Effects of Ultra-high Static Pressure and in Vitro Digestion on Phenolics, Antioxidant Activity and Structure from Sesame
-
摘要: 探究利用超高静压不同压力处理芝麻后经模拟体外消化,芝麻酚类物质及抗氧化活性的变化和两者之间的相关性,并利用流变仪和扫描电子显微镜观察芝麻微观结构变化。结果表明,不同压力处理后芝麻木脂素、总酚和总黄酮的含量明显高于未处理。200 MPa处理芝麻样品总木脂素、总酚和抗氧化活性综合指数(ACI)分别为(30.20±1.20) mg/100 g 、(473.04±13.73) µmol Rutin/100 g及(88.02±3.80) µmol Rutin/100 g,明显高于未处理值。无论从酚类物质的含量和抗氧化能力的强弱,200 MPa都是较为理想的处理条件。流变特性曲线表明压力为600 MPa处理时黏性最大,同时芝麻结构变得更加稳定。通过扫描电镜观察到随着压力的增加,样品表面变为疏松多孔,同时促进了消化酶的作用,有利于消化吸收。Abstract: This paper aimed to explore the changes in sesame phenolics and antioxidant activity and the correlation between the two after simulating in vitro digestion of sesame treated with ultra-high static pressure and different pressures, and observe the microstructure changes of sesame with rheometer and scanning electron microscope. The results showed that the contents of sesame lignans, total phenols and total flavonoids after different pressure treatments were significantly higher than those of untreated ones. The total lignans, total phenols and antioxidant activity composite index (ACI) of 200 MPa treated sesame samples were (30.20±1.20) mg/100 g, (473.04±13.73) µmol Rutin/100 g and (88.02±3.80) µmol Rutin/100 g, which were significantly higher than the untreated value. Regardless of the content of phenolic substances and the strength of antioxidant capacity, 200 MPa was an ideal treatment condition. The rheological characteristic curve showed that the viscosity was maximum when the pressure was 600 MPa, and the sesame structure became more stable. It was observed by scanning electron microscope that with the pressure change, the surface of the sample became loose and porous, and at the same time, it promoted the action of digestive enzymes, which was beneficial to improve the digestibility.
-
Keywords:
- sesame /
- ultra-high static pressure /
- in vitro digestion /
- phenolics /
- antioxidant activity /
- structure
-
芝麻在日常生活应用中具有很高的食用和药用价值。芝麻酚类物质包括酚酸、总酚、总黄酮、单宁(原花色素)、木脂素等[1]。促进脂质代谢、具有降低胆固醇[2-3]、高血压[4]、抗衰老、抗癌调节免疫系统等生理功能,并且在抗氧化方面也发挥着重要作用[5-6]。
超高静压(UHP)技术是将食品或生物制品等物料上使用10~1000 MPa的静态压力进行一段时间的处理。这一技术可以在常温或较低温度下对于食品进行杀菌和改善食品性质。相较于传统的芝麻热加工可有效避免加热过程中对其营养物质的破坏等不利影响[7]。
食品的消化是一个复杂的过程,影响因素较多。食物经过胃肠道的消化后,食品中的活性成分通过降解或转化成为容易吸收的小分子,从而发挥其生物学功能。食品本身的营养价值或抗氧化活性能力高却不一定能够对人体有用。所以,研究食品活性成分在人体的消化吸收并且被人体利用的情况,有利于食品的开发。模拟体外消化是生物利用率有价值的工具,消化过程中从食物基质中溶解并释放出来,在肠道中被吸收并被肝脏代谢,从而保持其活跃的生物学特性[8-9]。在食品中进行的体外消化对抗氧化活性的实验有很多,例如西兰花[10]、海藻[11]等植物类、肉类[12]和坚果[13]等。Chen等[14]在体外模拟消化实验中根据指数ACI评价芝麻的综合抗氧化能力,芝麻酚消化产物的抗氧化能力的影响很大,实验表明芝麻酚在芝麻消化产物中含量少但可能是抗氧化活性的重要来源。Ti等[15]研究稻米体外消化,结果发现糙米和粳米的多酚、黄酮及抗氧化能力出现了一定的上升。Dalmau等[16]采用不同的冷冻方式对甜菜根通过体外消化测定多酚含量、抗氧化活性和生物利用率,结果表明:液氮冷冻对甜菜根抗氧化剂和酚类化合物的生物可利用性的影响最大。通过上述可知,体外消化对食品的酚类物质的含量和及其抗氧化能力都具有一定的影响。
