Cloning and Expression Analysis of PacC from Penicillium italicum of Citrus Fruits Postharvest Pathogen
-
摘要: 为初步分析柑橘采后病原菌意大利青霉(Penicillium italicum)pH信号传导途径中转录因子PacC的功能特性,克隆了PacC基因并对其进行生物信息学和表达模式分析。结果表明:PacC基因全长1921 bp,有1个内含子,编码蛋白质的氨基酸数量为636个,共包含3个转录因子典型的锌指蛋白结构域。进化树分析显示,PacC与指状青霉(Penicillium digitatum)和产黄青霉(Penicillium chrysogenum)亲缘关系较近。离体培养条件下PacC在意大利青霉生长中稳定表达;培养基pH影响意大利青霉生长与PacC表达,酸性条件下表达量显著下调(P<0.05),碱性条件下表达量显著上调(P<0.05);碳源条件影响该基因表达,葡萄糖饥饿和回补均显著提高PacC表达(P<0.05);低浓度蔗糖引起培养液pH碱化,显著刺激PacC表达(P<0.05),高浓度蔗糖引起培养液pH酸化,PacC表达逐渐下调(P<0.05)。活体结果表明,不同品种柑橘果实接种意大利青霉会导致果皮pH下降;接种初始pH影响意大利青霉的致病力,PacC在侵染柑橘果实期间表达较为稳定。这些结果表明,环境pH和碳源供应均能影响意大利青霉PacC表达,影响意大利青霉的致病性。Abstract: In order to analyze the function of PacC, a pH-signaling transcription factor of Penicillium italicum, which was a postharvest pathogen of citrus fruits. The gene had 1921 bp cDNA and an intron, which encoded 636 amino acids and contains three typical zinc finger domains of transcription factors. Phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the PacC was clustered with Penicillium digitatum and Penicillium chrysogenum. In vitro test, the PacC gene was stably expressed during the growth of P.italicum. The pH of the medium affected the growth of P.italicum and the expression level of PacC, and the expression level was significantly down-regulated under acidic conditions(P<0.05), but significantly up-regulated under alkaline conditions(P<0.05). Carbon source conditions affected the expression of PacC. The expression of PacC was significantly increased by glucose starvation and supplementation(P<0.05). The pH alkalization of the medium was caused by low concentration sucrose, which significantly stimulated the expression of PacC(P<0.05), while the pH acidification of the medium was caused by high concentration sucrose, which gradually decreased