Preparation of Acetylated Acid-hydrolysis Modified Starch with High Degree of Substitution and Its Nanoparticles
-
摘要: 为了提高乙酰化淀粉在生物医学和靶向给药系统方面的应用,本文以普通玉米淀粉为原料,依次进行醇介质中的酸解和乙酰化处理,制备得到了高取代度的酸解乙酰化淀粉纳米颗粒,并且通过傅里叶变换红外光谱、X射线衍射、接触角测量、糊化曲线、扫描电子显微镜等表征手段探究了酸解条件对淀粉颗粒理化性质的影响。随后,用反溶剂法制成纳米颗粒,并确定了其粒径范围。结果表明:当酸解所用的乙醇体积浓度为70%,盐酸浓度为12.0 mol/L,温度为65 ℃时,酸解乙酰化淀粉的取代度由0.84提高至1.33,疏水性显著提高(P<0.05),样品颗粒粒径减小;通过反溶剂法制备淀粉颗粒,能够得到粒径在200 nm左右的淀粉纳米颗粒。Abstract: In order to improve the application of acetylated starch in biomedicine and targeted drug delivery system, ordinary corn starch was selected as the material, acid hydrolysis in alcohol medium before the acetylation was introduced in the preparation of the acetylated acid-hydrolysis modified starch with high degree of substitution. The effects of acid-hydrolysis conditions on physicochemical properties of the modified starches were investigated by means of FT-IR, XRD, contact angle measurement, pasting curve and scanning electron microscope. Subsequently, anti-solvent precipitation was introduced in the preparation of the starch nanoparticles, and the size range was determined. Based on the results, under the condition of 70% ethanol (v/v), 12 mol/L hydrochloric acid and 65 ℃, the substitution degree of acetylated starch increased from 0.84 to 1.33, the hydrophobicity significantly (P<0.05) improved and the particle size was reduced. Starch nanoparticles with a particle size of about 200 nm could be obtained through anti-solvent precipitation.
-
近年来,天然聚合物纳米颗粒在生物医学和靶向给药系统方面的应用引起了广泛关注[1]。纳米颗粒是大小为10~1000 nm的固体胶体颗粒[2],比表面积大、流动性好,在精准医疗和靶向释放方面多有报道[3-4]。迄今为止,已研究的纳米载药体系包括纳米颗粒、纳米凝胶、纳米乳液和纳米脂质体等[5-6]。淀粉是一种含量丰富、廉价、无毒、自然可再生的生物聚合物,以淀粉为原料制备的纳米颗粒具有可生物降解、生物相容性好、储存稳定等优点,是良好的靶向制剂的药物载体[7]。然而,天然淀粉易被胃肠道酶降解,且粒径较大,极大限制了其在纳米载药体系方面的应用[6]。Gg等[8]报道称,纳米颗粒的性质受其合成方法及条件的影响,而一个受控单分散的颗粒尺寸对其在生物医学和制药领域的应用是至关重要的,因此要对天然淀粉进行疏水改性,并降低分子粒径,从而改善其应用性能。
乙酰化是常见的淀粉改性方法[9],天然淀粉通过与醋酸酐、醋酸乙烯酯或醋酸反应,发生酯化,从而增加其疏水性[7]。不同取代度的乙酰化淀粉具有不同的理化性质和功能特性[10],高取代度的乙酰化淀粉在丙酮、氯仿等有机溶剂中具有较大的溶解度[1],具有热塑性、高疏水性和生物可降解性,过去常被用作工业涂层材料、热熔粘合剂等[11],近年来,其作为控释载体材料的研究成为了新的热点[12]。有报道称[13],随着取代度升高,淀粉颗粒形貌更接近球形。
酸解是通过降低淀粉链分子量和黏度来改善淀粉功能性的常用方法[14],酸改性淀粉的制备方法包括湿法、生物酶解二次酸化法、非水溶剂法等。其中,湿法酸解方法简单、易控制,常与其他方法复合进行淀粉复合改性[15],邢俊杰[16]通过酸解前处理与湿热复合,制备得到300 nm左右的淀粉纳米晶。目前,酸解预处理制备低取代度乙酰化淀粉已有报道[17-19],但鲜见其在制备高取代度乙酰化淀粉过程的作用研究,该方法或有利于降低空间位阻,提高乙酰化淀粉取代度,影响产品性能。因此,研究酸解工艺条件对酸解乙酰化淀粉结构、性质的影响,对后期制备性能良好的淀粉纳米颗粒具有重要意义。
本文对玉米淀粉进行酸解和乙酰化复合改性处理,探讨了不同酸解条件对酸解乙酰化淀粉理化性质及结构的影响,并采用反溶剂法制备淀粉纳米颗粒,为构建一种可控、有效的靶向给药系统提供新的思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玉米淀粉(水分含量为13.84 g/100 g) 山东诸城兴贸玉米开发有限公司;无水乙醇、盐酸、氢氧化钠、无水碳酸钠、乙酸、乙酸酐、硫酸、丙酮 均为分析纯,国药集团。
