Effect of Compound Protease Treatment on the Quality Characteristics of Wheat Germ Powder
-
摘要: 利用复合蛋白酶对小麦胚芽粉进行酶解处理,分析料液比、酶量以及酶解时间对小麦胚芽粉品质特性的影响。同时选取小麦胚芽酶解粉中水溶性指数最高的三组酶解粉与奶粉进行复配并作感官评定,以确定最佳复配比。结果表明,与小麦胚芽超微粉相比,蛋白酶酶解得到的小麦胚芽粉具有更好的品质。在料液比为1:5 g/mL、酶量为4400 U/g、反应时间为2.5 h时,小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数达到最大值,为60.6 g/g,与原粉和超微粉的水溶性指数30.22、30.65 g/g相比,酶解之后提高约两倍。在料液比1:4 g/mL、酶量为4400 U/g、反应时间为2.5 h时,吸光度值由未酶解小麦胚芽粉的0.501降低到0.348,酶解小麦胚芽粉中脂肪酶的活力达到最小值。经过复合蛋白酶酶解,小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数大大提高,小麦胚芽粉的脂肪酶活力有所下降,且酶解对麦胚芽粉的色差影响不显著。在与奶粉的复配实验中,小麦胚芽粉原粉、超微粉以及酶解粉在添加量为30%时,均获得最高的感官评分。Abstract: Wheat germ powder was hydrolyzed by compound protease, and the effects of ratio of material to liquid, amount of enzyme and hydrolysis time on the quality characteristics of wheat germ powder were analyzed. At the same time, three groups of enzyme hydrolyzed powder with the highest water solubility index of wheat germ hydrolyzed powder and milk powder were compounded and sensory evaluation was made to determine the best compound ratio. The results showed that the quality of wheat germ powder hydrolyzed by protease was better than that of wheat germ ultrafine powder. When the ratio of material to liquid was 1:5 g/mL, the amount of enzyme was 4400 U/g and the reaction time was 2.5 h, the water solubility index of wheat germ powder reached the maximum, which was 60.6 g/g. Compared with the water solubility index 30.22 and 30.65 g/g of raw powder and ultra-fine powder, the water solubility index of wheat germ powder increased by about two times after enzymatic hydrolysis. When the ratio of material to liquid was 1:4 g/mL, the amount of enzyme was 4400 U/g and the reaction time was 2.5 h, the absorbance value decreased from 0.501 to 0.348 of unhydrolyzed wheat germ powder, and the lipase activity in enzymatic hydrolyzed wheat germ powder reached the minimum. After enzymatic hydrolysis with compound protease, the water solubility index of wheat germ powder was greatly increased, the lipase activity of wheat germ powder decreased, and the effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the color difference of wheat germ powder was not significant. In the experiment of compounding with milk powder, whether it was wheat germ powder, ultra-fine powder or enzyme hydrolyzed powder, the highest sensory scores was obtained when the addition amount was 30%.
-
小麦胚芽是面粉加工中的副产品,是小麦中营养最丰富的部分,不仅含有丰富的蛋白质、脂肪、维生素和矿物质,还含有多种生理活性物质,包括谷胱甘肽、凝集素、黄酮类物质等,具有抗衰老、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降低总胆固醇、降低甘油三脂等功能,是一种极具开发潜力的小麦制粉副产品[1-4]。目前小麦胚芽主要应用于焙烤制成饼干和馒头等产品[5-6]。随着消费者更加追求快节奏的消费理念,市场上涌现了各种各样的代餐粉产品。将富含多种活性成分的小麦胚芽粉与优质乳粉复配成的小麦胚芽粉,是植物蛋白与乳蛋白的完美结合[7],提高了乳粉的营养价值,丰富了乳粉的口感。但是目前市场上出售的小麦胚芽粉大多是通过低温烘熟工艺制得,溶解性较差,并且由于小麦胚芽中高脂肪和高活性的脂肪酶的存在,极易造成酸败变质。所以把小麦胚芽粉用作食品原料以前,应利用物理或者化学的方法对其进行处理,这样才能够使胚芽的稳定性得到保障,使其在食品中得到更加广泛的应用[8]。
酶解改性具有反应速度快,反应条件温和,专一性强,无氨基酸破坏或消旋现象,原料中有效成分保存完全,无害物质产生,酶解作用过程可控等特点,与酸、碱水解蛋白产物相比,酶解产物含有更多比例的多肽及较少的游离氨基酸,安全性高[9]。因此酶解改性提高食品蛋白功能特性尤其受到食品科学领域学者的关注。何希强等[10]发现碱性蛋白酶能使不同水解度的酶解产物的溶解性有明显改善,最高可达95%左右。唐世涛[11]的研究表明枯草杆菌蛋白酶处理后显著提高了蛋黄粉的水分散性、溶解度和稳定系数。Zhao等[12]通过几种蛋白酶处理大米蛋白,研究酶的种类对大米蛋白功能性质和抗氧化活性的影响,结果显示:酶解蛋白相对于原料蛋白溶解性有大幅提升,抗氧化活性也有了提高。高亚奇[13]发现,经碱性蛋白酶处理的米糠,脂肪酶遭到破坏,活性受到抑制,在储存过程中对油脂的分解作用减弱,延缓了米糠的酸败。虽然酶解改性对可以显著提高蛋白产品的品质,提高其储存稳定性。然而,关于利用酶解法提升小麦胚芽粉品质的研究还鲜有报道。
因此,本实验以复合蛋白酶酶解小麦胚芽粉,探讨了不同料液比、酶活,酶解时间对小麦胚芽粉品质特性的影响,优化酶解最佳条件,并探究了酶解小麦胚芽粉与奶粉的复配的最佳比例,为小麦胚芽的开发利用提供理论依据,开阔了小麦胚芽的市场应用前景。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜的小麦胚芽粉、小麦胚芽超微粉 盐城市天福粉业有限公司;全家营养奶粉 雀巢有限公司;复合蛋白酶(活力单位120 U/mg) 上海索来宝生物科技有限公司;阿拉伯树胶 海麦克林生化科技有限公司;异丙醇 无锡市晶科化工有限公司;曲拉通X-100 合肥博美生物科技有限公司;氢氧化钠 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;磷酸二氢钾、磷酸氢二钾、硼酸、浓硫酸、盐酸、pH7.4磷酸缓冲溶液 上海国药试剂集团。
JCS-3000 g电子天平 凯丰集团有限公司;CM-5色差仪 柯尼卡美能达;SCIENTZ-12N型冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;WSJB-03型恒温磁力搅拌器 河南中良科学仪器有限公司;WH-2型微波旋涡混合仪 上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司;RS-03型多功能粉碎机 上海荣舒工贸有限公司;HH-4型数显恒温水浴锅 常州国华电器有限公司;SHZ-82A型水浴恒温振荡器 常州朗越仪器制造有限公司;TDL-5-A型低速大容量多管离心机 上海嘉鹏科技有限公司;H1850R型台式高速冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;电热恒温培养箱 南京盈鑫实验仪器有限公司;电热鼓风干燥箱 上海苏进仪器设备厂;日立U-3900紫外分光光度计 广州市仪德科学仪器有限公司;自动进样仪 弗尔德仪器设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 小麦胚芽粉基础成分的测定
