Screening of High-yielding Tetramethylpyrazine Bacillus and Its Effect on the Accumulation Process of Maotai-flavor Liquor
-
摘要: 为提高和稳定白酒中四甲基吡嗪含量,本研究从酱香大曲样品中分离出13株芽孢杆菌,通过蛋白酶透明圈试验初筛,选出5株产蛋白酶优良菌株。经过液态发酵试验筛选出一株高产四甲基吡嗪的功能菌,其发酵液中的四甲基吡嗪含量为12.22 mg/L,鉴定为地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168。将该菌株的种子培养液按0%、3%、5%和7%(v/w)接种到酱香型白酒堆积培养中与传统大曲协同发酵,堆积糟醅中乙偶姻和四甲基吡嗪的含量均有提高,其中接种量为7%时增量最大,四甲基吡嗪产量比对照组提高24.88%;理化指标总体变化较明显,氨基氮和总酸有所增加;地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168的添加对堆积糟醅的菌群结构影响不大,随着接种量的增加糟醅中芽孢杆菌属等各优势菌属丰度也随之增加。为功能菌在堆积过程中的应用研究奠定了基础。Abstract: In order to increase and stabilize the content of tetramethylpyrazine in liquor, 13 strains of Bacillus were isolated from Maotai Daqu samples, and 5 strains with excellent protease production were selected through the preliminary screening of protease transparent circle test. After a liquid fermentation test, a functional bacterium with high yield of tetramethylpyrazine was screened out. The content of tetramethylpyrazine in the fermentation broth was 12.22 mg/L, which was identified as Bacillus licheniformis GTBL-168. The seed culture solution of this strain was inoculated into the sauce-flavor liquor accumulation culture at 0%, 3%, 5%, and 7% (v/w) to synergize the fermentation with traditional Daqu, and accumulate acetoin and tetramethyl in the glutinous rice grains. The content of pyrazine increased, and the increasing was the largest when the inoculation amount was 7%, and the yield of tetramethylpyrazine increased by 24.88% compared with the control group, the overall changes in physical and chemical indexes were obvious, and the amino nitrogen and total acid increased, the addition of Bacillus licheniformis GTBL-168 had little effect on the microbial structure of the accumulated fermented grains. With the increasing of the inoculation amount, the abundance of Bacillus and other dominant bacteria in the fermented grains also increased. It would lay a foundation for the application of functional bacteria in the process of stacking fermentation.
-
Keywords:
- Maotai-flavor liquor /
- functional Bacillus /
- tetramethylpyrazine /
- acetoin /
- stacking fermentation
-