SW22恒温水浴锅 德国JULABO公司;SHB-Ⅲ型循环水式多用真空泵 郑州长城科工贸有限公司;UN110型烘箱 美墨尔特(上海)贸易有限公司;RO 5型磁力搅拌器 德国IKA公司;RJ-LD-50G 型低速立式大容量离心机 Eppendorf公司;RVA-rechmaster型快速黏度分析仪 澳大利亚Newport Scientific有限公司;DM-BA4500型光学显微镜 中国Motic公司;Quanta 200扫描电子显微镜 荷兰Fei公司;IS10傅立叶红外光谱仪 美国Nicolet公司;D8 Advance型X-射线衍射仪 德国Bruker公司;OCA15EC型视频光学接触角测量仪 德国德菲仪器股份有限公司;多角度粒度与高灵敏Zeta电位分析仪 美国布鲁克海文仪器公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酸解淀粉的制备
称取75 g干基玉米淀粉分散到一定浓度的乙醇溶液中,配制成25%(w/v)的淀粉乳,再加入3 mL一定浓度的盐酸,置于恒温水浴锅中,在一定温度下反应1 h后,加入一定量 1 mol/L的Na2CO3溶液至pH=7,终止反应,冰浴5 min,抽滤,采用50%(v/v)的乙醇洗涤沉淀3次,40 ℃过夜干燥,粉碎过100目筛,得到酸解淀粉。
1.2.2 不同酸解条件对酸解淀粉性质的影响
1.2.2.1 乙醇浓度对酸解淀粉性质的影响
盐酸浓度为12 mol/L,酸解温度为65 ℃,乙醇浓度为50%、70%、90%,不同乙醇浓度分别命名为A50、A70、A90。
1.2.2.2 盐酸浓度对酸解淀粉性质的影响
酸解温度为65 ℃,乙醇浓度为70%,盐酸浓度为6、9、12 mol/L,不同盐酸浓度分别命名为B6、B9、B12。
1.2.2.3 酸解温度对酸解淀粉性质的影响
乙醇浓度为70%,盐酸浓度为12 mol/L,酸解温度为55、65、75 ℃,不同酸解温度分别命名为C55、C65、C75。
1.2.3 酸解乙酰化淀粉的制备
称取1.2.1中样品10 g,加入30 mL乙酸和20 mL乙酸酐搅拌均匀后转移到水浴锅,缓慢滴加入2 mL浓硫酸作为催化剂。70 ℃下反应60 min,反应结束后,将反应体系倒入冰水中使得淀粉沉出,抽滤,并用去离子水洗涤多次,40 ℃过夜干燥,粉碎过筛得到酸解乙酰化淀粉产品。取1.2.1中酸解淀粉进行乙酰化处理(D),经过预实验得到取代度最高的组别A70B12C65D,以此为基础结合文献[17-19],选择三组常见酸解变量进行探究,得到八组酸解乙酰化淀粉,样品分别命名为A70B12C65D、A50B12C65D、A70B12C65D、A90B12C65D、A70B6C65D、A70B9C65D、A70B12C55D、A70B12C75D。
1.2.4 纳米颗粒的制备
取适量1.2.2中样品,加入丙酮,配制成10 mg/mL的乳液,搅拌60 min,备用。将丙酮溶液逐滴加入到40 mL去离子水中,使纳米颗粒逐渐沉出,室温下不断搅拌直至丙酮完全挥发,取样保存。
1.2.5 傅里叶变换红外(FTIR)分析
采用KBr压片法,将1.2.1与1.2.2中样品与溴化钾以1:60(w/w)的比例研磨均匀,取适量样品压成片后用红外光谱仪进行测试。扫描波数范围为4000~400 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,以空气为背景绘制红外谱图。
1.2.6 乙酰基和取代度测定
参考Whister等[20]的方法,并作适当修改。DS被定义为每个葡萄糖单位拥有一个取代基的平均位点数。准确称取1.2.2中样品1.5 g(精确至0.0001 g)于锥形瓶中,加入50 mL蒸馏水,5 mL乙醇,2~3滴酚酞,用0.05 mol/L NaOH调节至微粉色,再加入25 mL 0.5 mol/L的NaOH,室温下磁力搅拌1 h后,用0.2 mol/L HCl滴定至红色褪去,记录消耗盐酸体积,同时,做试剂空白实验,记录消耗盐酸体积。每组样品制备三组平行,按照下列公式计算样品的取代度:
式中:A表示乙酰基质量分数,%;V0表示空白样消耗盐酸标准溶液的体积,mL;V1表示样品消耗盐酸标准溶液的体积,mL;c表示HCl标准溶液浓度,mol/L;m表示干基样品质量,g;DS表示乙酰基取代度。
1.2.7 X射线衍射(XRD)
参考魏本喜[21]的方法,并作适当修改。将1.2.1与1.2.2中样品压片后放置于X-衍射仪中,设定扫描角度。测试条件为:扫描范围5°~40°,扫描速度0.5°/s,加速电压40 kV,电流20 mA,结果用MDI Jade 6.0积分计算结晶度。
1.2.8 接触角测试
参考何君[22]的方法,并作适当修改。称取1.2.2中淀粉样品0.25 g,放入标准模具,经红外压片机压至约0.7 mm薄片,通过高精度注射器系统滴加一滴2 μL的去离子水,同时通过高速相机以10帧/s的采集速度记录水滴在薄片表明的球形变化趋势,以OCA15EC接触角测量仪测定固定液的接触角。
1.2.9 糊化特性测定
参考陈梦雪等[23]的方法,并作适当修改。称取一定质量样品与25 g去离子水置于RVA专用铝盒中,配制成7%(w/w)浓度的淀粉乳,混匀后采用快速黏度分析仪在标准程序下测定淀粉糊黏度的变化,得到样品糊化曲线。
1.2.10 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)
参考李佳佳等[19]的方法,并作适当修改。将淀粉样品经离子溅射仪喷金固定,于10 kV加速电压下采用扫描电镜观察样品的微观形貌,放大倍数分别为1000和8000。
