Effect of Rosa roxburghii Wine on Lipid Metabolism Disorders in High Fat-induced Obese Mice
-
摘要: 目的:研究刺梨果酒对高脂诱导小鼠肥胖发生过程预防效果及其机理。方法:将50只小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、刺梨果酒低剂量组(0.25 mL/80 g)、中剂量组(0.5 mL/80 g)和高剂量组(1 mL/80 g),每组10只,实验时间8周。实验结束后,测定小鼠脏器指数、血清及肝脏脂代谢相关生理生化指标;应用qRT-PCR测定肝脏过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(Peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-α, PPARα)、固醇调节元件结合蛋白(Sterol-regulatory element binding proteins, SREBP1)、硬脂酰辅酶A去饱和酶(Stearyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase-1, SCD1)、乙酰辅酶A羧化酶(Acetyl-CoA carboxylases alpha, ACACA)、脂肪酸合成酶(Fatty acid synthase, FASN)、肝X受体(Liver X receptor, LXR)、腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase, AMPK)mRNA相对表达量。结果:与模型组相比,刺梨果酒可显著(P<0.05)减缓小鼠体重增加,降低脂肪指数及血清和肝脏中总胆固醇(Total cholesterol, TC)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride, TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(Low density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C)的含量,升高高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(Hight density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C)含量。此外,高剂量组可显著(P<0.05)下调小鼠肝脏中PPARα、AMPK、LXR、ACACA、SCD1、FASN基因表达水平。HE染色结果显示,剂量组能缓解肝细胞肿大,减少肝脏脂肪变性。结论:刺梨果酒对高脂诱导小鼠肥胖具有预防作用,可能与减少体内脂肪堆积,改善脂代谢紊乱有关。Abstract: Objective: To study the preventive effect and its mechanism of Rosa roxburghii wine on obesity process in high fat-induced mice. Method: 50 mice were randomly divided into a blank group, a model group, a low-dose (0.25 mL/80 g), a medium-dose (0.5 mL/80 g) and a high-dose Rosa roxburghii wine group (1 mL/80 g), each group of 10 mice, the experiment was carried out for 8 weeks. After the experiment, the viscera coefficient, serum and liver lipid metabolism-related physiological and biochemical indicators were measured. The mRNA relative expression of PPARα (Peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-α), SREBP1 (Sterol-regulatory element binding proteins), SCD1 (Stearyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase-1), ACACA (Acetyl-CoA carboxylases alpha), FASN (Fatty acid synthase), LXR (Liver X receptor) and AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) were measured by qRT-PCR. Results: Compared with model group, Rosa roxburghii wine could significantly (P<0.05) slow down the weight gain of mice, reduce fat index and total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) content in serum and liver, and increase the content of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). In addition, the high-dose group significantly down-regulated the mRNA relative expressions of PPARα, AMPK, LXR, ACACA, SCD1
