Inhibition Effect and Molecular Mechanism of Tea Polyphenols on the α-Amylase
-
摘要: 探究茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制特性并分析其分子作用机制。采用抑制动力学的方法评价茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用;通过荧光色谱法及圆二色谱法观察茶多酚对α-淀粉酶空间结构和稳定性的影响;利用分子对接技术,探究茶多酚与α-淀粉酶之间的分子相互作用。结果表明,茶多酚对于α-淀粉酶的活性具有明显的抑制作用,竞争类型为非竞争性抑制,半抑制浓度为1.35 mg/mL;茶多酚对α-淀粉酶具有荧光猝灭效应,其最大发射波长(λmax)出现红移,α-淀粉酶的二级结构由层状结构向螺旋结构转变,其稳定性显著降低;茶多酚通过氢键、疏水相互作用等与α-淀粉酶形成稳定复合物,从而降低了酶的催化活性。研究结果表明,茶多酚具有作为α-淀粉酶抑制剂的潜在价值。Abstract: In present study, the inhibitory effect and molecular mechanism of tea polyphenols on α-amylase were investigated. With the determination of inhibition kinetics, the inhibition of tea polyphenols on α-amylase was estimated. Then, by using the fluorescence chromatography and circular dichroism, the changes of spatial structure and stability of α-amylase were observed. Furthermore, the molecular docking was used to explore the molecular interactions between tea polyphenols and α-amylase. The results showed that tea polyphenols exhibited the inhibitory effect on α-amylase with a half maximal inhibitory concentration of 1.35 mg/mL in a non-competitive manner. There was a fluorescence quenching effect of tea polyphenols on α-amylase with the red-shift of maximum emission wavelength (λmax) in the fluorescence chromatography. Moreover, the secondary structure of α-amylase was found to change from the stratified structure to helical structure, which indicated the decreasing stability of α-amylase. By forming the hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interaction, tea polyphenols could bind to α-amylase as the stable complex which contributed to the decrease of enzyme activity. The results suggested that tea polyphenols had the potential value as α-amylase inhibitors.
-
Keywords:
- α-amylase /
- tea polyphenols /
- inhibition effect /
- molecular docking
-
