Comparative Analysis of Antioxidant Compounds and Antioxidant Activities in Vitro of Different Kiwifruit Juice
-
摘要: 本文以陕西省和四川省两大主产区的美味、中华和软枣3大种系12个品种猕猴桃为材料,测定其果汁中主要抗氧化活性物质多酚、类黄酮、VC和果实中单体酚含量,比较其体外抗氧化活性,并将抗氧化活性物质和果汁抗氧化能力进行相关性分析,筛选抗氧化物质含量高、抗氧化活性强的品种。结果表明,不同品种猕猴桃的抗氧化活性物质含量和抗氧化能力有显著性差异(P<0.05),VC在不同品种间的含量差异较大,范围在27.300~130.380 mg/100 g之间;软枣系两品种(益玉和绿迷)类黄酮含量显著高于其他品种(P<0.05);原儿茶酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、表儿茶素为猕猴桃中主要的多酚类化合物;红阳、翠香、亚特、华优对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除能力较强,益玉和绿迷对·OH的清除能力和总还原力较强;各品种猕猴桃多酚含量与总还原力具有显著相关性(P<0.05),单酚含量之间、单酚与抗氧化活性之间也有相关性。根据抗氧化活性进行聚类分析,可将12个品种猕猴桃分为6类。综合分析,12个品种中以软枣猕猴桃的抗氧化活性最强。研究结果为猕猴桃鲜食及加工过程中高抗氧化活性品种的选择提供了科学依据。Abstract: Twelve varieties of kiwifruit from the three major lines of Meiwei, Zhonghua and Ruanzao from the two main producing areas of Shaanxi and Sichuan provinces were used as test materials. The main antioxidant active substances, polyphenols, flavonoids, VC, and the content of monomer phenols in fruit were determined. The antioxidant activity in vitro was compared, and the correlation analysis between the antioxidant activity and the antioxidant capacity of fruit juice was carried out, and the varieties with high antioxidant content and strong antioxidant activity were screened out. Results showed that there were significant differences in the antioxidant activity content and antioxidant capacity of different varieties of kiwifruit (P<0.05). The content of VC varied greatly among different varieties, ranging from 27.300 to 130.380 mg/100 g. The content of flavonoids in two varieties of Ruanzao (Yiyu and Lvmi) was significantly higher than that of other varieties (P<0.05). Protocatechin, catechin, chlorogenic acid, and epicatechin were the main polyphenol compounds in kiwifruit. Hongyang, Cuixiang, Yate, and Huayou had strong scavenging ability on DPPH· and ABTS+·, while Yiyu and Lvmi had strong scavenging ability and total reducing power on ·OH. The content of polyphenols in each kiwifruit had a significant correlation with the total reducing power (P<0.05), and there were also correlations between the content of monophenols, and between monophenols and antioxidant activity. According to cluster analysis based on antioxidant activity, twelve varieties of kiwifruit could be divided into six categories. Comprehensive analysis showed that among the 12 varieties, Ruanzao had the strongest antioxidant activity. The research results would provide a scientific basis for the selection of kiwifruit varieties with high antioxidant activity during fresh food and processing.
-
Keywords:
- kiwifruit /
- cultivars /
- antioxidant compounds /
- antioxidant activities /
- cluster analysis (CA)
-
猕猴桃富含VC、果胶、糖类、有机酸、多酚、类黄酮、氨基酸及钾、钙等微量元素,其主要营养成分含量排名各种水果前列[1-2]。长期食用猕猴桃能有效补充人体维生素、强化免疫系统,缓解皮肤炎症、降低血清胆固醇含量,而且具有抗衰老、抗病毒、抗辐射、抗肿瘤及预防心脑血管疾病等作用[3]。研究表明这些功效与其富含多种天然抗氧化物质密切相关,猕猴桃中相关物质可清除人体内活性氧自由基,减轻自由基氧化反应对机体细胞和组织的损伤,延缓细胞衰老及慢性疾病的发生[4]。猕猴桃果汁因富含多酚、黄酮、VC等可以抑制脂质过氧化、清除自由基的抗氧化物质而倍受人们的青睐。为选育综合性较好的猕猴桃品种,许多研究者制定育种目标,对不同猕猴桃品种采后品质、酚类物质组成与含量、抗氧化活性等进行了研究。王菲等[5]研究表明软枣猕猴桃总黄酮具有较强清除DPPH·的能力和还原力,可有效抑制脂质过氧化,且对
