Study on the Interaction Mechanism between Galactomannan and Human Serum Albumin by Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking
-
摘要: 目的:研究半乳甘露聚糖对人血清白蛋白(HSA)光谱特性的影响及它们相互作用的机理。方法:本文利用光谱法判断半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的猝灭方式、结合位点数、结合作用力类型以及二级结构的变化,采用分子对接模拟技术得到结合作用力类型和长度,进一步研究半乳甘露聚糖和HSA相互作用的机制。结果:在半乳甘露聚糖的作用下,HSA内源荧光被有规律的猝灭,猝灭过程是自发进行的,机制为静态猝灭,结合位点数约为1,并且HSA的二级结构中α-螺旋含量减少了7.7%。分子对接结果表明,半乳甘露聚糖通过氢键和范德华力在HSA的亚结构域IIB中相互作用。结论:半乳甘露聚糖与HSA有较强的结合能力,并且结合是自发进行的。Abstract: Objective: To study the effect of galactomannan on the spectral characteristics of human serum albumin (HSA) and the mechanism of their interaction. Methods: Multispectroscopic analyses were used to determine the quenching method, number of binding sites, type of binding force, and changes in secondary structure between galactomannan and HSA. The type and length of binding force were obtained by molecular docking simulation, which further proved that the mechanism of interaction between galactomannan and HSA. Results: Under the action of galactomannan, the endogenous fluorescence of HSA was regularly quenched. The quenching process was spontaneous. The mechanism was static quenching. The number of binding sites was about 1, and the α-helix of HSA was reduced by 7.7%. The