Comparative Analysis of Black Tea Metabolites from Different Origins Based on Extensively Targeted Metabolomics
-
摘要: 为探究红茶代谢产物的产地差异,本实验采用感官审评方法及超高效液相色谱串联质谱(UPLC-MS/MS)的广泛靶向代谢组测定方法,对福建省福安市和尤溪县产红茶中的代谢产物进行比较分析。结果表明:福安红茶以“醇和”的滋味特征为主,尤溪红茶以“甘醇”的滋味特征为主。利用代谢组学方法在两地的红茶中鉴定出黄酮、酚酸类、脂质、有机酸、氨基酸及其衍生物等共937种代谢物,通过主成分分析(PCA)和正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)可以显著区分不同产地红茶,并鉴定出410种具有显著差异的代谢物。尤溪红茶中有291种差异代谢物的相对含量高于福安红茶,其中紫云英苷、表儿茶素(EC)、L-谷氨酰胺、L-天冬氨酸、L-赖氨酸、L-色氨酸、L-谷氨酸、绿原酸、苯乙胺和牡荆素-2''-O-鼠李糖苷等差异代谢产物对于两地红茶的不同滋味品质形成可能具有重要贡献。代谢通路分析发现,两地红茶的氨基酸和黄酮类物质代谢水平具有显著差异,可能是形成两地红茶滋味品质差异的原因。研究为茶叶产地鉴别提供理论依据。Abstract: In order to explore the origin differences of black tea metabolites, the metabolites in black tea produced in Fu 'an and Youxi of Fujian province were compared and analyzed by using sensory evaluation method and extensive targeting metabolomic determination method of ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). The results showed that, Fu'an black tea mainly tasted of “mellow and soft”, while Youxi black tea of “mellow and sweet”. A total of 937 metabolites including of flavonoids, phenolic acids, lipids, organic acids, amino acids and their derivatives were identified by metabonomics in the black tea of the two regions, through the principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) could significantly distinguish different producing area of black tea, and identified 410 species of metabolites with significant difference. The relative content of 291 different metabolites in Youxi black tea was higher than that of Fu 'an black tea, among which Astragalin, EC, L-glutamine, L-aspartic acid, L-lysine, L-tryptophan, L-glutamic acid, chlorogenic acid, phenethylamine, vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside might have important contributions to the formation of different taste and quality of black tea from the two regions. Metabolic pathway analysis showed that the metabolism levels of amino acids and flavonoids of black tea between the two places were significantly different, which might be the reason for the difference in the taste and quality of black tea between the two places. The research would provide a theoretical basis for the identification of tea origin.