糖尿病是一种因糖代谢紊乱而引发的慢性疾病,因其较高的患病率与死亡率而备受关注[1]。全球约90%糖尿病患者罹患的是Ⅱ型糖尿病[2]。大量研究表明,Ⅱ型糖尿病的发病与持续性的餐后高血糖症密切相关。因此,有效延缓餐后血糖浓度的上升已成为治疗糖尿病的重要举措[3]。目前,市场上用于糖尿病治疗的药物主要为阿卡波糖、伏格列波糖等糖类水解酶抑制剂,这类药物虽然可以有效抑制餐后血糖的上升,但长期服用会引发恶心、呕吐、肠胃胀气、肾功能紊乱等副作用以及抗药性逐渐增强等问题[4-5]。现代科学研究表明,来源于植物的无毒无害的多酚类提取物对α-淀粉酶具有较好的抑制活性[6-8]。因此,从天然植物资源中探寻安全、有效的多酚类抑制剂已成为食品、生物及医药领域的研究热点。
茶多酚是茶叶内多酚类物质的总称,也是其主要的天然活性物质。茶多酚主要包括儿茶素类物质,如表儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素、表儿茶素没食子酸酯、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epigallocatechin gallate,EGCG)等。研究表明茶多酚具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗肿瘤等多种功效,同时茶多酚在蛋白质沉淀、酶抑制方面表现出良好特性[9-10]。因此,研究茶多酚与α-淀粉酶的相互作用在多酚抑制剂的挑选中具有重要的意义。目前,国内外相关研究主要集中在提取物制备工艺的优化、提取溶剂的筛选与比较、不同种类及来源的茶叶抑制活性的差异及动物模型的活性评价[6-8],而系统地从动力学、光谱学及分子相互作用角度由表及里、从现象到机理较为系统地探讨和分析茶多酚对糖类消化酶抑制作用的研究较少。同时,通过观察和分析茶多酚与糖类消化酶相互作用过程中分子作用力、分子结合位点、空间结构的变化,进而探讨茶多酚抑制糖类消化酶活性的相关研究也较少。因此,从分子相互作用角度系统研究茶多酚对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制作用有益于拓宽和提升茶多酚在相关领域的资源化利用。
本文以茶多酚和α-淀粉酶为对象,采用抑制动力学和光谱学,分析了茶多酚对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制作用,并通过对荧光色谱法和圆二色谱法观察了茶多酚对α-淀粉酶空间结构的影响,进一步采用分子对接技术探究了茶多酚与α-淀粉酶相互作用过程中分子作用力、分子结合位点、空间结构的变化,从分子层面上初步揭示了茶多酚抑制α-淀粉酶活性的机理,为茶多酚在α-淀粉酶抑制剂方面的应用提供实验和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
茶多酚(纯度≥95%) 通泽生物科技有限公司;α-淀粉酶(酶活52 U/mg)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG) 阿拉丁试剂公司;实验用水 蒸馏水;3,5-二硝基水杨酸、亚硝酸钠、苯酚、酒石酸钾钠、可溶性淀粉、磷酸氢二钠、氢氧化钠、磷酸二氢钠等试剂 均为分析纯,成都科隆化工试剂厂。
ESJ210-4A型电子天平 沈阳龙腾电子有限公司;UV-2000型紫外可见分光光度计 尤尼柯(上海)仪器公司;Milii-Q Element超低元素型超纯水系统 上海晶仪科学仪器有限公司;F-7000型荧光色谱仪 日本Hitachi公司;Chirascan型圆二色谱仪 英国应用光物理公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用
采用Bernfeld法测定茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用[11]。取2.0 g可溶性淀粉溶于适量的磷酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH6.9),煮沸10 min,其间不断搅拌,冷却至室温后定容至200 mL,备用;以相同的溶剂配制0.02 mg/mL的α-淀粉酶溶液(酶活52 U/mg),这里的酶活定义为1 min内分解产生1 μmol麦芽糖所需要的α-淀粉酶的质量(mg),4 ℃冷藏备用。