水分含量的测定按GB 5009.3-2016的常压加热干燥法;灰分含量测定按GB 5009.4-2016方法;蛋白质含量的测定按凯氏定氮法;脂肪含量的测定按GB 5009.6-2016索氏抽提法;粗纤维的测定按GB 5009.88-2014方法。
1.2.2 小麦胚芽粉的蛋白酶酶解
准确称取15 g小麦胚芽粉,加入一定酶活力的复合蛋白酶,用磷酸缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)进行溶解。将试样置于磁力搅拌器上搅拌,搅拌完成后将试样置于100 ℃的水浴锅中灭酶5 min,然后将试样倒入洁净的培养皿中,置于冰箱冷冻室12 h进行冻结,冻结完成置于冷冻干燥机进行冷冻干燥,冷冻干燥完成后用粉碎机磨粉过60目筛备用。将未经酶解的小麦胚芽粉、小麦胚芽超微粉与经过复合蛋白酶酶解的小麦胚芽酶解粉进行对比实验。
1.2.3 单因素实验
1.2.3.1 不同料液比对蛋白酶酶解小麦胚粉品质特性的影响
准确称取15 g小麦胚芽粉,加入酶量为1600 U/g的复合蛋白酶,分别量取45、60、75、90 mL的磷酸缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)进行溶解,使得料液比为1:3,1:4,1:5和1:6 g/mL,酶解操作见1.2.2。
1.2.3.2 不同反应时间对蛋白酶酶解小麦胚粉品质特性的影响
准确称取15 g小麦胚芽粉,加入酶量为1600 U/g的复合蛋白酶,以料液比为1:4 g/mL的磷酸缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)进行溶解,分别置于恒温磁力搅拌器上反应0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5 h,酶解操作见1.2.2。
1.2.3.3 不同酶用量对蛋白酶酶解小麦胚粉品质特性的影响
准确称取15 g小麦胚芽粉,分别加入400、1200、2000、2800、3600、4400 U/g的复合蛋白酶,以料液比为1:4 g/mL的磷酸缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)进行溶解并置于恒温磁力搅拌器上,反应1 h后搅拌结束,酶解操作见1.2.2。
1.2.4 水溶性指数和吸水性指数
用分析天平准确称取2.500 g小麦胚芽粉,记重量为W0。将称好的试样对应放入相应编号的已知重量的50 mL塑料带盖离心管中,记离心管质量为W1。向各离心管中分别加入35 mL去离子水,用微型旋涡混合仪搅拌成悬浮液。将搅拌好的悬浮液置于30 ℃水浴中保温30 min,每隔是5 min间歇性搅拌。水浴完成后,将试样置于离心机以3000 r/min的速度离心15 min。取干燥至恒重的洁净玻璃皿,记重量为W2,并相应编号。将离心好的上清液按照对应的编号缓慢倒入相应的玻璃皿中,在105 ℃的烘箱中干燥至恒重,记质量为W3。对除去上清液的离心管和沉淀进行称重,记重量为W4[14]。
按照下式计算水溶性指数和吸水性指数:
水溶性指数(g/g)=W3−W2W0 (1) 吸水性指数(%)=W4−W1W0×100 (2) 1.2.5 色差的测定
取适量小麦胚芽粉置于培养皿中,使试样均匀地铺满整个培养皿内,将培养皿置于待测部位进行测量,记录L*、a*和b*值。每个样品重复测量3次,3次平均值作为该样品的最终色度值。其中L*是样品颜色的亮度,值越大越亮;a*、b*是色方向,+a*为红色方向,−a*为绿色方向,+b*为黄色方向,−b*为蓝色方向[15]。
按照下式计算色差值[16]
ΔE=√(L*−L*s)2+(a*−a*s)2+(b*−b*s)2 (3) 式中,Ls、as、bs为标准白色瓷板的测定值,分别为97.13、0.21、1.87。
1.2.6 脂肪酶活力测定
准确称量0.1 g小麦胚芽粉置于10 mL的具塞试管中,量取0.4 mL的磷酸缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)加入试管旋涡混合。用移液枪分别吸取0.2 mL的溶液甲(0.1 g对硝基苯酚月桂酸溶解在30 mL异丙醇中)和3 mL的溶液乙(0.4 g曲拉通X-100和0.1 g阿拉伯胶溶解在90 mL 0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液中)加入到盛有试样的试管中旋涡混合。将试管置于35 ℃水浴中震荡加热1 h后将其置于100 ℃的沸水浴中灭酶5 min,再快速冷却至室温。将上述反应物置于离心机中,以6000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液稀释,于410 nm处测定吸光度。以吸光度为指标比较脂肪酶活力,吸光度越大,脂肪酶活力也越大[17]。