四甲基吡嗪(tetramethyl pyrazine,TTMP),是一种天然的香料,具有烤焙、坚果、可可等香气,可以作为风味添加剂[1]。TTMP也是白酒中重要风味物质的组成成分,赋予白酒一定的保健作用,在不同香型的白酒中含量不同,在酱香型白酒中含量最高。白酒酿造过程中TTMP主要是由芽孢杆菌发酵代谢合成,一方面微生物通过糖酵解途径产生丙酮酸,两分子丙酮酸缩合形成α-乙酰乳酸,在α-乙酰乳酸脱羧酶的作用下生成乙偶姻;另一方面微生物酶分解原料中蛋白质和氨基酸产生氨,进而乙偶姻和氨发生非酶促反应合成TTMP。
通过分离筛选高产TTMP的微生物进而来稳定和提高白酒中四甲基吡嗪含量是一种常用的手段,徐岩等[2]将具有相应酿造功能的微生物菌剂进行复配组合,使用菌剂生产的芝麻香型白酒头段酒中的吡嗪类物质含量达到175 μg/L,相比未使用菌剂提高了33.6%。袁建国等[3]通过添加芽抱杆菌B-010,使芝麻香型白酒中的TTMP含量由0.4 mg/L提高到1.8 mg/L;张温清[4]将高产TTMP芽孢杆菌菌液接入芝麻香型白酒堆积糟醅中培菌后入窖发酵,结果发现,接种功能菌 XJB-104原酒中TTMP含量从0.06 mg/L增加到1.39 mg/L;王晓丹等[5]从高温大曲中分离得到的地衣芽孢杆菌添加到窖池中层的糟醅中,按照粹沙工艺制酒取样,结果最佳菌株添加量为5%,此时发酵后的酒醅TTMP含量为6.81 μg/g,是对照组的3.03倍,酒样中TTMP相对百分含量为0.028%。
TTMP在酱香型、芝麻香型和兼香型白酒中的含量显著高于其它香型白酒的主要原因,是都有堆积培菌过程,在堆积糟醅中有较高的含氧量,有利于好氧芽孢杆菌的生长代谢,合成较多的TTMP。如直接入窖发酵,糟醅中的氧在发酵前期很快被兼性厌氧的酵母菌等微生物耗尽,好氧芽孢杆菌的生长与TTMP的合成将受到限制。本研究从酱香型白酒大曲中筛选出的1 株高产TTMP的地衣芽孢杆菌,并将其种子液添加到酱香型白酒第5轮次的酒醅中进行堆积培菌,探究地衣芽孢杆菌对堆积培菌过程的影响,进而探讨在酱香白酒生产中使用的可行性,旨在通过该菌剂强化堆积培菌过程提高白酒中的TTMP含量,从而改善白酒的品质。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
糟醅、高温大曲 贵州国台酒业公司;氢氧化钠、斐林试剂、葡萄糖、硫酸、甲醛、盐酸等 均为国产分析纯;四甲基吡嗪、乙偶姻、无水乙醇 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;DNA提取试剂盒 成都福际生物技术有限公司。
7890B气相色谱仪、1200SL液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;CX21FS1型生物显微镜 日本OLYMPUS会社;LD5-10离心机 北京医用离心机厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 培养基与溶液
分离培养基的配制。LB培养基:蛋白胨20 g/L,酵母浸粉5 g/L,NaCl 10 g/L,pH 7.2,于121 ℃灭菌20 min。
酪蛋白琼脂培养基的配制。干酪素10.0 g,牛肉膏3 g,氯化钠5 g,磷酸氢二钠2 g,琼脂20 g,加蒸馏水定容至1000 mL,pH为7.0~7.2,121 ℃灭菌20 min。
一级种子培养基的配制。LB培养基:蛋白胨20 g/L,酵母浸粉5 g/L,NaCl 10 g/L,pH 7.2,于121 ℃灭菌20 min。
代谢发酵培养基的配制。12°BX高粱水解液,酵母浸粉15 g/L,K2HPO4 5 g/L,NaCl 5 g/L,pH调至6.0,于115 ℃灭菌20 min。
固态发酵培养基。贵州国台酒第5轮次蒸酒后糟醅。
0.1 mol/L PBS缓冲液:A液(0.1 mol/L KH2PO4):1.361 g KH2PO4溶于100 mL蒸馏水;B液(0.1 mol/L Na2HPO4):1.78 g Na2HPO4·2H2O溶于100 mL蒸馏水;A液与B液按照1:19的比例混合,pH为8.0,于115 ℃湿热灭菌20 min。
1.2.2 高产蛋白酶活力芽孢杆菌菌株的分离与筛选
1.2.2.1 菌种分离
称取大曲粉10 g,放入含有90 mL无菌生理盐水的三角瓶,在85 ℃水浴10 min,以200 r/min转速在37 ℃振荡培养箱过夜扩培,吸取培养液1 mL,放入装有9 mL无菌生理盐水的试管内,吹吸混匀,按上述操作继续稀释,稀释到1×10−6,取稀释度为1×10−4~1×10−6各1 mL分别涂板分离,以37 ℃培养24 h。分离出不同菌落形态的菌株,将菌株划线纯化,于−80 ℃下超低温保存。
1.2.2.2 高产蛋白酶活力菌株的筛选
蛋白酶透明圈实验:将分离得到的菌株用酪蛋白琼脂培养基做透明圈实验,以透明圈作为考察指标进行初筛。将菌株以点接法接种到酪蛋白琼脂培养基上,37 ℃倒置培养1 d后观察透明圈大小,并用直尺测量透明圈直径D(mm)和菌落直径d(mm)的比值(D/d),选出能产生较大透明圈的菌株。
1.2.3 高产TTMP菌株的筛选与分子鉴定
1.2.3.1 高产TTMP菌株的筛选
一级培养:将分离出的芽孢杆菌经活化后接入LB种子培养基培养24 h。
代谢发酵:按5%接种量接入装有50 mL代谢培养基的250 mL三角瓶中,以200 r/min转速在43 ℃下振荡培养84 h。代谢发酵结束后,利用HPLC检测发酵液中乙偶姻和四甲基吡嗪含量。
1.2.3.2 分子鉴定
采用细菌DNA提取试剂盒对各菌株提取菌株基因组DNA,利用细菌通用引物27F/1492R进行PCR扩增,PCR产物交由上海金唯智公司进行测序鉴定,对菌株进行16S rDNA序列分析。
1.2.4 地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168对酱香型白酒堆积过程的影响
在糟醅中加入7%的大曲粉拌匀,每个250 mL三角瓶中分装120 g,挑选代谢发酵液中TTMP含量最高的菌株,将其发酵液作为种子液按照0%、3%、5%、7%的比例接种于拌有大曲的糟醅中,拌匀,6层纱布封口,30 ℃堆积12 h,37 ℃堆积36 h,在无菌条件换成胶塞后继续在45 ℃下堆积24 h,同时做平行实验,测定堆积结束后糟醅的乙偶姻和TTMP含量、理化指标及菌群结构。
1.2.5 乙偶姻含量的检测方法
发酵液样品的前处理:取发酵液2 mL,12000 r/min离心5 min,取上清,用流动相5 mmol/L的稀硫酸溶液稀释10倍后用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,直接进样。
堆积糟醅样品的前处理:取10 g糟醅加100 mL蒸馏水超声30 min,12000 r/min离心2 min,取上清液经0.22 μm的水相膜过滤后进行液相色谱检测。
高效液相色谱条件:Aglient HPX-87H色谱柱(300 mm×7.8 mm×9 μm),检测器为示差检测器(RID)(45 ℃),柱温65 ℃,流动相为5 mmol/L的稀硫酸溶液,流速为0.6 mL/min,进样量20 μL。
采用HPLC检测乙偶姻含量,通过外标法进行乙偶姻的定量分析,标准回归方程为y=190998x−52137,R2=0.9935。
1.2.6 TTMP含量的检测方法
1.2.6.1 发酵液中TTMP的测定方法
样品的前处理:取发酵液2 mL,12000 r/min离心5 min,取上清,用40%乙醇溶液稀释10倍后用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤,直接进样。
高效液相色谱条件:色谱柱为Eclipse Plus C18(4.6×250 mm),紫外(Ultra Violet,UV)检测器,以甲醇:水(v/v)=35:65作为流动相,柱温40 ℃,流速为1 mL/min,检测波长278 nm,检测时间45 min,进样量20 μL。
采用HPLC检测发酵液中TTMP含量,通过外标法进行TTMP的定量分析,标准回归方程为y=63.563x−0.4614,R2=1。
1.2.6.2 堆积糟醅中TTMP的检测方法
样品的前处理:取50 g堆积培养结束后的糟醅加5 mL无水乙醇和200 mL蒸馏水进行蒸馏,接取100 mL馏分,将馏分经0.22 μm无机滤膜过滤后直接进样进行气相色谱分析,分析馏分中TTMP含量。
气相色谱条件:色谱柱 HP-INNOWAX(30 m×320 μm×0.25 μm);载气为纯度 99.99%的氮气;柱流速为0.8 mL/min;进样口温度200 ℃;检测器温度150 ℃;程序升温,起始温度50 ℃,保持8 min,以5 ℃/min升至150 ℃,保持15 min;进样体积为1 μL;分流进样,分流比为10:1。
采用GC检测堆积糟醅中TTMP含量,通过外标法进行TTMP的定量分析,标准回归方程为y=212.9x−230.85,R2=0.9995。
1.2.7 堆积糟醅理化指标的测定
酸度的测定:采用酸碱滴定指示剂法;残淀粉的测定:采用斐林试剂法;氨基酸态氮的测定:酸度计法;残糖的测定:斐林试剂法。具体参照DB 34/T 2264-2014《固态发酵酒醅分析方法》[6]。
1.2.8 糟醅群落组成分析
1.2.8.1 样品的前处理
将100 mL PBS缓冲液(pH8.0)和酒醅样品充分混合,使用布氏漏斗过滤混合液体,并用200 mL PBS缓冲液冲洗滤渣3~5次。将滤液在7000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心10 min,收集底部菌泥于−20 ℃保存。
1.2.8.2 群落组成分析
将预处理后的样品送至上海派诺森生物科技有限公司进行16S和ITS测序,按照QIIME2 dada2分析流程进行序列去噪或OTU聚类,使用云平台分析菌落多样性指数及群落组成变化情况。
1.3 数据处理
使用SPSS23分析实验数据,各实验均重复3次,所有数据均通过方差(ANOVA)方法进行分析,所有均值均以P<0.05的水平进行分离。通过差异分析了不同实验数据的意义。所得数据均使用Origin软件绘制数据柱状图。基于Illumina MiSeq测序平台,群落组成图利用R语言工具进行绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 高产蛋白酶活力芽孢杆菌菌株的分离与筛选
蛋白酶分解蛋白质生成的氨基酸为酿造体系提供N源,同时也是风味前体物质,氨基酸进一步分解生成氨,为合成TTMP提供了前体物质。按照1.2.2.2的方法进行蛋白酶透明圈实验,测得其透明圈直径与菌落直径比值HC值,结果如表1所示。菌株144的HC值最大,说明其对培养基中干酪素的分解利用能力较强,即产蛋白酶的活力较高。挑选HC值大于等于1.3的菌株进行液态代谢发酵。
表 1 透明圈HC值Table 1. HC value of the transparent circle菌种编号 菌落直径(mm) 透明圈直径(mm) HC值(D/d) 144 10.00 24.00 2.40 10 12.00 21.00 1.75 168 10.00 14.00 1.40 152 15.00 20.00 1.30 90 20.00 26.00 1.30 163 28.00 36.00 1.29 37 14.00 18.00 1.29 138 14.00 18.00 1.29 24 24.00 30.00 1.25 125 24.00 30.00 1.25 122 34.00 42.00 1.24 208 25.00 30.00 1.20 198 32.00 34.00 1.06 2.2 产TTMP芽孢杆菌的筛选与鉴定
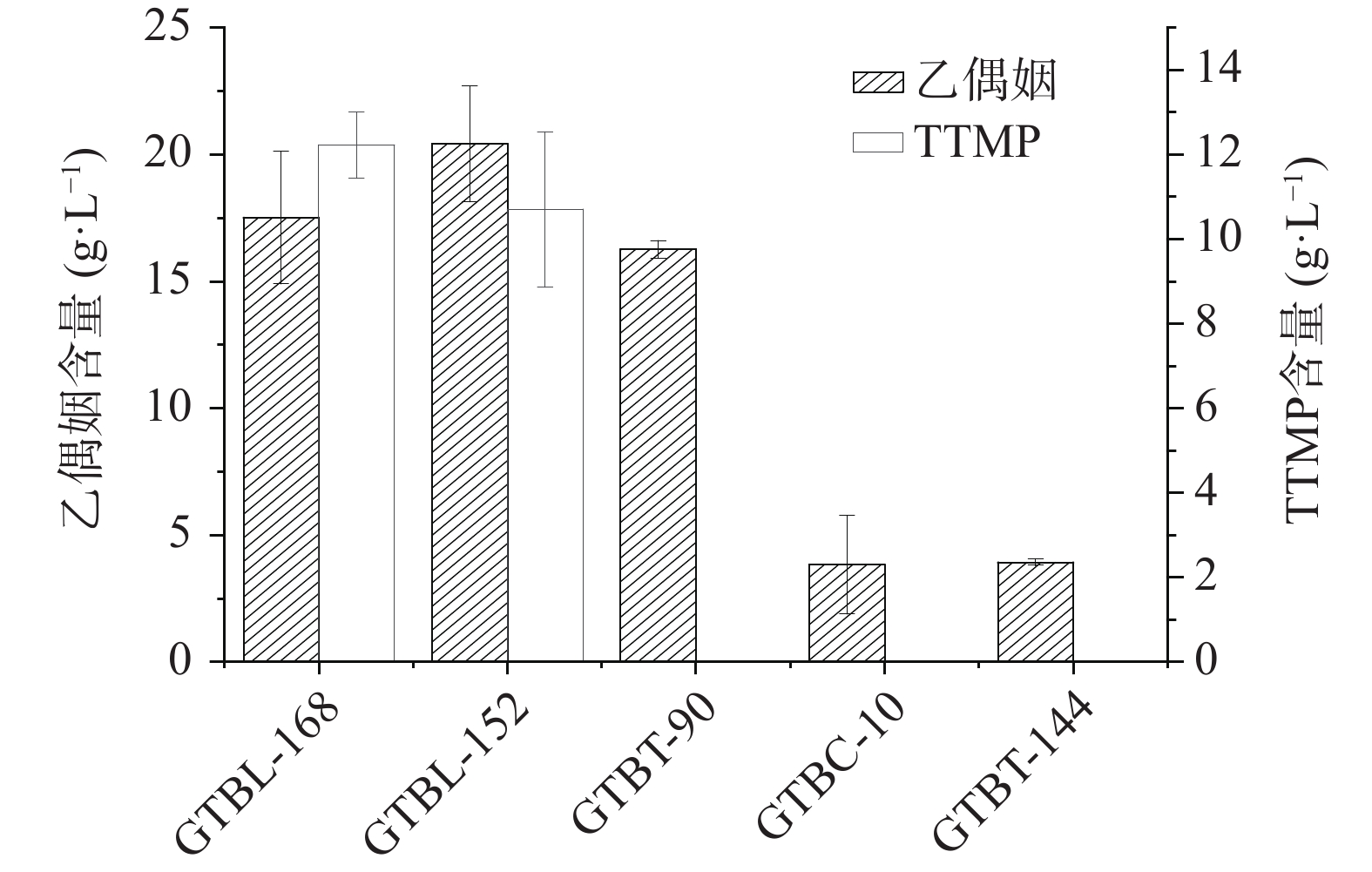
白酒中的TTMP由乙偶姻和氨反应生成。按照1.2.5和1.2.6的方法测定发酵液中乙偶姻和TTMP的含量,实验结果如图1所示。5株芽孢杆菌中有2株产TTMP,其中菌株GTBL-168产乙偶姻含量为17.51 g/L,产TTMP含量为12.22 mg/L。对照表1蛋白酶活性大小,菌株GTBT-144虽具有较高的蛋白酶活力,但产乙偶姻较少,而菌株GTBT-90乙偶姻含量较多,但蛋白酶活力相对较低,均未合成TTMP。因此,高产TTMP的功能菌筛选需同时具有较高的产蛋白酶和乙偶姻能力,该菌才可能代谢生成高含量的TTMP。
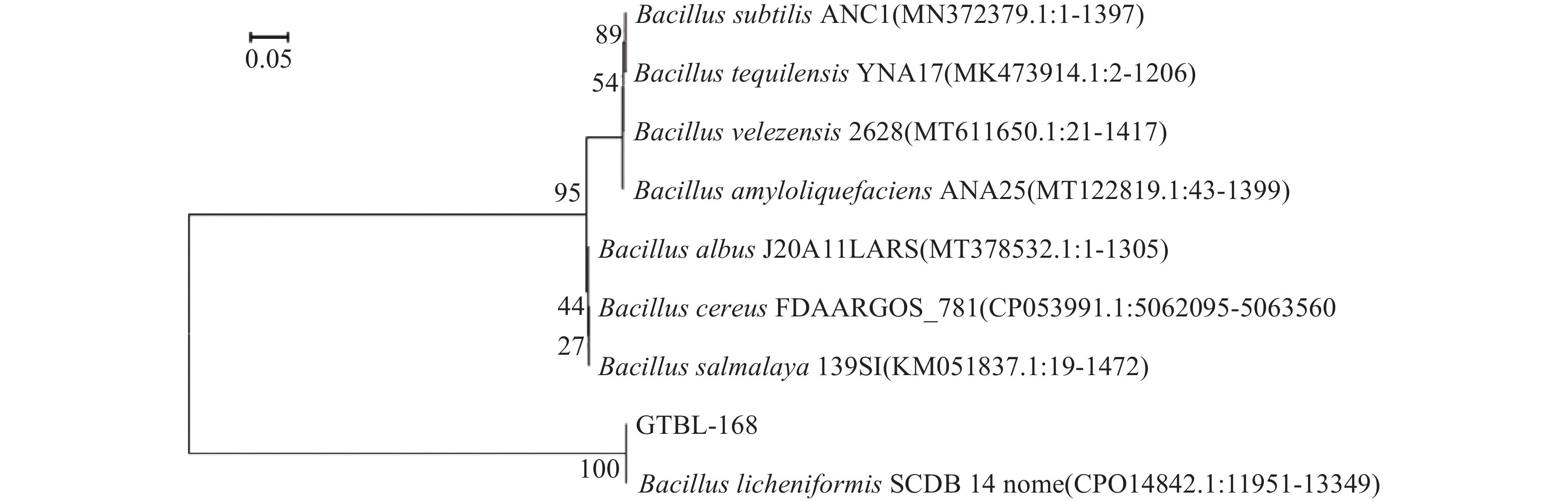
按照1.2.3.2的方法,将菌株GTBL-168测序结果提交至NCBI,并进行BLAST同源性比对,菌株GTBL-168与地衣芽孢杆菌的同源性达到99%以上,用 MEGA5.0构建系统发育树(图2)。通过系统发育树分析,将菌株GTBL-168鉴定为一株地衣芽孢杆菌(Bacillus licheniformis)。
2.3 地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168对堆积过程酒醅理化指标的影响
在酒的生产过程中,受不同的原料、菌种和生产工艺等因素的影响,酒的风味各有不同,酱香型白酒独特的高温堆积和高温制曲工艺对酱香风味有重要作用。在堆积过程加入功能芽孢杆菌与传统大曲协同堆积发酵,影响菌群结构,酒醅的理化指标受到影响,从而影响酒的质量。
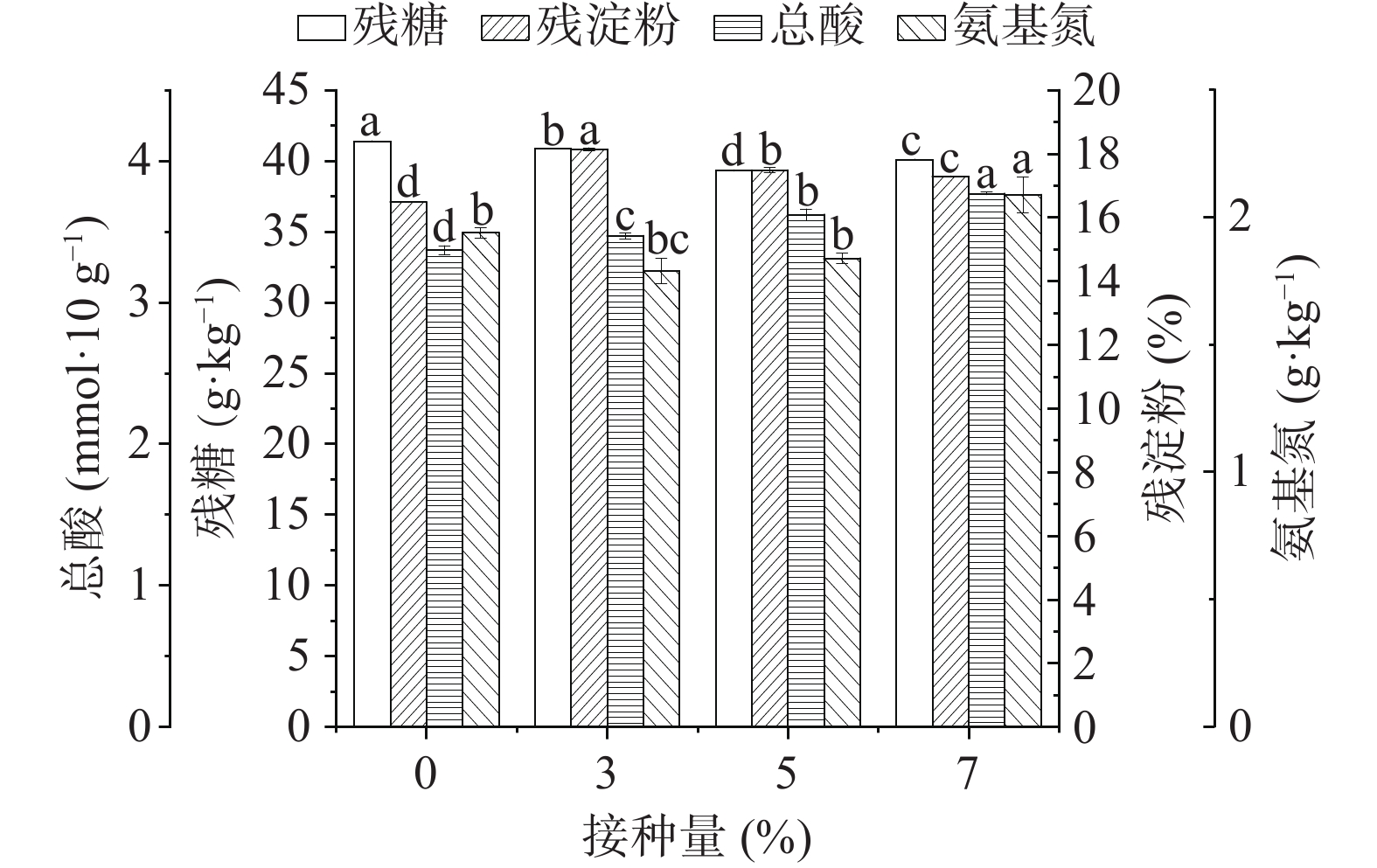
按照方法1.2.7测定堆积后糟醅的理化指标,结果如图3所示,在堆积过程结束后的糟醅中,相比于对照组实验,功能芽孢杆菌的添加对堆积过程各理化指标影响较明显,当接种量为7%时,总酸含量和氨基氮含量有所增加,氨基氮的增加促进了产酸菌的生长,从而总酸含量也有所提高。地衣芽孢杆菌所产蛋白酶最适作用pH为7.0[7],而糟醅酸度较大,不适于蛋白酶发挥作用,因此氨基氮含量较对照组差异不显著,芽孢杆菌接种量不断增加至7%时,才有一定的积累。
2.4 地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168对堆积糟醅中乙偶姻和TTMP含量的影响
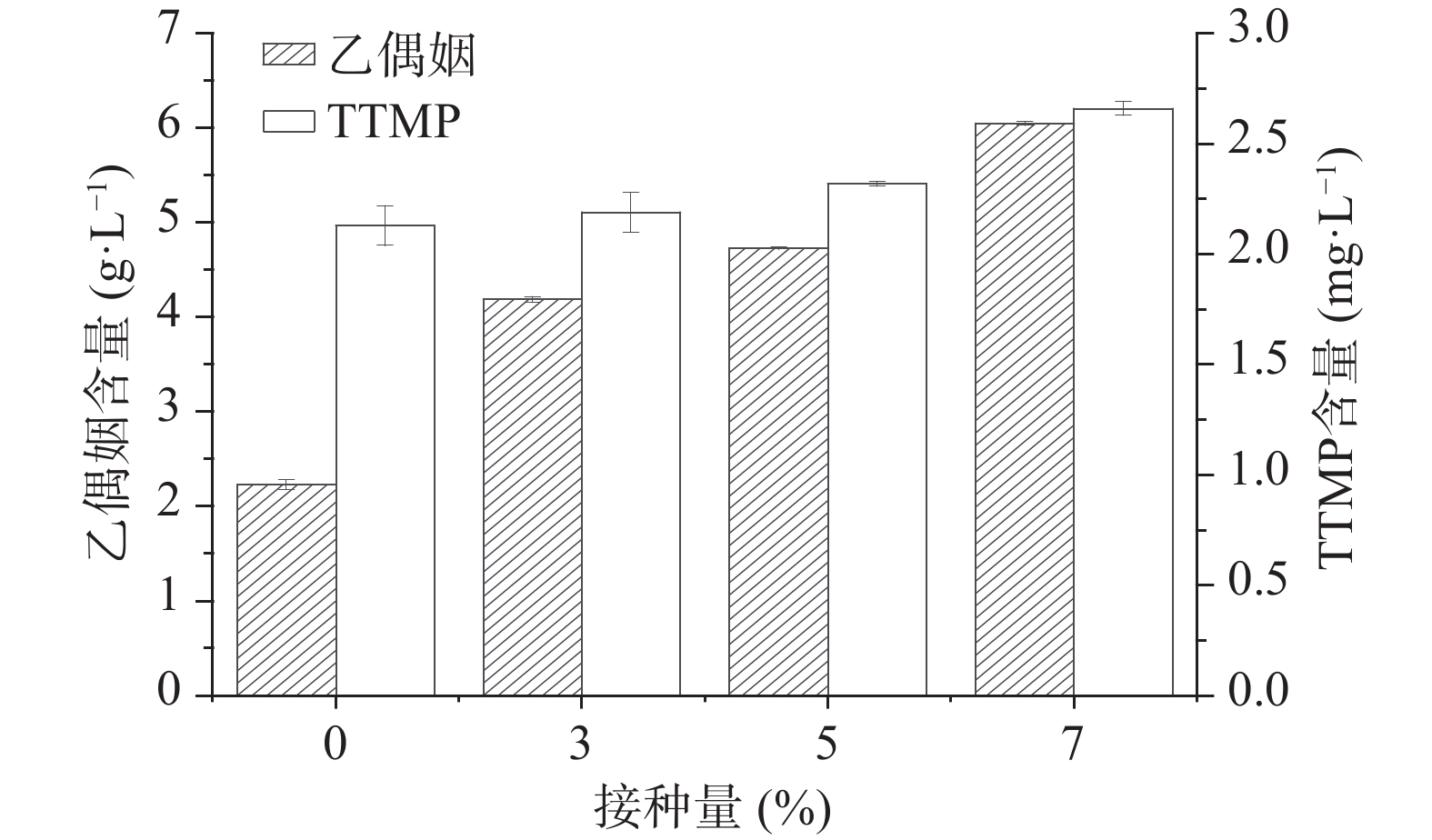
按照方法1.2.5和1.2.6分别检测糟醅中乙偶姻的含量和糟醅馏分中TTMP的含量,结果如图4所示,加菌组较空白组的酒醅中乙偶姻含量随接种量的增加而增加,当接种量为7%时乙偶姻含量为6.05 g/L,较对照组2.23 g/L增加了171.30%,同时TTMP含量也有所增加,当接菌量为7%时含量为2.66 mg/L,比对照组增加了24.88%。据报道乙偶姻和氨合成TTMP的最适pH为6.5[8],本次堆积实验中乙偶姻提高幅度大,而TTMP增加幅度较小,可能是由于白酒糟醅酸度较大,且体系中氨的含量较少,不利于乙偶姻转化合成TTMP。
2.5 地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168对堆积过程菌群结构的影响
利用16S、ITS测序技术对添加不同量功能菌进行堆积发酵实验后的糟醅中微生物进行多样性分析。对测序结果进行嵌体过滤,得到有效数据,后续所有分析将建立在有效数据的基础上进行。
2.5.1 堆积过程中细菌群落结构多样性分析
2.5.1.1 细菌群落测序数据统计
细菌测序结果共得到498423条高质量的序列,平均每个样本具有124605±7059条序。在OTU聚类结果中,对样品进行Alpha多样性分析,可估算环境群落物种的丰度和多样性[9]。分别用Chao指数和Shannon指数表示菌群丰富度指数和菌群多样性指数。Shannon可估计微生物多样性,Shannon值越大,群落多样性越高。Chao指数是用Chao1算法估计群落中含OTU数目的指数,在生态学中常用来估计物种总数,值越大代表物种总数越多。