取0.25 mL酶溶液于37 ℃水浴1 min,加入0.25 mL不同浓度的茶多酚溶液(0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4和1.6 mg/mL),37 ℃孵育4 min,随后加入0.5 mL淀粉溶液,混匀后于37 ℃孵育4 min,然后加入1 mL DNS试剂[12],沸水浴8 min,避光冷却至室温后加10 mL蒸馏水,于540 nm波长下测定混合溶液的吸光度。通过麦芽糖标准曲线(y=2.8167x−0.1421,其中x为吸光度,y为麦芽糖浓度(μmol/mL),R2=0.9932)计算酶活。以未添加α-淀粉酶的混合溶液为空白对照,计算茶多酚对于α-淀粉酶的抑制率,并求取半数抑制浓度(half maximal inhibitory concentration,IC50)。
抑制率(%)=A−BB×100 (1) 式中:A为有抑制剂时α-淀粉酶的活性,U/mg;B为无抑制剂时α-淀粉酶的酶性,U/mg。
1.2.2 抑制动力学分析
参考1.2.1节的方法,取0.25 mL的α-淀粉酶溶液与0.25 mL茶多酚溶液(0、0.6、1.0、1.4和1.8 mg/mL)混合,再加入0.5 mL淀粉溶液(4、6、8、10、12、14和16 mg/mL),充分反应后测定混合溶液的吸光度以得到不同底物浓度下的酶促反应速率。采用Lineweave-Burk双倒数作图法,以底物浓度的倒数(1/[S])为横坐标,反应速率(1/v)为纵坐标,绘制不同茶多酚浓度下的双倒数曲线图,判断抑制类型[13]。
1.2.3 荧光光谱分析
α-淀粉酶、茶多酚、EGCG溶液均用磷酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH6.9)配制。茶多酚反应组:α-淀粉酶溶液(1.0 mg/mL,3 mL)与0.2 mL茶多酚溶液混匀,使得茶多酚的最终浓度分别为0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0和1.2 mg/mL;EGCG反应组:α-淀粉酶溶液(1.0 mg/mL,3 mL)与0.2 mL的EGCG溶液混匀,使得EGCG的最终浓度分别为0、20、40、60、80、100和120 μmol/L)。将各反应组溶液置于不同温度(20、30、37 ℃)孵育5 min,测定其荧光吸光度,上述温度的选择依据预实验以及相似研究而定[14]。荧光激发波长为280 nm,扫描范围为290~450 nm,激发和发射缝均为5 nm,扫描速率为700 nm/min。
1.2.4 圆二色谱(circular dichroism,CD)分析
以磷酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH6.9)为溶剂,配制α-淀粉酶溶液(1 mg/mL)和茶多酚溶液(0.5 mg/mL),分别取1.5 mL两种溶液混匀,测定混合液的圆二色谱,扫描波长为260~200 nm,间隙为1 nm[15],未添加茶多酚的α-淀粉酶溶液作空白对照。通过CDpro软件(http://lamar.colostate.edu/~scream/CDPro)的Selcon3程序进行蛋白质二级结构的分析。
1.2.5 分子对接
采用Discovery Studio 2019(Version 16.1,SanDiego,CA,USA)的CDOCKER模块对α-淀粉酶与EGCG进行分子对接。α-淀粉酶结构(1HNY)从RCSB Protein Data Bank(http://www.rcsb.org/pdb)数据库中获取,去除体系内水分子后采用“Clean Protein”模块优化后使用;EGCG分子从Zinc数据库(http://zinc.docking.org/)内获取,并采用CHARMM力场对其结构优化后使用。然后,通过“Find Sites from Receptor Cavities”模块探寻α-淀粉酶和EGCG的最佳结合位点,选取最佳的结合位点,在“Receptor-Ligand Interactions”模块下的“Dock Ligands(CDOCKER)”子模块中展开分子对接,活性区域半径设置为5 Å,以α-淀粉酶为受体,以EGCG为配体,其他参数按照默认设置,对接完成后选取“-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY”打分最高的结合方式分析两者之间的分子作用力类型、占比和分子结合位点等情况。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验重复进行三次,结果以“平均值±标准差”的形式表示。实验结果使用Origin(2019b for window,OriginLab Corporation,MA,USA)进行统计学分析及绘图,显著性差异 P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用影响
