Effects of the Extract of Gnaphalium affine on the Oxidation and Structure of Myofibrillar Protein Induced by ·OH
-
摘要: 利用Fenton氧化体系模拟实际肉品氧化环境,研究添加不同浓度水平(0、1.2、6、30 mg/g蛋白)茶多酚(Tea polyphenols,TP)和鼠曲草提取物(Gnaphalium affine extract,GAE)对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白(MPs)氧化和结构变化的影响。结果表明:GAE具有较强的自由基清除能力,与TP均可显著抑制蛋白羰基的形成并促进蛋白巯基损失(P<0.05),尤其在高浓度条件下,TP和GAE分别抑制了36.89%、38.93%的羰基生成,分别促进了28.89%、27.40%的巯基损失。TP和GAE均对肌原纤维蛋白的内源荧光具有较强的猝灭作用,均促进蛋白结构进一步展开,加剧了氧化引起的α-螺旋构象的丧失,暴露更多的活性基团,显著增加了蛋白表面的疏水性和不溶性(P<0.05)。TP和GAE浓度越高,对肌原纤维蛋白的氧化和结构变化的影响越大,但GAE对MPs氧化调控及与蛋白的相互作用程度不及TP。Abstract: The effects of tea polyphenols (TP) and Gnaphalium affine extract (GAE) at different concentrations (0, 1.2, 6, 30 mg/g protein) on the oxidation and structural changes of porcine myofibrillar proteins (MPs) were studied using Fenton oxidation system to simulate the actual meat oxidation environment. The results showed that GAE had a strong ability to scavenging free radicals, which could significantly inhibit the formation of carbonyl group and promote the loss of sulfhydryl group (P<0.05), as did TP. Especially under high concentration, TP and GAE inhibited 36.89% and 38.93% carbonyl formation, and promoted 28.89% and 27.40% sulfhydryl loss, respectively. In addition, TP and GAE both had strong quenching effect on the endogenous fluorescence of MPs, promoted the further expansion of the protein structure, aggravated the loss of α-helical conformation caused by oxidation, exposed more active groups, and significantly increased the hydrophobicity on the protein surface and protein insolubility (P<0.05). The higher the concentration of TP and GAE, the greater the effect on the oxidation and structural changes of MPs, but GAE was not as effective as TP in regulating the oxidation of MPs and its interaction with proteins.
-
肌原纤维蛋白(Myofibrillar proteins, MPs)是肌肉中含量最高的蛋白,占肌肉总蛋白含量的55%~60%,是形成肌纤维的盐溶性结构蛋白群,主要包括肌球蛋白、肌动蛋白、原肌球蛋白、肌钙蛋白等[1],这类蛋白质不仅参与肌肉收缩、影响肉的嫩度,还决定着肉制品热诱导凝胶三维网络的形成,对肉制品的流变学特性、保水性、乳化性、质构、感官等品质起着至关重要的作用[2]。然而肌肉在加工过程中蛋白质极易受到活性氧自由基(ROS)中·OH的攻击而发生氧化变性,最终导致肉品质量变差。因此,肉蛋白的抗氧化是保障肉品质量的关键。然而出于对传统抗氧化剂化学合成毒性的担忧,目前,发掘同样具有抗氧化潜能的天然提取物用于肉蛋白抗氧化,成为肉品行业的研究热点。
天然提取物中含有丰富的植物多酚,具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗癌、防治心血管疾病且无毒无害、来源广泛等特性[3]。鼠曲草(Gnaphalium affine D. Don,清明草)作为我国传统野菜和药食同源植物,其富含黄酮类化合物(如槲皮素、芦丁、木犀草素等)与酚类物质(如没食子酸、绿原酸等),具有优良的抗菌、抗炎和抗氧化等生理功效[4]。现有研究表明,鼠曲草提取物是一种优良的自由基清除剂,具有较强的还原能力与良好的抗氧化效果,可抑制油脂氧化酸败[5]。但鼠曲草提取物对肉蛋白的影响非常复杂,直接将鼠曲草提取物应用于肉蛋白抗氧化和探究其与肉蛋白相互作用机制的研究甚少。