1.2.7 小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配
选取水溶性指数最大的三种酶解粉,将这三种酶解粉与奶粉以10%、20%、30%、40%和50%的比例进行复配,准确称取5 g复配粉,加入50 mL的不低于85 ℃的开水进行冲调[18]。
对相应比例的原粉和超微粉进行对比进行感官评分。由10位经过训练的学生组成感官评定小组,分别对样品的口感、风味、色泽和冲调性四个方面进行评价与评分,每项满分为25分,总分100分。感官评分标准见表1。
表 1 感官评分标准Table 1. Sensory scoring criteria项目 评分细则 分值(分) 口感(25分) 口感香甜,入口后润滑,细腻无颗粒或沉淀 18~25 口感香甜,入口后有少量沉淀或颗粒 9~17 口感香甜,入口后不润滑,有粗糙感,明显的不适口性 0~8 风味(25分) 具有小麦胚芽特有的麦胚香,牛奶的乳香,二者气味融合的很好 18~25 有小麦胚芽的香气,牛奶的奶味略浓;有一定的复合滋味,轻微腥味,无其他异味 9~17 小麦胚芽的香气淡,牛奶的味道太浓;无复合滋味,小麦胚芽的腥气明显 0~8 色泽(25分) 均匀一致有光泽的浅黄色 18~25 浅黄白色,光泽度差;黄色,光泽度差 9~17 白色;暗黄色,无光泽 0~8 冲调性(25分) 迅速溶解,均匀无分层,静置一段时间有微量的沉淀 18~25 有少量的结块,略搅拌结块溶解,静置一段时间有部分沉淀 9~17 有较多结块,搅拌后大部分结块溶解,部分不容,静置一段时间后有大量沉淀 0~8 1.3 数据处理
利用Origin8软件,对数据进行统计分析与做图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 小麦胚芽成分分析
所用小麦胚芽粉基本成分如表2所示,小麦胚芽粉的水分、粗纤维含量低于小麦粉[19],而脂肪、蛋白质、灰分均高于小麦粉。
表 2 小麦胚芽粉基础成分Table 2. Basic components of wheat germ flour成分 水分 脂肪 蛋白质 灰分 粗纤维 含量(%) 9.11 10.70 29.66 4.80 1.9 2.2 复合蛋白酶处理对小麦胚芽粉水溶性指数和吸水性指数的影响
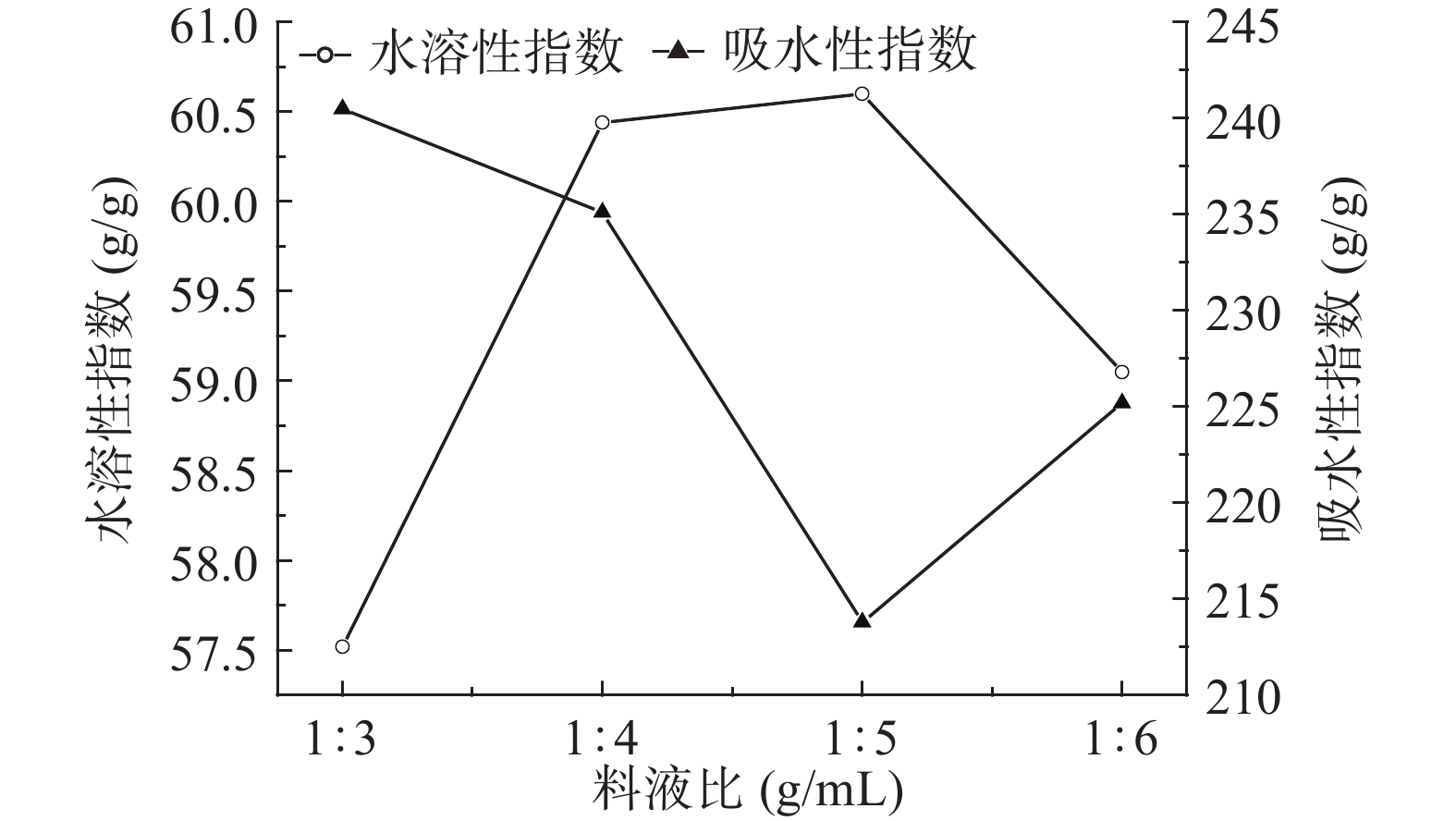
2.2.1 料液比对小麦胚芽粉水溶性指数和吸水性指数的影响
水溶性指数和吸水性指数是评价物料溶解性和冲调性的2个重要指标,水溶性指数越高,说明物料中可溶性物质越多,溶解性越好;吸水指数越高,说明物料吸水溶胀性和成胶性越好[20-22]。经本试验得知小麦胚芽原粉的水溶性指数为29.72 g/g,吸水性指数为272.83 g/g;小麦胚芽超微粉的水溶性指数为30.65 g/g,吸水性指数255.15 g/g。通过超微处理只能稍微提高小麦胚芽粉溶解性。
如图1所示,小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数随着料液比的增加先升高后降低,吸水性指数随着料液比的增加先降低后升高。小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数在料液比为1:5 g/mL时达到最大值60.6 g/g,但此时吸水性指数为最小值213.8 g/g。从原料的成分中可以看出小麦胚芽中蛋白质含量丰富(29.66%),当料液比低于1:5 g/mL时,小麦胚芽中的大分子蛋白质被复合蛋白酶降解成为小分子,导致蛋白质的三维结构被破坏,使得小麦胚芽的水溶性指数上升,吸水性指数下降[23],当料液比超过1:5 g/mL时,由于加液量过多,复合蛋白酶的浓度被稀释,降低了酶与底物(小麦胚芽中的蛋白质)的接触机会,导致酶解不充分,从而造成小麦胚芽的水溶性指数下降和吸水性指数上升。当料液比低于1:3 g/mL时,加液量过少,体系粘度太大,不利于底物和酶充分接触,同样降低了酶解作用效果。所以料液比应选择在1:5~1:3 g/mL之间比较适宜。
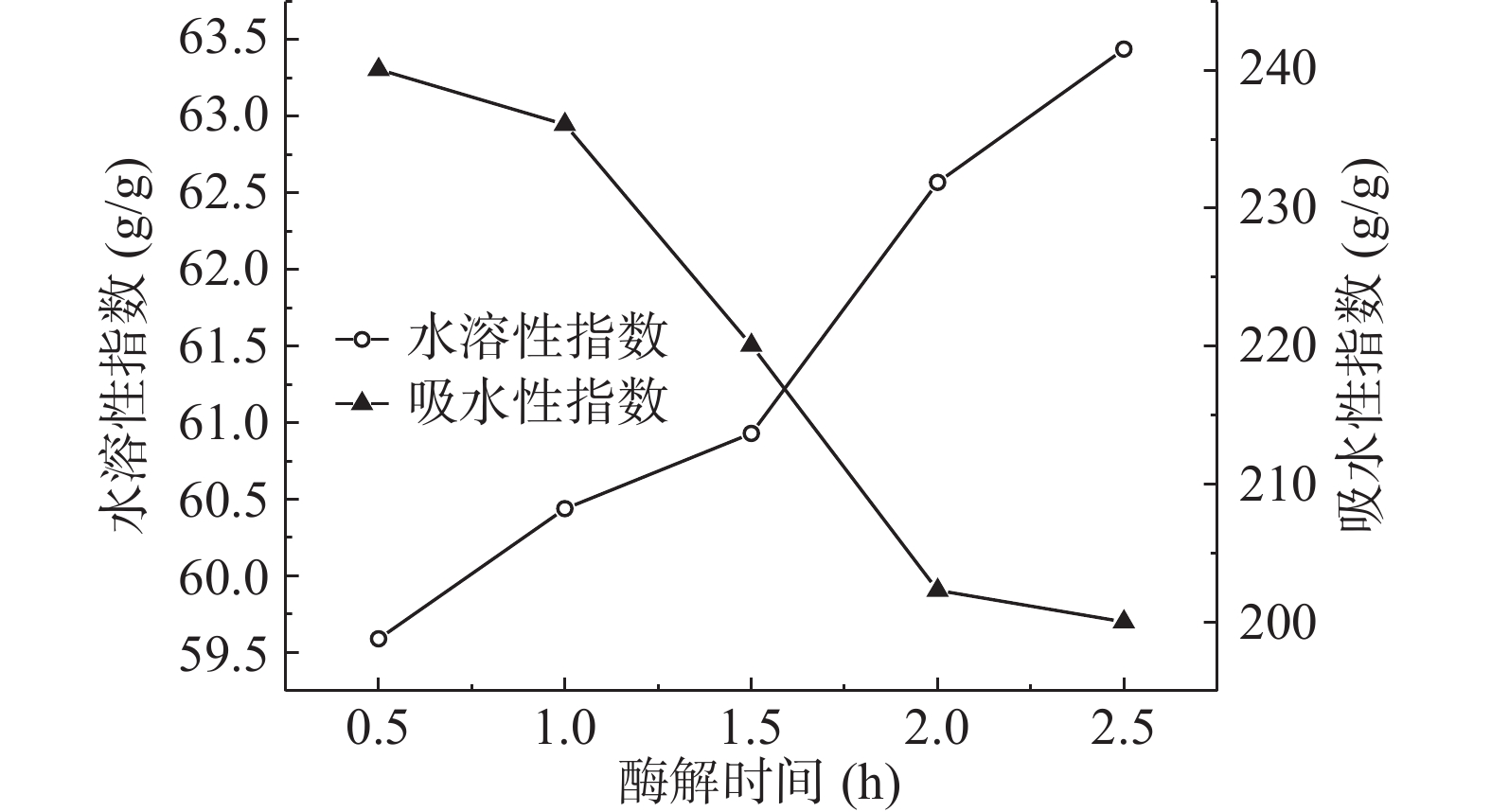
2.2.2 复合蛋白酶的作用时间对小麦胚芽粉水溶性指数和吸水性指数的影响