食品在人体消化过程中,食品内部结构对消化有一定的影响,消化过程中受胃酸,胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶等的影响,食品黏性的变化对于食品食用口感有一定的影响。食品内部结构的变化对于与酶的结合有一定的影响,提高与酶的结合从而促进消化吸收。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
芝麻 购自福建永辉超市,芝麻品种为“金黄麻”,产地江西省;芝麻酚、细辛素、芝麻素、芝麻林素、细辛素、没食子酸、芦丁标准品(> 98%) 均购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司;猪胃蛋白酶、猪胰酶、脂肪酶、猪胆酸钠、水溶性维生素E(Trolox) Sigma;α-淀粉酶(3700 U/g) 诺维信(中国)生物技术有限公司;丙酮、乙醇、正已烷、福林酚试剂、硝酸钠、三氯化铝、氯化钙、碳酸氢钠、盐酸 国药化学试剂有限公司;甲醇 色谱纯,德国 Merck 公司;DPPH、ABTS和FRAP试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;所有分离用有机溶剂 均为国产分析纯。
5L-HPP-600MPa型超高静压 包头科发高压科技有限责任公司;DZ-400-2 F型真空包装机 温州奔腾机械有限公司;Waters2698-2998型高效液相色谱仪 美国Waters公司;PHS-2F型pH计 温州奔腾机械有限公司;Spectramax Plus384型酶标仪 美谷分子仪器(上海)有限公司;SKY-200B型恒温培养振荡器 上海博迅实业有限公司医疗设备厂;SQP型电子天平 塞多利斯科学仪器有限公司 ;KQ5200E型超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;FW100型高速万能粉碎机 德国IKA集团;GL-20G-II型高速冷冻离心机 美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司;Milli-Q Academic型超纯水系统、QL-901N-1300型旋蒸仪 厦门精益兴业科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品预处理
称取300 g黑芝麻水洗3 min,经过2 h,100 ℃烘箱中烘干,烘干后的样品水分含量测定使用直接干燥法,参照国标(GB5009.3-2016)。干燥后将样品在粉碎机粉碎20 s过筛(60目)。各取芝麻粉10 g分装在密封袋中,再分别加入蒸馏水以制得芝麻样品。
超高静压处理样品分别装入聚丙烯袋中用真空包装机封口(−100 kPa抽真空),真空包装后放入处理装置中,升压速1 MPa/s,高压腔内温度保持在25 ℃、时间10 min。通过预实验后选取压力分别为60、200、400、600 MPa进行处理,并未经压力处理为空白组(CK)。
1.2.2 体外模拟消化产物的制备
参照Wang等[17]的实验方法,不同的压力处理后的芝麻样品提取后各取5 g装入离心管,加入20 mL水和500 μL的α-淀粉酶/CaCl2溶液(25 mL 1 mmol/L CaCl2中溶解32.5 mg的α-淀粉酶pH7.0)。在恒温振荡器振荡消化10 min(37 ℃)。然后加入6 mol/mL HCl将使其调节到pH2.0。加入0.1 g胃蛋白酶,37 ℃振荡消化1 h。采用0.9 mol/L的NaHCO3溶液调节其pH6.0。加入5 mL的胰液素-胆汁盐混合物(使用25 mL0.1 mol/L NaHCO3溶解0.1g的胰酶、0.625 g的胆酸钠和0.25 g脂肪酶)。再用0.9 mol/L的NaHCO3调节使其pH7.4,最后于37 ℃振荡消化2 h。从不同离心管各取3 g用于电镜和流变实验,各取1 g用于芝麻木脂素的测定,剩余的样品放至4 ℃下8000 r/min离心10 min,pH7.0,真空旋转蒸发器中至干(50 ℃),用60%甲醇润洗,并定容至10 mL,最后分装于10个2 mL的离心管中,−80 ℃下保存。用于芝麻总酚、总黄酮及抗氧化活性的测定。做三次平行实验。
1.2.3 芝麻木脂素的测定
参照Chen 等[18]方法,并加以修改,上述1 g的芝麻样品,置于10 mL的离心管中,将60%甲醇取5 mL加入,涡旋振荡后并放入超声机中超声10 min,将离心机调到10 ℃、8000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液;残渣再用上述提取条件和步骤重复提取两次,混合两次提取液并定容至10 mL,保存于−20 ℃下。每个样品做三个平行,上层清液过0.45 µm滤膜过滤后进行HPLC检测。
HPLC检测条件:色谱柱:Waters C18柱(4.6 mm × 250 mm,5 μm),柱温40 ℃,流速为0.8 mL/min,进样量20 μL,流动相为甲醇60%(A)和水40%(B),芝麻酚、芝麻素、芝麻林素和细辛素的检测波长依次是295、287、287、287 nm。
1.2.4 芝麻总酚、总黄酮的提取
参考Shi 等[19]和Chen 等[14]提取方法,并结合实验室设备做出相应调整。1 g的芝麻样品,加入10 mL正己烷并超声10 min,在4 ℃下8000 r/min离心10 min,倒掉上清液。加入10 mL,80%丙酮,超声10 min,4 ℃,8000 r/min离心10 min,保留上清液。重复两次。将上清液进行抽滤,滤液转移到100 mL圆底烧瓶中,旋蒸仪旋蒸至干(50 ℃)。用60%甲醇进行润洗,润洗液倒入离心管中并定容至10 mL,最后分装于10个2 mL的离心管中,−80 ℃下保存,做三个平行。