the expression of PacC(P<0.05). In vivo test, the inoculation of different citrus varieties with P.italicum would lead to the decrease of citrus peel, and the initial pH of inoculation had an important effect on the pathogenicity of P.italicum. The PacC gene was stably expressed throughout the infection process of P.italicum on citrus. These results indicated that both environmental pH and carbon source could affect the expression of PacC and the pathogenicity of P.italicum.
-
由意大利青霉(Penicillium italicum)和指状青霉(Penicillium digitatum)引起的青绿霉病害,通常造成柑橘采后总损失的90%[1]。意大利青霉较耐低温[2],因此在低温贮藏期间更易发病,由意大利青霉引发的青霉病害在全世界可造成柑橘采后损失的10%~30%[3-4]。化学杀菌剂是预防和控制采后柑橘病害的常用方法[5],近年来,随着人们对化学农药的日益关注,以及大量使用化学农药会导致病原菌的抗药性显著增强[6],引发食品安全和环境污染的风险,生产上需要安全有效的替代病害控制方法[7]。深入研究意大利青霉与柑橘果实在采后贮藏期间的相互作用对于防治青霉病具有重要意义[8]。
研究表明,环境pH会影响真菌的生长发育和代谢功能[9]。为了适应各种复杂严酷的生长环境,真菌存在一套响应和适应环境pH变化的机制[10-11]。目前已经对构巢曲霉(Aspergillus nidulans)、白色念珠菌(Candida albicans)和酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)中的pH响应机制进行了充分研究,此机制命名为PAL/RIM[12]。PAL/RIM已被确定由6个Pal蛋白PalA、PalB、PalC、PalF、PalH、PalI及关键转录因子PacC构成[13]。真菌在感受环境pH后,PAL/RIM通过信号传导,激活关键转录因子PacC,从而对环境pH做出响应[14]。
PacC被广泛报道在许多病原菌中起着正向调节作用。在核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)、炭疽菌(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)和指状青霉中[15],PacC缺失可以延缓病原菌的生长、降低病原菌的致病力以及减少次生代谢产物合成。在赭曲霉(Aspergillus ochraceus)中,PacC缺失对其生长、分生孢子形成和萌发、菌丝形态会产生影响[9]。PacC也被报道在尖孢镰刀菌(Fusarium oxysporum)[16]和禾谷镰刀菌(Fusarium graminearum)[17]致病力中起着负调节作用。表明PacC有一个复杂的调控网络来控制不同真菌病原体的致病力。关于PacC在意大利青霉中的具体功能未见报道。本试验克隆意大利青霉PacC基因,观察了PacC在酸碱处理、葡萄糖饥饿及回补、极限碳浓度诱导等条件下和致病过程中的表达规律,并研究了意大利青霉致病力与环境pH的关系,为进一步研究该基因在意大利青霉与柑橘果实互作中的调控作用奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