如图2所示,随着反应时间的增加小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数升高,吸水性指数降低。酶解反应0.5 h时,其水溶指数为59.59 g/g,吸水性指数为240.08 g/g;酶解反应2.5 h时,其水溶指数为63.44 g/g,吸水性指数为200.01 g/g。随着反应时间的延长,复合蛋白酶与底物的接触更加充分,反应也更加完全,从而得到更多的水溶性小分子肽,达到小麦胚芽的水溶性指数升高,吸水性指数降低的效果。当酶解时间为2.5 h时,小麦胚芽粉具有最高的水溶性指数,溶解性最好。
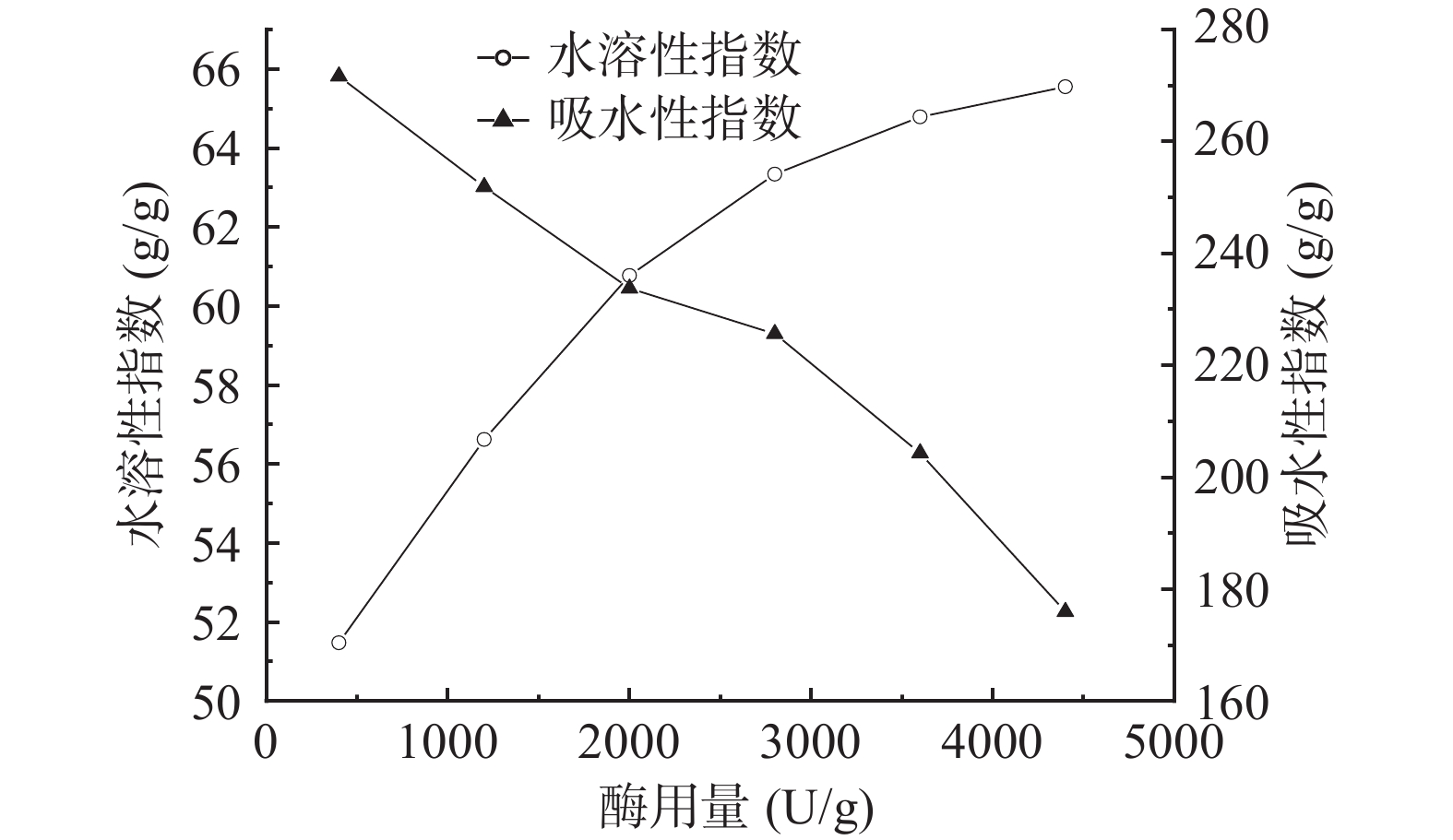
2.2.3 复合蛋白酶的用量对小麦胚芽粉水溶性指数和吸水性指数的影响
如图3所示,小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数随着复合蛋白酶酶量的增加而升高,当酶量达到3600 U/g时,水溶性指数随酶活力的增加而变化平缓。由于酶具有高度专一性,当底物浓度一定,随着酶用量的增加,蛋白酶与蛋白质分子的接触概率增加,从而使得在一定时间内能够获得更多的具有水溶性的小分子多肽;但当酶用量超过3600 U/g,小麦胚芽的水溶性指数增加减缓,这是因为随着酶活力的进一步增加,底物被饱和,过多的酶分子没有底物所作用的缘故。小麦胚芽的吸水性指数随着复合蛋白酶的酶活增加而降低,可能是由于蛋白质的三维结构在酶解过程中被破坏,导致了蛋白质的吸水性下降,从而降低了小麦胚芽的吸水性[24]。因此,酶用量为4400 U/g时,复合蛋白酶酶解的小麦胚芽粉有较好的水溶性指数。
2.3 复合蛋白酶处理对小麦胚芽粉色差的影响
通过超微处理,超微粉较原粉亮度提升,色差ΔE由25.64变化为22.46,差值ΔE’<4(表3),肉眼可看到较明显的色泽变化,但仍属可接受范围[25-26]。对于加入复合蛋白酶处理的小麦胚芽粉,亮度稍暗,颜色偏黄绿,可能是由于酶解产生的小分子多肽与小麦胚芽中的糖类物质发生了美拉德反应。色差ΔE’<4,属于可接受范围。不同料液比之间总色差ΔE的差值ΔE’<2,表明料液比的变化对小麦胚芽粉的色差无影响。L*值随着复合蛋白酶的反应时间的延长,整体呈下降趋势,色泽越来越暗;色差ΔE随着复合蛋白酶的反应时间的延长整体呈上升趋势,这可能是随着反应时间的延长,产生了更多地小分子多肽,并且延长了与糖类的反应时间,通过美拉德反应生成更多地褐色物质。但在反应2.0 h后色差变化趋于稳定,进一步延长反应时间,ΔE’<2,色泽变化不明显。在反应2.5 h时,ΔE为29.29,反应0.5 h时,ΔE为22.47,与原粉ΔE’<4,肉眼可看到较明显的色泽变化,但仍属可接受范围。随着复合蛋白酶酶活的增加,ΔE先逐渐增大然后下降,与原粉ΔE’<4,肉眼可看到较明显的色泽变化,但仍属可接受范围,在接下来与奶粉复配中,对色泽感官指标无影响。综上所述,复合蛋白酶的酶解对小麦胚芽粉的色差有微小的影响,但在特定应用范围内可以接受,对小麦胚芽粉的加工应用不设限。
表 3 复合蛋白酶的料液比、酶添加量、反应时间对小麦胚芽粉色差的影响Table 3. Effect of material-liquid ratio, enzyme addition and reaction time of compound protease on the color difference of wheat germ flour类别 ΔE 类别 ΔE 类别 ΔE 原粉 25.64 复合蛋白酶的酶量400 U/g 30.11 反应时间0.5 h 22.47 超微粉 22.46 复合蛋白酶的酶量1200 U/g 25.28 反应时间1.0 h 24.9 料液比值1:3 g/mL 29.2 复合蛋白酶的酶量2000 U/g 25.43 反应时间1.5 h 30.92 料液比值1:4 g/mL 24.79 复合蛋白酶的酶量2800 U/g 28.94 反应时间2.0 h 28.34 料液比值1:5 g/mL 29.32 复合蛋白酶的酶量3600 U/g 31.24 反应时间2.5 h 29.29 料液比值1:6 g/mL 29.14 复合蛋白酶的酶量4400 U/g 26.27 2.4 复合蛋白酶处理对小麦胚芽粉脂肪酶活力的影响
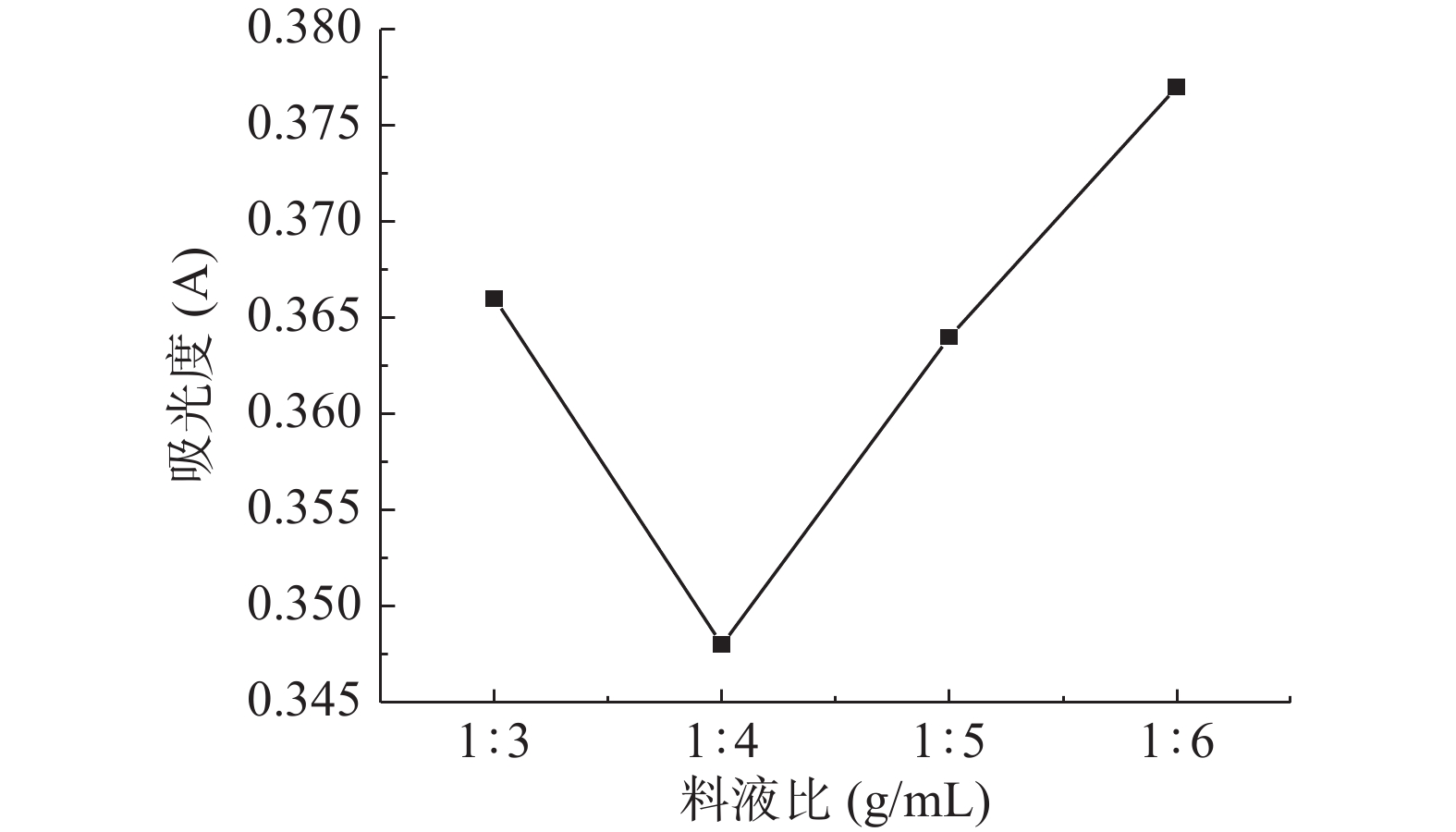
2.4.1 料液比对脂肪酶活力的影响
经本实验测得小麦胚芽原粉中含有的脂肪酶所对应的吸光度值为0.501,经过复合蛋白酶酶解处理后,吸光度值显著(P<0.05)下降,说明通过酶法对小麦胚芽脂肪酶进行稳定化处理是有效果的。由图4可知,小麦胚芽中的脂肪酶活力随着料液比的增加先降低后升高,且在料液比为1:4 g/mL时酶活力最弱。当料液比高于1:4 g/mL时,由于加液量过多,造成复合蛋白酶的浓度被稀释,降低了酶与底物(小麦胚芽中的脂肪酶)的接触机会,导致酶解不充分,脂肪酶灭活不够彻底;当料液比小于1:4 g/mL时,加液量过少,体系粘度太大,不利于底物和酶的充分接触,同样降低了灭酶效果。所以料液比最优条件为1:4 g/mL。
