菌与中草药结合是现代医学的创新点,为中草药及其功能性产品的研发开辟新思路。目前,有关中药玉竹的研究尚少,本试验采取益生菌发酵法来提高玉竹多糖的产率,该类方法条件温和,操作简便,效果显著,具有广阔的应用前景。本研究中所涉及的原料配方仍存在一定的局限性,在生产过程中可作进一步优化或调整,从而达到更高的发酵水平和降低成本的目的。
4. 结论
试验表明,枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹能有效提高玉竹多糖的含量,最终确定优化发酵工艺条件为:玉竹添加量4%、酵母提取粉3%,NaCl 1%,接种量3%、温度35 ℃、摇床转速160 r/min,发酵时间48 h。优化发酵工艺对玉竹开发利用具有一定参考价值;抗氧化试验结果表明,经枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵后,玉竹多糖的自由基清除率及总还原力均有所提高。
-
图 1 玉竹添加量对多糖提高率的影响
注:不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。
Figure 1. Effects of Polygonatum odoratum addition on increasing rate of polysaccharides
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface experiment
因素水平 −1 0 1 接种量(%) A 2 3 4 温度(℃) B 33 35 37 发酵时间(h) C 36 48 60 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计和结果
Table 2 Design and results of Box-Behnken experimental
试验号 A接种量 B温度 C发酵时间 Y提高率(%) 1 0 0 0 71.78 2 1 −1 0 65.48 3 1 0 1 65.21 4 −1 0 1 56.99 5 0 0 0 72.61 6 1 1 0 60.83 7 0 −1 −1 56.17 8 0 1 1 59.18 9 −1 0 −1 51.79 10 0 1 −1 50.14 11 0 0 0 69.32 12 −1 −1 0 56.16 13 0 −1 1 61.10 14 −1 1 0 55.07 15 1 0 −1 59.45 表 3 回归模型显著性及方差分析表
Table 3 Significance and variance analysis of regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 显著性 模型 655.93 9 72.88 47.48 0.0003 ** A 119.81 1 119.81 78.05 0.0003 ** B 23.46 1 23.46 15.28 0.0113 * C 77.70 1 77.70 50.62 0.0009 ** AB 3.17 1 3.17 2.07 0.2101 AC 0.075 1 0.075 0.049 0.8337 BC 4.22 1 4.22 2.75 0.1581 A2 94.85 1 94.85 61.79 0.0005 ** B2 169.77 1 169.77 110.60 0.0001 ** C2 225.11 1 225.11 146.65 < 0.0001 *** 残差 7.67 5 1.53 失拟项 1.82 3 0.61 0.21 0.8845 纯误差 5.85 2 2.93 总和 663.61 14 R2 0.9884 R2adj 0.9676 R2pre 0.9363 注:*表示显著差异(P<0.05),**表示较显著(P<0.001),***表示极显著(P<0.0001)。 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典 [M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015. National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[M]. Beijing: China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2015.
[2] 赵容, 许亮, 谢明, 等. 中药玉竹的本草考证[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23:227−234. [ZHAO R, XU L, XIE M, et al. Materia medica examination of the Chinese herb Polygonatum odoratum[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary,2017,23:227−234. [3] ZHAO P, ZHAO C C, XIA L, et al. The genus Polygonatum: A review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology: An Interdisciplinary Journal Devoted to Bioscientific Research on Indigenous Drugs,2018,214(25):274−291.
[4] CHEN Z, LIU J, KONG X, et al. Characterization and immunological activities of polysaccharides from Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2020,43(6):959−967.
[5] LI R, TAO A, YANG R, et al. Structural characterization, hypoglycemic effects and antidiabetic mechanism of a novel polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum Coll. et Hemsl[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,131:110687.