O−2 、·OH有一定的清除作用,得出软枣猕猴桃总黄酮具有显著的抗氧化活性。赵金梅等[1]测定10种猕猴桃果实品质及抗氧化活性,得出华优的VC、总酚含量及DPPH·清除率最高,营养价值较高,且猕猴桃的抗氧化能力与VC和总酚含量之间呈现较高相关性。张云等[6]选用红阳、米良一号、金艳猕猴桃为研究对象,得出红阳猕猴桃的可食部分总酚含量最高,其多酚提取液对DPPH·清除力和还原力最强,红阳和金艳具有较好的ABTS+·清除能力,且红阳的抗氧化活性与总酚含量的相关性最好,说明红阳中具有抗氧化活性的多酚类化合物的含量高。曹毛毛等[7]测定7种猕猴桃的理化特性和抗氧化活性,发现7种猕猴桃果实理化性质存在显著性差异,在抗氧化活性方面,秦美的DPPH·清除能力、Fe2+络合能力和Fe3+还原能力均最强,华优具有最强保护DNA氧化损伤的作用。我国猕猴桃资源丰富,各个主产区适宜种植的品种不同,针对不同产区、不同品系采后果实酚类物质组成及含量、抗氧化性研究尚未见报道。因此,研究以国内陕西、四川2个主产区的12个主栽的红心、黄心、绿心猕猴桃为试材,探究果实抗氧化活性及相关物质含量,筛选营养价值高、抗氧化活性强的猕猴桃品种,发挥品种优势,为功能性食品的开发提供理论支持。1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
猕猴桃 试验选取3个品系、12个品种猕猴桃,包括美味系(海沃德、徐香、亚特、翠香),中华系(华优、红阳、东红、祁红、黄金果、金艳),软枣系(益玉、绿迷)。不同品种猕猴桃达到各自商业采收成熟度时采收,不同品种采收时间不一致,选择大小基本一致、无病虫害、无机械损伤的果实,采收后于室温下放置后熟,采样情况见表1;福林酚、1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazide,DPPH)、2,2-联-(乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵(Diammonium2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate),ABTS) 分析纯,美国Sigma公司;没食子酸、VC、H2O2、水杨酸、三氯乙酸等 分析纯,天津市天力化学试剂有限公司;甲醇、没食子酸、原儿茶酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、表儿茶素、咖啡酸、对香豆酸、阿魏酸、根皮苷、芦丁、槲皮素、杨梅素等单体酚标品 色谱纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司。
表 1 猕猴桃品种及采样情况Table 1. Cultivars of kiwifruit and sampling condition编号 品种 种系 果肉色泽 产地 采样时间 北纬 东经 1 华优 中华[8] 黄肉黄心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 2 红阳 中华 黄肉红心 陕西眉县 2019/9/10 34.28° 107.75° 3 祁红 中华 黄肉红心 陕西眉县 2019/10/8 34.28° 107.75° 4 东红 中华 黄肉红心 四川邛崃 2019/9/15 30.41° 103.46° 5 黄金果 中华 黄肉黄心 陕西杨凌 2019/9/29 34.27° 108.08° 6 金艳 中华 黄肉黄心 陕西杨凌 2019/9/29 34.27° 108.08° 7 徐香 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 8 翠香 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西眉县 2019/9/10 34.28° 107.75° 9 亚特 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 10 海沃德 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/15 34.16° 108.22° 11 益玉 软枣 绿肉绿心 四川雅安 2019/8/6 30.01° 103.03° 12 绿迷 软枣 绿肉绿心 四川雅安 2019/8/6 30.01° 103.03° 紫外分光光度计 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;HH-S6双列六孔型电热水浴锅 北京科伟有限公司;HC-3018R高速冷冻离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;KQ-700DE型数控超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;WGL-230B电热鼓风干燥箱 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;电子计数秤 上海友声衡器有限公司;LC-20A高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
待猕猴桃果实硬度为1.0 kg/m2以下时进行榨汁处理。每个品种取20个果实,去皮后榨汁,汁液用200目滤布过滤,直接使用鲜榨猕猴桃汁进行测定。
1.2.2 VC含量的测定
采用高效液相色谱法测定[9],准确称取10 g果肉放入破碎机中,加入20 mL 0.1%的偏磷酸溶液打成匀浆,转入离心管中于8000 r/min离心15 min,吸取上清液2.5 mL至容量瓶(25 mL)中,用0.1%的偏磷酸溶液定容,混匀后用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤到样品瓶中待测。色谱柱:Inertsil/Wondasil C18柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);流动相:0.1%偏磷酸溶液:甲醇=96:4(v/v);流速:0.8 mL/min;检测波长:243 nm;柱温:30 ℃;进样量:10 μL。
1.2.3 多酚含量的测定
采用福林酚法[10],以没食子酸为标准物质测定多酚的含量。准确称取25 mg没食子酸,去离子水溶解后定容至25 mL,以该没食子酸溶液为原液,依次配制成质量浓度分别为0、20、60、100、150、200、300、400、500、600 μg/mL的梯度液。取100 μL标准液与400 μL去离子水于试管中,加100 μL福林酚试剂混匀,6 min后加入1 mL 7% Na2CO3溶液和0.8 mL去离子水,混匀后避光放置,90 min后测定OD760 nm。样品测定时取100 μL猕猴桃汁,其余操作同上。以没食子酸质量浓度(x)为横坐标,吸光度值(y)为纵坐标绘制没食子酸标准曲线。标准曲线回归方程为y=0.0034x+0.0932,R2=0.9927。
1.2.4 类黄酮含量的测定
采用AlCl3显色法[11],以芦丁为标准物质测定黄酮的含量。准确称取芦丁标准品26.0 mg于烧杯中,加入70%的乙醇溶解后转入50 mL容量瓶定容,得到0.52 mg/mL的标准液。准确量取标准溶液0.0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0 mL置于25 mL容量瓶中,依次加入70%乙醇3.0 mL、5%亚硝酸钠0.75 mL,摇匀放置5 min,再加入10%硝酸铝溶液0.5 mL,摇匀放置6 min,最后加入5%氢氧化钠溶液4 mL,用蒸馏水定容至25 mL,摇匀,静置15 min后,测定OD510 nm。样品测定时取2 mL猕猴桃汁,其余操作同上。以芦丁质量浓度(x)为横坐标,吸光度值(y)为纵坐标绘制芦丁标准曲线。标准曲线回归方程为y=11.415x−0.0017,R2=0.9977。