and FASN. The HE staining results showed that Rosa roxburghii wine could relieve hepatocellular enlargement and reduce hepatic steatosis. Conclusion: Rosa roxburghii wine has a preventive effect on high-fat-induced obesity in mice, which may be attributed to its ability to reduce fat accumulation and improve lipid metabolism disorders. -
Keywords:
- Rosa roxburghii wine /
- high-fat diet /
- obesity /
- lipid metabolisim
-
肥胖是由多种因素引起的慢性疾病[1]。据国办新闻(2020年)报道,我国居民肥胖已超过50%[2]。研究表明,肥胖可导致高血压、高脂血症、冠心病等多种疾病[3]。肥胖的治疗方式主要有矫正、药物治疗和减肥手术三种,但常伴有严重的副作用[4]。药食同源食品具有保健治疗综合功效,毒副作用甚微,既可调节机体生理活动和预防疾病,也能长期服用,现已被广泛运用于医疗保健及食品行业中[5],研究证明药食同源食品中黄酮、皂苷、多糖、生物碱等有效成分可起到抗肥胖的作用[6-8]。因此,寻求来源于食品或药食同源食品中具有减肥降脂功效的原辅料显得非常必要。刺梨作为我国药食同源水果,富含有机酸、维生素C、超氧化物歧化酶、黄酮、多酚、多糖等多种活性成分,可作为健胃消食功效的中药用于方剂中[9]。迄今,也有多种以刺梨为原料制成的食品、药品,如:刺梨果酒、刺梨茶、刺梨冻干粉胶囊等[10]。其中,刺梨发酵型果酒酒精含量较低,保留了刺梨中维生素、氨基酸和矿物质等营养元素,具有调节人体新陈代谢、控制胆固醇水平及促进血液循环等保健功能[11-13]。
近年来,刺梨在降血糖[14]、血脂[15]、抗癌[16]和抗动脉粥样硬化[17]等方面的研究取得了一定的效果。但目前关于刺梨参与宿主脂质代谢作用机制的报道较少,隋怡等[18]研究发现黔产刺梨果汁具有降低小鼠体质量的作用,黔产刺梨含药血清可诱导PPARα基因表达显著增加,加速脂肪组织分解利用从而达到减肥的目的,但并未深入探究刺梨参与脂质代谢的作用机制。孙兆峰等[19]发现刺梨叶对2型糖尿病大鼠的脂代谢具有一定的治疗作用,但并未深入进行机理研究。夏星等[20]研究发现小鼠服用刺梨提取物后,肝糖原含量会显著增加,但对其作用机理及机体糖原的合成机制并未进行进一步研究。
综上所述,虽已有报道证实刺梨具有降血脂、降血糖、促进脂肪分解利用等功效,但针对以刺梨为原料发酵制成的刺梨果酒在调节脂代谢及其机制上的研究还未见报道,且前期研究发现一定量的刺梨果酒可改善STZ诱导的1-型糖尿病大鼠糖代谢紊乱。因此,本文以刺梨果酒为研究对象,探究其对高脂诱导小鼠肥胖的预防作用及其在基因水平上的作用机制,从而为刺梨果酒作为功能性食品预防肥胖提供更深层次的理论依据,同时提高刺梨果酒的附加值和综合利用价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
刺梨果酒 实验室自制;昆明种雄性小鼠,SPF级、22~24 g、50只 由辽宁长生生物技术股份有限公司提供,生产许可证:SCXK(辽)2015-0001;红星二锅头酒(56%vol) 北京红星股份有限公司;总蛋白定量测试盒(BCA法)、甘油三酯(TG)测定试剂盒、总胆固醇(TC)测定试剂盒、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)测定试剂盒、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)测定试剂盒、丙二醛(MDA)测定试剂盒 由南京建成生物科技有限公司提供;定量引物 华大基因合成;M-MLV反转录酶(200 U/μL)10000 U、RNase Inhibitor 美国普洛麦格;5×Buffer TaKaRa;DNA marker DL2000 宝生物工程有限公司;基础饲料 由重庆腾鑫生物技术有限公司提供;高脂饲料配方如表1所示[21]。
表 1 高脂饲料配方Table 1. Formula of high-fat feed成分 含量(%) 基础饲料 78.8 猪油 10 蛋黄粉 10 胆固醇 1 胆盐酸 0.2 Nano Drop 1000微量紫外分光光度计 美国 Thermo公司;FSH-2可调高速匀浆器 江苏省金坛市环宇科学仪器厂;Light Cycler Nano 荧光定量 PCR 仪 美国罗氏公司;L5S紫外分光光度计 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司;1000梯度 PCR仪 美国BIO-RAD公司;SpectraMax190连续波长多功能酶标仪 美国Molecular Devices公司;H1-16KR高速冷冻离心机 湖南可成仪器设备有限公司;Eclipse Ci-L光学显微镜 日本Nikon公司;荧光定量试剂、荧光定量膜和荧光定量板子 伯乐生命医学产品(上海)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 刺梨果酒
刺梨果酒参照李劲松[22]的方法并适当改进,其主要步骤为:挑选适宜成熟度、无病虫害的刺梨鲜果进行清洗、揉搓,装入容器,调整糖度,控温发酵,陈酿,过滤,密封存储等。因新酿的刺梨果酒涩味较重,滋味弱,而2年陈酿的刺梨果酒涩味及滋味均较好,市场接受度也是最好的,故选取2年陈酿的刺梨果酒进行本实验。
1.2.2 动物饲养
实验经贵州大学动物实验伦理委员会批准(编号:EAE-GZU-2020-P003),符合动物实验伦理。将50只体质量为22~24 g的4~6周龄健康雄性昆明小鼠饲养在通风良好,室温(23±2)℃,相对湿度50%~55%,12 h/12 h明暗交换的环境中,自由摄食和饮水。小鼠适应性饲养一周后,按体质量随机分为5组(n=10):空白组、模型组、刺梨果酒低剂量组、刺梨果酒中剂量组及刺梨果酒高剂量组,为确保低、中、高剂量组每只小鼠为等剂量灌胃(80 g体质量小鼠分别灌胃0.25、0.5、1 mL剂量的刺梨果酒)于每日上午9:00~11:00进行灌胃。空白与模型组灌胃与中剂量等酒度、等剂量(0.5 mL/80 g)的红星二锅头。饲养期间除空白组外,其余各组饲喂高脂饲料。持续饲喂8周,期间自由饮水和摄食,每周记录采食量、饮水量和体质量,并调整灌胃剂量。动物饲养末期,将小鼠禁食不禁水12 h后,在麻醉状态下测量小鼠体长,腹围,眼眶取血后,解剖,取出肝脏、心脏、肾脏、脾脏、腹部脂肪等用冰冻生理盐水洗净后,用吸水纸除去表面水滴,进行称重后转移至−80 ℃,其中,脏器指数参照1.2.3计算,腹部脂肪、脂肪指数参照1.2.5计算。