1.2.11 Zeta电位测定
取1.2.3中样品,用去离子水制备浓度为1.0 mg/mL的溶液,使用Zeta电位分析仪测定25 ℃的Zata电位,水折射率为1.330,黏度为0.8872 mPa·s。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据为3次平行测量的平均值,实验数据取平均值,并以平均值±标准差(
2. 结果与分析
2.1 特征基团分析
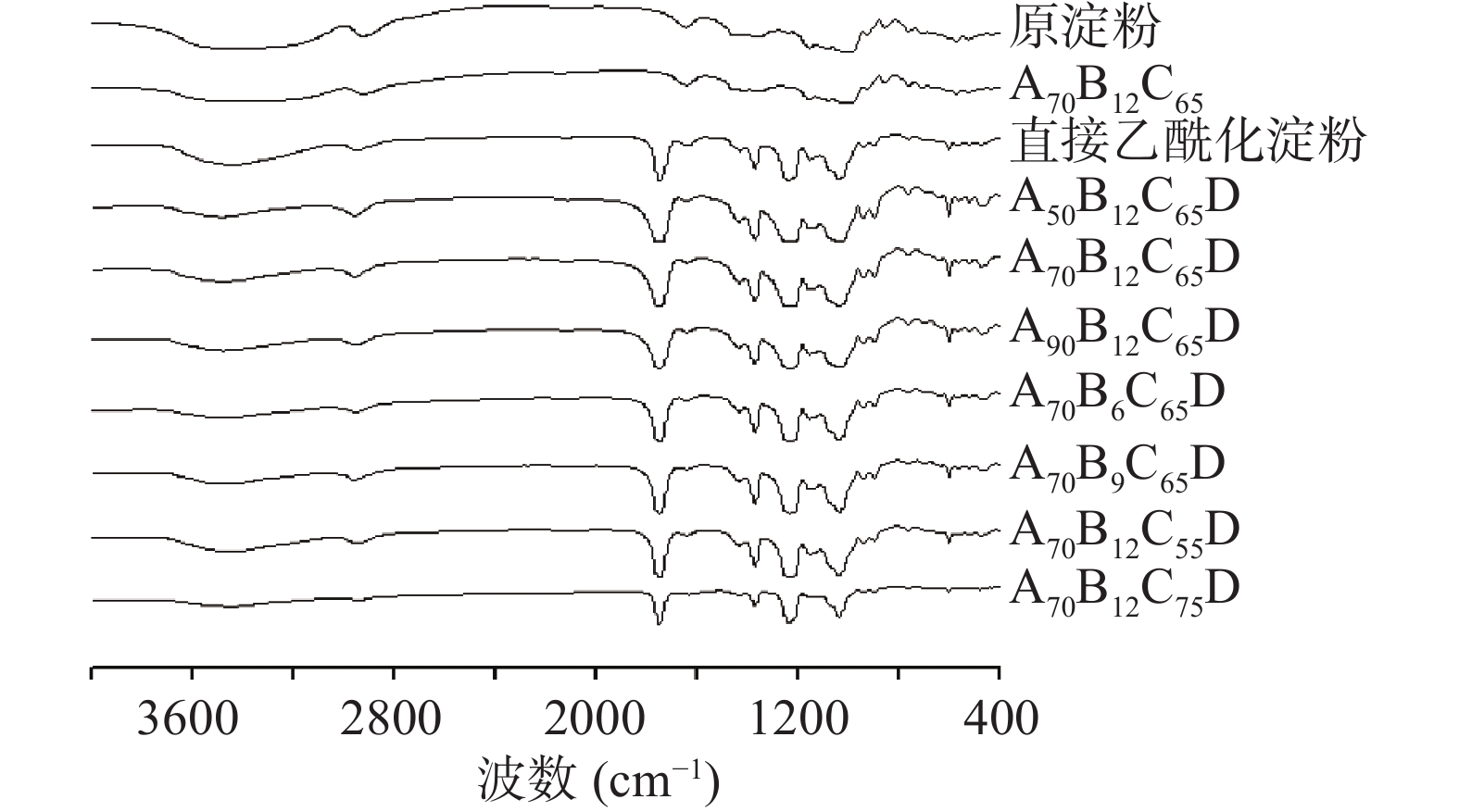
利用淀粉颗粒的葡萄糖单元的官能团对红外光的选择性吸收原理,对样品进行红外光谱测试,从而判断样品的乙酰基取代情况。以原淀粉、酸解淀粉作为参照,对乙酰化是否成功进行定性分析,红外图谱如图1所示。酸解后没有引入新的基团,但由于酸解使得淀粉分子链变短、聚合度降低,分子链上的结合水与淀粉分子的相互作用力下降,结合水减少,导致在3420 cm−1附近的O-H伸缩振动峰略有减小[24];乙酰化改性后出现新的吸收峰,1750 cm−1处出现C=O伸缩振动峰,1435、1375 cm−1处出现CH3弯曲振动峰[25],1240、1163 cm−1处出现C-O-C伸缩振动峰,说明各组样品均成功引入乙酰基基团[26]。
2.2 不同酸解条件对取代度的影响
在乙酰化过程中,淀粉分子中每个脱水葡萄糖单元上三个羟基被乙酰基取代的程度即表示为取代度[7]。不同乙酰化淀粉的取代度如表1所示,未经酸预处理的直接乙酰化淀粉取代度为0.84,在较高浓度酸(12 mol/L)及较低温度(55~65 ℃)的酸解预处理条件下,乙酰化淀粉的取代度均有所提高。其中,盐酸浓度的改变对乙酰化淀粉取代度的影响最为显著(P<0.05) ,随着盐酸浓度由6 mol/L增加至12 mol/L,取代度由0.62增加至1.33,这是由于高浓度盐酸能够提高淀粉的酸解程度[27],从而暴露更多取代位点[28],这与唐洪波等[27]的报道结果一致。而温度的升高并不一定能够提高取代度,在75 ℃酸解条件下,得到的乙酰化淀粉取代度较直接乙酰化淀粉低,为0.73,这可能是由于此温度高于淀粉的糊化温度,导致分子间氢键断裂,乙醇溶剂渗入并与淀粉紧密结合[29],阻碍了乙酰化试剂的进入。随着乙醇浓度的增加,乙酰化淀粉取代度先增后减,这可能是因为高浓度醇对结晶区有保护作用[30],从而降低了反应过程中乙酰基的取代效果。当乙醇浓度为70%(v/v),盐酸浓度为12 mol/L,酸解温度为65 ℃时,取代度达到最大,为1.33,是乙酰化的最佳条件。乙酰基为疏水性基团,高取代度的酸解乙酰化淀粉是反溶剂法制备纳米微球的良好原料。
表 1 不同酸解条件处理的酸解乙酰化淀粉取代度Table 1. Degree of substitution of acid-thinned acetylated starch treated by different acidolysis conditions2.3 结晶结构分析
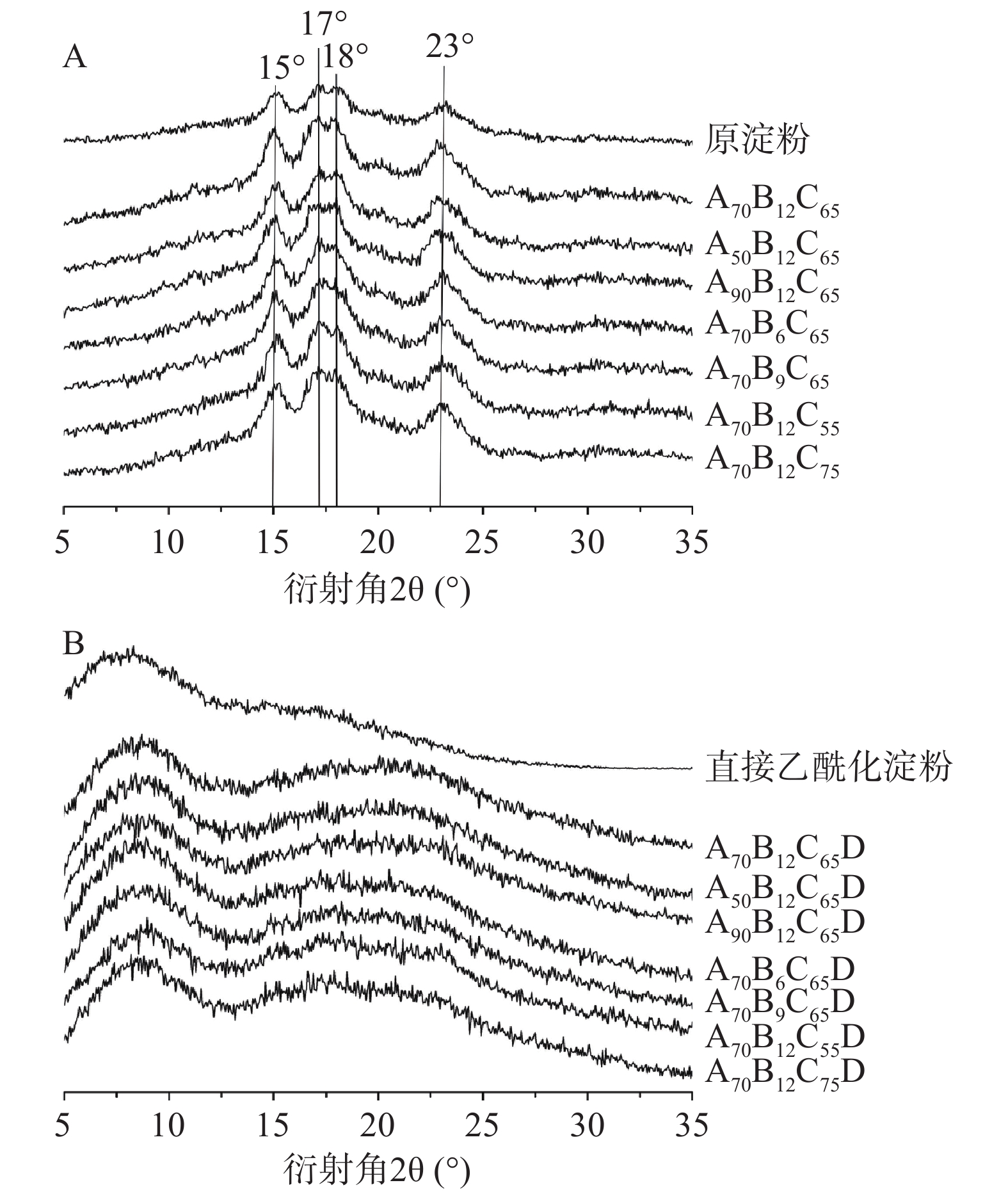
原淀粉、酸解淀粉和酸解乙酰化淀粉的X射线衍射图谱如图2所示。由图2A可知,酸解淀粉与原淀粉晶型相同,为典型的A型淀粉[11],分别在15°、17°、18°和23°处有衍射峰,说明酸解没有改变淀粉的结晶结构,这与Utrilla-Coello等[31]的报道一致。表2反映了酸解淀粉及原淀粉的结晶度。由图2A和表2可知,酸解后淀粉的结晶区增加,结晶度更显著(P<0.05) ,这是由于酸解过程优先发生于非结晶区[32],从而使得结晶区相对比例增加。
表 2 不同酸解淀粉的结晶度Table 2. Crystallinity of different acid-hydrolyzed starches样品 结晶度(%) 原淀粉 21.18±0.38a A50B12C65 22.51±0.24c A70B12C65 25.25±0.10f A90B12C65 21.82±0.13b A70B6C65 27.85±0.65g A70B9C65 25.15±0.57f A70B12C55 24.90±0.11de A70B12C75 24.35±0.13d 由图2B可知,酸解淀粉经乙酰化改性后,原来的A型衍射峰全部消失,在9°和21°左右出现了两个宽峰,为典型的无定形图案[11]。淀粉高度有序的结晶结构由分子内和分子间氢键构成[1],乙酰基的引入削弱了氢键的形成,并导致原双螺旋结构被破坏[12];但在取代度未达到一定大小的情况下,部分未被取代的羟基仍能形成氢键,因此存在强度较弱的晶体峰。与直接乙酰化淀粉相比,酸解乙酰化淀粉在9°和21°处的峰更突出,这是因为酸解过程将单个双螺旋从支链淀粉分离,消除了空间限制,从而允许双螺旋重排,形成更多的晶体结构[28]。与结晶区相比,无定形区结构疏松,具有较高渗透性,化学活性较高[33],有利于后续纳米颗粒的制备。
2.4 接触角分析
接触角可以体现样品的疏水程度,接触角越大则样品疏水性越强[34]。酸解淀粉和原淀粉亲水性极强,无法测定其水接触角。不同酸解条件乙酰化淀粉的水接触角如表3所示,乙酰化淀粉接触角为50°~60°。结合表2和表3可知,随酸解乙酰化淀粉取代度的增加,接触角不断增大,即疏水性提高。这可能是因为乙酰化淀粉通过在淀粉分子中引入疏水性基团乙酰基,使部分羟基结构被破坏,进而破坏了氢键作用[35],使其接触角随取代度的增大而显示增加趋势。由于本文所用的乙酰化样品取代度高,故疏水性相比原淀粉更强,更有利于提高其在良溶剂丙酮溶液中的分散度,以制备粒径更小的淀粉纳米颗粒。