1.2.5 单体酚的测定
采用高效液相色谱法[12],不同品种猕猴桃样品用50%甲醇超声波辅助提取。色谱柱:Inertsil/Wondasil C18柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);柱温30 ℃;进样量10 μL;流动相流速0.8 mL/min;运行时间50 min;检测波长280 nm。流动相A:0.1%磷酸水溶液,流动相B:甲醇。起始B浓度0,10 min时B浓度30%,20 min时B浓度48%,28 min时时B浓度53%,40 min时B浓度57.5%,42 min时B浓度70%,45 min时B浓度0。以没食子酸、原儿茶酸、儿茶素、绿原酸等为标准品,绘制标准曲线,采用峰面积归一化法进行定量,其结果用μg/100 g表示。
1.2.6 抗氧化活性测定
抗氧化活性的测定参照张淑娟等[13]的方法并略作修改,其中清除率为50%时的果汁浓度为半抑制浓度(IC50),用来表示抗氧化能力。
1.2.6.1 清除DPPH·能力的测定
取不同品种猕猴桃果汁于4 ℃、8000 r/min离心15 min,上清液稀释成不同浓度备用。取不同浓度果汁稀释液1 mL于试管中,加入2 mL 0.5 mmol/mL DPPH溶液,加无水乙醇至4 mL,摇匀置暗处反应30 min后,测定OD517 nm。按式(1)计算DPPH自由基清除率。
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=(1−Aj/A0)×100 (1) 式中:Aj为样品+DPPH溶液的吸光度;A0为DPPH溶液+无水乙醇的吸光度。
1.2.6.2 清除ABTS+·能力的测定
取不同品种猕猴桃果汁于4 ℃、8000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液用无水乙醇稀释成不同浓度备用。将14 mmol/L ABTS+·溶液与4.9 mmol/L K2S2O8溶液等体积混合,于4 ℃避光反应14 h,然后用无水乙醇稀释至波长734 nm处吸光度为0.7±0.02,取2.8 mL该溶液分别加入25 μL稀释后的猕猴桃汁,加无水乙醇至3 mL,室温避光反应6 min后测定OD734 nm。按式(2)计算ABTS+·清除率。
ABTS+⋅清除率(%)=(A0−Aj/A0)×100 (2) 式中:A0为加空白乙醇的ABTS+·溶液的吸光度;Aj为样品与ABTS+·溶液反应6 min后的吸光度。
1.2.6.3 ·OH清除率的测定
取不同品种猕猴桃果汁于4 ℃、8000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液用蒸馏水稀释成不同浓度。取稀释后的样品1.0 mL于试管中,依次加入2 mL 6 mmol/L FeSO4溶液、2 mL 6 mmol/L水杨酸,混匀后静置10 min,加入6 mmol/L H2O2溶液2 mL,混匀后静置30 min测定OD510 nm。按式(3)计算·OH清除率。
⋅OH清除率(%)=[1−(Aj−Ai)/A0]×100 (3) 式中:Aj为加入样品后的吸光度;A0为空白对照液的吸光度;Ai为不加H2O2时样品的吸光度。
1.2.6.4 还原能力的测定
取不同品种猕猴桃果汁于4 ℃、8000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液稀释后备用。取稀释后的果汁1.0 mL于试管中,加入2.5 mL 0.2 mol/L PBS(pH6.6)及1%铁氰化钾溶液各2.5 mL,50 ℃水浴20 min后迅速冷却,加入2.5 mL 10%TCA溶液,于4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液0.5 mL,加4.5 mL蒸馏水及0.5 mL质量分数为0.1% FeCl3溶液,混匀,10 min后测定OD700 nm。
1.2.7 多酚、类黄酮、VC、果实单体酚含量与体外抗氧化能力的相关性分析
对不同品种猕猴桃汁清除DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH、总还原能力与总酚、类黄酮、VC、单体酚含量之间进行相关性分析,采用Person进行相关性分析,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
1.3 数据处理
实验均重复3次,结果以平均数±标准误差表示。采用SPSS 19.0软件中的单因素方差分析对试验数据进行处理,数据多重比较采用Duncan法[7],聚类距离采用欧式距离平均法,聚类方法采用Ward法。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 果汁样品主要成分测定结果
已有研究报道,食用猕猴桃能有效降低某些疾病的发病率,发挥作用的物质主要为果实中的抗氧化活性成分,包括酚类物质、VC等,它们通过抑制人体内氧化反应来清除自由基,从而延缓或抑制油脂及其他物质被氧化[14-15]。VC是一种水溶性抗氧化剂,在机体内抗氧化酶的协同下参与多种清除自由基活动,猕猴桃中VC有降低血和肝中脂质的作用,研究发现猕猴桃果汁可明显降低高胆固醇血症小鼠的血清总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白和极低密度脂蛋白含量,提高其血清高密度脂蛋白胆固醇含量[16-17]。不同品种猕猴桃果汁主要成分如表2所示。VC是猕猴桃汁的一个重要营养指标,由表2可知,不同品种猕猴桃汁的VC含量存在较大变异系数(>20%),其含量变化幅度在27.300~130.380 mg/100 g之间,从高到低依次为亚特>华优>东红>翠香>金艳>红阳>黄金果>祁红>海沃德>绿迷>徐香>益玉。酚类物质是一类广泛存在于水果中的多羟基化合物的总称,是一种重要次生代谢产物,通过苯丙烷代谢途径合成,对果实的色泽、风味、抗病性及采后贮藏保鲜均有一定的影响,也是决定果汁饮料抗氧化能力的主要物质之一[17]。研究结果显示,祁红猕猴桃果汁多酚含量最高,徐香中最低。绝大多数植物体内都含有黄酮类化合物,它们在植物的生长、发育、开花、结果以及抗菌防病等方面起着重要的作用。黄酮类化合物因酚羟基上的氢原子可与过氧自由基结合生成黄酮自由基,进而与其他自由基反应,从而终止自由基链式反应,起到抗氧化作用[18]。不同猕猴桃汁的类黄酮含量存在较大变异系数,其中软枣系两个品种猕猴桃(益玉和绿迷)含量最高,海沃德含量最低,而且中华系猕猴桃类黄酮平均含量显著大于美味系猕猴桃(P<0.05)。