results of molecular docking showed that galactomannan interacted in HSA subdomain IIB through hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces. Conclusions: The interaction between galactomannan and HSA was strong, and the binding was spontaneous.
-
半乳甘露聚糖(C18H32O16,Galactomannan)是一种由D-甘露糖和D-半乳糖单体组成的多糖[1],主要来源于种子的胚乳(例如豆科)或微生物[2]。有研究表明半乳甘露聚糖具有抗肿瘤[3]和对机体免疫功能产生影响的免疫调节活性[4],对参与人体先天性和获得性免疫的重要免疫细胞具有调节作用[5]。它还可以与细胞表面的特定受体结合以激活各种细胞内信号转导途径,促进细胞因子或抗体的产生,从而调节人体的免疫功能[6]。作为一种功能性多糖,由于其特殊的抗肿瘤性和免疫调节功能,使得其受到越来越多研究学者的关注[7]。
人血清白蛋白(Human Serum Albumin, HSA)是一条由585个氨基酸残基构成的多肽链[8],分子量约为66 kDa[9],其形状类似于心型[10]。HSA共有3个同源结构域[11],分别为Domain Ⅰ(1-195)、Domain Ⅱ(196-383)、Domain Ⅲ(384-585)[12-13]。每个结构域可以进一步分为两个亚结构域(IA,IB,IIA,IIB,IIIA和IIIB),其中的亚域以槽口相对的方式形成圆筒状结构[14],几乎所有的疏水性氨基酸残基都包埋在圆筒腔内,形成疏水腔[15]。HSA在各种外源和内源性化合物的转运和递送,以及物质的排泄中起着重要作用[16],是人体内最合适的转运蛋白[17]。研究半乳甘露聚糖与HSA结合,不仅有利于了解半乳甘露聚糖在人体的吸收、运输、分布和代谢[18],阐明它们相互作用的机制,而且对于探索功能性多糖的性质具有重要意义。
为了进一步研究半乳甘露聚糖与HSA作用机理,本文采用紫外-可见光吸收法(Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy, UV-Vis)、荧光光谱法(Fluorescence spectrometry, RF)、圆二色光谱法(Circular dichroism spectroscopy, CD)和分子对接法(Molecular docking),探索半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的机理。其中,紫外-可见光吸收法灵敏度和选择性较好,且设备使用简便,易于操作,它被广泛地用于蛋白质的定性及定量分析[19]。通过分析蛋白质与分子结合前后,蛋白质的紫外可见光吸收光谱中吸光值的变化,能判断它们之间是否存在相互作用[20]。