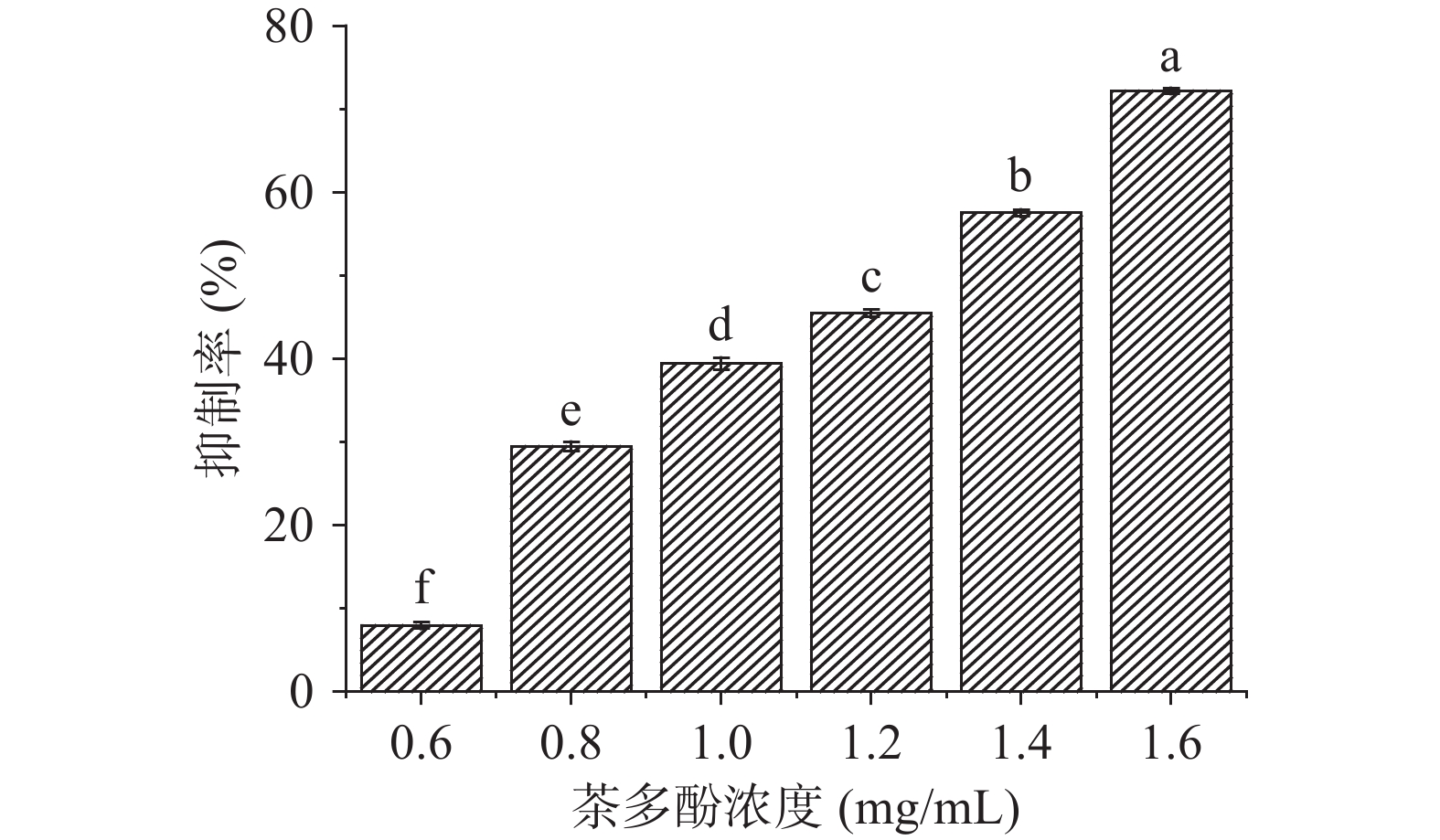
茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制能力以IC50值的大小进行表示,即α-淀粉酶的活力降低一半时所需茶多酚的浓度[16]。由图1所示,随着茶多酚浓度的增大,其对α-淀粉酶的抑制率显著提高(P<0.05),当茶多酚浓度为1.6 mg/mL时,抑制率高达72.19%。此外,通过曲线拟合后得出茶多酚对于α-淀粉酶的半抑制浓度IC50值为1.35 mg/mL。虽然与临床用药物阿卡波糖(IC50=0.089 mg/mL)相比,茶多酚对于α-淀粉酶的抑制能力较低,但其与鼠尾草酸(IC50=1.12 mg/mL)等天然提取物的抑制效果相似[15],且具有易于生产、价格低廉、绿色安全等优点。结果表明,茶多酚在α-淀粉酶抑制剂的开发中具有潜在的价值。
2.2 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制动力学分析结果
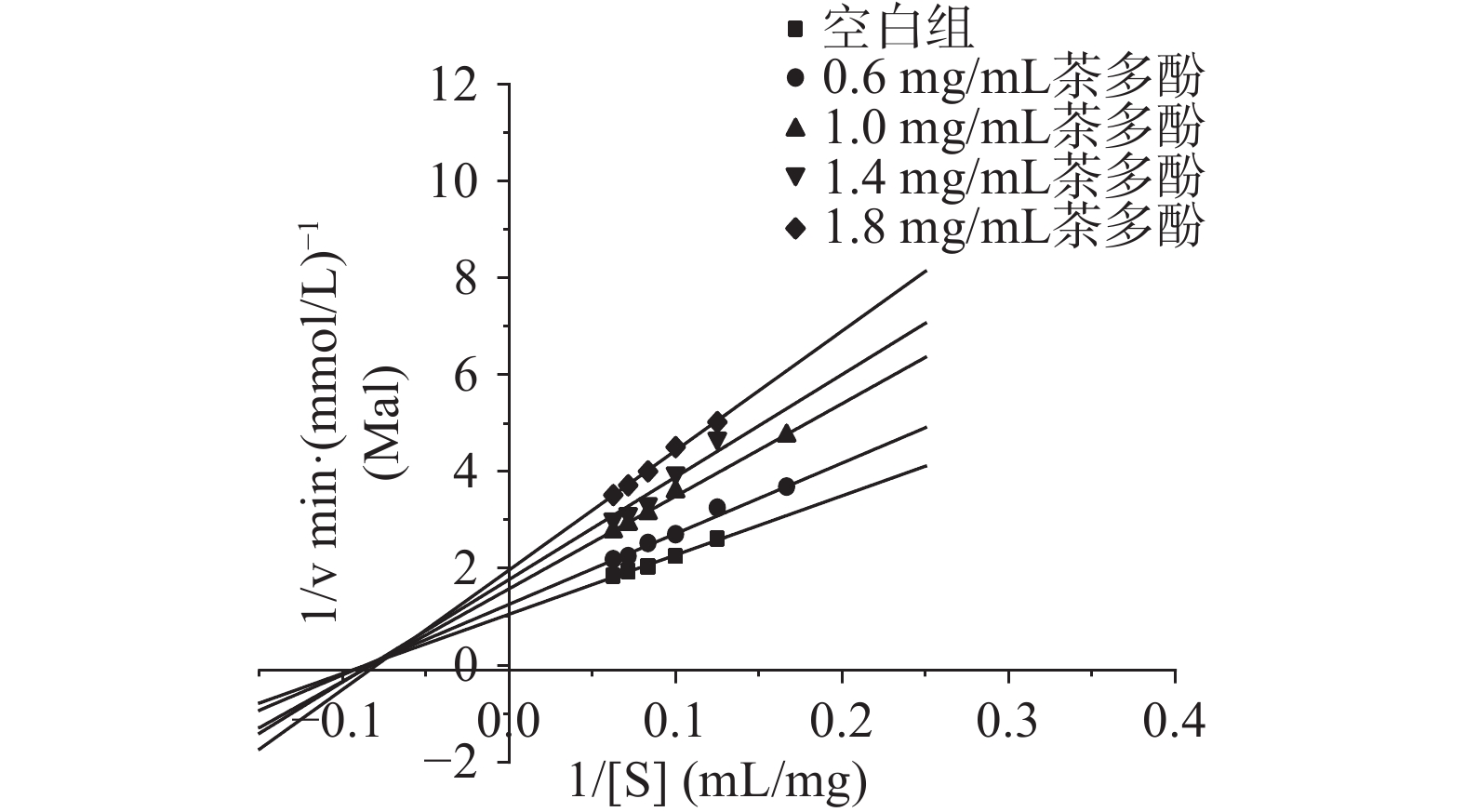
由图2所示,随着茶多酚浓度的提高,直线的斜率增大,与y轴的交点上移,即最大反应速率(Vmax)减小,且几乎所有茶多酚受试浓度下的直线都交于第二象限的一点,表明茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制类型为非竞争性抑制。非竞争性抑制遵守动力学Cornish-Bowden方程[17]:
1v=KmVmax(1+[C]Kic)1[S]+1Vmax(1+[C]Kiu) (2) 式中:v为酶促反应速率,mmol/(L·min);Km为米氏常数,mg/mL;Vmax为最大反应速率,mmol/(L·min);C为抑制剂浓度,mg/mL;S为淀粉浓度,mg/mL;Kic为竞争性抑制常数;Kiu为反竞争性抑制常数。
由Cornish-Bowden方程可知,只有当Kic和Kiu都存在时,1/v与1/[S]的双倒数图才可以在不同抑制剂浓度下恒过第二象限的定点,由此可以判断茶多酚对于α-淀粉酶呈非竞争性抑制,即茶多酚既可以和α-淀粉酶结合又可以和α-淀粉酶-淀粉复合物结合。推测是由于茶多酚属于混合物,其内不同成分对于α-淀粉酶的抑制类型不尽相同,整体表现为非竞争性抑制。由图2可知,当淀粉的浓度逐渐上升时,酶促反应的速率之间的差距减少,表明底物浓度的提高可以适当缓解茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用,这与茶多酚的竞争性抑制特性强于反竞争性抑制特性的特征有关[18]。
2.3 茶多酚及主要成分EGCG对α-淀粉酶的荧光猝灭效应
在一定的激发波长下,蛋白质中的色氨酸、酪氨酸及苯丙氨酸可以发射荧光,从而使得蛋白质具有荧光特性,蛋白质的荧光特性与这些氨基酸残基所处的微环境密切相关[19]。α-淀粉酶由496个氨基酸残基组成,包括17个色氨酸,因此α-淀粉酶荧光特性的变化可以直接反映酶空间结构的变化[20]。
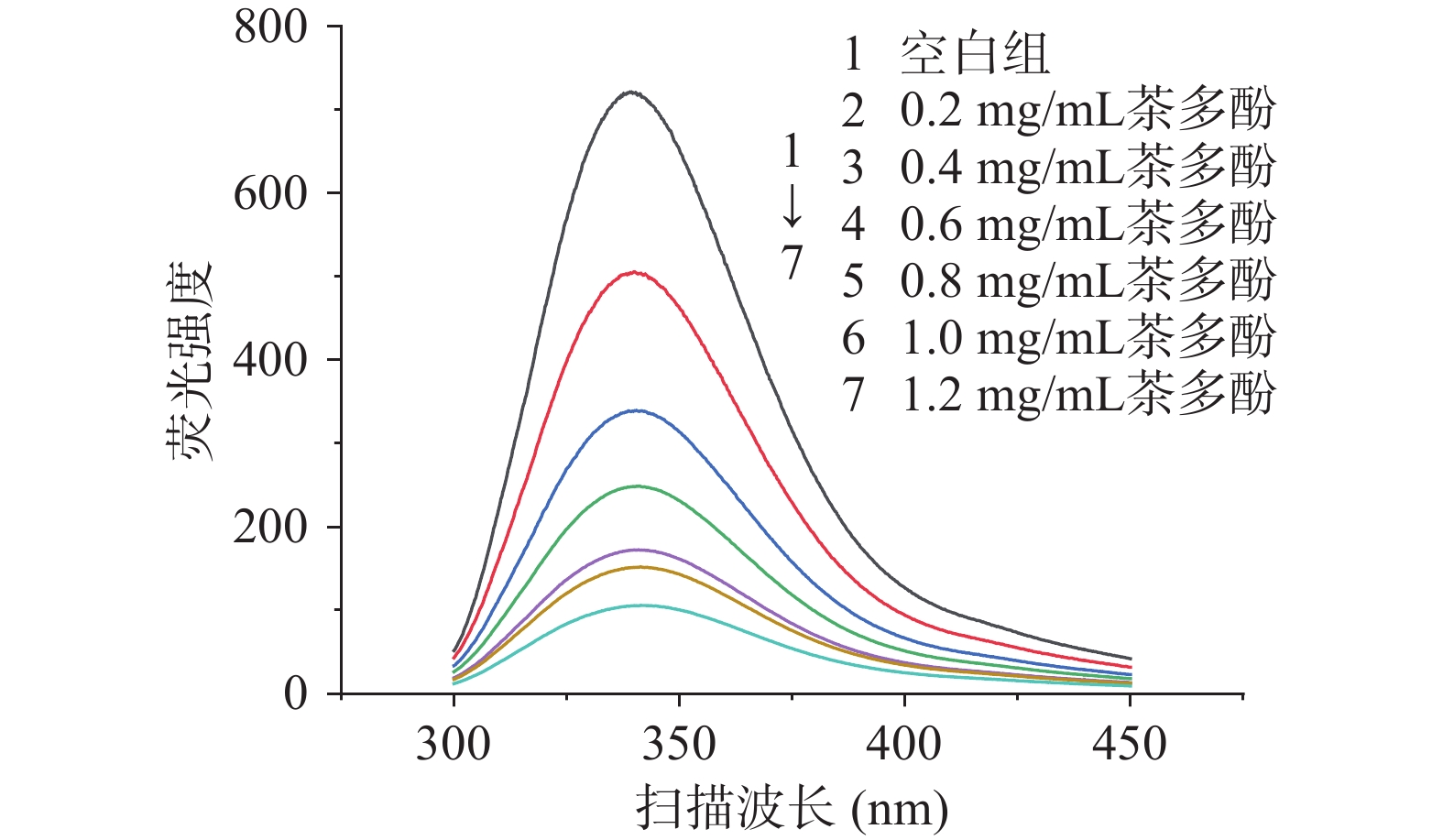
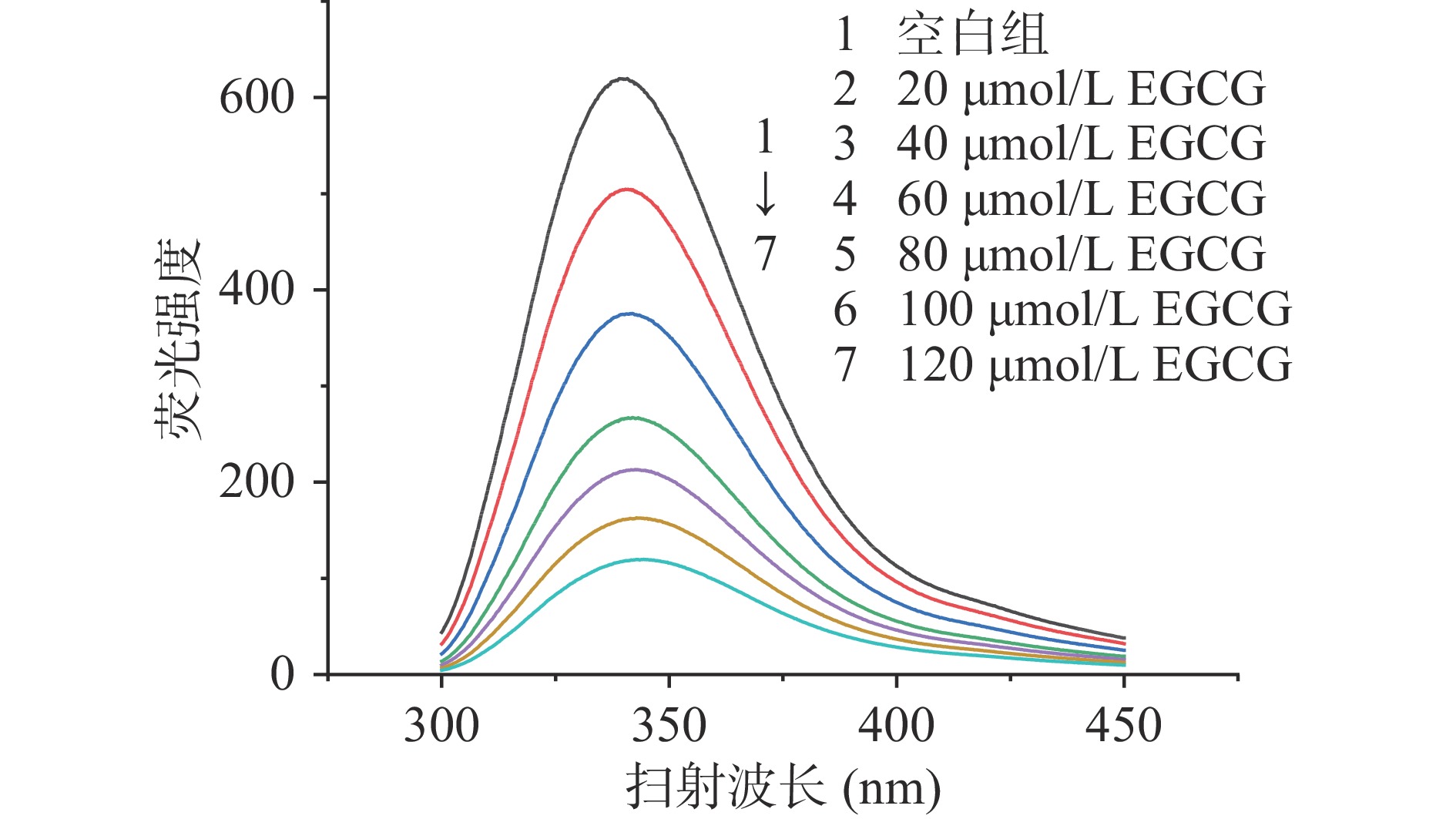
由图3可见,随着茶多酚浓度的增大,α-淀粉酶的荧光发射峰显著下降,且最大发射波长(λmax)发生了轻微的红移,当茶多酚添加浓度达到1.2 mg/mL时,最大发射波长由340 nm红移至342 nm。由图4可见,茶多酚主要成分EGCG对α-淀粉酶荧光特性的影响与茶多酚类似,这与徐冬兰等人探究咖啡酰奎尼酸类物质对α-淀粉酶的荧光特性影响相似[15]。Gong等[4]在利用荧光色谱法研究苹果多酚对于α-葡糖苷酶构象影响时,也出现了最大发射波长红移的现象。荧光色谱中最大发射波长的红移意味着蛋白质的部分结构发生舒展以及酶的热力学稳定性下降,推测可能是由于茶多酚通过疏水相互作用与较强芳香性及疏水性的氨基酸结合,从而使得蛋白质更多肽链暴露于溶剂环境之下[4,21]。