意大利青霉(Penicillium italicum)菌株P-5 从自然发病柑橘果实上分离,接种表现出典型的青霉病症状,经进一步鉴定后,PDA培养基中保存;PDA、PDB、LB培养基 实验室自制;脐橙、冰糖橙、皇帝柑等橙子 均购于湖北省武汉市洪山区华中农业大学农贸市场;胶回收试剂盒、质粒抽提试剂盒、真菌RNA抽提试剂盒 上海生工有限公司;荧光定量PCR试剂盒、DNA Marker、Ex Taq聚合酶、T4连接酶 宝生物工程(大连)有限公司;HiScript® II Q RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper)反转录试剂盒 南京诺唯赞生物科技有限公司。
qTOWER2.2实时定量PCR仪 德国耶拿分析仪器股份有限公司;Gel Doc XR+凝胶成像仪 美国伯乐Bio-Rad公司;SHZ-82A气浴恒温振荡箱 金坛市宏华仪器厂;YXQ-LS-18SI手提式压力蒸汽灭菌器 上海博讯实业有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 PacC基因的克隆
从GenBank上分别下载Penicillium digitatum(GenBank登录号:XP014537353.1)、Penicillium chrysogenum(GenBank登录号:NW003020078.1)、Aspergillus niger(GenBank登录号:AAA32690.1)和Penicillium decumbens(GenBank登录号:AGY46356.1)的PacC同源序列,并用DNAMAN软件进行多序列比对,获得PacC基因及其上、下游序列,将其分为A、B、C、D四段,每段之间设有重叠区域以确保结果可信度,使用Primer Preimer5软件设计引物,见表1。
表 1 PCR扩增所用引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences used for PCR amplification引物名称 引物序列 引物名称 引物序列 PacC-U-F
PacC-U-R
PacC-1-F
PacC-1-R
PacC-2-F
PacC-2-RTTCGGCTGGCTAAGCCAATG
AATACCGCTTTGCTAAGCCTGG
CGGTCTTGGTCTTCTGGT
CGGCATAGGAGTTAGGGTC
CCTATCAATGGCATCAACG
GACGGACCTTCTCAACCCPacC-D-F
PacC-D-R
Actin-F
Actin-R
Q-PacC-F
Q-PacC-RCCTGGGTTGAGAAGGTCC
ATGGCGTATGTTTGGGTG
CATTGAGCACGGTGTTGTCA
CTGGGTCATCTTCTCACGGT
CGCAAAAGCACCAACAACCT
CTTCAAATCCTGGGGACGCT用真菌RNA抽提试剂盒提取意大利青霉的RNA,以提取的RNA为模板用HiScript® II Q RT SuperMix for qPCR(+gDNA wiper)反转录试剂盒反转录得到cDNA,操作均参照试剂盒说明书,以合成的cDNA为模板,PacC-U-F/PacC-U-R、PacC-1-F/PacC-1-R、PacC-2-F/PacC-2-R、PacC-D-F/PacC-D-R(表1)为引物对A、B、C、D四个片段进行PCR扩增,并进行电泳检测。PCR扩增反应体系为:Ex Taq聚合酶0.1 μL,2.5 mmol/L dNTP Mixture 1.6 μL,10×PCR Buffer 2 μL,10 μmoL/L上下游引物各1 μL,cDNA 1 μL,双蒸水补足体积至10 μL。反应程序为:预变性94 ℃ 5 min;变性94 ℃ 30 s,退火56 ℃ 30 s,延伸72 ℃ 60 s/kb, 30个循环;保温72 ℃ 10 min。将扩增得到的四个片段进行纯化回收,送至上海生工生物技术公司进行测序。将测序结果使用软件Seqman进行拼接,得到意大利青霉的PacC基因及其上下游序列。
1.2.2 PacC基因的生物信息学分析
对PacC基因上游序列进行启动子区域和顺式调控元件预测(http://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/promoter.html;http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)。利用MEGA7.0软件进行PacC蛋白的系统进化树构建,并对其相关结构域进行预测(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/)。
