Mechanism of Astragalus-Ligustrum lucidum in the Treatment of Immunodeficiency Diseases Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
-
摘要: 本文利用网络药理学和分子对接技术探索黄芪-女贞子治疗免疫缺陷病(IDD)的作用机制。综合利用TCMSP、Swiss Tagert Prediction和Genecards等在线数据库搜集黄芪-女贞子化学成分及治疗IDD靶点,构建黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的“化合物-靶点-疾病”和蛋白互作网络;基于DAVID数据库及ClueGo插件进行潜在靶点的基因本体(GO)注释及KEGG通路富集分析;采用Vina软件对活性成分与潜在靶点进行分子对接验证结合活性。网络分析获得黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的31个活性成分和81个靶点;GO功能富集分析表明黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD可能涉及MAP激酶活性的正向调节等152条生物过程和α-β T细胞活化等23个免疫系统过程,KEGG通路结果显示参与癌症途径、前列腺癌等91条KEGG通路;分子对接结果显示山奈酚等成分与MAPK1等蛋白结合稳定。黄芪-女贞子通过多种活性成分协同作用于不同靶点、多种途径发挥辅助治疗IDD的作用,可为开发成对应的膳食补充剂提供参考。Abstract: The network pharmacology and molecular docking technology were applied to explore the mechanism of trratment Immunodeficiency Diseases (IDD) of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum. Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP), Swiss Tagert Prediction, Genecards and other online databases were used to select the active compounds and potential targets of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum, and build the compound-target-disease network and protein-protein interaction network. The enrichment of gene ontology (GO) function analysis by DAVID and ClueGo and the pathway enrichment analysis by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) were carried out. Finally, molecular docking studies were carried out to verify the binding of core components and targets. A total of 31 active components and 81 targets of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum in the treatment of IDD were obtained by network analysis. The results of GO function enrichment analysis showed that the treatment of Astragalus-Ligustrum lucidum may involved 152 biological processes such as the positive regulation of MAP kinase activity and 23 immune system processes such as α-β T cell activation. The results of KEGG pathway showed that it were 91 KEGG pathways involved in cancer pathways and prostate cancer. The results of molecular docking showed that kaempferol had good binding activity to MAPK1
and other proteins. The molecular mechanism of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum in the treatment of IDD indicated the synergistic features of multi-component, multi-target, and multi-pathway, which provided reference for the development of dietary supplements. -
Keywords:
- network pharmacology /
- Astragalus /
- Ligustrum lucidum /
- immunodeficiency /
- molecular docking
-