1.2.5 总酚含量的测定
参考Wang等[20]、Chen等[14]师聪等[21]方法,并加以修改,本实验根据福林酚法测定。将提取液取150 μL与400 μL蒸馏水和100 μL福林酚试剂混匀,静置5~6 min。再加入1.0 mL的6% Na2CO3溶液和1 mL超纯水后反应90 min。用紫外分光光度计在765 nm下的吸光度值(A765 nm)。总酚含量以每100 g芝麻样品含有没食子酸的mg数( (GAE)/100 g,DW)表示。以没食子酸为对照绘制标准曲线,在A765 nm为纵坐标(Y),以浓度为横坐标(X),绘制的标准曲线为:Y=0.0008X+0.0006(R2=0.9998)。根据标准曲线计算芝麻样品中的总酚含量。
1.2.6 总黄酮含量的测定
总黄酮含量的测定参考Dimitrios等[22]和徐洪宇等[23]的方法,并略做修改。将提取液1 mL加入150 μL 5%硝酸钠溶液反应6 min,加入0.3 mL 10% AlCl3溶液反应6 min,然后加入1 mL 1 mol/L 氢氧化钠并定容至4 mL。测510 nm下的吸光值(A510 nm)。芦丁作为标准品绘制标准曲线。总黄酮含量以每100 g样品相当于芦丁mg数(µmol /100 g,DW)。以A510 nm为纵坐标(Y),以浓度为横坐标(X),绘制的标准曲线为:Y=0.0013X+0.002(R2=0.9982)。根据标准曲线计算芝麻样品中的总黄酮含量。
1.2.7 抗氧化活性的测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除能力法
参考Chen等[14]和陆俊等[24]的方法,在96孔微量培养板中每孔加入0.2 mL甲醇0.03 mL DPPH现配的溶液和0.03 mL样品提取液。酶标仪在537 nm处测量吸光值(A537 nm)。以每100 g芝麻样品的Trolox当量(μmol(TE)/100 g,DW)表示。
以A537 nm为纵坐标(Y),以浓度为横坐标(X),绘制的标准曲线为:Y=0.0008X+0.0933(R2=0.9868)。根据标准曲线计算芝麻样品中的DPPH值。
1.2.7.2 ABTS法
使用ABTS试剂盒测定。按照试剂盒说明在培养板每孔加入测定液。在734 nm处测量吸光值(A734 nm)。最终结果以每100 g芝麻样品干重的Trolox当量抗氧化能力(μmol (TE)/100 g,DW)表示。
以A734 nm为纵坐标(Y),以浓度为横坐标(X),绘制的标准曲线为:Y=0.0004X+0.1337(R2=0.9707)。根据标准曲线计算芝麻样品中的ABTS值。
1.2.7.3 FRAP法
参考文献方法[25-26]。使用FRAP试剂盒测定样品抗氧化能力,在培养板每孔加入180 μL FRAP工作液:检测缓冲液、基质液、底物液=10:1:1配制而成,与5 μL的1 mg/mL的样品溶液或者5 μL Trolox标准溶液。在593 nm处测定(A593 nm)。最终结果以每100 g芝麻样品干重的Trolox当量抗氧化能力(μmol(TE)/100 g,DW)表示。
以A593 nm为纵坐标(Y),以浓度为横坐标(X),绘制的标准曲线为:Y=0.000X−0.2273(R2=0.9835)。根据标准曲线计算芝麻样品中的FRAP值。
1.2.7.4 抗氧化活性综合指数(ACI)
以上的方法都具有单一性,因此参考文献[14]对三种方法的值进行综合评价。计算公式如下:
ACI(%)=(DPPH值DPPH最大值+ABTS值ABTS最大值+FAPR值FAPR最大值)/3×100 1.2.8 流变特性的测定
参考任欣等[27]和仇记红等[28]取少量未处理和高压(60、200、400、600 MPa)经过10 min处理的芝麻样品置于流变仪的测定平台上,选取直径为60 mm的锥板模具,选定稳剪切测试程序,启动流变仪,设定流变仪温度为25 ℃,剪切速率为变量,变化范围0.01~100 s−1 。每个样品平行测定两次。
用幂律方程进行模型拟合描述:
η=Kγn−1 式中,η —表观黏度( Pa·s ); γ —剪切速率(s−1); K—稠度系数(Pa·sn); n—幂律指数(量纲=1)。当n=1时,为牛顿液体;当n<1时,为假塑性流体;当n>1 时,为胀塑性流体。
1.2.9 芝麻扫描电子显微镜(SEM)
将未处理和高压(60、200、400、600 MPa)处理10 min的芝麻样品各一份经过模拟体外消化后进行SEM观察,并通过放大500倍观察芝麻样品通过压力处理后的微观形貌结构变化[29]。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS Statistics 24软件分别结果及相关性分析,并利用SigmaPlot 12.5软件、Origin96_24软件作图。实验结果为均值±标准差的形式表示。显著性水平设定为P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻酚类物质、抗氧化的影响及其相关性
2.1.1 芝麻木脂素液相色谱图及标准曲线
四种芝麻木脂素的色谱图、保留时间和标准曲线如图1和表1所示。
表 1 四种芝麻木脂素保留时间和标准曲线Table 1. Retention time and standard curve of four kinds of sesame lignans芝麻木脂素 保留时间