1.2.3 PacC基因的定量表达分析
1.2.3.1 菌龄对意大利青霉生长过程中PacC基因表达的影响
参考范明等[18]的方法,取在PDA培养基上的意大利青霉孢子,制备1×106 CFU/mL孢子菌悬液,并涂布于含玻璃纸的PDA培养基上,于26 ℃培养,分别取培养2、4、6、8、10和12 d的菌丝,液氮速冻后−80 ℃备用。
1.2.3.2 酸碱处理对意大利青霉生长和PacC基因表达的影响
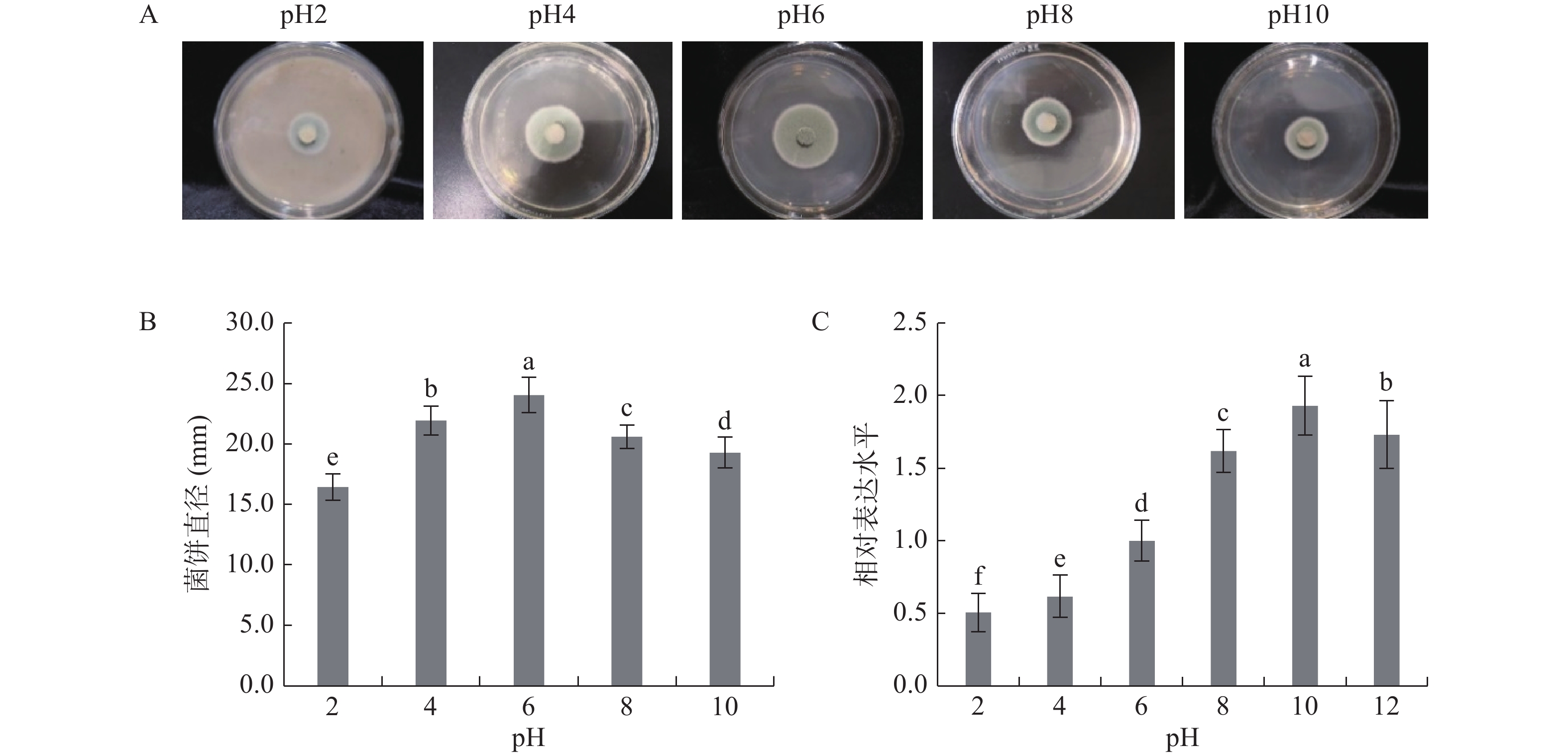
参考Yang等[19]的方法,略有修改。取200 µL孢子悬液均匀涂布于25 mL PDA培养基中,待长出白色的幼嫩的菌丝后,用1 cm的打孔器打取菌饼,反贴于含20 mL不同pH的PDA培养基的培养皿中,5 d后观察并通过十字交叉法测量菌落直径。
参考范明等[18]的方法,将孢子悬液于PDB培养基中,于26 ℃恒温摇床中120 r/min培养2 d,过滤收集菌丝。称取1.60 g湿菌丝,移至不同pH的PDB培养基中继续培养24 h。以pH6的PDB培养的菌丝作空白对照,收集菌丝,液氮速冻后-80 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3.3 葡萄糖饥饿和回补对意大利青霉PacC基因表达的影响
按照1.2.3.2的方法培养并收集菌丝,参考范明等[18]的方法,取8.00 g湿菌丝于500 mL锥形瓶中,加入300 mL 50 mmol/L KCl溶液,4 ℃饥饿24 h,收集菌丝液氮速冻后-80 ℃保存备用。取饥饿24 h的菌丝过滤并冲洗,取1.00 g湿菌丝重悬于20 mL 10%(w/v)葡萄糖溶液中进行回补,收集菌丝液氮速冻后−80 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3.4 蔗糖浓度对意大利青霉生长过程中的pH和PacC基因表达的影响
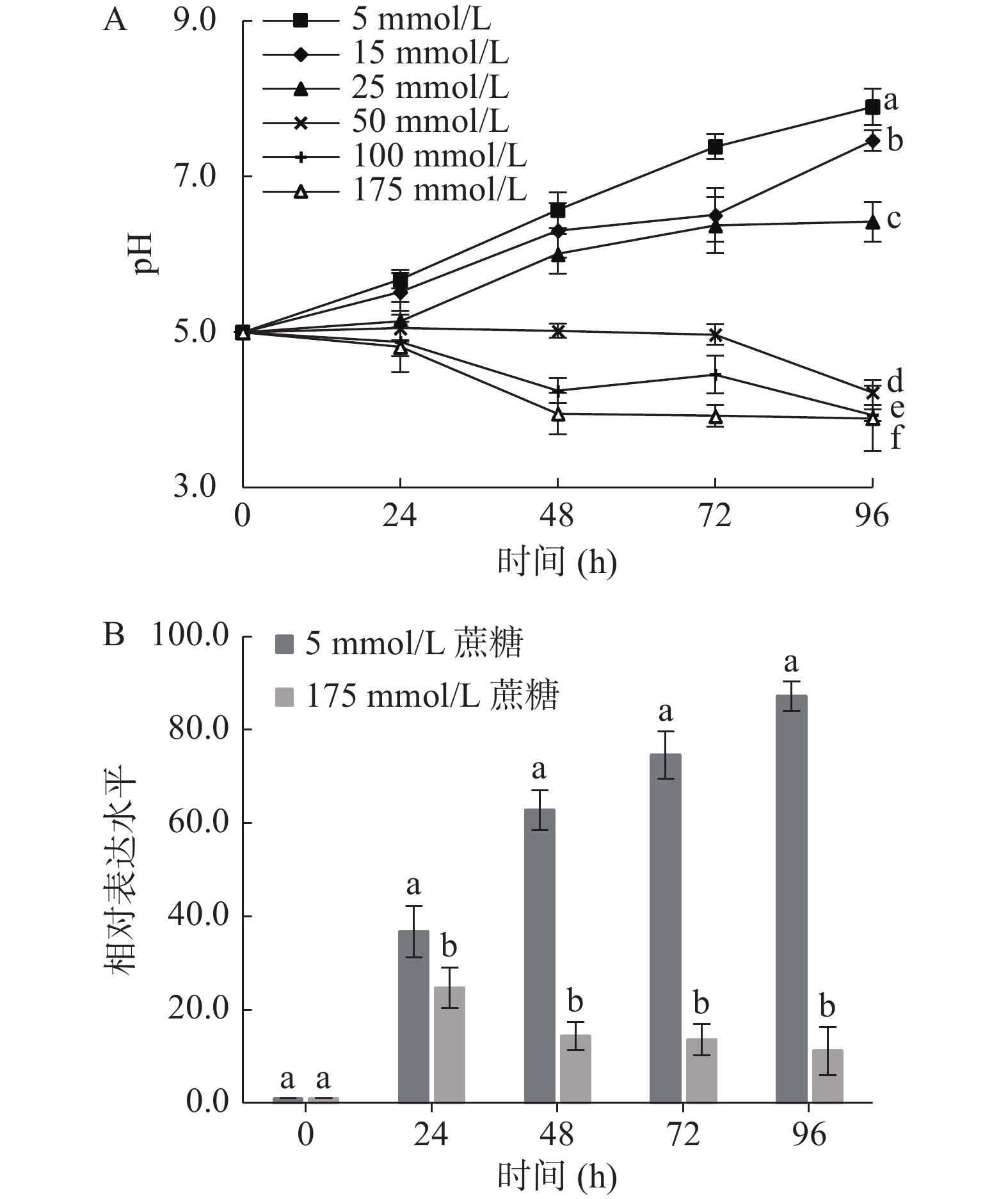
按照1.2.3.2的方法培养并收集菌丝,取2.00 g湿菌丝,分别置于蔗糖浓度为5、15、25、50、100、175 mmol/L的培养基中,继续在摇床振荡培养,每隔24 h吸取培养基上清液测量其pH。用于RNA提取的样品,液氮速冻后−80 ℃备用。
以意大利青霉肌动蛋白基因(β-Actin)作为内参基因,检测在不同条件下PacC基因在转录水平上的相对表达量。收集各时间段的菌丝,提取总RNA,反转录后通过qRT-PCR检测PacC的表达水平。qRT-PCR反应体系为:SYBR Green PCR Master Mix 5 μL,不同样本的cDNA 1 μL,上下游引物(β-Actin引物:Actin-F/R;PacC引物:Q-PacC-F/R,见表1)10 μmoL/L 1 μL,双蒸水补足体积至10 μL。反应程序为:预变性95 ℃ 30 s;变性95 ℃ 5 s,延伸60 ℃ 30 s,40个循环收集荧光信号。每个样品三次重复,采用2−∆∆Ct公式进行计算相关基因表达量。
1.2.4 环境pH与意大利青霉致病力的关系及侵染过程中PacC的表达分析
1.2.4.1 意大利青霉对不同柑橘品种果皮pH的影响
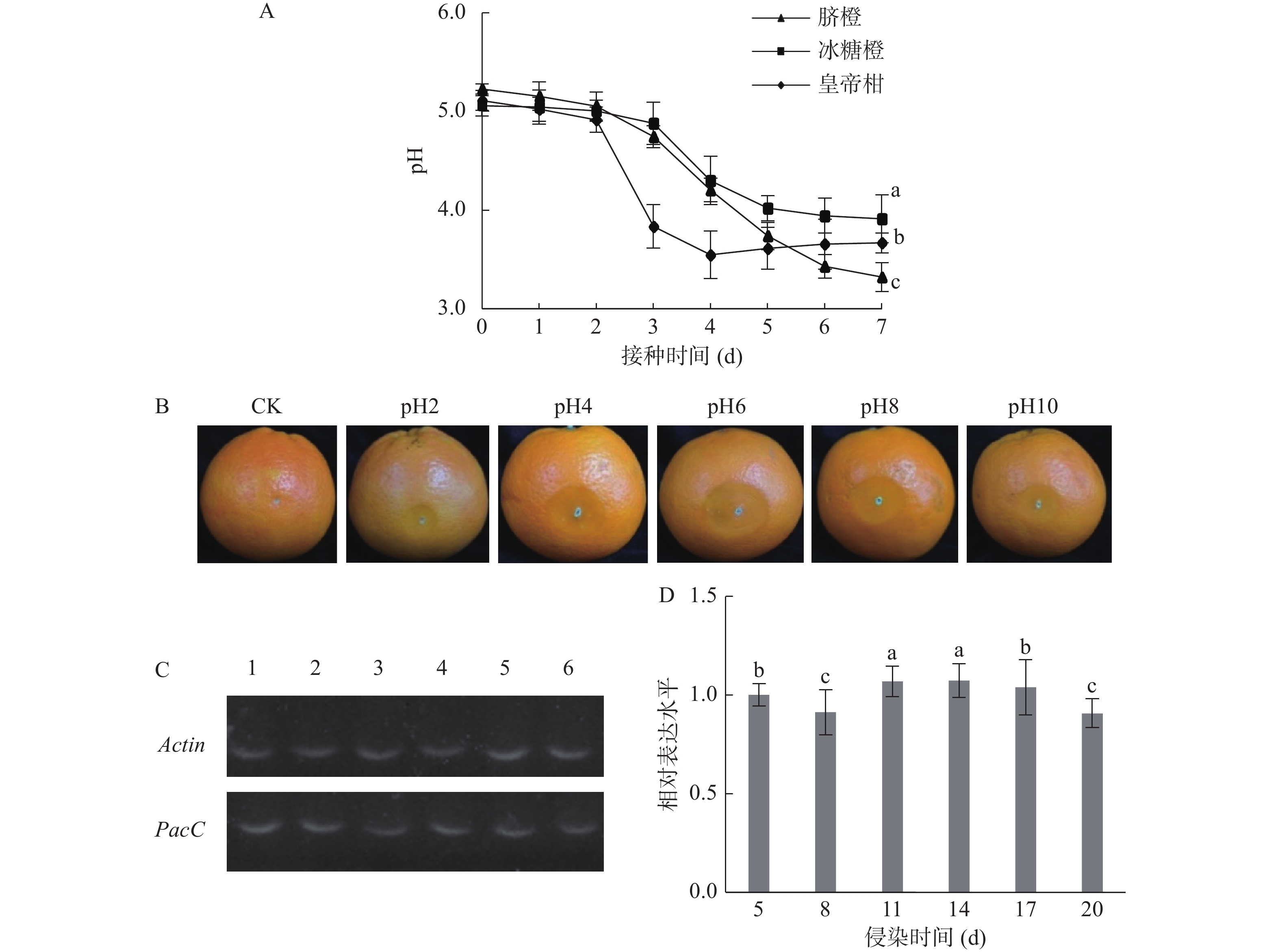
新鲜橙子在体积分数0.1%次氯酸钠溶液中浸泡2 min,蒸馏水冲洗2次晾干。用针刺在果实表面扎出深度为0.2 cm左右的孔。接种10 µL 106 CFU/mL孢悬于伤口处,26 ℃放置。每隔24 h拿出3个品种的果实,无菌刀片取样,无菌研磨机研磨,12000×g离心5 min,吸取上清液,测果皮的pH。
1.2.4.2 环境pH对意大利青霉致病力的影响
配制不同pH的溶液,然后接种青霉至不同pH的溶液之中,配成1×106 CFU/mL的孢悬。按上述条件处理脐橙并接种,以无菌水做对照,每天观察,并隔24 h补加一次之前加的菌液。
1.2.4.3 侵染过程中PacC的定量表达分析