免疫缺陷病(Immunodeficiency Disease, IDD)是由遗传或者后天因素造成免疫系统受损,表现为免疫力低下,可使患者发生感染、肿瘤等恶性疾病的几率大大增加。由遗传因素引发的称为原发性免疫缺陷病,主要由基因突变引发,包含STAT1、RAC2、IL6R等400 多种基因缺陷或突变[1]。获得性免疫缺陷病多由病毒、恶性肿瘤、感染等后天性因素导致免疫功能出现暂时或永久性的损伤,如艾滋病。目前,针对免疫缺陷的治疗手段如干细胞移植、免疫球蛋白替代疗法以及抗病毒疗法等可提高患者生存率,但治疗费用昂贵,且相关技术手段不够成熟[2-3]。
黄芪和女贞子既是传统中医药又均被卫生部列入保健食品目录,因具有良好的补益作用和丰富的营养价值,民间将其作为药膳来应用,可用于治疗免疫力低下,促进正常免疫功能的恢复,辅助治疗由肿瘤或其他疾病引起的虚损[4-5]。有研究指出黄芪-女贞子联合高效抗逆转录疗法能更好地帮助艾滋病患者的免疫系统重建,能够提高T细胞免疫水平,起到增强疗效的作用,并可降低患者的骨髓抑制发生率[6-7]。黄芪-女贞子含有的黄酮、多糖、皂苷、三萜、环烯醚萜等活性成分,对免疫系统有诸多调节功能,能够增强体液免疫和细胞免疫等能力[8-9],在治疗IDD上具有很大的潜力,但黄芪、女贞子治疗IDD的具体机制尚未明确。
网络药理学结合计算机分析、生物信息学等多学科,通过构建网络分析各种化合物与网络中关键节点之间的关系以此显示中药的物质基础和作用机制,其整体性和系统性与中药多个成分作用不同靶点特点基本吻合[10-11]。本研究拟通过网络药理学筛选黄芪-女贞子干预IDD的潜在成分和作用靶点,分析潜在靶点参与的生物过程和通路,来解释黄芪-女贞子辅助治疗IDD的作用机制。为开发IDD患者膳食补充剂提供理论依据。
1. 研究方法
1.1 黄芪-女贞子活性成分筛选
在中药系统药理数据库及分析平台TCMSP数据库[12]中搜集黄芪-女贞子中化学成分,以OB≥30%,DL≥0.18(OB:口服生物利用度,DL:类药性)作为标准来搜集活性化合物,同时查找相关文献对没入选但有相关活性研究的成分进行补充,以此建立黄芪-女贞子活性成分数据库。
1.2 活性成分靶点预测及疾病靶点搜集
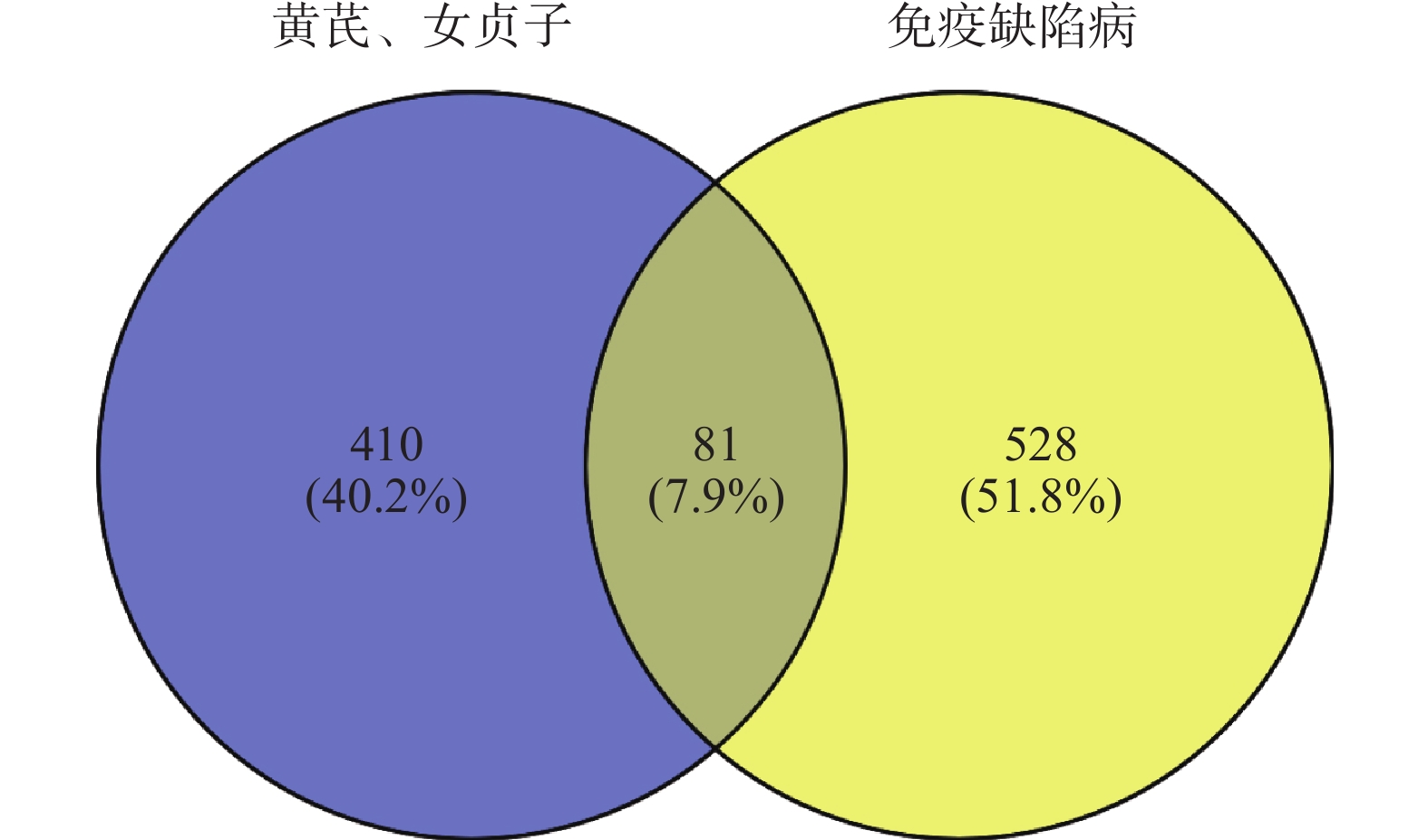
各个活性成分.mol2格式文件来源于TCMSP数据库,然后转化为SMILES文件,TCMSP数据库未检索到的化合物到PubChem数据库下载SDF文件,再在Swiss Tagert Prediction数据库[13]上传各活性成分SMILES或SDF文件预测各化合物靶点(Probability>0),并以此建立黄芪-女贞子的活性成分靶点文件,在GeneCards数据库查找“Immunodeficiency disease”搜集相关靶点(Relevance score>20)。将活性成分预测靶点与疾病靶点绘制韦恩图取交集为黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的潜在靶点。
1.3 “活性成分-靶点-疾病”网络图的构建
获取来的活性成分、潜在靶点和疾病靶点信息借助Cytoscape_v3.7.1将三者之间的关系构建成网络图来阐述黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的有效机制。
1.4 蛋白互作(PPI)网络构建
在STRING数据库中检索黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD 的潜在81 个靶点,设置目标为智人(Homo sapiens),选择置信度“evidence”,相互作用评分大于0.9,隐藏游离节点,找到TSV文件并下载,用Cytoscape_v3.7.1打开进行拓扑学分析。
1.5 GO和KEGG富集分析
基于DAVID 6.8平台进行交集基因的GO和KEGG通路富集分析,GO分析包括生物过程、分子功能和细胞组分(BP、MF、CC),全部选择P值<0.05和FDR<0.05的条目,得到潜在靶点参与的过程和作用通路,并根据P值排序选取靠前条目利用微生信平台[10]进行柱状图和气泡图可视化绘制。利用Cytoscape_v3.7.1的ClueGo和Cluepedia的插件对交集靶基因分析GO免疫系统过程,选择使用GO术语融合和限制P值≤0.05,设置Level最小为4最大为7、最小富集基因数为3、Kappa Score为0.4,并构建靶点-免疫过程网络图。
1.6 分子对接
取PPI网络中Degree(度)值排名前5作为受体蛋白,“活性成分-靶点-疾病”网络中活性成分节点度值排名靠前作为配体分子,登录PDB数据库[14]下载受体蛋白结构,利用PyMOL-2.3.4及AutoDockTools软件对蛋白和配体分子进行前处理,然后引用Vina进行分子对接预测配体小分子与蛋白结合能,选择最低结合能为最优构象。将受体配体对接文件经PyMOL处理后上传至Plip在线网站将验证结果进行可视化。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 药物化学成分筛选
在TCMSP数据库中黄芪(HQ)检索到20种化合物,女贞子(NZZ)检索到13种化合物,两味药共检索到31 种化合物,包括白桦脂酸、华良姜素、常春藤皂苷元等,其中,槲皮素(A1)和山奈酚(A2)为两味药共有成分,同时查找文献发现黄芪中黄芪多糖、黄芪总皂苷以及女贞子中的齐墩果酸、熊果酸、红景天苷对免疫有调节作用[9, 15-16],故将以上成分补充共计36 种成分建立黄芪-女贞子活性成分数据集,见表1。