2.4 茶多酚主要成分EGCG对α-淀粉酶的猝灭类型分析结果
荧光猝灭类型分为静态猝灭和动态猝灭,其中动态猝灭遵守Stern-Volmer方程[14]:
F0F=1+Kqτ0c (3) 式中:F0为未加淬灭剂时的荧光强度;F为加入淬灭剂后的荧光强度;Kq为荧光猝灭速率常数,L/(mol·s);τ0为荧光分子的初始平均寿命,生物大分子一般为10−8 s;c为猝灭剂浓度,mol/L。
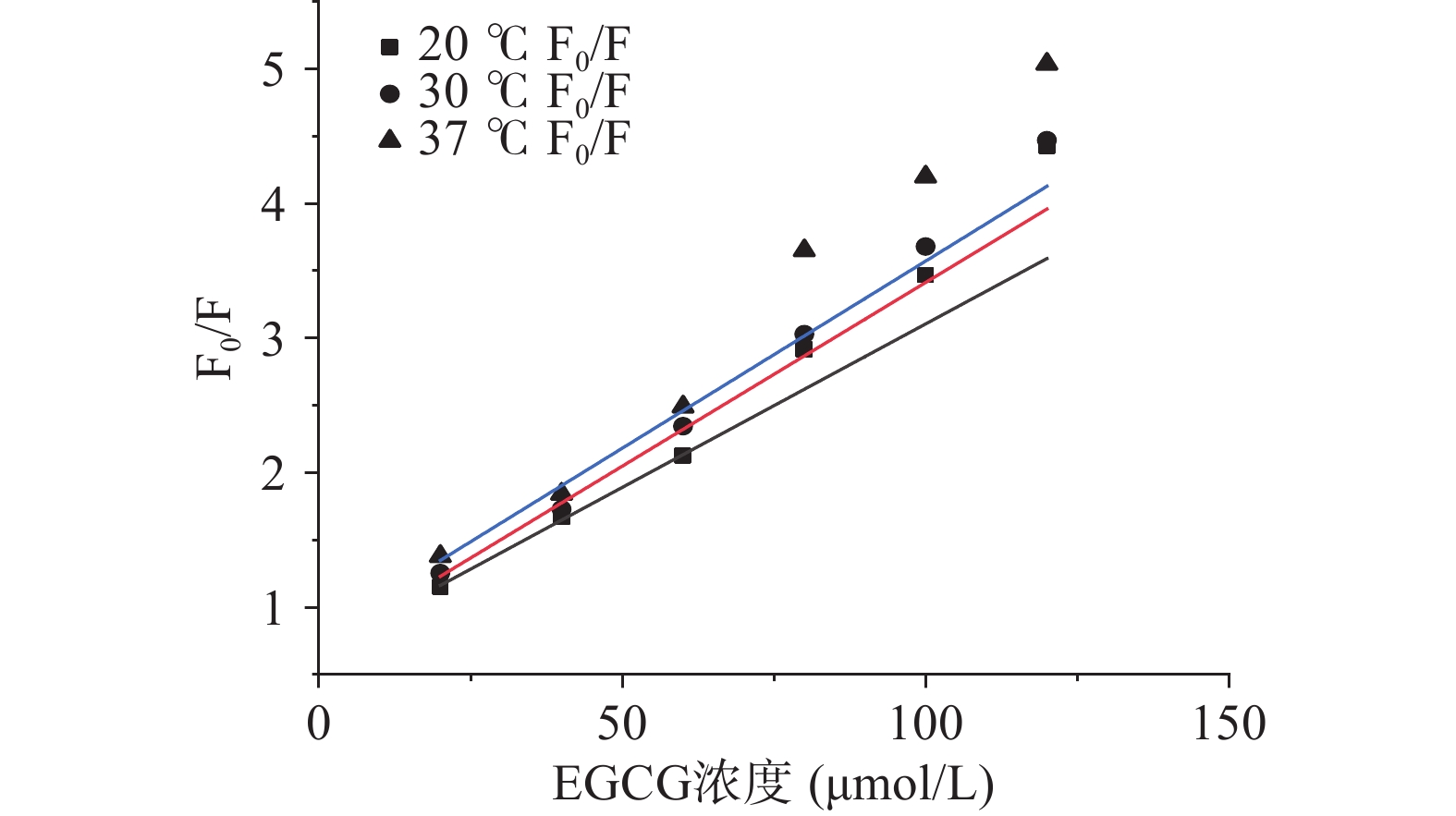
由于茶多酚为混合物,因此采用其主要成分EGCG分析二者间的猝灭类型。如图5所示,在不同温度(20、30、37 ℃)下,当EGCG的添加浓度低于80 μmol/L时,其浓度与F0/F呈现良好的线性关系,其猝灭速率常数分别为6.78×1013、6.85×1013、7.93×1013 L/(mol·s),远远高于动态猝灭中各种荧光猝灭剂对生物大分子(主要是蛋白质)的最大碰撞猝灭常数2×1010 L/(mol·s)[22],这说明该浓度梯度内,EGCG对α-淀粉酶的荧光猝灭类型为静态猝灭。当EGCG的添加浓度大于80 μmol/L时,其浓度与F0/F呈非线性关系,且曲线朝向y轴,这可能是由于较高浓度EGCG的添加,增大了其与发光氨基酸残基之间的碰撞概率,猝灭类型由原来单一的静态猝灭转变为了动态-静态猝灭混合的形式[23]。
2.5 茶多酚主成分EGCG与α-淀粉酶间的结合常数
当EGCG添加浓度低于80 μmol/L时,其对α-淀粉酶的荧光猝灭类型为静态猝灭,符合以下方程[14]:
lgF0−FF=lgKa+nlgc (4) 式中:F0为未加淬灭剂时的荧光强度;F为加入淬灭剂后的荧光强度;Ka为表观结合常数;n为结合位点数;c为猝灭剂浓度,mol/L。
以lgc为横坐标(x),以lg(F0-F)/F为纵坐标(y)作图,拟合和计算不同温度下结合常数(Ka)与结合位点数(n)。
由表1可知,20 ℃下EGCG与α-淀粉酶的结合常数达到了107数量级,随着温度的升高,二者的结合常数逐渐下降,结合位点数降低,表明温度的升高影响了EGCG与α-淀粉酶之间的结合能力。这可能是由于EGCG主要通过氢键与酶发生结合,而温度的升高降低了氢键的稳定性,进而抑制了二者的结合。
表 1 不同温度下EGCG与α-淀粉酶的结合常数和结合位点数Table 1. Binding constant and site of EGCG with α-amylase under different temperatures猝灭剂 T(℃) 回归方程 n Ka(L/mol) EGCG 20 y=1.8485x+7.8938 1.8485 7.83×107 30 y=1.5156x+6.5277 1.5156 3.37×106 37 y=1.2340x+5.3714 1.2340 2.35×105 2.6 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶二级结构的影响
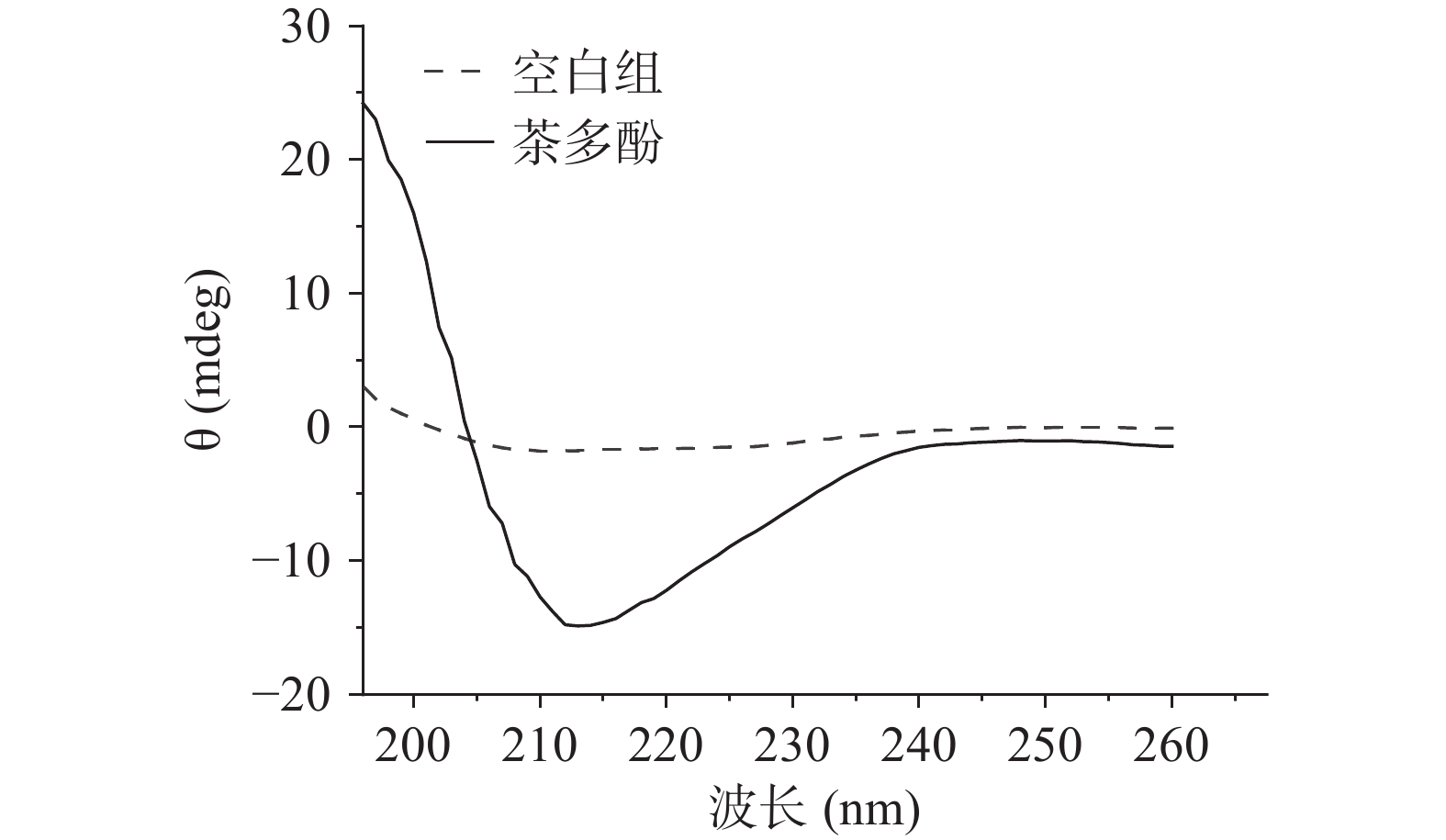
本实验利用圆二色谱法来测定蛋白质二级结构的变化[24]。由图6可知,茶多酚的加入显著改变了α-淀粉酶的二级结构。其中,α-螺旋在208及220 nm下具有两个特征负峰[25],茶多酚的加入使得两处负峰的面积明显增大,表明茶多酚的添加提高了α-淀粉酶中α-螺旋的含量。由表2可见,茶多酚的添加使得α-螺旋含量由31.0%增大至80.2%,而其中β-折叠、β-转角以及无规卷曲的占比显著下降。结果表明,茶多酚的添加使得α-淀粉酶的二级结构由层状结构向螺旋结构转变,进而影响了酶的活性。同时,圆二色谱所反映的蛋白质二级结构的变化也与荧光实验结果相互验证。研究表明,α-螺旋结构的大量增加意味着α-淀粉酶的结构变得更加松散[26],蛋白质的部分结构展开。这与上述荧光色谱中最大发射波长红移所表示的蛋白结构变化一致[21],都表明了茶多酚是通过改变α-淀粉酶的空间结构实现其抑制作用。
表 2 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶二级结构的影响Table 2. Effect of tea polyphenol on the α-amylase’s secondary structure抑制剂浓度 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规卷曲(%) 0 31.0 18.5 20.7 28.9 茶多酚0.5 g/L 80.2 0.2 5.2 14.5 2.7 分子对接
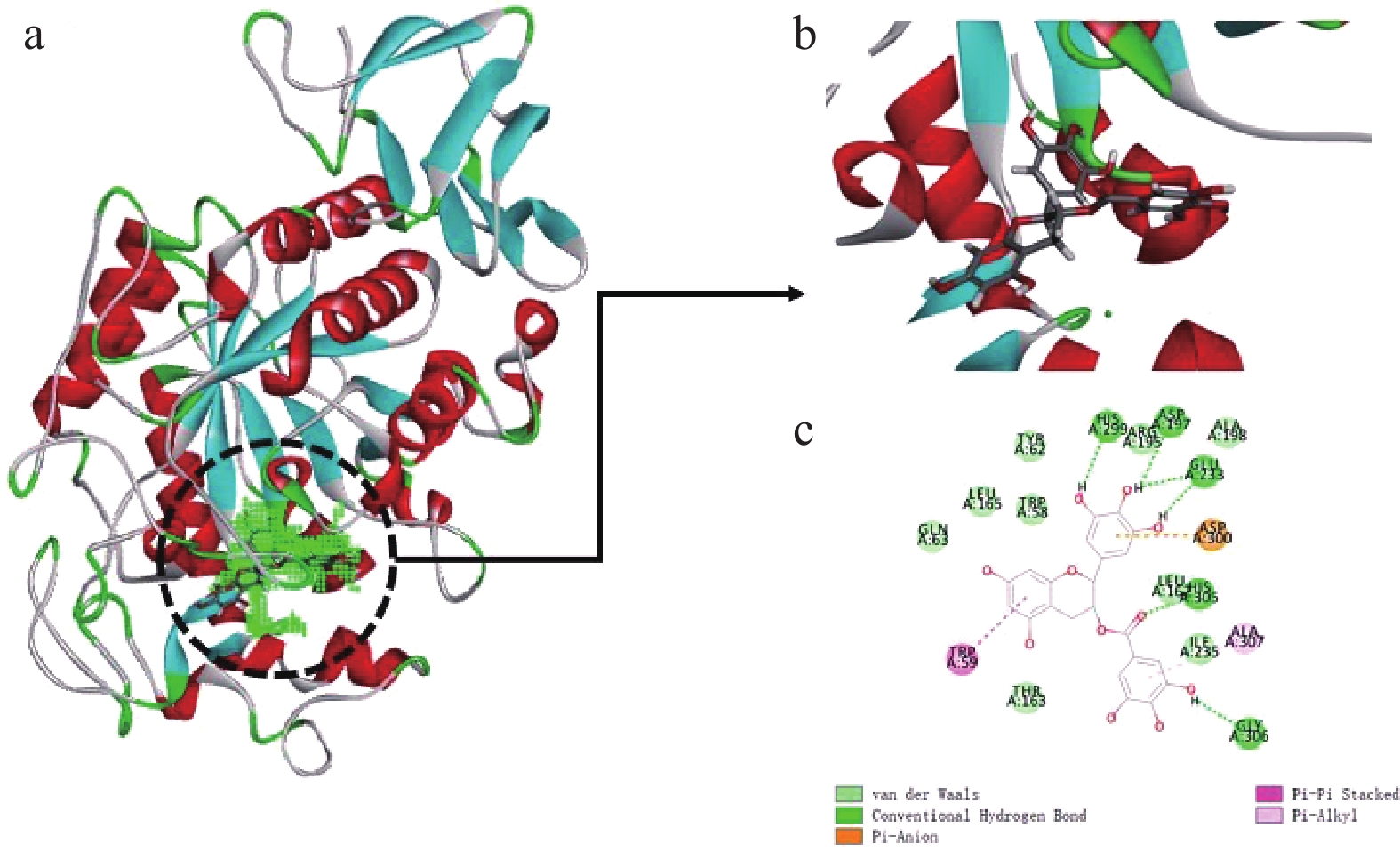
选取“-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY”打分值最高的构象进行分析,分子对接结果如图7所示。
由图7可知,EGCG主要通过氢键、疏水相互作用等分子作用力与α-淀粉酶的His299、Asp197、His305、Gly306、Trp59、Glu233以及Asp300等氨基酸残基结合。相关文献表明,Glu233、Asp197以及Asp300为α-淀粉酶的关键催化位点,对于其催化活性具有重要影响[27]。由此可以推测,EGCG能够与α-淀粉酶的催化位点结合,竞争性地抢夺淀粉与α-淀粉酶之间的结合区域,从而降低α-淀粉酶的催化效率。抑制动力学实验表明,茶多酚属于非竞争性抑制,既具有竞争性特性又具有反竞争性特性,EGCG在其竞争性特性中具有重要作用,而其反竞争性抑制特性与其它成分相关[18]。
由表3可见,EGCG主要通过氢键与α-淀粉酶残基结合,与其他多酚类物质(如黄酮类、酚酸类)相似,苯环上羟基结构起到了重要的作用[15,28],羟基参与形成的氢键在图7(c)中显示了5种可能的方式。与其他多酚不同,EGCG苯环上的没食子酰基也参与了氢键的形成。研究表明,随着没食子酰基的增加,茶多酚对α-淀粉酶的抑制能力显著提升[29]。EGCG通过疏水相互作用与TRP59残基周围的疏水腔结合,进而影响其微环境的极性[30],这可能是由于EGCG分子苯环上的电子与色氨酸内的C=C双键上的电子形成共轭体系。同时,有研究表明没食子酰基的C=O双键也参与了共轭[28],使得EGCG影响了TRP59的荧光特性,从而导致了荧光色谱实验中所出现的荧光猝灭现象。以上结果表明,EGCG可以通过氢键和疏水相互作用与α-淀粉酶形成复合物,从而改变酶的空间结构,进而降低其对淀粉的催化能力。
表 3 EGCG与α-淀粉酶之间的分子作用力类型Table 3. Methods of molecular force between α-amylase and EGCG成键原子 成键类型 A:HIS305:HD1 - EGCG:O1 氢键 EGCG:H43 - A:GLU233:OE2 氢键 EGCG:H44 - A:ASP197:OD1 氢键 EGCG:H44 - A:GLU233:OE1 氢键 EGCG:H45 - A:HIS299:NE2 氢键 EGCG:H48 - A:GLY306:O 氢键 A:TRP59 - EGCG 疏水相互作用 A:TRP59 - EGCG 疏水相互作用 EGCG - A:ALA307 疏水相互作用 A:ASP300:OD1 - EGCG 静电作用力 3. 结论
茶多酚主成分EGCG以氢键和疏水相互作用与Glu233、Asp197以及Asp300等α-淀粉酶催化活性位点结合,竞争性抑制酶的催化活性;茶多酚分子与TRP59等氨基酸的结合,使得蛋白质发生荧光猝灭效应,随着浓度的上升,猝灭类型会逐步由静态猝灭向动态与静态混合猝灭转变,表现为蛋白结构舒展,疏水腔暴露于外界环境。α-淀粉酶的二级结构随茶多酚的添加发生明显变化,层状结构向螺旋结构转变,酶的天然结构遭到破坏。实验结果表明茶多酚可通过氢键和疏水相互作用与α-淀粉酶形成复合物,从而发挥对α-淀粉酶催化活性的抑制作用。研究为茶多酚在糖尿病患者可食性食品中的应用提供了理论和实践基础。
-
表 1 不同温度下EGCG与α-淀粉酶的结合常数和结合位点数
Table 1 Binding constant and site of EGCG with α-amylase under different temperatures
猝灭剂 T(℃) 回归方程 n Ka(L/mol) EGCG 20 y=1.8485x+7.8938 1.8485 7.83×107 30 y=1.5156x+6.5277 1.5156 3.37×106 37 y=1.2340x+5.3714 1.2340 2.35×105 表 2 茶多酚对α-淀粉酶二级结构的影响
Table 2 Effect of tea polyphenol on the α-amylase’s secondary structure
抑制剂浓度 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规卷曲(%) 0 31.0 18.5 20.7 28.9 茶多酚0.5 g/L 80.2 0.2 5.2 14.5 表 3 EGCG与α-淀粉酶之间的分子作用力类型
Table 3 Methods of molecular force between α-amylase and EGCG
成键原子 成键类型 A:HIS305:HD1 - EGCG:O1 氢键 EGCG:H43 - A:GLU233:OE2 氢键 EGCG:H44 - A:ASP197:OD1 氢键 EGCG:H44 - A:GLU233:OE1 氢键 EGCG:H45 - A:HIS299:NE2 氢键 EGCG:H48 - A:GLY306:O 氢键 A:TRP59 - EGCG 疏水相互作用 A:TRP59 - EGCG 疏水相互作用 EGCG - A:ALA307 疏水相互作用 A:ASP300:OD1 - EGCG 静电作用力 -
[1] World Health Organization. World health statistics 2021: Monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals[EB/OL]. Geneva: WHO, 2021. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027053
[2] International Diabetes Federation. IDF DIABETES ATLAS Ninth edition 2019[EB/OL]. IDF, 2019. https://diabetesatlas.org/en/
[3] KAWAMURA-KONISHI Y, WATANABE N, SAITO M, et al. Isolation of a new phlorotannin, a potent inhibitor of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes, from the brown alga sargassum patens[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(22):5565−5570. doi: 10.1021/jf300165j
[4] GONG T, YANG X, BAI F T, et al. Young apple polyphenols as natural α-glucosidase inhibitors: In vitro and in silico studies[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2020,96:103625. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103625
[5] ETXEBERRIA U, DE LA GARZA A L, CAMPIN J, et al. Antidiabetic effects of natural plant extracts via inhibition of carbohydrate hydrolysis enzymes with emphasis on pancreatic alpha amylase[J]. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets,2012,16(3):269−297. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.664134
[6] 霍梦恩, 李冬利, 罗小燕, 等. 陈年乌龙茶的生化成分及其降脂降糖活性研究[J]. 茶叶通讯, 2019, 46(4): 472−478. HUO M E, LI D L, LUO X Y, et al. Study on the biochemical composition of aged oolong teas and its hpyerglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in vitro[J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2019, 46(4): 472−478.