按照王萌等[8]的方法,新鲜橙子在0.1%次氯酸钠溶液中浸泡2 min,并用蒸馏水冲洗。在果实腰部造伤,深度约3 mm。将意大利青霉菌丝饼反贴至果实伤口处,然后放置于26 ℃下,分别于5、8、11、14、17、20 d收集病部组织,并抽提RNA,反转录得到cDNA。以cDNA为模板,利用意大利青霉β-Actin和PacC引物进行半定量PCR,循环数设置为26,确保扩增处于对数期(β-Actin引物:Actin-F/R;PacC引物:Q-PacC-F/R,见表1)。PCR反应程序为:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s;56 ℃ 30 s;72 ℃ 10 s;72 ℃ 5 min。对不同样品cDNA分别扩增β-Actin和PacC,PCR扩增产物在含有溴化乙锭的10 g/L琼脂糖凝胶中电泳,并进行拍照。
1.3 数据处理
用Excel软件进行数据处理和作图,所有数据均为3次重复所得,分析采用SPSS 23软件对试验数据进行单因素方差分析,应用最小显著差数(LSD)法检验差异显著性(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 PacC基因的克隆及生物信息学分析
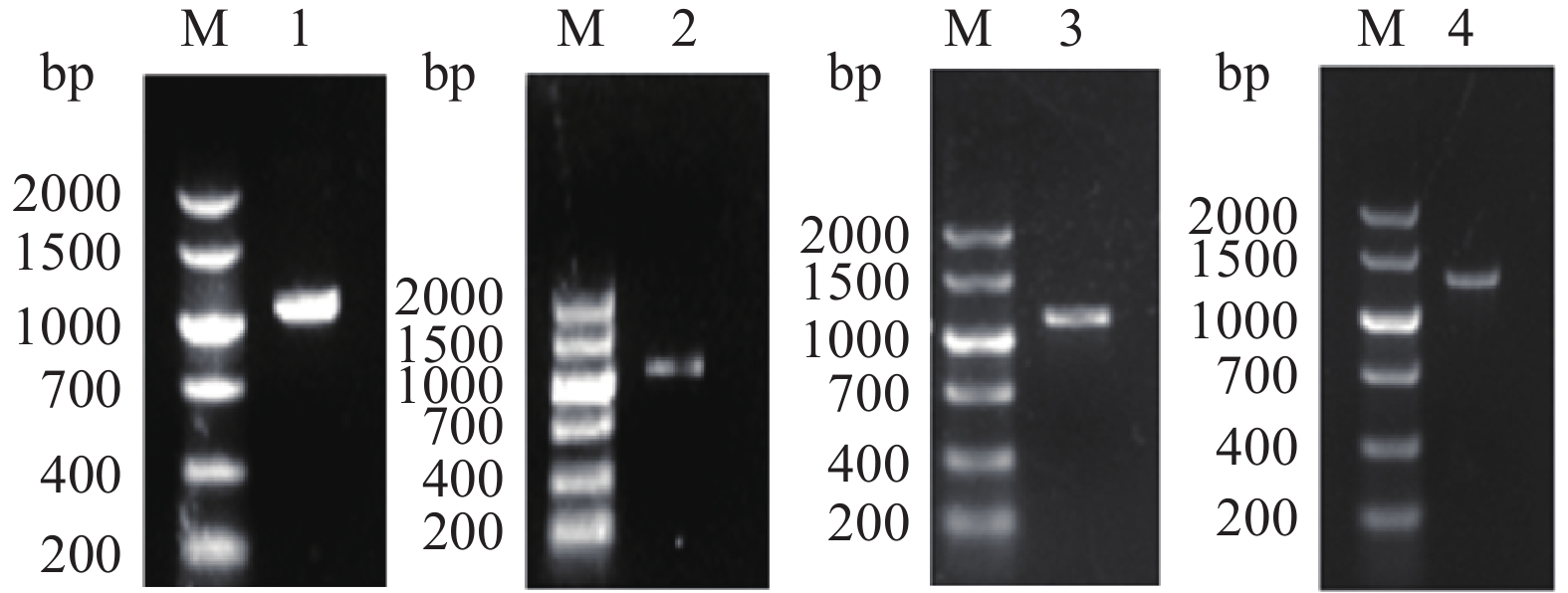
利用引物对以意大利青霉cDNA为模板,将PacC及侧翼序列分成A、B、C、D四个片段进行扩增,片段之间有重叠区域,扩增后经电泳进行验证,将目的条带割胶回收并克隆测序(图1)。将测序结果用软件Seqman进行拼接,得到PacC基因完整序列及其上下游部分序列信息。
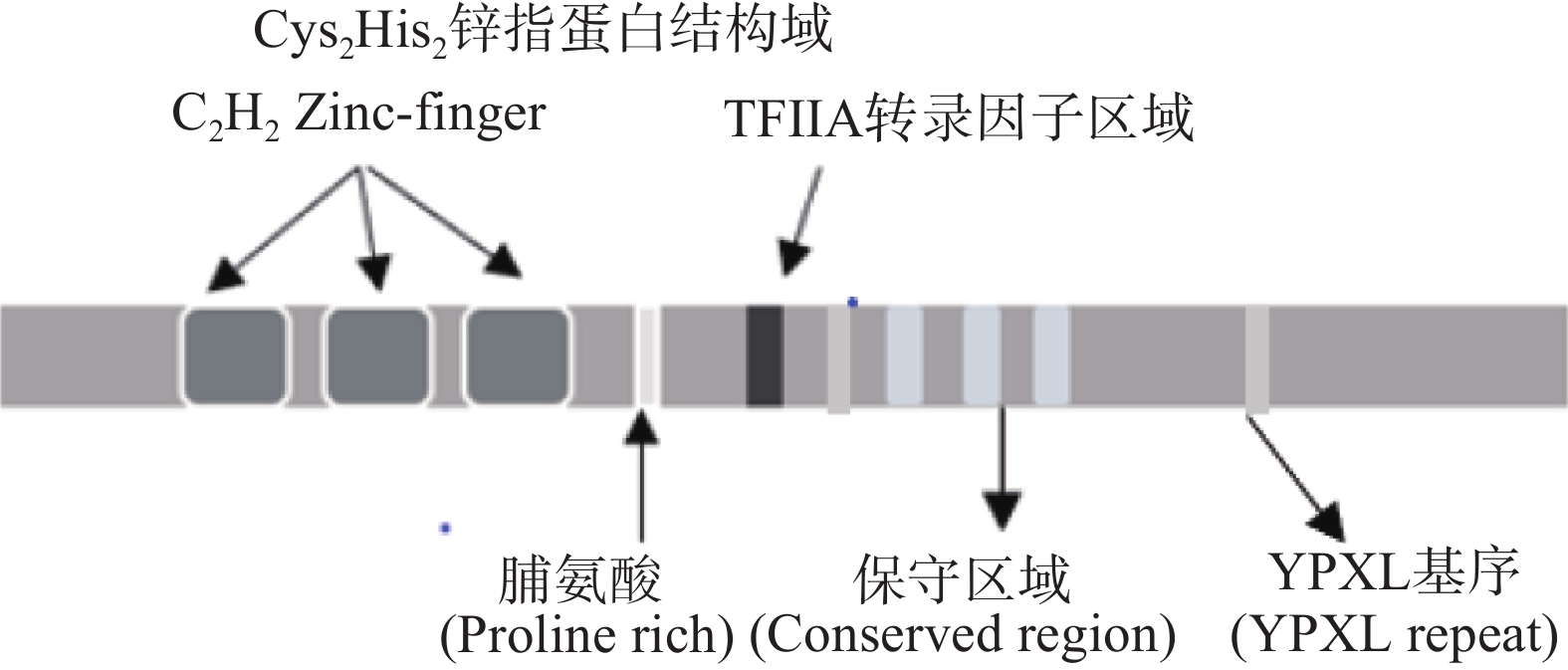
意大利青霉基因组中只有单一的PacC基因,PacC基因序列和cDNA开放阅读框(open reading frame,ORF)的大小为1921 bp,且编码蛋白质的氨基酸数量为636个。如图2所示,预测PacC含有3个保守的Cys2His2锌指蛋白结构域,在87~305氨基酸之间有1个富含脯氨酸(PPPPPPP)的区域,2个PacC典型的YPXL基序,3个高度保守的区域,在192~400氨基酸之间有一个TFIIA转录因子的区域,它可以结合到启动子区域,是基因表达所必需的通用转录起始因子。
根据测序获得的PacC基因序列,发现PacC上游序列片段大小为1201 bp,然后使用BDGP网址在线预测PacC基因的核心启动子,预测结果显示该启动子可能位于PacC基因上游101~801 bp,并在基因上游序列可能含有3个PacC的DNA结合位点5′-GCCARG-3′,表明PacC在不同条件通过积极调控自身的表达来适应各种环境条件。同时,对部分顺式调控元件进行分析,发现在该基因上游序列中,存在核心启动子元件TATA-box、增强子元件CAAT-box,从而增强基因转录的效率(图3)。
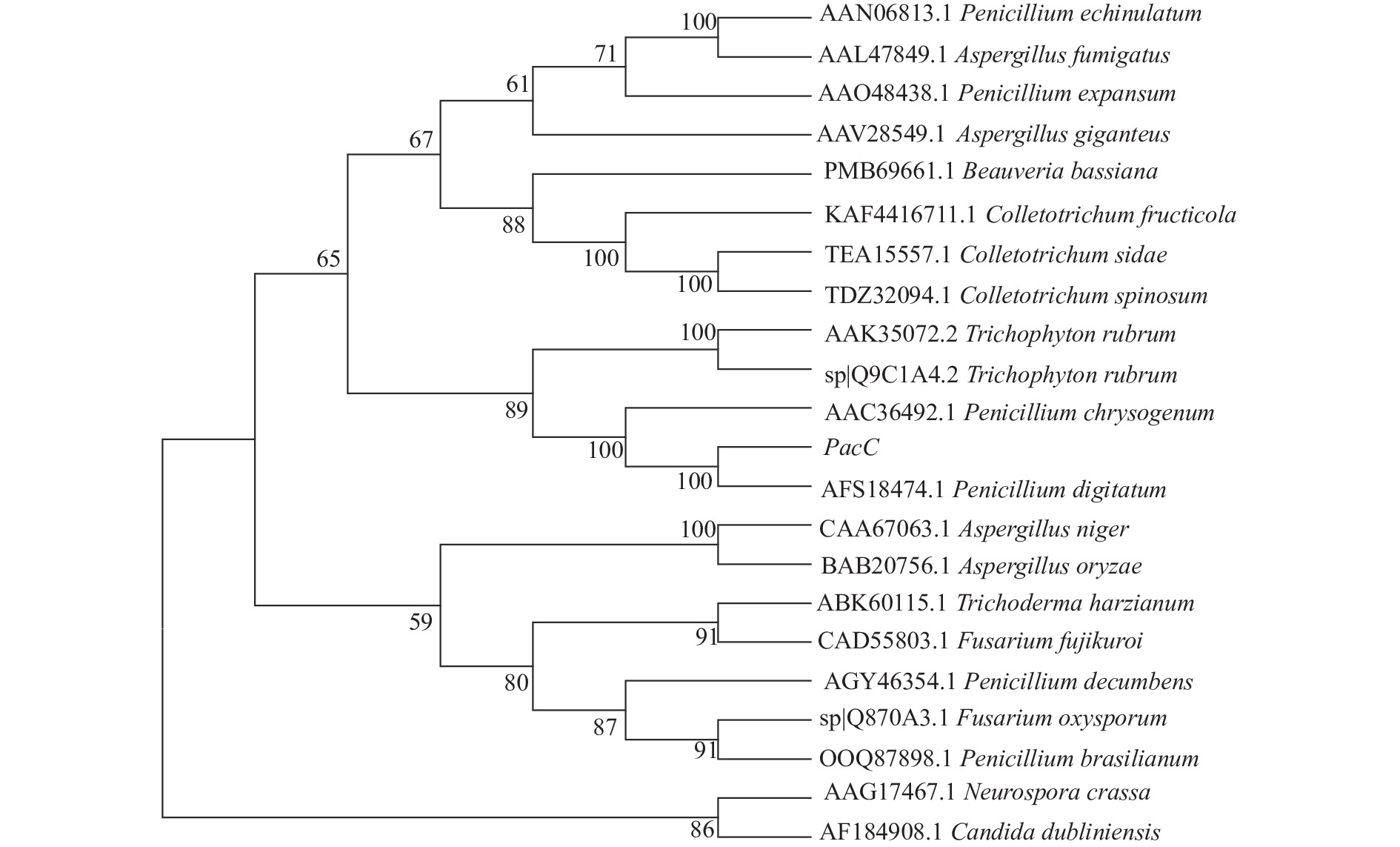
将PacC序列进行蛋白比对,对比结果发现,意大利青霉PacC与指状青霉(Penicillium digitatum)和产黄青霉(Penicillium chrysogenum)的PacC的同源性较高,其相似度达到87.1%以上。采用邻接法构建系统进化树,发现意大利青霉PacC与指状青霉和产黄青霉亲缘关系近,与白色念珠菌、尖孢镰刀菌亲缘关系远(图4)。
2.2 PacC定量表达分析
2.2.1 生长过程中PacC基因的表达分析
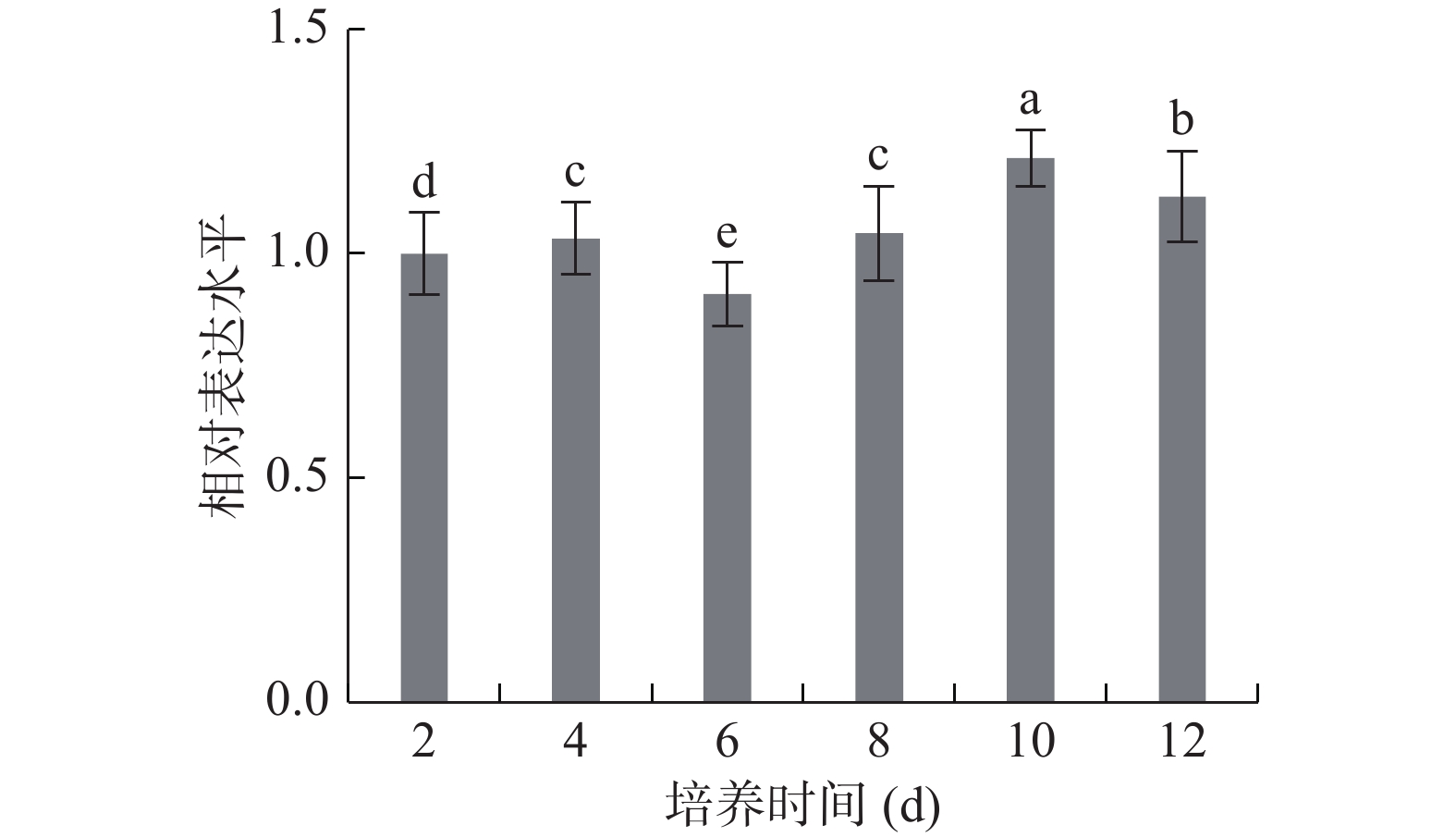
对培养不同时间的意大利青霉PacC表达量进行了分析表明,PacC在意大利青霉生长前期(2和4 d)、中期(6和8 d)、后期(10和12 d)表达量变化较为平缓且维持在较高表达水平(1.0左右)。推测在意大利青霉生长过程中,PacC维持意大利青霉生长所需的pH,从而维持意大利青霉生长所需的酸碱平衡(图5)。
2.2.2 不同条件下PacC基因的表达分析
2.2.2.1 酸碱处理对PacC基因表达的影响