-
Keywords:
- black tea /
- metabolomics /
- different metabolites /
- taste /
- origin
-
红茶属于全发酵茶,福建是红茶的发源地,其主产区分布于闽中和闽东一带,其中福安市、蕉城区、柘荣县、寿宁县、尤溪县、大田县、政和县、松溪县等地区的红茶产量较高[1],“福云6号”作为福建大面积栽培的品种,有较好的红茶适制性,是福安市主推茶树品种之一,也是尤溪县主栽茶树品种之一,占茶园面积的60%以上。由于红茶具有降血糖[2]、抗氧化[3]、抗病毒[4]、抗癌[5]、抗炎[6]等保健功效,深受消费者的喜爱。然而,不同产区红茶品质各不相同,导致价格差异大,市场出现冒用优质产地的现象,损害了消费者利益,也影响福建茶叶区域品牌的建设,因此探究一种科学的茶叶产地与品质鉴别技术十分必要。
目前国内外已有大量针对茶叶的产地与品质鉴别的研究,主要采用气相色谱-质谱联用法(GC-MS)[7]、液相色谱-质谱联用法(LC-MS)[8]、稳定性同位素[9]、近红外光谱[10]、矿物质元素[11]、核磁共振[12]等检测技术。彭云等[13]采用顶空固相微萃取(HS-SPME)结合气相色谱-质谱联用技术(GC-MS)对云南、湖北、福建三个不同产地红茶的香气物质进行了鉴定和分析,发现滇红工夫中有26种特有成分,宜红工夫中有4种,而闽红工夫中则有6种,明确了不同产地红茶香气品质形成的化学物质基础,可以实现不同产地红茶的鉴别。赵恬欢[14]利用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-OES)和质谱法(ICP-MS),对中国、印度等5个国家红茶的25种矿质元素含量进行测定,利用主成分分析可以有效的区分不同产地的红茶。滋味是判断茶叶品质的重要指标,也是消费者选择茶叶产品的重要依据。宋楚君等[15]采用LC-MS方法对我国10个典型产区代表性红茶样品中的主要滋味物质进行分析比较,结果表明华南、西南茶区红茶呈醇厚型的滋味风格,儿茶素类及其氧化产物生物碱和有机酸类物质为其主要滋味贡献物质,江北、江南茶区红茶呈清鲜型的滋味风格,游离氨基酸为其主要滋味贡献物质,由此可以对不同产区红茶进行判别。可见,目前对于茶叶产地判别的主要分析手段都还无法获得代谢物的全部信息,而代谢组学作为一门新兴技术,通过高通量检测和多元数据处理将信息系统性整合,能够对小分子代谢产物进行定性定量分析,与其他分析方法相比,该技术较易发现不同样品的代谢物差异,从而能更全面、准确地区分样品的产地[16]。王春波等[17]采用代谢组学技术分析了贵州3个不同产区都匀毛尖的代谢差异,在正、负离子模式下分别鉴定出237种和164种代谢物,利用多元统计方法筛选出6种差异显著的产地标志物,成功区分不同产区的都匀毛尖。然而,目前关于不同产地红茶的代谢组学研究仍较为欠缺。
本研究基于广泛靶向代谢组学分析福安市和尤溪县两地由福云6号单一品种所制红茶样品的代谢产物,通过多元统计与KEGG通路分析筛选差异代谢物进而区分不同产地的红茶,分析可能造成红茶滋味品质差异的原因,以期为福建红茶产地鉴别及溯源提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
尤溪红茶 共20份,由尤溪县光兴茶业有限公司和尤溪县云富茶叶有限公司提供(产自坂面镇和台溪乡);福安红茶 共20份,由福安市农垦集团有限公司和福建新坦洋茶业股份有限公司提供(产自城阳镇、潭头镇、上白石镇、甘棠镇、社口镇和松罗乡);全部茶样均是福云6号单一品种制成的成品红茶(2020年春茶,等级相似)。
超高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;三重四级杆质谱仪(Applied Biosystems 4500 QTRAP) 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;SB-C18色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.8 µm) 美国安捷伦公司;MM 400研磨仪 Retsch
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 审评取样
参照GB/T 23776-2018茶叶感官审评方法中的红茶感官审评方法,由6名高级评茶员(3名男性和3名女性)对40份茶样的滋味进行评价与评分,最后从两个产地各筛选出1份总体得分高且具有代表性的茶样进行后续的代谢组学分析。
1.2.2 样品制备方法
将样品放入5 mL离心管,置于冻干机(Scientz-100 F)中真空冷冻干燥,再用研磨仪研磨(30 Hz,1.5 min)至粉末状,称取100 mg的粉末,加入70%甲醇水溶液1.2 mL,每30 min涡旋提取30 s、重复6次后置于4 ℃冰箱过夜;12000 r/min离心10 min,吸取上清液,0.22 μm滤膜过滤样品并保存于进样瓶中,两个产地的红茶样品,分别重复取样3次、制备后进行UPLC-MS/MS分析。
1.2.3 质控样品
质控样本(quality control samples,QC)由2组不同产地红茶提取物等量混合制备而成,与分析样本采用相同的方法处理和检测,重复3次。在仪器检测的过程中,每10个检测分析样本中插入1个QC样本,以监测整个分析过程的重复性。
1.2.4 分析条件
1.2.4.1 液相色谱条件
色谱柱:Agilent SB-C18(1.8 µm,2.1 mm×100 mm);流动相:A相为超纯水(加入0.1%的甲酸),B相为乙腈(加入0.1%的甲酸);洗脱梯度:0.00 min B相比例为5%,9.00 min内B相比例线性增加到95%,并维持在95% 1.00 min,10.00~11.10 min,B相比例降为5%,并以5%平衡至14 min;柱温40 ℃;进样量4 μL;流速0.35 mL/min。
1.2.4.2 质谱条件
电喷雾离子源(electrospray ionization,ESI)进行海量数据采集,操作参数如下:涡轮喷雾温度为550 ℃;离子喷雾电压(IS)5500 V(正离子模式)/−4500 V(负离子模式);离子源气体I(GSI),气体II(GSII)和帘气(CUR)分别设置为50、60和25 psi,碰撞诱导电离参数设置为高。在三重四级杆(triple quadrupole,QQQ)和线性离子阱(LIT)模式下分别用10和100 μmol/L聚丙二醇溶液进行仪器调谐和质量校准。在QQQ中,每个离子对根据优化的去簇电压(declustering potential,DP)和碰撞能(collision energy,CE)进行扫描检测[18]。
1.3 数据处理
通过比较离子碎片模式、保留时间和m/z值,并通过迈维(武汉)生物技术有限公司自建数据库和公共数据库对代谢物进行鉴定。利用三重四级杆质谱的多反应监测模式(multiple reaction monitoring,MRM)对代谢物进行定量,获得不同样本的代谢物质谱并对其进行峰面积积分,最后不同样本的相同代谢物中的质谱出峰进行积分校正。采用R软件(https://www.r-project.org/)对鉴定的代谢产物进行主成分分析(PCA)和正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA)。根据OPLS-DA模型获得的变量重要性投影(variable importance in project,VIP)评分,将VIP≥1,fold change≥2或fold change≤0.5的代谢物定义为差异代谢物(significant changed metabolites,SCMs),同时将得到的相应差异代谢物通过代谢通路数据库KEGG Pathways(KEGG,www.genome.jp/kegg)进行解析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同产地红茶感官品质分析
由感官审评结果可见(表1),福安红茶(FF)的滋味以醇和为主,尤溪红茶(YF)以甘醇为主;福安红茶(FF)的香气以薯香、焦糖香为主,尤溪红茶(YF)以甜香为主。
表 1 不同产地红茶感官审评结果Table 1. Sensory evaluation results of black tea from different origins茶样 滋味特征 香气特征 得分(分) 福安红茶(FF) 醇和,带桂圆味,尚醇 带薯香,焦糖香 91 尤溪红茶(YF) 甘醇,顺滑,尚醇 甜香,尚浓 91 2.2 不同产地红茶代谢组学分析
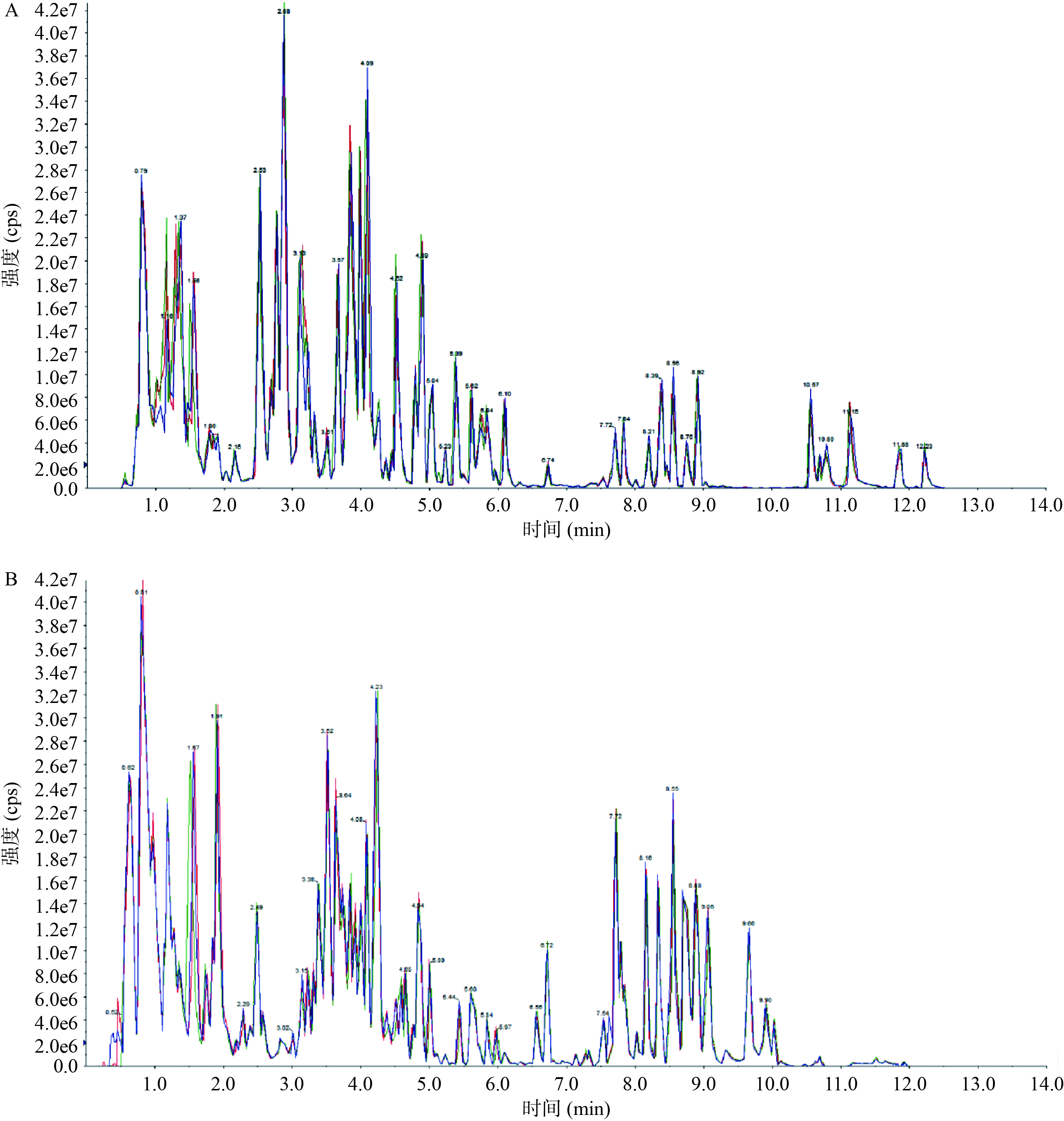
通过UPLC-MS/MS技术检测,图1是质控样本分别在正、负离子检测模式下得到的质谱总离子流色谱图(TIC)进行谱图叠加比较的结果,可见其谱图的重叠性很高,说明检测方法的信号稳定性好,得出的数据结果可靠。
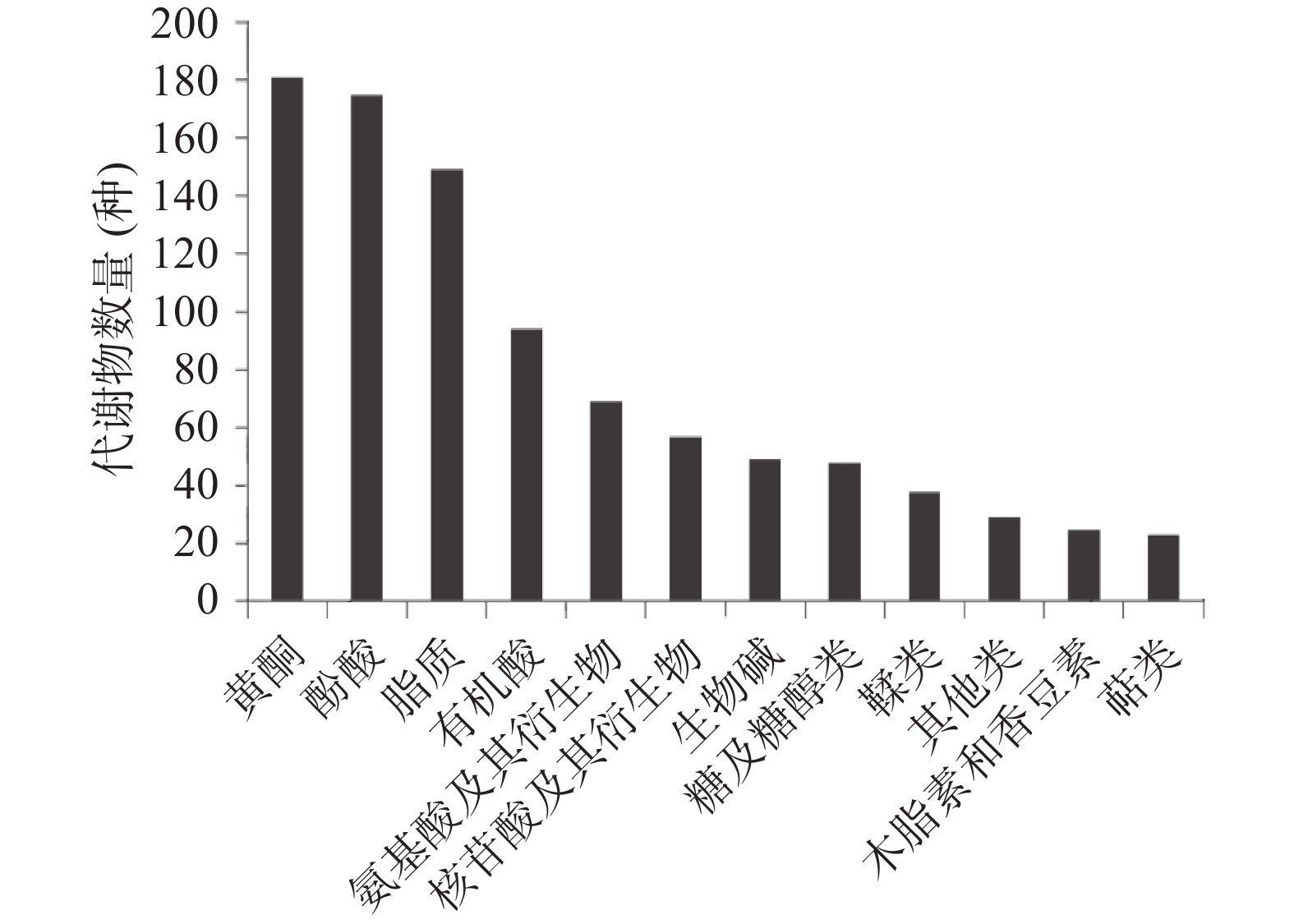