(min)回归线 标准曲线方程 R2 芝麻酚 3.785 Y=1.68e+0.04X−8.25e+0.004 0.9975 芝麻素 7.403 Y=7.88e+0.03X−3.03e+0.004 0.9960 细辛素 8.512 Y=2.34e+0.03X−1.17e+0.004 0.9941 芝麻林素 15.236 Y=3.28e+0.03X−2.32e+0.004 0.9939 2.1.2 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻木脂素组成的影响
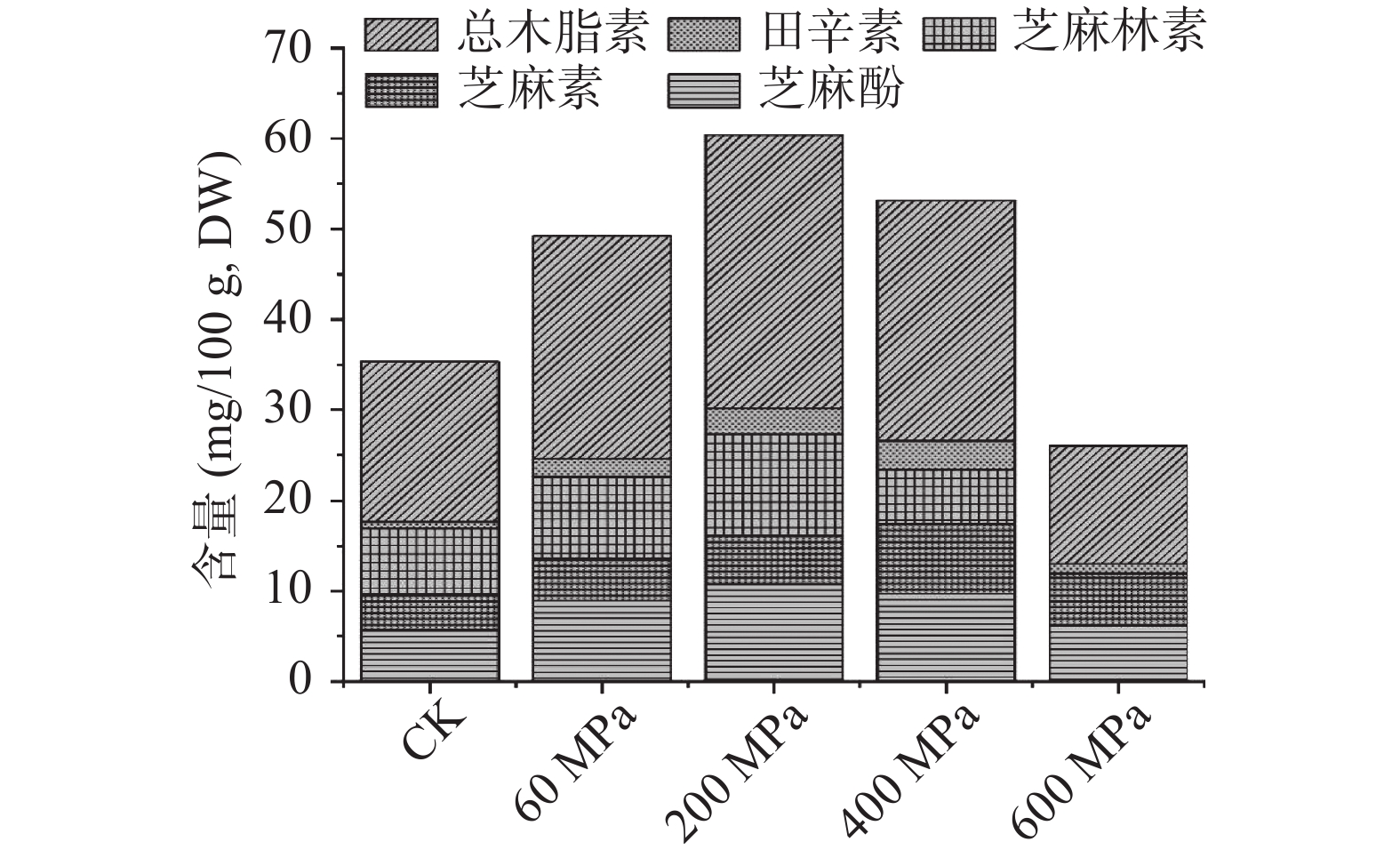
本研究对超高静压不同压力处理后芝麻在体外消化过程中木脂素含量变化进行了分析,结果如图2所示。在经过体外消化后,芝麻的木脂素含量总体变化明显,随着压力的增大,芝麻木脂素含量先增加后减小,总体相较于未处理的芝麻木脂素的含量增加较为显著。但在压力为600 MPa时芝麻林素未检测到。芝麻酚、芝麻素、芝麻林素、细辛素和总木脂素的含量分别在压力200、400、200、400、200 MPa时达到最大,含量分别为(10.80±0.36)、(7.72±0.46)、(11.18±0.61)、(3.15±0.43)、(30.20±1.20)mg/100 g。
2.1.3 超高静压和体外消化对总酚、总黄酮含量的影响
如表2所示。随着压力的增大,总酚含量先升高后降低,在压力200 MPa时达到最大,含量为(527.40±25.67) mg GAE/100 g。200 MPa之后总酚含量依次递减。与未经压力处理的样品相比,压力处理后的总酚含量整体变化显著增大(P<0.05),最大含量与未处理相比增加了31.8%。芝麻的总黄酮含量总体变化明显,随着压力的增大,总黄酮含量先升高后降低,在压力400 MPa时达到最大,含量为(1077.20±29.24) µmol Rutin/100 g,与未处理相比增加35.2%。由此可知,芝麻总酚、总黄酮的含量随着压力的增加而增加,但压力过大也会使总酚、总黄酮受到破坏。该结论与Ti等[15]的研究结果相同。
表 2 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻总酚、总黄酮的影响Table 2. Effect of ultra-high static pressure and in vitro digestion on total phenols and flavonoids of sesame压力
(MPa)总酚
(mg/100 g)总黄酮
(mg/100 g)CK 359.70±18.81c 697.82±44.05c 60 506.62±26.08a 974.14±45.57b 200 527.40±25.67a 1055.34±34.86ab 400 473.04±13.73ab 1077.20±29.24a 600 436.06±32.44b 972.56±25.20b 注:同行字母不同表示差异显著,P<0.05;表3同。 综上所述,不同压力处理后的芝麻经体外消化后的芝麻木脂素、总酚和总黄酮的含量大于未处理,可能是因为压力的增加有利于结合态酚类物质的产生。但是随着压力的增大,其酚类物质有所降低,可能是样品因压力和消化过程中酶的影响,使芝麻中的结合态的酚类转化为游离态进而被释放出来,使酚类物质增加,但是加大压力芝麻细胞壁和酶活发生变化,可能使芝麻酚类物质溶解度加大,进而导致芝麻酚类物质降低。
2.1.4 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻抗氧化活性的影响
结果如表3所示,在经过一系列体外消化后,芝麻的DPPH自由基清除能力随着压力增加总体变化明显,芝麻DPPH值先升高后降低,在压力200 MPa时达到最大,含量为(327.17±31.66) µmol Rutin/100 g,与未处理相比增加了21.7%,与600 MPa相比减小了25.6%。
表 3 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻抗氧化能力的影响Table 3. Effect of ultra-high static pressure and in vitro digestion on antioxidant ability of sesame压力
(MPa)DPPH值
(μmol/100 g)ABTS值
(μmol/100 g)FARP值
(μmol/100 g)ACI值
(μmol/100 g)CK 262.89±25.13bc 519.59±19.93c 2488.18±126.72c 69.92±1.56c 60 315.08±17.51ab 641.75±18.06b 3015.08±204.87b 80.40±2.11ab 200 327.17±31.66a 720.50±26.34a 3383.83±331.97ab 88.02±3.80a 400 297.17±37.17abc 657.17±21.95b 3500.50±227.46a 83.12±7.23ab 600 243.42±32.67c 637.75±32.85b 3433.42±175.71ab 77.95±2.53b 芝麻的ABTS自由基清除能力变化进行了分析。在经过一系列体外消化后,芝麻的ABTS自由基清除能力总体变化显著,随着压力的增大,在压力200 MPa时达到最大,含量为(720.50±26.34)µmol Rutin/100 g,与未处理相比增加了27.9%。
芝麻的FRAP值总体变化不明显,随着压力的增大,芝麻FRAP值先升高后降低,在压力400 MPa时达到最大,含量为(3500.5±227.46)µmol Rutin/100 g,与未处理相比增加了28.9%。
芝麻的ACI值总体变化明显,随着压力的增大,芝麻ACI值先升高后降低,在压力200 MPa时达到最大,含量为(88.02±3.80)µmol Rutin/100 g,与未处理相比增加了20.6%。由此可知,芝麻抗氧化活性随着压力的增加而增加,但压力过大也会使其降低。
2.1.5 芝麻酚类物质含量与抗氧化活性的相关性分析
超高静压处理后的芝麻在体外消化后酚类物质和抗氧化活性的相关性如表4所示,可得两者存在明显的相关性。芝麻酚、芝麻林素、细辛素和总酚与DPPH自由基清除能力呈现正相关。芝麻酚、芝麻林素、细辛素和总酚可能是DPPH自由基清除能力中发挥重要作用。芝麻酚、细辛素、总酚和总黄酮与ABTS自由基清除能力呈正相关,芝麻素、细辛素、总酚和总黄酮与FRAP呈正相关。上述可知,不同测定方法和酚类物质的相关性各不相同。
表 4 体外消化产物中酚类物质和抗氧化能力的皮尔森相关性分析Table 4. Pearson's correlation analysis of phenolic substances and antioxidant capacity after in vitro digestion芝麻酚 芝麻素 芝麻林素 细辛素 总木脂素 总酚 总黄酮 DPPH ABTS FRAP ACI ACI 0.755** 0.419 0.341 0.769** 0.490 0.849** 0.843** 0.705** 0.931** 0.733** 1 FRAP 0.448 0.650** 0.217 0.582* 0.768** 0.551* 0.829** 0.092 0.752** ABTS 0.758** 0.456 0.236 0.753** 0.534* 0.889** 0.844** 0.606* 1 DPPH 0.740** 0.084 0.672** 0.600* 0.010 0.681** 0.441 1 总黄酮 0.740** 0.640* 0.057 0.768** 0.673** 0.772** 1 总酚 0.765** 0.304 0.413 0.762** 0.262 1 总木脂素 0.345 0.859** -0.382 0.571* 1 细辛素 0.888** 0.579* 0.452 1 芝麻林素 0.618* 0.271 1 芝麻素 0.384 1 芝麻酚 1 注:*:表示两组数据的相关性为显著(P<0.05);**:表示两组数据的相关性为极显著(P<0.01)。 综合三种测定方法,由相关性分析可知,芝麻酚、细辛素、总酚和总黄酮与ACI值都存在相关性,总酚与ACI的相关系数最高,为0.849(P<0.05),说明这些物质对芝麻消化产物的抗氧化能力的影响较大。芝麻酚、细辛素可能在芝麻抗氧化中发挥着重要作用,此外,总酚、总黄酮能在酚类物质中抗氧化活性方面发挥着重要作用[30-31]。
综上所述,芝麻抗氧化活性受压力的影响而变化可能是由于芝麻酚类物质的变化而引起的。并且由上述图2、表2、表3可知,芝麻酚类物质与抗氧化活性随压力增加的变化趋势较为相似,更加说明芝麻酚类物质对抗氧化活性有一定的影响。
2.2 高压处理和体外消化对芝麻流变特性及结构的影响
2.2.1 高压处理和体外消化对芝麻流变特性的影响
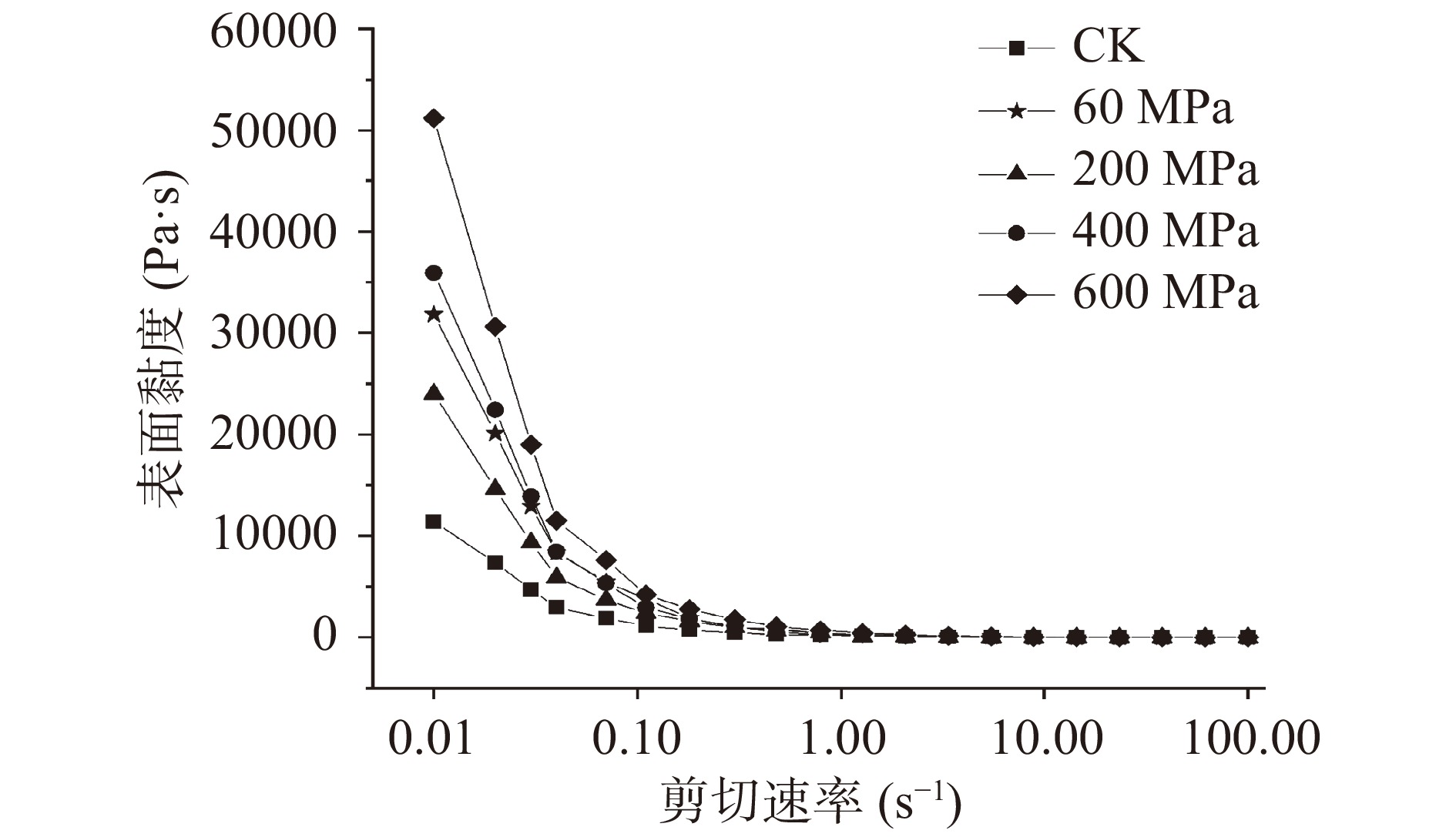
流变特性的研究对产品的质地和稳定性十分重要[32]。假塑性流变特性属于是非牛顿流体的一种,其表观黏度随剪切速率的增加而减小,也称为剪切稀化。本实验是对超高静压处理后的芝麻样品经过体外消化后的流变特性分析。其表观黏度随剪切速率的变化曲线可较好地拟合幂律方程(R2>0.99)。为了更清晰地表达出不同压力处理后芝麻样品的流变特性变化,流变测定过程中以剪切速率1 s−1内的数据进行作图如图3、表5。由图3所示,经过不同的高压处理后的芝麻表面黏度值与未处理相比均有所增加。特别是在剪切速率较低时较为显著。初始黏度值:原样为11400 Pa·s,60 MPa处理后为31800 Pa·s,200 MPa处理后为24000 Pa·s,400 MPa处理后为35900 Pa·s,600 MPa处理后为51200 Pa·s,此后,表面黏度随着剪切速率的增加而迅速减小,在不同的压力处理后的表面黏度不再有显著差异。同一剪切速率下,芝麻表面黏度值随着压力的增大而增加。其中,600 MPa处理后的黏性最大,K=476.61。与表3的数据相结合,在高压处理前、后,样品流变指数n的变化范围为0.00011~0.00043,远小于1,属于假塑性流体,且n值越小,其假塑性越强。并且芝麻剪切稀化现象越明显。稠度系数K值随着压力的增加而增加,说明芝麻内部分子间的排列方式变化使结构更加的稳定。与郭泽镔等[33]对于超高静压处理莲子淀粉在不同的处理时间下,莲子淀粉流变特性的影响有一定的相似性。
表 5 超高静压处理芝麻的流变状态参数Table 5. Rheological parameters of sesame seeds treated by ultra-high static pressure项目 CK 60 MPa 200 MPa 400 MPa 600 MPa 幂律公式 η=216.06γ−0.92281 η=367.96γ−0.9952 η=280.60γ−0.9645 η=447.96γ−0.9251 η=476.61γ−1.0137 R2 0.99989 0.99981 0.99962 0.99957 0.99984 稠度系数(K/Pa·sn) 216.06 367.96 280.60 447.96 476.61 流变指数 n/1 0.00011 0.00019 0.00038 0.00043 0.00016 2.2.2 高压处理和体外消化后芝麻形貌结构的分析
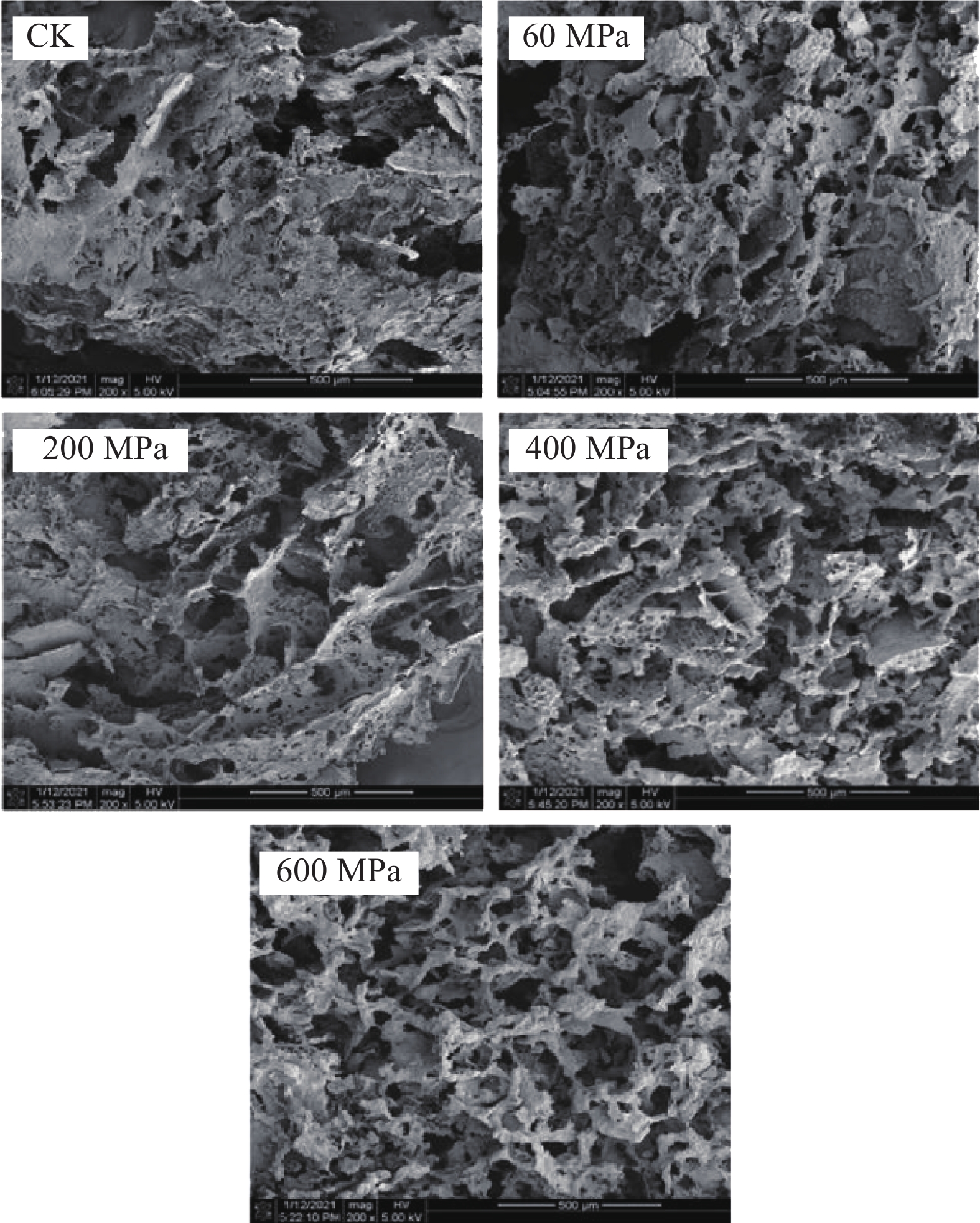
本研究是对超高静压处理后的芝麻经过体外消化后的形貌结构变化的分析。如图4所示,从左到右依次是未处理、60、200、400、600 MPa压力处理后的芝麻电镜图。未处理时的芝麻为聚集片状,结构紧密。由于芝麻未经压力处理,只是经过消化,只受酶作用。通过芝麻被压力处理,由于机械能的作用,内外压力差异较大,存在于物料内部水分溢出,聚集紧密的结构逐渐出现孔状结构,随着压力的增加小孔增多,分布较为均匀,结构变得更加的松散,有利于酶分子进入,对于消化吸收有一定的促进作用。
3. 结论
不同压力处理后芝麻木脂素、总酚和总黄酮的含量大于未处理。200 MPa处理芝麻样品无论从酚类物质的含量,还是抗氧化能力的强弱,都是较为理想的处理条件。由相关性分析得到,芝麻酚、细辛素、总酚和总黄酮具有较强的抗氧化能力。
不同压力处理后的芝麻经过体外消化后的流变特性和形貌结构变化分析。同一剪切速率下,芝麻表面黏度值随着压力的增大而增加,当压力为600 MPa处理时黏性最大,使芝麻食用口感变得更加黏滑适口。同时芝麻结构变得更加稳定。并在加压过程中,芝麻内部由于分子间氢键断裂,结构变化,空间位阻的减小,有助于消化酶的进一步作用。
由上述可知,超高静压处理芝麻后经模拟体外消化后芝麻的酚类物质含量、抗氧化活性及结构特性的变化都更优于未进行超高静压处理。本实验为芝麻综合利用方面提供了理论和技术参考。
-
表 1 四种芝麻木脂素保留时间和标准曲线
Table 1 Retention time and standard curve of four kinds of sesame lignans
芝麻木脂素 保留时间
(min)回归线 标准曲线方程 R2 芝麻酚 3.785 Y=1.68e+0.04X−8.25e+0.004 0.9975 芝麻素 7.403 Y=7.88e+0.03X−3.03e+0.004 0.9960 细辛素 8.512 Y=2.34e+0.03X−1.17e+0.004 0.9941 芝麻林素 15.236 Y=3.28e+0.03X−2.32e+0.004 0.9939 表 2 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻总酚、总黄酮的影响
Table 2 Effect of ultra-high static pressure and in vitro digestion on total phenols and flavonoids of sesame
压力
(MPa)总酚
(mg/100 g)总黄酮
(mg/100 g)CK 359.70±18.81c 697.82±44.05c 60 506.62±26.08a 974.14±45.57b 200 527.40±25.67a 1055.34±34.86ab 400 473.04±13.73ab 1077.20±29.24a 600 436.06±32.44b 972.56±25.20b 注:同行字母不同表示差异显著,P<0.05;表3同。 表 3 超高静压和体外消化对芝麻抗氧化能力的影响
Table 3 Effect of ultra-high static pressure and in vitro digestion on antioxidant ability of sesame
压力
(MPa)DPPH值
(μmol/100 g)ABTS值
(μmol/100 g)FARP值
(μmol/100 g)ACI值
(μmol/100 g)CK 262.89±25.13bc 519.59±19.93c 2488.18±126.72c 69.92±1.56c 60 315.08±17.51ab 641.75±18.06b 3015.08±204.87b 80.40±2.11ab 200 327.17±31.66a 720.50±26.34a 3383.83±331.97ab 88.02±3.80a 400 297.17±37.17abc 657.17±21.95b 3500.50±227.46a 83.12±7.23ab 600 243.42±32.67c 637.75±32.85b 3433.42±175.71ab 77.95±2.53b 表 4 体外消化产物中酚类物质和抗氧化能力的皮尔森相关性分析
Table 4 Pearson's correlation analysis of phenolic substances and antioxidant capacity after in vitro digestion
芝麻酚 芝麻素 芝麻林素 细辛素 总木脂素 总酚 总黄酮 DPPH ABTS FRAP ACI ACI 0.755** 0.419 0.341 0.769** 0.490 0.849** 0.843** 0.705** 0.931** 0.733** 1 FRAP 0.448 0.650** 0.217 0.582* 0.768** 0.551* 0.829** 0.092 0.752** ABTS 0.758** 0.456 0.236 0.753** 0.534* 0.889** 0.844** 0.606* 1 DPPH 0.740** 0.084 0.672** 0.600* 0.010 0.681** 0.441 1 总黄酮 0.740** 0.640* 0.057 0.768** 0.673** 0.772** 1 总酚 0.765** 0.304 0.413 0.762** 0.262 1 总木脂素 0.345 0.859** -0.382 0.571* 1 细辛素 0.888** 0.579* 0.452 1 芝麻林素 0.618* 0.271 1 芝麻素 0.384 1 芝麻酚 1 注:*:表示两组数据的相关性为显著(P<0.05);**:表示两组数据的相关性为极显著(P<0.01)。 表 5 超高静压处理芝麻的流变状态参数
Table 5 Rheological parameters of sesame seeds treated by ultra-high static pressure
项目 CK 60 MPa 200 MPa 400 MPa 600 MPa 幂律公式 η=216.06γ−0.92281 η=367.96γ−0.9952 η=280.60γ−0.9645 η=447.96γ−0.9251 η=476.61γ−1.0137 R2 0.99989 0.99981 0.99962 0.99957 0.99984 稠度系数(K/Pa·sn) 216.06 367.96 280.60 447.96 476.61 流变指数 n/1 0.00011 0.00019 0.00038 0.00043 0.00016 -
[1] ZHANG X, ZHANG L, XIN L U, et al. Formulation optimization of extruded sesame-based food products using mixture design and fuzzy evaluation[J]. Food Science,2018,39(4):248−253.
[2] 李亚会. 白芝麻与黑芝麻功能品质差异的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2018. LI Y H. Study on the difference of functional quality between white sesame and black sesame[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2018.
[3] 汪学德, 崔英德, 刘兵戈, 等. 芝麻各成分相关性分析[J]. 中国油脂,2015,40(11):99−103. [WANG X D, CUI Y D, LIU B G, et al. Correlation analysis of sesame components[J]. China Olis & Fats,2015,40(11):99−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2015.11.020 [4] WANG L, ZHANG Y, LI P, et al. HPLC analysis of seed sesamin and sesamolin variation in a sesame germplasm collection in China[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society,2012,89(6):1011−1020. doi: 10.1007/s11746-011-2005-7
[5] EWEDA S M, NEWAIRY A, ABDOU H M, et al. Bisphenol A-induced oxidative damage in the hepatic and cardiac tissues of rats: The modulatory role of sesame lignans[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 19(1). 1−11.
[6] 王荣, 赵佳, 冯怡, 等. 黑芝麻总黄酮的体内抗氧化作用研究[J]. 中国油脂,2020,45(7):42−44. [WANG R, LIU J, FENG Y, et al. Study on antioxidant effect of total flavonoids in black sesame[J]. China Olis & Fats,2020,45(7):42−44. doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.07.010 [7] TSL A, ALTDJ A, MS A, et al. High pressure processing (HPP) of pea starch: Effect on the gelatinization properties[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,76:361−369. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.07.036
[8] GUNATHILAKE K D P P, RANAWEERA K K D S, RUPASINGHE H P V. Change of phenolics, carotenoids, and antioxidant capacity following simulated gastrointestinal digestion and dialysis of selected edible green leaves[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,245(Apr.15):371−379.
[9] PÉREZ-BURILLO S, MEHTA T, ESTEBAN-MUOZ A, et al. Effect of in vitro digestion-fermentation on green and roasted coffee bioactivity: The role of the gut microbiota[J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 279(3).
[10] MR A, TMC A, HCDSH A, et al. Encapsulation of broccoli extract by electrospraying: Influence of in vitro simulated digestion on phenolic and glucosinolate contents, and on antioxidant and antihyperglycemic activities - Science direct[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,339:128075.