[6] 赖隽晖, 李秀霞. 药用植物玉竹药理作用研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2021(2):132−135. [LAI J H, LI X X. Research progress on the pharmacological effects of medicinal plant Polygonatum odoratum[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Science,2021(2):132−135. [7] WANG H Y, LI Q M, YU N J, et al. Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide regulates hepatic glucose homeostasis and pancreatic β-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,211:39−48. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.101
[8] YAN W, FEI Y, LIU L, et al. Polygonatum odoratum polysaccharides modulate gut microbiota and mitigate experimentally induced obesity in rats[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(11):3587. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113587
[9] 朱琪, 李庚喜, 曾立, 等. 玉竹多糖对高脂饮食诱导的大鼠肥胖和非酒精性脂肪肝的作用[J]. 中成药,2021,43(6):1612−1617. [ZHU Q, LI G X, ZENG L, et al. Effects of Polygonatum odoratum polysaccharide on high-fat diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine,2021,43(6):1612−1617. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.06.043 [10] 周骏, 惠晓亮, 毛滢, 等. 玉竹多糖对2型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢的影响及机制研究[J]. 中国现代应用学,2021,38(10):1181−1187. [ZHOU J, HUI X L, MAO Y, et al. Effects and mechanism of polysaccharide of Polygonatum odoratumon glucolipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Modern Applied Pharmacology,2021,38(10):1181−1187. [11] FILANNINO P, CAVOSKI I, THLIEN N, et al. Lactic acid fermentation of cactus cladodes(Opuntia ficusindica L.) generates flavonoid derivatives with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties[J]. PloS One,2016,11(3):e0152575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152575
[12] 郭云霞, 吴国江, 魏萌, 等. 响应面法优选N-14菌株发酵黄芪总多糖的工艺条件[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21:38−41. [GUO Y X, WU G J, WEI M, et al. Response surface methodology to optimize the process conditions for the fermentation of total polysaccharides of Astragalus membranaceus by strain N-14[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulation,2015,21:38−41. [13] 武洪志, 宋玉卓, 王志龙, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌发酵复方中草药工艺优化[J]. 中国饲料,2016(20):26−31. [WU H Z, SONG Y Z, WANG Z L, et al. Process optimization of Bacillus subtilis fermentation of compound Chinese herbal medicine[J]. China Feed,2016(20):26−31. [14] WANG G H, CHEN C Y, TSAI T H, et al. Evaluation of tyrosinase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of Angelica dahurica root extracts for four different probiotic bacteria fermentations[J]. Journal of Bioscience & Bioengineering,2017:679−684.
[15] 李暄. 发酵麸皮多糖提取, 分离纯化及生物活性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. LI X. Extraction, purification and bioactivity of fermented bran polysaccharides[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019.
[16] CAO C, LIU Y, LI Y, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant potential of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus velezensis SN-1 from spontaneously fermented Da-Jiang[J]. Glycoconjugate Journal,2020,37(2):1−11.
[17] 郎久义, 齐旭阳, 侯英雪, 等. 冬虫夏草液体发酵产胞外多糖的实验条件[J]. 大连工业大学学报,2009,28:107−107. [LANG J Y, QI X Y, HOU Y X, et al. Experimental conditions for the production of extracellular polysaccharides by liquid fermentation of Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology,2009,28:107−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1404.2009.02.008 [18] LIANG X X, GAO Y Y, PAN Y, et al. Purification, chemical characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides isolated from Mycena dendrobii[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,203:45−51.
[19] 柴美灵, 李娜, 乔宏萍, 等. Box-Behnken法优化甘草多糖提取工艺及其体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(23):192−200. [CHAI M L, LI N, QIAO H P, et al. Box-Behnken method to optimize the extraction process of licorice polysaccharide and its in vitro antioxidant activity[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(23):192−200. [20] 宗鑫妍, 徐德昌, 聂少平, 等. 玉竹多糖分离纯化、理化性质及抗氧化功能[J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版),2019,43(1):70−75. [ZONG X Y, XU D C, NIE S P, et al. Isolation and purification, physicochemical properties and antioxidant functions of polysaccharides from Polygonatum odoratum[J]. Journal of Nanchang University(Science Edition),2019,43(1):70−75. [21] ZONG X, XU D C, NIE S, et al. Isolation, purification, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Polygonatum odoratum[J]. Journal of Nanchang University(Natural Science), 2019.
[22] 薛文娟. 佛手益生菌发酵工艺优化和发酵产物分析[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学, 2018. XUE W J. Optimization of probiotic fermentation process and analysis of fermentation products of Fructobacillus foetida[D]. Shanghai : Shanghai University of Applied Technology, 2018.
[23] 李嘉懿, 张红星, 谢远红, 等. 益生菌发酵复方中草药产多糖的工艺优化[J]. 北京农学院学报,2018,33(3):83−87. [LI J Y, ZHANG H X, XIE Y H, et al. Process optimization of polysaccharide production by probiotic fermentation of compound Chinese herbal medicines[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural College,2018,33(3):83−87. [24] 刘洋, 金顺义, 常娟, 等. 复合益生菌发酵中草药前后活性成分变化[J]. 安徽农业科学,2017,45(34):123−125. [LIU Y, JIN S Y, CHANG J, et al. Changes in active ingredients of compound probiotic bacteria before and after fermentation of Chinese herbal medicines[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science,2017,45(34):123−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.34.039 [25] MENG F, YANG W, CAO B. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus subtilis strain BY-3, a thermophilic and efficient cellulase-producing bacterium on untreated plant biomass[J]. Lett Appl Microbiol, 2014.