表 2 不同品种猕猴桃果汁主要成分Table 2. Major ingredients of different kiwifruit juice品种 VC(mg/100 g) 多酚(mg/mL) 类黄酮(mg/mL) 华优 100.440+0.300b 0.686+0.140bcd 0.032+0.004de 红阳 54.360+11.250d 0.614+0.026cd 0.023+0.000b 祁红 50.470+9.530e 0.835+0.016a 0.045+0.001a 东红 99.400+9.820b 0.770+0.008ab 0.027+0.001ef 黄金果 51.010+3.420e 0.650+0.026bcd 0.036+0.002d 金艳 56.010+2.450d 0.734+0.006abc 0.028+0.001ef 徐香 31.930+5.650h 0.577+0.084d 0.024+0.001fg 翠香 96.740+7.270c 0.644+0.037bcd 0.026+0.002f 亚特 130.380+8.110a 0.768+0.099ab 0.019+0.008g 海沃德 38.440+1.430f 0.620+0.036cd 0.013+0.004h 益玉 27.300+1.950i 0.726+0.080abc 0.061+0.002a 绿迷 34.600+5.340g 0.662+0.025bcd 0.056+0.002b 平均值 64.260 0.690 0.030 标准差 33.660 0.080 0.010 变异系数(%) 52.380 11.100 44.850 注:同列小写字母不同表示差异显著,P<0.05。 酚类物质的含量决定了果实的抗氧化能力[19]。由表3可知,不同品种猕猴桃的多酚类组成有显著性差异(P<0.05)。原儿茶酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、表儿茶素含量相对较高,为猕猴桃中最主要的多酚类化合物。这与李琛等[12]对不同品种猕猴桃单酚含量的测定结果一致。儿茶素为红阳、翠香、亚特、益玉、绿迷中含量最多的酚类,但不同品种含量差异较大。美味系猕猴桃单酚种类最丰富,基本包括了测定的12种酚类。中华系猕猴桃中槲皮素含量均未检出,而且祁红、东红、黄金果和金艳四个品种均未检出根皮苷、芦丁和槲皮素。酚类物质总含量大小依次排序为徐香>红阳>亚特>金艳>绿迷>华优>翠香>黄果>益玉>海沃德>祁红>东红。
表 3 不同品种猕猴桃单体酚含量(μg/100 g)Table 3. Polyphenol composition and content of different kiwifruit (μg/100 g)品种 没食子酸 原儿茶酸 儿茶素 绿原酸 表儿茶素 咖啡酸 对香豆酸 阿魏酸 根皮苷 芦丁 槲皮素 杨梅素 总酚 华优 1.68±0.07 6.18±0.02 4.31±0.02 2.47±0.04 2.43±0.02 0.51±0.06 0.06±0.04 0.17±0.01 0.46±0.01 0.21±0.04 / 7.39±0.02 25.87±0.14 红阳 0.58±0.03 1.51±0.01 27.56±0.36 9.02±0.04 7.04±0.01 0.46±0.04 0.12±0.02 0.16±0.02 0.24±0.05 0.49±0.01 / / 47.17±0.03 祁红 0.84±0.02 0.70±0.03 2.92±0.02 7.36±0.04 3.52±0.04 0.28±0.05 0.03±0.04 0.08±0.03 / / / / 15.73±0.28 东红 0.42±0.10 / 0.38±0.04 1.78±0.06 0.57±0.04 0.78±0.02 0.19±0.06 / / / / / 4.13±0.15 黄金果 0.55±0.05 0.48±0.01 1.63±0.04 4.83±0.04 1.51±0.02 0.04±0.03 0.02±0.07 0.07±0.06 / / / 13.01±0.07 22.14±0.27 金艳 4.29±0.09 2.48±0.01 8.32±0.05 2.754±0.01 8.73±0.06 1.08±0.03 0.07±0.09 0.09±0.08 / / / 6.11±0.06 33.91±0.01 徐香 0.65±0.04 3.09±0.01 9.38±0.23 9.23±0.02 13.39±0.07 2.14±0.08 0.58±0.08 0.16±0.04 0.17±0.00 0.99±0.03 0.31±0.00 7.25±0.01 47.34±0.05 翠香 0.51±0.05 1.37±0.02 4.47±0.08 3.67±0.04 2.92±0.01 0.94±0.05 0.07±0.05 0.09±0.05 0.25±0.00 0.33±0.04 0.30±0.00 8.52±0.07 23.42±0.23 亚特 1.63±0.06 6.59±0.02 11.35±0.09 2.75±0.03 13.26±0.05 0.95±0.01 0.14±0.01 0.15±0.05 0.18±0.00 0.85±0.05 0.34±0.03 / 38.19±0.37 海沃德 1.29±0.01 0.77±0.01 6.15±0.07 2.32±0.01 7.02±0.03 0.83±0.01 0.10±0.02 0.13±0.01 0.21±0.00 0.10±0.08 / 1.15±0.04 20.06±0.07 益玉 3.41±0.02 2.53±0.02 4.60±0.04 3.87±0.01 2.33±0.01 0.89±0.04 0.13±0.04 0.10±0.01 / 3.15±0.05 0.34±0.05 / 21.36±0.14 绿迷 1.32±0.02 5.41±0.01 7.70±0.08 4.16±0.02 6.19±0.04 1.73±0.03 0.20±0.01 0.23±0.01 / 1.12±0.09 0.48±0.04 3.99±0.09 32.52±0.09 平均值 1.43 2.59 7.40 4.52 5.74 0.89 0.14 0.12 0.12 0.60 0.15 3.95 注:“/”表示未检出。 2.2 不同品种猕猴桃汁对DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH的清除效果和总还原力
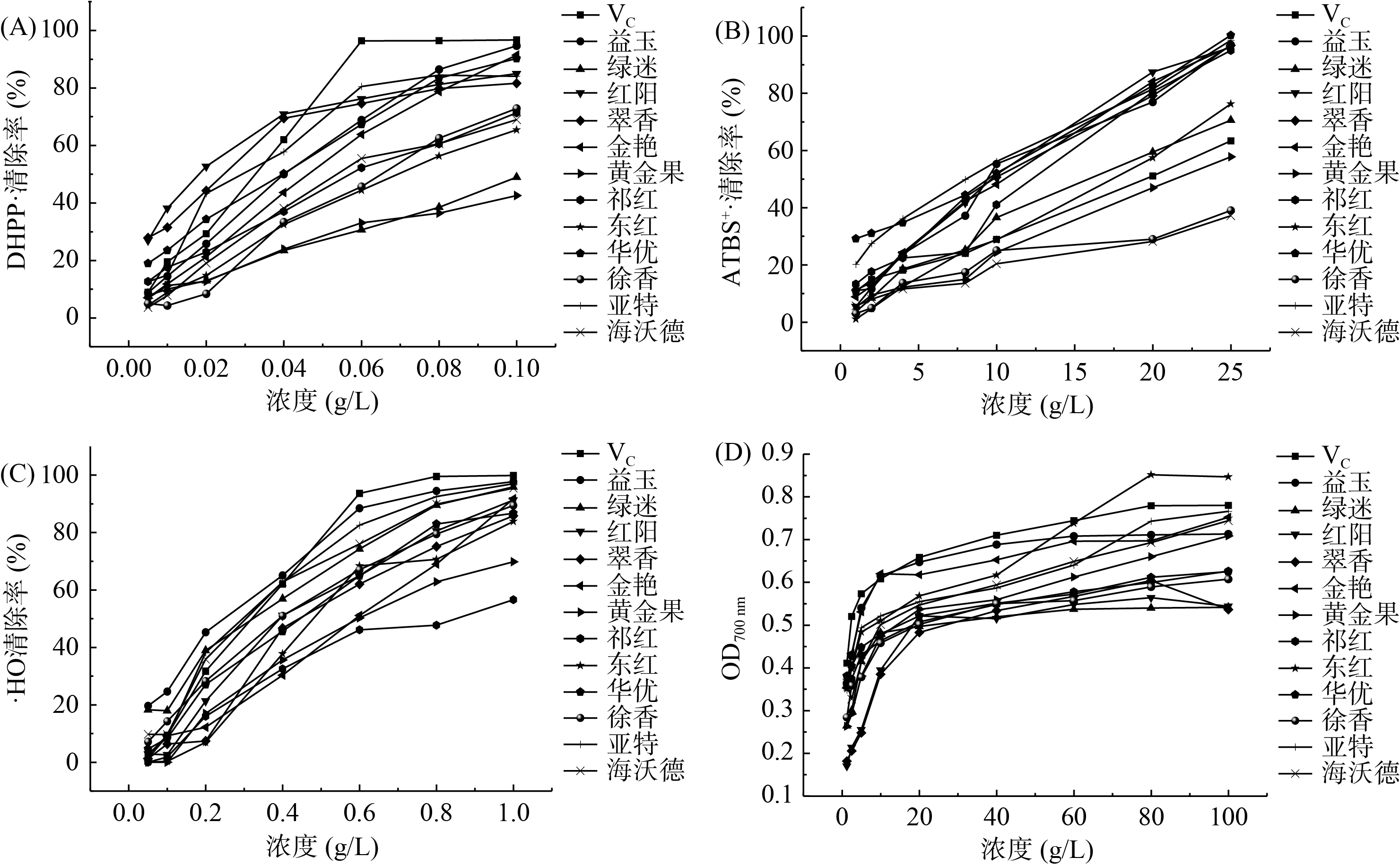
由图1结合表4进行分析,VC对照和不同品种猕猴桃汁样品对DPPH自由基的清除能力与样品添加体积有较密切关系,ABTS+·、·OH的清除效果、还原力和体积之间也有同样关系,呈现较好的量效关系,由半抑制浓度表可看出12个品种猕猴桃汁清除DPPH·效果排序依次为:红阳>翠香>VC>亚特>华优>益玉>金艳>祁红>海沃德>徐香>东红>绿迷>黄金果;由表4可看出清除ABTS+·效果排序依次为:华优>亚特>红阳>翠香>金艳>益玉>祁红>绿迷>东红>VC>黄金果>徐香>海沃德,由排序可知大多数猕猴桃对ABTS+·清除效果优于VC,综上得出,红阳、翠香、亚特、华优对DPPH·和ABTS+·两者的清除能力较强;由表4可看出清除·OH效果排序依次为:益玉>绿迷>VC>亚特>海沃德>徐香>华优>红阳>翠香>祁红>金艳>黄金果>东红;综合分析得出12个品种猕猴桃汁还原力大小依次为:金艳>益玉>绿迷>祁红>亚特>海沃德>华优>黄金果>东红>徐香>VC>翠香>红阳。铁还原力(FRAP)法不是针对某一种自由基的清除能力,它反映的是样品总的还原能力,样品的总还原能力越强,对自由基的清除率越高,其抗氧化性越强。因此,可用来表征样品总的抗氧化活性[19],其中10个品种猕猴桃汁还原力都大于VC,这印证了猕猴桃抗氧化能力较强的特点,综上两个指标可得益玉和绿迷清除·OH能力和总还原力较强。
表 4 不同品种猕猴桃汁抗氧化活性的IC50[5]Table 4. IC50 of antioxidant activity of different varieties in kiwifruit juice[5]浓度(g/L) VC 华优 红阳 祁红 东红 黄金果 金艳 徐香 翠香 亚特 海沃德 益玉 绿迷 DPPH· 0.037 0.042 0.025 0.062 0.072 0.114 0.050 0.067 0.031 0.040 0.064 0.045 0.104 ABTS+· 19.300 8.830 11.200 12.280 16.800 21.740 11.300 32.960 11.270 9.090 36.170 11.490 16.690 ·OH 0.388 0.497 0.502 0.571 0.801 0.654 0.581 0.473 0.548 0.402 0.406 0.310 0.381 图1的曲线经拟合,从方程得到表4不同品种猕猴桃汁抗氧化活性的IC50。