各堆积样本细菌群落测序数据如表2所示,按照相似性将得到的样品所对应的分类序列条数归类为可操作分类单元(operational taxonomic unit,OTU)。其中,接种量为3%的堆积糟醅中OTU数量最多,共2229个,所有样品共有的细菌OTU数量为170;Chao值代表细菌丰富度指数,Shannon值代表细菌多样性指数,各堆积酒醅样品的Chao1指数在1586.38~3107.84之间,Shannon指数在5.36~6.92之间,接种量为3%的堆积糟醅的Shannon指数最高,值为6.92;所有样本的覆盖率(Coverage)在0.9826~0.9926之间,所以测序结果能够完整反映各接种量堆积糟醅样品细菌菌群组成信息。可见功能菌的添加对堆积过程细菌菌群结构有所影响。
表 2 酒醅细菌菌落测序数据统计分析Table 2. Statistical analysis of bacteria community sequencing data of fermented grains样品 优质序列数 OTU数 Chao指数 Shannon Coverage GTBL168-0% 116186 1734 2467.25 6.28 0.9873 GTBL168-3% 122683 2229 3107.84 6.92 0.9826 GTBL168-5% 126503 1092 1586.38 5.36 0.9926 GTBL168-7% 133051 1166 1934.20 5.68 0.9890 2.5.1.2 不同接种量堆积样品细菌种群结构分析
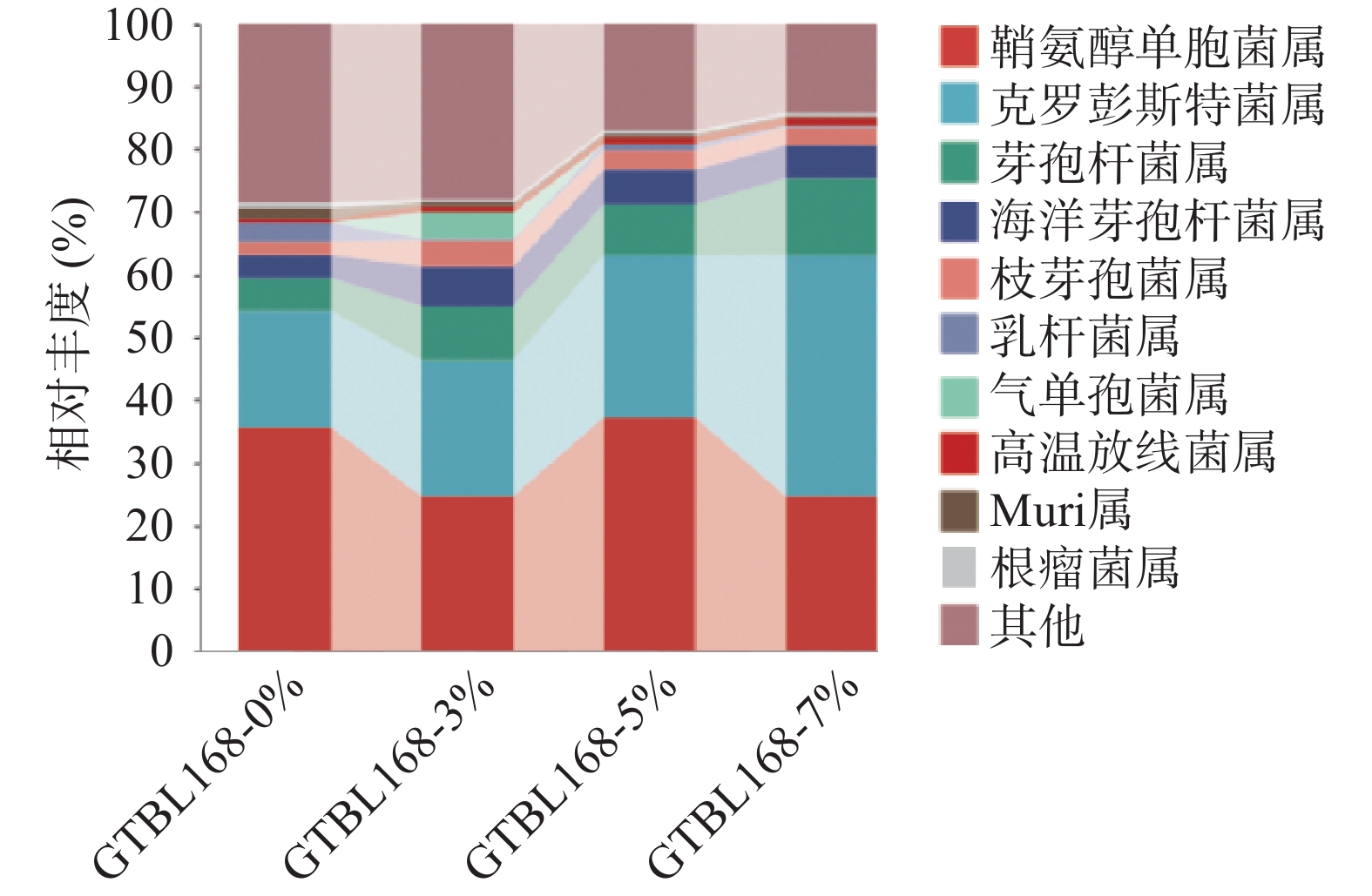
对比不同接种量堆积糟醅中属水平下细菌群落结构组成,四个堆积糟醅中细菌属水平TOP10如图5所示,其中丰度大于1%的有9个属,包括鞘氨醇单胞菌属(Sphingomonas)、克罗彭斯特菌属(Kroppenstedtia)、芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、海洋芽孢杆菌属(Oceanobacillus)、枝芽孢菌属(Virgibacillus)、乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)、气单孢菌属(Aeromonas)、高温放线菌属(Thermoactinomyces)、Muribaculaceae属。其中,有4个属丰度较高,是堆积过程的绝对优势菌属,分别是鞘氨醇单胞菌属(Sphingomonas)、克罗彭斯特菌属(Kroppenstedtia)、芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)、海洋芽孢杆菌属(Oceanobacillus)。其中鞘氨醇单胞菌属(Sphingomonas)占绝对优势,相对丰度为24.55%~37.12%,且丰度随着功能菌接种量的变化而变化。克罗彭斯特菌属(Kroppenstedtia)相对丰度为18.58%~38.58%,丰度随着功能菌接种量的增加而增加,丰度从最初的18.58%增加至38.58%。芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)相对丰度随着功能菌接种量的增加而增加,从最初的4.99%增加至12.21%。海洋芽孢杆菌属(Oceanobacillus)随接种量的增加先增加后减少,接种量为3%时丰度最大,为6.44%。
![]() 图 5 属水平下细菌群落结构组成分析注:其他为相对丰度<1%的菌门以及未得到分类学注释的OTU之和;图6同。Figure 5. Distribution of bacterial community structure at genus level
图 5 属水平下细菌群落结构组成分析注:其他为相对丰度<1%的菌门以及未得到分类学注释的OTU之和;图6同。Figure 5. Distribution of bacterial community structure at genus level鞘氨醇单胞菌属(Sphingomonas)广泛存在于堆积酒醅中,具有较强的代谢能力,可将糖类物质转变成酸。可以推测该菌属可能是导致堆积糟醅酸含量较高的重要原因。克罗彭斯特菌属(Kroppenstedtia),是高温大曲中细菌厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)的第2优势菌属,且是一种嗜热菌属[10]。王欢等[11]也发现其为酱香白酒机械化酿造的核心细菌属。目前在白酒中的作用尚不明确。在洋河大曲评定高通量测序中,为优等曲的优势菌属,是有益菌[12]。袁再顺[2]发现其与酸性蛋白酶,纤维素酶,糖化酶和液化酶的活力呈显著正相关。芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)是白酒酱香风味物质的主要贡献菌属,是产四甲基吡嗪的主要菌种。枯草芽孢杆菌和地衣芽孢杆菌能够产生典型的酱香风味,气质分析发现这俩株菌代谢产生了5-甲基糠醛、β-苯乙醇、苯乙酸、α-亚麻酸等新的风味成分[13]。一些枯草芽孢杆菌、环状芽抱杆菌等均有较强的蛋白酶和淀粉酶活力,可以降解原料中的大分子物质[14]。其随着接种量的增加丰度不断增加,与在接种量7%时TTMP含量最高相吻合,可见其是堆积糟醅中TTMP的主要功能菌。海洋芽孢杆菌属(Oceanobacillus),主要分布于深海环境、发酵食品与发酵设备[15]。在酱香型白酒高温大曲传统制曲和机械制曲过程中第二次翻曲阶段,该属为主要菌属,但具体功能未见报道[16]。且该属的某些物种可以用于生产工业酶制剂,包括氧化酶、淀粉酶、过氧化氢酶、酯酶和脲酶等[17]。