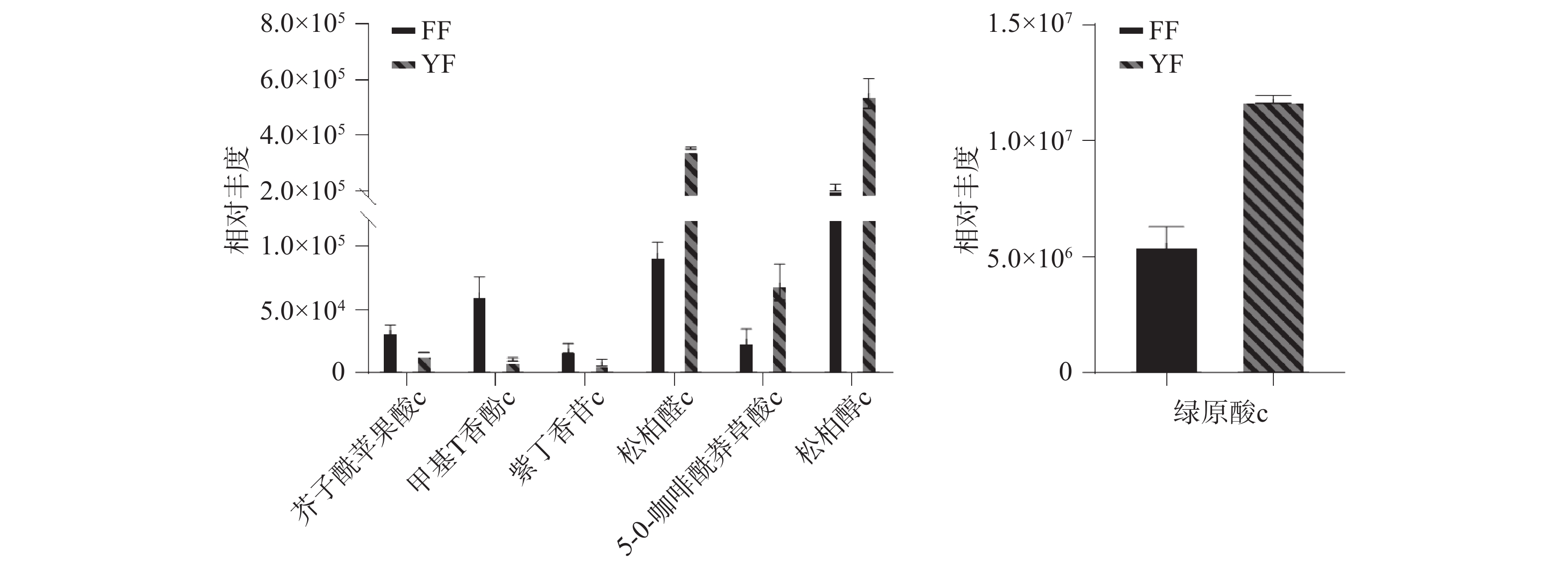
结果在两地红茶中共鉴定出12类937种代谢物,如图2所示,其中包括黄酮类181种(黄酮醇58种、黄酮55种、黄烷醇类21种、黄酮碳糖苷19种等)、酚酸类175种(草酸、绿原酸、松柏醇、松柏醛、紫丁香苷、芥子酰苹果酸、5-O-咖啡酰莽草酸等)、脂质149种(游离脂肪酸66种、甘油酯18种等)、有机酸94种(富马酸、马来酸、奎宁酸、3,5-二羟基-3-甲基戊酸等)、氨基酸及其衍生物69种(L-谷氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺、L-天冬酰胺、L-天冬氨酸、L-精氨酸、L-赖氨酸、L-色氨酸等)、核苷酸及其衍生物57种(烟酸腺嘌呤二核苷酸、L-墨喋呤、胞嘧啶等)、生物碱49种(生物碱27种、酚胺12种等)、糖及糖醇类48种(木糖醇、麦芽糖、松二糖、蔗糖等)、鞣类38种(茶黄素、原花青素B1等)、其他类29种(维生素13种等)、木脂素和香豆素25种(7-羟基香豆素、松脂醇等)、萜类23种(熊果醛、夏罗草酮等)。
2.3 不同产地红茶代谢组学差异分析
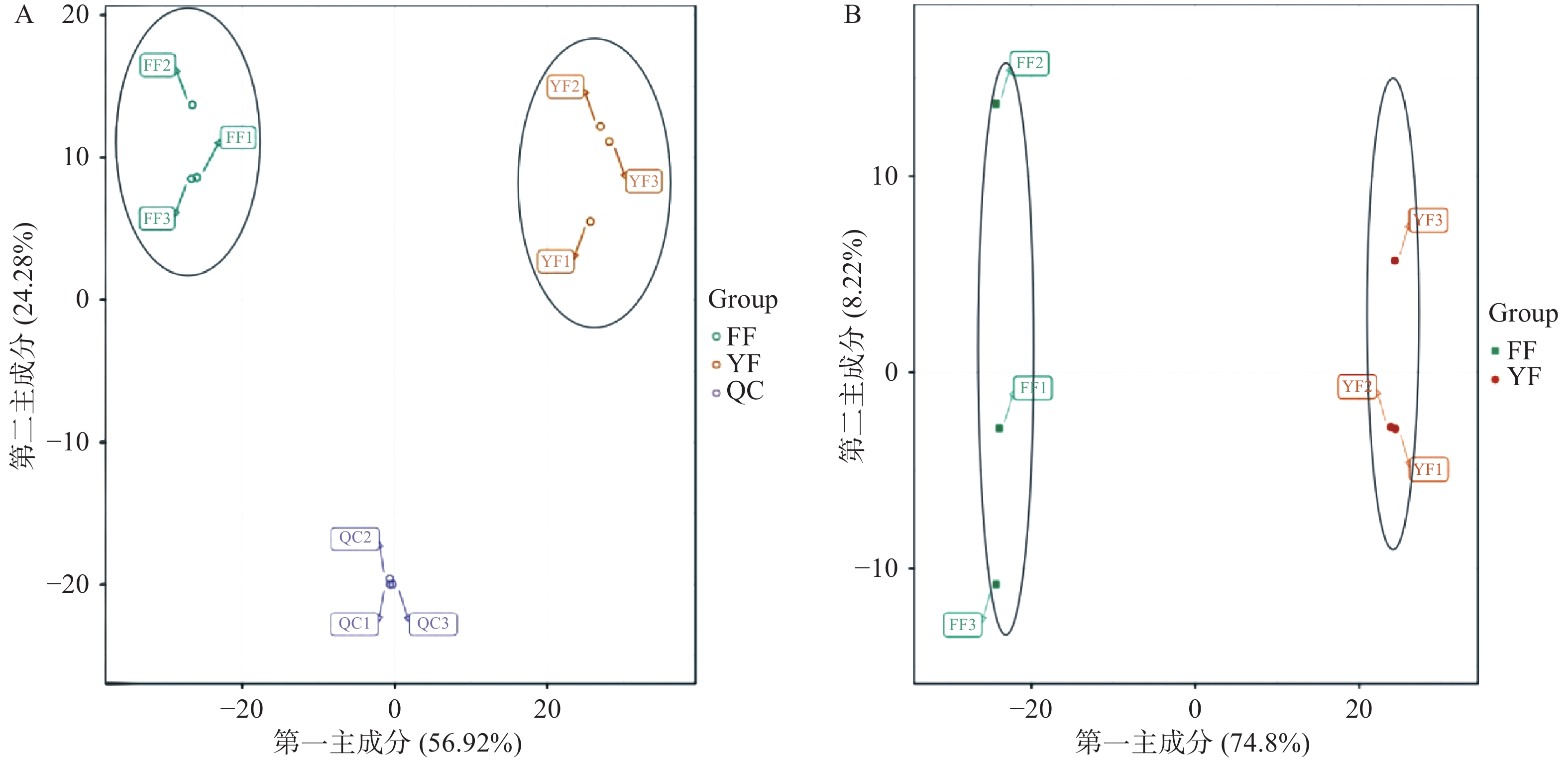
通过对样品(包括质控样品)进行PCA分析和OPLS-DA分析。如图3A所示,第一主成分(PC1)的贡献率为56.92%,第二主成分(PC2)的贡献率为24.28%,两组样本表现出显著的分离趋势;如表2所示,主成分的累计贡献率达94.03%,因此在PCA结果上能够从总体上反映福安红茶和尤溪红茶之间的代谢物差异;如图3B所示,OPLS-DA模型得到两个主成分,PC1的贡献率为74.8%,PC2的贡献率是8.22%,两组样品的区分效果非常显著;如表3所示,OPLS-DA模型的评价参数中的指标均大于0.5且Q2>0.9,说明OPLS-DA模型构建良好,预测性可靠且有意义,可根据VIP值分析筛选差异代谢物。
表 2 PCA分析可解释变异结果(%)Table 2. Variation results based on PCA (%)PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 主成分累计贡献率 56.92 81.19 86.50 90.88 94.03 主成分方差占比 56.92 24.28 5.31 4.37 3.15 表 3 OPLS-DA模型的评价参数Table 3. The parameters of OPLS-DAs样品 R2X R2Y Q2 FF vs YF 0.83 1 0.994 注:R2Y和R2X:表示模型解释率;Q2:表示模型预测能力。 2.4 尤溪红茶与福安红茶差异代谢物分析
2.4.1 不同产地红茶差异代谢物鉴定与分析
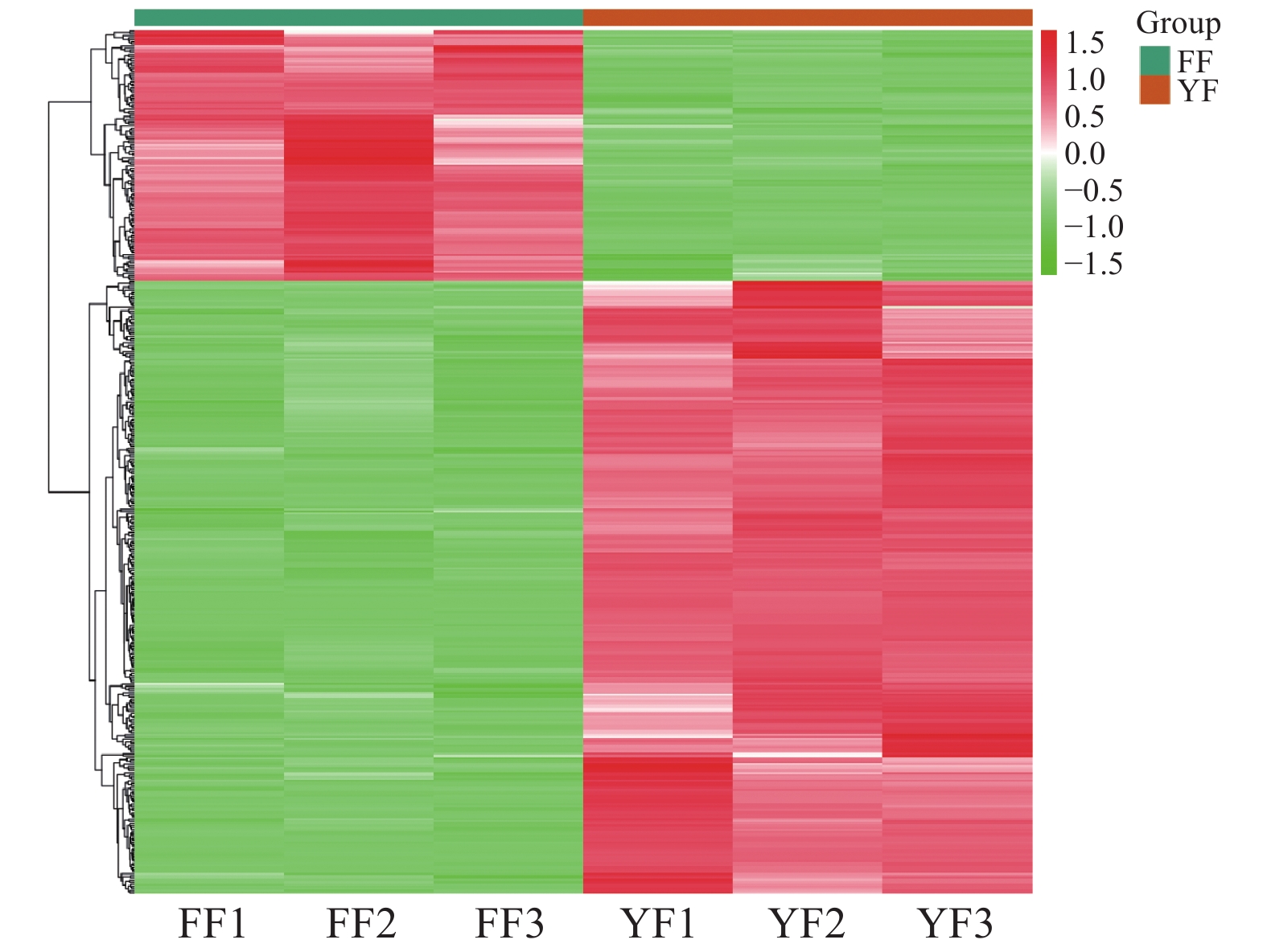
基于OPLS-DA结果,筛选VIP≥1的差异代谢物。如图4所示,福安红茶和尤溪红茶的代谢产物中鉴定出共12类410种具有显著差异的代谢物,占所有代谢物的43.8%,说明不同产区的红茶代谢物质差异显著。在410种差异代谢成分中,尤溪红茶有291种成分呈上调表达,即相对含量显著高于福安红茶,119种成分呈下调表达,即相对含量显著低于福安红茶,上调代谢物的数量远大于下调代谢物的数量。其中差异代谢物较多的是脂质、酚酸类、黄酮、氨基酸及其衍生物、有机酸5种类别,分别占比为17.5%、17.3%、17.0%、10.7%、7.3%。在所有差异代谢物中,总体上有30种黄酮、27种酚酸类、14种糖类、12种有机酸、9种生物碱物质在福安红茶中的相对含量更高,68种脂质、44种酚酸类、40种黄酮、38种氨基酸及其衍生物、24种核苷酸及其衍生物、18种有机酸、16种生物碱物质在尤溪红茶中的相对含量更高。两地红茶代谢物种类和含量上的差异,形成了各不相同的滋味特征。黄酮类物质是黄酮苷类和黄酮醇类的总称,总体上呈柔和涩味,可增强咖啡碱苦味[19]。福安红茶中有30种黄酮类物质的相对含量较高,尤溪红茶中有40种黄酮类物质的相对含量较高,在多种物质共同作用下,两地红茶滋味有一定的醇厚度。
2.4.2 不同产地红茶主要差异代谢成分分析
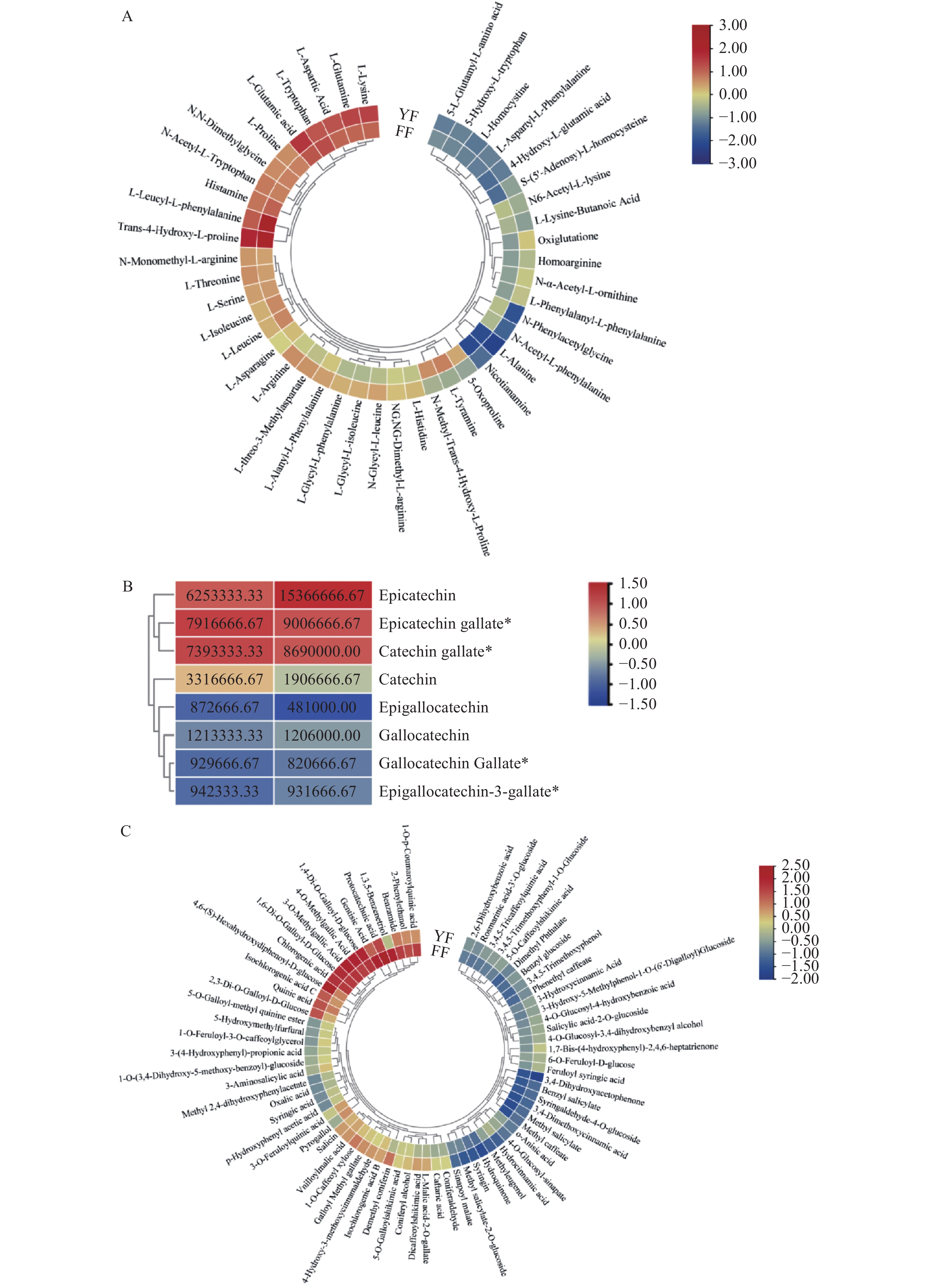
为了更清晰地观察福安红茶和尤溪红茶主要差异代谢物的折叠变化,利用TBtools生成了氨基酸及其衍生物、酚酸类以及儿茶素类化合物的热图,如图5所示。多酚类及其氧化产物、氨基酸、生物碱和有机酸等是影响红茶滋味的主要风味物质[15]。如图5A所示,在尤溪红茶中大部分氨基酸物质的含量都显著高于福安红茶,尤其是丙氨酸、苏氨酸、丝氨酸和脯氨酸等甜味氨基酸[20],其中L-苏氨酸上调6.3倍,与感官审评结果相一致,说明氨基酸物质可以作为区分不同产地红茶的关键差异代谢物。