2.3 猕猴桃汁的多酚、类黄酮、VC含量与体外抗氧化活性的相关性分析
研究表明,植物的抗氧化活性与其生物活性物质含量之间存在一定的相关性[20]。从表5可以看出,样品中的多酚含量与总还原力有显著相关性(P<0.05),总还原能力是检验果汁饮料整体抗氧化能力的一项重要指标,说明多酚是影响猕猴桃果汁抗氧化能力的关键因素。多酚与DPPH·、·OH清除率相关性较弱(相关系数分别为0.178和−0.214)。猕猴桃清除DPPH·和ABTS+·的能力呈现显著相关性(P<0.05)。通过单酚含量与抗氧化活性之间相关性可得,芦丁与类黄酮、槲皮素有显著相关性,咖啡酸与对香豆酸、槲皮素、表儿茶素有显著相关性,阿魏酸与原儿茶酸、·OH有显著相关性(P<0.05)。
表 5 不同品种猕猴桃汁抗氧化能力与主要活性成分的相关系数Table 5. Correlation coefficients between antioxidant ability and the main active ingredients of kiwifruit juice多酚 类黄酮 VC 没食
子酸原儿
茶酸儿茶素 绿原酸 表儿
茶素咖啡酸 对香
豆酸阿魏酸 根皮苷 芦丁 槲皮素 杨梅素 DPPH· ABTS+· ·OH 总还
原力多酚 1 类黄酮 0.300 1 VC 0.361 −0.434 1 没食子酸 0.279 0.285 −0.176 1 原儿茶酸 0.012 0.110 0.329 0.273 1 儿茶素 −0.377 −0.296 −0.075 −0.042 0.164 1 绿原酸 −0.328 0.047 −0.466 −0.362 −0.177 0.537 1 表儿茶素 −0.243 −0.438 −0.009 0.136 0.450 0.502 0.307 1 咖啡酸 −0.362 0.020 −0.248 0.123 0.381 0.089 0.144 0.610* 1 对香豆酸 −0.445 −0.131 −0.260 −0.195 0.164 0.157 0.448 0.569 0.824** 1 阿魏酸 −0.459 0.101 −0.210 0.050 0.733** 0.478 0.261 0.516 0.470 0.296 1 根皮苷 −0.400 −0.495 0.430 −0.217 0.407 0.289 −0.021 0.134 −0.057 0.019 0.402 1 芦丁 −0.036 0.600* −0.343 0.399 0.287 0.071 0.078 0.067 0.344 0.269 0.254 −0.182 1 槲皮素 −0.151 0.384 −0.061 0.071 0.522 0.017 0.035 0.345 0.688* 0.435 0.478 −0.108 0.668* 1 杨梅素 −0.457 −0.044 −0.037 −0.105 0.006 −0.297 0.009 −0.126 0.010 0.018 0.038 0.143 −0.285 −0.031 1 DPPH· 0.178 −0.145 0.257 0.551 0.258 0.308 −0.067 0.198 0.005 −0.064 0.017 0.422 0.306 −0.020 −0.335 1 ABTS+· 0.568 0.255 0.484 0.356 0.276 0.167 −0.156 −0.225 −0.367 −0.533 −0.092 0.128 0.132 0.002 −0.245 0.616* 1 ·OH −0.214 0.096 −0.270 0.471 0.540 0.447 0.132 0.570 0.378 0.088 0.732** 0.242 0.486 0.481 −0.224 0.445 0.123 1 总还原力 0.646* 0.398 −0.209 0.460 0.020 −0.374 −0.214 0.020 −0.181 −0.373 −0.109 −0.533 0.179 0.040 −0.298 −0.038 0.099 0.269 1 注:“*”表示差异显著,“**”表示差异极显著。 2.4 聚类分析
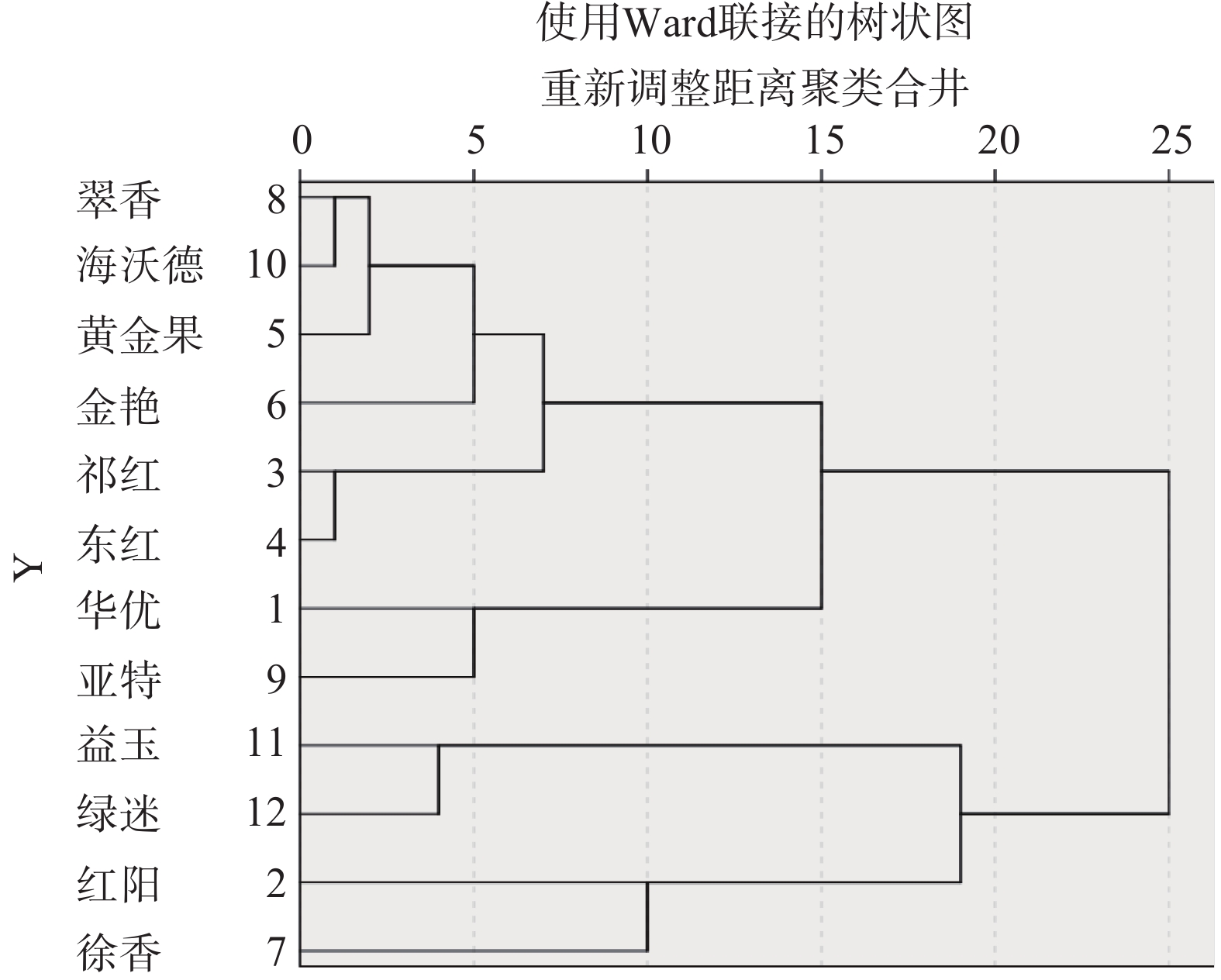
聚类分析过程是把样本依照品质特性相似性逐渐聚合在一起,相似度最大的优先聚合,着重区分类别内和类别间元素组成,最终按照类别的综合性质使多个品种聚合,从而达到聚类目的[21]。为了从整体上对不同品种猕猴桃汁中抗氧化物质及单酚含量差异进行分析,对相关数据标准化后进行系统聚类分析,结果如图2所示。在欧式距离6.0处可将12个品种猕猴桃样品分为6类,第一类为软枣系品种益玉和绿迷,软枣猕猴桃含丰富多酚类化合物,且主要以黄酮类化合物为主[22],对应表1也可看出益玉和绿迷中类黄酮含量在12个品种中较高,黄酮类化合物通常被认为是最有效的抗氧化剂,结合本实验室梁锦等[23]前期对猕猴桃制汁适应性的研究,得出益玉、绿迷具有较强的抗氧化能力,但软枣猕猴桃目前种植面积小,尚未大规模商业化栽培[24],理论上较适宜加工为营养丰富的果汁、果酒等饮料。第二类为红阳,第三类为徐香,第四类为华优、亚特,这三类为陕西省种植面积最广,抗氧化活性较高的常见主栽品种,加工经济性较高,适宜大规模加工为产品。第五类为两个红心品种祁红、东红,均为中华猕猴桃亚科中红阳的变种[8],且抗氧化成分相似。红心猕猴桃目前栽培面积和产量逐渐增大,其果肉沿中轴呈放射状红色,糖分较高,酸度极低,且果香浓郁、典型[25],发展势头强劲,其价格也比一般绿心猕猴桃贵2~3倍,鲜食最佳。第六类为翠香、海沃德、黄金果、金艳,其由于抗氧化物质相似被聚为一类[26]。其中海沃德、黄金果和金艳VC含量较低,酸甜口感较差。此次聚类依据的是抗氧化物质及单酚含量,未能把中华猕猴桃与美味猕猴桃进行种间区分。
3. 结论
对12种猕猴桃汁样品抗氧化活性成分及体外抗氧化活性进行测定。结果发现12种样品的多酚含量在0.577~0.835 mg/mL之间,类黄酮含量在0.013~0.061 mg/mL之间,相比较而言,益玉、绿迷多酚、类黄酮含量在12种猕猴桃中相对较高。VC变化幅度在27.30~130.38 mg/100 g之间,其中亚特VC含量最高,益玉中最低。通过HPLC对不同品种猕猴桃样品酚类成分测定与分析,得出原儿茶酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、表儿茶素含量相对最高,为猕猴桃中最主要的多酚类化合物。
通过DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH和FRAP这4种体外抗氧化方法来比较不同品种猕猴桃汁样品抗氧化活性,综合比较可知红阳、翠香、亚特和华优对DPPH·、ABTS+·清除能力较强;益玉和绿迷对清除·OH能力较强,总还原能力在12个猕猴桃样品中也较强,这与软枣系猕猴桃含丰富黄酮类化合物有密切关系。相关性分析发现VC、多酚、类黄酮含量和某些单酚类成分与抗氧化能力间有显著相关性(P<0.05)。