表 1 黄芪-女贞子活性成分信息Table 1. Information on active components of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum编号 MOL ID 中文名 OB(%) DL 分子式 HQ1 MOL000211 白桦脂酸 55.38 0.78 C30H48O3 HQ2 MOL000239 华良姜素 50.83 0.29 C17H14O6 HQ3 MOL000296 常春藤皂苷元 36.91 0.75 C29H50O HQ4 MOL000033 36.23 0.78 C30H52O HQ5 MOL000354 异鼠李素 49.6 0.31 C16H12O7 HQ6 MOL000371 53.74 0.48 C18H1805 HQ7 MOL000374 41.72 0.69 C29H38O16 HQ8 MOL000378 鼠李素 74.69 0.3 C16H12O7 HQ9 MOL000379 黄芪异黄烷苷 36.74 0.92 C23H26O10 HQ10 MOL000380 美迪紫檀素 64.26 0.42 C17H16O5 HQ11 MOL000387 联苯双酯 31.1 0.67 C20H18O10 HQ12 MOL000392 刺芒柄花素 69.67 0.21 C16H12O4 HQ13 MOL000398 109.99 0.3 C17H16O6 HQ14 MOL000417 毛蕊异黄酮 47.75 0.24 C16H12O5 HQ15 MOL000433 叶酸 68.96 0.71 C19H19N7O6 HQ16 MOL000438 异琥珀酰氨醇 67.67 0.26 C17H18O5 HQ17 MOL000439 49.28 0.62 C29H38O15 HQ18 MOL000442 39.05 0.48 C17H14O6 HQ19 黄芪多糖[15] C10H7ClN2O2S HQ20 黄芪总皂苷[16] C28H32O17 NZZ1 MOL000358 beta-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 C29H50O NZZ2 MOL004576 花旗松素 57.84 0.27 C15H12O7 NZZ3 MOL005146 女贞果苷D 48.87 0.71 C27H36O13 NZZ4 MOL005147 女贞果苷D(苷元) 54.41 0.47 C21H26O8 NZZ5 MOL005169 40.23 0.82 C32H54O3 NZZ6 MOL005190 圣草酚 71.79 0.24 C15H12O6 NZZ7 MOL005195 83.12 0.8 C22H26O10 NZZ8 MOL005209 光泽乌头碱 30.11 0.75 C24H35NO4 NZZ9 MOL005211 长蒴黄麻甙 65.45 0.23 C35H52O14 NZZ10 MOL005212 长蒴黄麻甙(苷元) 103.23 0.78 C23H32O6 NZZ11 MOL000006 木犀草素 36.16 0.25 C15H10O6 NZZ12 齐墩果酸[9] C30H48O3 NZZ13 红景天苷[9] C14H20O7 NZZ14 熊果酸[9] C30H48O3 A1 MOL000098 槲皮素 46.43 0.28 C15H10O7 A2 MOL000422 山奈酚 41.88 0.24 C15H10O6 注:HQ1-HQ20代表黄芪成分,NZZ1-NZZ14代表女贞子成分,A1、A2为共同成分。 2.2 活性成分靶点和疾病靶点
Swiss Tagert Prediction平台得到黄芪22个成分对应429个靶点,女贞子16个成分对应491个靶点,将黄芪、女贞子对应靶点合并删除重复值共得到有效靶点491个,在GeneCards数据库得到免疫缺陷病相关靶点共609个,与黄芪-女贞子预测靶点共有靶点81个包括TNF和ADA等,见图1和表2。
表 2 黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD潜在靶点Table 2. Potential target of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum in the treatment of IDD靶点名称 Uniprot ID 靶点名称 Uniprot ID 靶点名称 Uniprot ID TNF P01375 SRC P12931 ERBB2 P04626 ADA P00813 PPARG P37231 MAPT P10636 JAK3 P52333 TTR P02766 CASP3 P42574 STAT3 P40763 VCP P55072 MMP1 P03956 PTPRC P08575 APP P05067 IGF1 R P08069 AKT1 P31749 PRF1 P14222 RAF1 P04049 PIK3R1 P27986 LRRK2 Q5S007 MMP 3P08254 SNCA P37840 CCND1 P24385 FLT3 P36888 GBA P04062 COMT P21964 ABL 1P00519 LCK P06239 MME P08473 ADAM17 P78536 PIK3CD O00329 AR P10275 PRKCD Q05655 RET P07949 CTSD P07339 BRAF P15056 TERT O14746 BCL2 P10415 CHEK2 O96017 MPO P05164 PTPN1 1 Q06124 MMP9 P14780 CFTR P13569 SERPINE1 P05121 PLG P00747 IL2 P60568 ABCB1 P08183 RORC P51449 HRAS P01112 EP300 Q09472 SHH Q15465 PNP P00491 CD81 P60033 TYR P14679 CASP8 Q14790 NR3C1 P04150 ESR2 Q92731 MAPK1 P28482 NOS2 P35228 ALK Q9UM73 G6PD P11413 MDM2 Q00987 CDK 4P11802 KIT P10721 SRC P12931 ALOX5 P09917 PIK3CA P42336 PPARG P37231 F2 P00734 MTOR P42345 TTR P02766 JUN P05412 ESR1 P03372 VCP P55072 TLR9 Q9NR96 EGFR P00533 APP P05067 MIF P14174 ELANE P08246 PRF1 P14222 VDR P11473 2.3 “活性成分-潜在靶点-疾病”网络关系图
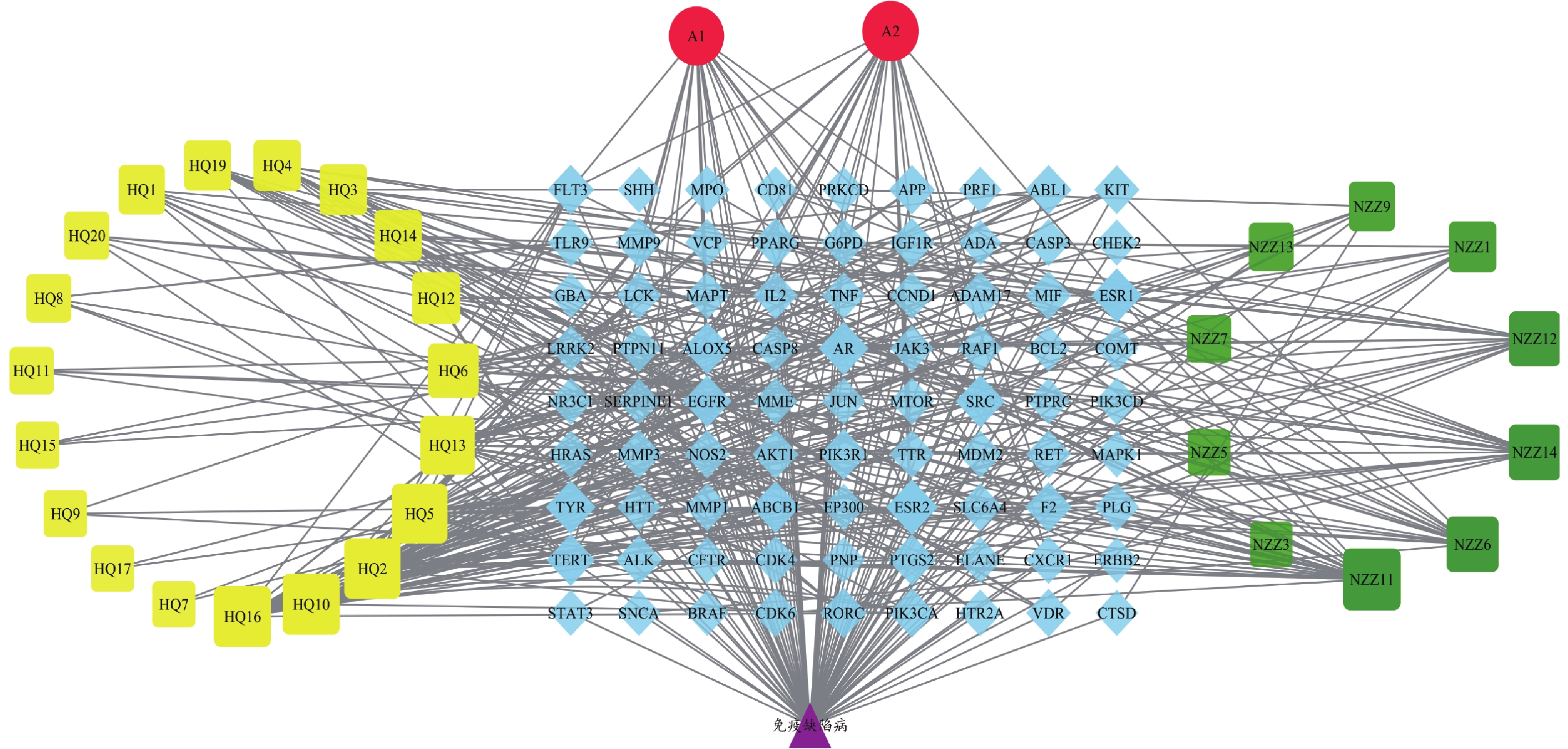
利用Cytoscape_v3.7.1软件绘制黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的“活性成分-靶点-疾病”网络图(如图2)。网络图共涉及Nodes(节点)113个,Edges(边)428条。图中黄色方块代表黄芪活性成分,绿色方块代表女贞子活性成分,红色圆圈代表黄芪-女贞子共有成分,蓝色菱形代表药物干预疾病潜在靶点,紫色三角代表疾病,以degree值大小设置节点面积大小并按大小顺序进行排列筛选,排名前5的活性成分为NZZ11(木犀草素)、HQ16(异琥珀酰氨醇)、HQ10(美迪紫檀素)、HQ2(华良姜素)和A2(山奈酚),推测这些化合物可能是黄芪-女贞子治疗免疫缺陷病的主要活性成分。
从网络图中可以预测黄芪-女贞子36个成分中共有31个活性成分可作用于IDD,另外5种成分没有对应IDD靶点,其中,多数成分在已有研究中具有良好的免疫调节作用。如槲皮素除了可以增强环磷酰胺(CTX)的抗肿瘤作用,还可以提高免疫缺陷小鼠的外周血白细胞数目和巨噬细胞吞噬作用,促进T细胞、B细胞增殖来修复CTX所造成的免疫抑制[17-18];山奈酚可以抑制小鼠淋巴细胞凋亡和活化的促炎因子,提高淋巴细胞活力,增加抗炎细胞因子和CD4+T水平(T淋巴细胞)来提高免疫力[19-20];红景天苷可以促进小鼠T/B淋巴细胞增值率,从而提高免疫功能[21],可以增加宿主RIG-I
等天然免疫因子,提高宿主免疫力,同时可激活IRF-3基因,增加Ⅰ型干扰素的表达以发挥其抗病毒作用[22];季宇彬等[23]研究发现肿瘤模型小鼠经黄芪多糖给药后可有助于其改善红细胞生理功能,增强红细胞CR1免疫活性、恢复免疫功能;圣草酚具有一定的抗氧化活性,可以增强NK细胞、T淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞的杀伤活性发挥免疫调节作用[24]。IDD患者免疫系统受损,而这些活性物质可以增强B细胞、巨噬细胞等免疫细胞活性,推测黄芪-女贞子可通过激活免疫系统来干预IDD。异鼠李素可抑制金黄色葡萄球菌的α溶血素表达而产生一定的抑菌作用[25];木犀草素可降低IL-6 和TNF-α的表达来降低大肠埃希菌对呼吸道上皮细胞的感染,还可以影响一些参与自噬的信号分子以阻止癌症的发展,如促进Beclin-1的表达刺激细胞自噬来诱导肝癌细胞死亡[26-27]。IDD患者由于免疫屏障被破坏从而会引发恶性肿瘤、感染、自身免疫性疾病等复杂性疾病,如上述,不同有效活性成分具有不同药理作用,不仅能够调节免疫系统,还有抑制肿瘤、抗感染等作用,体现了中药干预疾病发展的整体性和综合性。 2.4 PPI网络构建
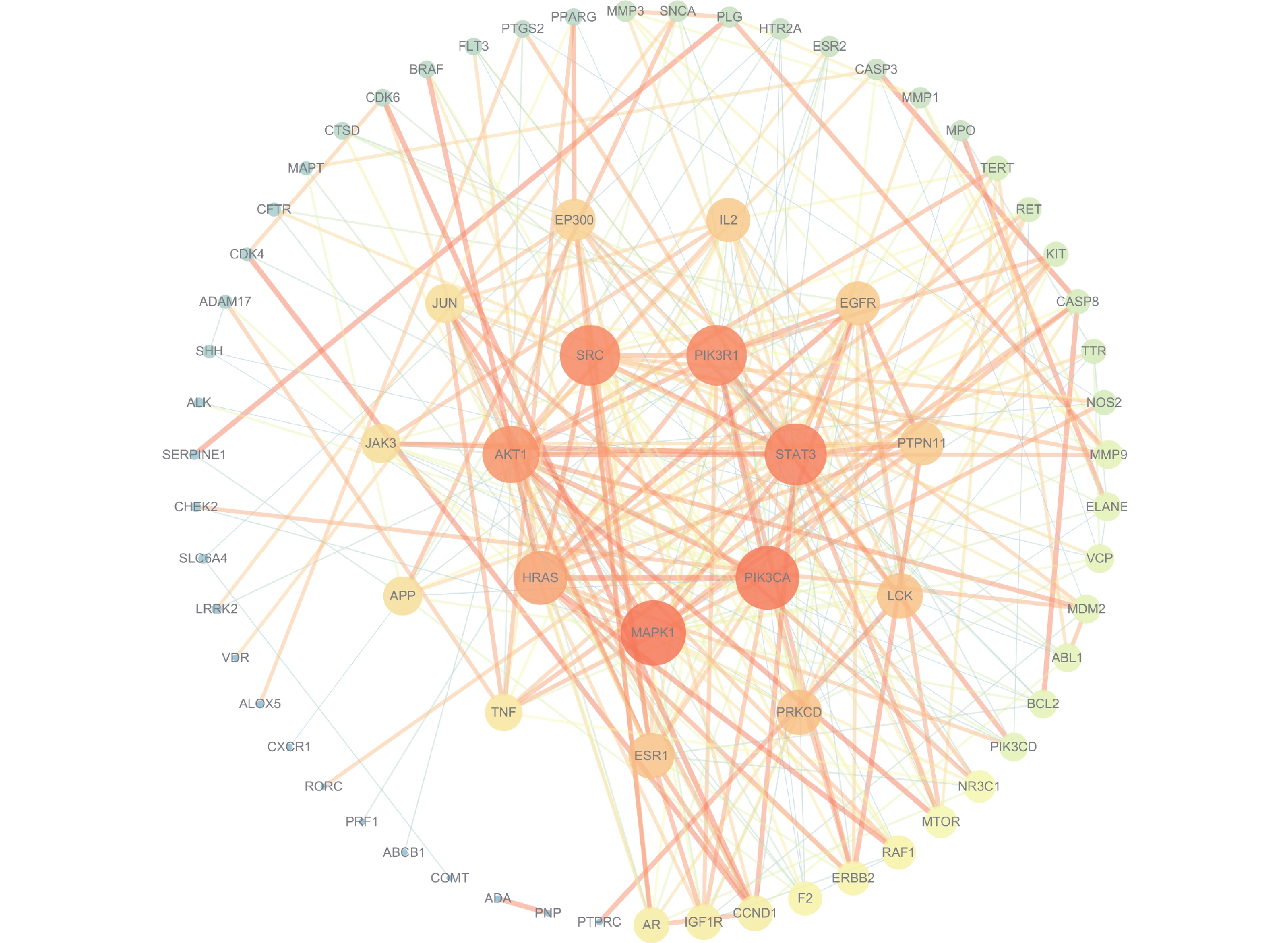
将STRING数据库中检索到的81个潜在靶点绘制成PPI网络图(如图3),该网络图包含73个节点和293条边,平均节点度值为8,有8个游离节点被隐藏。圆形节点大小表示度(degree)值,连线粗细和颜色深浅表示结合分数,度值越大表示该靶点越关键,根据PPI网络图分析可知,MAPK1
、PIK3CA、STAT3、PIK3R1、SRC、AKT1、HRAS等靶点可能是黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的关键靶点。 IDD的主要原因在于免疫系统遭到破坏从而导致系统疾病,因此,治疗IDD的重点在于帮助患者免疫重建,同时对于由免疫缺陷而引发的病症也进行对症治疗,如炎症、肿瘤等[2]。信号传导与转录激活因子-3(STAT3)是细胞存活和凋亡的关键调节因子,其可参与IL-6信号通道和诱导IL-17A、IL23受体、干扰素调节因子4等与Th-17细胞分化和增殖等相关基因的表达,STAT3的过度激活会影响T细胞发育造成免疫抑制,影响促炎介质的产生和抑制抗原呈现从而降低免疫细胞的抗肿瘤作用[28-29],同时STAT3
突变也会导致IDD的发生[30],SRC家族激酶是非受体酪氨酸激酶,包含Lck、Fyn、Lyn等具有相似结构功能的成员,在免疫应答等生理过程有重要作用[31],相关研究指出SRC 家族激酶作为一个整体参与了人外周血T细胞抗原受体的下调,抑制Lck和Fyn的表达会损伤T细胞的激活和效应功能[32]。 AKT1参与调节细胞功能,JIA等[33]发现AKT1参与抑制HIF-α依赖的糖酵解途径来调节髓源性抑制细胞的免疫抑制活性,对炎症损伤有保护作用。这些靶点主要涉及免疫细胞增殖分化和炎症反应的调控,推测黄芪-女贞子活性成分通过作用于这些靶点来减轻免疫抑制,促进免疫细胞发育,以及抗肿瘤从而综合干预IDD。 2.5 GO富集分析和KEGG富集分析
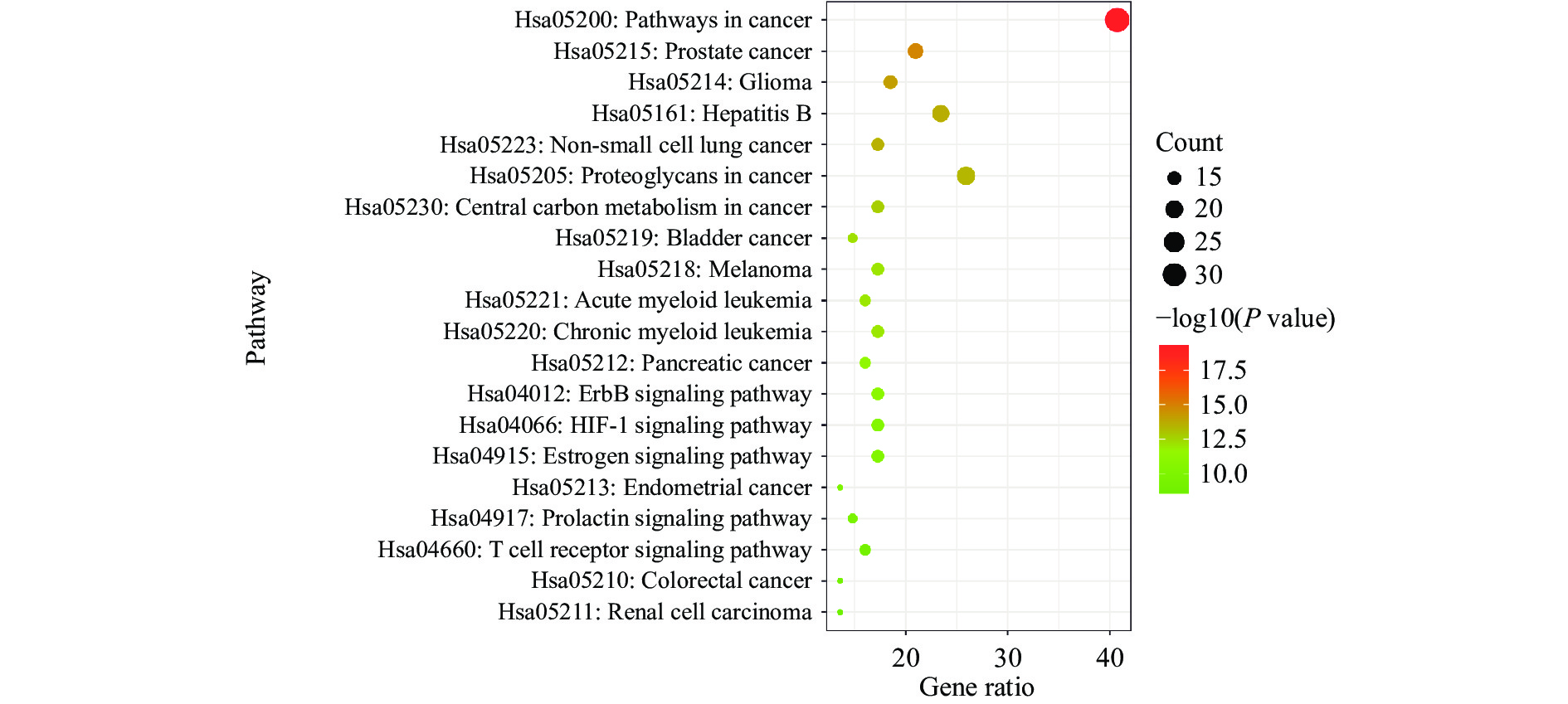
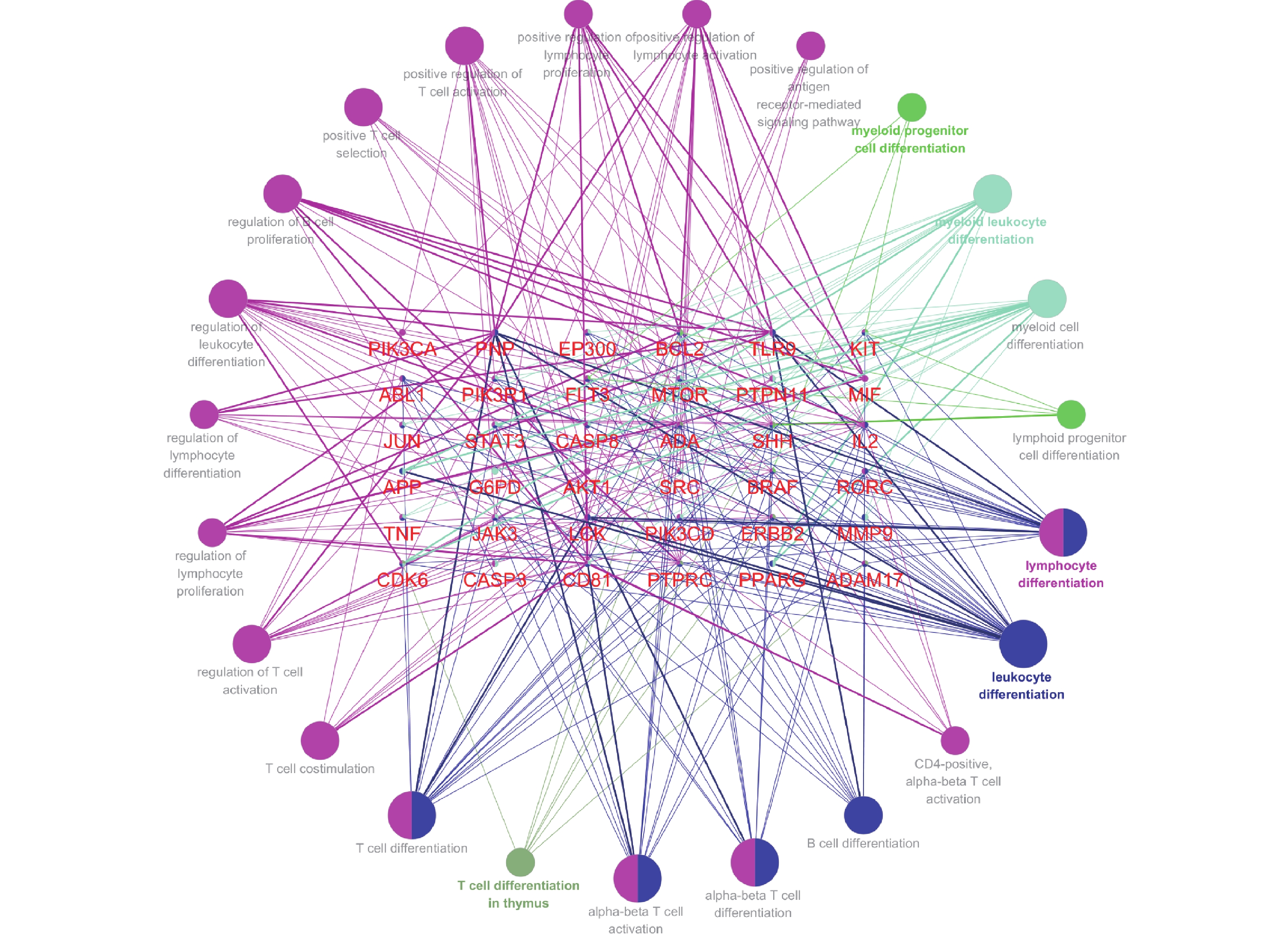
DAVID 6.8平台中通过选择“Homo sapiens”限制P值<0.05和FDR<0.05得到81个交集基因涉及152条生物过程(Biological Process,BP),33条细胞组分(Cellular Component,CC),40条分子功能(Molecular Function,MF)。根据P值从小到大筛选BP、CC和MF排名前十绘制柱状图(如图4)。生物过程主要涉及药物反应,MAP激酶活性的正向调节和蛋白质磷酸化的正向调节等;细胞组分中主要影响细胞溶质、质膜、膜筏等;分子功能包括相同蛋白结合、不同蛋白结合、酶结合等。KEGG富集分析结果显示81个交集基因涉及91条KEGG通路,同样根据P值排序靠前的有Pathways in cancer、Prostate cancer、Glioma和Hepatitis B等通路 (如图5)。此外,将黄芪-女贞子干预免疫缺陷病81个潜在靶点基因导入ClueGo插件进行GO免疫系统过程分析,得到36个靶点共涉及到α-β T细胞活化等23条免疫系统过程,见图6。图中方形排列代表黄芪-女贞子干预IDD的相关靶点,外圈圆形排列代表免疫系统过程。
GO富集分析表明黄芪-女贞子干预IDD涉及到药物反应,MAP激酶活性的正向调节等生物过程,α-β T细胞活化、α-β T细胞分化等免疫系统过程,MAP激酶参与细胞生长、凋亡等一系列生理活动,如岩白菜素可以刺激巨噬细胞MAP激酶激活产生抗分岐杆菌效应分子从而给宿主提供免疫保护[34];KEGG富集分析显示癌症途径、癌症中的蛋白质、乙肝、ErbB信号通路、HIF-1信号等通路可能是黄芪-女贞子干预免疫缺陷病的关键通路。有研究表明下调HIF-1信号通路可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖分化[35],邓哲[36]发现薯蓣丸可通过HIF-1α信号通路增加肿瘤淋巴细胞CD8和CD4表达来杀死癌细胞。GO免疫系统过程分析结果显示黄芪-女贞子可通过参与α-β T细胞活化等过程调节免疫系统。本研究推测黄芪-女贞子参与多个生物过程和免疫过程,通过免疫和癌症相关通路综合作用于免疫缺陷病。
2.6 分子对接验证
为了验证黄芪-女贞子活性成分对其干预疾病潜在靶点作用的可能性,选取了MAPK1、PIK3CA、STAT3、PIK3C1和SRC作为受体(PPI网络图节点排名前五),在PDB数据库下载受体蛋白晶体文件:MAPK1(PDB ID:4zxt)、PIK3CA(PDB ID:6pys)、STAT3(PDB ID:6njs)、PIK3C1(PDB ID:5sxb)和SRC(PDB ID:2bdj),根据受体蛋白原配体确定对接口袋,和图2中度值排名前5的活性成分(NZZ11、HQ10、HQ16、HQ2、A2)在Vina软件中进行25次分子对接预测了靶点与成分之间的结合能(kcal/mol),见图7。
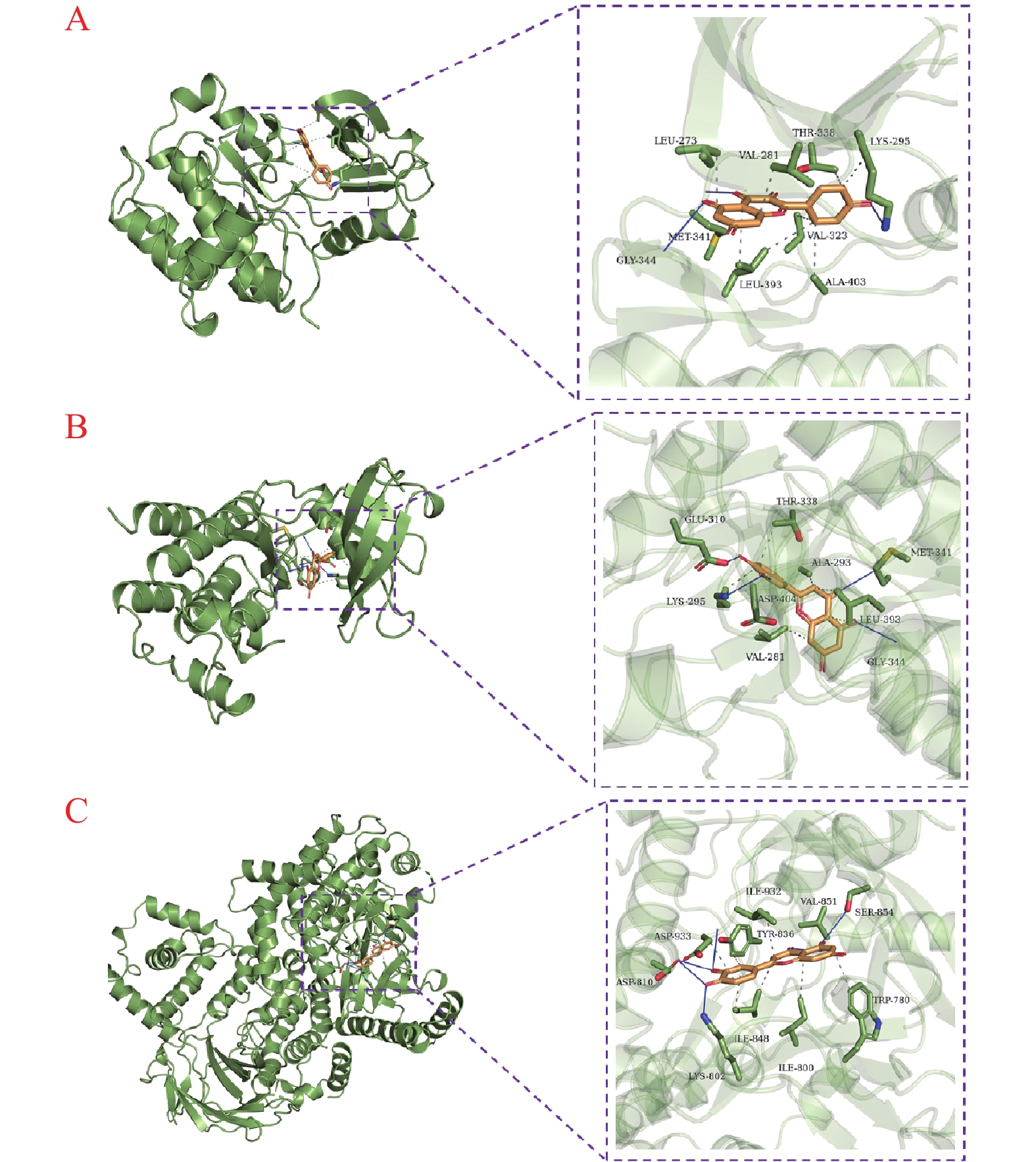
一般认为配体和受体结合能为负数就表示它们之间可以结合,结合能越小,其对接活性越大,发生作用的可能性越大,结合能小于-5 kcal/mol就代表两者之间有良好的结合性。对接结果显示A2(山奈酚)与SRC(2bdj)结合能最低,为−9.6 Kcal/mol,其次是NZZ11(木犀草素)与SRC(2bdj),结合能为−9.4 Kcal/mol,NZZ11(木犀草素)与PIK3CA(6pys),结合能为−8.9 Kcal/mol,将它们对接模式进行可视化(如图8)。A2(山奈酚)与SRC蛋白的LEU-273、VAL-281、LYS-295等氨基酸残基形成疏水作用,与LYS-295、MET-341和GLY-344形成氢键,见图8A;NZZ11(木犀草素)与SRC蛋白的VAL-281、ALA-293、LYS-295等氨基酸残基形成疏水作用,与LYS-295、GLU-310、MET-341、GLY-344和ASP-404形成氢键,见图8B;NZZ11(木犀草素)与PIK3CA蛋白的TRP-780、ILE-800、TYR-836等氨基酸残基形成疏水作用,与LYS-802、ASP-810、VAL-851和SER-854氨基酸残基形成氢键作用,见图8C。分子对接结果显示黄芪-女贞子的主要活性成分可以很好地与预测的主要潜在靶点结合在一起,验证了这些成分治疗IDD的可能性。
3. 结论
本研究利用网络药理学相关理论初步研究黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD的活性成分、潜在靶点和作用途径,黄芪-女贞子中木犀草素和槲皮素等活性成分作用于MAPK1、PIK3CA、STAT3等关键靶点,通过免疫和癌症相关通路综合发挥辅助治疗免疫缺陷病的作用。分子对接预测黄芪-女贞子主要活性成分与IDD关键靶点的结合能较低,具有良好的结合活性。黄芪-女贞子不仅能调节免疫系统还有抗感染、抗肿瘤等作用,体现了其在干预免疫缺陷病时具有整体性、系统性特点,和中医在诊治疾病的标本兼顾的思想基本吻合。本文初步解释黄芪-女贞子在免疫缺陷病作用机制,为后续研究提供研究思路和方向,也为将黄芪-女贞子开发成调节免疫缺陷病患者身体机能的膳食补充剂提供参考。
-
表 1 黄芪-女贞子活性成分信息
Table 1 Information on active components of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum
编号 MOL ID 中文名 OB(%) DL 分子式 HQ1 MOL000211 白桦脂酸 55.38 0.78 C30H48O3 HQ2 MOL000239 华良姜素 50.83 0.29 C17H14O6 HQ3 MOL000296 常春藤皂苷元 36.91 0.75 C29H50O HQ4 MOL000033 36.23 0.78 C30H52O HQ5 MOL000354 异鼠李素 49.6 0.31 C16H12O7 HQ6 MOL000371 53.74 0.48 C18H1805 HQ7 MOL000374 41.72 0.69 C29H38O16 HQ8 MOL000378 鼠李素 74.69 0.3 C16H12O7 HQ9 MOL000379 黄芪异黄烷苷 36.74 0.92 C23H26O10 HQ10 MOL000380 美迪紫檀素 64.26 0.42 C17H16O5 HQ11 MOL000387 联苯双酯 31.1 0.67 C20H18O10 HQ12 MOL000392 刺芒柄花素 69.67 0.21 C16H12O4 HQ13 MOL000398 109.99 0.3 C17H16O6 HQ14 MOL000417 毛蕊异黄酮 47.75 0.24 C16H12O5 HQ15 MOL000433 叶酸 68.96 0.71 C19H19N7O6 HQ16 MOL000438 异琥珀酰氨醇 67.67 0.26 C17H18O5 HQ17 MOL000439 49.28 0.62 C29H38O15 HQ18 MOL000442 39.05 0.48 C17H14O6 HQ19 黄芪多糖[15] C10H7ClN2O2S HQ20 黄芪总皂苷[16] C28H32O17 NZZ1 MOL000358 beta-谷甾醇 36.91 0.75 C29H50O NZZ2 MOL004576 花旗松素 57.84 0.27 C15H12O7 NZZ3 MOL005146 女贞果苷D 48.87 0.71 C27H36O13 NZZ4 MOL005147 女贞果苷D(苷元) 54.41 0.47 C21H26O8 NZZ5 MOL005169 40.23 0.82 C32H54O3 NZZ6 MOL005190 圣草酚 71.79 0.24 C15H12O6 NZZ7 MOL005195 83.12 0.8 C22H26O10 NZZ8 MOL005209 光泽乌头碱 30.11 0.75 C24H35NO4 NZZ9 MOL005211 长蒴黄麻甙 65.45 0.23 C35H52O14 NZZ10 MOL005212 长蒴黄麻甙(苷元) 103.23 0.78 C23H32O6 NZZ11 MOL000006 木犀草素 36.16 0.25 C15H10O6 NZZ12 齐墩果酸[9] C30H48O3 NZZ13 红景天苷[9] C14H20O7 NZZ14 熊果酸[9] C30H48O3 A1 MOL000098 槲皮素 46.43 0.28 C15H10O7 A2 MOL000422 山奈酚 41.88 0.24 C15H10O6 注:HQ1-HQ20代表黄芪成分,NZZ1-NZZ14代表女贞子成分,A1、A2为共同成分。 表 2 黄芪-女贞子治疗IDD潜在靶点
Table 2 Potential target of Astragalus and Ligustrum lucidum in the treatment of IDD
靶点名称 Uniprot ID 靶点名称 Uniprot ID 靶点名称 Uniprot ID TNF P01375 SRC P12931 ERBB2 P04626 ADA P00813 PPARG P37231 MAPT P10636 JAK3 P52333 TTR P02766 CASP3 P42574 STAT3 P40763 VCP P55072 MMP1 P03956 PTPRC P08575 APP P05067 IGF1 R P08069 AKT1 P31749 PRF1 P14222 RAF1 P04049 PIK3R1 P27986 LRRK2 Q5S007 MMP 3P08254 SNCA P37840 CCND1 P24385 FLT3 P36888 GBA P04062 COMT P21964 ABL 1P00519 LCK P06239 MME P08473 ADAM17 P78536 PIK3CD O00329 AR P10275 PRKCD Q05655 RET P07949 CTSD P07339 BRAF P15056 TERT O14746 BCL2 P10415 CHEK2 O96017 MPO P05164 PTPN1 1 Q06124 MMP9 P14780 CFTR P13569 SERPINE1 P05121 PLG P00747 IL2 P60568 ABCB1 P08183 RORC P51449 HRAS P01112 EP300 Q09472 SHH Q15465 PNP P00491 CD81 P60033 TYR P14679 CASP8 Q14790 NR3C1 P04150 ESR2 Q92731 MAPK1 P28482 NOS2 P35228 ALK Q9UM73 G6PD P11413 MDM2 Q00987 CDK 4P11802 KIT P10721 SRC P12931 ALOX5 P09917 PIK3CA P42336 PPARG P37231 F2 P00734 MTOR P42345 TTR P02766 JUN P05412 ESR1 P03372 VCP P55072 TLR9 Q9NR96 EGFR P00533 APP P05067 MIF P14174 ELANE P08246 PRF1 P14222 VDR P11473 -
[1] 何庭艳, 赵晓东, 杨军. 原发性免疫缺陷病分类更新(2019版)解读[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2020,58(8):624−627. [HE T Y, ZHAO X D, YANG J. Interpretation of the classification of human inborn errors of immunity (2019 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics,2020,58(8):624−627. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200218-00099 [2] SHAPIRO R S, WASSERMAN R L, BONAGURA V, et al. Emerging paradigm of primary immunodeficiency disease: Individualizing immunoglobulin dose and delivery to enhance outcomes[J]. Journal of Clinical Immunology,2017,37(2):190−196. doi: 10.1007/s10875-014-9990-x