1.2.3 脏器指数测定
根据小鼠脏器重量与体重,按下列公式对各脏器指数进行计算[23]。
脏器指数(mg/g)=脏器总重(mg)/体重(g) 1.2.4 Lee’s指数测定
根据小鼠体长和体重,按下列公式进行计算[24]。
Lee's指数=3√体质量(g)×103/体长(cm) 1.2.5 脂肪指数测定
脂肪指数(mg/g)=脂肪湿重(mg)/体重(g)[25]
1.2.6 理化指标测定
血清和肝脏中TG、TC、LDL-C、HDL-C含量测定,其步骤参考试剂盒说明书进行。
1.2.7 HE染色
将各组小鼠肝脏,经4%多聚甲醛固定,固定状态良好后,进行修剪、脱水、包埋、切片、染色、封片制作切片,苏木精-伊红(Hematoxylin-eosinstaining, HE)染色,光学显微镜下观察肝脏组织结构并分析。
1.2.8 qRT-PCR的分析
从组织样品中提取总RNA,使用Oiagen提取并反转录得cDNA,使用紫外分光光度计测定RNA浓度。实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应用于检测相关基因的表达,以β-actin为内参并采用2−ΔCt法计算各基因相对表达,操作步骤如下[26-27]:总RNA提取→反转录及cDNA的合成与检测→荧光定量PCR检测,各基因的引物序列如表2。
表 2 实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应的引物序列Table 2. The sequence of quotations for real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction基因 Forward primer(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') SREBP1 GGCCATCGACTACATCCGCTTC CGTCTCCACCACTTCGGGTT AMPK CGGGGTCATTCTCTATGCTT TTTAAACCACTCGTGTTCCCT LXR CTCTGCAATCGAGGTCATGCTT CCCGGTTGTAACTGAAGTCCT PPARα TCGGGATGTCACACAATGCAA AGTTTCCGAATCTTTCAGGTCGT ACACA CATCCGGCGACTTACGTTC AAACTTATCCCTTGCTCGGAA FASN TCAACCTGCTCCTGAAGCCGAA GCCTCAGAGCGACAATATCCAC SCD1 GCACATCAAAACTTCACCACGTT CTACTCTTGTGACTCCCGTCT β-actin ACATCCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCC TACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCAC 1.3 数据处理
实验数据均采用均数±标准差(
ˉx ±s)表示,组间分析比较用单因素方差分析,全部统计学分析均由SPSS22.0完成,并用LSD、Duncan法进行组间两两比较,以P<0.05表示差异,具有统计学意义。2. 结果与分析
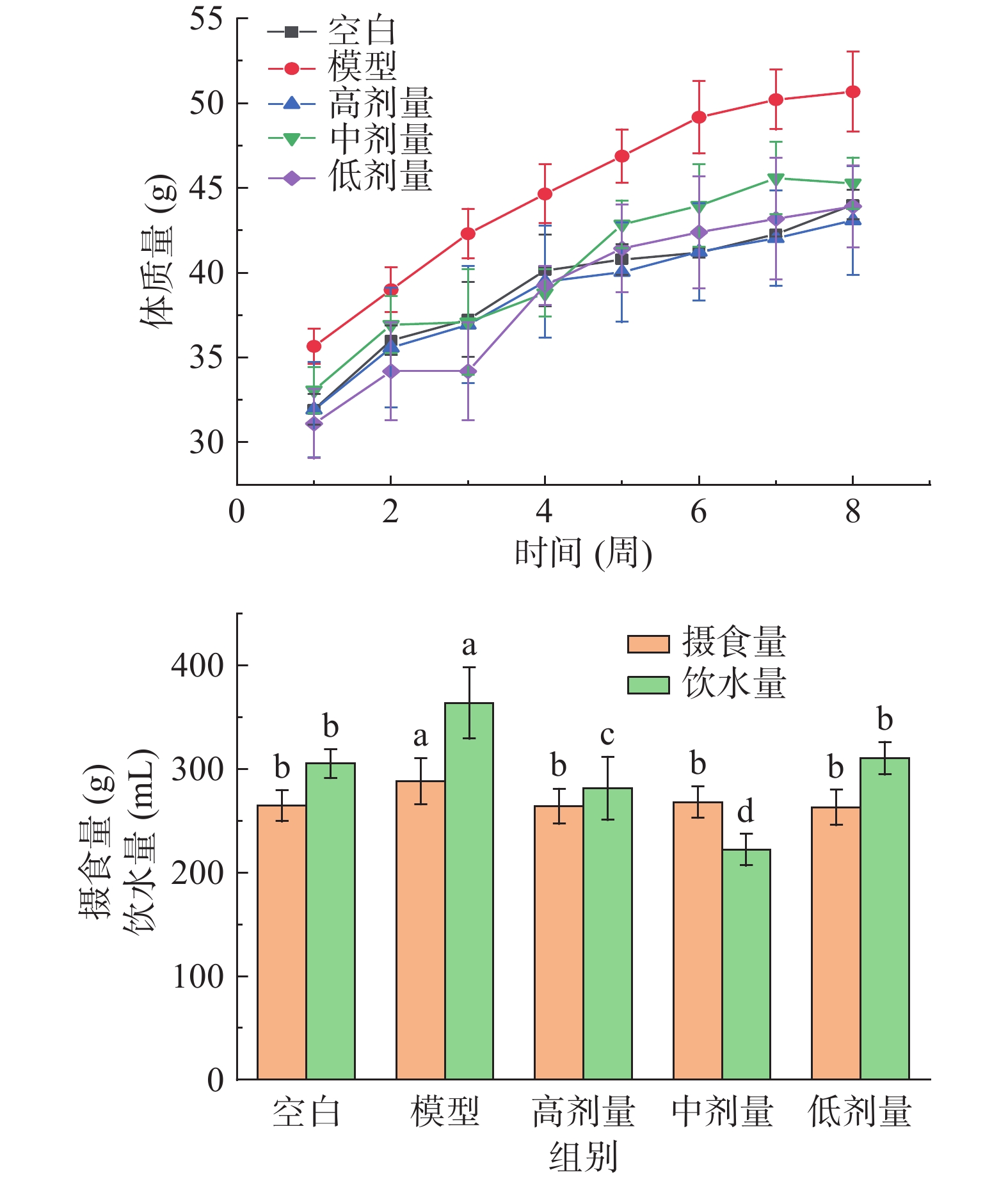
2.1 对小鼠体质量、进食量和饮水量的影响
检验肥胖最直接的体现是体质量指标[28]。如图1所示,刺梨果酒干预8周期间,与空白组相比,模型组小鼠体质量稳定增长,进食量与饮水量分别显著(P<0.05)升高了8.97%、19.16%。相比模型组,剂量组小鼠进行8周刺梨果酒干预后小鼠体质量明显下降。其中,刺梨果酒低剂量组在干预第2周小鼠体质量下降趋势较大,到第3周逐渐上升但始终低于模型组。刺梨果酒高剂量组,在截至第8周小鼠体质量比中、低剂量组都要低。此外,使用高、中、低剂量刺梨果酒对小鼠进行8周灌胃后,小鼠摄食量显著减少(P<0.05)。实验结果表明,刺梨果酒可有效降低小鼠体质量,对高脂诱导小鼠肥胖模型具有一定的预防作用。
2.2 对小鼠脏器指数的影响
肥胖会引起机体内脏器的变化,从而影响机体营养分配与代谢[29]。由表3可知,与空白组相比,模型组小鼠脏器指数呈增长趋势,其心脏、肝脏、肾脏、脾脏分别显著(P<0.05)增加20.5%、36.3%、28.8%、48.9%,这与小鼠长期高脂饮食有关。与模型组相比,剂量组脏器指数均显著(P<0.05)降低,可能是果酒中酒精含量低且吸取了刺梨中的全部营养而富含Vc、黄酮等多种活性成分,摄入适量刺梨果酒后,起到了清热、助消化、消食等作用,进而很好地消化了堆积在体内的食物,降低了体内脂肪的堆积。因此,摄入适量的刺梨果酒可通过降低体内脂肪堆积,从而达到缓解肥胖的目的。
表 3 刺梨果酒对小鼠脏器指数的影响(n=10)Table 3. Effect of Rosa roxburghii wine on viscera coefficient of mice(n=10)组别 心脏(mg/g) 肝脏(mg/g) 肾脏(mg/g) 脾脏(mg/g) 空白组 0.200±0.011bc 1.580±0.143 b 0.553±0.022 b 0.094±0.009b 模型组 0.242±0.023a 2.153±0.310a 0.712±0.049a 0.140±0.027a 高剂量组 0.179±0.017c 1.519±0.177 b 0.575±0.030 b 0.090±0.005 b 中剂量组 0.207±0.008bc 1.610±0.155 b 0.563±0.024 b 0.083±0.012 b 低剂量组 0.189±0.014bc 1.551±0.063 b 0.577±0.048 b 0.090±0.015 b 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 2.3 对小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、Lee’s指数和脂肪指数的影响