聚类分析是根据对象的特征进行分类,达到减少研究对象的目的,旨在将性质相近的对象归为一类,本文通过聚类分析初步判断哪些品种属于抗氧化活性成分相似的品种,为后续研究抗氧化活性较高且相似的品种提供理论依据,有助于实践中的加工与利用[27]。本文对不同品种猕猴桃样品的抗氧化活性成分的差异性进行系统聚类分析,12个品种猕猴桃样品分为6类,第一类为软枣系的益玉和绿迷,第二类为红阳,第三类徐香,第四类为华优、亚特,第五类为两个红心品种祁红、东红,第六类为翠香、海沃德、黄金果、金艳。我国是世界上最大的猕猴桃生产国,100%果汁、非浓缩还原汁[28]、猕猴桃果酒等含有更多营养与功能成分的饮料受到消费者推崇,功能饮料零售额年均复合增长率达到17.1%,市场前景较好。故关于猕猴桃汁抗氧化活性的研究对加工功能果汁饮料十分必要,并可为猕猴桃果汁、果酒等加工企业选择抗氧化能力强的品种提供一定的参考。
-
表 1 猕猴桃品种及采样情况
Table 1 Cultivars of kiwifruit and sampling condition
编号 品种 种系 果肉色泽 产地 采样时间 北纬 东经 1 华优 中华[8] 黄肉黄心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 2 红阳 中华 黄肉红心 陕西眉县 2019/9/10 34.28° 107.75° 3 祁红 中华 黄肉红心 陕西眉县 2019/10/8 34.28° 107.75° 4 东红 中华 黄肉红心 四川邛崃 2019/9/15 30.41° 103.46° 5 黄金果 中华 黄肉黄心 陕西杨凌 2019/9/29 34.27° 108.08° 6 金艳 中华 黄肉黄心 陕西杨凌 2019/9/29 34.27° 108.08° 7 徐香 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 8 翠香 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西眉县 2019/9/10 34.28° 107.75° 9 亚特 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/10 34.16° 108.22° 10 海沃德 美味 绿肉绿心 陕西周至 2019/10/15 34.16° 108.22° 11 益玉 软枣 绿肉绿心 四川雅安 2019/8/6 30.01° 103.03° 12 绿迷 软枣 绿肉绿心 四川雅安 2019/8/6 30.01° 103.03° 表 2 不同品种猕猴桃果汁主要成分
Table 2 Major ingredients of different kiwifruit juice
品种 VC(mg/100 g) 多酚(mg/mL) 类黄酮(mg/mL) 华优 100.440+0.300b 0.686+0.140bcd 0.032+0.004de 红阳 54.360+11.250d 0.614+0.026cd 0.023+0.000b 祁红 50.470+9.530e 0.835+0.016a 0.045+0.001a 东红 99.400+9.820b 0.770+0.008ab 0.027+0.001ef 黄金果 51.010+3.420e 0.650+0.026bcd 0.036+0.002d 金艳 56.010+2.450d 0.734+0.006abc 0.028+0.001ef 徐香 31.930+5.650h 0.577+0.084d 0.024+0.001fg 翠香 96.740+7.270c 0.644+0.037bcd 0.026+0.002f 亚特 130.380+8.110a 0.768+0.099ab 0.019+0.008g 海沃德 38.440+1.430f 0.620+0.036cd 0.013+0.004h 益玉 27.300+1.950i 0.726+0.080abc 0.061+0.002a 绿迷 34.600+5.340g 0.662+0.025bcd 0.056+0.002b 平均值 64.260 0.690 0.030 标准差 33.660 0.080 0.010 变异系数(%) 52.380 11.100 44.850 注:同列小写字母不同表示差异显著,P<0.05。 表 3 不同品种猕猴桃单体酚含量(μg/100 g)
Table 3 Polyphenol composition and content of different kiwifruit (μg/100 g)
品种 没食子酸 原儿茶酸 儿茶素 绿原酸 表儿茶素 咖啡酸 对香豆酸 阿魏酸 根皮苷 芦丁 槲皮素 杨梅素 总酚 华优 1.68±0.07 6.18±0.02 4.31±0.02 2.47±0.04 2.43±0.02 0.51±0.06 0.06±0.04 0.17±0.01 0.46±0.01 0.21±0.04 / 7.39±0.02 25.87±0.14 红阳 0.58±0.03 1.51±0.01 27.56±0.36 9.02±0.04 7.04±0.01 0.46±0.04 0.12±0.02 0.16±0.02 0.24±0.05 0.49±0.01 / / 47.17±0.03 祁红 0.84±0.02 0.70±0.03 2.92±0.02 7.36±0.04 3.52±0.04 0.28±0.05 0.03±0.04 0.08±0.03 / / / / 15.73±0.28 东红 0.42±0.10 / 0.38±0.04 1.78±0.06 0.57±0.04 0.78±0.02 0.19±0.06 / / / / / 4.13±0.15 黄金果 0.55±0.05 0.48±0.01 1.63±0.04 4.83±0.04 1.51±0.02 0.04±0.03 0.02±0.07 0.07±0.06 / / / 13.01±0.07 22.14±0.27 金艳 4.29±0.09 2.48±0.01 8.32±0.05 2.754±0.01 8.73±0.06 1.08±0.03 0.07±0.09 0.09±0.08 / / / 6.11±0.06 33.91±0.01 徐香 0.65±0.04 3.09±0.01 9.38±0.23 9.23±0.02 13.39±0.07 2.14±0.08 0.58±0.08 0.16±0.04 0.17±0.00 0.99±0.03 0.31±0.00 7.25±0.01 47.34±0.05 翠香 0.51±0.05 1.37±0.02 4.47±0.08 3.67±0.04 2.92±0.01 0.94±0.05 0.07±0.05 0.09±0.05 0.25±0.00 0.33±0.04 0.30±0.00 8.52±0.07 23.42±0.23 亚特 1.63±0.06 6.59±0.02 11.35±0.09 2.75±0.03 13.26±0.05 0.95±0.01 0.14±0.01 0.15±0.05 0.18±0.00 0.85±0.05 0.34±0.03 / 38.19±0.37 海沃德 1.29±0.01 0.77±0.01 6.15±0.07 2.32±0.01 7.02±0.03 0.83±0.01 0.10±0.02 0.13±0.01 0.21±0.00 0.10±0.08 / 1.15±0.04 20.06±0.07 益玉 3.41±0.02 2.53±0.02 4.60±0.04 3.87±0.01 2.33±0.01 0.89±0.04 0.13±0.04 0.10±0.01 / 3.15±0.05 0.34±0.05 / 21.36±0.14 绿迷 1.32±0.02 5.41±0.01 7.70±0.08 4.16±0.02 6.19±0.04 1.73±0.03 0.20±0.01 0.23±0.01 / 1.12±0.09 0.48±0.04 3.99±0.09 32.52±0.09 平均值 1.43 2.59 7.40 4.52 5.74 0.89 0.14 0.12 0.12 0.60 0.15 3.95 注:“/”表示未检出。 表 4 不同品种猕猴桃汁抗氧化活性的IC50[5]