2.4.2 复合蛋白酶的作用时间对小麦胚芽粉脂肪酶活力的影响
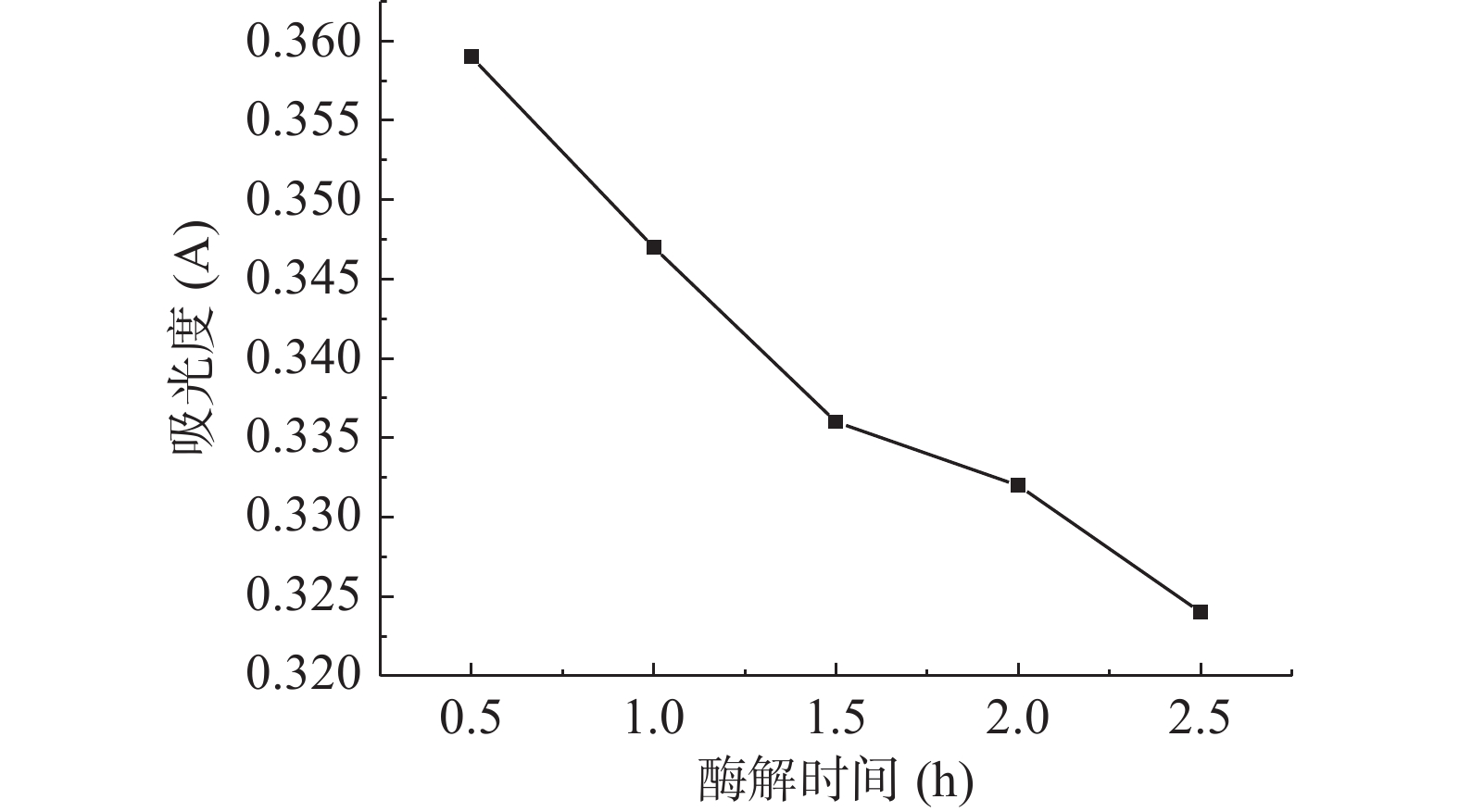
由图5可知,小麦胚芽的脂肪酶活力随着复合蛋白酶的反应时间的延长而下降。随着反应时间的延长,复合蛋白酶与底物脂肪酶接触的更加充分,反应也更加完全,脂肪酶被灭的越彻底,从而达到更好的稳定小麦胚芽的效果[27]。因此,当反应时间为2.5 h时对脂肪酶的抑制最有效。
2.4.3 复合蛋白酶的用量对小麦胚芽粉脂肪酶活力的影响
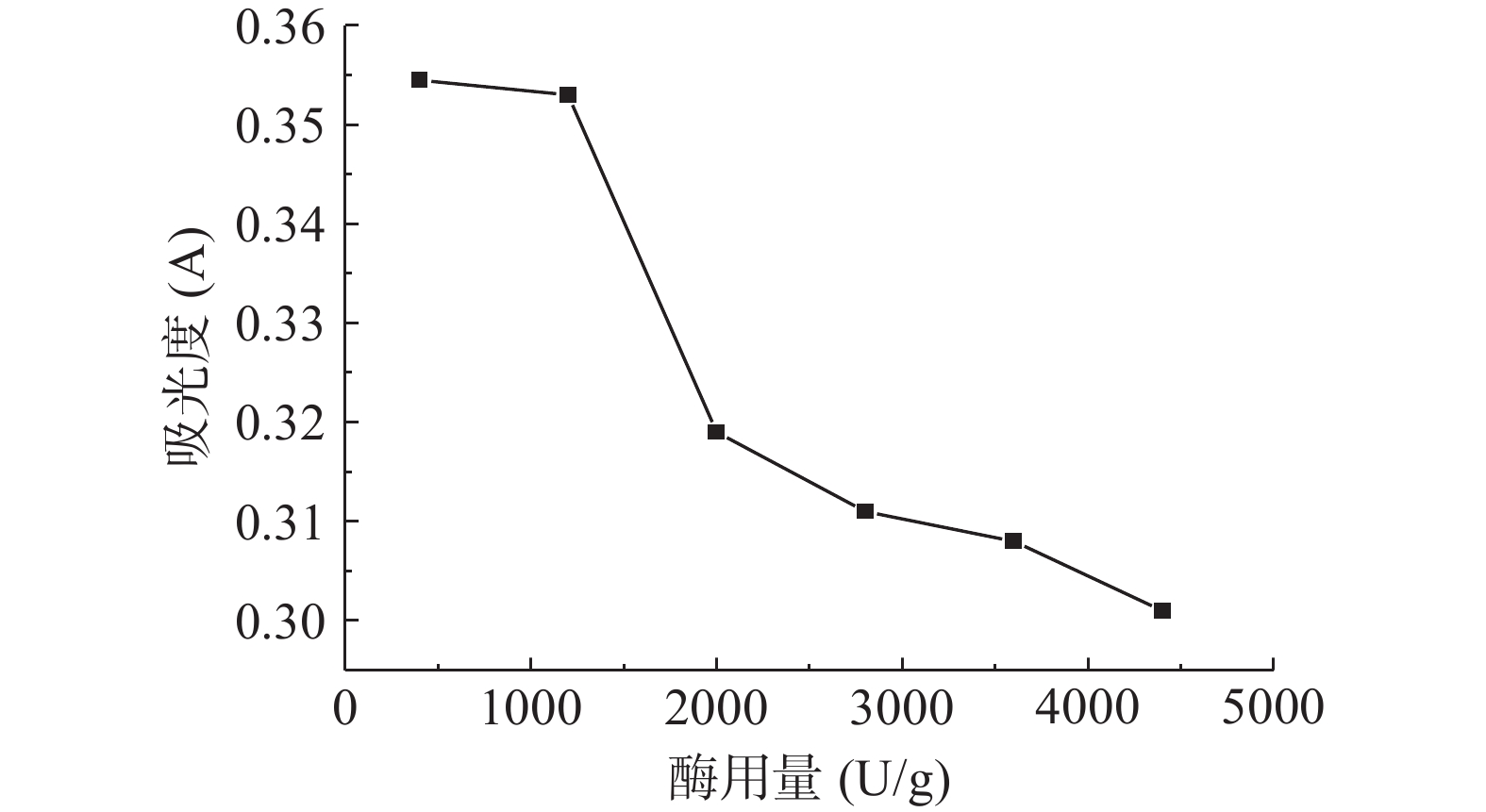
由图6可知,小麦胚芽粉的脂肪酶活力随着复合蛋白酶的酶用量的增加而下降。先是迅速下降,当复合蛋白酶的酶活达到一定浓度时就下降得比较平缓。由于酶的专一性,复合蛋白酶酶活的增加意味着酶的浓度的升高,在底物浓度一定时,提高酶浓度会加速酶解反应进程,所以脂肪酶活力迅速下降,但当酶浓度升高到与底物浓度近饱和时,整个反应速度已然达到最大,再逐步提高酶的浓度也改变甚微,因此脂肪酶活力下降的平缓[28-29]。选择酶用量4400 U/g为最优条件,进行下一步实验。
2.5 小麦胚芽粉奶粉的复配结果
将小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配不仅可以丰富产品的营养价值还可以提高小麦胚芽粉的商业价值。由表4的感官评分结果可知,在相同比例下,添加酶解的小麦胚芽粉的产品感官评分大于添加未经酶解的小麦胚芽粉的实验组。这是由于复合蛋白酶水解后的小麦胚芽粉的水溶性指数远大于原粉,使其冲调性能优于原粉实验组。当小麦胚芽粉添加量为30%时,感官评分平均值大于其他组。因为当小麦粉比例过大时,麦腥味较重,严重影响复配粉风味,感官评分较差;当小麦胚芽粉比例过小时,奶味略重,掩盖住了小麦胚芽粉的特有风味。所以选择30%的水溶性指数最高的酶解小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配,能得到最优小麦胚芽粉奶粉复配比例。
表 4 小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配的感官评分结果Table 4. Sensory score table of the mixture of wheat germ powder and milk powder项目 评分(分) 复配比例 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 原粉 43 57 70 40 20 超微粉 45 62 80 47 32 料液比1:4 g/mL的酶解粉 50 67 90 58 40 酶量4400 U/g的酶解粉 55 68 79 53 33 反应时间2.5 h酶解粉 53 73 98 64 49 3. 结论
实验结果表明,当料液比为1:4 g/mL,酶解时间为2.5 h,酶量为4400 U/g酶解效果最好。复合蛋白酶使小麦胚芽粉的溶解性大大提高,脂肪酶活力受到抑制,但同时对小麦胚芽粉的色差影响不显著,说明复合蛋白酶酶解对小麦胚芽粉具有较好的改良作用。且由结果可知复合蛋白酶酶解小麦胚芽粉的品质优于未酶解小麦胚芽粉和小麦胚芽超微粉。将小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配,发现小麦胚芽粉添加量为30%时,代餐粉冲调性好,味道佳,营养价值被大大提升。此实验是对复合蛋白酶酶解小麦胚芽粉的初步探究,下一步还可继续研究温度、pH、金属离子对其酶解效果的影响。
-
表 1 感官评分标准
Table 1 Sensory scoring criteria
项目 评分细则 分值(分) 口感(25分) 口感香甜,入口后润滑,细腻无颗粒或沉淀 18~25 口感香甜,入口后有少量沉淀或颗粒 9~17 口感香甜,入口后不润滑,有粗糙感,明显的不适口性 0~8 风味(25分) 具有小麦胚芽特有的麦胚香,牛奶的乳香,二者气味融合的很好 18~25 有小麦胚芽的香气,牛奶的奶味略浓;有一定的复合滋味,轻微腥味,无其他异味 9~17 小麦胚芽的香气淡,牛奶的味道太浓;无复合滋味,小麦胚芽的腥气明显 0~8 色泽(25分) 均匀一致有光泽的浅黄色 18~25 浅黄白色,光泽度差;黄色,光泽度差 9~17 白色;暗黄色,无光泽 0~8 冲调性(25分) 迅速溶解,均匀无分层,静置一段时间有微量的沉淀 18~25 有少量的结块,略搅拌结块溶解,静置一段时间有部分沉淀 9~17 有较多结块,搅拌后大部分结块溶解,部分不容,静置一段时间后有大量沉淀 0~8 表 2 小麦胚芽粉基础成分