2.5.2 堆积过程中真菌群落结构多样性分析
2.5.2.1 真菌群落测序数据统计
真菌测序结果共得到514831条高质量的序列,平均每个样本具有128707±16879条序列。分别用Chao指数和Shannon指数表示菌群丰富度指数和菌群多样性指数。各堆积样本真菌群落测序数据如表3所示,按照相似性将得到的样品所对应的分类序列条数归类为可操作分类单元(operational taxonomic unit, OTU)。其中,空白实验的堆积糟醅中OTU数量最多,共104个,所有样品共有的真菌OTU数量为31;Chao值代表真菌丰富度指数,Shannon值代表真菌多样性指数,各堆积酒醅样品的Chao1指数在71.50~118.10之间,Shannon指数在1.95~2.63之间,接种量为7%的堆积糟醅的Shannon指数最高,值为2.63;所有样本的覆盖率(Coverage)在0.999958~0.999984之间,所以测序结果能够完整反映各接种量堆积糟醅样品真菌菌群组成信息。可见功能菌的添加对堆积过程真菌菌群结构有所影响。
表 3 酒醅真菌菌落测序数据统计分析Table 3. Statistical analysis of fungal community sequencing data of fermented grains样品 优质序列数 OTU数 Chao指数 Shannon Coverage GTBL168-0% 110955 104 118.10 2.20 0.999973 GTBL168-3% 125906 56 73.51 2.03 0.999975 GTBL168-5% 151643 56 71.50 1.95 0.999984 GTBL168-7% 126327 70 86.67 2.63 0.999958 2.5.2.2 不同接种量堆积样品真菌种群结构分析
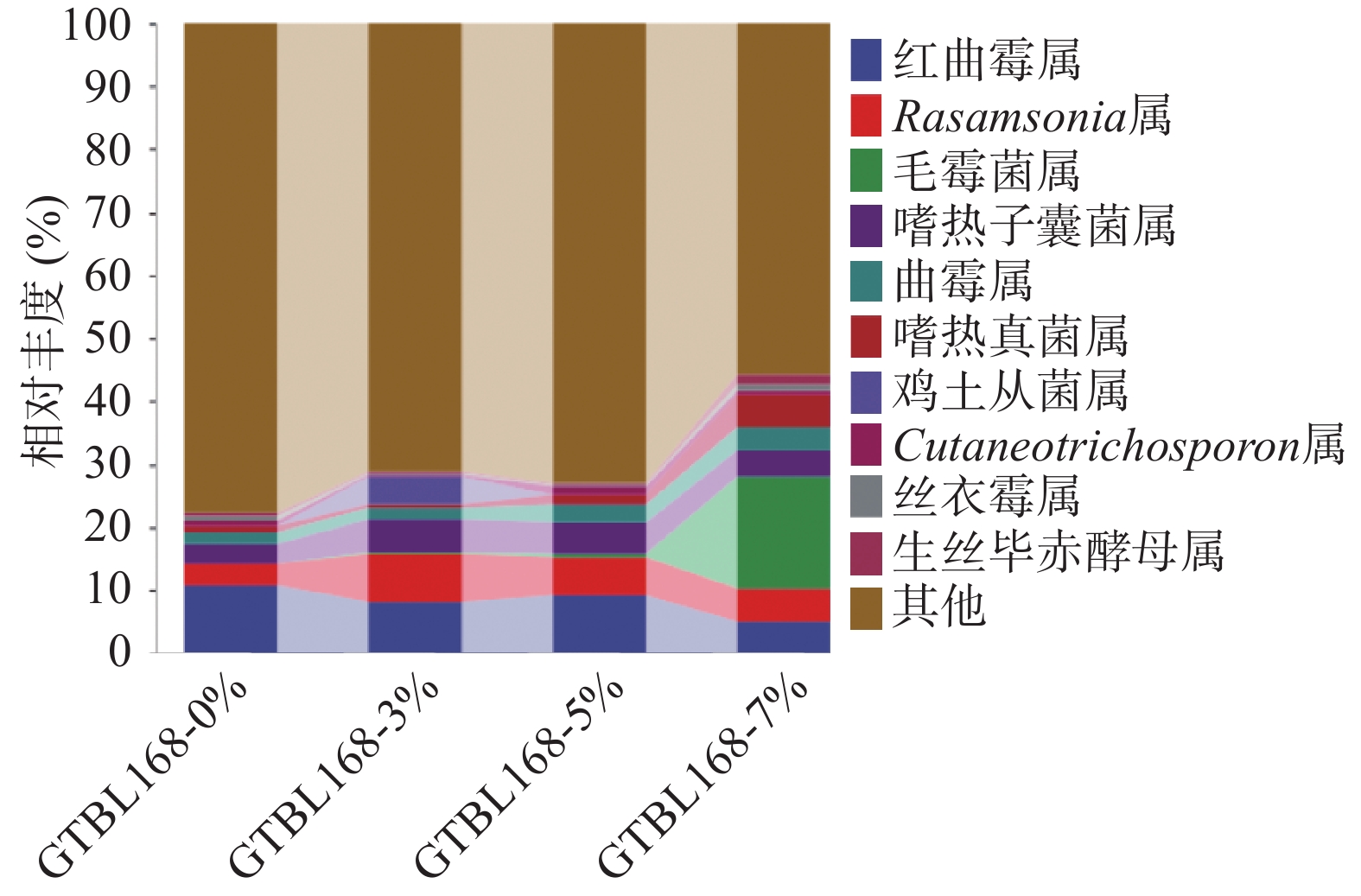
对比不同接种量堆积糟醅中属水平下真菌群落结构组成,将丰度低于1%的菌属合并在“其他”中显示,四个堆积糟醅中真菌属水平TOP10如图6所示,其中丰度大于1%的有9个属,主要包括红曲霉属(Monascus)、Rasamsonia、毛霉属(Mucor)、嗜热子囊菌属(Thermoascus)、曲霉属(Aspergillus)、嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)、鸡土从菌属(Termitomyces)、生丝毕赤酵母属(Hyphopichia)。其中,有5个属丰度较高,是堆积过程的优势菌属,分别是红曲霉属(Monascus)、Rasamsonia、嗜热子囊菌属(Thermoascus)、曲霉属(Aspergillus)、嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)。其中红曲霉属(Monascus)相对丰度为4.91%~10.79%,丰度随着功能菌接种量的变化而变化。Rasamsonia属相对丰度为3.48%~7.57%,在接种量3%时丰度最大。嗜热子囊菌属(Thermoascus)相对空白来说,添加功能菌后的堆积糟醅中其相对丰度均有所增加,且接种量3%时丰度最大。
红曲霉属(Monascus),是白酒酿造过程中的重要功能菌属,有较高的糖化酶、蛋白酶等多种酶活力,同时具有较强的酯化能力,且在白酒酿造中产生丰富的香味物质,从而平衡协调口感,增强酒体的绵柔度[18]。其也是红心曲中主要产红色素的优势菌株。固态发酵时可以产酯类物质,在酱香型白酒中发现有红曲霉的大曲是好曲[19]。红曲霉可以产生淀粉酶、蛋白酶、纤维素酶、脂肪酶和酯酶,且具有生产红曲色素、Lovastatin、麦角固醇和乙醇的能力[20]。芽孢杆菌的添加使红曲霉相对丰度降低,可能是因为其他菌属因氮源增加而丰度增加,但红曲霉生长较慢,从而使相对丰度减少。Rasamsonia属是一种丝状真菌,在堆积糟醅及大曲的微生物多样性实验中均有发现[21-23],目前功能尚不明确。嗜热子囊菌属(Thermoascus),是酱香型白酒大曲中的优势菌群[24],能够产生热稳定的水解酶,在白酒酿造过程中能够降解原料中的淀粉或纤维素大分子物质,是重要的功能菌属[25]。曲霉属(Aspergillus)也是一种丝状真菌,该菌属为酱香型白酒大曲和酒醅中的优势菌属,环境耐受性较强,可以同时分泌产生糖化酶和蛋白酶,是酱香型白酒酿造过程中的重要产酶功能菌[26]。其可以调控大曲和酒醅的糖化力、酯化力、液化力,并且代谢产生有机酸等,催化生成芳香脂类物质,进而改善酒体风味[27]。嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)是酱香型白酒发酵过程的优势菌属,能产生高活力且耐热的纤维素酶、蛋白酶等酶类,有利于微生物的繁殖生长代谢以及产酒生香[16]。
3. 结论与讨论