因此,本实验采用Fenton氧化体系模拟实际肌肉加工过程中存在的·OH,选用购买的茶多酚(Tea polyphenols,TP)和自提的鼠曲草提取物(Gnaphalium affine extract,GAE)作为植物提取物代表,用于肌肉蛋白抗氧化,以探讨·OH诱导的氧化对MPs理化特性的影响、TP/GAE与MPs相互作用对MPs理化特性及构象的影响,并阐明相关机理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜猪背最长肌 重庆市南岸区人人乐超市(4 ℃冷藏);茶多酚(纯度97%) 上海阿拉丁试剂公司;干鼠曲草 四川省广安市;2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸水溶液(5%,TNBS) 北京偶合科技有限公司;水溶性维生素E(Trolox)、牛血清蛋白(BSA)、芦丁(标准品)、L-抗坏血酸、甘氨酸、L-亮氨酸、乙二醇二乙醚二胺四乙酸(EGTA)、哌嗪-1,4-二乙磺酸(PIPES) 均为分析纯,上海阿拉丁试剂公司;5,5-二硫代双-(2-硝基苯甲酸)(DTNB)、溴酚蓝、溴化钾、2,4-二硝基苯肼(DNPH)、结晶紫、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、ABTS、过氧化氢(H2O2,30%)、三氯化铁 均为分析纯,上海阿达玛斯试剂有限公司。
UV-1900紫外可见分光光度计 上海翱艺仪器有限公司;V2000可见分光光度计 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;KQ3200DE数控超声波清洗机 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;TDZ5-WS多管架自动平衡离心机、TDZ4-WS低速台式离心机 长沙湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;TGL-20高速冷冻离心机 四川蜀科仪器有限公司;Ultra-Turrax T25高速均质匀浆机 德国IKA-WERKE;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海贤德实验仪器有限公司;日立F-7000荧光分光光度仪 日本日立公司;IRPrestige-21傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 日本岛津公司;DGG-9076A 电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海齐欣科学仪器有限公司;pHS-3C+酸度计 成都世纪方舟科技有限公司;MM12B绞肉机 广东省韶关市大金食品机械厂;LGJ-10冷冻干燥机 北京松源华兴科技发展有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鼠曲草提取物的制备
参照高浩祥等[5]的提取方法。干鼠曲草经60 ℃电热恒温鼓风干燥箱烘干4 h后粉碎,过100目筛后获得干鼠曲草粉。取干鼠曲草粉50 g与1000 mL乙醇溶液(70%,v/v)混合,45 ℃下超声波(300 W)辅助提取80 min,提取液减压抽滤,滤液经60 ℃真空浓缩至100 mL,浓缩液经冷冻干燥48 h得鼠曲草提取物,所得提取物保存于棕色干燥皿中备用。
1.2.2 肌原纤维蛋白的提取
以猪背最长肌为实验原材料,参照PARK等[6]描述的方法提取肌原纤维蛋白。取50 g猪肉解冻(4 ℃,4 h),切条剁碎后置于绞肉机中于低档位运行30s,肉泥使用5倍体积的僵直缓冲液(10 mmol/L磷酸钠,0.1 mol/L NaCl,2 mmol/L MgCl2和1 mmol/L EGTA,pH7.0)稀释后使用高速均质匀浆机分散1 min。匀浆经冷冻离心(10000 r/min,10 min,4 ℃)后倾去上清液,所得沉淀再次加入5倍体积僵直缓冲液,重复上次步骤共三次。此后所得沉淀加入5倍体积0.1 mol/L NaCl溶液,匀浆后过滤除去残余结缔组织,用0.1 mol/L HCl调pH为7.0后离心(10000 r/min,10 min,4 ℃),所得白色膏状沉淀即为肌原纤维蛋白。整个提取过程在0~4 ℃条件下进行,所得肌原纤维蛋白膏置于碎冰中保存并于48 h内使用。以BSA作为标准蛋白,采用双缩脲法测定其蛋白含量[7],测得肌原纤维蛋白膏蛋白含量为40%左右。
1.2.3 TP/GAE添加及氧化处理
参照曹云刚[8]的样品处理方法并加以改进。称取适量MPs蛋白膏,分别加入不同体积的TP/GAE溶液(6 mg/mL,溶解于15 mmol/L PIPES缓冲液(含0.6 mol/L NaCl,pH6.25)),搅拌均匀后加入Fenton氧化体系于4 ℃下氧化12 h。最终蛋白浓度为40 mg/mL,氧化体系浓度为(30 μmol/L FeCl3,100 μmol/L抗坏血酸,3 mmol/L H2O2),TP/GAE含量分别为:0(OX),1.2(TP-L/GAE-L),6(TP-M/GAE-M),30(TP-H/GAE-H)mg/g蛋白质。氧化反应通过添加Trolox(1 mmol/L,终浓度)终止。未添加任何物质及氧化剂但含有Trolox的蛋白溶液作为未氧化对照(Blank)。
1.2.4 鼠曲草提取物的主成分含量及自由基清除能力测定
1.2.4.1 总黄酮、总酚含量的测定
参考陈红梅等[9]的方法测定总黄酮含量。首先制作芦丁标准曲线,准确称取芦丁标品20 mg溶于40%乙醇溶液并定容至50 mL容量瓶中,得到质量浓度为0.4 mg/mL的芦丁标液。分别吸取0、1、2、3、4、5 mL标液于25 mL容量瓶中,加40%乙醇溶液补至12.5 mL摇匀后依次加入5% NaNO2溶液0.5 mL,摇匀静置6 min,加入10%硝酸铝溶液0.5 mL,摇匀静置6 min,加入4% NaOH溶液5 mL,用40%乙醇溶液定容至刻度摇匀静置15 min后于510 nm处测定吸光度。以芦丁标液的质量浓度(mg/mL)为横坐标,吸光度(A)为纵坐标,得到的标准曲线方程:y=11.2125x+0.00767,R2=0.9995。准确称取100 mg鼠曲草提取物溶于40%乙醇溶液并定容至100 mL,吸取1 mL样液于25 mL容量瓶按以上操作测定黄酮含量。鼠曲草提取物中总黄酮含量计算公式如下:
提取物总黄酮含量(%)=m⋅V1⋅V0V2⋅W⋅1000×100 式中:m表示标曲上查得的质量浓度,mg·mL−1;V1表示反应体积,mL;V0表示配制的溶液体积,mL;V2表示取样量,mL;W表示提取物质量,g。
参考SYMONS等[10]的方法测定总酚含量。首先制作没食子酸标准曲线,配制1 mg/mL没食子酸标准液100 mL,分别吸取0、1、2、3、4、5 mL标液于100 mL容量瓶并用水定容至刻度。分别取各浓度梯度标液1 mL于刻度试管内,依次加入福林酚试剂5 mL,摇匀静置5 min,加入20 mg/mL碳酸钠溶液4 mL,加水定容至刻度,摇匀静置30 min后于765 nm处测定吸光度。以没食子酸标液的质量浓度(μg/mL)为横坐标,吸光度(A)为纵坐标,得到的标准曲线方程:y=0.0069x+0.0066,R2=0.9993。准确称取25 mg鼠曲草提取物溶解于水并定容至25 mL,吸取1 mL样液于刻度试管按以上操作测定总酚含量。鼠曲草提取物中总酚含量的计算公式与总黄酮计算公式一致。
1.2.4.2 自由基清除能力测定
a.OH自由基清除能力[11]。首先使用30%乙醇溶液分别配制1.0 mg/mL的GAE和VC储备液,并将储备液稀释为0.05 mg/mL。分别取0.5 mL结晶紫溶液(0.4 mmol/L)、0.7 mL H2O2溶液(5.0 mmol/L)和0.7 mL FeSO4溶液(10.0 mmol/L)于一系列10 mL比色管中,各管用磷酸氢二钠-柠檬酸缓冲液(pH4.0)定容至10 mL,摇匀放置30 min后于580 nm处测吸光度Ab,同时测定不加H2O2吸光度A0。再按上述步骤在加H2O2之前分别加入不同量稀释储备液,测得吸光度As。以样品浓度(mg/mL)为横坐标,清除率(%)为纵坐标拟合曲线,计算半抑制浓度(IC50)。
OH自由基清除率(%)=As−AbA0−Ab×100 b. DPPH自由基清除能力[11]。同时取不同浓度梯度的GAE(0.063、0.125、0.250、0.500、1.000 mg/mL)和VC(0.016、0.031、0.047、0.063、0.125 mg/mL)样液0.5 mL于10 mL比色管中,加入4.5 mL DPPH溶液(0.04 mg/mL),摇匀放置30 min后测定517 nm下的吸光度A0。以30%乙醇溶液作为对照,其他操作同样品组,测其吸光度值A。以样品浓度(mg/mL)为横坐标,清除率(%)为纵坐标拟合曲线,计算半抑制浓度(IC50)。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A−A0A×100 c. ABTS自由基清除能力[8]。准确称取0.0960 g ABTS和0.0116 g过硫酸钾,无水乙醇溶解并定容于25 mL棕色容量瓶中,摇匀室温避光反应12 h,形成ABTS+·储备液。使用前再次使用无水乙醇稀释,使其在734 nm处吸光度为0.800左右,为ABTS+·工作液。样品的测定:同时取不同浓度梯度GAE(0.016、0.020、0.031、0.063、0.125 mg/mL)和VC(0.004、0.008、0.012、0.016、0.020 mg/mL)样液1.0 mL于10 mL比色管中,加入4 mL ABTS+·工作液,混匀避光6 min后于734 nm处测吸光度(A0),以无水乙醇溶液作为对照,其他操作同样品组,测其吸光度值A。以样品浓度(mg/mL)为横坐标,清除率(%)为纵坐标拟合曲线,计算半抑制浓度(IC50)。此处ABTS自由基的清除率计算公式同DPPH自由基。
1.2.5 羰基含量测定
MP的羰基含量采用2,4-二硝基苯肼(DNPH)法进行测定。参照段丽菊等[12]的方法,并略作修改。取摇匀后的样液2 mL置于20 mL离心管,加入4 mL 10 mmol/L DNPH(用2 mol/L HCl溶解), 漩涡混匀,37 ℃避光反应1 h,每隔10 min漩涡1次,此后加入5 mL 20% TCA溶液充分漩涡以沉淀蛋白并终止反应,离心(4000 r/min,10 min)。倾去上清液,所得沉淀用10 mL洗色液(乙醇/乙酸乙酯,1:1,v/v)充分洗涤并离心(4000 r/min,10 min),重复三次,以除去未反应的DNPH。三次洗涤后挥干有机溶剂,加入10 mL 6mol/L盐酸胍溶液(溶解于20 mmol/L NaH2PO4,pH2.3),37 ℃温育15 min,离心(4000 r/min,10 min)。上清液于370 nm处测定羰基含量,使用6 mol/L盐酸胍调零。样品空白中加入4 mL 2 mol/L HCl,其余步骤同上。羰基浓度用摩尔消光系数22.0 mmol/(L·cm)来计算。羰基含量用每毫克蛋白中含有多少nmol的羰基来表示。
羰基含量(nmol⋅mg−1蛋白)=ΔAε⋅d⋅CV反总V样×103 式中:∆A表示反应管吸光度减去对照管吸光度;ε表示摩尔消光系数,22.0 mmol/(L·cm);d表示比色光径,cm;C表示蛋白质量浓度,mg·mL−1;V反总表示盐酸胍体积,mL;V样表示样液体积,mL。
1.2.6 总巯基含量测定
MP的总巯基含量参照GUO等[13]的测定方法,使用DTNB试剂进行测定。使用Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液(10.4 g/L Tris,6.9 g/L甘氨酸,1.2 g/L EDTA,pH8.0)配制1% NaCl溶液将40 mg/mL的肌原纤维蛋白分散液稀释为5 mg/mL。准确吸取蛋白稀释液0.5 mL,先后加入使用Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液配制的1.5% SDS溶液5 mL及0.5 mL Ellman’s试剂(使用Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液配制的4 mg/mL DTNB溶液),室温避光反应15 min后于412 nm波长处测其吸光度。以Tris-甘氨酸缓冲液代替蛋白液作为试剂空白。