表 3 不同酸解乙酰化淀粉的接触角Table 3. Contact angle of different acetylated acid hydrolysis modified starch样品 接触角(°) 原淀粉 − 酸解淀粉 − 直接乙酰化淀粉 50.9±0.03b A50B12C65D 51.1±0.71b A70B12C65D 60.1±0.28d A90B12C65D 53.7±1.06c A70B6C65D 49.0±0.71a A70B9C65D 50.5±0.49ab A70B12C55D 53.4±1.13c A70B12C75D 49.0±0.71a 2.5 糊化特征值
酸处理可以降低淀粉分子量,从而影响淀粉的糊化特征值[16,36]。乙酰化淀粉疏水性较强,在水溶液中分散性差,难以测定糊化特征值。不同酸解淀粉的糊化特征值如表4所示,酸处理可以使玉米淀粉的糊化黏度显著下降(P<0.05) ,这可能是由于淀粉吸水膨胀主要发生在无定型区,酸进入无定型区,水解其中的糖苷键,使淀粉颗粒结构减弱,限制淀粉吸水膨胀,大幅度降低淀粉糊化黏度[16, 37]。乙酰化淀粉溶解度差,不能使用该方法测定其糊化曲线。随着乙醇浓度的增加,酸解淀粉的峰值黏度不断降低,最低黏度、最终黏度、崩解值、回生值均随乙醇浓度的增加而下降,这是由于乙醇的脱水作用能够抑制由淀粉颗粒吸水过多导致的颗粒膨胀,随着乙醇浓度增加,脱水作用增强,酸进入到较少膨胀的无定形区,使淀粉颗粒结构变弱,淀粉的黏度因此下降[38]。随着反应温度的升高,酸解淀粉的峰值黏度显著降低,最低黏度等值均显著下降,当反应温度达到75 ℃时,淀粉的黏度较小,这是由于温度高于淀粉糊化温度时,淀粉分子间氢键断裂,进一步加强了酸对淀粉的水解作用。相较于原淀粉,盐酸浓度的改变对酸解淀粉糊化黏度不构成显著影响,这可能是由于淀粉分子的聚合度在较低盐酸浓度下已降低至一定程度,使其黏度降低趋缓[39]。较低的糊化黏度也反映了较小的淀粉粒径,有利于制备粒径更小的淀粉纳米颗粒。
表 4 不同酸解淀粉的糊化特征值Table 4. Gelatinization characteristic values of different acid-hydrolyzed starches样品 糊化温度(℃) 峰值黏度(mPa·s) 最低黏度(mPa·s) 最终黏度(mPa·s) 崩解值(mPa·s) 回生值(mPa·s) 原淀粉 74.6±0.35e 1892.5±16.26h 1349.5±2.12g 2388.0±29.70f 543.0±18.38g 1038.5±31.82e A50B12C65 73.5±0.14b 550.5±0.71f 177.0±11.31e 274.5±6.36d 373.5±12.02e 97.5±4.95b A70B12C65 73.7±0.28bc 335.0±6.00c 93.0±4.24c 173.0±2.83c 242.0±4.24c 80.0±1.41b A90B12C65 74.2±0.14de 212.5±0.71b 59.5±0.71b 99.5±0.71b 153.0±0.00b 40.0±0.00a A70B6C65 73.2±0.07b 520.0±8.49e 122.0±4.24d 249.5±0.71d 398.0±4.24f 127.5±3.54c A70B9C65 74.0±0.07cd 461.0±5.66d 123.0±0.00d 252.5±2.83d 333.0±5.66d 130.0±2.83c A70B12C55 72.5±0.28a 1115.0±4.24g 533.5±20.51f 888.5±4.95e 582.0±11.31h 357.5±12.02d A70B12C75 73.5±0.14b 56.0±1.41a 17.0±0.00a 34.0±1.41a 39.00±1.41a 17.0±1.41a 2.6 扫描电子显微镜观察结果分析
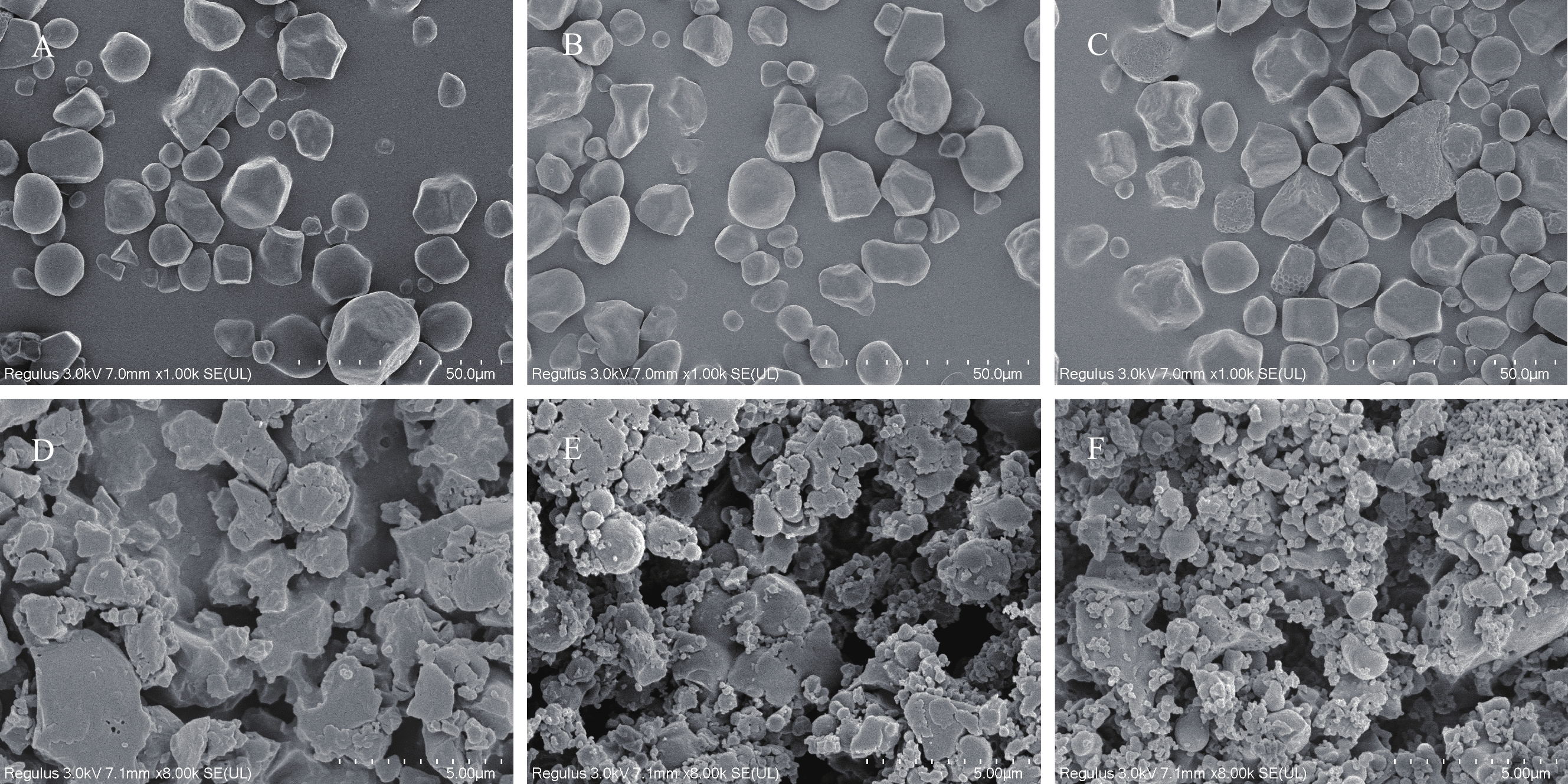
为了比较乙酰化改性对酸解淀粉颗粒形态及大小的影响,对酸解淀粉乙酰化改性前后的形态特征进行扫描电镜观察。由于多组酸解乙酰化淀粉的扫描电镜颗粒大小、形状基本相同,现以取代度相差较大的三组酸解乙酰化淀粉样品与其酸解淀粉进行对比分析。由图3可知,酸解淀粉乙酰化处理后颗粒变小,团聚现象出现,且取代度越高,得到的淀粉颗粒粒径越低,颗粒形貌越好[13]。
由图3可知,酸解淀粉颗粒饱满,为形状不规则的多面体,棱角分明,粒径大小相似,粒径范围约为60~260 μm。结合表5可知,酸解程度越大,淀粉颗粒表面有腐蚀和损伤现象越明显[40],这表明这些酸解淀粉表面结晶结构被破坏[41]。酸解淀粉经乙酰化分解为不均匀的不规则形状,粒径范围约为10~50 μm,且随着取代度的提高,淀粉颗粒明显减小且粒径分布变窄,同时出现团聚现象。这可能是因为淀粉颗粒减小会导致表面活化能升高[42],有利于发生分子间聚集。随取代度的提高,淀粉上的羟基逐渐被疏水性乙酰基取代,分子间氢键减少,疏水缔合能力增强[43]。结合郭春香[7]的研究,高取代度乙酰化淀粉在不良溶剂中扩散相对均匀,与低取代度乙酰化淀粉相比,其成球性好且淀粉纳米微球大小均匀。
表 5 不同取代度的乙酰化淀粉纳米颗粒粒径分布Table 5. Particle diameter distributions of acetylated starch nanoparticles with different degree of substitution样品 粒径(nm) 直接乙酰化淀粉 364.27±26.98d A70B9C65D 271.43±10.43c A50B12C65D 191.14±3.80b A70B12C65D 121.56±0.47a 2.7 淀粉纳米颗粒粒径