Table 4 IC50 of antioxidant activity of different varieties in kiwifruit juice[5]
浓度(g/L) VC 华优 红阳 祁红 东红 黄金果 金艳 徐香 翠香 亚特 海沃德 益玉 绿迷 DPPH· 0.037 0.042 0.025 0.062 0.072 0.114 0.050 0.067 0.031 0.040 0.064 0.045 0.104 ABTS+· 19.300 8.830 11.200 12.280 16.800 21.740 11.300 32.960 11.270 9.090 36.170 11.490 16.690 ·OH 0.388 0.497 0.502 0.571 0.801 0.654 0.581 0.473 0.548 0.402 0.406 0.310 0.381 表 5 不同品种猕猴桃汁抗氧化能力与主要活性成分的相关系数
Table 5 Correlation coefficients between antioxidant ability and the main active ingredients of kiwifruit juice
多酚 类黄酮 VC 没食
子酸原儿
茶酸儿茶素 绿原酸 表儿
茶素咖啡酸 对香
豆酸阿魏酸 根皮苷 芦丁 槲皮素 杨梅素 DPPH· ABTS+· ·OH 总还
原力多酚 1 类黄酮 0.300 1 VC 0.361 −0.434 1 没食子酸 0.279 0.285 −0.176 1 原儿茶酸 0.012 0.110 0.329 0.273 1 儿茶素 −0.377 −0.296 −0.075 −0.042 0.164 1 绿原酸 −0.328 0.047 −0.466 −0.362 −0.177 0.537 1 表儿茶素 −0.243 −0.438 −0.009 0.136 0.450 0.502 0.307 1 咖啡酸 −0.362 0.020 −0.248 0.123 0.381 0.089 0.144 0.610* 1 对香豆酸 −0.445 −0.131 −0.260 −0.195 0.164 0.157 0.448 0.569 0.824** 1 阿魏酸 −0.459 0.101 −0.210 0.050 0.733** 0.478 0.261 0.516 0.470 0.296 1 根皮苷 −0.400 −0.495 0.430 −0.217 0.407 0.289 −0.021 0.134 −0.057 0.019 0.402 1 芦丁 −0.036 0.600* −0.343 0.399 0.287 0.071 0.078 0.067 0.344 0.269 0.254 −0.182 1 槲皮素 −0.151 0.384 −0.061 0.071 0.522 0.017 0.035 0.345 0.688* 0.435 0.478 −0.108 0.668* 1 杨梅素 −0.457 −0.044 −0.037 −0.105 0.006 −0.297 0.009 −0.126 0.010 0.018 0.038 0.143 −0.285 −0.031 1 DPPH· 0.178 −0.145 0.257 0.551 0.258 0.308 −0.067 0.198 0.005 −0.064 0.017 0.422 0.306 −0.020 −0.335 1 ABTS+· 0.568 0.255 0.484 0.356 0.276 0.167 −0.156 −0.225 −0.367 −0.533 −0.092 0.128 0.132 0.002 −0.245 0.616* 1 ·OH −0.214 0.096 −0.270 0.471 0.540 0.447 0.132 0.570 0.378 0.088 0.732** 0.242 0.486 0.481 −0.224 0.445 0.123 1 总还原力 0.646* 0.398 −0.209 0.460 0.020 −0.374 −0.214 0.020 −0.181 −0.373 −0.109 −0.533 0.179 0.040 −0.298 −0.038 0.099 0.269 1 注:“*”表示差异显著,“**”表示差异极显著。 -
[1] 赵金梅, 高贵田, 薛敏, 等. 不同品种猕猴桃果实的品质及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(9):118−122. [ZHAO J M, GAO G T, XUE M, et al. Fruit quality and antioxidant activity of different kiwifruit varieties[J]. Food Science,2014,35(9):118−122. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201409024 [2] LEONTOWICZ H, LEONTOWICZ M, LATOCHA P, et al. Bioactivity and nutritional properties of hardy kiwifruit Actinidia arguta in comparison with Actinidia deliciosa ‘Hayward’ and Actinidia eriantha ‘Bidan’[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,196:281−291. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.127
[3] 张培书, 何伍金, 马关雪, 等. “红阳”猕猴桃采后存放过程中的品质变化[J]. 北方园艺,2019,440(17):114−123. [ZHANG P S, HE W J, MA G X, et al. The quality changes of “Hongyang” kiwifruit during postharvest storage[J]. Northern Horticulture,2019,440(17):114−123. [4] 李丽霞. 不同品种猕猴桃皮、肉、籽酚类组分分析及抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018. LI L X. Analysis of phenolic components in skin, meat and seed of different kiwifruits and study on antioxidant activity[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University, 2018.