总巯基(μ mol⋅g−1蛋白)=73.53⋅A412⋅DC 式中:A412表示吸光度;D表示稀释倍数;C表示样品浓度,mg·mL−1。
1.2.7 自由氨基含量测定
MP中的自由氨基含量按照褚千千等[14]的描述进行测定。准确吸取200 µL稀释后的蛋白样品(4 mg/mL)置于玻璃试管中,加入2 mL 1% SDS溶液(溶于0.2 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液,pH8.2)和1 mL 0.01% TNBS,振荡混匀后于50 ℃水浴锅中避光反应30 min,再加入2 mL 0.1 mol/L Na2SO3终止反应,15 min冷却至室温后,测定420 nm 处吸光度值。相同操作下用蒸馏水代替TNBS反应液作为样品空白。同时分别配制0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mmol/L的L-亮氨酸溶液,并分别按以上测定方法测定各浓度梯度L-亮氨酸溶液的吸光度,以L-亮氨酸浓度(mmol/L)为横坐标,吸光度(A)为纵坐标,得到标准曲线方程:y=0.5091x+0.0816,R2=0.9995。样品自由氨基含量依据所绘标准曲线来确定,计算公式如下:
自由氨基含量(nmol⋅mg−1蛋白)=Cc×103 式中:C表示样品吸光度对应标曲查得的浓度,mmol/L;c表示样品蛋白质量浓度,mg·mL−1。
1.2.8 肌原纤维蛋白结构分析
1.2.8.1 二级结构测定
采用傅立叶变换红外光谱仪分析MPs的二级结构,参考ZHANG等[15]的方法,准确称量冻干样品粉末2 mg,溴化钾200 mg,混合移至玛瑙研钵研磨至无反光点,使用压片机压制成透明薄片,在红外光谱仪上扫描,扫描范围为400~4000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数为32。使用PeakFit4.12软件提取蛋白质酰胺Ι带1700~1600 cm−1波段图谱,对其进行基线校正、傅里叶去卷积和二阶导数拟合处理,进而根据各指认峰及面积分析蛋白质二级结构变化。
1.2.8.2 内源性色氨酸荧光光谱分析
参考CAO等[16]的测定方法。用15 mmol/L PIPES 缓冲液(含0.6 mol/L NaCl,pH6.25)将样品稀释为蛋白浓度0.4 mg/mL,吸取3 mL置于光程为1 cm的石英比色皿中,经283 nm波长激发,记录下300~450 nm的发射光谱,激发和发射狭缝均为10 nm,电压设为400 V,扫描速度为240 nm/min。相同条件下记录溶剂发射光谱,并从样品发射光谱中扣除以排除干扰。
1.2.8.3 表面疏水性测定
参考熊杰等[17]文中所述的方法并加以改进。用20 mmol/L的磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH6.0)将样品稀释为蛋白浓度为5 mg/mL的溶液。吸取5 mL于10 mL的塑料离心管中,加入50 μL 1 mg/mL BPB溶液涡旋混匀,离心(4000 r/min,10 min)。转移上清液于另一套干净的离心管,再次离心后于595 nm处测定吸光度值(A)。作为对照(A0),以磷酸盐缓冲液取代样品溶液,其他操作相同。以蛋白绑定结合的BPB含量作为疏水性指标:
BPB结合量(μg)=50μ g×A0−AA0 1.2.9 溶解度测定
参照周扬等[18]的方法,并略作修改。将40 mg/mL的MPs蛋白液稀释10倍后经冷冻离心(4 ℃,10000 r/min,15 min),测上清液的蛋白质量浓度,上清液和原液中蛋白质量浓度均采用双缩脲试剂法。蛋白溶解度计算公式如下:
溶解度(%)=上清液蛋白质量浓度原蛋白液蛋白质量浓度×100 1.3 数据处理
每组数据设计三次重复,利用软件Origin8.0整理数据并作图分析,所有数据的显著性差异由软件SPSS 19.0进行ANOVA分析所得,差异显著水平P为0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 鼠曲草提取物的主成分含量及其清除自由基的能力
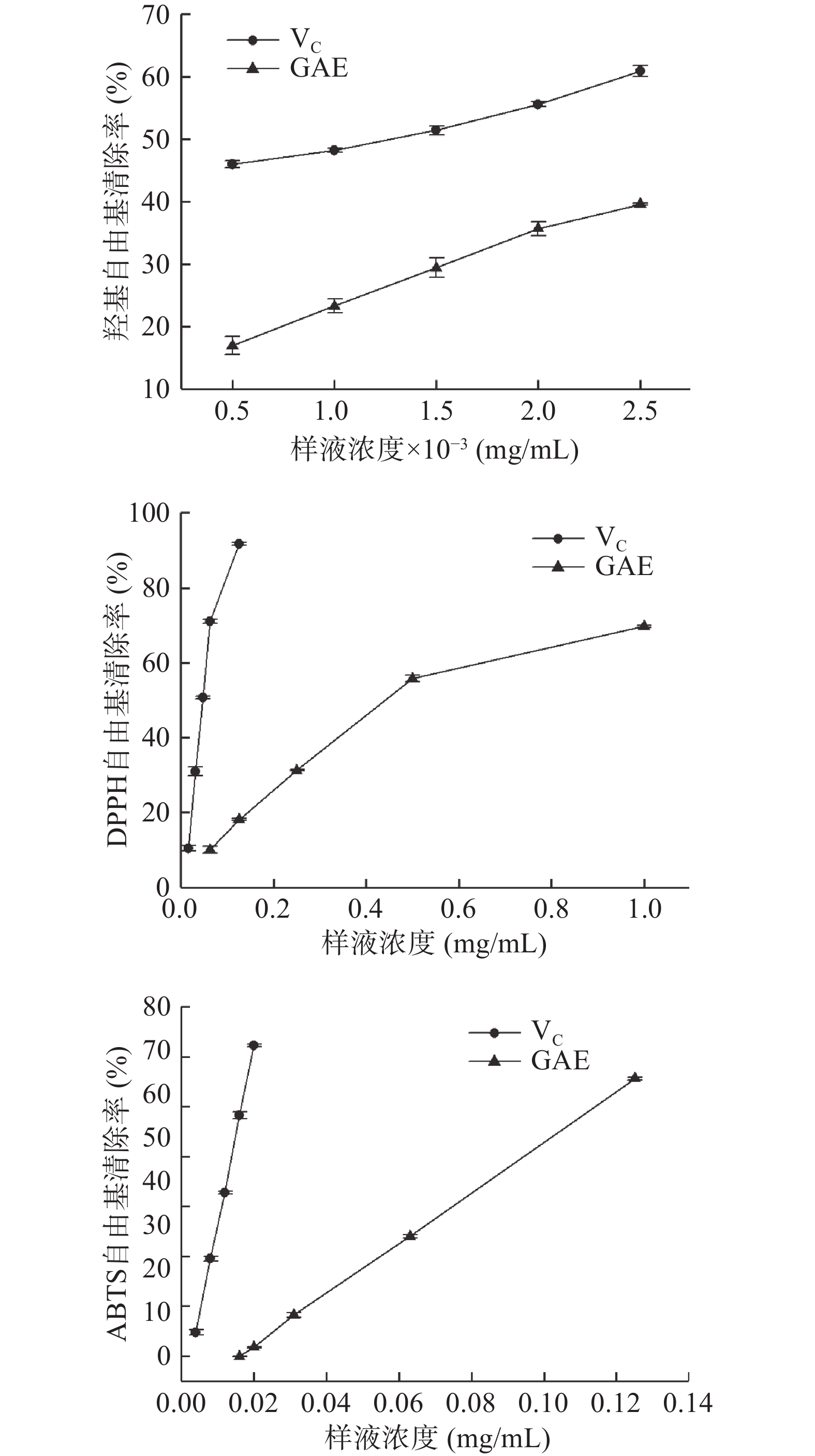
蛋白质氧化机制与脂肪氧化机制类似,都是自由基链式反应,尤其是活性氧所携带的·OH氧化能力最强,最易引发蛋白氧化[19]。因此测定GAE中总黄酮与总酚含量以及清除自由基的能力可初步了解其抗氧化性能。经测定GAE中总黄酮含量为37.09%,总酚含量为67.50%,说明GAE富含黄酮及酚类物质,具有潜在的抗氧化能力。就清除自由基而言,半抑制浓度越低,表明清除半数自由基所需的量越少,清除效果越佳。如表1所示,GAE清除三种自由基中·OH所需的半抑制浓度最低,其次是ABTS自由基和DPPH自由基。与VC的抑制效果相比,GAE对OH、DPPH、ABTS三种自由基的抑制效果分别约为VC的1/3、1/10、1/7。由图1也可看出,与VC相比,GAE清除OH自由基的斜率与VC最接近、ABTS自由基次之,DPPH自由基相差最大。由此表明,GAE清除OH和ABTS自由基的能力较强,清除DPPH自由基的能力相对较弱。总的来说,鼠曲草提取物具有一定清除自由基的效果,可干预调控蛋白质的氧化。高浩祥等[5]也曾验证过GAE对自由基的清除效果,并将其应用于油脂抗氧化,能有效改善油脂氧化酸败。
表 1 鼠曲草提取物对自由基的半抑制浓度Table 1. Semi-inhibitory concentration of free radical in the extract of Gnaphalium affine成分 IC50(μg/mL) OH自由基清除率 DPPH自由基清除率 ABTS自由基清除率 VC 1.29±0.13b 44.75±1.29b 13.80±0.45b GAE 3.59±0.36a 445.45±3.14a 91.46±1.85a 注:同列不同字母表示不同成分对同一自由基清除率间差异显著,P<0.05。 2.2 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs中羰基含量的影响
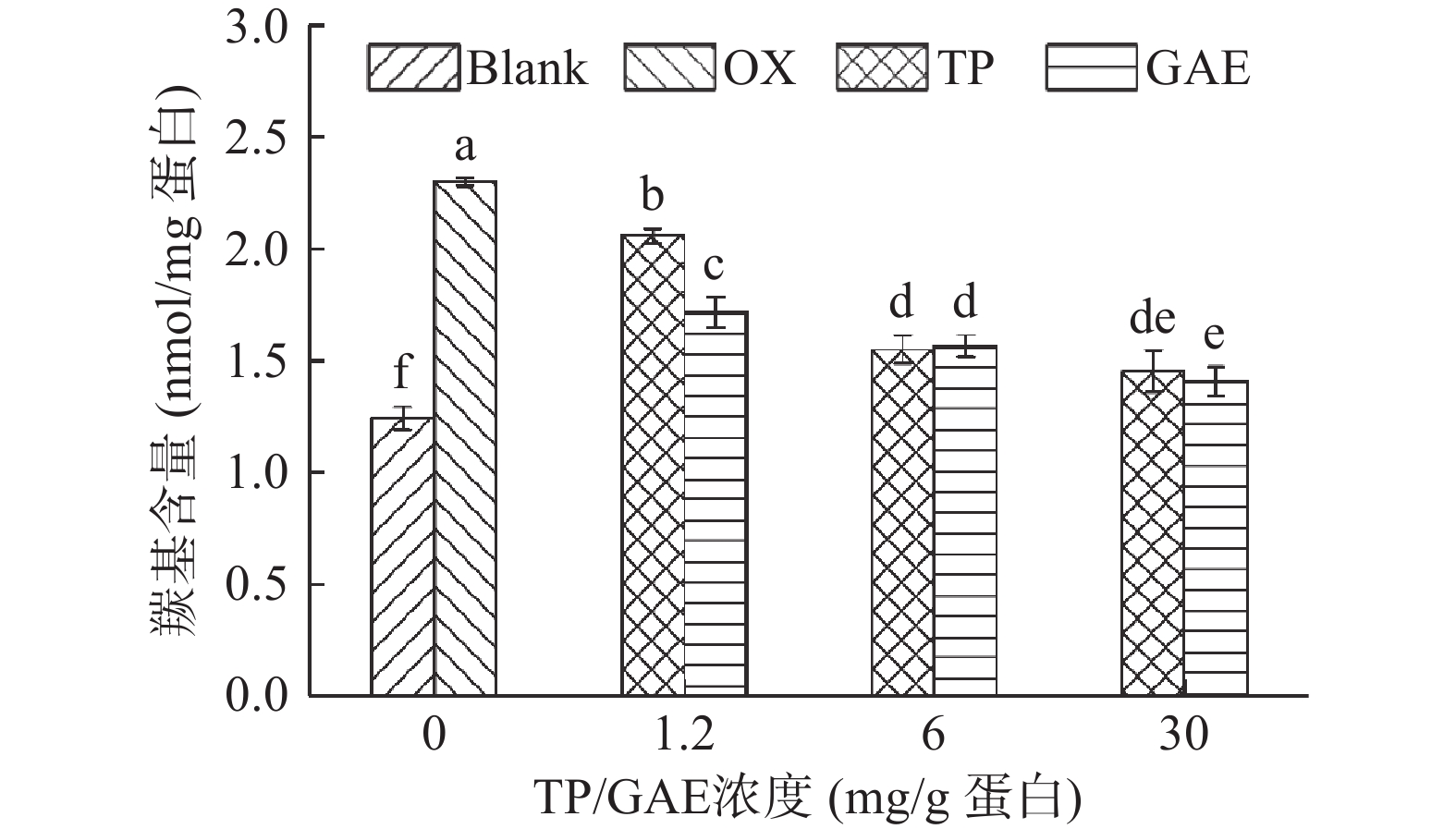
蛋白质中带有NH或NH2的侧链氨基酸官能团遇到ROS极易被氧化生产羰基衍生物,因此羰基含量普遍被认为是判断蛋白质氧化程度的重要指标之一[19]。通常认为羰基含量越高,蛋白氧化越严重。如图2所示,未氧化MPs的羰基含量为1.24 nmol/mg,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,MPs羰基含量显著升高至2.30 nmol/mg(P<0.05)。在氧化对照基础上,TP和GAE的存在均显著降低了MPs羰基含量(P<0.05),尤其在高浓度条件下,TP和GAE对羰基的抑制效果分别高达36.89%、38.93%,由此表明TP和GAE均能明显抑制蛋白氧化,且抑制效果对其浓度具有依赖性,但低浓度条件下TP的抑制效果不及GAE。TP和GAE的添加对MPs羰基含量的影响可能主要归因于黄酮类、酚类物质是良好的氢供体,具有极强清除自由基的能力[20]。此外,富含黄酮及酚类的物质对MPs羰基化的干预效能,前人已有类似报道:绿茶提取物和迷迭香提取物可有效抑制猪肉香肠中蛋白羰基的生成[21];桑葚多酚可有效抑制广东香肠中蛋白羰基生成[22];甘草提取物可有效抑制猪肉[8]或鸡肉[17]贮藏过程中羰基衍生物的产生,因此GAE与众多天然提取物一样具有阻碍蛋白羰基化、防止蛋白氧化的潜能。
2.3 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs中总巯基含量的影响
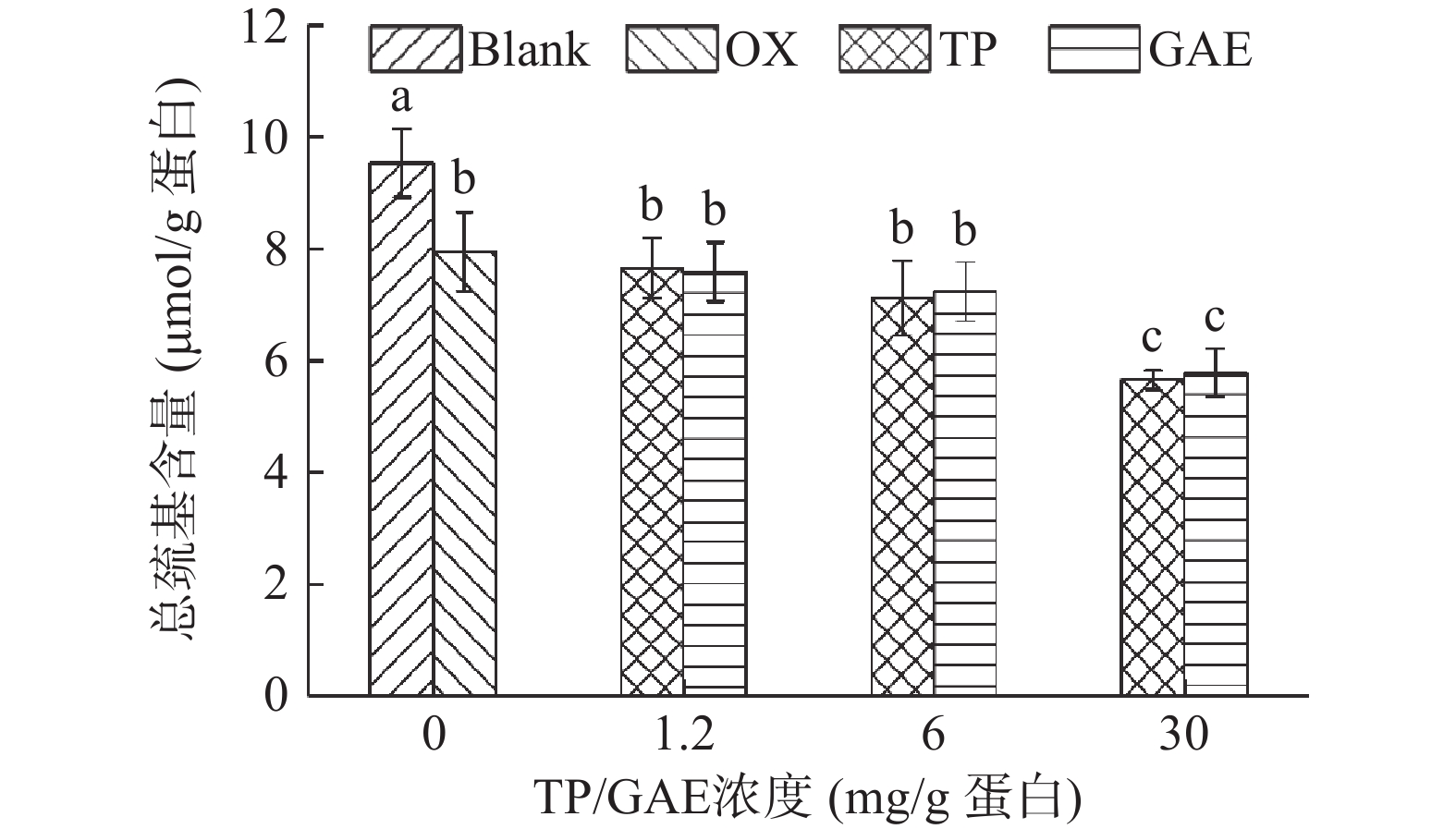
半胱氨酸中的巯基同样容易被ROS氧化转化成二硫键,因此巯基的损失也可作为蛋白氧化的标志。如图3所示,未氧化MPs总巯基含量为9.529 µmol/g,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,其总巯基含量显著降低了16.66%(P<0.05)。这是由于氧化导致蛋白质结构部分展开,半胱氨酸中的活性巯基暴露,受·OH攻击后形成二硫键或进一步被氧化为磺酸类或其他氧化产物,从而导致巯基损失[23]。在1.2 mg/g和6 mg/g浓度下,TP和GAE的添加所导致MPs巯基损失程度与氧化对照无显著性差异(P>0.05)。当TP和GAE的添加量高达30 mg/g时,均显著降低了MPs巯基含量(P<0.05)。高浓度TP/GAE在氧化的基础上进一步促进MPs巯基损失,在OX处理组的基础上TP、GAE分别损失28.89%、27.40%,可能原因是TP和GAE中的酚类物质与蛋白质相互作用形成“巯基-醌”加合物[24]。酚类物质造成氧化后蛋白巯基的进一步损失也存在类似报道,GUO等[13]研究的六种酚类物质(没食子酸、绿原酸、没食子酸丙酯、槲皮素、儿茶素和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯)在氧化基础上均进一步显著降低MPs巯基含量(P<0.05)。
2.4 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs中自由氨基含量的影响
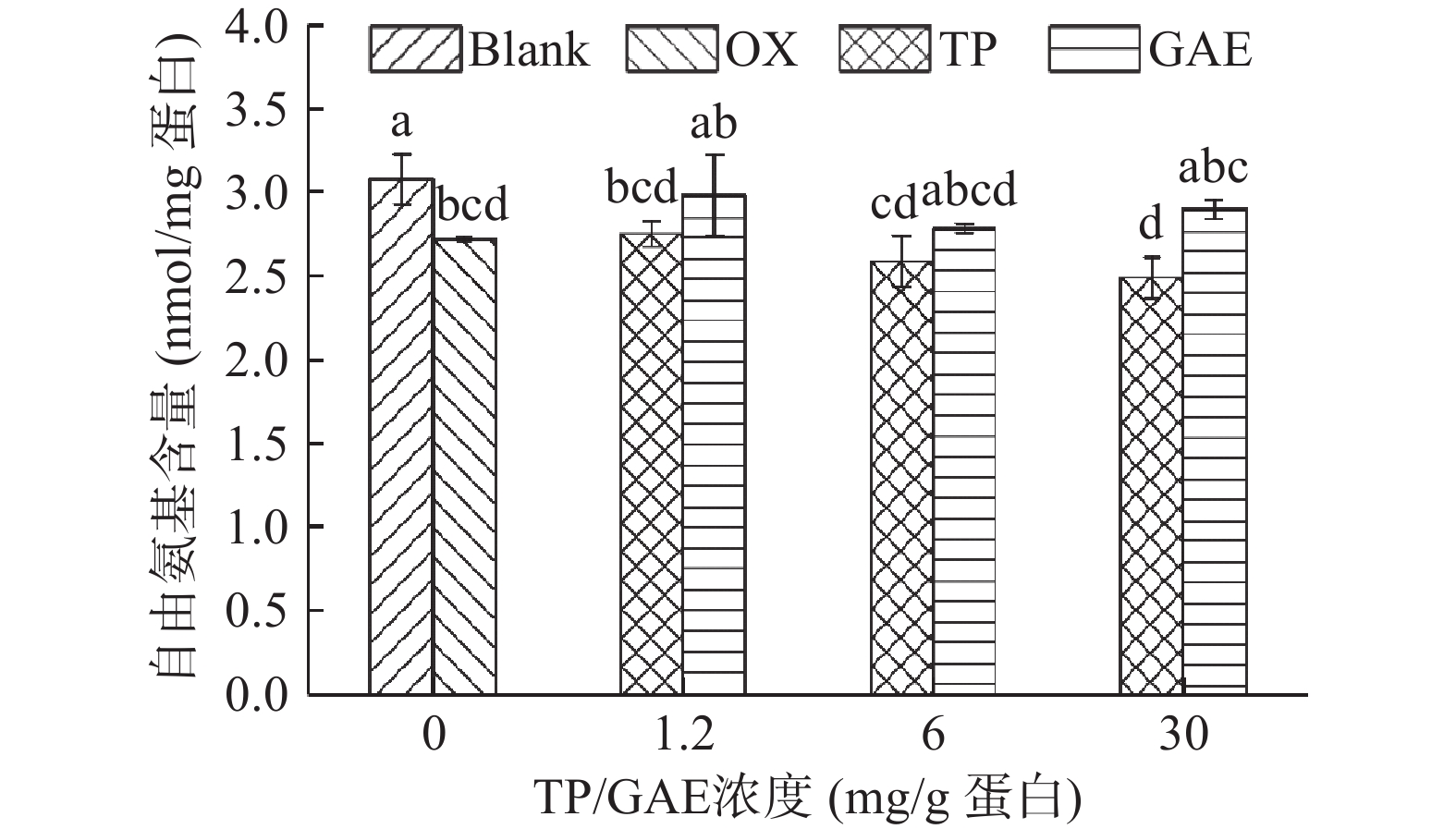
赖氨酸中的
ϵ -NH2基团非常容易受到自由基攻击,通过脱氨基过程转化为羰基,而形成的羰基又可能与NH2共价结合进一步降低自由氨基的含量[25]。如图4所示,未氧化MPs的自由氨基含量为3.08 nmol/mg,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,其自由氨基含量显著降低了11.69%(P<0.05)。GAE的添加对MPs自由氨基的影响较小,与未氧化MPs氨基含量相当。TP的添加并不能有效阻止自由氨基的损失,其损失程度接近氧化空白组,相反高浓度TP的存在进一步加剧了自由氨基的损失,在氧化对照基础下降低了8.42%。可能原因是测定自由氨基过程中所添加的SDS破坏了非共价相互作用,导致TP的氧化产物醌类或半醌类物质与氨基共价结合生成“氨基-醌”加合物[26]。彭林等[27]的报道表明酚类物质与自由基反应后会转变为半醌自由基结构或醌类物质,易与暴露在氧化环境中的蛋白巯基和氨基发生加成反应,生成“巯基-醌”和“氨基-醌”加合物。2.5 不同浓度TP/GAE对肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响
2.5.1 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs二级结构的影响
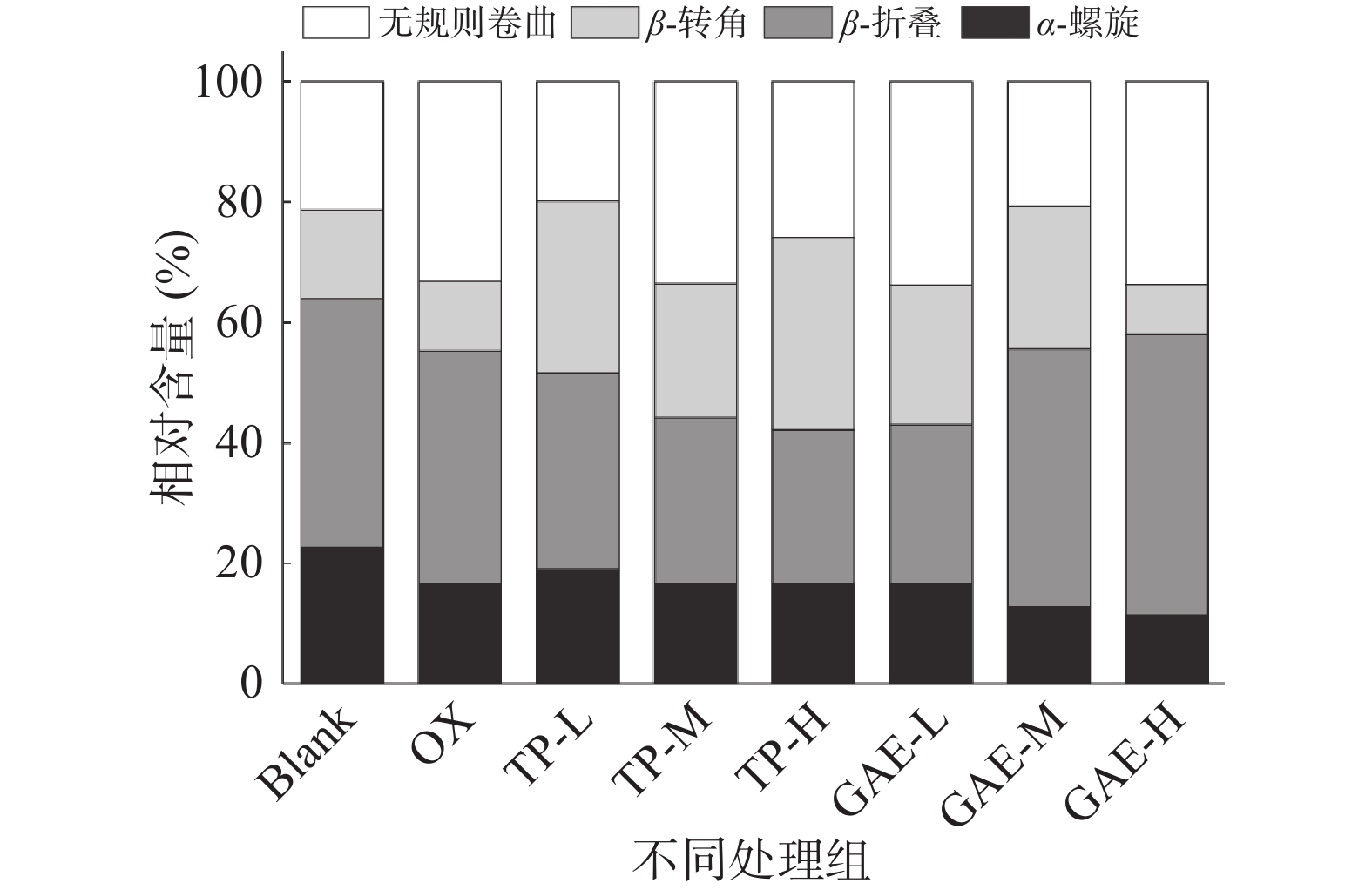
如图5所示,氧化后MPs的α-螺旋结构明显减少,无规则卷曲结构增多。ZHANG等[28]也曾报道蛋白氧化会促使α-螺旋结构向β-结构或无规则卷曲结构转变,导致α-螺旋结构损失。与氧化对照相比,低浓度TP会导致部分β-折叠损失,α-螺旋增加。中、高浓度TP的α-螺旋结构恢复与氧化对照无明显差异,且α-螺旋向β-折叠或无规则卷曲结构转变。α-螺旋解旋可能是因为酚类物质所含酚羟基破坏了可维持α-螺旋结构稳定的羰基氧(C=O)和氨基氢(NH)之间形成的氢键。与氧化对照相比,低浓度GAE对α-螺旋结构无显著影响;中浓度GAE进一步促进α-螺旋转变为β-折叠且α-螺旋解旋率为31.78%,β-折叠增加了20.65%。高浓度GAE促使β-转角损失,转变为无规则卷曲结构。这与JIA等[29]发现绿原酸、阿魏酸、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯三种酚类物质与β-乳球蛋白结合均会诱导α-螺旋结构向β-结构转变和TANG等[30]发现MP的α-螺旋解旋对迷迭香酸具有浓度依赖性,浓度越高,α-螺旋结构越少的结论大体一致。α-螺旋结构解旋和β-结构损失表明TP/GAE会与蛋白质相互作用,会促使部分蛋白质二级结构无序与松散,有利于促进蛋白质交联。
2.5.2 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs内源性色氨酸荧光的影响
蛋白质所含色氨酸与酪氨酸残基是蛋白质内源荧光的主要来源[31]。一般来说,当蛋白质处于折叠状态时,色氨酸及酪氨酸残基被包埋在蛋白内核,蛋白质荧光强度较高;而当蛋白质结构展开时,色氨酸及酪氨酸残基暴露在蛋白质表面被溶剂的极性环境屏蔽了部分荧光,则会导致色氨酸荧光猝灭。因此,蛋白质的三级结构的变化常用内源性色氨酸荧光强度进行表征分析[8]。如图6所示,与未氧化的MPs相比,氧化12 h后MPs的荧光强度降低且出现不太明显的红移现象,最大荧光发射值
λm 从336 nm红移到337 nm。TP和GAE的添加均进一步导致MPs荧光强度的降低且出现蓝移现象。与OX相比,TP的λm 从337 nm蓝移到334~336 nm,GAE的λm 从337 nm蓝移到334~335 nm。TP和GAE两种物质的加入引起了MPs的λm 蓝移,表明Trap的微环境变得更加疏水。此处与邵晓等[32]所研究槲皮素和芦丁对MPs的影响结果一致。在氧化对照基础上,色氨酸荧光强度随着TP和GAE两种物质浓度的升高而急剧降低。可能原因是氧化后蛋白质三级结构展开,TP和GAE与色氨酸及酪氨酸残基结合部分屏蔽了荧光发射,或是TP和GAE中含有水溶性酚类,提高了色氨酸微环境极性[33]。2.5.3 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs表面疏水性的影响
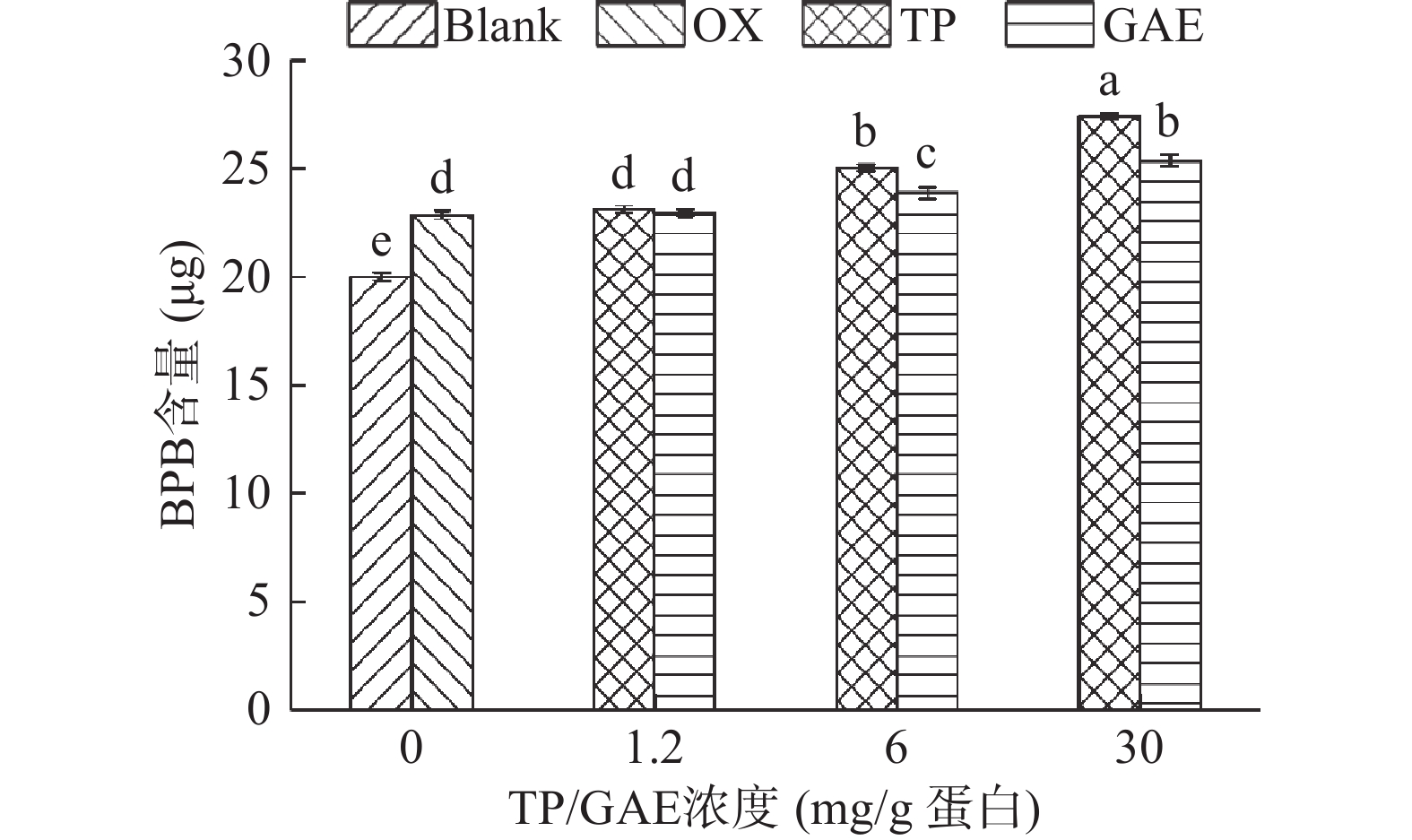
表面疏水性反映的是蛋白质表面的疏水性氨基酸残基的数量,蛋白质去折叠暴露在表面的疏水性氨基酸越多,表明疏水性越大[34]。通常BPB用于结合蛋白质分子表面的疏水性结合位点,因此蛋白质表面疏水性常用表征方法是蛋白质与BPB的结合量[35]。如图7所示,未氧化MPs的BPB结合量为19.99 µg,氧化后其显著增加了14.27%(P<0.05)。这是因为蛋白质暴露于氧化环境中导致部分蛋白结构展开,暴露在蛋白质表面的疏水性残基与BPB结合使得蛋白质表面疏水性增强[23]。TP和GAE的添加均引起了蛋白质结构的展开,浓度越高,MP的表面疏水性越大,尤其是浓度为30 mg/g时,与氧化对照相比,两种添加物处理组的BPB结合量分别显著上升了20.01%、10.97%(P<0.05)。结合色氨酸荧光分析结果,进一步表明TP和GAE的添加均会促进蛋白结构的进一步展开,暴露更多的疏水性残基,从而有利于多酚与蛋白质发生疏水相互作用。
2.6 不同浓度TP/GAE对MPs溶解度的影响
蛋白质溶解度可从侧面反映其表面疏水情况,通常表面疏水性越大,溶解度便越小[8]。如图8所示,溶解度的变化趋势正好与表面疏水性相反,与未氧化MPs相比氧化后的MPs溶解度从71.32%显著降低至45.78%(P<0.05)。TP和GAE的存在均进一步促进MPs溶解度降低,TP处理组更为显著(P<0.05)。蛋白质溶解度下降的原因可能是蛋白质分子间的静电斥力减弱或疏水基团相互作用导致蛋白分子部分聚集,从而引起溶解度下降[36]。周扬等[18]研究的酚类物质迷迭香酸的添加同样会导致肌球蛋白表面疏水性升高且溶解度降低。
3. 结论
茶多酚和鼠曲草提取物的添加对MPs的氧化状态及结构变化都产生了介导调控作用。GAE清除自由基和羰基含量测定结果表明,GAE清除·OH的能力最强,与TP一样能有效抵抗·OH引发的MPs的氧化,抗氧化效果显著(P<0.05)。巯基和自由氨基含量的测定结果表明,TP的存在会进一步促进MPs巯基和自由氨基的损失,且高浓度(30 mg/mL)损失更为严重,但GAE的存在仅明显促进MPs巯基损失,对自由氨基的影响较小。傅立叶变换红外光谱、色氨酸荧光、表面疏水性和溶解度表明,TP和GAE的存在促进了MPs结构展开、色氨酸残基暴露,导致α-螺旋含量降低、色氨酸荧光猝灭、表面疏水性增加和溶解度下降。因此,GAE对MPs氧化和结构的介导调控可为植物提取物用于蛋白抗氧化和蛋白结构改性提供理论参考。
-
表 1 鼠曲草提取物对自由基的半抑制浓度
Table 1 Semi-inhibitory concentration of free radical in the extract of Gnaphalium affine
成分 IC50(μg/mL) OH自由基清除率 DPPH自由基清除率 ABTS自由基清除率 VC 1.29±0.13b 44.75±1.29b 13.80±0.45b GAE 3.59±0.36a 445.45±3.14a 91.46±1.85a 注:同列不同字母表示不同成分对同一自由基清除率间差异显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] 常海军, 周文斌. 畜禽肉制品加工工艺与技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2018: 56−59. CHANG Haijun, ZHOU Wenbin. Process and technology of animal and poultry meat products[M]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press, 2018: 56−59.
[2] 夏秀芳, 孔保华, 张宏伟. 肌原纤维蛋白凝胶形成机理及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2009,30(9):264−268. [XIA Xiufang, KONG Baohua, ZHANG Hongwei. Research progress on the formation mechanism and influencing factors of myofibrillar protein gel[J]. Food Science,2009,30(9):264−268. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.09.062 [3] SHAH M A, BOSCO S J, MIR S A. Plant extracts as natural antioxidants in meat and meat products[J]. Meat Science,2014,98(1):21−33. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2014.03.020
[4] 王利民, 何春梅, 刘彩玲, 等. 鼠曲草属植物的活性成分及其功效研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报,2019,31(10):63−69. [WANG Limin, HE Chunmei, LIU Cailing, et al. Progress in the research on the active components and efficacy of the plants of the Gnaphalium L[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2019,31(10):63−69. [5] 高浩祥, 薛凡, 何强, 等. 鼠曲草提取物对食用油脂贮藏过程中氧化酸败的抑制及机理研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(4):148−151, 157. [GAO Haoxiang, XUE Fan, HE Qiang, et al. Inhibition and mechanism of rancidity of edible oil during storage by extracts from Gnaphalium affine[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2017,38(4):148−151, 157. [6] PARK D, XIONG Y L, ALDERTON A L. Concentration effects of hydroxyl radical oxidizing systems on biochemical properties of porcine muscle myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,101(3):1239−1246. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.03.028
[7] 周非白. 氧化修饰对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白结构与功能特性的调控研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016: 35−36. ZHOU Feibai. Regulation of structural and functional properties of porcine myofibrillar protein by oxidative modification[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016: 35−36.
[8] 曹云刚. 植物多酚对肉蛋白氧化稳定性和功能特性的影响机理及应用[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2016: 13−14. CAO Yungang. Effect mechanism and application of plant polyphenols on oxidative stability and functional properties of meat protein[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2016: 13−14.
[9] 陈红梅, 谢翎. 响应面法优化半枝莲黄酮提取工艺及体外抗氧化性分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(2):45−50. [CHEN Hongmei, XIE Ling. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity analysis of flavonoids from Scutellaria chinensis by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2016,37(2):45−50. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201602008 [10] SYMONS L J, BRENNAN C S. The influence of(13) (14)-β-D-clucan-rich fractions from barley on the physicochemical properties and in vitro reducing sugar release of white wheat breads[J]. Journal of Food Science,2004,69(69):C463−C467.