[3] BLANCO E, IZOTOVA N, BOOTH C, et al. Immune reconstitution after gene therapy approaches in patients with X-Linked severe combined immunodeficiency disease[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2020,11:608653. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.608653
[4] 骆紫燕, 卿德刚, 孙宇, 等. 管花肉苁蓉苯乙醇苷的巨噬细胞激活作用及其与当归、黄芪在调节免疫方面的协同作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(21):311−316. [LUO Z Y, QING D G, SUN Y, et al. Activation of macrophage of phenylethanol glycosides extracted from cistanche tubulosa and its synergisticeffect with Angelica sinensis and Astragalus propinquus in regulating immunity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(21):311−316. [5] 高赛. 贞芪扶正胶囊全过程质量控制研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2020. GAO S. Study on quality control of Zhenqi Fuzheng capsules in the whole process[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2020.
[6] 张金松. HIV/AIDS患者线粒体DNA多态性及贞芪扶正颗粒对患者免疫重建影响的研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2017. ZHANG J S. Thestudy on mitochondrial DNA polymorphism of HIV/AIDS patients and effect of Zhenqi Fuzheng granule on immune reconstitution of patients[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2017
[7] 邓昕, 周淑娟, 王丽, 等. 贞芪扶正胶囊联合常规西医对艾滋病患者疗效及对其T细胞免疫的影响[J]. 中国临床医生杂志,2020,48(12):1453−1456. [DENG X, ZHOU S J, WANG L, et al. Effect of Zhenqi Fuzheng capsule combined with conventional western medicine on AIDS patients and T cell immunity[J]. Chinese Clinical Doctor,2020,48(12):1453−1456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2020.12.021 [8] FU J, WANG Z H, HUANG L F, et al. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi)[J]. Phytother Res,2014,28:1275−1283. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5188
[9] LIU J, LIU Z Y, WANG L L, et al. Bioactivity-guided isolation of immunomodulatory compounds from the fruits of Ligustrum lucidum[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,274:114079. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114079
[10] LUO T T, LU Y, YAN S K, et al. Network pharmacology in research of Chinese medicine formula: Methodology, application and prospective[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine,2020,26(1):72−80. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3064-0
[11] DAN W C, LIU J L, GUO X Y, et al. Study on medication rules of traditional Chinese medicine against antineoplastic drug-induced cardiotoxicity based on network pharmacology and data mining[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: ECAM,2020,2020:7498525.