在研究蛋白质与分子的相互作用过程中,荧光光谱可以测定荧光强度、发射光谱等[21],得到如荧光的发射峰的特征、结合常数、猝灭常数和作用力类型等信息,从而分析结合前后蛋白质结构和蛋白质周围环境的变化等[22-23]。圆二色光谱对于蛋白质的二级结构很敏感,是研究蛋白质构象及其变化较为有效的方法,能够测定和分析相互作用过程中所引起的构象变化并对其进行定量分析,是研究蛋白质构型及其分子间相互作用的重要光谱手段之一[24-25]。分子对接是一种利用计算机技术和理论相结合而产生的新方法,通过计算机程序模拟分子间的结合过程,能更观地呈现出分子与蛋白质相互作用的过程和结果[26-27]。本实验通过分析光谱所得参数,计算得到结合常数和猝灭常数等信息。利用三种光谱实验的结论,结合分子对接技术进行分析比较,使它们的结论相互验证和补充,从而达到实验和理论共同验证半乳甘露聚糖和HSA相互作用的目的。进一步阐明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的机理,为半乳甘露聚糖在医学和食品化学的发展提供可靠的科学依据,并为半乳甘露聚糖在食品领域的广泛应用提供参考资料。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
磷酸盐缓冲液颗粒(PBS)(分析纯)、人血清白蛋白(纯度>95%) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;氢氧化钠 分析纯,广东光华科技股份有限公司;半乳甘露聚糖 纯度>95%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;实验用水 均为超纯水。
FA1004N分析天平 上海拓西电子科技有限公司;HJ-6B数显恒温磁力搅拌器 常州市万合仪器制造有限公司;HH-2数显恒温水浴锅 常州澳华仪器有限公司;UV-1750紫外可见分光光度计、RF-6000荧光分光光度计 日本岛津公司;Chriascan数字式圆二色光谱仪 英国应用光物理公司;pHS-3C pH计 上海雷磁仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 溶液配制
HSA溶液:将HSA溶于PBS缓冲溶液中,配制成浓度7.0×10−6 mol/L的HSA储备液,保存于4 ℃冰箱保存在暗处备用;半乳甘露聚糖溶液:用超纯水配制,浓度分别为0.5、4.0、8.0、10.0、20.0、34.0、52.0、76.0×10−6 mol/L。然后按照1:1的比例混合HSA溶液与半乳甘露聚糖溶液,室温下静置0.5 h后使用,所有溶液现配现用[28-29]。
1.2.2 紫外可见吸收光谱