反溶剂法是利用溶解于良溶剂的聚合物在与不良溶剂接触时受到的挤压作用制备纳米颗粒的方法[44]。不同取代度的乙酰化淀粉纳米颗粒粒径分布如表5所示。表5分别是取代度0.69、0.86、1.33的酸解乙酰化淀粉及取代度0.84的直接乙酰化淀粉通过反溶剂法制备出的淀粉纳米的粒径分布图。酸解乙酰化纳米淀粉的平均粒径明显减小,分别为271.43、189.25、121.56 nm,且粒径分布较集中。以上结果说明,该纳米颗粒制备方法对不同取代度的酸解乙酰化淀粉都有较好的效果。原淀粉微球粒径过大(微米级,49.52599±3.20600 μm),讨论价值不高,故不再进行分析。
由表5可知,相比直接乙酰化淀粉制备的淀粉纳米颗粒,酸解乙酰化纳米淀粉的平均粒径明显减小,这说明酸解预处理可以通过降低淀粉样品分子量并改变淀粉分子表面和内部的一些属性,显著降低淀粉纳米颗粒粒径,这与李令金[45]的报道一致。同时,酸解乙酰化淀粉取代度对纳米颗粒的粒径产生了显著影响,结合表5取代度数据分析可知,取代度更高的组别纳米颗粒粒径更小,这可能是因为取代度增加有利于提高乙酰化淀粉在良溶剂丙酮溶液中的分散性[1],从而制备粒径更小的淀粉纳米颗粒。结合前人报道[43,46],酸预处理可以通过降低淀粉分子量和提高酸解乙酰化淀粉的取代度,降低乙酰化纳米淀粉颗粒的粒径。
3. 结论
本文探讨了不同酸解预处理条件对淀粉乙酰化取代度以及纳米颗粒粒径大小的影响。对不同条件的酸解样品进行乙酰化处理后,发现以乙醇浓度70%、盐酸浓度12 mol/L、温度65 ℃的酸解条件预处理乙酰化淀粉的取代度及接触角最大,达到1.33,相较直接乙酰化淀粉得到明显提高,进一步证明酸解预处理能够增大乙酰化取代度,从而使疏水性提高。此外,对结晶结构和微观形貌的分析表明,酸解对淀粉表面结构的初步破坏能够帮助淀粉在乙酰化后得到的淀粉颗粒粒径进一步减小。用反沉淀法制备微球并表征其粒径,纳米颗粒粒径最低可达121.56,相对直接乙酰化淀粉显著降低(P<0.05)。综上所述,适当强度的酸解预处理能够有效增加淀粉的乙酰化改性程度,减小淀粉纳米颗粒的粒径。在本文条件下,乙醇浓度70%、盐酸浓度12 mol/L、温度65 ℃的酸解条件处理效果对后续改性的影响最明显,但酸解程度与乙酰化程度并非呈线性相关性,其中的机理还有待进一步的探索讨论。本文的研究结果为淀粉基纳米载体在生物医药等领域的应用提供了理论基础。
-
表 1 不同酸解条件处理的酸解乙酰化淀粉取代度
Table 1 Degree of substitution of acid-thinned acetylated starch treated by different acidolysis conditions
表 2 不同酸解淀粉的结晶度
Table 2 Crystallinity of different acid-hydrolyzed starches
样品 结晶度(%) 原淀粉 21.18±0.38a A50B12C65 22.51±0.24c A70B12C65 25.25±0.10f A90B12C65 21.82±0.13b A70B6C65 27.85±0.65g A70B9C65 25.15±0.57f A70B12C55 24.90±0.11de A70B12C75 24.35±0.13d 表 3 不同酸解乙酰化淀粉的接触角
Table 3 Contact angle of different acetylated acid hydrolysis modified starch
样品 接触角(°) 原淀粉 − 酸解淀粉 − 直接乙酰化淀粉 50.9±0.03b A50B12C65D 51.1±0.71b A70B12C65D 60.1±0.28d A90B12C65D 53.7±1.06c A70B6C65D 49.0±0.71a A70B9C65D 50.5±0.49ab A70B12C55D 53.4±1.13c A70B12C75D 49.0±0.71a 表 4 不同酸解淀粉的糊化特征值
Table 4 Gelatinization characteristic values of different acid-hydrolyzed starches
样品 糊化温度(℃) 峰值黏度(mPa·s) 最低黏度(mPa·s) 最终黏度(mPa·s) 崩解值(mPa·s) 回生值(mPa·s) 原淀粉 74.6±0.35e 1892.5±16.26h 1349.5±2.12g 2388.0±29.70f 543.0±18.38g 1038.5±31.82e A50B12C65 73.5±0.14b 550.5±0.71f 177.0±11.31e 274.5±6.36d 373.5±12.02e 97.5±4.95b A70B12C65 73.7±0.28bc 335.0±6.00c 93.0±4.24c 173.0±2.83c 242.0±4.24c 80.0±1.41b A90B12C65 74.2±0.14de 212.5±0.71b 59.5±0.71b 99.5±0.71b 153.0±0.00b 40.0±0.00a A70B6C65 73.2±0.07b 520.0±8.49e 122.0±4.24d 249.5±0.71d 398.0±4.24f 127.5±3.54c A70B9C65 74.0±0.07cd 461.0±5.66d 123.0±0.00d 252.5±2.83d 333.0±5.66d 130.0±2.83c A70B12C55 72.5±0.28a 1115.0±4.24g 533.5±20.51f 888.5±4.95e 582.0±11.31h 357.5±12.02d A70B12C75 73.5±0.14b 56.0±1.41a 17.0±0.00a 34.0±1.41a 39.00±1.41a 17.0±1.41a 表 5 不同取代度的乙酰化淀粉纳米颗粒粒径分布