在菌丝生长过程中,对照组(pH6)的菌饼直径均高于其他pH条件下的菌饼直径,且弱碱条件(pH8)对意大利青霉菌丝生长的抑制高于弱酸条件(pH4),表明环境pH对意大利青霉菌丝生长有显著影响(P<0.05),碱性条件更能显著抑制意大利青霉的生长(图6A~图6B,P<0.05)。进一步对环境pH调控因子PacC基因的表达进行分析,发现PacC基因表达量在酸性条件下显著下调(P<0.05),在碱性条件下显著增加(P<0.05),表明PacC的表达依赖于环境pH,且PacC是一个碱性诱导基因(图6C)。
2.2.2.2 葡萄糖饥饿和回补对PacC基因表达的影响
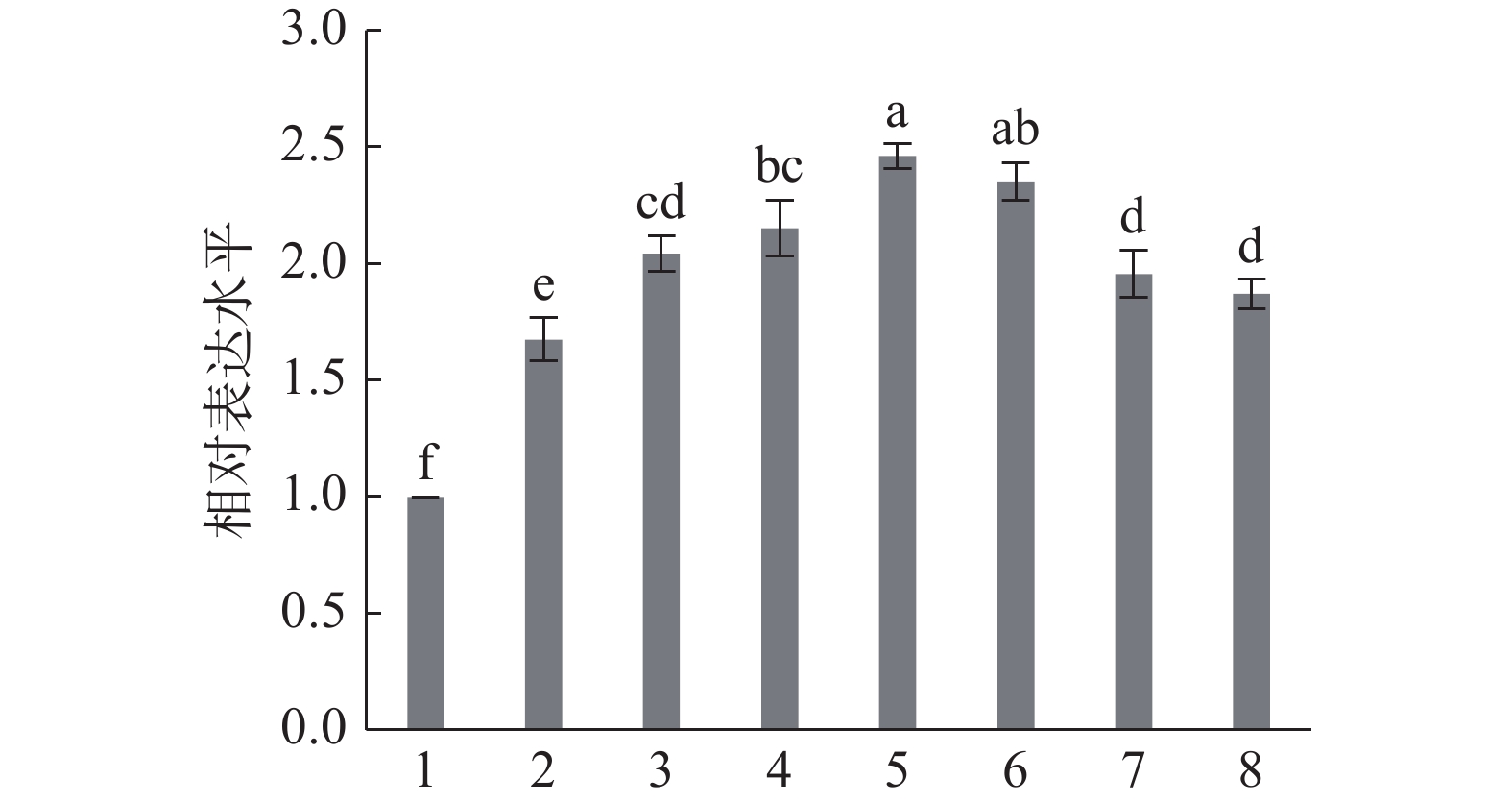
研究表明,糖代谢信号传导途径可能影响PacC表达。Louw等[20]研究发现由于成熟度不同的果实中糖的种类和含量不同,病原菌对成熟度不同的果实侵染时感染部位pH有所差异,从而通过分泌小分子调节环境pH,这导致致病因子PacC上调。将意大利青霉菌丝进行葡萄糖饥饿及回补处理发现,葡萄糖回补会使PacC基因的表达量显著上调(P<0.05),且在回补30 min时PacC基因量上调为2.46,达到峰值,这表明碳源(葡萄糖)通过分泌小分子会诱导意大利青霉PacC的表达(图7)。
2.2.2.3 蔗糖浓度对意大利青霉生长过程中的pH及PacC表达的影响
为了进一步明确碳源对PacC表达的影响,以蔗糖(水果中的主要糖)为主要碳源,分析蔗糖浓度对意大利青霉生长过程中的pH调节模式的影响,结果发现(图8A):在不同蔗糖浓度下,意大利青霉调节pH的模式不同。低蔗糖浓度下,意大利青霉引起pH上升;高蔗糖浓度下,意大利青霉导致培养环境酸化,如在5 mmol/L蔗糖条件下培养96 h后,培养基pH上升到7.89;而在175 mmol/L蔗糖条件下,培养基pH下降为3.88。进而分析两种极端碳浓度下意大利青霉培养不同时间PacC基因的表达,结果显示(图8B):在5 mmol/L蔗糖下,随培养时间延长和培养基逐步碱化,PacC的相对表达显著提高了87.2倍(P<0.05);在175 mmol/L蔗糖下,意大利青霉PacC的表达诱导作用较小。
2.3 环境pH与意大利青霉致病力的关系及侵染过程中PacC的表达分析
不同品种的柑橘果实,接种处果皮pH均呈下降趋势,但果实发病部位pH的变化因品种不同有所差异,皇帝柑的pH下降最快,冰糖橙的pH下降偏慢(图9A)。这表明,意大利青霉侵染促使柑橘果皮pH下降。将不同pH下的意大利青霉孢子悬液接种脐橙,10 d后发现强酸强碱环境下(pH2和pH10)意大利青霉的致病力明显弱于其他pH环境。pH6时意大利青霉的致病力最强且明显高于在弱酸弱碱环境中(pH4和pH8)的致病力(图9B)。Peñalva等[21]研究发现病原菌在侵染宿主时会改变环境pH,从而激活pH转录因子PacC,以增强其致病力。从以上结果发现,环境pH与意大利青霉致病力会相互影响,故猜测可能与PacC有关。所以实验进一步观察侵染初期到侵染后期PacC的表达量,发现PacC基因的表达较为稳定(图9C~图9D)。
3. 讨论与结论
在田间收获、包装或运输过程中,意大利青霉会通过果皮伤口侵染果实,从而产生病害[22]。在侵染过程中,面对复杂多变的环境pH变化,微生物必须迅速应对并及时调节以进行最适生长。目前在许多病原菌中存在一套响应和适应环境pH变化的机制,这个机制通常由PAL/RIM全局调控。PAL/RIM机制中的关键转录因子PacC在病原菌生长发育和致病力中有重要作用。
本试验成功克隆到意大利青霉PacC基因,并对其生物信息学特性进行了初步分析。PacC基因含有3个保守的Cys2His2锌指蛋白结构域,与指状青霉、构巢曲霉、酿酒酵母有相同的结构域[12]。表明意大利青霉的PacC具有高度保守性和特异性,且与其他真菌中的PacC发挥着同样功能。研究表明PacC通过直接结合特定的DNA序列(5'-GCCARG-3')来调控基因表达[23]。在酿酒酵母中,PacC通过与自身启动子区域结合进行自我抑制调控[24]。在意大利青霉PacC基因上游序列发现3个PacC的结合位点,进一步表明这种自我抑制调控的可能性。