Table 2 Basic components of wheat germ flour
成分 水分 脂肪 蛋白质 灰分 粗纤维 含量(%) 9.11 10.70 29.66 4.80 1.9 表 3 复合蛋白酶的料液比、酶添加量、反应时间对小麦胚芽粉色差的影响
Table 3 Effect of material-liquid ratio, enzyme addition and reaction time of compound protease on the color difference of wheat germ flour
类别 ΔE 类别 ΔE 类别 ΔE 原粉 25.64 复合蛋白酶的酶量400 U/g 30.11 反应时间0.5 h 22.47 超微粉 22.46 复合蛋白酶的酶量1200 U/g 25.28 反应时间1.0 h 24.9 料液比值1:3 g/mL 29.2 复合蛋白酶的酶量2000 U/g 25.43 反应时间1.5 h 30.92 料液比值1:4 g/mL 24.79 复合蛋白酶的酶量2800 U/g 28.94 反应时间2.0 h 28.34 料液比值1:5 g/mL 29.32 复合蛋白酶的酶量3600 U/g 31.24 反应时间2.5 h 29.29 料液比值1:6 g/mL 29.14 复合蛋白酶的酶量4400 U/g 26.27 表 4 小麦胚芽粉与奶粉复配的感官评分结果
Table 4 Sensory score table of the mixture of wheat germ powder and milk powder
项目 评分(分) 复配比例 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 原粉 43 57 70 40 20 超微粉 45 62 80 47 32 料液比1:4 g/mL的酶解粉 50 67 90 58 40 酶量4400 U/g的酶解粉 55 68 79 53 33 反应时间2.5 h酶解粉 53 73 98 64 49 -
[1] GELMEZ N, KNCAL N S, YENER M E. Optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of antioxidants from roasted wheat germ based on yield, total phenolic and tocopherol contents, and antioxidant activities of the extracts[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2009,48(3):217−224. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2008.11.002
[2] 陈飞雪, 包志华. 小麦胚芽营养价值及发酵食品的研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2016,3(45):66−67. [CHENG F X, BAO Z H. Research progress on nutritional value and fermented food of wheat germ[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products,2016,3(45):66−67. [3] RIZZELLO C G, NIONELLI L, CODA R, et al. Effect of sourdough fermentation on stabilisation, and chemical and nutritional characteristics of wheat germ[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,119(3):1079−1089. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.08.016
[4] SRIVASTAVA A K, SUDHA M L, LEELAVATHI V B. Studies on heat stabilized wheat germ and its influence on rheological characteristics of dough[J]. European Food Research & Technology, 2007.