Table 5 Particle diameter distributions of acetylated starch nanoparticles with different degree of substitution
样品 粒径(nm) 直接乙酰化淀粉 364.27±26.98d A70B9C65D 271.43±10.43c A50B12C65D 191.14±3.80b A70B12C65D 121.56±0.47a -
[1] NAJAFI S M, BAGHAIE M, ASHORI A. Preparation and characterization of acetylated starch nanoparticles as drug carrier: Ciprofloxacin as a model[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,87:48−54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.030
[2] EL-NAGGARL M E, EL-RAFIE M H, EL-SHEIKH M A, et al. Synthesis, characterization, release kinetics and toxicity profile of drug-loaded starch nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,81:718−729. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.09.005
[3] TIAN S, CHEN Y, CHEN Z, et al. Preparation and characteristics of starch esters and its effects on dough physicochemical properties[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2018(12):1−7.
[4] 付大鹏. 新型载药纳米体系的构建及其促进血栓溶解作用的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2020. FU D P. Construction of a novel drug loaded nano system and its effect on promoting thrombolysis[D]. Wulumuqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2020.
[5] GU F, LI B Z, XIA H, et al. Preparation of starch nanospheres through hydrophobic modification followed by initial water dialysis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015(115):605−612.
[6] 姬娜. 淀粉基口服胰岛素纳米复合物的制备及性能研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2019. JI N. Facribaction and characterization of starch-based nanocomposites for oral insulin delivery[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019.
[7] 郭春香. 淀粉基材料乙酰化修饰及其纳米微球制备与表征[D]. 长春: 长春大学, 2018. GUO C X. Acetylation modification of starch substrate and preparation and characterization of nanometer microspheres[D]. Changchun: Changchun University, 2018.
[8] GG A, DM A, AM B, et al. Synthesis of controlled size starch nanoparticles (SNPs)-science direct[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020:250.
[9] ALI T M, HASNAIN A. Physicochemical, morphological, thermal, pasting, and textural properties of starch acetates[J]. Food Reviews International,2016,32(2):161−180. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2015.1057842
[10] GARG S, JANA A K. Characterization and evaluation of acylated starch with different acyl groups and degrees of substitution[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,83(4):1623−1630. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.015