儿茶素类化合物是茶多酚的主要成分,其含量的多少直接影响茶叶品质[21]。儿茶素中的酯类儿茶素有较强的苦涩味和收敛性,而非酯型儿茶素的涩味和收敛性都较弱,回味爽口[22]。如图5B所示,两地红茶中的儿茶素(C)、没食子儿茶素(GC)、表没食子儿茶素(EGC)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(ECG)、儿茶素没食子酸酯(CG)、没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(GCG)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(EGCG)均无显著差异,而非酯型儿茶素表儿茶素(EC)在尤溪红茶中显著上调,可能是其具有顺滑细腻口感的原因。
具有酸味的草酸和谷氨酰胺可同时影响红茶滋味的“醇味”和“厚味”,推测酸类化合物对“厚”的影响极大[23]。如图5C所示,福安红茶中草酸的含量显著上调,而尤溪红茶中的谷氨酰胺显著上调,可能是使得不同产地红茶滋味中的“醇、厚”的感官体验相似的原因,因此草酸和谷氨酰胺在一定程度上也可以作为区分两地红茶的差异代谢物。
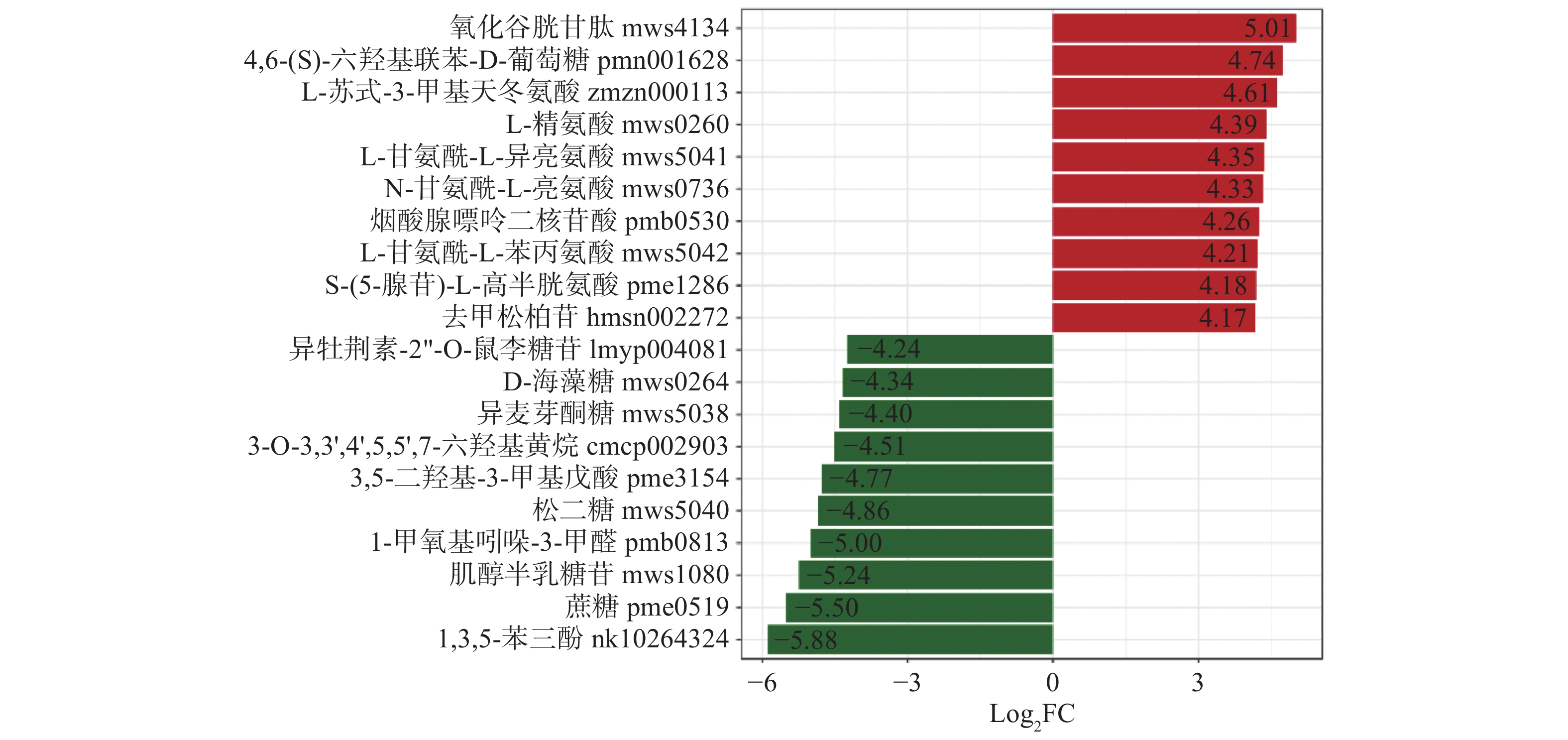
计算样品中代谢成分定量信息的差异倍数变化、并进行log2处理,变化排名在前的20个差异表达代谢成分如图6所示。与福安红茶相比,尤溪红茶有7种氨基酸及其衍生物(氧化谷胱甘肽、L-苏式-3-甲基天冬氨酸、L-精氨酸、L-甘氨酰-L-异亮氨酸、N-甘氨酰-L-亮氨酸、L-甘氨酰-L-苯丙氨酸、S-(5-腺苷)-L-高半胱氨酸、),2种酚酸类(4,6-(S)-六羟基联苯-D-葡萄糖、去甲松柏苷),1种核苷酸及其衍生物(烟酸腺嘌呤二核苷酸)的相对含量显著高于福安红茶;5种糖类(D-海藻糖、异麦芽酮糖、松二糖、肌醇半乳糖苷、蔗糖),两种黄酮(异牡荆素-2''-O-鼠李糖苷、3-氧-(3,4-二羟基-5-甲氧基苯甲酰基)3,3',4',5,5',7-六羟基黄烷),一种生物碱(1-甲氧基吲哚-3-甲醛),一种酚酸类(1,3,5-苯三酚),一种有机酸(3,5-二羟基-3-甲基戊酸)的相对含量显著低于福安红茶。结果表明,尤溪红茶中相对含量较高的主要差异代谢物是氨基酸及其衍生物,而福安红茶中的则是糖类物质。其中尤溪红茶中L-精氨酸的含量上调21倍,会产生苦味和甜味[24];而福安红茶中蔗糖的含量则上调45.2倍,但在感官审评结果中并没有突显甜味差异,主要是由于茶叶中糖类含量较低、对甜味强度的影响很小,这与Scharbert等[25]的研究结论是一致的。
2.4.3 不同产地红茶差异代谢物通路分析
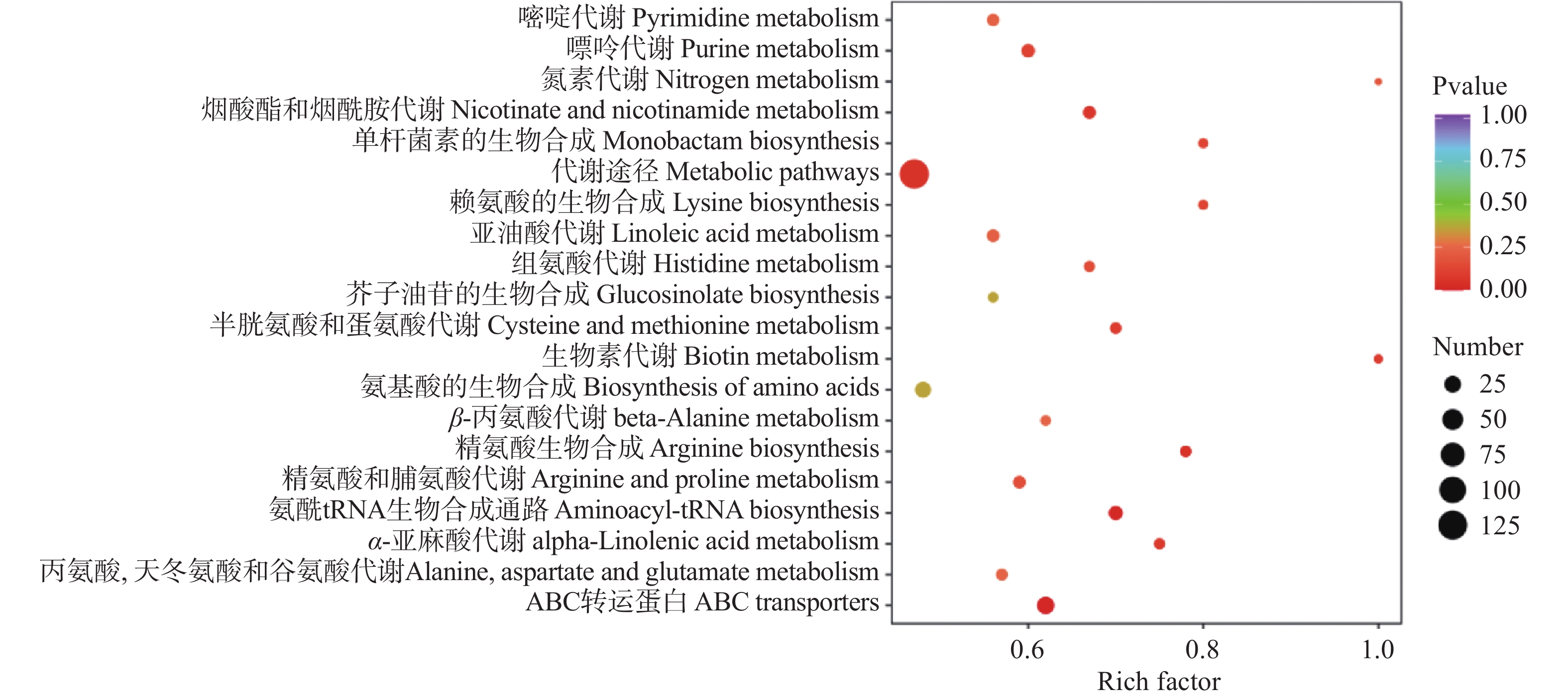
通过KEGG数据库对差异代谢物进行通路富集分析,共有84条通路,在鉴定出来的410种差异显著的代谢物中被KEGG注释到的个数为164个,其中有114个差异代谢物显著上调,50个差异代谢物显著下调,主要分布在20条代谢途径中(图7),其中富集程度最高的(pvalue值越接近0,表示富集越显著)前5条通路分别为:①ABC转运蛋白通路(ABC transporters),主要包括核苷酸及其衍生物、氨基酸及其衍生物、糖类等28种代谢成分;②氨酰tRNA生物合成通路(Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis),主要包括核苷酸及其衍生物、氨基酸及其衍生物等14种代谢成分;③精氨酸生物合成通路(Arginine biosynthesis),主要包括氨基酸及其衍生物、有机酸等7种代谢成分;④代谢途径(Metabolic pathways),主要包括核苷酸及其衍生物、氨基酸及其衍生物、糖类、有机酸、生物碱、酚酸类、黄酮、维生素等127种代谢成分;⑤烟酸酯和烟酰胺代谢(Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism),主要包括核苷酸及其衍生物、有机酸、维生素等10种代谢成分。
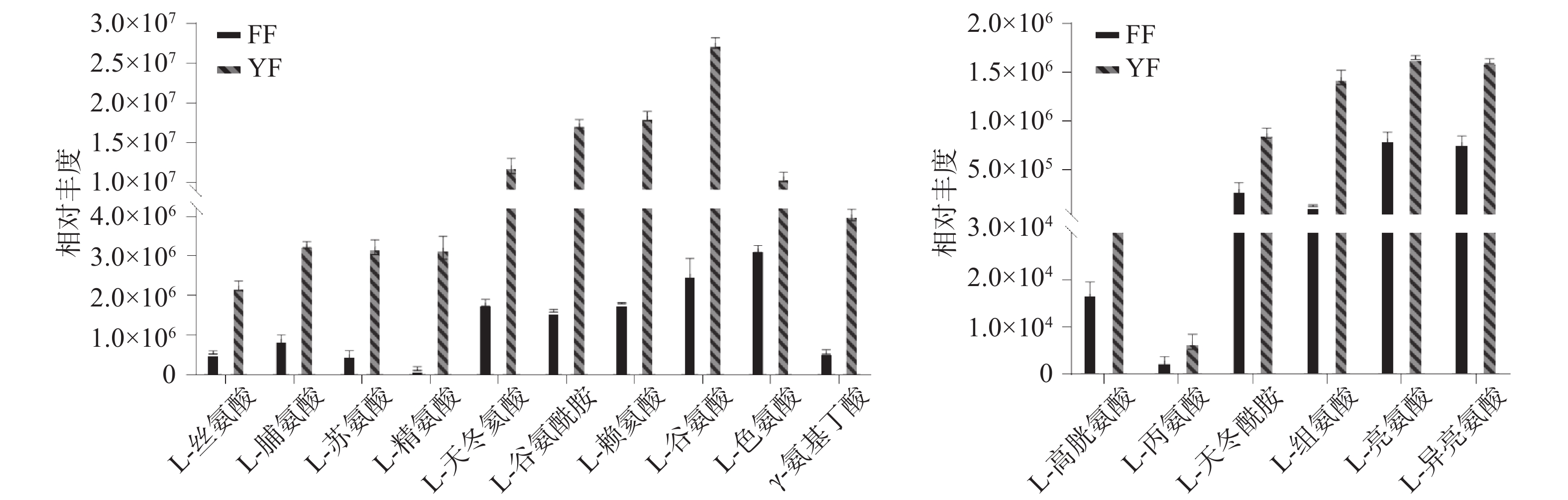