取3组试管每组9支,精密量取3 mL浓度为7.0×10−6 mol/L的HSA溶液置于其中,再向其中依次加入等比的半乳甘露聚糖溶液浓度分别为0、0.5、4.0、8.0、10.0、20.0、34.0、52.0×10−6 mol/L,最后一组只含有半乳甘露聚糖浓度为76.0×10−6 mol/L,充分混匀后,在室温下静置0.5 h。以相同条件下的空白试剂(PBS缓冲溶液)为参比,放在1 cm石英吸收池内,在200~400 nm区间内,单色器狭缝宽度设置为1 nm,在室温下使用紫外分光光度计进行光谱扫描[30]。以上操作重复三次,取其平均值。
1.2.3 荧光光谱
取3组试管每组9支,分别加入7.0×10−6 mol/L的HSA溶液和等比的半乳甘露聚糖溶液,浓度分别为0、0.5、4.0、8.0、10.0、20.0、34.0、52.0×10−6 mol/L,最后一组只含有浓度为76.0×10−6 mol/L半乳甘露聚糖。充分混匀后,将第一组混合溶液于20 ℃静置0.5 h,第二组于25 ℃恒温水浴0.5 h,第三组于30 ℃恒温水浴0.5 h,第四组于37 ℃恒温水浴0.5 h,使用荧光光度计进行光谱扫描。荧光光谱参数设置激发波长λex=280 nm,石英比色皿1 cm,激发与发射狭缝宽度均为5 nm,发射光谱记录在290~500 nm之间,以相同条件下的空白试剂(PBS缓冲溶液)作为对照[31-32]。以上操作重复三次,取其平均值。并对数据进行内滤荧光效应的校正,使用校正后的数据作图。
1.2.4 圆二色光谱
用pH7.40的磷酸盐缓冲溶液配制浓度为7.0×10−6 mol/L的HSA溶液,依次向溶液中加入等量的半乳甘露聚糖溶液,浓度分别为0、0.5、4.0、8.0、10.0、20.0、34.0、52.0、76.0×10−6 mol/L,充分混匀后,在室温下静置0.5 h,使用圆二色光谱仪进行光谱扫描。圆二色光谱参数设置为,扫描速率100 nm/min,样品池的光径为0.2 cm,响应时间0.5 s,分辨率0.1 nm,累积次数3次,扫描的波长范围为190~260 nm[33-34]。以上操作重复三次,取其平均值。
1.2.5 分子对接
使用软件Discovery Studio 2016(DS)进行分子对接模拟,首先从Brookhaven蛋白质数据库(RCSB)下载HSA的晶体结构文件(ID:1H9Z);再从PubChem下载半乳甘露聚糖的3D晶体结构文件(CID:439336)。对HSA进行预处理,除去所有水分子,添加氢原子,再计算电荷。利用ChemBio3D Ultra 12.0软件对半乳甘露聚糖的分子结构进行优化,使其处于能量最低、构象最优的状态。使用DS中的CDOCKER模块进行分子对接,半乳甘露聚糖作为配体,HSA作为受体,选择整个蛋白作为潜在的结合位点,使用盲对接方法。根据所得-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY值判定最优构象。
1.3 数据处理