[11] HAN F, GAO C, LIU M, et al. Synthesis, optimization and characterization of acetylated corn starch with the high degree of substitution[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,59:372−376. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.04.080
[12] 张若娣. 乙酰化淀粉微球的制备研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014. ZHANG R D. Preparation of acetylated starch microspheres[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2014.
[13] BISMARK S, ZHU Z, BENJAMIN T. Effects of differential degree of chemical modification on the properties of modified starches: Sizing[J]. Journal of Adhesion,2018,94(2):97−123. doi: 10.1080/00218464.2016.1250629
[14] 董晓刚. 微晶纤维素的改性及其在热塑性淀粉复合材料中的应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012. DONG X G. Modification of microcrystalline cellulose and its application in thermoplastic composites[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012.
[15] 彭雅丽. 酸解酯化复合变性大米淀粉的制备及其在淀粉膜中的应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2011. PENG Y L. Prepa-ration of acidolysis-esterification composite modified rice starch and its application in starch film[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural Unieversity, 2011.
[16] 邢俊杰. 酸解-湿热处理复合改性淀粉多阶段糊化特性及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018. XING J J. Study on the multi-stage gelatinization behaviors of dual modified starch with acid hydrolysis and heat-moisture treatment[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018.
[17] 姜毅. 碎米生产酸解醋酸酯复合变性淀粉的研究[J]. 粮食科技与经济,2012,37(5):39−41. [JIANG Y. Study on the production of acidolytic acetate compound modified starch from broken rice[J]. Food Science and Technology and Economy,2012,37(5):39−41. [18] 徐忠, 王铎, 赵丹, 等. 酸解乙酰化玉米复合变性淀粉工艺研究[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版),2010,26(6):684−687, 691. [XU Z, WANG Y, ZHAO D, et al. Study on preparation and properties of acetylated acid hydrolysis modified starch[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce(Natural Science Edition),2010,26(6):684−687, 691. [19] 李佳佳, 高群玉. 酸预处理对蜡质玉米乙酰化淀粉性质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(23):97−100,105. [LI J J, GAO Q Y. Influence of prior acid treatment on acetylation of waxy maize starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(23):97−100,105. [20] WHISTLER R L, BEMILLER J N, PASCHALL E F. Starch chemistry and technology[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1984.