[26] 朱庆贺, 苗艳, 兰世捷, 等. 解淀粉芽胞杆菌固态发酵当归培养基的研究[J]. 中国兽药杂志,2021,55(4):44−50. [ZHU Q H, MIAO Y, LAN S J, et al. Study of solid-state fermentation of Angelica sinensis medium by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens[J]. China Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2021,55(4):44−50. [27] 窦富超. 地衣芽孢杆菌SN02004-01产胞外多糖发酵条件优化及降血糖活性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. DOU F C. Optimization of fermentation conditions and hypoglycemic activity of extracellular polysaccharides produced by Bacillus licheniformis SN02004-01[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020.
[28] 郭舒, 刁新平, 宋玉卓, 等. 复方中草药饲料添加剂发酵工艺的研究[J]. 饲料工业,2015,36:23−26. [GUO S, DIAO X P, SONG Y Z, et al. Study on the fermentation process of compound herbal feed additives[J]. Feed Industry,2015,36:23−26. [29] 武洪志, 王芳芳, 许灵敏, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌发酵金樱子的工艺优化[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2017,44(1):12−21. [WU H Z, WANG F F, XU L M, et al. Process optimization of Bacillus subtilis fermentation of chinaberry[J]. China Veterinary Animal Husbandry,2017,44(1):12−21. [30] 孔利华,高书锋,雷平,等. 饲用枯草芽孢杆菌JY24发酵条件的优化[J]. 贵州农业科学,2019,47:60−65. [KONG L H, GAO S F, LEI P, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions of bacillus subtilis JY24[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2019,47:60−65. [31] YUN C, YAO F, KE M, et al. Polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicines: Extraction, purification, modification, and biological activity[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(12).
[32] ALKANI H. A review on free radicals and antioxidants[J]. Infectious Disorders-Drug Targets(Formerly Current Drug Targets-Infectious Disorders),2020,20(1):16−26.
[33] WU Y T, HUO Y F, XU L, et al. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Porphyra haitanensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,165(16):2116−2125.
[34] LIU C, CUI Y, PI F W, et al. Extraction, purification, structural characteristics, biological activities and pharmacological applications of Acemannan, a polysaccharide from Aloe vera: A review[J]. Molecules(Basel, Switzerland), 2019.
[35] 薛燕, 李丽, 刘光荣, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖液态发酵工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(9):155−159. [XUE Y, LI L, LIU G R, et al. Study on the liquid fermentation process of Dendrobium ferruginum polysaccharide and its antioxidant activity[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2017,38(9):155−159. [36] 罗游. 番石榴叶多糖活性分析及分离鉴定与发酵提升[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. LUO Y. Analysis of guava leaf polysaccharide activity and isolation, identification and fermentation enhancement[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 杨悦,刘梦圆,肖文军. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与L-茶氨酸对乙醇脱氢酶和乙醛脱氢酶活性的体外协同作用. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(04): 260-265 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁树洽,谢昕雅,刘助生,廖贤军,刘仲华,蔡淑娴. 茶叶成分EGCG与L-theanine联合应用的神经保护作用研究. 茶叶科学. 2024(05): 779-792 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韦柳花,赖兆荣,邓慧群,罗小梅,邱勇娟,诸葛天秋,黄金丽. 茶树良种紫鹃不同茶类适制性研究. 农业与技术. 2023(12): 4-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 薛璐,邢宇航,段志豪,陈绵鸿,周伟,李如一,李积华. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与燕麦β-葡聚糖复合物的形成及表征. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 124-132 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 吴颖,曲爱丽,纪荣全,王程安. 高花青素柏塘紫芽茶适制性的研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(12): 3875-3883 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 程倩,冯雪萍,陈昭,李春阳,张雪,张海波. 高效液相色谱法测定复合果汁饮品中茶氨酸的含量. 食品安全导刊. 2022(24): 87-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载:

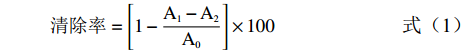
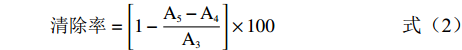
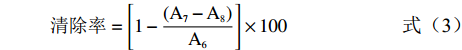

 下载:
下载:



