Mechanism of Curcumin and/or Aerobic Exercise Improving Pyroptosis in Myocardium of Hyperlipidemic Rats
-
摘要: 研究姜黄素和/或有氧运动改善高脂血症大鼠心肌细胞焦亡的作用机制。50只5周龄雄性SD大鼠随机分为普通膳食+安静组(RDC组)、高脂膳食+安静组(HDC组)、高脂膳食+有氧运动组(HDM组)、高脂膳食+姜黄素+安静组(HDCC组)和高脂膳食+姜黄素+有氧运动组(HDCM),每组10只。第3周起,HDCC、HDCM组以400 g/(kg·d)姜黄素灌胃,其余组以等体积0.5%羧甲基纤维素钠灌胃;HDM、HDCM组进行有氧运动干预,其他组无任何运动干预。6周干预结束后24 h,观察各组大鼠心脏组织形态,检测血液、心肌组织相关生化指标。结果显示:血清总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三脂(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C),HDC组较RDC组均显著升高(P<0.01);血清TC、TG,HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均显著降低(P<0.01);血清TC,HDCM组较HDCC、HDM显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);血清LDL-C,HDCC组、HDCM组较HDC组显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),HDCM组较HDCC组、HDM组均显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。血清高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)水平,HDC组较RDC组显著降低(P<0.05);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01);HDCM组较HDM组均显著升高(P<0.01)。RDC组心肌形态正常,HDC组出现炎性损伤;HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组明显改善,其中HDCM组最为显著。心肌白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、白细胞介素-18(IL-18)含量,HDC组较RDC组均显著升高(P<0.01);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均显著降低(P<0.01);HDCC、HDM组较HDCM组显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。心肌损伤标志物肌酸激酶同工酶MB型(CK-MB),HDC组较RDC组均显著升高(P<0.01);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均显著降低(P<0.01);HDCM组较HDCC、HDM显著降低(P<0.01)。心肌NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(ASC)、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶1(Caspase1)蛋白质表达(H-score),HDC组显著高于RDC组(P<0.01);HDCC组、HDM组、HDCM组显著低于HDC组(P<0.05或P<0.01);HDCC组、HDM组显著高于HDCM组(P<0.05或P<0.01)。从而说明,为期6周的姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预可以改善高脂血症大鼠心肌细胞焦亡,抑制过度炎症反应,保护心脏功能/结构,其机制可能与抑制NLRP3/Caspase1通路活化相关。二者联合干预效果最佳。Abstract: To study the mechanism of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise improving pyroptosis in myocardium of hyperlipidemic rats. Fifty 5-week-old male SD rats were randomly divided into normal diet control group (RDC), high fat diet control group (HDC), high fat diet with curcumin group (HDCC), high fat diet with aerobic exercise group (HDM), high fat diet with curcumin and aerobic exercise group (HDCM), ten in each group. From the third week, group HDCC and HDCM were injected intragastrically with curcumin at 400 g/(kg·d), and the other groups were given an equal volume of 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose. Group HDM and HDCM performed aerobic exercise intervention, and the other groups did not. Twenty-four hours after the end of 6-week-intervention, the myocardial microstructure in each group was observed, blood and myocardium related biochemical indicators were tested. The results showed that, serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), HDC were significantly higher than RDC (P<0.01). Serum TC and TG, HDCC, HDM and HDCM were significantly lower than HDC (P<0.01). Serum TC, HDCM decreased significantly compared with HDCC and HDM (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Serum LDL-C, HDCC and HDCM were significantly lower than HDC (P<0.05 or P<0.01), HDCM was significantly lower than HDCC and HDM (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), HDC was significantly lower than RDC (P<0.05), HDCC, HDM and HDCM significantly were higher than HDC (P<0.05 or P<0.01), HDCM was significantly higher than HDM (P<0.01). The myocardial microstructure of RDC was normal, there were inflammatory injury in myocardium of HDC, injury in HDCC, HDM, HDCM were improved significantly, and HDCM was the most significant in the three. Myocardial interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), HDC was significantly higher than RDC (P<0.01), HDCC, HDM and HDCM were significantly lower than HDC group (P<0.01), HDCC and HDM were significantly higher than HDCM (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Myocardial injury marker creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), HDC was significantly higher than RDC (P<0.01), HDCC, HDM and HDCM were significantly lower than HDC (P<0.01), HDCM was significantly lower than HDCC and HDM (P<0.01). The H-score of myocardial NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD (ASC) and cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 (Caspase1), HDC was significantly lower than RDC (P<0.01), HDCC, HDM and HDCM were significantly higher than HDC (P<0.05 or P<0.01), HDCC and HDM were significantly lower than HDCM (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Therefore, the 6-week curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention could improve pyroptosis in myocardium of hyperlipidemic rats, inhibit excessive inflammatory response, and protect the heart function/structure, which might be related to inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase1 pathway. The effect of combined intervention was better.
-
Keywords:
- curcumin /
- aerobic exercise /
- hyperlipidemia /
- rat /
- pyroptosis
-
脂代谢异常致高脂血症是诱发心肌慢性炎症反应、功能紊乱、结构受损的重要原因[1]。细胞焦亡作为细胞程序性、炎性死亡方式,广泛存在于心血管疾病发生过程中,抑制细胞焦亡的发生与发展能够有效抑制炎症因子的生成和炎症反应,降低组织损伤程度[2]。脂代谢异常诱发的炎性小体激活可以诱导焦亡发生,大量释放炎症因子,引发强烈炎症反应,加速心血管疾病的发生与发展。适宜强度的有氧运动对于高血脂、炎症等多种心血管危险因素均具有良好改善作用[3]。高脂饮食易诱发大鼠高脂血症的同时,心肌NOD样受体蛋白3(NOD-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)等焦亡相关蛋白及相关炎症因子表达大幅升高,心肌组织形态发生改变,而有氧运动可以实现有效逆转[1]。姜黄素是源自姜黄的多酚类化合物,具有改善细胞焦亡,抑制炎症反应的潜在作用[4]。但二者单独或联合干预能否改善高脂血症大鼠心肌细胞焦亡及炎症反应,保护心脏功能/结构,尚未见报道。
本研究建立高脂饮食诱导高脂血症大鼠模型,通过观察脂代谢相关指标、心肌组织病理学诊断、心肌损伤标志物、心肌炎症因子及细胞焦亡相关蛋白表达等多层次指标,探讨姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预改善高脂血症大鼠心肌细胞焦亡水平,保护心脏的作用机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
姜黄素(curcumin) 纯度>95%,宁波中药制药股份有限公司(CP20191007);羧甲基纤维素钠 纯度>99%,北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司;白细胞介素-1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、白细胞介素-18(interleukin-18,IL-18)酶联免疫试剂盒 北京华英生物技术研究所;NLRP3、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶1(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1,Caspase1)抗体 武汉爱博泰克生物科技有限公司;凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing CARD,ASC)抗体 美国Santa Cruz;5周龄SD大鼠(SPF级,雄性,180~200 g,生产许可证编号:SCXK(京)2016-0002)、基础饲料及高脂饲料(60%脂肪热量比饲料,生产许可证编号:SCXK京2019-0010) 斯贝福(北京)生物技术有限公司。
FA2004N电子天平 上海精密仪器有限公司;NR-B17CC型超低温冰箱 日本松下电器产业株式会社;电子组织匀浆器 美国Kimble公司;LG 10-3A高速冷冻离心机 北京医用离心机厂;DR-200BS酶标分析仪 无锡华卫德朗;AU480生化分析仪 美国Beckman;LEICA RM2016病理切片机 德国RM公司;Pannoramic MIDI全自动数字切片扫描系统 匈牙利3D HISTECH公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 动物分组
经7 d适应性饲养及训练后,将符合实验要求的50只雄性SD大鼠按体重分为5组(随机数字法),每组10只:普通膳食+安静组(RDC组)、高脂膳食+安静组(HDC组)、高脂膳食+姜黄素+安静组(HDCC组)、高脂膳食+有氧运动组(HDM组)和高脂膳食+姜黄素+有氧运动组(HDCM)。实验过程中,室内温度控制在20~24 ℃,相对湿度控制在55%~75%,昼夜明暗交替时间:12/12 h。各组大鼠每天自由摄食饮水;RDC组以普通饲料喂养,其他各组以高脂饲料喂养。第3周起,HDCC和HDCM组根据文献[5]及预实验确定最佳剂量为400 g/(kg·d)、体积为5 mL/kg,每次训练前0.5 h灌胃姜黄素溶液(0.5%羟甲基纤维素钠配成混悬液),每天1次,其余各组均以等体积0.5%羧甲基纤维素钠灌胃;HDM和HDCM组进行有氧运动干预[6],坡度:5°,速度:70%~75%最大摄氧量,运动时长:1 h,频率:1次/d,6 d/w,其他组无任何运动干预。干预持续时间:6 w。
1.2.2 实验动物取材
末次训练结束后24 h,乌拉坦适度麻醉大鼠后腹主动脉取血,室温自然凝固,待血清出现后4 ℃离心10 min,3000 r/min,分离血清,−20 ℃冻存待测。开腹后,迅速取出心脏,去除非心脏组织后以预冷的生理盐水冲洗,滤纸吸干表面水分后,取部分左心室心肌组织剪成小块后称取重量,根据组织重量:体积=1:9的比例置于预冷的生理盐水中洗净血污,随后充分研磨制成10%的心肌组织匀浆液,5000 r/min离心5 min取上层清液待测。另取部分左心室心肌组织浸入4%多聚甲醛固定液固定,用于心肌组织病理诊断。
1.2.3 血脂水平、心肌损伤标志物及心肌细胞炎症因子含量的测定
血清甘油三脂(triglyceride,TG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high-density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、肌酸肌酶同工酶MB型(creatine kinase-MB,CK-MB)采用全自动生化分析仪测定。心肌IL-1β、IL-18采用酶联免疫法用试剂盒进行测定。
1.2.4 心肌组织病理诊断
取经多聚甲醛固定心肌组织,经脱水、透明、包埋、切片后HE染色进行病理诊断。
1.2.5 免疫组化法检测心肌组织相关蛋白质表达水平
免疫组化法检测心肌NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1蛋白质表达水平。石蜡切片经脱蜡至水、抗原修复、阻断内源性过氧化物酶、一抗和二抗孵育、DAB显色、复染细胞核、封片。数字扫描仪进行断面全景扫描,计算组织化学评分[7]:细胞核阳性由强至弱依次为深棕、棕黄、浅黄,蓝色为阴性。H-score =(浅黄色细胞密度×1)+(棕黄色细胞密度×2)+(深棕色细胞密度×3)。
1.3 数据处理
数据以平均数±标准差(
根据2×2析因设计的方差分析,将HDC组、HDCC组、HDM组及HDCM组大鼠血清和心肌相关生化指标等数据纳入分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠血脂水平的影响
长期高脂饮食会破坏脂质代谢,诱发高脂血症,主要表现为血脂水平异常。Zhao等[8]表明,有氧运动能够有效改善血脂代谢,防控高脂血症的发生与发展。姜黄素具有良好的抗氧化和降血脂特性。Saker等[9]研究发现,姜黄素可以有效改善长期黄油饮食小鼠脂代谢紊乱及对器官结构的有害影响。科学运动和合理营养是健康的两大支柱,二者的联合干预能够有效改善高脂血症,保护相关器官功能和结构。张亚莉等[10]研究发现中等强度运动和大蒜素均可有效降低高脂血症大鼠血脂水平,且两者具有协同效应,联合干预效果最佳。刘静等[11]研究发现有氧运动联合丹皮酚干预能够明显改善由高脂饮食诱导的肥胖伴脂质代谢紊乱,能够降低肝脏指数,有效调节脂质代谢缓解脂肪蓄积,效果优于单独干预。
在本研究中,为期8周实验结束后,与RDC组相比,HDC组血清TC、TG、LDL-C均极显著升高(P<0.01);与HDC组相比,HDCC、HDM、HDCM组血清TC、TG均极显著降低(P<0.01);HDCM组血清TC较HDCC、HDM显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);HDCM组与HDCC组、HDM组间血清TG无显著性差异(P>0.05)。对于血清LDL-C水平,与HDC组相比,HDCC组、HDCM组显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),HDM组与HDC组间无显著性差异(P>0.05);HDCM组较HDCC组、HDM组均显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。对于血清HDL-C水平,HDC组较RDC组显著降低(P<0.05);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均显著升高(P<0.05或P<0.01);HDCM组较HDM组极显著升高(P<0.01),与HDCC组无显著性差异(P>0.05,表1)。基于相关文献及以上结果说明,8周高脂饮食诱发大鼠高脂血症,血脂水平异常;姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预可以有效改善大鼠血脂水平,其中联合干预效果最佳,与相关研究较为一致。
表 1 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠血脂水平的影响Table 1. Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on blood lipid of high-fat diet rats组别 血清TC
(mmol/L)血清TG
(mmol/L)血清HDL-C
(mmol/L)血清LDL-C
(mmol/L)RDC 2.11±0.46 0.89±0.27 0.70±0.16 0.55±0.27 HDC 3.48±0.58** 3.43±0.92** 0.57±0.08** 0.99±0.26** HDCC 2.30±0.34##△ 1.05±0.30## 0.79±0.10## 0.75±0.16#△ HDM 2.38±0.22##△△ 0.86±0.32## 0.67±0.12#△△ 0.86±0.11△△ HDCM 1.85±0.30## 0.68±0.14## 0.86±0.11## 0.57±0.12## 注:与RDC相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;与HDC组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01;与HDCM组相比,△P<0.05,△△P<0.01;表2~表3同。 2.2 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌损伤标志物及心肌细胞炎症因子含量的影响
脂代谢紊乱是诱发心肌慢性炎症反应的重要原因之一。有氧运动具有良好的抑炎作用,可以有效地抑制炎症诱发的心肌损伤,保护心脏。Chen等[1]研究发现有氧运动降低高脂饮食大鼠血脂水平的同时可以通过减少炎症、纤维化和凋亡来逆转心脏重构。Yang等[12]研究发现早期中等强度有氧运动可以下调阿霉素引发的炎症反应,降低CK-MB水平,改善心肌形态及功能。姜黄素亦可通过抑制炎症反应,保护心脏。Zeng等[13]研究发现8周50 mg/kg姜黄素干预可以有效降低高脂饮食小鼠心肌炎症及细胞凋亡水平,改善心肌形态。Liu等[14]研究发现姜黄素具有抗冠状动脉微栓塞心肌损伤的作用,其作用机制与抑制心肌炎症反应有关。何柳[15]研究发现姜黄素联合有氧运动较二者单独干预能够更为有效地降低血液及心肌炎症因子水平,延缓炎性衰老,保护心脏。
本研究中,为期8周实验结束后,对于心肌IL-1β、IL-18含量,HDC组较RDC组均极显著升高(P<0.01);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均极显著降低(P<0.01);HDCM组较HDCC、HDM组显著降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。对于心肌损伤标志物CK-MB,HDC组较RDC组均极显著升高(P<0.01);HDCC、HDM、HDCM组较HDC组均极显著降低(P<0.01);HDCM组较HDCC、HDM显著降低(P<0.01,表2)。以上结果说明,8周高脂饮食诱发大鼠高脂血症的同时,引发心肌炎症反应及损伤;姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预可以有效改善炎症反应及损伤程度,其中联合干预效果最佳,与相关研究较为一致。
表 2 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌损伤标志物及心肌细胞炎症因子含量的影响Table 2. Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on myocardial injury markers and inflammatory factors of high-fat diet rats组别 血清CK-MB
(U/L)心肌IL-1β
(pg/mg)心肌IL-18
(pg/mg)RDC 217.48±37.31 3.63±0.79 6.52±1.18 HDC 513.27±70.73** 7.54±0.74** 10.64±1.09** HDCC 393.57±73.90##△△ 5.29±0.52##△△ 8.08±1.05##△ HDM 405.51±87.02##△△ 5.60±0.45##△△ 8.65±1.10##△△ HDCM 260.09±62.08## 3.97±0.62## 6.78±1.15## 2.3 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌组织形态的影响
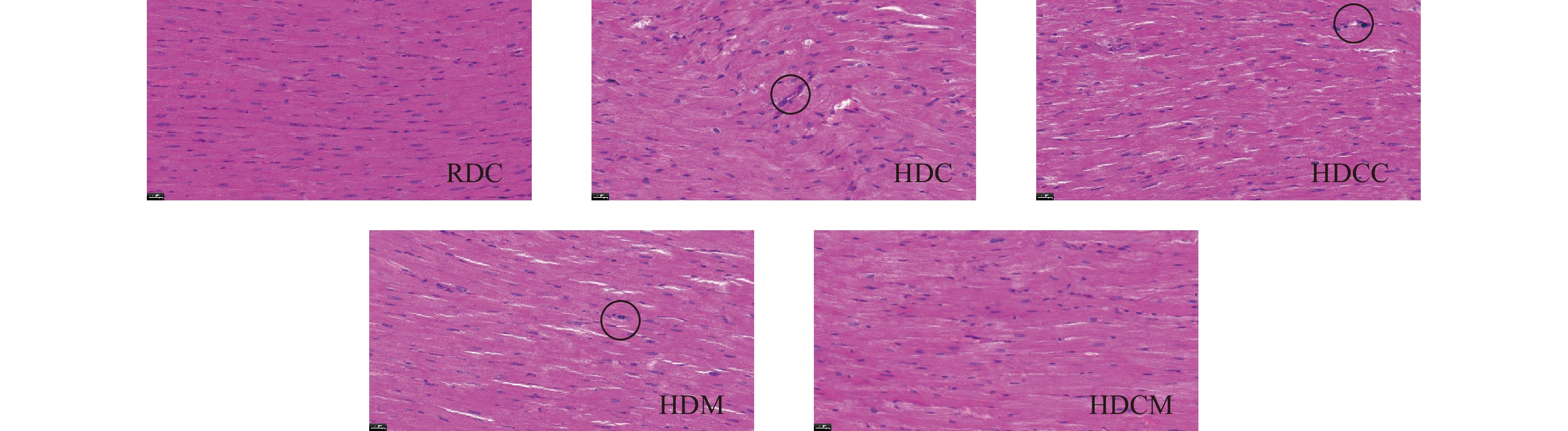
各组大鼠心肌组织病理学观察显示(图1),RDC组大鼠心肌纤维结构清晰,染色均匀,细胞质呈红色,细胞核呈蓝黑色,细胞排列规律,境界清楚。HDC组大鼠心肌纤维排列紊乱,细胞肥大,着色不均,可见明显淋巴细胞聚集,提示有慢性炎症变化。HDCC、HDM、HDCM组大鼠心肌纤维排列较整齐,细胞形态较完整,偶见心肌纤维肿胀和轻度淋巴细胞聚集,较高脂饮食组明显改善,其中联合干预组改善情况最显著。以上结果表明,8周高脂饮食诱发大鼠心肌炎性损伤;姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预可以有效改善损伤程度,其中联合干预效果最佳。
2.4 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌焦亡相关蛋白表达的影响
细胞焦亡在心血管疾病的发生、发展中具有重要作用[2],其以细胞溶解和大量炎性细胞因子释放为特征。NLRP3炎症小体由NLRP3、ASC和Caspase-1等组成。NLRP3炎症小体激活可生成具有活性的Caspase-1,而Caspase-1不仅能促进IL-1β的成熟和释放,还可以直接诱导细胞焦亡[16]。NLRP3的激活与饮食和运动有着明显的交互作用。Yu等[17]研究发现姜黄素可以有效抑制阿霉素诱发的心肌细胞焦亡,保护心脏功能/结构损伤。Yin等[4]研究发现姜黄素可以通过下调NLRP3、Caspase-1表达,抑制细胞焦亡,改善新生大鼠坏死性微小结肠炎。赵金理[18]研究发现姜黄素可以姜黄素干预可以显著抑制氧化三甲胺诱发动脉粥样硬化中焦亡相关分子Caspase-1、NLRP3、IL-1β的过度表达,且具有浓度效用。卞学鹏等[19]研究发现12周有氧运动可以显著降低胰岛素抵抗小鼠海马细胞焦亡相关蛋白及炎症因子表达。Chen等[1]研究亦发现,有氧运动可以改善高脂血症大鼠心肌焦亡及炎症反应。
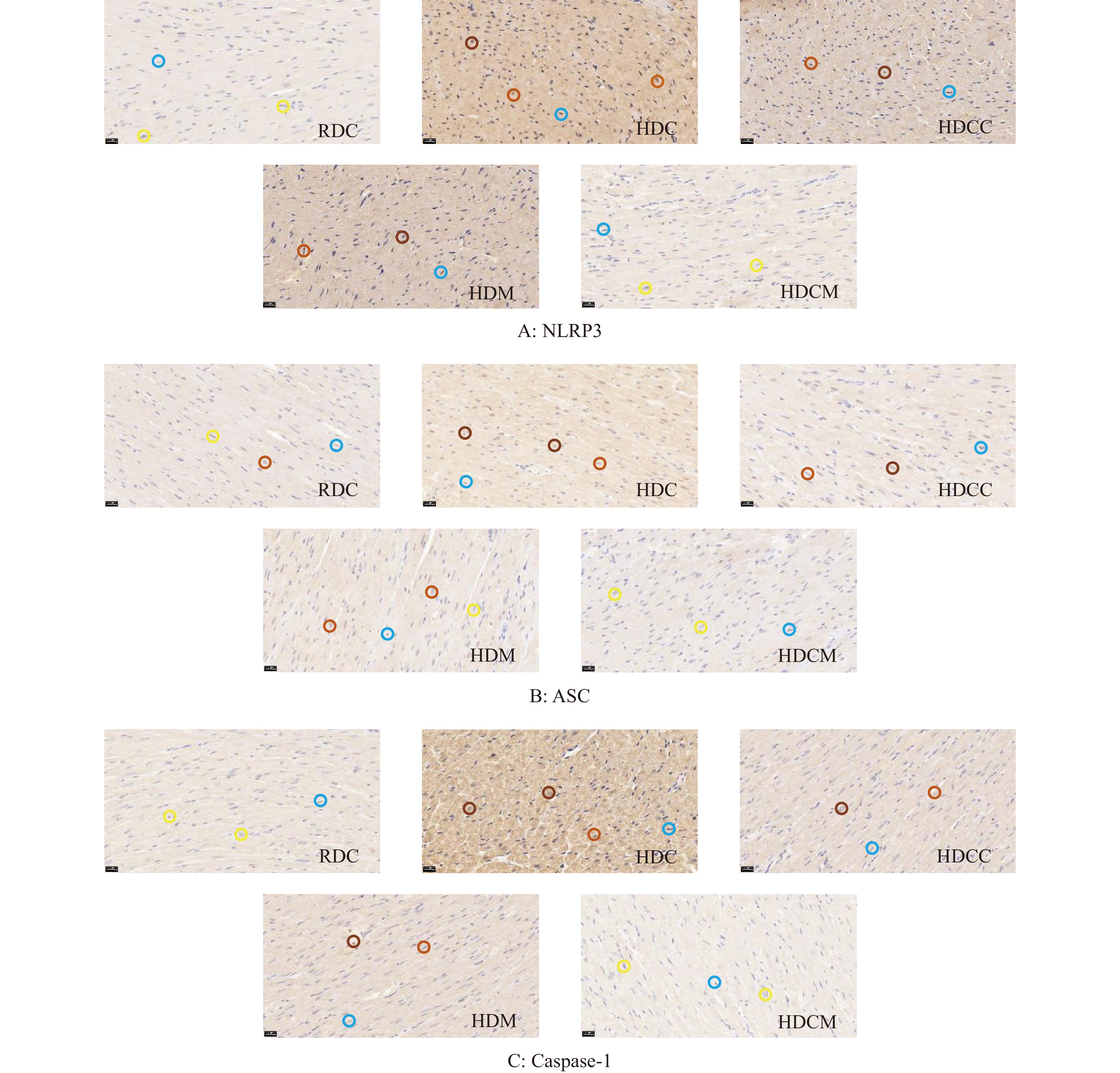
本研究中,为期8周实验结束后,心肌组织NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1表达(H-score),HDC组极显著高于RDC组(P<0.01),HDCC组、HDM组、HDCM组显著低于HDC组(P<0.05或P<0.01),其中NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1,HDCM组显著低于HDCC组、HDM组(P<0.05或P<0.01,表3,图2)。以上结果表明,细胞焦亡参与了高脂血症大鼠心肌损伤过程;姜黄素可能通过阻断NLRP3的组装和活化,抑制焦亡相关分子ASC、Caspase-1、IL-1β的过度表达[4,17-18];有氧运动可能通过改善高脂饮食诱发的炎症反应,降低NLRP3炎症小体自身及其上下游相关分子改善焦亡[1,19-20]。联合干预效果最佳。
表 3 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌焦亡相关蛋白表达的影响(H-score)Table 3. Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on expression of myocardial pyroptosis related proteins of high-fat diet rats (H-score)组别 NLRP3 ASC Caspase-1 RDC 62.21±5.20 77.13±6.74 73.30±4.95 HDC 100.78±6.84** 94.78±3.50** 110.31±9.48** HDCC 83.02±9.91#△ 80.09±6.29#△ 95.41±7.58#△ HDM 79.87±8.02##△ 82.09±8.87#△ 94.35±8.09#△ HDCM 65.78±6.36## 66.76±6.02## 78.25±7.03## 3. 结论
本研究中,8周高脂饮食诱发大鼠高脂血症的同时,心肌细胞焦亡及炎症反应加剧,心肌组织出现炎性损伤并出现结构异常。姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预均可以抑制焦亡相关因子的过度表达,发挥保护作用,其中以联合干预效果最佳。
-
表 1 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠血脂水平的影响
Table 1 Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on blood lipid of high-fat diet rats
组别 血清TC
(mmol/L)血清TG
(mmol/L)血清HDL-C
(mmol/L)血清LDL-C
(mmol/L)RDC 2.11±0.46 0.89±0.27 0.70±0.16 0.55±0.27 HDC 3.48±0.58** 3.43±0.92** 0.57±0.08** 0.99±0.26** HDCC 2.30±0.34##△ 1.05±0.30## 0.79±0.10## 0.75±0.16#△ HDM 2.38±0.22##△△ 0.86±0.32## 0.67±0.12#△△ 0.86±0.11△△ HDCM 1.85±0.30## 0.68±0.14## 0.86±0.11## 0.57±0.12## 注:与RDC相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;与HDC组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01;与HDCM组相比,△P<0.05,△△P<0.01;表2~表3同。 表 2 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌损伤标志物及心肌细胞炎症因子含量的影响
Table 2 Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on myocardial injury markers and inflammatory factors of high-fat diet rats
组别 血清CK-MB
(U/L)心肌IL-1β
(pg/mg)心肌IL-18
(pg/mg)RDC 217.48±37.31 3.63±0.79 6.52±1.18 HDC 513.27±70.73** 7.54±0.74** 10.64±1.09** HDCC 393.57±73.90##△△ 5.29±0.52##△△ 8.08±1.05##△ HDM 405.51±87.02##△△ 5.60±0.45##△△ 8.65±1.10##△△ HDCM 260.09±62.08## 3.97±0.62## 6.78±1.15## 表 3 姜黄素和/或有氧运动干预对高脂饮食大鼠心肌焦亡相关蛋白表达的影响(H-score)
Table 3 Effect of curcumin and/or aerobic exercise intervention on expression of myocardial pyroptosis related proteins of high-fat diet rats (H-score)
组别 NLRP3 ASC Caspase-1 RDC 62.21±5.20 77.13±6.74 73.30±4.95 HDC 100.78±6.84** 94.78±3.50** 110.31±9.48** HDCC 83.02±9.91#△ 80.09±6.29#△ 95.41±7.58#△ HDM 79.87±8.02##△ 82.09±8.87#△ 94.35±8.09#△ HDCM 65.78±6.36## 66.76±6.02## 78.25±7.03## -
[1] CHEN X D, LI H Y, WANG K W, et al. Aerobic exercise ameliorates myocardial inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis in high-fat-diet rats by inhibiting P2X7 purinergic receptors[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2019,10:1286. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01286
[2] 周志友, 陈佩儿, 郑杰, 等. 焦亡及其在心血管疾病中的作用研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2019,59(4):99−102. [ZHOU Z Y, CHEN P E, ZHENG J, et al. Research progress of pyroptosis and its role in cardiovascular disease[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2019,59(4):99−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.04.027 [3] ZHANG J W, HUANG C, MENG X X, et al. Effects of different exercise interventions on cardiac function in rats with myocardial infarction-sciencedirect[J]. Heart, Lung and Circulation,2020,30(5):773−780.
[4] YIN Y Y, WU X L, PENG B, et al. Curcumin improves necrotising microscopic colitis and cell pyroptosis by activating Sirt1/Nrf2 and inhibiting the TLR4 signalling pathway in newborn rats[J]. Innate Immunity,2020,26(7):609−617. doi: 10.1177/1753425920933656
[5] MOHAMMADI S, KAYEDPOOR P, KARIMZADEH-BARDEI L, et al. The effect of curcumin on TNF-α, IL-6 and CRP expression in a model of polycystic ovary syndrome as an inflammation state[J]. Journal of Reproduction and Infertility,2017,18(4):352−360.
[6] 何诗依, 李铁瑛, 严露, 等. 4周有氧运动对Apelin基因敲除鼠糖耐量和骨骼肌糖代谢相关基因表达的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(6):479−485. [HE S Y, LI T Y, YAN L, et al. Effects of 4-week aerobic exercise on glucose tolerance and glucose metabolism related gene expression in skeletal muscle of apelin knockout mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Sports Medicine,2019,38(6):479−485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2019.06.007 [7] YEO W, CHAN S L, MO F K, et al. Phase I/II study of temsirolimus for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-a correlative study to explore potential biomarkers for response[J]. BMC Cancer,2015,15:395−405. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1334-6
[8] ZHAO S, ZHONG J, SUN C, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise on TC, HDL-C, LDL-C and TG in patients with hyperlipidemia: A protocol of systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine,2021,100:10.
[9] SARKER S, HAQUE MI, SUJAN K M, et al. Curcumin attenuates butter fat induced hyperlipidemia in mice[J]. Journal of Bangladesh Agricultural University,2019,17(2):220−225. doi: 10.3329/jbau.v17i2.41972
[10] 张亚莉, 黄小明, 华岩. 运动联合大蒜素降低高脂血症大鼠血脂的实验研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2020,47(7):126−129. [ZHANG Y L, HUANG X M, HUA Y. Effect of moderate intensity exercise combined with allicin on blood lipid metabolism and hepatic tissue oxidative injury among rats with high fat[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2020,47(7):126−129. [11] 刘静, 肖明中. 有氧运动联合丹皮酚PLGA纳米粒对肥胖伴高脂血症大鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(12):88−93. [LIU J, XIAO M Z. Protective effect of aerobic exercise combined with paeonol poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles on obese rats with hyperlipidemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine,2019,29(12):88−93. [12] YANG H L, HSIEH P L, HUNG C H, et al. Early moderate intensity aerobic exercise intervention prevents doxorubicin-caused cardiac dysfunction through inhibition of cardiac fibrosis and inflammation[J]. Cancers,2020,12(5):1102. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051102
[13] ZENG C, ZHONG P, ZHAO Y, et al. Curcumin protects hearts from FFA-induced injury by activating Nrf2 and inactivating NF-κB both in vitro and in vivo[J]. Journal of Molecular & Cellular Cardiology,2015,79:1−12.
[14] LIU Y, LIU Y H, HUANG X C, et al. Protective effects and mechanism of curcumin on myocardial injury induced by coronary microembolization[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,2019,120(4):5695−5703. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27854
[15] 何柳. 有氧运动结合姜黄素对中老年大鼠心肌炎症反应的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学, 2016: 19-24. HE L. The effects of curcumin and cerobic exercise on inflammation reaction in myocardium in middle-aged rats[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2016: 19-24.
[16] COLL N S, EPPLE P, DANGL J L. Programmed cell death in the plant immune system[J]. Cell Death and Differentiation,2011,18(8):1247−1256. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.37
[17] YU W, QIN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Curcumin suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis via a PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent manner[J]. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy,2020,10(4):752−769. doi: 10.21037/cdt-19-707
[18] 赵金理. 姜黄素拮抗氧化三甲胺致血管内皮细胞焦亡及其机制研究[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2020: 17-29. ZHAO J L. Curcumin antagonizes vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis induced by trimethylamine oxide and its mechanism[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2020: 17-29.
[19] 卞学鹏, 姬瑞方, 刘蓓蓓, 等. 有氧运动降低胰岛素抵抗小鼠海马细胞焦亡相关蛋白及炎症因子的表达[J]. 生理学报,2020,72(4):455−462. [BIAN X P, JI R F, LIU BB, et al. Aerobic exercise reduces the expression of pyroptosis-related proteins and inflammatory factors in hippocampus of mice with insulin resistance[J]. Acta Physiologica Sinica,2020,72(4):455−462. [20] 崔笑梅, 曹建民, 张静, 等. 有氧运动联合黑果枸杞对高脂膳食大鼠心肌脂代谢某些指标的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2020,36(4):301−305. [CUI X M, CAO J M, ZHANG J, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise combined with Lycium ruthenicum on some indicators of myocardial lipid metabolism in rats with high-fat diet[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2020,36(4):301−305. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5932.2020.065 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 曹文利,尹俊涛,雷勇,刘艳怀,代绍娟,曹秋月. 红豆核桃复合乳饮料配方优化及稳定性研究. 食品工业. 2025(02): 96-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王明明,陈银艳,余智瑾,盛军,赵存朝. 均质和杀菌条件对核桃油微胶囊化的影响及贮藏稳定性. 食品科学. 2024(06): 199-207 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 袁照森,吴鸣,王芷琦,余珺如,甘智颖,刘晓飞. 加工方式对米乳饮料稳定性的研究进展. 食品科技. 2024(09): 167-174 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 胡雨晴,牛秀梅,王美美,刘静,张瑞,高惠颖,马志恒,吕长鑫. 黑果腺肋花楸红树莓复合饮料配方优化及贮藏品质研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(04): 234-242 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 薛建娥,沈辉,罗岳伟,兰明珠,吕高鹏,白建. 红枣核桃酸奶的贮藏品质及胃肠液环境下抗氧化研究. 中国酿造. 2022(02): 119-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 黄丽,黄素君,黄澳,叶江平,罗忠国,罗舜菁. 高压射流磨制备全谷物浓浆饮品的研究. 粮食与食品工业. 2022(01): 15-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周蕾. 气相色谱-质谱法测定植物蛋白饮料中植物甾醇和胆固醇. 中国酿造. 2021(05): 177-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



