Comparison between Three Different Origins of Dendrobium officinale Polysaccharides and Their Initial Pharmacological Activity Evaluations
-
摘要: 本文通过对云南、丹霞、浙江三个不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖进行了同样的提取、分离、纯化,分别对其分子量、单糖组成、红外光谱进行比较,以及初步的药理活性评价,来讨论不同产地的铁皮石斛差异。采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法(High Performance Gel Permeation Chromatography,HPGPC)对纯化的多糖片段进行分子量测定、利用高效液相色谱法(High Performance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC)测定单糖组成、红外光谱(Infrared Spectroscopy, IR)测定多糖结构,应用MTT法观察多糖片段对两种肿瘤细胞(Hela细胞和HT-29细胞)增殖作用的影响。结果表明,云南种铁皮石斛多糖片段分子量为757623 u;浙江种铁皮石斛多糖片段分子量为605958 u;丹霞种铁皮石斛多糖片段分子量为663240 u。铁皮石斛多糖的单糖组成主要为甘露糖和葡萄糖,其中甘露糖与葡萄糖比值大小为云南种>丹霞种>浙江种,且多糖进行纯化后比值会进一步升高。红外光谱吸收及特征峰提示,铁皮石斛多糖主要含有甘露糖和葡萄糖,且所含糖为β型。铁皮石斛多糖纯化可以改变单糖组成比例,提高甘露糖含量,不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖在分子量、单糖组成及红外光谱吸收存在一定差异,且对HT-29肿瘤细胞具有一定的抑制作用,其中丹霞种的铁皮石斛多糖片段对两种肿瘤细胞均有较好的抑制增殖作用(48 h),具体关联性有待进一步研究。Abstract: In this paper, comparisons of the the molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, infrared spectrum were made between Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides from three different provenances, namely Yunnan, Danxia and Zhejiang. Together with the evaluation of preliminary pharmacological activity, the differences of Dendrobium candidum from different areas were discussed. High performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC) was used to determine the molecular weight of the purified polysaccharide fragments, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the composition of monosaccharides, infrared spectroscopy (IR) was used to determine the structure of polysaccharides, and MTT method was used to observe the effect of polysaccharide fragments on the proliferation of two kinds of tumor cells (Hela cells and HT-29 cells). The results showed that the molecular weight of the polysaccharide fragment of Dendrobium officinale in Yunnan was 757623 u, the molecular weight of polysaccharide fragment of Dendrobium officinale in Zhejiang was 605958 u, and the molecular weight of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide fragment in Danxia was 663240 u. The monosaccharide composition of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide was mainly mannose and glucose. In terms of the ratio of mannose to glucose, Yunnan species>Danxia species>Zhejiang species. Moreover, the ratio of polysaccharides would further increase after purification. Infrared spectrum absorption and characteristic peaks suggested that Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides mainly contained mannose and glucose, and the sugars contained were β-type. Purification of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides could change the composition ratio of monosaccharides and increase the content of mannose. There were certain differences in molecular weight, monosaccharide composition and infrared spectroscopy of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides from different provenances, and they had certain inhibitory effect on HT-29 cells. Particularly, the polysaccharide fragments of Dendrobium officinale from Danxia species had a relatively good inhibitory effect on the proliferation of the two tumor cells under the 48 h experimental determination. The specific correlation needs to be further studied.
-
“北有人参,南有石斛”,铁皮石斛分布广泛,目前种植区域主要有云南广西、广东丹霞、浙江福建等几大产区[1]。石斛在《本草纲目》中有“补五脏虚劳羸瘦,强阴益精。久服,厚肠胃”[2]等记载。而铁皮石斛作为石斛中在2010年版《中国药典》中被单独收录,且作为药食同源的佳品,在食品行业中应用广泛,市场上石斛茶、石斛酒、石斛饮料、石斛面条等食品和保健品层出不穷[3],并宣称石斛类产品具有提高免疫力、抗肿瘤或抗衰老等功效。研究发现,铁皮石斛的主要活性成分有多糖、黄酮、茋类、酚类和挥发油等[4-8],而多糖作为铁皮石斛中含量最高的成分,具有良好的抗氧化[9]、抗肿瘤[10]、调节胃肠道功能[11-12]、降血糖[13]以及提高机体免疫力[14-15]等作用。
但铁皮石斛现有的主要有效成分的评价指标一般体现为多糖总含量,不仅缺乏特异性,且并非多糖含量越高越好。目前,铁皮石斛的研究主要集中在成分分离、结构鉴定及药理药效研究[16-17],但由于价格昂贵,市场上产品繁多杂乱,品质良莠不齐,研究者多采用单一的铁皮石斛来源进行研究,缺乏比较性研究。不同产地、不同部位、不同采收时间等不同研究操作下获得的实验结果也很难以进行有效的比较[18]。多糖的分离纯化及结构鉴定的难度很大,这与其结构复杂有很大的关系[19-20],且由于提取、分离、降解的方法不同,获得的多糖片段差异较大[21-22]。目前多糖提取主要采用水提醇沉法,部分研究采用纤维素凝胶树脂和葡聚糖凝胶柱等进行纯化后的片段进行研究[23],在多糖的其他指标里,主要有测定分子量[24]、单糖组成比例[25-26]及外红光谱[27]等。
本研究通过收集主要的三大道地产区的铁皮石斛,参考以上常规方法对其进行结构鉴定及分析,拟通过相同的提取分离纯化方式,在前期稳定方法获得多糖片段的情况下[28],得到一个相对稳定分子量的多糖片段,通过比较其初步的结构表征,探讨不同铁皮石斛的差异及活性,为铁皮石斛的种植产地、产品开发的原材料选择及质量评价提供一定的参考,也为进一步的石斛多糖药理活性评价奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
云南种铁皮石斛鲜条(批号20140412) 由课题组成员陶盛昌购自淘宝店;浙江种铁皮石斛鲜条(批号20160315) 由浙江朱旭升先生提供;丹霞种铁皮石斛鲜条(批号:20160425) 由福建省连城冠江铁皮石斛有限公司江仁辉先生提供;以上三种铁皮石斛经广州中医药大学中药学院研究员魏刚教授鉴定分别为云南种铁皮石斛、浙江本地种铁皮石斛、丹霞种铁皮石斛;纯净水 华润怡宝食品饮料(深圳)有限公司;乙酸铵、苯酚 天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮(PMP) 阿拉丁;盐酸溶液、氢氧化钠、磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;乙腈 色谱纯,德国Merk公司;石油醚、无水乙醇、正丁醇、三氯甲烷 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;浓硫酸 广州市东红化工厂;MTT(噻唑蓝粉剂)、DMSO(二甲基亚砜) Sigma公司;FBS(胎牛血清) Hyclone公司;双抗、DMEM培养液、胰酶 Gibco公司;所有分离用有机溶剂 均为国产分析纯;葡聚糖T系列(5000 u,批号00269;11000 u,批号00270;80000 u,批号00892;15000 u,批号008 93;273000 u,批号00894;667000 u,批号00896) 美国Sigma公司;DEAE纤维素DE-52 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;Sephacryl S-300 High Resolution GE公司;单糖标准品(D-葡萄糖、D-甘露糖、鼠李糖、木糖、半乳糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖) 中国食品药品检定研究院;Hela细胞株(人宫颈癌细胞,Cat:KG042,LOT20160912)、HT-29细胞株(结肠癌细胞,Cat:KG042,LOT20160912) 凯基生物有限公司。
LC-20AT型高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;蒸发光散射检测器ELSD 6000 广州万谱仪器有限公司;AB204-N型精密电子天平 梅特勒-托利多(Mettler Toledo)公司;TYXH-1漩涡混合器 上海乔跃电子有限公司;EYELA OSB-2100旋转蒸发仪 埃朗科技国际贸易(上海)有限公司;电热恒温水浴锅 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;PHB-1 数字式pH计 上海三信仪表厂;SCIENTZ-10N冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;TD-5-A离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;TC-15电热套式恒温器 新华市医疗器械厂;中压层析柱(3.5 cm×55 cm、1.6 cm×80 cm)、HL-2D恒流泵 上海沪西仪器分析有限公司;DM34 mm透析袋 上海士锋生物科技有限公司;CO2细胞培养箱 德国 Heraeus公司;MULTISKAN GO酶标仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;MIT-2显微镜 日本奥林巴斯。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 铁皮石斛粗多糖的提取分离
分别精密称取不同种源的铁皮石斛粉末各10 g,置于1000 mL的圆底烧瓶中,加入石油醚100 mL,加热回流2 h,取出,放冷,过滤,弃去滤液,滤渣烘干后,以同样的方法重复提取两次,合并滤液,减压浓缩至合适的体积,放冷,并边搅拌边缓慢的加入四倍体积的无水乙醇醇沉,得到白色絮状的多糖沉淀,并置于4 ℃冰箱过夜。以4000 r/min离心10 min,取沉淀,获得多糖后置于60 ℃烘箱烘干。将多糖用热水按1:100 g/mL重新溶解,置于分液漏斗中,根据样品和Sevag试剂(三氯甲烷:正丁醇=4:1)的体积比为4:1的比例,缓慢加入Sevag试剂,振荡5 min,静置后弃去下层溶液,以5000 r/min离心15 min,重复三次除去多糖溶液中的蛋白。最后,移除上层溶液加入四倍体积的无水乙醇重新醇沉,得到粗多糖[28],分别命名为YN(云南)、DX(丹霞)、ZJ(浙江),称重分别为2.2、1.4、1.4 g。密封干燥保存,备用。
1.2.2 纤维素凝胶树脂DEAE-52纯化多糖
分别精密称取1.2.1提取的三个不同种源的铁皮石斛粗多糖YN、DX、ZJ各300 mg,各加入10 mL的蒸馏水溶解,溶解完全后经0.45 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,缓慢上样到纤维素凝胶树DEAE-52进行洗脱。上样量为300 mg/10mL,流速为1 mL/min,采用纯水洗脱,用自动收集器每10 min收集一管,采用《中国药典》苯酚硫酸法[29]测定吸光度,并绘制吸收曲线,根据吸收曲线收集洗脱液,浓缩,冷冻干燥,得到多糖。
1.2.3 葡聚糖凝胶Sephacryl S-300纯化多糖
将上述1.2.2得到的三份多糖各精密称取100 mg,分别溶解于5 mL热水中,待溶解完全后经0.45 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,缓慢上样到葡聚糖凝胶Sephacryl S-300进行洗脱。上样量为100 mg/5 mL,流速为0.5 mL/min,采用0.2 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱,用自动收集器每10 min收集一管,采用苯酚硫酸法测定吸光度并绘制吸收曲线,根据吸收曲线收集洗脱液,浓缩,透析,冷冻干燥,分别得到三个不同种源的多糖片段,并命名为YN-WDOPA、DX-WDOPA、ZJ-WDOPA。密封干燥保存,备用。
1.2.4 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖分子量测定
采用超高效液相色谱仪和蒸发光散射检测器测定多糖分子量,分别称取已知分子量(5000、11000、80000、150000、273000、667000 u)的葡聚糖标准品各10 mg溶解于2 mL的纯净水中,待完全溶解后经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,进样量为5 μL,安捷伦凝胶色谱柱(Agilent,PL aquagel-OH MIXED-H, 300 mm×7.5 mm,8 μm)与保护柱(Agilent,PL aquagel-OH Guard,50 mm×7.5 mm, 8 μm)串联,流动相为20 mmol/L乙酸铵溶液,流速为0.5 mL/min,柱温箱40 ℃,漂移管110 ℃,气体流速为2.0 L/min,增益1。根据标准品的保留时间及分子量,做出lgMw-RT标准曲线。将不同种源的多糖YN-WDOPA、DX-WDOPA、ZJ-WDOPA按照上述方法处理,一并进样,测量分子量。
1.2.5 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖单糖组成及比例差异
1.2.5.1 供试品制备
分别精密称取样品YN、YN-WDOPA、ZJ、ZJ-WDOPA、DX、DX-WDOPA各2 mg,溶解于2 mL纯净水中,再分别精密吸取各样品溶液1000 μL,置于5 mL的安瓿瓶中,精密加入3 mol/L盐酸溶液500 μL,封口后置于110 ℃条件下水解1 h,取出,放冷,再加入3 mol/L NaOH溶液调节pH至7.0,即得水解液。精密吸取水解液400 μL置于5 mL安瓿瓶中,再加入0.3 mol/L NaOH溶液400 μL和0.5 mol/L PMP溶液250 μL,混匀,在70 ℃的条件下衍生反应100 min,取出后加入0.3 mol/L盐酸溶液450 μL,漩涡混匀,加入三氯甲烷2 mL萃取,漩涡混匀,离心(4000 r/min)10 min,弃去氯仿层,重复萃取3~5遍,直至氯仿层无颜色,水层过0.22 μm微孔滤膜,即得供试品溶液。
1.2.5.2 混标对照品溶液制备
精密称取各单糖标准品适量,加水溶解,使其浓度皆为3 mg/L,精密吸取混标对照品溶液400 μL置于5 mL安瓿瓶中,再按照“1.2.5.1”供试品的制备方法制备混标对照品溶液。
1.2.5.3 单糖组成测定
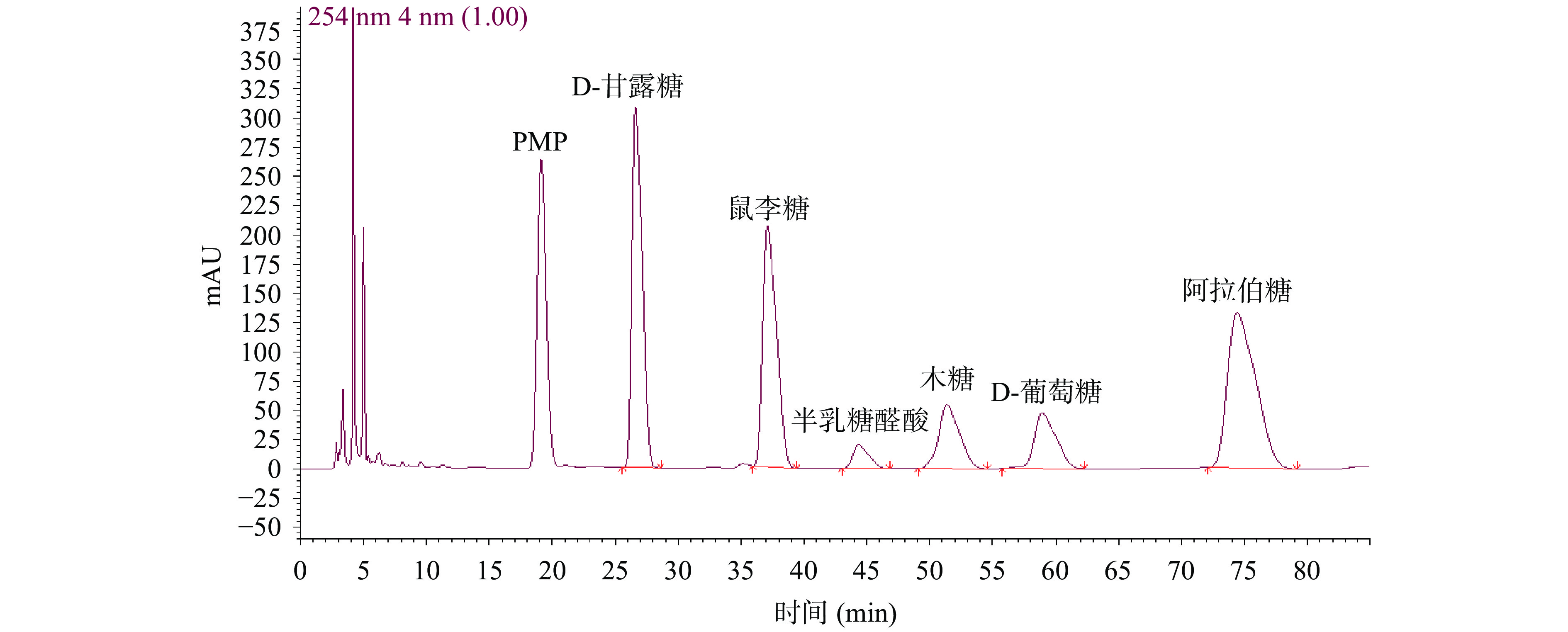
采用超高效液相色谱仪进行单糖组成测定,色谱柱为安捷伦Eclipse XDB-C18(5 μm,4.6 mm×250 mm);流动相A-B=乙腈-乙酸铵(0.02 mol/L),梯度洗脱:0~18 min:16.8%A;18~20 min:16.8%~25%A;20~30 min:25%~30%A;30~35 min:30%A;柱温30 ℃;流速为1 mL/min;进样量10 μL;检测波长250 nm。将配置好的混标对照品溶液和供试品溶液依次进样。
1.2.6 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖的红外光谱比较
称取三个多糖片段样品YN-WDOPA、DX-WDOPA、ZJ-WDOPA各2 mg,分别加入溴化钾200 mg左右,混合均匀,在红外灯下研磨至均匀细粉并进行压片,片状应透明无颗粒,在4000~400 cm−1范围下进行红外扫描。
1.2.7 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖的初步药理活性比较
实验应用MTT法观察三个不同种源的多糖片段分别对Hela细胞和HT-29细胞增殖作用的影响。将对数生长期的肿瘤细胞加入到96孔板中,细胞计数浓度为3×104 个/mL,每孔100 μL,放入培养箱继续培养,将配制好的母液(4 mg多糖加入1 mL的PBS溶液,浓度为4 mg/mL)用无菌0.22 μm微孔滤膜滤过,再用无血清DMEM配成25、50、100、200、400 μg/mL系列浓度的多糖溶液,96孔板弃去上清液,每孔加入100 μL多糖溶液,每个样品每个浓度设4个复孔。以加入等量100 μL培养基作为空白组对照,分别在培养24、48 h后测定其OD值。比较不同浓度下各个片段的细胞抑制率,从而比较它们的抗肿瘤活性。抑制率均与空白对照组进行比较,计算公式为:
抑制率(%)=(空白组−给药组)空白组×100 。1.3 数据处理
本研究选择的是三个不同产地的成熟期大棚仿生种植的铁皮石斛样品,经3次重复性实验进行测定,采用软件SPSS20.0进行分析,P<0.05为有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 三个不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖DEAE-52吸收曲线
YN、DX、ZJ三个粗多糖的DEAE-52吸光度测定结果如图1所示,可以明显看出,不同种源的DEAE-52洗脱曲线基本相似,只是吸光度的大小有所差异,代表洗脱下来的多糖含量的高低不同,而有吸收的范围是基本一致的,可以用于确定大致需要的洗脱时间。分别按其主要吸光度范围合并相应管数的多糖溶液,浓缩,干燥。
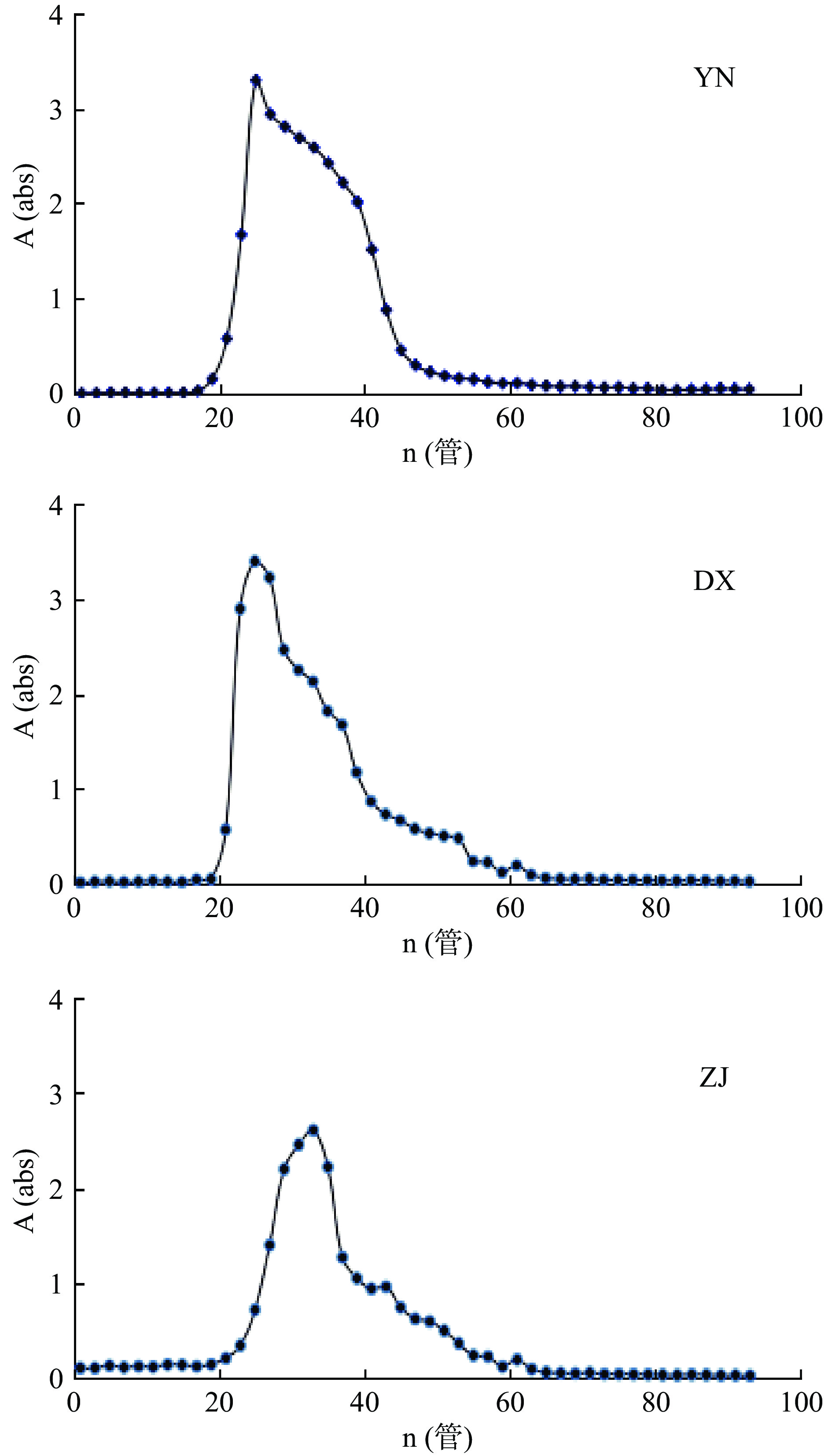
2.2 三个不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖Sephacryl S-300吸收曲线
三个不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖片段的Sephacryl S-300吸光度测定如图2所示:三个批次的Sephacryl S-300洗脱曲线基本相似,而吸光度的大小存在差异,有吸收的管数存在细微的差别,故分别收集吸光度较大且共有的第一个峰的管数,即第21~45管的多糖溶液,合并,浓缩,透析,干燥。
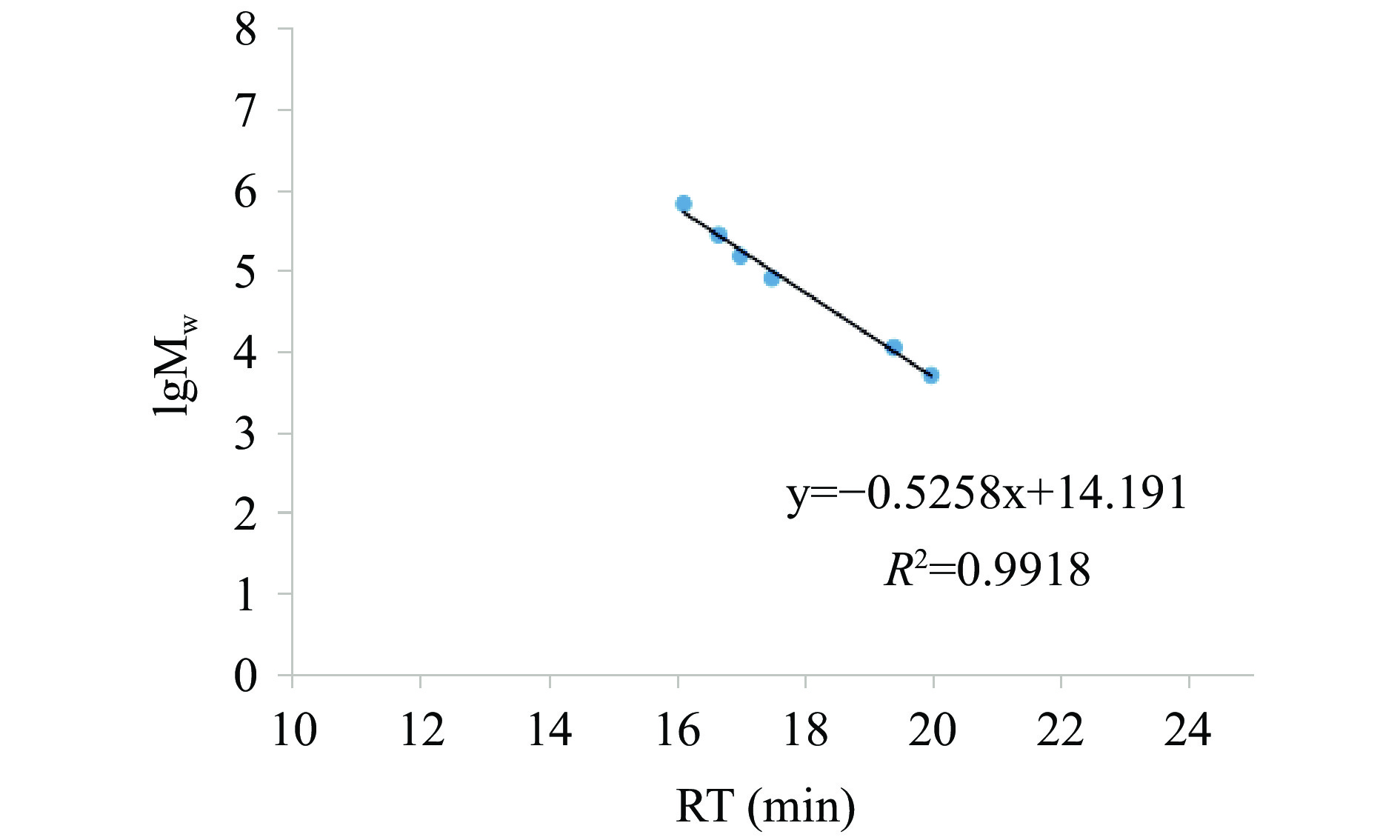
2.3 超高效凝胶渗透色谱法测定多糖分子量
如图3所示,y=−0.5258x+14.191,R2
=0.9918,表明线性关系良好。YN-WDOPA分子量为757623 u;ZJ-WDOPA计算分子量为605958 u;DX-WDOPA的分子量为663240 u。现有的研究报道,不同来源、不同提取分离纯化方法得到的铁皮石斛分子量差异很大,但由于提取、分离的方法不同,从一百多万到几千的分子量都有[30],本实验方法下多糖分子量,符合现有报道范围,但也提示,在相同的方法下制备的多糖片段,不同种源分子量有差异,但总体还在同一量级范围内(RSD=11.33%)。 2.4 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖单糖组成及比例测定
如图4、图5显示,以及表1的单糖面积计算,实验所选择的三个产地的铁皮石斛多糖经水解后,存在的主要单糖为甘露糖和葡萄糖,且云南种铁皮石斛多糖无论是在粗多糖阶段还是分离纯化后的阶段,其甘露糖与葡萄糖的比值,均大于丹霞种和浙江种,而丹霞种与浙江种铁皮石斛多糖片段的单糖组成比例相差不大,说明实验所选的这三个不同产地的铁皮石斛之间,多糖的结构存在一定的差异,此外,经过DEAE-52及凝胶Sephacryl S-300洗脱后,单糖组成及比例均发生了明显的变化,说明在纯化多糖的过程中,纤维素凝胶树脂的洗脱提高了甘露糖与葡萄糖的比值,从而改变了多糖的结构。
表 1 三个种源多糖片段的单糖组成及比例Table 1. Monosaccharide composition and ratio of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide from three different provenances样品 甘露糖:葡萄糖 YN 3.71 DX 2.89 ZJ 2.58 YN-WDOPA 7.09 DX-WDOPA 5.95 ZJ-WDOPA 5.93 2.5 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖的红外光谱比较
由图6可知,三个不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖片段在红外光谱上具有较高的相似性,3400 cm−1处的强吸收峰为O-H的伸缩振动形成,C-H键的伸缩振动则产生了2930 cm−1附近的特征峰存在,1030 cm−1特征峰的C-O键及1642 cm−1特征峰的C-O-H键弯曲振动均提示,DX-WDOPA、YN-WDOPA、ZJ-WDOPA三个片段为糖类化合物。811 cm−1附近的红外吸收处为甘露糖的特征峰,这也与单糖的组成及比例的测定结果相吻合,876 cm−1和760 cm−1附近的特征峰表明,该片段所含的糖为β型[31]。
2.6 不同种源铁皮石斛多糖的初步药理活性比较
2.6.1 多糖对Hela细胞增殖作用的影响
如图7、图8所示,与空白组相比较,三个产地的铁皮石斛多糖片段对Hela细胞的增殖均具有一定的抑制作用,其中在24 h的实验中,YN-WDOPA在低浓度的时候具有一定的抑制作用,在25、50 μg/mL与空白组对比具有统计学意义(P<0.05),ZJ-WDOPA的作用更为明显,各浓度下均对Hela细胞增殖具有抑制作用(P<0.05)。云南种的活性随着浓度的增加,呈现先降低后升高的趋势,可能多糖在低浓度时并无抑制作用,作为肿瘤细胞的“营养剂”,低多糖浓度促进细胞增殖,随着多糖浓度增加,才展现一定的抗肿瘤活性。但总体对Hela细胞的抑制率在最高浓度也未能达到一个较高水平(30%左右)。在48 h的结果中,三个种源的多糖片段均表现出了较好的抗肿瘤活性(P<0.05),其中在低浓度25 μg/mL下,浙江种达到46.97%,丹霞种的抑制率除了在低浓度作用较好(32.53%)外,在50~400 μg/mL下,抑制率逐渐增加。
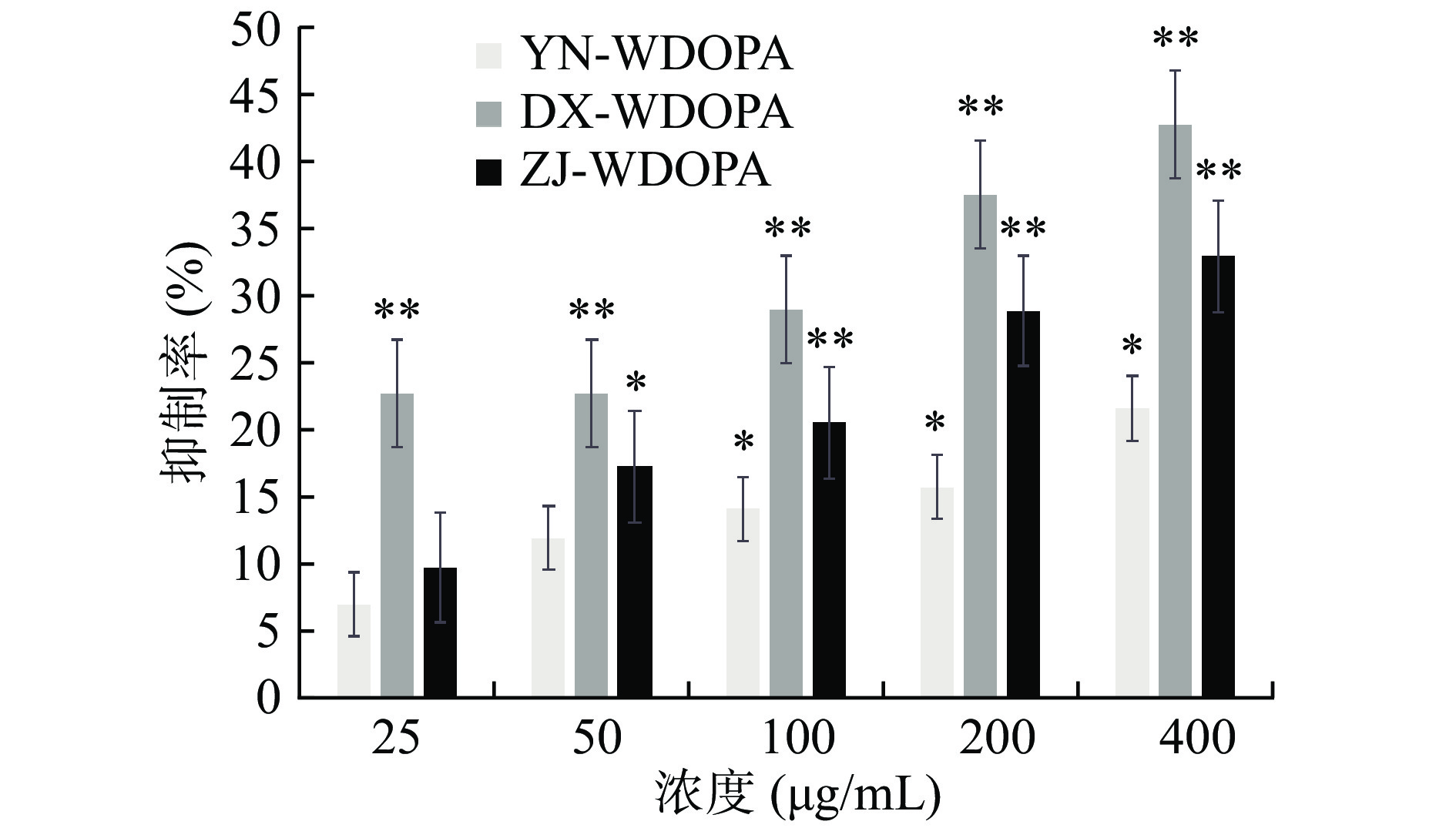
2.6.2 多糖对HT-29细胞增殖作用的影响
如图9、图10所示,与空白对照组相比较,24 h的实验结果中,三个产地的铁皮石斛多糖片段对HT-29细胞的增殖抑制作用都很弱,基本在20%以下,大多数浓度的抑制率不具有统计学差异(P>0.05)。在48 h的实验结果中,三个产地的铁皮石斛多糖均与浓度有一定的关系,随着浓度的增加,抑制率不断攀升,其中丹霞种的作用效果最好,在400 μg/mL的浓度下,抑制率达到了42.82%(P<0.01),说明该丹霞种的铁皮石斛多糖片段对人宫颈癌细胞具有一定活性,可为进一步的体外或动物实验提供一定参考。
3. 讨论与结论
本实验主要采用同样的方法对三个不同种源的铁皮石斛进行比较及初步的活性评价,实验结果显示不同种源的铁皮石斛多糖在含量、分子量、单糖组成及比例和抗肿瘤活性上均有一定的差异性。本实验中的分离提取纯化方法简单易行,重现性较好。而实验中纤维素凝胶树脂DEAE-52和葡聚糖凝胶Sephacryl S-300的纯化能够改变多糖的单糖组成比例,这一发现还需要进一步的结构研究进行阐释。
在三个不同产地铁皮石斛的活性比较中,除低剂量的浙江种的铁皮石斛多糖纯化片段对Hela细胞有一定抑制作用外,对该细胞作用并不明显。但在对HT-29的抑制上,丹霞种铁皮石斛的的抑制率与多糖的提高而增加,可为铁皮石斛活性研究提供一定的参考,但具体更深入的原因有待进一步的研究。
铁皮石斛分布广泛,据很多文献研究发现,不同生长期、不同年限、不同种植方法之间的铁皮石斛多糖也都存在较大差异,本次研究仅选择成熟期大棚仿生种植的铁皮石斛进行研究,后续应当收集更多批次的铁皮石斛样品进行多糖实验,才能得到更具说服力的实验数据。
在现在的铁皮石斛产品研发中,一般显示的主要评价指标为石斛总多糖,而在本实验中发现,同样方法下获得的石斛多糖片段结构和活性均存在一定差异,那么仅单纯依靠多糖的总量去评价铁皮石斛品质的高低,是需要进一步的研究去确定的,如内在的多糖分子量大小、单糖组成比例及结构解析,可能更加影响多糖的药理活性。这也对目前铁皮石斛种植及产品开发的方向具有一定参考意义。
-
表 1 三个种源多糖片段的单糖组成及比例
Table 1 Monosaccharide composition and ratio of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide from three different provenances
样品 甘露糖:葡萄糖 YN 3.71 DX 2.89 ZJ 2.58 YN-WDOPA 7.09 DX-WDOPA 5.95 ZJ-WDOPA 5.93 -
[1] 焦连魁, 曾燕, 张继聪, 等. 石斛属优质道地药材生产技术概述[J]. 中国现代中药,2021,23(4):734−740. [JIAO L K, ZENG Y, ZHANG J C, et al. A summary of cultivation technology of high quality and daodi Dendrobium medicinal materials[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2021,23(4):734−740. [2] 罗迪, 庞璐, 赵兴, 等. 浅析《本草纲目》中铁皮石斛的功能主治[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2013,29(3):108−109. [LUO D, PANG L, ZHAO X, et al. Analysis on the functions and indications of Dendrobium officinale in "Compendium of Materia Medica"[J]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2013,29(3):108−109. [3] XING L, MIAO Y, LI N, et al. Molecular structure features and lactic acid fermentation behaviors of water- and alkali-soluble polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore,2021,58(2):532−540. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04564-6
[4] 奚航献, 刘晨, 刘京晶, 等. 铁皮石斛化学成分、药理作用及其质量标志物(Q-marker)的预测分析[J]. 中草药,2020,51(11):3097−3109. [XI H X, LIU C, LIU J J, et al. Chemical components and pharmacological action for Dendrobium officinale and its prediction analysis on Q-marker[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2020,51(11):3097−3109. [5] ZUO S, YU H, ZHANG W, et al. Comparative metabolomic analysis of Dendrobium officinale under different cultivation substrates[J]. Metabolites,2020,10(8):1−14.
[6] REN Z, QIU F, WANG Y, et al. Network analysis of transcriptome and LC-MS reveals a possible biosynthesis pathway of anthocyanins in Dendrobium officinale[J]. Biomed Research International,2020,2020:6512895.
[7] LI M, YUE H, WANG Y, et al. Intestinal microbes derived butyrate is related to the immunomodulatory activities of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,149:717−723. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.305
[8] HU J, HUANG W, ZHANG F, et al. Variability of volatile compounds in the medicinal plant Dendrobium officinale from different regions[J]. Molecules,2020,25(21):5046−5055. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215046
[9] HUANG S, CHEN F, CHENG H, et al. Modification and application of polysaccharide from traditional Chinese medicine such as Dendrobium officinale[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,157:385−393. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.141
[10] TAO S, HUANG C, TAN Z, et al. Effect of the polysaccharides derived from Dendrobium officinale stems on human HT-29 colorectal cancer cells and a zebrafish model[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,41(5):100995.
[11] FU Y, ZHANG J, CHEN K, et al. An in vitro fermentation study on the effects of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides on human intestinal microbiota from fecal microbiota transplantation donors[J]. J Funct Food,2019,53:44−53. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.12.005
[12] LI L, YAO H, LI X, et al. Destiny of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide after oral administration: Indigestible and nonabsorbing, ends in modulating gut microbiota[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(21):5968−5977. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01489
[13] CHEN H, NIE Q, HU J, et al. Metabolism amelioration of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide on type II diabetic rats[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,102:105582.
[14] LIANG J, LI H, CHEN J, et al. Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides alleviate colon tumorigenesis via restoring intestinal barrier function and enhancing anti-tumor immune response[J]. Pharmacological Research,2020,148:104417.