[12] RU J L, LI P, WANG J A, et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. Journal of Cheminformatics,2014,6:13. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
[13] DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. Swiss target prediction: Updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2019,47:W357−W364. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz382
[14] BURLEY S K, BERMAN H M, BHIKADIYA C, et al. Protein data bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1).
[15] 李钦, 胡继宏, 高博, 等. 黄芪多糖在免疫调节方面的最新研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(2):199−206. [LI Q, HU J H, GAO B, et al. Advances on immunoregulation effect of Astragalus polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2017,23(2):199−206. [16] 马园园, 王静, 罗琼, 等. 黄芪总皂苷药理作用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(7):153−157. [MA Y Y, WANG J, LUO Q, et al. Pharmacological effects and research progress of total Astragalus saponins[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,22(7):153−157. [17] QIAO Y, CAO Y, YU K, et al. Preparation and antitumor evaluation of quercetin nanosuspensions with synergistic efficacy and regulating immunity[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020:589.
[18] 田瑞雪, 孙耀宗, 姚有昊, 等. 槲皮素对免疫低下小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国现代医药杂志,2019,21(9):13−16. [TIAN R X, SUN Y Z, YAO Y H, et al. Effect of quercetin on immune function in immunocompromised mice[J]. Modern Medicine Journal of China,2019,21(9):13−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9463.2019.09.004 [19] JIA Z, CHEN A, WANG C, et al. Amelioration effects of kaempferol on immune response following chronic intermittent cold-stress[J]. Research in Veterinary Science,2019,125:390−396. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.08.012
[20] 杨佳. 山奈酚对小鼠淋巴细胞活力与焦亡的影响[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. YANG J. Effects of kaempferol on lymphocytes viability and pyroptosis in mice[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019
[21] 陈伟, 马小琴, 范文玺, 等. 红景天主要成分对小鼠免疫细胞的促增殖转化作用[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2016,33(1):38−42. [CHEN W, MA X Q, FAN W X, et al. Major efficacy component of Rhodiola stimulate proliferation and transformation on mouse immune cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2016,33(1):38−42. [22] NAVITA S, MISHRA K P, LILLY G. Salidroside exhibits anti-dengue virus activity by upregulating host innate immune factors[J]. Archives of Virology,2016,161(12):3331−3344. doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-3034-1
[23] 季宇彬, 汲晨锋. 黄芪多糖对肿瘤模型小鼠红细胞免疫功能的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2013,29(9):2042−2046. [JI Y B, JI C F. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharide on immune function of erythrocyte in tumor model mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(9):2042−2046. [24] MOKDAD-BZEOUICH I, MUSTAPHA N, SASSI A, et al. Investigation of immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of eriodictyol through its cellular anti-oxidant activity[J]. Cell Stress and Chaperones,2016,21(5):773−781. doi: 10.1007/s12192-016-0702-8
[25] 迟戈夫. 异鼠李素抗金黄色葡萄球菌α溶血素和分选酶A作用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016. CHI G F. The inhibitory effect of isorhamnetin on Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin and Sortase A[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
[26] MILAD A, ZAHRAA, TAHEREH F, et al. Autophagy regulation using luteolin: New insight into its anti-tumor activity.[J]. Cancer Cell International,2020,20(1):537−546. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01634-9
[27] 黄志勇, 孙凤军, 袁慊, 等. 木犀草素降低大肠埃希菌对呼吸道上皮细胞感染的作用机制研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2020,40(7):781−785. [HUANG Z Y, SUN F J, YUAN Q, et al. Effect of luteolin on reducing the infection of Escherichia coli in respiratory epithelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2020,40(7):781−785. [28] TOHID G, ZOHREH B, AREZOO H, et al. Targeting STAT3 in cancer and autoimmune diseases.[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2020,878:173107. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173107
[29] ZOU S, TONG Q, LIU B, et al. Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Molecular Cancer,2020,19(1):145−164. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7
[30] 姚安琪, 陈可可, 贺湘玲, 等. 疑难病研究: STAT3基因突变致免疫失调综合征[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志,2021,23(4):397−401. [YAO A Q, CHEN K K, HE X L, et al. Immune dysregulation syndrome caused by STAT3 gene mutation: A complicated case study[J]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics,2021,23(4):397−401. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2012167 [31] 张佳鑫, 蒋一凡, 雷昕诺, 等. Src和Abl酪氨酸蛋白激酶家族参与病原微生物感染的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报,2019,46(10):2781−2786. [ZHANG J X, JIANG Y F, LEI X N, et al. Research advances in Src and Abl tyrosine protein kinase family involved in pathogenic microbial infection[J]. Microbiology China,2019,46(10):2781−2786. [32] DONK L E H, ATES L S, SPEK J, et al. Separate signaling events control TCR downregulation and T cell activation in primary human T cells[J]. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease,2021,9(1):223−238. doi: 10.1002/iid3.383
[33] JIA A, WANG Y X, WANG Y F, et al. The kinase AKT1 potentiates the suppressive functions of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in inflammation and cancer[J]. Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2021,18(4):1074−1076.
[34] DWIVEDI V P, DEBAPRIYA B, VINOD Y, et al. The phytochemical bergenin enhances T Helper 1 responses and anti-mycobacterial immunity by activating theMAP kinase pathway in macrophages[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology,2017,7:149−158. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00149
[35] 周晓霞, 邓洁, 张维, 等. MiR-600通过抑制HIF-1α信号通路降低宫颈癌细胞的增殖能力[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2021,41(2):210−215. [ZHOU X X, DENG J, ZHANG W, et al. MiR-600 suppresses HeLa cell proliferation by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2021,41(2):210−215. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.02.07 [36] 邓哲. 薯蓣丸抑制HIF-1α改善肝癌微环境缺氧与免疫逃逸的机制研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南中医药大学, 2020. DENG Z. Study on the mechanism of Shuyuwan decoction suppressing HIF-1α to improve the microenvironment hypoxia and immune escape of liver cancer[D]. Changsha: Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 佘梦龙,谢恒. 蔬菜食品安全溯源监管体系的完善探讨. 食品安全导刊. 2024(03): 30-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 江晓玲. 食品安全风险溯源技术在食品行业中的应用探索. 现代食品. 2024(10): 16-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卢朝亮. 对“互联网+餐饮”安全监管问题的探讨. 中外食品工业. 2024(22): 23-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张龙梅,伍星华,李思寰,李媛. 区块链+物联网技术在湘西地区农产品溯源中的应用. 经济研究导刊. 2023(10): 42-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马蔷,胡延东,周佳炫,李晶晶,韩阳. 数字夜市CSA营销模式设计研究——基于乡村振兴战略背景下. 北方经贸. 2023(06): 89-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孙传恒,魏玉冉,邢斌,徐大明,李登奎,张航. 基于智能合约和数字签名的马铃薯种薯防窜溯源研究. 农业机械学报. 2023(07): 392-403 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 梅海波,吴江,张惠. 基于区块链技术的采购管理研究. 中国物流与采购. 2023(13): 34-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王丹蕾,王传钊. 基于区块链技术的溯源系统助力农产品实现“真”绿色. 产业创新研究. 2023(18): 79-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 余鲲鹏,李伟,雷鑫. 食品供应链领域企业区块链技术采纳行为整合模型构建研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(21): 61-70 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 李敏. 中餐厅食品安全管理存在的问题与对策研究. 食品安全导刊. 2023(20): 19-21+25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