本文运用软件Excel和Origin 2018计算光谱实验数据及画图,获得半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的猝灭机理、结合常数、猝灭常数及热力学参数。使用软件CDPro分析圆二色光谱数据,得到相互作用前后HSA二级结构的变化。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 紫外可见吸收光谱分析
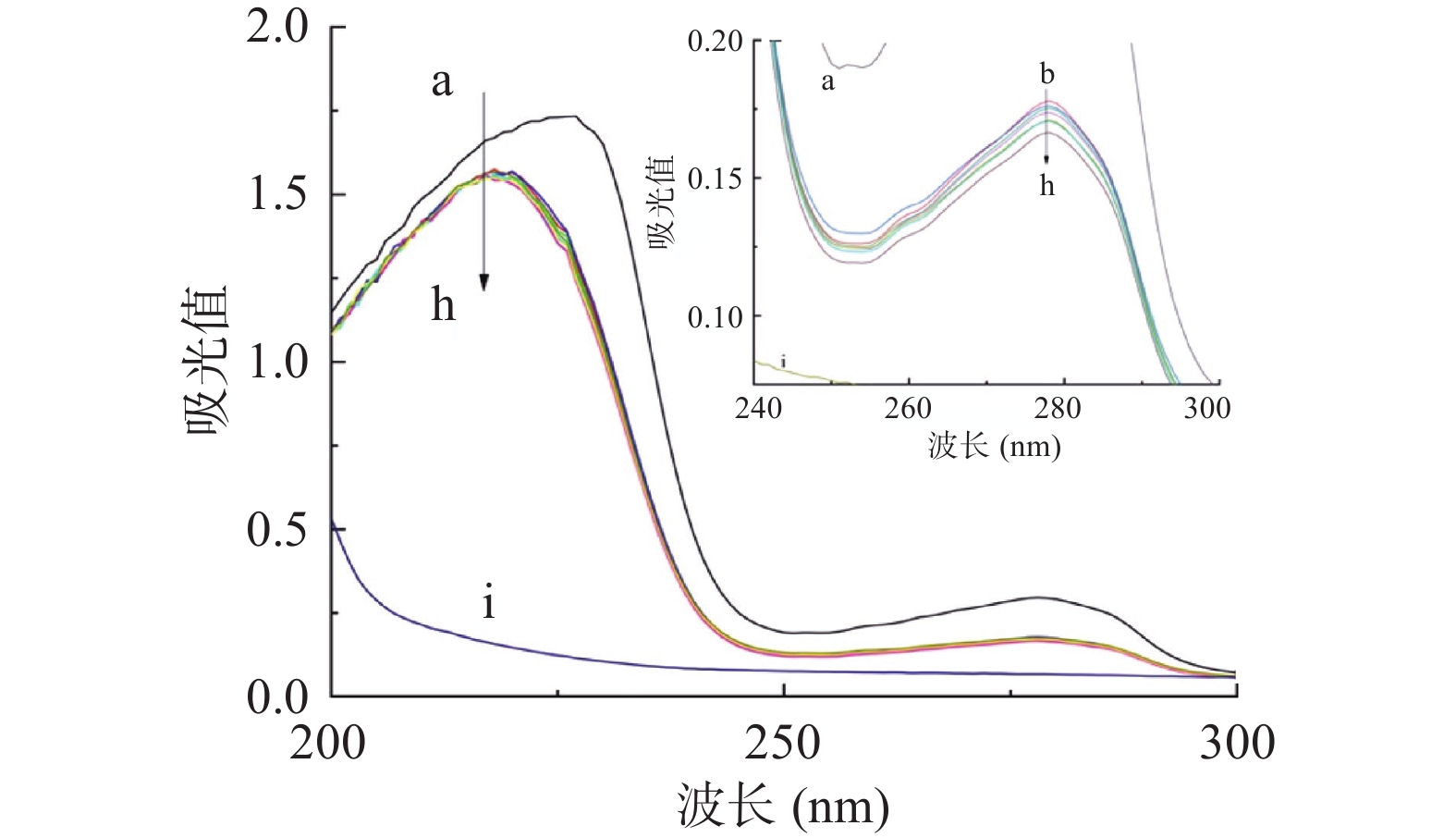
紫外可见吸收光谱法是一种简单有效的技术,可以判断配体-蛋白质之间是否有新的复合物形成,还可以检测配体-蛋白质复合物结合而引起的蛋白质结构变化,因此它可以用于研究配体与蛋白质的相互作用[35]。半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的UV-Vis光谱如图1所示。在实验条件下,半乳甘露聚糖几乎没有UV吸收,而HSA在227和278 nm处具有很强的吸收率。半乳甘露聚糖添加后,HSA的吸光度明显下降,半乳甘露聚糖-HSA吸收光谱发生蓝移。可以合理地解释,在227 nm处的峰对应于蛋白质中肽键的吸收,观察到的蓝移表示与半乳甘露聚糖相互作用后HSA二级结构含量的变化,复合结构产生的减色效果,使吸收强度减弱[36]。HSA在278 nm处显示的吸收带,主要是由HSA固有芳香族氨基酸残基——色氨酸残基(Trp)、酪氨酸残基(Tyr)和苯丙氨酸残基(Phe)的芳香π系统中的π-π*电子跃迁,这与陈蓉蓉[37]的研究结果相一致。
2.2 荧光光谱分析
HSA具有三种固有的荧光团,包括Trp、Tyr和Phe残基。HSA的固有荧光主要由Trp残基贡献,因为Phe残基的量子产率非常低。当Tyr离子被氨基、羧基或Trp接近或离子化时,Tyr的荧光几乎被猝灭[38]。由于HSA的固有荧光对微环境非常敏感,所以当HSA的局部环境稍有变化时,其固有荧光将显著降低。如蛋白质的构象转变,生物分子的结合以及变性等都是造成荧光强度下降的原因[39]。
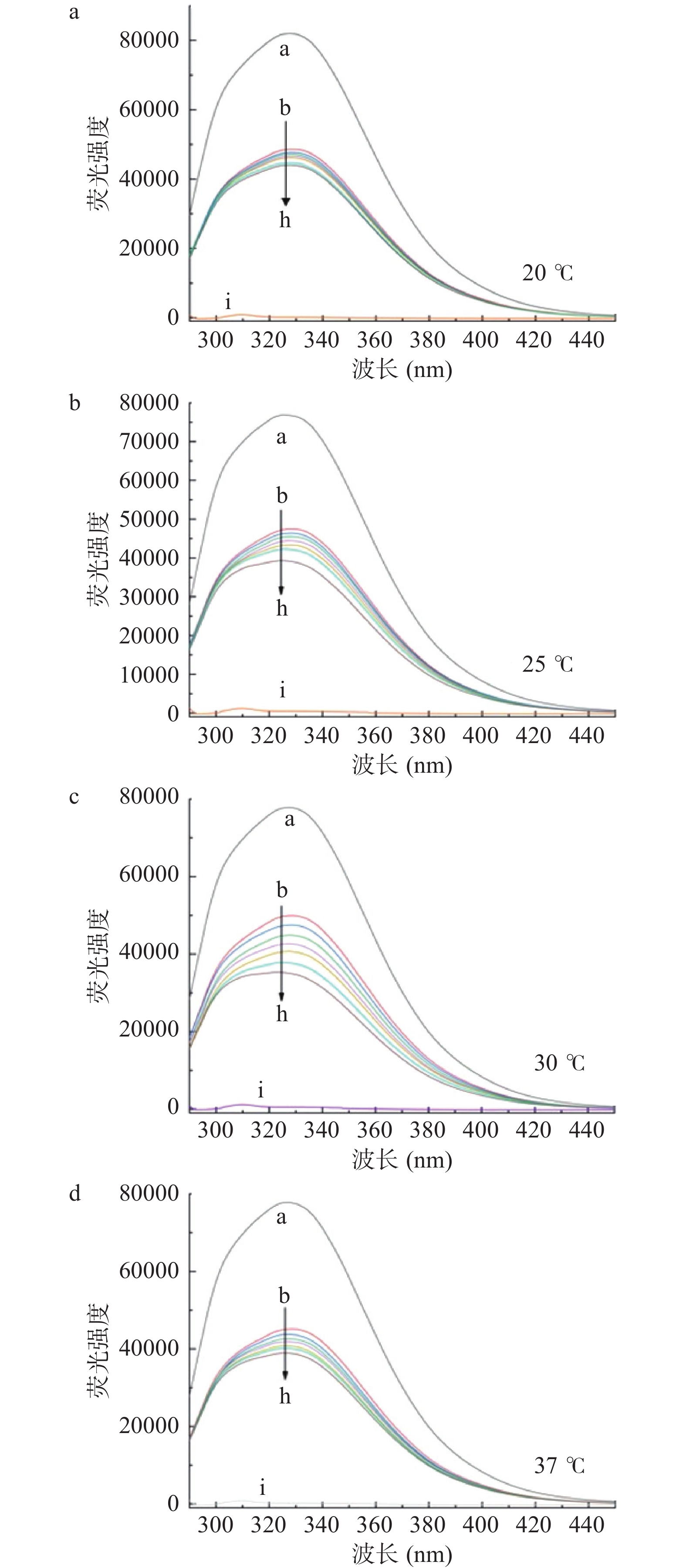
四种温度下,HSA的荧光发射光谱如图2所示,HSA的最大发射波长为328 nm,半乳甘露聚糖的加入引起荧光发射光谱的巨大变化,随着半乳甘露聚糖加入的浓度增大,导致HSA内源荧光的猝灭,荧光强度呈现出有规律的下降。半乳甘露聚糖导致HSA固有荧光的猝灭,但没有改变HSA的最大值和峰的形状。根据张丽娇[40]的研究,该结果表明半乳甘露聚糖可以与HSA结合,从而猝灭蛋白质的固有荧光。
用于研究荧光猝灭的一种经典模型名为斯特恩沃尔默(Stern–Volmer)方程(1),可分析配体对蛋白质荧光的猝灭机理,以计算出配体与蛋白质的猝灭常数、猝灭速率常数、结合常数及结合点数[41]。利用(1)方程和推导公式(2)计算双分子猝灭速率常数Kq和猝灭常数KSV,判断半乳甘露聚糖对HSA的荧光猝灭类型;采用双对数方程(3)计算半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的结合常数Ka和结合位点数n。计算公式如下:
F0/F=1+kqτ0[Q]=1+KSV[Q] (1) kqτ0=Ksv (2) 式中:F0是不存在猝灭剂时的稳态荧光强度;F是存在猝灭剂时的稳态荧光强度;KSV是斯特恩-沃尔默猝灭常数;[Q]是猝灭剂的浓度;kq是双分子猝灭速率常数;τ0是不存在猝灭剂的荧光寿命,此处为不含半乳甘露聚糖的HSA的荧光寿命,约为10−8 s[42]。
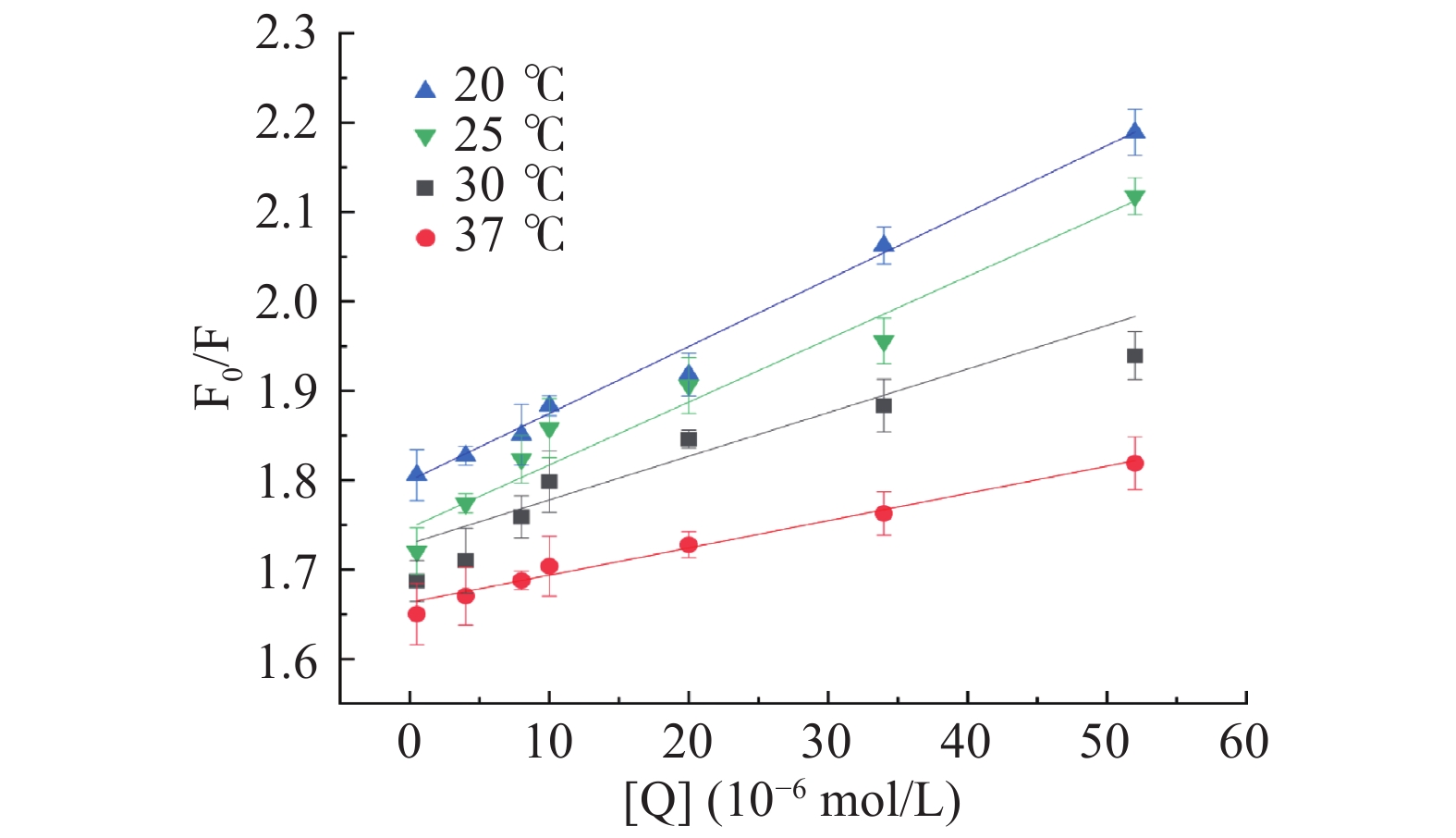
计算结果如图3和表1,随着半乳甘露聚糖的加入,HSA荧光强度显著降低,吸收光谱有了明显的变化,并且其最大发射波长发生微小蓝移,表明半乳甘露聚糖对HSA的内源荧光有明显的猝灭作用,也说明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA发生了相互作用使其构象发生改变[43]。结合Yadzi等[44]的研究,随着温度的升高,猝灭常数Ksv减小,表明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA的荧光猝灭类型属于静态猝灭。而且从表1可以看出,Kq大于最大扩散碰撞猝灭常数(2.0×1010 L·mol−1·s−1),这也能表明静态猝灭作用占主导地位。
表 1 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的猝灭常数KSV、猝灭速率常数KqTable 1. Quenching constants KSV, and biomolecular quenching rate constant (Kq) for the interaction of HSA with galactomannan at 4 different temperatures温度(℃) Ksv×103( L·mol−1) Kq×1011( L·mol−1·s−1) R2 20 7.491±0.063 7.491±0.063 0.9905 25 7.032±0.012 7.032±0.012 0.9594 30 4.889±0.024 4.889±0.024 0.9089 37 3.056±0.003 3.056±0.003 0.9829 使用改良的Stern-Volmer双对数回归方程(3)来计算半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的结合常数(Ka)和结合位点数(n)。计算公式如下:
lg[F0−FF]=lgKa+nlg[Q] (3) 式中:Ka为结合常数;n为结合位点数。
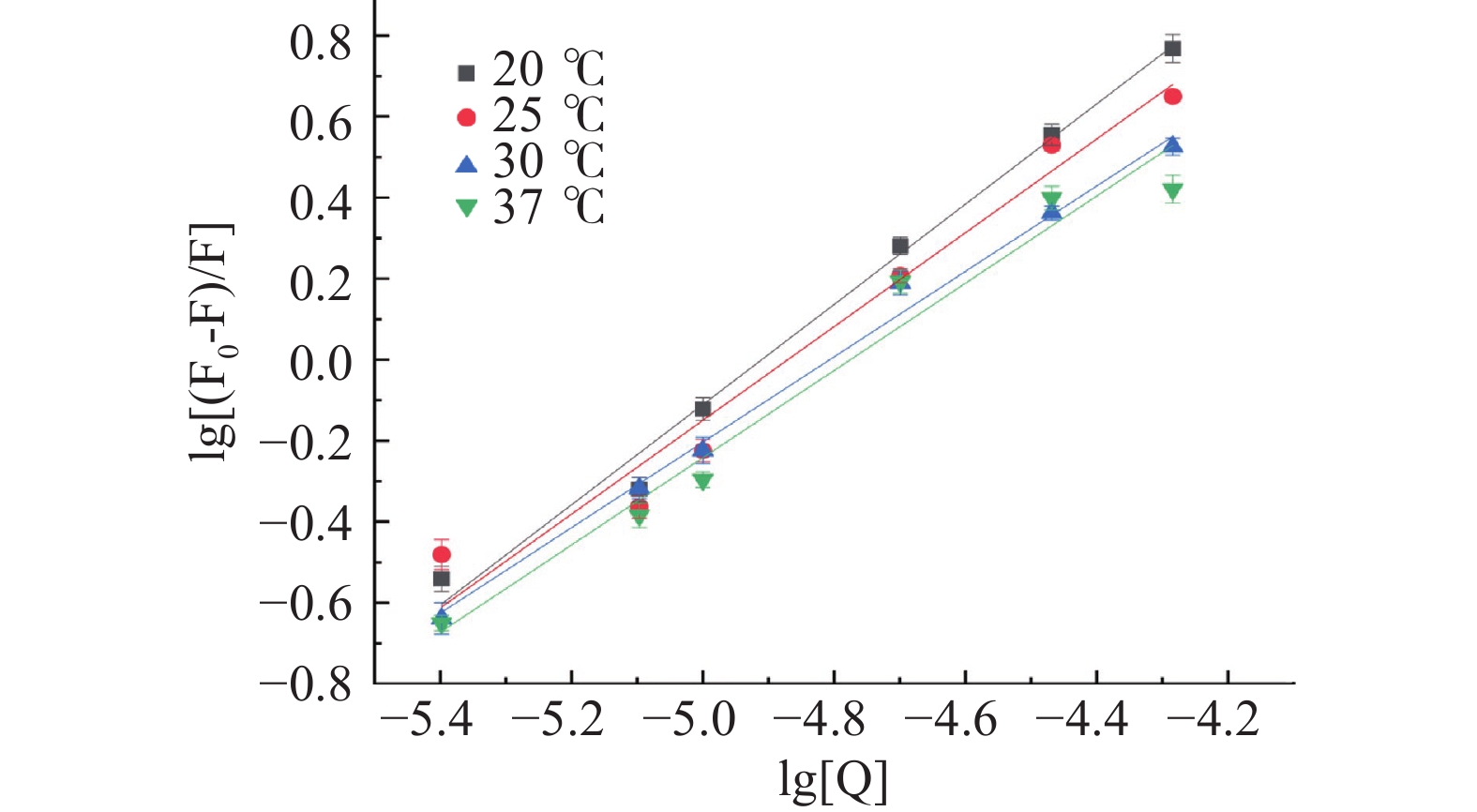