研究表明,PacC作为环境pH的调节因子,对微生物的生命活动起到关键作用,在细胞壁生物合成、稳态、氧化还原过程、水解酶活性、跨膜转运和与真菌毒力相关的基因调控中具有直接调控功能[25]。PacC缺失会导致灵芝[26]、粉色面包菌(Neurospora crassa)[27]、赭曲霉和球孢白僵菌(Beauveria bassiana)的生长速率变慢。本试验研究也发现PacC在意大利青霉菌丝生长的整个过程中维持较高表达水平,表明PacC在意大利青霉生长过程中发挥着重要作用。在外界环境pH下,不同基因在维持细胞外环境pH稳定的过程中发挥着不同作用[18]。Luo等[28]研究表明PacC缺失会导致球孢白僵菌在碱性条件下生长速率变慢。Chen等[15]对扩展青霉(Penicillium expansum)的研究中也有同样发现。本试验也发现碱性条件对意大利青霉生长的抑制高于酸性条件,表明PacC在碱性条件下发挥着重要调控作用。研究表明,在趾间毛癣菌(Trichophyton interdigitale)中,PacC表达与环境pH相关,即酸性pH抑制PacC表达,碱性pH诱导PacC表达[14]。本研究也发现意大利青霉PacC在碱性条件下表达量显著上调,表明PacC是一个碱性诱导基因。
研究发现,病原菌可以通过碳浓度来调节致病菌分泌的小分子改变环境pH,从而导致PacC表达量发生变化[29]。本试验研究发现意大利青霉经过葡萄糖回补处理,导致PacC基因表达量上调,推测碳源可能诱导了PacC表达。进一步以蔗糖为主要碳源,发现意大利青霉对碳浓度的响应有所差异,即在低碳浓度(5 mmol/L)下使培养基碱化,高碳浓度(175 mmol/L)下使培养基酸化。分析极限碳浓度下PacC表达,发现低碳浓度会诱导PacC的表达提高,这个结果与Bi等[29]观察到低碳浓度诱导扩展青霉PacC表达提高62.1倍的结果一致,表明PacC的表达与碳浓度有关。
病原菌与寄主互作过程中环境pH是影响病原菌致病力的重要因素,这主要是环境pH调控因子PacC发挥作用。目前已发现PacC影响一些病原菌的致病力。汪汉成等[30]研究发现环境pH会严重影响烟草青枯病菌(Ralstonia solanacearum)的致病力。本试验对意大利青霉和环境pH的关系进行研究,发现环境pH对意大利青霉的致病力有着重要影响,且不同品种柑橘接种意大利青霉后会导致果皮pH下降。进一步观察了环境pH调控基因PacC在意大利青霉侵染柑橘过程中的表达,发现PacC基因表达较为稳定,表明PacC可能与意大利青霉致病性相关。
综上所述,PacC对不同pH和碳源条件下意大利青霉的生长和致病力发挥重要调控作用,进一步分析侵染过程中相关碳代谢重点基因与酸碱代谢的重点基因,有助于深入认识PacC在意大利青霉致病过程中所起的作用。
-
表 1 PCR扩增所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used for PCR amplification
引物名称 引物序列 引物名称 引物序列 PacC-U-F
PacC-U-R
PacC-1-F
PacC-1-R
PacC-2-F
PacC-2-RTTCGGCTGGCTAAGCCAATG
AATACCGCTTTGCTAAGCCTGG
CGGTCTTGGTCTTCTGGT
CGGCATAGGAGTTAGGGTC
CCTATCAATGGCATCAACG
GACGGACCTTCTCAACCCPacC-D-F
PacC-D-R
Actin-F
Actin-R
Q-PacC-F
Q-PacC-RCCTGGGTTGAGAAGGTCC
ATGGCGTATGTTTGGGTG
CATTGAGCACGGTGTTGTCA
CTGGGTCATCTTCTCACGGT
CGCAAAAGCACCAACAACCT
CTTCAAATCCTGGGGACGCT -
[1] ZHANG Z F, ZHU Z R, MA Z H, et al. A molecular mechanism of azoxystrobin resistance in Penicillium digitatum UV mutants and a PCR-based assay for detection of azoxystrobin-resistant strains in packing or store-house isolates[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2009,131(23):157−161.