氨基酸类物质参与ABC转运蛋白、氨酰tRNA生物合成、精氨酸生物合成、烟酸酯和烟酰胺代谢、氨基酸生物合成、苯丙氨酸代谢等多条通路,被KEGG注释到的有29种,其中有25种显著上调,4种显著下调,是两地红茶的代谢物中重要的部分,对其风味和品质有着密切关系。如图8所示,尤溪红茶中γ-氨基丁酸上调了7倍,是茶叶中一种重要的生物活性成分,有各种健康益处[26],此结果可能有助于尤溪开发和生产富含γ-氨基丁酸的茶叶。从图8还能看出,L-谷氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺、L-天冬酰胺、L-天冬氨酸、L-精氨酸、L-赖氨酸、L-色氨酸以及L-组氨酸等都在尤溪红茶中显著上调。其中L-谷氨酸和L-谷氨酰胺呈鲜味[20];L-天冬氨酸有酸味、略带鲜味,而L-天冬酰胺带有苦味,但这两种氨基酸在适宜条件下可结合形成阿斯巴甜物质,其甜度是蔗糖的200倍[27];L-精氨酸、L-赖氨酸L-色氨酸和L-组氨酸都是苦味氨基酸,前两者均可产生苦味和甜味,后两者则可以作为神经递质前体[24,28],并且这些上调的氨基酸物质都参与了7条以上的代谢通路,其中L-天冬氨酸和L-谷氨酸参与了19条代谢通路,分别上调6.7倍和10.9倍,因此,以上这些氨基酸物质的相互作用可能是形成尤溪红茶优良的品质和滋味特征的原因。Ji等[29]发现光照强度较高的茶叶中氨基酸含量较低,尤其是亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、谷氨酰胺、丙氨酸、苏氨酸、天冬酰胺和天冬氨酸,由此可以推测形成两地红茶不同滋味特征的原因,可能是尤溪和福安两地因其地理位置的差异,产生不同的光照强度导致的。综上所述,相对于福安红茶,尤溪红茶是一种富含各种氨基酸物质的茶叶,涉及氨基酸代谢相关的通路对不同产地红茶的滋味品质有着重要影响。
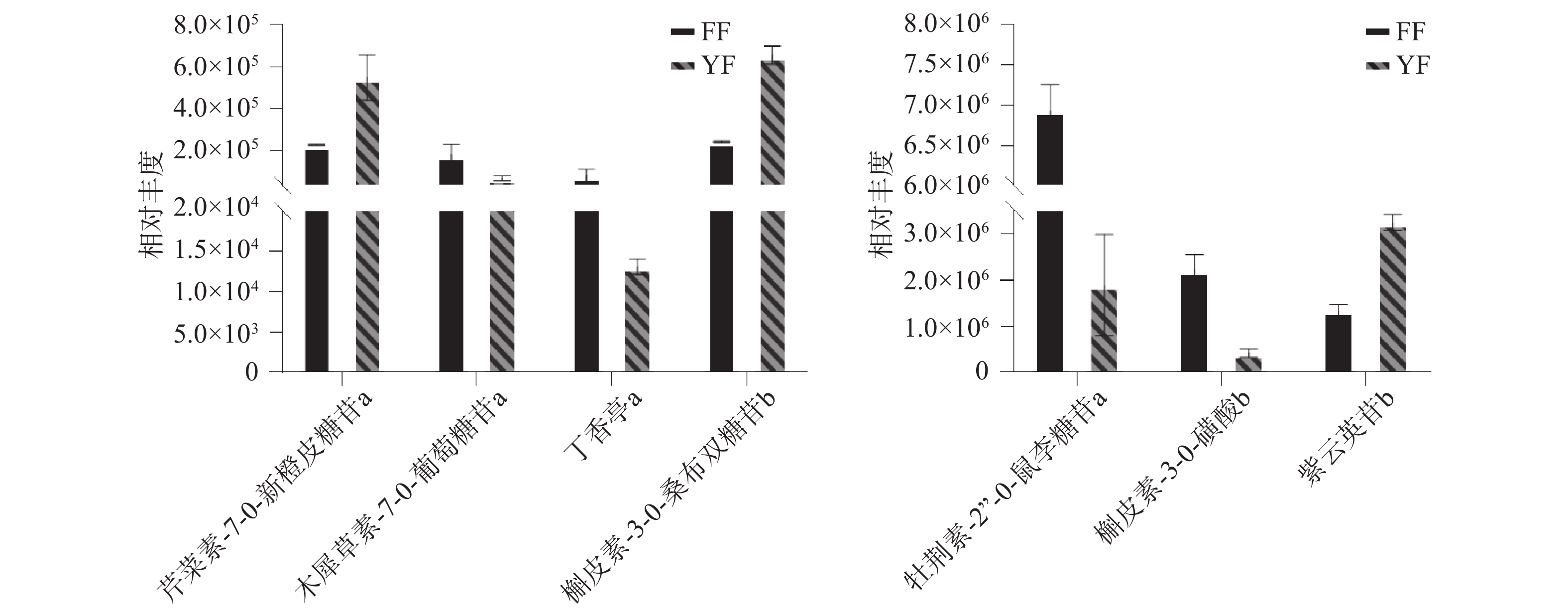
Wu等[24]研究发现,黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成以及苯丙氨酸代谢这两个代谢通路与茶叶的风味和生物活性显著相关。Dai等[30]也认为几种黄酮类化合物在茶叶味觉品质的季节变化中起主要作用,其中苯丙烷生物合成通路、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成通路以及黄酮类生物合成通路是合成黄酮-3-醇、黄酮醇、黄酮醇苷、酚酸和原花青素等特征酚类化合物最关键的途径。如图9所示,发现在黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成通路中,尤溪红茶有较高水平的黄酮醇(槲皮素-3-O-桑布双糖苷、紫云英苷)和黄酮类化合物(芹菜素-7-O-新橙皮糖苷、木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷),其中紫云英苷在尤溪红茶中上调了2.4倍,岳翠男等[23]也发现紫云英苷在红茶滋味中的回甘作用影响较大,可见,紫云英苷在尤溪红茶的滋味特征中可能也有重要贡献。另一方面,福安红茶也有较高水平的黄酮醇(槲皮素-3-O-磺酸)和黄酮类化合物(丁香亭、牡荆素-2''-O-鼠李糖苷)。
如图10所示,在苯丙烷生物合成通路中,尤溪红茶有4种酚酸物质显著上调,其中绿原酸的含量较高,上调了2.1倍,它在茶汤中呈苦涩味,并随着浓度的增加而增强[31],福安红茶有3种酚酸物质显著上调。
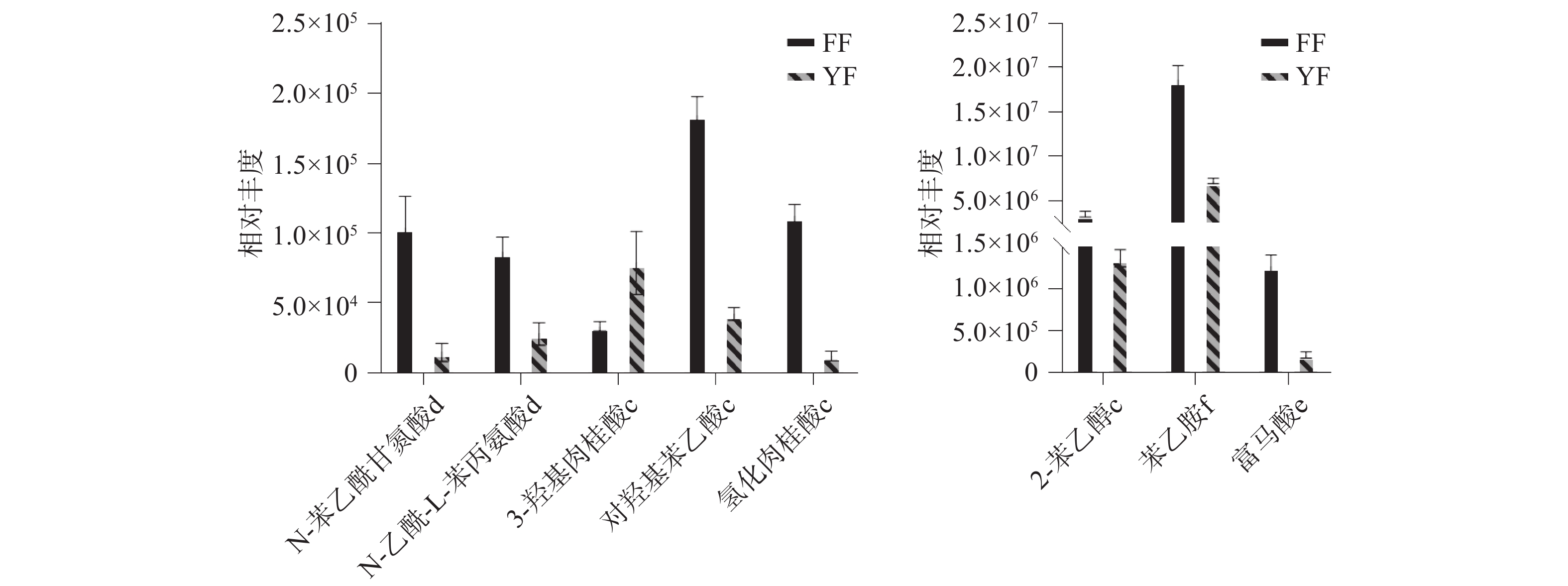
如图11所示,在苯丙氨酸代谢通路中,福安红茶的生物碱物质苯乙胺和有机酸物质富马酸都显著上调,分别升高了2.6倍和6.1倍,其中富马酸不仅参与了苯丙氨酸代谢通路,还参与其他共12条代谢通路,说明其在茶叶滋味品质中起到一定的作用,另外苯乙胺也作为一种神经递质,可以提高细胞外液中多巴胺的水平,使人感到身心愉悦[30],在一定程度上也可以作为评价茶叶品质的指标。
3. 结论
利用超高效色谱和串联质谱技术对福安红茶和尤溪红茶两个不同产地红茶进行广泛靶向代谢组学测定,在两地红茶的代谢产物中鉴定出共12类410种显著差异的代谢物,占所有代谢物的43.8%,说明不同产区的红茶代谢物质差异显著。通过对410种差异代谢成分的差异倍数进行log2处理,发现尤溪红茶中相对含量较高的主要差异代谢物是氨基酸及其衍生物,福安红茶相对含量较高的主要差异代谢物是糖类物质。此外,通过VIP值和FC值,进一步筛选到紫云英苷、表儿茶素(EC)、L-谷氨酰胺、L-天冬氨酸、L-赖氨酸、L-色氨酸、L-谷氨酸、绿原酸、苯乙胺和牡荆素-2''-O-鼠李糖苷等差异代谢产物对于两地红茶的不同滋味品质形成可能具有重要贡献。KEGG代谢通路分析发现,福安和尤溪产地红茶的氨基酸和黄酮类物质代谢水平具有显著差异,涉及氨基酸代谢和黄酮类代谢相关的通路对不同产地红茶的滋味品质有着重要影响。
综上,本研究结果可以作为判别福安红茶和尤溪红茶的依据,进一步阐明两地红茶品质的差异。由于不同产地红茶的滋味品质是受各种因素综合影响的,今后还需扩大红茶样本,并增加不同产地、不同季节、不同工艺等的比较分析,为福安和尤溪今后的红茶产品开发和生产提供参考。