[15] CHEN Y, WANG Y, LYU P, et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveal the regulation mechanism underlying MeJA-induced accumulation of alkaloids in Dendrobium officinale[J]. Journal of Plant Research,2019,132(3):419−429. doi: 10.1007/s10265-019-01099-6
[16] 谢唐贵, 陈敬民, 李燕婧. 不同产地铁皮石斛水提物的抗疲劳作用研究[J]. 云南中医中药杂志,2018,39(8):66−67. [XIE T G, CHEN J M, LI Y J. Study on anti-fatigue effect of aqueous extracts from Dendrobium candidum in different producing areas[J]. Yunnan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,39(8):66−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2349.2018.08.030 [17] 陈燕兰, 钟淳菲, 徐雅囡, 等. 不同地区铁皮石斛的品质差异研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(8):123−130. [CHEN Y L, ZHONG C F, XU Y N, et al. Study on quality differences of Dendrobium officinale in different areas[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(8):123−130. [18] MAI Y, YANG Z, JI X, et al. Comparative analysis of transcriptome and metabolome uncovers the metabolic differences between Dendrobium officinale protocorms and mature stems[J]. All Life,2020,13(1):346−359. doi: 10.1080/26895293.2020.1781699
[19] 韩邦兴, 陈凌霄, 邓勇, 等. 糖谱法结合多元色谱分析比较铁皮石斛功能性多糖结构特征[J]. 药物分析杂志,2018,38(1):41−49. [HAN B X, CHEN L X, DENG Y, et al. Characterization and comparison of specific polysaccharides in Dendrobium officinale by using saccharide mapping and chromatographic methods[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal,2018,38(1):41−49. [20] LUO Y, REN Z, DU B, et al. Structure identification of vicenin II extracted from Dendrobium officinale and the reversal of TGF-1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma cells through TGF-/Smad and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways[J]. Molecules,2019,24(1):144−160. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010144
[21] 黄丽, 文凤娟, 李桂琼, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖提取工艺及优化研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2017,32(5):884−888. [HUANG L, WEN F J, LI G Q, et al. Research on optimizing extraction technology of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2017,32(5):884−888. [22] ZHANG X, LUO Y, WEI G, et al. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of the degradations of polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale and their suitable molecular weight range on inducing Hela cell apoptosis[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2019,2019:4127360.
[23] TAO S, LEI Z, HUANG K, et al. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of two novel polysaccharides derived from the stem of Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo[J]. J Funct Food,2019,57:121−134. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.04.013
[24] YANG K, LU T, ZHAN L, et al. Physicochemical characterization of polysaccharide from the leaf of Dendrobium officinale and effect on LPS induced damage in GES-1 cell[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,149:320−330. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.026
[25] KE Y, ZHAN L, LU T, et al. Polysaccharides of Dendrobium officinale Kimura & Migo leaves protect against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in vitro and vivo[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2020,5263:49.
[26] YU Z, ZHANG G, DA SILVA J A T, et al. The beta-1, 3-galactosetransferase gene DoGALT2 is essential for stigmatic mucilage production in Dendrobium officinale[J]. Plant Science,2019,287:110179.
[27] KUANG M, LI J, YANG X, et al. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic effect via stimulating glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion of two polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,241:116326.
[28] 黄俊彬, 黄丹丹, 陈欢欢, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖分子量测定及其影响因素分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(7):81−85. [HUANG J B, HUANG D D, CHEN H H, et al. The effects of heating and ultrasonic degradation on the molecular weight of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(7):81−85. [29] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典. 2015版一部[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015: 282. National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. 2015 Edition One[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2015: 282.
[30] 鲍素华, 查学强, 郝杰, 等. 不同分子量铁皮石斛多糖体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科学,2009,30(21):123−127. [BAO S H, ZHA X Q, HAO J, et al. In vitro antioxidant activity of polysaccharides with different molecular weights from Dendrobium candidum[J]. Food Science,2009,30(21):123−127. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.21.029 [31] 陶盛昌. 铁皮石斛水溶性多糖分离纯化、结构特征及免疫活性研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2016. TAO S C. Study on structural idenfication and immune activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from the stems of Dendrobium officinale Kimum et Migo[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2016.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 张新圻,朱顺华,钟秀来,罗庆,熊爱生,谭国飞. 不同水芹种质资源的形态、花青素含量及相关基因表达量分析. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(02): 105-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张博,王雨婷,刘洁,李加会,吴鸿飞. 经典药对“瓜蒌-薤白”治疗痰瘀互结心血管疾病的血清代谢组学研究. 中国中药杂志. 2024(01): 232-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 罗庆,张新圻,李梦瑶,朱顺华,熊爱生,谭国飞. 药食同源植物水芹的研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报. 2024(08): 1221-1233 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 邢啸林,陈丹,况勇,徐文娟,黄然,甘德芳. 水芹SSR分子标记开发与遗传多样性分析. 江苏农业学报. 2024(07): 1285-1296 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李冬霞,张凡,王洧,南建. 水芹贮藏保鲜和开发利用研究进展. 农产品加工. 2023(02): 66-69+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱顺华,罗庆,李梦瑶,孟平红,钟秀来,王堃,陈志峰,谭国飞,熊爱生. 水芹雄性不育材料的鉴定及营养品质分析. 植物科学学报. 2023(03): 343-348 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 倪子怡,许海,詹旭,朱广伟,程新良,胡亮,王裕成,郑文婷. 刈割对千岛湖生态浮床植物生长与氮素净化效率的影响. 环境工程学报. 2023(08): 2494-2504 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘杰,刘吉祥,常雅军,陈婷,刘晓静,孙林鹤,姚东瑞. LC-SIM-Orbitraq测定无土栽培水芹不同器官中有机酸含量. 中国瓜菜. 2023(09): 80-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王丹,万娜,黄金妮,陈敏妮,杨兹伟,汤祝华. 多壁碳纳米管净化-色谱质谱技术测定水芹中多农药残留. 食品科技. 2023(09): 276-284 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘吉祥,杜凤凤,孙林鹤,王巍,赵慧君,姚东瑞,常雅军. 无土栽培水芹不同器官的氨基酸特征及其资源化利用潜力分析. 中国蔬菜. 2022(07): 34-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 季青霞,陈伟,毕艳红,赵祥杰,白青云,王朝宇. 超声波辅助提取水芹中黄酮类化合物的工艺研究. 包装与食品机械. 2022(06): 25-30+38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