[2] ERASMUS A, LENNOX C L, KORSTEN L, et al. Imazalil resistance in Penicillium digitatum and P. italicum causing citrus postharvest green and blue mold: Impact and options[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2015,107:66−76. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.05.008
[3] CHEN C Y, QI W W, PENG X, et al. Inhibitory effect of 7-demethoxytylophorine on Penicillium italicum and its possible mechanism[J]. Microorganisms,2019,7(2):36. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7020036
[4] TANNOUS J, BARDA O, LUCIANO R D, et al. New insight into pathogenicity and secondary metabolism of the plant pathogen Penicillium expansum through deletion of the epigenetic reader SntB[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:610. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00610
[5] WANG M S, RUAN R X, LI H Y. The completed genome sequence of the pathogenic ascomycete fungus Penicillium digitatum[J]. Genomics,2021,113(2):439−446. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.01.001
[6] FERNANDES T R, SEGORBE D, PRUSKY D, et al. How alkalinization drives fungal pathogenicity[J]. Plos Pathogens,2017,13(11):e1006621. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006621
[7] VYLKOVA S. Environmental pH modulation by pathogenic fungi as a strategy to conquer the host[J]. Plos Pathogens,2017,13(2):e1006149. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006149
[8] 王萌, 杨书珍, 刘寒寒, 等. 柑橘采后病原菌意大利青霉creA基因的克隆及表达分析[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2019(4):45−54. [WANG M, YANG S Z, LIU H H, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of creA from Penicillium italicum, a postharvest pathogen of citrus fruits[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2019(4):45−54. [9] WANG Y, LIU F, WANG L Q, et al. pH-signaling transcription factor AopacC regulates ochratoxin A biosynthesis in Aspergillus ochraceus[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(17):4394−4401. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00790
[10] VIRGILIO S, BERTOLUNI M C. Functional diversity in the pH signaling pathway: An overview of the pathway regulation in Neurospora crassa[J]. Current Genetics,2018,64(3):529−534. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0772-x
[11] CERVANTES J A, SILVA G A, PLIEGO A R, et al. The UMAG_00031 gene from Ustilago maydis encodes a putative membrane protein involved in pH control and morphogenesis[J]. Archives of Microbiology,2020,202(4):2221−2232.
[12] LAMB T M, MITCHELL A P. The transcription factor Rim101p governs ion tolerance and cell differentiation by direct repression of the regulatory genes NRG1 and SMP1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology,2003,23(2):677−686. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.677-686.2003
[13] CERVANTES J A, RUIZ H J. Identification of a novel member of the pH responsive pathway Pal/Rim in Ustilago maydis[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology,2019,59(1):14−23. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201800180
[14] da-SILVA L G, MARTINS M P, SANCHES P R, et al. Saline stress affects the pH-dependent regulation of the transcription factor PacC in the dermatophyte Trichophyton interdigitale[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology,2020,51(4):1585−1591. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00313-1
[15] CHEN Y, LI B Q, XU X D, et al. The pH-responsive PacC transcription factor plays pivotal roles in virulence and patulin biosynthesis in Penicillium expansum[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2018,20(11):4063−4078. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14453
[16] CARACUEL Z, CASANOVA C, RONCERO M, et al. pH response transcription factor PacC controls salt stress tolerance and expression of the P-Type Na+-ATPase Ena1 in Fusarium oxysporum[J]. Eukaryotic Cell,2003,2(6):1246−1252. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.6.1246-1252.2003
[17] MERHEJ J, RICHARD F, BARREAU C. The pH regulatory factor Pad1 regulates Tri gene expression and trichothecene production in Fusarium graminearum[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology,2011,48(3):275−284. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2010.11.008
[18] 范明, 彭丽桃, 闫等, 等. VmaH和PMA在指状青霉中的表达及其作为潜在杀菌作用靶点的可能性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(6):126−133. [FAN M, PENG L T, YAN D, et al. Expression of VmaH and PMA in Penicillium digitatum and their potentials as antimicrobial targets[J]. Food Science,2021,42(6):126−133. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191230-348 [19] YANG S Z, LIU L M, LI D M, et al. Use of active extracts of poplar buds against Penicillium italicum and possible modes of action[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,196:610−618. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.101
[20] LOUW J P, KORSTEN L. Impact of ripeness on the infection and colonization of Penicillium digitatum and P. expansum on plum[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2019,149:148−158. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.11.024
[21] PENALVA M A, TILBURN J, BIGNELL E, et al. Ambient pH gene regulation in fungi: Making connections[J]. Trends in Microbiology,2008,16(6):291−300. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.03.006
[22] FADDA A, SARAIS G, LAI C, et al. Control of postharvest diseases caused by Penicillium spp. with myrtle leaf phenolic extracts: In vitro and in vivo study on mandarin fruit during storage[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(10):4229−4240. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11062
[23] YAN H B, FANG T S, XU H H, et al. The pH-sensing Rim101 pathway positively regulates the transcriptional expression of the calcium pump gene PMR1 to affect calcium sensitivity in budding yeast[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2020,532(3):453−458. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.083
[24] RASCLE C, DIERYCKX C, DUPUY J W. The pH regulator PacC: A host-dependent virulence factor in Botrytis cinerea[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports,2018,10(5):555−568. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12663
[25] MARTINS M P, MARTINEZ N M, SANCHES P R, et al. The pH signaling transcription factor PAC-3 regulates metabolic and developmental processes in pathogenic fungi[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2019,10(10):2076.
[26] WU F L, ZHANG G, REN A, et al. The pH-responsive transcription factor PacC regulates mycelial growth, fruiting body development, and ganoderic acid biosynthesis in Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Mycologia,2016,108(6):1104−1113.
[27] VIRGILIO S, CUPERTINO F B, BERNARDES N E, et al. Molecular components of the Neurospora crassa pH signaling pathway and their regulation by pH and the PAC-3 transcription factor[J]. Plos One,2016,11(8):e0161659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161659
[28] LUO Z B, REN H. The PacC transcription factor regulates secondary metabolite production and stress response, but has only minor effects on virulence in the insect pathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2017,19(2):788−802. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13648
[29] BI F C, BARAD S, MENT D, et al. Carbon regulation of environmental pH by secreted small molecules that modulate pathogenicity in phytopathogenic fungi[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology,2016,17(8):1178−1195. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12355
[30] 汪汉成, 郭华, 蔡琳, 等. 不同渗透压及pH环境对烟草青枯病菌致病力的影响[J]. 植物保护学报,2019,46(4):754−761. [WANG H C, GUO H, CAI L, et al. Effects of different osmolality and pH conditions on the pathogenicity of Ralstonia solanacearum in tobacco leaves[J]. Journal of Plant Protection,2019,46(4):754−761.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