-
表 1 不同产地红茶感官审评结果
Table 1 Sensory evaluation results of black tea from different origins
茶样 滋味特征 香气特征 得分(分) 福安红茶(FF) 醇和,带桂圆味,尚醇 带薯香,焦糖香 91 尤溪红茶(YF) 甘醇,顺滑,尚醇 甜香,尚浓 91 表 2 PCA分析可解释变异结果(%)
Table 2 Variation results based on PCA (%)
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 主成分累计贡献率 56.92 81.19 86.50 90.88 94.03 主成分方差占比 56.92 24.28 5.31 4.37 3.15 表 3 OPLS-DA模型的评价参数
Table 3 The parameters of OPLS-DAs
样品 R2X R2Y Q2 FF vs YF 0.83 1 0.994 注:R2Y和R2X:表示模型解释率;Q2:表示模型预测能力。 -
[1] 廖泽明, 黄雅雯, 郭雅玲. 福建红茶产业优势与发展思考[J]. 福建茶叶,2017,39(3):1−3. [LIAO Z M, HUANG Y W, GUO Y L. The advantages and development thinking of Fujian black tea industry[J]. Fujian Tea,2017,39(3):1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2291.2017.03.001 [2] 周阳, 肖文军, 林玲, 等. 红茶及其发花红砖茶对高血糖模型小鼠的降血糖作用[J]. 茶叶科学,2019,39(4):415−424. [ZHOU Y, XIAO W J, LIN L, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of black tea and Fungus fermented black brick tea on hyperglycemic model mice[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2019,39(4):415−424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2019.04.006 [3] 乔小燕, 李波, 何梓卿, 等. 黄化英红九号红茶体外抗氧化活性分析[J]. 农产品质量与安全,2018,5:85−90. [QIAO X Y, LI B, HE Z Q, et al. Analysis of antioxidant activity of Huanghuayinghong No. 9 black tea in vitro[J]. Quality and Safety of Agro-Products,2018,5:85−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8255.2018.04.016 [4] SUSMIT M, TISHYA S, SHIVRAJ N, 等. 绿茶和红茶多酚类化合物的抗病毒活性在新型冠状病毒肺炎预防和治疗中的应用[J]. 中国茶叶,2021,43(1):1−9. [SUSMIT M, TISHYA S, SHIVRAJ N, et al. Antiviral activity of green tea and black tea polyphenols in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A review[J]. China Tea,2021,43(1):1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3150.2021.01.001 [5] TAN Q, PENG L, HUANG Y, et al. Structure-activity relationship analysis on antioxidant and anticancer actions of theaflavins on human colon cancer cells[J]. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry,2018,67(1):159−170.