四种温度下半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的双对数结果见图4。半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的Ka和结合位点数n见表2。由图4和表2可知,随着温度的升高,半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的Ka值虽然从1.069×106减小到1.191×105 L/mol,但它们均达到104数量级,这说明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的荧光猝灭类型均以静态猝灭为主,动态猝灭可以忽略不计[45],也能进一步说明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA能形成稳定的复合物,这与Afrin[46]所得结论一致。从表2可知,不同温度条件下,半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的结合位点数n均接近1,说明它们的结合比例约为1:1[47]。
表 2 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的结合常数Ka、结合位点数nTable 2. Binding constants Ka and binding sites n for the interaction of HSA with galactomannan at four different temperatures温度(℃) Ka×105(L/mol) n R2 20 10.690 ±0.013 1.237±0.061 0.9906 25 3.133±0.067 1.158±0.069 0.9679 30 1.301±0.039 1.054±0.043 0.9931 37 1.191±0.051 1.077±0.047 0.9692 然后使用热力学方程(4)和(5)分别计算半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的热力学参数(自由能变ΔG,焓变ΔH和熵变ΔS)。计算公式如下:
lnKa=−ΔHRT+ΔSR (4) ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=−RTlnKa (5) 式中:T为热力学温度(K);Ka为不同温度下相应的结合常数;R是热力学常数,其值为8.314 J·mol−1·K−1;ΔG是自由能变;ΔH是焓变;ΔS是熵变[46-47]。
通过热力学方程(4)和(5)计算半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的热力学参数ΔH、ΔS和ΔG见表3。由表3可知,不同温度条件下(293.15、298.15、303.15和310.15 K),半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用过程中的ΔG分别为−33.027、−31.922、−30.816和-29.269 kJ/mol,均小于0,则说明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA的结合过程是自发进行的。