刺梨果酒对高脂诱导肥胖小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、Lee’s指数和脂肪指数的影响见表4。与空白组相比,模型组小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、Lee’s指数、脂肪指数均显著(P<0.05)增加,其原因是长期高脂饮食后产生了大量的脂肪堆积在体内。相比模型组,刺梨果酒剂量组小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、脂肪指数均显著(P<0.05)降低。此外,Lee’s指数作为肥胖指标,其Lee’s指数越大,肥胖就越明显,实验结果表明,摄入适量刺梨果酒干预8周后,与模型组相比,刺梨果酒剂量组均可显著(P<0.05)降低小鼠体内Lee’s指数。体内腹部脂肪的累积会导致肝脏脂代谢紊乱、高血脂、胰岛素抵抗等代谢综合症[30]。因此,摄入适量的刺梨果酒可通过减少体内腹部脂肪堆积,降低肝脏脂质异常的风险,从而起到预防或缓解肥胖的效果。
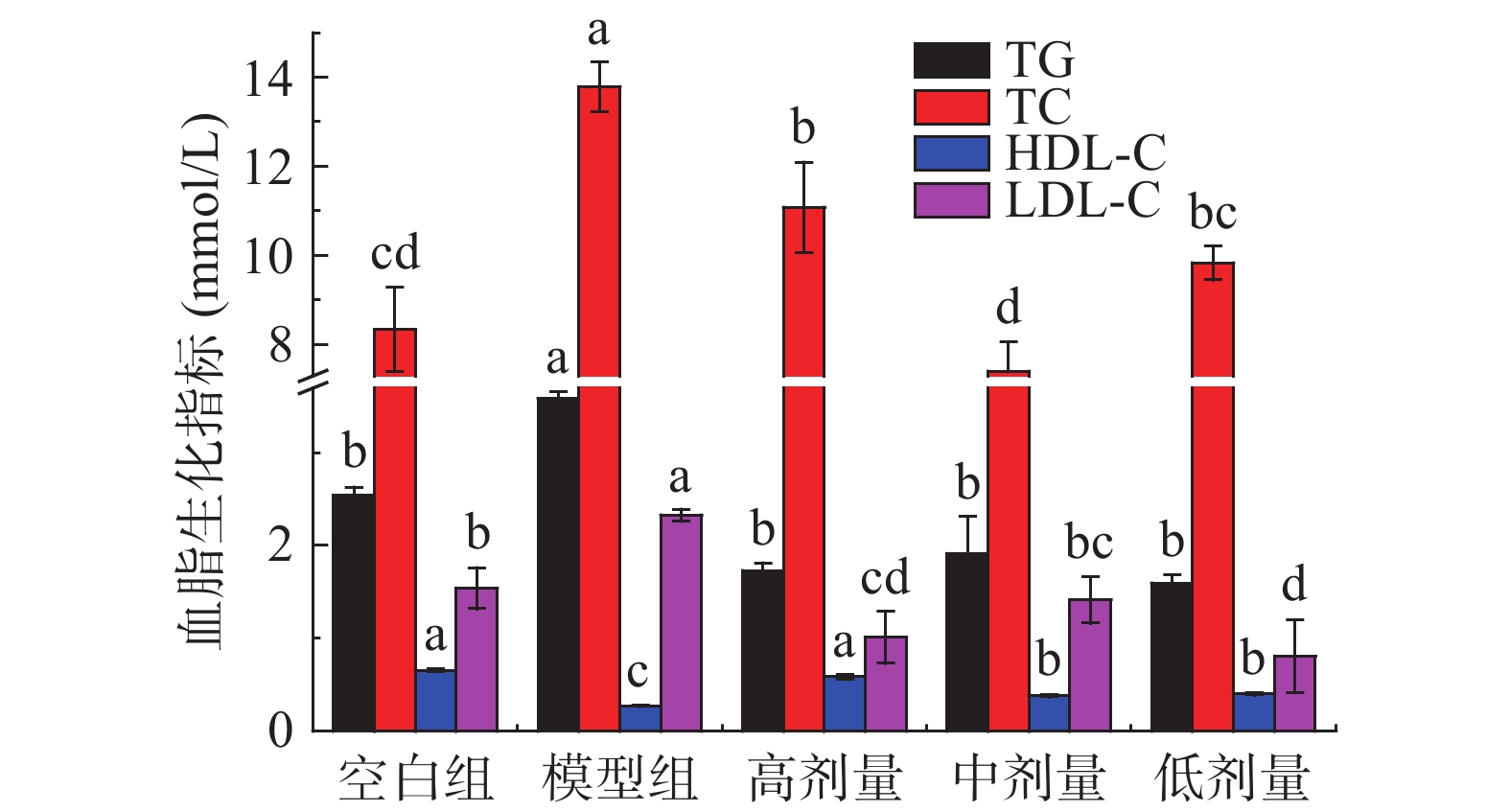
表 4 刺梨果酒对小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、Lee’s指数和脂肪指数的影响(n=10)Table 4. Effects of Rosa roxburghii wine on abdominal circumference, abdominal fat, Lee's index and fat index of mice(n=10)组别 腹围(cm) 腹部脂肪(mg/g) Lee’s指数 脂肪指数(mg/g) 空白组 8.033±0.208 c 0.276±0.044 b 309.619±2.740 b 0.006±0.001 b 模型组 9.500±0.300a 0.707±0.080a 331.565±11.813a 0.014±0.002a 高剂量组 8.567±0.451 bc 0.295±0.184 b 307.186±10.817 b 0.009±0.001 b 中剂量组 8.767±0.231 b 0.385±0.072 b 300.620±18.377 b 0.008±0.001 b 低剂量组 8.833±0.379 b 0.310±0.173 b 308.887±3.000b 0.007±0.003 b 2.4 对血脂水平的调节作用
血液中脂质水平是机体脂代谢是否正常的重要判断标准[28]。如图2所示,与空白组相比,模型组血清中TG、TC、LDL-C水平分别显著(P<0.05)升高41.07%、65.26%、51.19%,HDL-C含量显著(P<0.05)降低58.99%。WANG等[25]指出,当脂质代谢紊乱时,血脂指标一般表现为TC、TG、LDL-C水平升高,HDL-C水平降低。可见,长期高脂饮食会引起血脂代谢紊乱。与模型组相比,刺梨果酒高、中、低剂量组小鼠血脂水平得到改善,TG水平分别显著(P<0.05)降低51.75%、46.63%、55.52%;TC水平分别显著(P<0.05)降低19.60%、46.31%、28.69%;LDL-C含量分别显著(P<0.05)降低56.69%、39.37%、65.35%;HDL-C含量分别升高116.36%、40.89%、48.33%。实验结果说明,摄入刺梨果酒对高脂诱导引起的血脂水平变化具有拮抗作用,可通过调节血脂水平来改善脂质代谢紊乱。
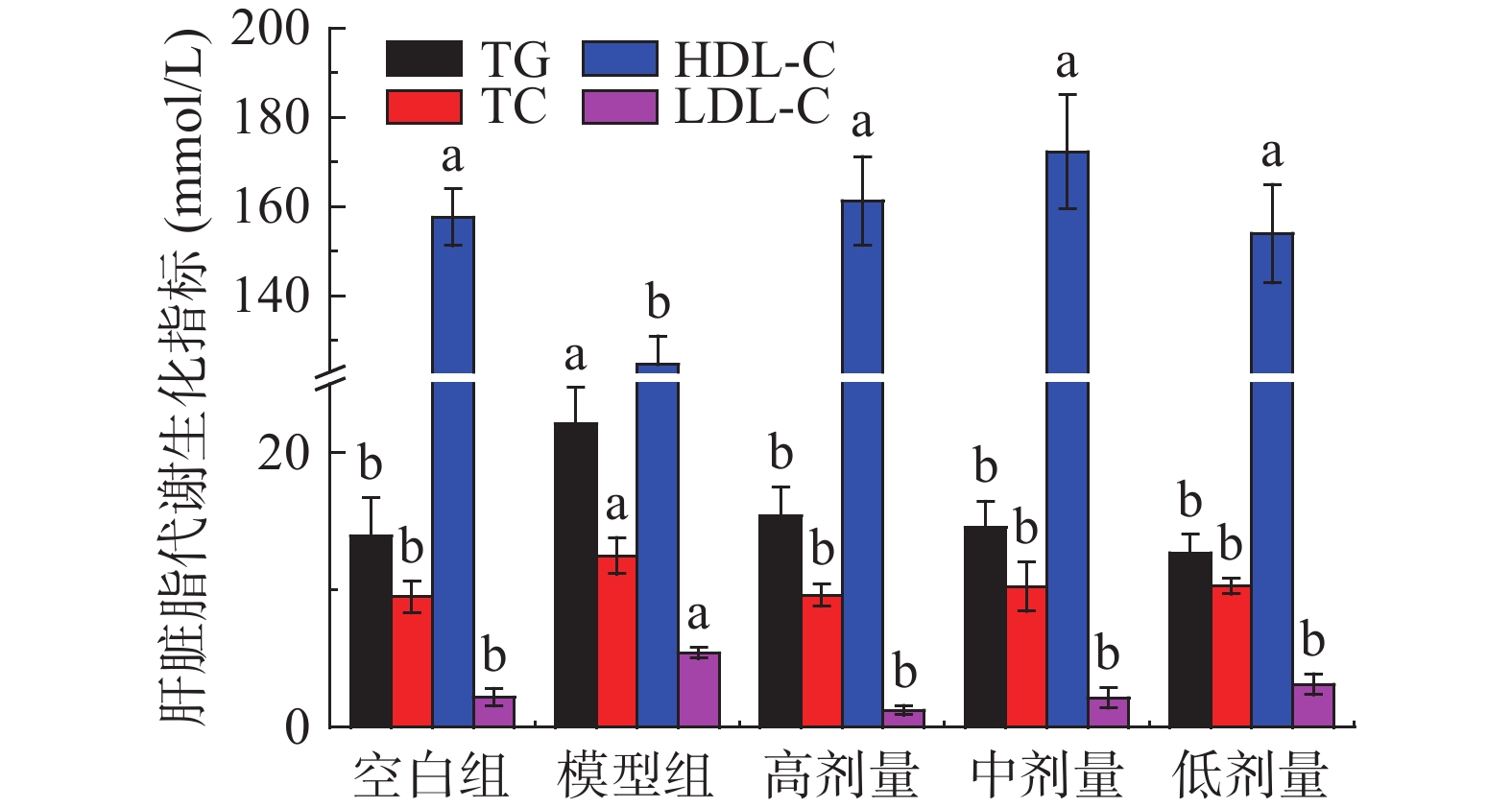
2.5 对小鼠肝脏脂质水平的调节作用
肥胖导致的脂质新生可使肝内脂质堆积增加,导致肝功能紊乱[31-32]。刺梨果酒对高脂诱导肥胖小鼠肝脏脂质水平的影响见图3。与空白组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏中TG、TC、LDL-C水平分别显著(P<0.05)升高58.52%、31.58%、146.34%,HDL-C含量显著(P<0.05)下降20.93%。相比模型组,高、中、低剂量刺梨果酒干预8周后,TG水平分别显著(P<0.05)降低30.37%、34.11%、42.52%;TC水平分别显著(P<0.05)降低23.00%、18.00%、17.67%;LDC-C含量分别显著(P<0.05)降低77.23%、60.40%、40.11%;HDL-C含量分别显著(P<0.05)升高29.41%、38.24%、23.53%。实验结果表明,摄入适量的刺梨果酒可有效调节小鼠肝脏脂质水平,降低TG、TC、LDL-C含量、升高HDL-C含量。
2.6 肝脏病理学分析
由图4可知,空白组小鼠组织肝细胞排列紧密,肝窦未见明显挤压或扩张。相比空白组,模型组小鼠组织肝细胞空泡变性,血管周围肝细胞出现肿胀,胞质疏松淡染,说明长期高脂诱导会引起小鼠肝脏组织脂肪变性。刺梨果酒高、中、低剂量组相比模型组,其组织肝细胞排列较紧密,肝窦未见明显挤压或扩张且血管周围肝细胞肿胀和脂质疏松淡染现象有所缓解。说明摄入刺梨果酒能减少肝脏脂肪变性的风险。
2.7 对肝脏脂代谢关键信号通路的影响
2.7.1 AMPK信号通路
AMPK信号传导可参与脂质代谢途径[33]。ACACA作为AMPK的下游靶点是脂肪酸合成的关键酶,在脂代谢调节方面起重要作用。活化的AMPK可导致ACACA活性降低,且可以通过增加PPARα表达增强脂肪酸氧化,促进脂肪酸β氧化分解及提高脂质分解水平[34]。为此,本实验研究了该信号通路中的关键基因,来探讨高脂诱导肥胖小鼠调节脂质代谢的机制,其相关基因mRNA表达水平如图5所示。与空白组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏中AMPK、ACACA、PPARα mRNA表达水平显著(P<0.05)上调。摄入刺梨果酒长期干预后,高剂量组均可显著(P<0.05)下调AMPK、ACACA、PPARα mRNA表达水平,分别下调83.27%、58.34%、48.88%;中剂量组均显著(P<0.05)下调AMPK、PPARα mRNA表达水平;但低剂量组对其关键基因AMPK、ACACA、PPARα mRNA表达水平呈上调趋势,其原因可能是组成这几种关键酶的复合物包含了一个家族中的不同基因及调控因子,经不同剂量干预后会存在部分基因上调、部分下调。但从实验的总体来看,摄入适量剂量的刺梨果酒可通过下调肝脏脂代谢相关脂肪酸合成关键酶,进而提高脂质分解水平,达到预防肥胖的目的。
2.7.2 SREBP1信号通路
SREBP1作为脂质代谢重要转录因子,主要调控脂肪酸和胆固醇的生物合成。SREBP1可激活下游多种参与脂肪酸合成的转录包括FASN、SCD1