[6] FU G, WANG H, CAI Y, et al. Theaflavin alleviates inflammatory response and brain injury induced by cerebral hemorrhage via inhibiting the nuclear transcription factor kappa beta-related pathway in rats[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther,2018,12:1609−1619. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S164324
[7] 王淑燕, 赵峰, 饶耿慧, 等. 基于电子鼻和ATD-GC-MS技术分析茉莉花茶香气成分的产地差异[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(15):234−239. [WANG S Y, ZHAO F, RAO G H, et al. Origin Difference Analysis of Aroma Components in Jasmine Tea Based on Electronic Nose and ATD-GC-MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(15):234−239. [8] CHENG L Z, YANG Q Q, CHEN Z Y, et al. Distinct changes of metabolic profile and sensory quality during Qingzhuan tea processing revealed by LC-MS-based metabolomics[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(17):4955−4965. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00581
[9] LIU H L, ZENG Y T, ZHAO X, et al. Improved geographical origin discrimination for tea using ICP-MS and ICP-OES techniques in combination with chemometric approach[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(8):3507−3516. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10392
[10] 王子浩, 刘洋, 李明玺, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术的信阳毛尖产地判别[J]. 分子植物育种,2019,17(21):7161−7166. [WANG Z H, LIU Y, LI M X, et al. Geographical origin discriminant of Xinyang maojian tea by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2019,17(21):7161−7166. [11] 杨纯, 颜鸿飞, 吕小园, 等. 元素指纹图谱用于安化黑茶的原产地判别[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(16):286−291. [YANG C, YAN H F, LV X Y, et al. Geographical origin discrimination of Anhua dark tea by elemental fingerprint[J]. Food Science,2020,41(16):286−291. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190304-033 [12] WU X, LIU Y, GUO J Q, et al. Differentiating pu-erh raw tea from different geographical origins by H-NMR and U-HPLC/Q-TOF-MS combined with chemometrics[J]. Journal of Food Science,2021,86(3):779−791. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15624
[13] 彭云, 李果, 刘学艳, 等. 不同产地红茶香气品质的SPME/GC-MS分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(9):237−244. [PENG Y, LI G, LIU X Y, et al. SPME/GC-MS analysis of aroma quality of black tea from different producing areas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(9):237−244. [14] 赵恬欢. 不同地区红茶矿质元素分析及产地特征研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2015. ZHAO T H. Analysis of mineral elements content of black from different origins and their origin characteristics[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2015.
[15] 宋楚君, 范方媛, 龚淑英, 等. 不同产地红茶的滋味特征及主要贡献物质[J]. 中国农业科学,2020,53(2):383−394. [SONG C J, FANG F Y, GONG S Y, et al. Taste characteristic and main contributing compounds of different origin black tea[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2020,53(2):383−394. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.02.012 [16] 戴宇樵, 吕才有. 代谢组学技术在茶学中的应用研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学,2019,47(2):24−28. [DAI Y Q, LV C Y. Advances in the application of metabonomics in tea science[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(2):24−28. [17] 王春波, 吕辉, 韦玲冬, 等. 不同产地都匀毛尖茶代谢组学研究[J]. 河南农业大学学报,2021,55(3):422−428. [WANG C B, LV H, WEI L D, et al. Metabolomics study of Dunyun maojian tea from different geographical origin J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,2021,55(3):422−428.
[18] CHEN W, GONG L, GUO Z L, et al. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics[J]. Molecular Plant,2013,6(6):1769−1780. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst080
[19] SCHARBERT S, HOLZMANN N, HOFMANN T. Identification of the astringent taste compounds in black tea infusions by combining instrumental analysis and human bioresponse[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(11):3498−3508. doi: 10.1021/jf049802u
[20] YU Z M, YANG Z Y. Understanding different regulatory mechanisms of proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous amino acid formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) provides new insights into the safe and effective alteration of tea flavor and function[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020,60(5):844−858. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1552245
[21] LIU J, ZHANG Q, LIU M, et al. Metabolomic analyses reveal distinct change of metabolites and quality of green tea during the short duration of a single spring season.[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(16):3302−3309. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00404
[22] 杨晨, 戴伟东, 吕美玲, 等. 基于UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS的不同产地普洱生茶化学成分差异研究[J]. 茶叶科学,2017,37(6):605−615. [YANG C, DAI W D, LV M L, et al. Study on the chemical constituents of Pu-erh teas from different areas by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2017,37(6):605−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2017.06.007 [23] 岳翠男, 秦丹丹, 蔡海兰, 等. 赣北工夫红茶滋味特征及关键化合物分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(2):260−267. [YUE Q N, QIN D D, CAI H L, et al. Taste characteristics and key compounds analysis of Congou black tea in northern Jiangxi province[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(2):260−267. [24] WU T, ZOU R, PU D, et al. Non-targeted and targeted metabolomics profiling of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in response to its intercropping with Chinese chestnut[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2021,21(1):1−17. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02777-7
[25] SCHARBERT S, HOFMANN T. Molecular definition of black tea taste by means of quantitative studies, taste reconstitution, and omission experiments[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53(13):5377−5384. doi: 10.1021/jf050294d
[26] LIAO J, WU X, XING Z, et al. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) accumulation in tea (Camellia sinensis L. ) through the GABA shunt and polyamine degradation pathways under anoxia[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(14):3013−3018. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00304
[27] LEAN M E, HANKEY C R. Aspartame and its effects on health[J]. BMJ,2004,329(7469):755−756. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7469.755
[28] TOMOYA M, HIDEO E. Improvement of the bitterness and astringency of green tea by sub-critical water extraction[J]. Japanese Society for Food Science and Technology,2013,19(3):471−478.
[29] JI H G, LEE Y R, LEE M S, et al. Diverse metabolite variations in tea (Camellia sinensis L. ) leaves grown under various shade conditions revisited: A metabolomics study[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(8):1889−1897. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04768
[30] DAI W, QI D, YANG T, et al. Nontargeted analysis using ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry uncovers the effects of harvest season on the metabolites and taste quality of tea (Camellia sinensis L.)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(44):9869−9878. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03967
[31] 李明超, 刘莹, 杨洋, 等. 紫娟茶主要化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(8):2293−2299. [LI M C, LIU Y, YANG Y, et al. Research advance in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Zijuan tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2019,10(8):2293−2299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.08.032 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张玉龙,屈佩,徐可东,初永忠,孙畅,宫于琛,霍明宇,王宗灵,张学雷,庞敏. 毒死蜱水生生物毒性效应研究进展. 生态毒理学报. 2024(05): 135-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 貌达,刘美,杨诗嘉,向昕,王涛,闵宇航. 食品抽检监测新风险挖掘及应对策略. 食品工业. 2023(10): 316-321 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王珺冀,林枧在,张茜,曹德艳,赵思源,朱美霖. 沿海地区水产品中多溴联苯醚污染水平及健康风险评估. 现代食品. 2023(19): 146-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