从大曲中分离出了13株菌,并挑选出蛋白酶透明圈HC值大于等于1.3的5株菌株进行液态发酵培养,结果筛选出了一株产TTMP含量较高的地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168,其产乙偶姻含量为17.51 g/L,产TTMP含量为12.22 mg/L;结合产蛋白酶情况可以发现,高产TTMP的功能菌需同时具有较高的产蛋白酶和乙偶姻能力,该菌才可能代谢生成高含量的TTMP,研究结果为进一步选育高产TTMP菌株提供了理论指导。
将该功能菌株的液态发酵液作为种子液添加到拌有大曲的糟醅中协同堆积培养,通过加菌组和空白组酒醅的对比,该功能芽孢杆菌提高了堆积糟醅中TTMP的含量,当接菌量为7%时增量最大,乙偶姻含量为6.05 g/L,较对照组2.23 g/L增加了171.30%,TTMP含量为2.66 mg/L,比对照组增加了24.88%,可能是因为糟醅酸度较高且氨含量不足,因此乙偶姻转化合成TTMP效率较低,而氨含量的不足可能是因为蛋白酶活力不高导致的。如果对该菌株通过诱变等手段提高其蛋白酶活力,则可能会大辐度提高TTMP的产量。
功能菌的添加对堆积过程糟醅的理化性质影响较明显,氨基氮含量和总酸均有所提高,推测是氨基氮的提高促进了产酸菌的生长;堆积糟醅中除红曲霉属以外的其他优势细菌属和真菌属相对丰度均有所增加,可能是因为芽孢杆菌的添加提高了糟醅中氮源含量从而促进了其他菌属的生长,而红曲霉生长速度较慢导致相对丰度降低;且糟醅中芽孢杆菌属丰度的增加与TTMP含量增加相吻合。地衣芽孢杆菌GTBL-168的添加对白酒整体风味的影响,有待通过进一步生产试验验证。
-
图 5 属水平下细菌群落结构组成分析
注:其他为相对丰度<1%的菌门以及未得到分类学注释的OTU之和;图6同。
Figure 5. Distribution of bacterial community structure at genus level
表 1 透明圈HC值
Table 1 HC value of the transparent circle
菌种编号 菌落直径(mm) 透明圈直径(mm) HC值(D/d) 144 10.00 24.00 2.40 10 12.00 21.00 1.75 168 10.00 14.00 1.40 152 15.00 20.00 1.30 90 20.00 26.00 1.30 163 28.00 36.00 1.29 37 14.00 18.00 1.29 138 14.00 18.00 1.29 24 24.00 30.00 1.25 125 24.00 30.00 1.25 122 34.00 42.00 1.24 208 25.00 30.00 1.20 198 32.00 34.00 1.06 表 2 酒醅细菌菌落测序数据统计分析
Table 2 Statistical analysis of bacteria community sequencing data of fermented grains
样品 优质序列数 OTU数 Chao指数 Shannon Coverage GTBL168-0% 116186 1734 2467.25 6.28 0.9873 GTBL168-3% 122683 2229 3107.84 6.92 0.9826 GTBL168-5% 126503 1092 1586.38 5.36 0.9926 GTBL168-7% 133051 1166 1934.20 5.68 0.9890 表 3 酒醅真菌菌落测序数据统计分析
Table 3 Statistical analysis of fungal community sequencing data of fermented grains
样品 优质序列数 OTU数 Chao指数 Shannon Coverage GTBL168-0% 110955 104 118.10 2.20 0.999973 GTBL168-3% 125906 56 73.51 2.03 0.999975 GTBL168-5% 151643 56 71.50 1.95 0.999984 GTBL168-7% 126327 70 86.67 2.63 0.999958 -
[1] 董雪姣, 姜伊鸣, 于暕辰, 等. 川芎嗪衍生物及其药理活性研究进展[J]. 中南药学,2012,10(4):294−299. [DONG X J, JIANG Y M, YU W C, et al. Research progress of ligustrazine derivatives and their pharmacological activities[J]. Zhongnan Pharmacy,2012,10(4):294−299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2981.2012.04.017 [2] 袁再顺. “破堆移位”对酱香型白酒冬季堆积发酵的影响研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019. YUAN Z S. Study on the influence of “breaking pile displacement” on winter accumulation and fermentation of Maotai-flavor liquor[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019.