[35]。LXR作为胆固醇调控转录因子,可提高SREBP1转录水平[36],进而促进胆固醇向胆汁酸转化。本实验探讨了脂肪酸氧化的相关基因,其基因表达水平如图6所示。与空白组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏中LXR、FASN、SCD1 mRNA表达水平分别显著(P<0.05)上调23.96%、109.70%、376.72%,SREBP1 mRNA表达水平显著(P<0.05)下调23.27%。相比模型组,长期干预后,低剂量可显著(P<0.05)上调SREBP1 mRNA表达水平;高、中剂量可显著(P<0.05)下调LXR、SCD1 mRNA表达水平,且中剂量也可显著(P<0.05)下调FASN mRNA表达水平。由此可见,适量的刺梨果酒可激活脂质代谢中的重要转录因子,促进脂肪酸氧化,进而调节肝脏脂质代谢。 3. 讨论
肥胖主要以体内脂肪增多、血脂异常为主要特征[37]。肝脏作为机体重要代谢器官,主要参与内源性脂肪合成和运输[38]。肝脏不能储存脂肪,但当脂质代谢动态失衡时,TG就会堆积在肝细胞中,导致肝脂肪退化[39]。此外,TC含量异常升高,也会提高患病风险[40]。在肝脏中,LDL-C主要将胆固醇运输到肝脏中合成胆酸,但易被泡沫细胞氧化,进而导致心血管疾病[41]。血浆中大多数脂质以HDL-C形式存在,HDL-C参与了胆固醇从外周组织到肝脏的逆向运输,对动脉粥样硬化形成具有拮抗作用[42-43]。研究表明,肥胖人群体内HDL-C水平低于非肥胖人群[44]。另有研究报道,当肝脏脂质代谢紊乱时,其血脂指标一般表现为TC、TG、LDL-C水平升高,HDL-C水平降低[45]。本实验通过建立高脂诱导肥胖小鼠模型评价刺梨果酒在调节脂质代谢紊乱及预防肥胖方面的效果,其结果显示,采用不同剂量刺梨果酒干预8周后,与模型组相比,剂量组小鼠体质量生长呈下降趋势,血清及肝脏中TG、TC、LDL-C含量显著(P<0.05)降低,HDL-C含量显著(P<0.05)升高,肝组织中脂质累积也有所缓解。此外,本研究还显示,刺梨果酒能减缓对高脂诱导引起肥胖小鼠脏器系数的扩增,降低体内脂肪堆积、Lee’s指数,进而达到预防或缓解肥胖的目的。刺梨果酒体现的这些效果与相关文献报道血脂及肝脏水平TG、TC、LDL-C和HDL-C指标相关结果一致[46-48]。
肝脏是脂质代谢的重要场所,其代谢过程极其复杂,受多种因素共同调节[49-50]。其中,PPARα可调节肝脏组织中脂肪β氧化速率[51]。LXR可调节胆汁酸合成[52]。SREBP1作为调控肥胖患者体内新生脂肪关键转录因子,可由PPARα上调而被激活最终促进FASN mRNA基因表达,加快TC、LDL受体、脂肪等物质合成[53-55]。此外,SREBP1
可控制许多参与胆固醇和脂质代谢的基因,其中,SREBP1和SCD1可介导脂肪形成和脂质在组织中累积[56]。ACACA是脂肪酸生物合成关键酶,此酶的活性控制着脂肪酸的合成速度,继而控制脂肪酸含量,ACACA经AMPK磷酸化后可抑制脂肪酸合成[57]。HARWOOD等[58]研究发现通过降低ACACA活性,可减少动物中脂肪酸的生物合成。另有研究显示,AMPK 的激活也能增加分解代谢,降低ACACA、SREBP、FAS等脂质合成有关因子表达及代谢速率,调节脂质合成与利用[59-60]。本次实验结果显示,经8周干预治疗后,刺梨果酒高剂量组可显著(P<0.05)下调脂肪酸合成关键酶ACACA的表达水平,且高、中剂量组均可显著(P<0.05)下调脂质合成中AMPK、PPARα、LXR、SCD1 的相关因子表达水平,其结果与相关文献报道一致[61-64]。但经长期干预后,低剂量组对其脂肪酸合成关键酶及脂质合成相关因子的表达呈上调趋势,且中剂量组对其脂肪酸合成关键酶ACACA的基因表达也上调,原因可能是许多关键酶其本身就是复合物,而组成酶的复合物包含了一个家族的多个基因和不同的调控因子,而它们之间的调控机制又极为复杂,因此,针对不同剂量干预后其基因会出现部分上调,部分下调。但从总体上可以看出摄入适量的刺梨果酒干预后,可降低脂肪和胆固醇的合成,增加脂肪酸氧化,进而减少高脂诱导小鼠的肥胖及小鼠肝脏脂肪蓄积来达到预防肥胖的目的。 4. 结论
实验结果表明,低、中、高剂量刺梨果酒均能减缓由高脂诱导小鼠引起的体质量增加和脏器的扩增。经刺梨果酒干预后,可有效降低小鼠血清和肝脏脂质水平,还有助于减少体内脂肪堆积,从而达到预防或减轻肥胖的目的。此外,高剂量组还可通过下调脂肪酸合成关键酶及脂质合成相关因子表达来介导脂肪的形成和脂质在肝脏的累积。其基因表达水平客观的说明了刺梨果酒可调节脂代谢及可能存在的作用机制,为摄入适量的刺梨果酒预防肥胖提供了更深入的理论依据,与此同时提高了贵州省刺梨果酒的附加值和综合利用价值。但本文仍存在许多不足,需进一步从蛋白水平验证刺梨果酒抑制高脂诱导肥胖所涉及的具体信号通路及分子调节机制。
-
表 1 高脂饲料配方
Table 1 Formula of high-fat feed
成分 含量(%) 基础饲料 78.8 猪油 10 蛋黄粉 10 胆固醇 1 胆盐酸 0.2 表 2 实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应的引物序列
Table 2 The sequence of quotations for real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction
基因 Forward primer(5'-3') Reverse primer(5'-3') SREBP1 GGCCATCGACTACATCCGCTTC CGTCTCCACCACTTCGGGTT AMPK CGGGGTCATTCTCTATGCTT TTTAAACCACTCGTGTTCCCT LXR CTCTGCAATCGAGGTCATGCTT CCCGGTTGTAACTGAAGTCCT PPARα TCGGGATGTCACACAATGCAA AGTTTCCGAATCTTTCAGGTCGT ACACA CATCCGGCGACTTACGTTC AAACTTATCCCTTGCTCGGAA FASN TCAACCTGCTCCTGAAGCCGAA GCCTCAGAGCGACAATATCCAC SCD1 GCACATCAAAACTTCACCACGTT CTACTCTTGTGACTCCCGTCT β-actin ACATCCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCC TACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCCAC 表 3 刺梨果酒对小鼠脏器指数的影响(n=10)