[11] HUANG Z, CHEN Q, HU K, et al. Effects of in vitro simulated digestion on the free and bound phenolic content and antioxidant activity of seven species of seaweeds[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2020,42(3):e13532.
[12] LUO J, TAYLOR C, NEBL T, et al. Effects of macro-nutrient, micro-nutrient composition and cooking conditions on in vitro digestibility of meat and aquatic dietary proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,254(jul.15):292.
[13] HERMELO P H, LAMAS J P, LORES M, et al. Polyphenol bioavailability in nuts and seeds by an in vitro dialyzability approach[J]. Food Chemistry,2018:S2120214919.
[14] CHEN Y, LIN H, LIN M, et al. Effect of roasting and in vitro digestion on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity of water-soluble extracts from sesame[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2020:111239.
[15] TI H, ZHANG R, LI Q, et al. Effects of cooking and in vitro digestion of rice on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity[J]. Food Research International, 2015, 76(Pt 3): 813−820.
[16] DALMAU M E, LLABRÉS P J, EIM V S, et al. Influence of freezing on the bioaccessibility of beetroot (Beta vulgaris) bioactive compounds during in vitro gastric digestion[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(3):1055−1065. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9272
[17] WANG J, CHI Y, YUAN C, et al. Physicochemical properties, in vitro digestibility and antioxidant activity of dry-heated egg white protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,246:18. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.128
[18] CHEN J, CHEN Y, TIAN J, et al. Simultaneous determination of four sesame lignans and conversion in Monascus aged vinegar using HPLC method[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,256(Aug.1):133.
[19] SHI L K, LIU R J, JIN Q Z, et al. The contents of lignans in sesame seeds and commercial sesame oils of China[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society,2017,94(8):1035−1044. doi: 10.1007/s11746-017-3018-7
[20] WANG H, WANG J, GUO X, et al. Effect of germination on lignan biosynthesis, and antioxidant and antiproliferative activities in flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.)[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,205(Aug.15):170−177.
[21] 师聪, 解春芝, 张建萍, 等. 覆盆子不同极性溶剂提取物的抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(1):220−224. [SHI C, JIE C Z, ZHANG J P, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activity of raspberry extracts with different polar solvents[J]. Food Science & Technology,2021,46(1):220−224. [22] DIMITRIOS B. Sources of natural phenolic antioxidants[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2006,17(9):505−512.
[23] 徐洪宇, 蒯宜蕴, 詹壮壮, 等. 果皮中酚类物质含量, 抗氧化活性及在体外消化过程中成分的变化[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(15):23−30. [XU H Y, KUAI Y Y, ZHAN Z Z, et al. The content of phenolic substances in the peel, antioxidant activity and changes in composition during in vitro digestion[J]. Food Science,2019,40(15):23−30. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180806-046 [24] 陆俊, 敦惠瑜, 向孝哲, 等. 体外模拟胃, 肠消化对6种黑色食品抗氧化成分及其活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(5):47−56. [LU J, DUN H Y, XIANG X Z, et al. The Effect of simulated stomach and intestinal digestion in vitro on the antioxidant components and activities of six black foods[J]. Food Science,2018,39(5):47−56. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201805008 [25] LIN Z, LIN X, MEHMOOD A A, et al. Phytochemical contents and antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of selected black and white sesame seeds[J]. Biomed Res Int,2016,2016:8495630.
[26] 叶贤江, 苏志琛, 林晓娟, 等. 基于生物信息学与分子对接技术对坛紫菜降血压肽的筛选及活性研究[J]. 食品科学,2021:1002−6630. [YE X J, SU Z C, LIN X J, et, al. Screening and activity study of antihypertensive peptides fromPorphyra haitanensis based on bioinformatics and molecular docking technology[J]. Food Science,2021:1002−6630. [27] 任欣, 娄阁, 沈群. 高压热处理对复合芝麻酱品质特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(8):140−148. [RRN X, LOU G, SHEN Q. The effect of high pressure heat treatment on the quality characteristics of compound sesame paste[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science & Technology,2016,16(8):140−148. [28] 仇记红, 侯利霞. 浸泡及萌芽处理对芝麻酱流变特性影响的研究[J]. 中国调味品,2018,43(5):54−60. [CHOU J H, HOU L X. Study on the effect of soaking and sprouting treatment on the rheological properties of tahini sauce[J]. China Condiment,2018,43(5):54−60. [29] 李宁宁, 李钊, 赵圣明, 等. 地皮菜添加量对鸡胸肉糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):53−59. [LI N N, LI Z, ZHAO S M, et al. Effect of addition of ground vegetables on the gel properties of chicken breast minced meat[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):53−59. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191031-348 [30] 林晓慧. 黑白芝麻体外模拟消化前后植物化学成分组成, 抗氧化及抗增殖活性的探究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. LI X H. Study on the phytochemical composition, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of black and white sesame before and after simulated digestion in vitro [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[31] 苗字叶, 姚亚亚, 刘阳星月, 等. 超高静压改性麦麸对其功能性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(19):164−171. [MIAO Z Y, YAO Y Y, LIU Y X Y, et, al. The effect of ultra-high static pressure modified wheat bran on its functional properties[J]. Food Science,2019,40(19):164−171. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180929-333 [32] 靳学远, 张培旗. 辣木叶总黄酮超高压提取工艺条件的优化[J]. 轻工科技,2020(7):1−6. [LE X Y, ZHANG P Q. Optimization of ultra-high pressure extraction process conditions for total flavonoids of Moringa oleifera leaves[J]. Guangxi Journal of Light Industry,2020(7):1−6. [33] 郭泽镔. 超高压处理对莲子淀粉结构及理化特性影响的研究[D].福州: 福建农林大学, 2014. GUO Z B. Study on the influence of ultra-high pressure treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of lotus seed starch [D]. Fujian: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2014.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 常虹,王爽,周家华,李文生,王云香,王宝刚. 体外模拟消化对鲜切苹果皮渣黄酮类物质及其还原力的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(20): 39-44 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 耿宏庆,康梦瑶,杨凯麟,陆今明,彭松林,赵紫悦,尚永彪. 高压微射流处理对微晶纤维素-猪油Pickering乳液的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(22): 60-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄师荣,闫瑞,刘欢,唐敏,陈东方. 不同的体外模拟消化方法对腌榨菜叶抗氧化活性的影响. 农产品加工. 2022(21): 1-7+13 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