[3] 袁建国, 赵纪文, 李峰, 等. 一种细菌微生物提高白酒品质的方法: 中国, 104250594A[P]. 2014-12-31. YUAN J G, ZHAO J W, LI F, et al. A method for bacteria and microorganisms to improve the quality of liquor: China, 104250594A[P]. 2014-12-31.
[4] 张温清. 芝麻香型白酒四甲基吡嗪形成及其高产TTMP酿造工艺研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2020. ZHANG W Q. Study on the formation of sesame-flavored liquor tetramethylpyrazine and its high-yield TTMP brewing process[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020.
[5] 王晓丹, 雷安亮, 王婧, 等. 产四甲基吡嗪地衣芽孢杆菌的应用[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(2):35−38. [WANG X D, LEI A L, WANG J, et al. Application of tetramethylpyrazine-producing Bacillus licheniformis[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(2):35−38. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2017.02.008 [6] 安徽省质量技术监督局. 固态发酵酒醅分析方法: DB 34/T 2264—2014[S]. 北京: 国家标准化管理委员会, 2014. Quality and Technical Supervision Bureau of Anhui Province. Analysis method of solid-state fermented mash: DB 34/T 2264—2014[S]. Beijing: National Standardization Administration, 2014.
[7] 刘唤明, 张芷欣, 洪鹏志, 等. 耐高温蛋白酶产生菌的筛选及酶学特性的初步研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(3):133−136. [LIU H M, ZHANG Z X, HONG P Z, et al. Screening of thermostable protease-producing bacteria and preliminary study on its enzymatic characteristics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(3):133−136. [8] 丁雪梅. 酒曲中高产四甲基吡嗪菌株的选育及发酵优化[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2015. DING X M. Breeding and fermentation optimization of high-yield tetramethylpyrazine strains in distiller’s yeast[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[9] LI B, ZHANG X, GUO F, et al. Characterization of tetracycline resistant bacterial community in saline activated sludge using batch stress incubation with high-throughput sequencing analysis[J]. Water Research,2013,47(13):4207−4216. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.04.021
[10] 姚粟, 葛媛媛, 李辉, 等. 利用非培养技术研究芝麻香型白酒高温大曲的细菌群落多样性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2012,38(6):1−6. [YAO S, GE Y Y, LI H, et al. Study on the bacterial community diversity of sesame-flavor liquor high temperature Daqu using non-cultivation technology[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2012,38(6):1−6. [11] 王欢, 席德州, 黄永光, 等. 酱香型白酒机械化酿造不同轮次堆积发酵细菌菌群结构多样性分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(2):188−195. [WANG H, XI D Z, HUANG Y G, et al. Diversity analysis of bacterial flora structure in different rounds of stacked fermentation for mechanized brewing of Maotai-flavor liquor[J]. Food Science,2020,41(2):188−195. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181218-202 [12] 苏葛, 王晓慧, 董大伟, 等. 高通量测序技术在洋河大曲质量等级判定中的应用[J]. 酿酒科技,2019(1):86−90. [SU G, WANG X H, DONG D W, et al. Application of high-throughput sequencing technology in the quality grade judgment of Yanghe Daqu[J]. Winery Science and Technology,2019(1):86−90. [13] 王霜, 缪礼鸿, 张明春, 等. 浓酱兼香型酒醅中产酱香芽孢杆菌的筛选及发酵风味成分分析[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(10):61−65. [WANG S, MIAO L H, ZHANG M C, et al. Screening of Bacillus soy-scented Bacillus from thick sauce and flavor wine grain and analysis of fermented flavor components[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(10):61−65. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2017.10.014 [14] 庄名扬, 王仲文, 孙达孟, 等. 酱香型习酒功能菌的选育及特征组分的研究[J]. 酿酒科技,1996(3):13. [ZHUANG M Y, WANG Z W, SUN D M, et al. Selection of Maotai-flavored wine-producing functional bacteria and study of its characteristic components[J]. Winemaking Science and Technology,1996(3):13. [15] YUMOTO I. Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi sp. nov., a halotolerant obligate alkaliphile isolated from the skin of a rainbow trout(Oncorhynchus mykiss), and emended description of the genus Oceanobacillus[J]. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology,2005,55(4):1521.
[16] 郭敏. 基于高通量测序对酱香大曲制曲微生态多样性的研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2018. GUO M. Research on the micro-ecological diversity of sauce-flavored Daqu based on high-throughput sequencing[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2018.
[17] TOMINAGA T, AN S Y, OYAIZU H, et al. Oceanobacillus soja sp. nov. isolated from soy sauce production equipment in Japan[J]. Journal of General & Applied Microbiology,2009,55(3):225.
[18] 方跃进. 红曲霉在我国白酒生产中的作用[J]. 中国酿造,2013,32(4):133−135. [FANG Y J. The role of monascus in the production of Chinese liquor[J]. China Brewing,2013,32(4):133−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2013.04.030 [19] 周靖, 吴天祥. 酱香大曲中红曲霉的筛选及其酶活性能研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2013(10):24−26. [ZHOU J, WU T X. Screening of monascus from maotai-flavor daqu and study on its enzyme activity[J]. Wine Making Science and Technology,2013(10):24−26. [20] 刘秀, 郭坤亮, 张艳梅, 等. 茅台酒曲中分离红曲霉酶系及发酵性能研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2006(2):31−33. [LIU X, GUO K L, ZHANG Y M, et al. Separation of monascus enzyme system from Moutai liquor koji and study on its fermentation performance[J]. Liquor Science and Technology,2006(2):31−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9286.2006.02.005 [21] 方程, 杜海, 徐岩. 大曲丝状真菌的物种多样性及其次级代谢产物的合成潜力[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(15):1−8. [FANG C, DU H, XU Y. Species diversity of Daqu filamentous fungi and the synthesis potential of secondary metabolites[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(15):1−8. [22] 孙利林, 李立郎, 胡萍, 等. 酱香型白酒第四轮次酒酿造过程中真菌多样性分析[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(11):24−30. [SUN L L, LI L L, HU P, et al. Analysis of fungal diversity during the fourth round of Maotai-flavor liquor brewing[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(11):24−30. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.11.006 [23] 王彦华. 福矛窖酒酿造环境微生物区系结构分析[J]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2016. WANG Y H. Analysis of the microbial flora structure in the brewing environment of Fumaojiao Liquor[J]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2016.
[24] 沈毅, 程伟, 邓小波, 等. 酱香高温大曲、酒醅和窖泥的真菌多样性分析[J]. 酿酒科技,2019(3):17−23. [SHEN Y, CHENG W, DENG X B, et al. Analysis of fungal diversity in sauce-flavored high-temperature Daqu, glutinous rice and pit mud[J]. Wine Making Science and Technology,2019(3):17−23. [25] JAIN K K, DEY T B, KUMAR S, et al. Production of thermostable hydrolases (cellulases and xylanase) from Thermoascus aurantiacus RCKK: A potential fungus[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering,2015,38(4):787−796. doi: 10.1007/s00449-014-1320-4
[26] 黄永光. 酱香型白酒酿造中Aspergillus hennebergii及其分泌酸性蛋白酶的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2014. HUANG Y G. Study on Aspergillus hennebergii and its secretion of acid protease in the brewing of Maotai-flavor liquor[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2014.
[27] DORN-IN S, HÖLZEL C S, JANKE T, et al. PCR-SSCP-based reconstruction of the original fungal flora of heat-processed meat products[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2013,162(1):71−81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.12.022





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