Table 3 Effect of Rosa roxburghii wine on viscera coefficient of mice(n=10)
组别 心脏(mg/g) 肝脏(mg/g) 肾脏(mg/g) 脾脏(mg/g) 空白组 0.200±0.011bc 1.580±0.143 b 0.553±0.022 b 0.094±0.009b 模型组 0.242±0.023a 2.153±0.310a 0.712±0.049a 0.140±0.027a 高剂量组 0.179±0.017c 1.519±0.177 b 0.575±0.030 b 0.090±0.005 b 中剂量组 0.207±0.008bc 1.610±0.155 b 0.563±0.024 b 0.083±0.012 b 低剂量组 0.189±0.014bc 1.551±0.063 b 0.577±0.048 b 0.090±0.015 b 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 表 4 刺梨果酒对小鼠腹围、腹部脂肪、Lee’s指数和脂肪指数的影响(n=10)
Table 4 Effects of Rosa roxburghii wine on abdominal circumference, abdominal fat, Lee's index and fat index of mice(n=10)
组别 腹围(cm) 腹部脂肪(mg/g) Lee’s指数 脂肪指数(mg/g) 空白组 8.033±0.208 c 0.276±0.044 b 309.619±2.740 b 0.006±0.001 b 模型组 9.500±0.300a 0.707±0.080a 331.565±11.813a 0.014±0.002a 高剂量组 8.567±0.451 bc 0.295±0.184 b 307.186±10.817 b 0.009±0.001 b 中剂量组 8.767±0.231 b 0.385±0.072 b 300.620±18.377 b 0.008±0.001 b 低剂量组 8.833±0.379 b 0.310±0.173 b 308.887±3.000b 0.007±0.003 b -
[1] PSA B, XSA B. Proteomic analysis of liver in diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice under Fructus Rosa roxburghii action-Science Direct[J]. Journal of Proteomics,2020:230.
[2] 刘月姣. 《中国居民营养与慢性病状况报告(2020年)》发布[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2020, 26(12): 2. LIU Y J. The Report on the Nutritional and Chronic Diseases of Chinese Residents (2020) was published[J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition. 2020, 26(12): 2.
[3] 雁鸣. 肥胖可诱发多种疾病[N]. 中国消费者报, 2019(007). YAN M. Obesity can induce a variety of diseases[N]. China Consumer Daily, 2019(007).
[4] QU L, LIU Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Kiwifruit seed oil ameliorates inflammation and hepatic fat metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,52:715−723. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.12.003
[5] 赵鹏葳, 简敬一, 任孟月. 药食同源中药治疗肥胖症的有效成分和机制研究进展[J]. 广东药科大学学报,2021,37(3):141−149. [ZHAO P W, JIAN J Y, REN M Y. Advances in the study of the active ingredients and mechanisms of the treatment of obesity by medicinal homologous Chinese medicine[J]. Guangdong Pharmaceutical University,2021,37(3):141−149. [6] CHEN G L, LI H J, ZHAO Y, et al. Saponinsfeom stems and leaves of Panax ginseng prevent obesity via regulating thermoogenesis, lipogenesis and lipolysis in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice[J]. Food Chem Tocicol,2017,106:393−403. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.06.012
[7] SHEN C Y, WAN L, WANG T X, et al. Citrus aurantium L. var. amara Engl. inhibited lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1cells and Caenorhabditis elegans and prevented obesity in high fat diet-fed mice[J]. Phares,2019,147:104347.