[5] 肖蕊. 小麦胚芽制备及饼干加工技术研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2016. XIAO R. Study on wheat germ preparation and biscuit processing technology[D]. Xianyang: Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2016.
[6] 刘心悦. 小麦胚芽粉影响面团特性与馒头品质研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2018. LIU X Y. Study on the effect of wheat germ powder on dough properties and steamed bread quality [D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018.
[7] LOI C C, EYRES G T, BIRCH E J. Effect of milk protein composition on physicochemical properties, creaming stability and volatile profile of a protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsion[J]. Food Research International,2019,120(6):83−91.
[8] 肖亚玲. 小麦胚芽及其提取物营养价值分析及加工工艺研究进展[J]. 山东工业技术,2019(7):241. [XIAO Y L. Research progress on nutritional value analysis and processing technology of wheat germ and its extract[J]. Shandong Industrial Technology,2019(7):241. [9] 柴华, 赵谋明, 王金水. 食品蛋白质酶解改性提高功能特性的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2008(1):286−288. [CHAI H, ZHAO M M, WANG J S. Research progress on improving functional properties of food protein by enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2008(1):286−288. [10] 何希强, 肖怀秋, 李玉珍. 豌豆蛋白酶法水解及产物特性研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2012,20(5):8−11. [HE X Q, XIAO H Q, LI Y Z. Study on enzymatic hydrolysis of pea protein and characteristics of its products[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foodstuffs,2012,20(5):8−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2012.05.003 [11] 唐世涛. 超声联合蛋白酶酶解对蛋黄粉溶解性及乳化稳定性的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. TANG S T. Effect of ultrasound combined with protease hydrolysis on solubility and emulsifying stability of egg yolk powder [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019.
[12] ZHAO Q, XIONG H, SELOMULYA C, et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of rice dreg protein: Effects of enzyme type on the functional properties and antioxidant activities of recovered proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,134(3):1360−1367. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.033
[13] 高亚奇. 酶改善米糠稳定性及米糠活性肽的制备与性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. GAO Y Q. Study on enzyme improving stability of rice bran and preparation and properties of bioactive peptides from rice bran [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[14] 蔡利, 甘国超, 巩发永, 等. 速溶苦荞羹的研制[J]. 现代食品,2020(10):200−203. [CAI L, GAN G C, GONG F Y, et al. Development of instant Tartary buckwheat soup[J]. Modern Food,2020(10):200−203. [15] 张智勇, 孙辉, 王春, 等. 利用色彩色差仪评价面条色泽的研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2013,21(2):55−58. [ZHANG Z Y, SUN H, WANG C, et al. The study on the evaluation of noodle color by color colorimeter[J]. Grain, Oil and Food Technology,2013,21(2):55−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2013.02.017 [16] 赵学伟. 小米挤压加工特性研究[D]. 陕西: 西北农林科技大学, 2006. ZHAO X W. Study on the extrusion characteristics of millet [D]. Shanxi: Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2006.
[17] 张磊科. 酶法和微波稳定米糠研究[D]. 南京: 南京财经大学, 2012. ZHANG L K. Studies on enzymatic and microwave stabilization of rice bran[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, 2012.
[18] 黄延胜, 唐青涛, 宁初光, 等. 速溶固体奶茶的制作工艺研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2015,43(7):3l0−312. [HUANG Y S, TANG Q T, NING C G, et al. Study on the processing technology of instant milk tea[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science,2015,43(7):3l0−312. [19] 高向阳, 宋莲军, 黄勇, 等. 南阳彩色小麦营养成分的初步研究[J]. 河南农业大学学报,2003(4):331,334−334. [GAO X Y, SONG L J, HUANG Y, et al. Preliminary study on the nutritional components of Nanyang color wheat[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,2003(4):331,334−334. [20] 杨红丹. 杂豆粉及其淀粉理化性质与功能特性研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2011. YANG H D. Study on physicochemical and functional properties of mixed bean powder and its starch [D]. Xianyang: Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology, 2011.
[21] NJOKI P, FALLER J F. Development of an extruded plantain corn soy weaning food[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2010,36(4):415−423.
[22] 沈丹, 孟娇, 曹龙奎. 响应面法优化鹰嘴豆淀粉膨化工艺条件及水溶性与吸水性的研究[J]. 农产品加工,2015(6):1−8. [SHEN D, MENG J, CAO L K. Response surface methodology to optimize the expansion conditions of chickpea starch and its water solubility and water absorption[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2015(6):1−8. [23] 崔沙沙, 钟俊桢, 方冲, 等. 不同低水解度的大米蛋白溶解性与结构变化的关系[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(7):86−91. [CUI S S, ZHONG J Z, FANG C, et al. Relationship between solubility and structure change of rice protein with different low degree of hydrolysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(7):86−91. [24] 和丽, 熊海涛, 王雪峰, 等. 响应面试验优化复合酶法制备青刺果抗菌肽的工艺研究[J]. 中国油脂,2021,46(6):33−37. [HE L, XIONG H T, WANG X F, et al. Optimization of preparation of antimicrobial peptides from Prinsepia utilis Royle by compound enzymes using response surface methodology[J]. China Fats and Oils,2021,46(6):33−37. [25] GONALVES E M, PINHEIRO J, ABREU M, et al. Modelling the kinetics of peroxidase inactivation, colour and texture changes of pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima L) during blanching[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2007,81(4):693−701. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.01.011
[26] HOU L, WANG Y, HU X, et al. Effect of high pressure carbon dioxide on the quality of carrot juice[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2009,10(3):321−327.
[27] 夏陈, 栢凤女, 宋艳, 等. 酶法稳定化新鲜米糠的研究[J]. 食品工业,2015,36(11):152−155. [XIA C, BAI F N, SONG Y, et al. Studies on the enzymatic stabilization of fresh rice bran[J]. Food Industry,2015,36(11):152−155. [28] WANG J J, XUA L, WAN Y, et al. Purification and characterization of a new metallo-neutral protease for beer brewing from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SYB-001[J]. Applied Biochemistry Biotechnology,2013,170(8):2021−2033. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0350-8
[29] LIU X F, WANG Z Y, WANG J J, et al. Expression of GAI gene and disruption of PEP4 gene in an industrial brewer’s yeast strain[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,2009,49(1):117−123. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02627.x
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 常逍柯,田潇凌,林顺顺,李梦琴,田争争,高恩红. 不同制粉方式对黑小麦全麦粉及饼干品质影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(21): 266-272 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王冬,任健,王志鹏,宋春丽. 酶预处理对黑珍珠糯玉米粉分散性的影响研究. 齐齐哈尔大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 69-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)








 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