[7] 孙世利, 郭芸彤, 陈海强, 等. 英红九号六大茶类生化成分分析及体外活性评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(9):159−165. [SUN S L, GUO Y T, CHEN H Q, et al. Analysis of biochemical components and evaluation of the in vitro activity of six categories of tea made of yinghong NO. 9[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(9):159−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.09.030 [8] LI X P, LI S Y, CHEN M, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits starch digestion and improves glucose homeostasis through direct or indirect activation of PXR/CAR-mediated phase II metabolism in diabetic mice[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(9):4651−4663.
[9] HE Q, LV Y P, YAO K. Effects of tea polyphenols on the activities of α-amylase, pepsin, trypsin and lipase[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,101(3):1178−1182. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.03.020
[10] 高浩祥, 陈南, 徐乾达, 等. 茶多酚在油炸过程中对马铃薯片品质及其贮藏稳定性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(9): 20−25, 33. GAO H X, CHEN N, XU Q D, et al. Effect of tea polyphenols on the quality and storage stability of potato chips during frying[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(9): 20−25, 33.
[11] 王鑫, 王峙力, 谢静南, 等. 甜玉米芯多糖对 α-淀粉酶抑制作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(10):48−54. [WANG X, WANG Z L, XIE J N, et al. Inhibition of polysaccharide on α-amylase from sweet corncob[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(10):48−54. [12] 王俊丽, 聂国兴, 曹香林, 等. 不同 DNS试剂测定木糖含量的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2010,31(7):1−4. [WANG J L, NIE G X, CAO X L, et al. Effects of different DNS reagents in determination of xylose content[J]. Food Research and Development,2010,31(7):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2010.07.001 [13] 姚林锋, 何强. 单宁酸与胰α-淀粉酶作用特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2014, 35(3): 63−66. YAO L F, HE Q. Interaction between tannic acid and pancreatic a-amylase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(3): 63−66.
[14] 范志飞, 曾维才, 戴吉领, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与猪胰脂肪酶的相互作用[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(7):20−23. [FAN Z F, ZENG W C, DAI J L, et al. Interaction of epigallocatechin-3-gallate with porcine pancreas lipase[J]. Food Science,2013,34(7):20−23. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201307005 [15] 徐冬兰, 王晴川, 曾晓雄, 等. 苦丁冬青苦丁茶咖啡酰奎尼酸类物质与α-淀粉酶的相互作用特性[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(13):6−12. [XU D L, WANG Q C, ZENG X X, et al. Interaction properties of caffeoylquinic acid derivatives from Ilex kudingcha C. J. Tseng with α-amylase[J]. Food Science,2016,37(13):6−12. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201613002 [16] CER R Z, MUDUNURI U, STEPHENS R, et al. IC50-to-Ki: A web-based tool for converting IC50 to Ki values for inhibitors of enzyme activity and ligand binding[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2009,37:441−445. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn931
[17] EISENTHAL R, CORNISH-BOWDEN A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters[J]. The Biochemical Journal,1974,139(3):715−720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715
[18] SUN L J, WARREN F J, NETZEL G, et al. 3 or 3′-Galloyl substitution plays an important role in association of catechins and theaflavins with porcine pancreatic α-amylase: The kinetics of inhibition of α-amylase by tea polyphenols[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,26:144−156. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.07.012
[19] 王守业, 徐小龙, 刘清亮, 等. 荧光光谱在蛋白质分子构象研究中的应用[J]. 化学进展, 2001, 13(4): 257−260. WANG S Y, XU X L, LIU Q L, et al. The application of fluorescence spectroscopy in the study on protein conformation[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2001, 13(4): 257−260.
[20] BUISSON G, DUÉE E, HASER R, et al. Three dimensional structure of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase at 2.9 A resolution. Role of calcium in structure and activity[J]. EMBO Journal,1987,6(13):3909−3916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02731.x
[21] SUN L J, WARREN F J, GIDLEY M J, et al. Mechanism of binding interactions between young apple polyphenols and porcine pancreatic α-amylase[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,283:468−474. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.087
[22] 王公轲, 席辉, 田芳, 等. 光谱和分子模拟法研究乙硫异烟胺与木瓜蛋白酶的分子作用机制[J]. 化学学报,2011,69(1):95−100. [WANG G K, XI H, TIAN F, et al. Mechanism of molecular interaction between ethionamide and papain: Spectroscopic and molecular simulation investigations[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,2011,69(1):95−100. [23] LAKOWIZ J R. Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy[M]. 3th ed. Boston: Springer, 2006: 284.
[24] 张莉, 刘倩倩, 吴长玲, 等. 多酚与蛋白质相互作用研究方法进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(24):340−345. [ZHANG L, LIU Q Q, WU C L, et al. Progress research methods for the interaction between polyphenols and proteins[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(24):340−345. [25] GAO M R, XU Q D, ZENG W C. Effect of tea polyphenols on the tenderness of yak meat[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2020,44(5):14433.
[26] CAI X, YU J N, XU L M, et al. The mechanism study in the interactions of sorghum procyanidins trimer with porcine pancreatic α-amylase[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,174:291−298. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.131
[27] MACGREGOR E A, JANECEK S, SVENSSON B. Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α-amylase family of enzymes[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta,2001,1546(1):1−20. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(00)00302-2
[28] PIPARO E L, SCHEIB H, FREI N, et al. Flavonoids for controlling starch digestion: Structural requirements for inhibiting human α-amylase[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2008,51(12):3555−3561. doi: 10.1021/jm800115x
[29] CAO J W, ZHANG Y, HAN L, et al. Number of galloyl moieties and molecular flexibility are both important in alpha-amylase inhibition by galloyl-based polyphenols[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(5):3838−3850.
[30] 王静, 刁翠茹, 王华丽, 等. 鼠尾草酸对α-淀粉酶的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(3):12−17. [WANG J, DIAO C R, WANG H L, et al. Inhibitory mechanism of carnosic acid on alpha-amylase[J]. Food Science,2020,41(3):12−17. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181211-137 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李亚俐,王雪莉,石柳,吴文锦,陈胜,陈朗,郭晓嘉,熊光权,汪兰,孙智达. 壳聚糖-绿原酸复合保鲜剂对冷藏鮰鱼片食用品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2025(01): 42-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 武玫怡,焦文娟,赵甜甜,刘俊,周芳,刘伟峰,张业辉,南海军,陈晓瑛,黄利华. 高静水压与水煮处理对热带海参品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2025(01): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 崔燕,刘韩欣,朱麟,尚海涛,林旭东,陈曙颖,宣晓婷. 超高压杀菌对大黄鱼理化性质及滋味、风味的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 44-55 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