[8] KWON E Y, LLEE J, KIM Y J, et al. Seabuckthorn leaves extract and flavonoid glycosides extract from seabuckthorn leaves amelio rates adiposity, hepaticsteatosis, insulinresistance, and inflammation in diet-induced obrsity[J]. Nutrients,2017,9(6):569. doi: 10.3390/nu9060569
[9] XU J, VIDYARTHI S K, BAI W, et al. Nutririonalconstituents, health benefits and processing of Rosa roxburghii: A review[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,60:103456. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103456
[10] 王怡, 李贵荣, 朱毅. 刺梨食品研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(18):213−218. [WANG Y, LI G R, ZHU Y. Progress in the research of pear foods[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(18):213−218. [11] LEE J C, KIM J D, HSIEH F H, et al. Production of black rice cake using ground black rice and medium-grain brown rice[J]. Int J Food Sci Tech,2008,43(6):1078−1082. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01569.x
[12] HAZELWOOD L A, DARAN J M, VAN MARIS A J A, et al. The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: A century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism[J]. Appl environ microb,2008,74:2259−2266. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02625-07
[13] JU Y, ZHUO J X, LIU B, et al. Eating from the wild: Diversity of wild edible plans used by Tibetans in Shangri-la region, Yunnan, China[J]. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed,2013,9(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-9-28
[14] CHEN P, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Study on hypolipidemic activity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt
, propolis and crataegus oral liquid[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(8):78−83,72. [15] CHEN X M, TAN S M, HUANG Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of Rosa roxburghii juice on type 1 diabetic mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(8):13−20.
[16] YU L M, FANG N, YANG X S, et al. Effects of Rosa roxburghii extract on proliferation and differentiation in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells and CD34(+) haematopoietic cells[J]. Journal of Health Science,2007,53(1):10−15. doi: 10.1248/jhs.53.10
[17] HUANG X L, YAN H Q, ZHAI L S, et al. Characterization of the Rosa roxburghii Tratt transcriptome and analysis of MYB genes[J]. PLOS ONE,2019,14(3):e0203014. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203014
[18] 隋怡, 杨平, 夏仁侠. 基于黔产刺梨“消食”作用的减肥活性及其机制研究[J]. 亚太传统医药,2020,16(9):25−28. [SUI Y, YANG P, XIA R X. Based on the weight loss activity and its mechanism of "eating"pears[J]. Asia Pacific Traditional Medicine,2020,16(9):25−28. [19] 孙兆峰, 张霞, 夏作理. 刺梨叶对2型糖尿病大鼠脂代谢的影响[J]. 社区医学杂志,2015,13(10):53−55. [SUN Z F, ZHANG X, XIA Z L. Effect of prickly pear leaves on the metabolism of rat fat in type 2 diabetes[J]. Journal of Community Medicine,2015,13(10):53−55. [20] 夏星, 钟振国, 廖林枝, 等. 刺梨提取物影响小鼠抗疲劳及耐缺氧能力的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2012,23(7):1664−1666. [XIA X, ZHONG Z G, LIAO L Z, et al. The study of pear extract affecting the anti-fatigue and hypoxia resistance of mice[J]. Time Jane's National Medicine,2012,23(7):1664−1666. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2012.07.030 [21] 林武, 吴丽萍. 高脂饲料致高脂血症大鼠模型的研究[J]. 现代实用医学,2013,25(2):171−172, 185. [LIN W, WU L P. Study on the model of hyperlipidemia rats in high-fat feed[J]. Modern Practical Medicine,2013,25(2):171−172, 185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2013.02.030 [22] 李劲松. 刺梨果酒的酿造方法: CN105331481B[P]. 2018. LI J S. How to make pear fruit wine. CN105331481B[P]. 2018.
[23] HE W S, WANG M G , PAN X X , et al. Role of plant stanol derivatives in the modulation of cholesterol metabolism and liver gene expression in mice[J]. Food Chemistry, 2013, 140(1-2): 9-16.
[24] 金玲凤, 刘小伟, 卢放根, 等. 大鼠非酒精性脂肪形成过程中肝脏蛋白质组动态变化的研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2014,24(21):26−32. [JIN L F, LIU X W, LU F G, et al. Study on the dynamic changes of liver proteomics during non-alcoholic fat formation in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Medicine,2014,24(21):26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2014.21.006 [25] WANG S N, YU H S, GU C M, et al. Preventive effect of soybean insoluble dietary fiber on high fat diet induced obesity in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):295−301, 314.
[26] REN T Y, ZHU Y P, XIA X J, et al. Zanthoxylum alkyamides ameliorate protein metabolism disorder in STZ-induced diabetic rats[J]. Jurnal of Molecular Endocrinology,2017,58(3):113−125. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0218
[27] YOU Y M, REN T, ZHANG S Q, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of Zanthoxylum alkylamides by enhancing glucose metabolism and ameliorating pancreatic dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Food & Function, 2015, 6(9): 3144-3154.
[28] ZHANG Y H, WANG X, WANG W L, et al. Effects of grape seed proanthocyanins on high-fat and high-sugar diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):112−120.
[29] LAFONTAN M, GIRARD J. Impact of visceral adipose tissue on liver metabolism; Part I: Heterogeneity of adipose tissue and functional properties of visceral adipose tissue[J]. Diabetes & Metabolism,2008,34(4):317−327.
[30] LIU S, FU MEI R, HU SOPHIA H, et al. Accuracy of body weight perception and obesity among Chinese Americans[J]. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice, 2015, 10: S48-S56.
[31] MARCHESINI G, MOSCATIELLO S, DIDOMIZIO S, et al. Obesity associated liver disease[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2008,93(11S):S74−S80.
[32] FABBRINI E, SULLIVAN S, KLEIN S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications[J]. Hepatology(Baltimore, Md.), 2010, 51(2): 679-689.
[33] RUHL C E, EVERHART J E. Determinants of the association of overweight with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase activity in the United States[J]. Gastroenterology,2003,124(1):71−79. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50004
[34] QU L L, YU B, LI Z, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates oxidative stress and proinflammatory response in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2016, 30(3): 402-411.
[35] SCHETZ M, DE JONG A, DEANE A M, et al. Obesity in the critically ill: A narrative review[J]. Intensive Care Medicine,2019:1−13.
[36] OH S Y, PARK S K, KIM J W, et al. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase β gene is regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 in liver[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2003,278(31):28410−28417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300553200
[37] YOSHIKAWA T, SHIMANO H, AMEMIYA K, et al. Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol l regulatory element-binding protein-1 gene promoter[J]. Mol cell Biol 2001, 21(9): 2991-3000.
[38] LIM S. A new international journal targeting the pathophysiology and treatment of obesity and metabolic syndrome[J]. J Obes Meta Syndr,2017,26(2):81−83.