[11] 刘骏. 结晶紫分光光度法测定Fenton反应产生的羟自由基[J]. 武汉工业学院学报,2005(2):53−55. [LIU Jun. Determination of hydroxyl radicals produced by Fenton reaction by crystal violet spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of Wuhan Polytechnic University,2005(2):53−55. [12] 段丽菊, 刘英帅, 朱燕, 等. DNPH比色法: 一种简单的蛋白质羰基含量测定方法[J]. 毒理学杂志,2005(4):320−322. [DUAN Liju, LIU Yingshuai, ZHU Yan, et al. DNPH colorimetry: A simple method for the determination of protein carbonyl content[J]. Journal of Toxicology,2005(4):320−322. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3127.2005.04.027 [13] GUO A, JIANG J, TRUE A D, et al. Myofibrillar protein cross-linking and gelling behavior modified by structurally relevant phenolic compounds[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(4):1308−1317. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04365
[14] 褚千千, 韩秋煜, 陈必文, 等. 一种蛋白质游离氨基含量测定方法的探究—三硝基苯磺酸(TNBS)法[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020:1−8. [CHU Qianqian, HAN Qiuyu, CHEN Biwen, et al. A new method for the determination of protein free amino-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020:1−8. [15] ZHANG R, PANG X, LU J, et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound pretreatment on functional and structural properties of micellar casein concentrates[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2018,47:10−16. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.04.011
[16] CAO Y, AIN, TRUE A D, et al. Effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate incorporation on the physicochemical and oxidative stability of myofibrillar protein−soybean oil emulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,245:439−445. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.111
[17] 熊杰, 伯朝英, 常海军. 甘草提取物对冷藏鸡肉糜脂肪和蛋白质氧化及品质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):75−81, 88. [XIONG Jie, BO Zhaoying, CHANG Haijun. Effects of licorice extract on lipid and protein oxidation and quality characteristics of frozen chicken meat[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(1):75−81, 88. [18] 周扬, 陈雪珂, 戴宏杰, 等. 溶液体系中迷迭香酸与肌球蛋白的相互作用及其对蛋白理化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):14−21. [ZHOU Yang, CHEN Xueke, DAI Hongjie, et al. Interaction between rosmarinic acid and myosin in solution system and its effect on physicochemical properties of the protein[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):14−21. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190523-275 [19] BAO Y, ERTBJERG P. Effects of protein oxidation on the texture and water-holding of meat: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2019,59(22):3564−3578. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1498444
[20] SHAHIDI F, AMBIGAIPALAN P. Phenolics and polyphenolics in foods, beverages and spices: Antioxidant activity and health effects−A review[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2015,18:820−897. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.06.018
[21] JONGBERG S, TORNGREN M A, GUNVIG A, et al. Effect of green tea or rosemary extract on protein oxidation in Bologna type sausages prepared from oxidatively stressed pork[J]. Meat Science,2013,93(3):538−546. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.11.005
[22] XIANG Rong, CHENG Jingrong, ZHU Mingjun, et al. Effect of mulberry (Morus alba) polyphenols as antioxidant on physiochemical properties, oxidation and bio-safety in Cantonese sausages[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,116(C):108504−108504.
[23] 李银. 蛋白氧化对肌肉保水性的影响机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014: 12−13. LI Yin. Study on the influence mechanism of protein oxidation on muscle water retention[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014: 12−13.
[24] TANG C B, ZHANGW G, DAI C, et al. Identification and quantification of adducts between oxidized rosmarinic acid and thiol compounds by UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap and MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(3):902−911. doi: 10.1021/jf5044713
[25] CAO Y, XIONG Y L. Chlorogenic acid-mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,180:235−243. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.036
[26] OZDAL T, CAPANOGLU E, ALTAY F. A review on protein-phenolic interactions and associated changes[J]. Food Research International,2013,51(2):954−970. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.02.009
[27] 彭林, 马良, 戴宏杰, 等. 多酚与肌原纤维蛋白相互作用机制及其对蛋白特性的影响研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(11):239−246. [PENG Lin, MA Liang, DAI Hongjie, et al. Advances in the study of the interaction mechanism between polyphenols and myofibrillar proteins and their effects on protein properties[J]. Food Science,2020,41(11):239−246. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190530-373 [28] ZHANG Z, XIONG Z, LU S, et al. Effects of oxidative modification on the functional, conformational and gelling properties of myofibrillar proteins fromCulter alburnus[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:1442−1452. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.052
[29] JIA J, GAO X, HAO M, et al. Comparison of binding interaction between beta-lactoglobulin and three common polyphenols using multi-spectroscopy and modeling methods[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,228:143−151. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.131
[30] TANG Changbo, ZHANG Wangang, ZOU Yufeng, et al. Influence of RosA-protein adducts formation on myofibrillar protein gelation properties under oxidative stress[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,67:197−205. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.006
[31] 李春翼, 王启明, 唐瑜婉, 等. 热诱导对麦醇溶蛋白/芦丁相互作用及其乳液流变学特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(18):27−34. [LI Chunyi, WANG Qiming, TANG Yuwan, et al. Effect of thermal induction on malt/rutin interaction and rheological properties of emulsions[J]. Food Science,2020,41(18):27−34. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191212-133 [32] 邵晓, 张宁, 孙乐彤, 等. 槲皮素和芦丁对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(2):26−30. [SHAO Xiao, ZHANG Ning, SUN Letong, et al. Effects of quercetin and rutin on the structure of pork myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(2):26−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.02.006 [33] CAO Y, MA W, HUANG J, et al. Effects of sodium pyrophosphate coupled with catechin on the oxidative stability and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,104(C):105722−105722.
[34] 窦川林, 林静, 董唯, 等. 茶多酚处理对泥鳅微冻贮藏过程中肌原纤维蛋白功能性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(23):250−256. [DOU Chuanlin, LIN Jing, DONG Wei, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols on the functional properties of myofibrillar protein during microfrozen storage of loach[J]. Food Science,2018,39(23):250−256. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201823037 [35] CHELH I, GATELLIER P, SANTÉ-LHOUTELLIER V. Technical note: A simplified procedure for myofibril hydrophobicity determination[J]. Meat Science,2006,74(4):681−683. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2006.05.019
[36] 贾娜, 谢振峰, 李儒仁, 等. 迷迭香提取物与NaCl协同改善肌原纤维蛋白凝胶特性[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(3):28−33. [JIA Na, XIE Zhenfeng, LI Ruren, et al. The synergistic effect of rosemary extract and NaCl on the gel properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2018,39(3):28−33. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201803005 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 汤凯,武运,王雪,马文瑞,陈卫林,张珍珍,黄文书,杜木英. 伊犁地区奶疙瘩中乳酸菌的筛选及其特性研究. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 188-195 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 高逸,张健,陈国辉,辛迪,彭芸,戚晨晨,翟磊,姚粟. 乳酸菌CICC 6282的鉴定、生物学特性及其在发酵辣椒中的应用. 中国酿造. 2024(02): 53-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘玲,郭锦宁,李欢欢,黄铠埼,冯昌洋,徐学锋. 豉香型白酒醪液源耐酸乳杆菌La50发酵特性研究. 中国酿造. 2024(06): 74-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 马牧然,刘菲菲,余治权. 低糖乳酸菌耐受性和功能性分析. 食品研究与开发. 2023(07): 14-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张孟雨,李尧,彭嘉屹,陈禹豪,曾凤婷,钟青萍. 高产EPS乳酸片球菌的航天育种及其EPS性能研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(17): 158-167 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 张雪静,牛红红,苗欣宇,华梅,孙慕白,刘文健,王景会. 自然发酵玉米液中乳酸菌的分离、鉴定及益生特性研究. 中国酿造. 2023(08): 129-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张佳萍,夏宁,滕建文,韦保耀,黄丽,张博. 腐乳酸浆水中产β-葡萄糖苷酶乳酸菌的研究. 中国调味品. 2023(10): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王梓桐,刘堉萍,汪超,王健,张温清,商亚芳,魏兆军,马意龙. 乳酸菌与酵母菌联合发酵改善食品品质研究进展. 中国酿造. 2023(10): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张雪梅. 熏马肠中产蛋白酶菌株的筛选及酶学特性测定. 现代食品. 2023(18): 214-217 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李吉琴,展丽梅,自绍平,梅会友,高彦航,徐虎,徐乐,鲍国樱,李杰,曹振辉. 昆明犬源乳酸菌的分离、鉴定与益生特性研究. 动物营养学报. 2023(12): 8133-8147 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)













 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