[5] 王菲, 栾云峰, 刘长江. 软枣猕猴桃总黄酮体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2011(17):168−171. [WANG F, LUAN Y F, LIU C J. Antioxidant activity in vitro of total flavonoids of Actinidia arguta[J]. Food Science,2011(17):168−171. [6] 张云. 猕猴桃多酚分离鉴定及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2019. ZHANG Y. Isolation, identification and antioxidant activity of kiwi fruit polyphenols[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2019.
[7] 曹毛毛, 卢泽绵, 高慧, 等. 不同品种猕猴桃果实的理化性质及抗氧化活性[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2018,48(2):231−237. [CAO M M, LU Z M, GAO H, et al. Physical and chemical properties and antioxidant activities of different varieties of kiwifruit[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2018,48(2):231−237. [8] 方金豹, 钟彩虹. 新中国果树科学研究70年猕猴桃[J]. 果树学报,2019,36(10):1352−1359. [FANG J B, ZHONG C H. 70 years of scientific research on fruit trees in new China kiwi fruit[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2019,36(10):1352−1359. [9] 李国秀, 刘小宁, 李劼. 高效液相色谱法测定猕猴桃中的VC含量[J]. 保鲜与加工,2016(5):89−93. [LI G X, LIU X N, LI J. Determination of VC content in kiwi fruit by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Fresh-keeping and Processing,2016(5):89−93. [10] 杨小兰, 袁娅, 郭晓晖, 等. 超高压处理对不同品种猕猴桃汁多酚含量及其抗氧化活性影响[J]. 食品科学,2013,1:73−77. [YANG X L, YUAN Y, GUO X H, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure treatment on the polyphenol content and antioxidant activity of different kiwifruit juices[J]. Food Science,2013,1:73−77. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201324015 [11] 王华, 曹婧, 翟丽娟, 等. 猕猴桃果肉提取物抗氧化活性研究[J]. 华北农学报,2013,28(2):144−149. [WANG H, CAO J, ZHAI L J, et al. Antioxidant activity of kiwi fruit pulp extract[J]. North China Agricultural Journal,2013,28(2):144−149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.02.026 [12] 李琛, 张婷, 罗安伟, 等. 8种猕猴桃抗氧化活性评价及基于HPLC与FT-IR指纹分析的品种区分[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(6):288−297. [LI C, ZHANG T, LUO A W, et al. Evaluation of eight kinds of kiwifruit antioxidant activity and classification based on HPLC and FT-IR fingerprint analysis[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(6):288−297. [13] 张淑娟, 徐怀德, 米林峰. 光皮木瓜汁体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科学,2011,21:56−61. [ZHANG S J, XU H D, MI L F. Study on the antioxidant activity of papaya juice in vitro[J]. Food Science,2011,21:56−61. [14] 左丽丽, 王振宇, 樊梓鸾, 等. 猕猴桃多酚的生理功能研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2013,34(11):117−120,127. [ZUO L L, WANG Z Y, FAN Z L, et al. Progress in the physiological functions of kiwi fruit polyphenols[J]. Food Research and Development,2013,34(11):117−120,127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2013.11.031 [15] BARTWAL A, MALL R, LOHANI P, et al. Role of secondary metabolites and brassinosteroids in plant defense against environmental stresses[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2013,32(1):216−232. doi: 10.1007/s00344-012-9272-x
[16] 千春录, 陶蓓佩, 陈方霞, 等. 1-MCP对猕猴桃果实品质和细胞氧化还原水平的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2012,12(2):9−13. [QIAN C L, TAO B P, CHEN F X, et al. Effects of 1-MCP on kiwi fruit quality and cellular redox levels[J]. Preservation and Processing,2012,12(2):9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2012.02.003 [17] ZUO L L, WANG Z Y, FAN Z L, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant and antiproliferative properties of three Actinidia (Actinidia kolomikta, Actinidia arguta, Actinidia chinensis) extracts in vitro[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2012,13(5):5506−5518. doi: 10.3390/ijms13055506
[18] 郭长江, 杨继军, 李云峰, 等. FRAP法测定水果不同部分抗氧化活性[J]. 中国公共卫生,2003,7:85−87. [GUO C J, YANG J J, LI Y F, et al. Determination of antioxidant activity of different parts of fruits by FRAP method[J]. Chinese Public Health,2003,7:85−87. doi: 10.11847/zgggws2003-19-01-48 [19] KIM J G, BEPPU K, KATAOKA I. Varietal differences in phenolic content and astringency in skin and flesh of hardy kiwifruit resources in Japan[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2009,120(4):551−554. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2008.11.032
[20] 旷慧, 王金玲, 姚丽敏, 等. 6种东北地区红树莓果渣提取物的抗氧化活性差异[J]. 食品科学,2016,1:63−68. [KUANG H, WANG J L, YAO L M, et al. Differences in antioxidant activity of six red raspberry pomace extracts in Northeast China[J]. Food Science,2016,1:63−68. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620011 [21] 高惠璇. 应用多元统计分析[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2005. GAO H X. Applied multivariate statistical analysis[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2005.
[22] SOCHA R, JUSZCZAK L, PIETRZYK S, et al. Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of herbhoneys[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,113(2):568−574. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.08.029
[23] 梁锦, 黄天姿, 李瑞娟, 等. 不同品种猕猴桃制汁适应性评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(24):210−218,225. [LIANG J, HUANG T Z, LI R J, et al. Evaluation on the adaptability of different varieties of kiwifruit juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(24):210−218,225. [24] 牛强, 申健, 刘悦, 等. 软枣猕猴桃主要活性成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,419(3):339−344,350. [NIU Q, SHEN J, LIU Y, et al. Research progress on the main active ingredients and pharmacological activities of Actinidia arguta[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,419(3):339−344,350. [25] 王丹, 梁锦, 黄天姿, 等. 基于主成分和聚类分析的不同品种猕猴桃鲜食品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(7):8. [WANG D, LIANG J, HUANG T Z, et al. Evaluation of fresh food quality of different kiwifruit varieties based on principal component and cluster analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(7):8. [26] 张东峰, 陈家豪, 郭静, 等. 7种柑橘多酚、黄酮含量及其抗氧化活性比较研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,4(6):69−74. [ZHANG D F, CHEN J H, GUO J, et al. Comparative study on the contents and antioxidant activity of seven kinds of citrus polyphenols and flavonoids[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,4(6):69−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.06.013 [27] 冉军舰, 孙华迪, 陈晓静, 等. 基于主成分与聚类分析的35个苹果品种多酚综合评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(8):139−144,155. [RAN J J, SUN H D, CHEN X J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of polyphenols in 35 apple varieties based on principal component and cluster analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(8):139−144,155. [28] 郑妍, 张春岭, 刘慧, 等. UPLC法测定猕猴桃果汁中的酚类物质含量[J]. 果树学报,2018,35(8):1006−1015. [ZHENG Y, ZHANG C L, LIU H, et al. Determination of phenolic substances in kiwi fruit juice by UPLC method[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2018,35(8):1006−1015. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 程娟娟,程江华,蔡永萍,万娅琼,徐雅芫. 大豆肽的功能活性及在食品加工产业中的应用. 中国调味品. 2024(06): 200-205 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