[39] 傅宝玉. 肝脏与脂肪代谢障碍—肝脏在机体脂类代谢中的作用[J]. 辽宁医学杂志,2004,18(2):57−58. [FU B Y. Liver and fat metabolism disorders—the role of the liver in body lipid metabolism[J]. Liaoning Medical Journal,2004,18(2):57−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1722.2004.02.001 [40] RECCIA I, KUMAR J, AKLADIOS C, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A sign of systemic disease[J]. Metabolism-clinical & Experimental,2017:94−108.
[41] P ANGULO. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutr Rev, 2007, 65(suppl 1): 57−63.
[42] SIEKMANL. Reference methods for total cholesterol and total glycer[J]. European Journal of Clinical Chemistry & Clinical Biochemistry Journal of the Forum of European Clinical Chemistry Societies,2009,29:277−279.
[43] PATHTHINIGE C S, SIRISENA N D, DISSANAYAKE V. Genetic determinants of inherited susceptibility to hypercholesterolemia a comprehensive literature review[J]. Lipids Health Dis,2017,16(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0488-4
[44] 周慧娟. 高脂膳食对肝脏脂代谢的影响及其机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2018. ZHOU H J. Effect of high-fat diet on liver lipid metabolism and its mechanism[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2018.
[45] LUSCHER T F, LANDMESSER U, VON ECKARDSTEIN A, et al, Hight-desitylipoprotein: Vascular protective effects, dysfunction, and potential as therapeutic target[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114(1): 171-182.
[46] 于平, 汪晓辉. 植物乳杆菌对大鼠体内血清胆固醇含量的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(8):45−52. [YU P, WANG X H. Effect of plant Lactobacillus on serum cholesterol levels in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2016,16(8):45−52. [47] 王康乐, 陆震鸣, 陈露, 等. 云芝多糖组分对酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保肝活性测试[J]. 食药用菌,2018,26(4):235−239. [WANG K L, LU Z M, CHEN L, et al. The polysaccharide components of Yunzhi were tested for liver preservation activity in alcoholic liver damage mice[J]. Medicinal Bacteria,2018,26(4):235−239. [48] 符佳, 李维, 周佳仪, 等. 虎杖醇提物对高脂诱导肥胖大鼠肠道菌群的调节作用[J]. 成都大学学报(自然科学版),2020,39(3):264−271. [FU J, LI W, ZHOU J Y, et al. The regulation of high-fat induced intestinal flora in obese rats[J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition),2020,39(3):264−271. [49] 何冬萍, 朱晓萍, 陈丽玲, 等. 葛根红曲提取物对高脂饲料诱导肥胖小鼠的抗肥胖功效[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(11):25−30. [HE D P, ZHU X P, CHEN L L, et al. Gergen red curvature extract on high-fat feed induced obesity in obese mice anti-obesity effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2019,19(11):25−30. [50] 何帅, 王明友, 赵季军, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯预防高脂饮食诱导的大鼠肥胖[J]. 西部医学,2020,32(4):496−499, 504. [HE S, WANG P Y, ZHAO J J, et al. Tableless children who did not eat catetonin did not eat ester to prevent obesity in rats induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Western Medicine,2020,32(4):496−499, 504. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2020.04.008 [51] XUEQUANH, RUILI Z, YINGYING X, et al. The protective effects of polysaccharides from Agaricusblazei Murill against cadmium-induced oxidant stress and inflammatory damage in chicken livers[J]. Biological Trace Element Research,2016,178(1):1−10.
[52] SHIH C C, LIN C H, WU J B. Eriobotrya japonica improves hyperlipidemia and reverses insulin resistance in high-fat-fed mice[J]. Phytotherapy Research Ptr,2010,24(12):1769−1780. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3143
[53] PAWLAK M, LEFEBVRE P, STAELS B. Molecular mechanism of PPAR alpha action and its impact on lipid metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2015,62(3):720−733. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.039
[54] DING C , LIANG Y , TIAN M , et al. Inhibitory effects of pepper extract on high-fat diet-induced obesity and gene expression in mice[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology,2017,33(5):1−6, 13.
[55] OUCHFOUN M, EID H M, MUSALLAM L, et al. Labrador tea (Rhododendron groenlandicum) attenuates insulin resistance in a diet-induced obesity mouse model[J]. Eur J Nutr,2016,55(3):941. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0908-z
[56] HAN X, CUI Z Y, SONG J, et al. Acanthoic acid modulates lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via FXR/LXRs -dependent manner[J]. Chem Biol Interact,2019,311:108794. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108794
[57] WANG G, HUANG W, XIA Y, et al. Cholesterol-lowering potentials of Lactobacillus strains overexpression of bile salt hydrolase on high cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice[J]. Food & Function, 2019.
[58] HARADA N, ODA Z, HARA Y, et al. Hepatic de novo lipogenesis is present in liver-specific ACC1-deficient mice[J]. Molecular & Cellular Biology,2007,27(5):1881.
[59] JR H H, PETRAS S F, SHELLY L D, et al. Isozyme-nonselective N-substituted bipiperidylcarboxamide acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitors reduce tissue malonyl-CoA concentrations, inhibit fatty acid synthesis, and increase fatty acid oxidation in cultured cells and in experimental animals.[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2003,278(39):37099−37111. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304481200
[60] HERZIG S, SHAW R J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2018,19(2):121−35. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.95
[61] 王紫涵, 罗金定, 吕慧婕, 等. 二氢杨梅素经激活SIRT1-AMPK通路抑制高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠肝脏脂质沉积[J]. 中国药理学通报,2021,37(1):107−113. [WANG Z H, LOU J D, LV H J, et al. Dihydrophydrometin inhibited liver lipid deposition in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet by activating the SIRT1-AMPK pathway[J]. Chinese Pharmacology Bulletin,2021,37(1):107−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2021.01.017 [62] 靳雅倩, 马朋, 王同壮, 等. 6-姜烯酚通过抑制SCD1表达改善db/db小鼠肝脏脂肪变性的研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(1):50−56. [JIN Y Q, MA P, WANG T Z, et al. 6-Turpene phenol improved liver fat degeneration in db/db mice by inhibiting SCD1 expression[J]. New Chinese Medicine and Clinical Pharmacology,2021,32(1):50−56. [63] 黄莉莉, 黄小强, 张小琴, 等. 岩藻黄质对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠胰岛素抵抗的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(1):171−176. [HUANG L L, HUANG X Q, ZHANG X Q, et al. Effects of rock algae yellow matter on insulin resistance in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Chinese Medicine Journal,2021,46(1):171−176. [64] 梁曦, 张喆, 吕优优, 等. 益生菌通过下调FXR缓解高胆固醇诱导的高脂血症[A]. 中国食品科学技术学会. 中国食品科学技术学会第十七届年会摘要集[C]. 中国食品科学技术学会: 中国食品科学技术学会, 2020: 2. LIANG X, ZHANG J, LV Y Y, et al. Probiotics relieve high cholesterol-induced hyperlipidemia by lowering FXR[A]. Chinese Society of Food Science and Technology. Summary of the 17th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Academy of Food Science and Technology[C]. Chinese Society of Food Science and Technology: Chinese Society of Food Science and Technology, 2020: 2.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘晓飞,吴鸣,吴浚滢,张光,石彦国,张娜. 预糊化协同超微粉碎对碎米蛋白品质的影响. 中国食品学报. 2024(12): 205-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