[21] 魏本喜. 淀粉纳米晶的制备、分散、改性及乳化性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2015. WEI B X. Starch nanocrystal: Preparation, dispersion, modification and its emulsifying property[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[22] 何君. 马铃薯抗性淀粉在发酵乳中的应用研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2018. HE J. Study on application of potato resistant starches in yogurt[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018.
[23] 陈梦雪, 李飞, 李光磊. 酸解甘薯淀粉及糊化粘度特性研究[J]. 农业科技与装备,2016(6):38−40. [CHEN M X, LI FEI, LI G L. Study on acidolysis sweet potato starch and its gelatinization viscosity properties[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment,2016(6):38−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1161.2016.06.015 [24] 吴杰, 马致远, 陈培涵, 等. 低分子质量淀粉的制备及其结构研究[J]. 中国科技论文,2017,12(12):1371−4. [WU J, MA Z Y, CHEN P H, et al. Preparation and structual analysis of low molecular weight starch[J]. Chnia Sciencepaper,2017,12(12):1371−4. [25] LEI M, FEIYANG X, HAOCUN K, et al. Moderate vinyl acetate acetylation improves the pasting properties of oxidized corn starch[J]. Starch-Stärke,2020,73:2000079.
[26] LIN D, ZHOU W, YANG Z, et al. Study on physicochemical properties, digestive properties and application of acetylated starch in noodles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,128:948−956. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.176
[27] 唐洪波, 马冰洁. 乙酰化酸解复合变性淀粉的制备及性能研究[J]. 食品科学,2007,28(1):47−50. [TANG H B, MA B J. Study on preparation and properties of acetylated acid hydrolysis modified starch[J]. Food Science,2007,28(1):47−50. [28] WANG S, COPELAND L. Effect of acid hydrolysis on starch structure and functionality: A review[J]. C R C Critical Reviews in Food Technology,2015,55(8):1081−1097. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2012.684551
[29] 邓放明, 夏延斌, 莫新良等. 淀粉颗粒糊化新工艺初探[J]. 湖南农学院学报,1995(1):61−66. [DENG F M, XIA Y B, MO X L, et al. Preliminary study on new technology of starch granule gelatinization[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural College,1995(1):61−66. [30] 卢未琴. 醇介质中不同链淀粉含量玉米淀粉微晶的制备及其性质研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2010. LU W Q. Study on the properties and preparation of maize starch crystallites with different amylose content in alcohol medium[D]. Guangzhou: South China Universtity of Technology, 2010.
[31] UTRILLA-COELLO R G, HERNANDEZ-JAIMES C, CARRILLO-NAVAS H, et al. Acid hydrolysis of native corn starch: Morphology, crystallinity, rheological and thermal properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,103:596−602. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.046
[32] ZHANG H, ZHOU X, HE J, et al. Impact of amylosucrase modification on the structural and physicochemical properties of native and acid-thinned waxy corn starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,220:413−419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.030
[33] 耿凤英. 预处理对淀粉结构及化学反应活性的影响[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2010. GENG F Y. Influence of pretreatment on strcture and chemical reaction activity of starch[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2010.
[34] 胡琼恩. 淀粉接枝共聚物的制备及应用研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2018. HU Q E. Preparation and application of starch graft copolymer[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2018.
[35] RAHIM A, KADIR S, JUSMA N. The influence degree of substitution on the physicochemical properties of acetylated arenga starches[J]. International Food Research Journal,2017,24(1):102−107.
[36] 陈惠娟, 孙科祥, 李光磊. 酸解因素对淀粉黏度特性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2010,35(1):168−170, 174. [CHEN H J, SUN K X, LI G L. Acid-modified factors to the influence on the viscosity specific property of starch[J]. Food Science,2010,35(1):168−170, 174. [37] ZHENG H L, SHYH Y L, YUNG H C. Effect of acid-alcohol treatment on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of maize and potato starches[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2003,53(4):475−482. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00145-0
[38] 王斌, 张本山, 刘培玲. 乙醇溶剂保护法制备非晶颗粒态玉米淀粉[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2007(3):75−77, 81. [WANG B, ZHANG B S, LIU P L. Preparation of non-crystal granular corn starch by ethanol’s protect[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2007(3):75−77, 81. [39] 左迎峰, 顾继友, 张彦华, 等. 酸解温度和时间对玉米淀粉性能的影响[J]. 西南林业大学学报,2012,32(5):107−110. [ZUO Y F, GU J Y, ZHANG Y H, et al. Effect of acid hydrolysis temperature and time on properties of corn starch[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University(Natural Sciences),2012,32(5):107−110. [40] 赵凯, 雷鸣, 刘丽艳, 等. 乙酰化羟丙基复合改性玉米淀粉物化特性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2019,34(10):29−35. [ZHAO K, LEI M, LIU L Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of acetylated and hydroxypropylated dual-modified corn starch[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2019,34(10):29−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2019.10.006 [41] 李明宇. 乙酰化二淀粉磷酸酯的制备及性质研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨商业大学, 2013. LI M Y. Study on preparation and characterization of acetylated distarch phosphate[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2013.
[42] 侯淑瑶, 代养勇, 刘传富, 等. 高压均质法制备甘薯纳米淀粉及其表征[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(12):233−238, 242. [HOU S Y, DAI Y Y, LIU C F, et al. Preparation and characterization of sweet potato starch nanoparticles by high pressure homogenization[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(12):233−238, 242. [43] 范少锋. 乙酰化直链玉米淀粉的制备及性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2016. FAN S F. Preparation, property and characterization of acetylated amylose corn starch[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2016.
[44] DENG S, GIGLIOBIANCO M R, CENSI R, et al. Polymeric nanocapsules as nanotechnological alternative for drug delivery system: current status, challenges and opportunities[J]. Nanomaterials,2020,10(5):847. doi: 10.3390/nano10050847
[45] 李令金. 空心硬胶囊用酸解羟丙基复合变性淀粉的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2018. LI L J. Study on acid-hydrolyzed-hydroxypropylated starch applied to hollow hard capsules[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2018.
[46] 吴娟. 基于干热酸解法淀粉纳米颗粒的制备及应用基础研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. WU J. Preparation and applied basic research of starch nanoparticles based on dry-hot acid hydrolysis[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 周敏,韩青,李彩凤. 菊苣根多糖酶法辅助双水相提取工艺优化及其降脂活性研究. 天然产物研究与开发. 2025(02): 283-292 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)








 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