根据Eftink等[48-50]研究可知,当ΔH<0,ΔS<0时,主要作用力为氢键和范德华力;当ΔH<0或ΔH≈0,ΔS>0时,主要作用力为静电作用力;当ΔH>0,ΔS>0时,主要作用力为疏水相互作用。半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用的ΔS和ΔH值分别为−221.061 J/mol·K−1和−97.831 kJ/mol,均小于0,这说明半乳甘露聚糖与HSA相互作用过程中的主要作用力为氢键和范德华力。
表 3 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的热力学参数Table 3. Thermodynamic parameters of the interaction between HSA and galactomannan at 4 different temperatures温度(K) ΔH(kJ/mol) ΔS(J/mol·K−1) ΔG(kJ/mol) 293.15 −97.831 −221.061 −33.027 298.15 −31.922 303.15 −30.816 310.15 −29.269 2.3 圆二色光谱分析
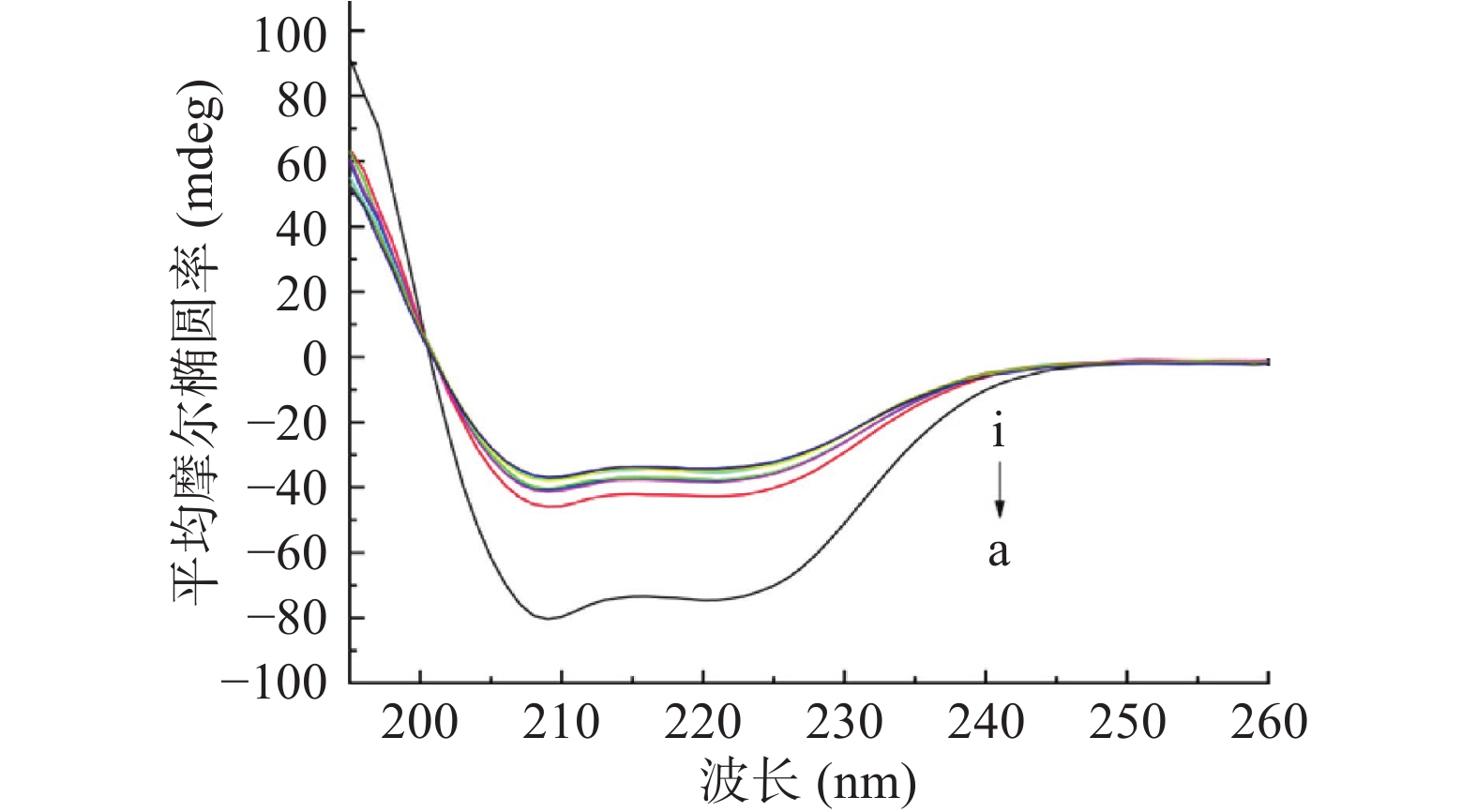
圆二色光谱是一种敏感的技术,通常用于表征蛋白质的定量结构,特别是用于二级结构的测定,以监测HSA和HSA-半乳甘露聚糖复合物的二级结构的构象变化和改变[51]。HSA的CD光谱的主要特征是在约208和222 nm处有两个负带和在193 nm处有正带,这是α-螺旋结构的典型特征[52]。从图5可以看出,CD光谱的峰值随着半乳甘露聚糖的添加而变化,表明HSA的二级结构发生了明显变化。通过软件CD Pro计算半乳甘露聚糖添加前后HSA二级结构含量的变化,发现游离的HSA包含约54.4%的α-螺旋,18.8%的β-折叠,14.0%的β-转角和13.3%的无规卷曲。而与10.0 μmol/L的半乳甘露聚糖相互作用后,β-折叠、β-转角和无规卷曲含量分别增加到21.4%、15.4%和16.8%,而α-螺旋减少到46.7%。然而,CD谱图中的形状或峰位置没有变化,这表明和半乳甘露聚糖结合后HSA的基本结构得以保持。HSA的部分排列导致了α-螺旋的减少,这表明半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的结合改变了蛋白质的二级结构并降低了α-螺旋的稳定性[53]。这与很多研究结果相一致[54-56],HSA的二级结构被破坏,α-螺旋的含量减少,无规卷曲的含量增加,这主要是由于多糖和蛋白质的结合导致蛋白质解开并转变成无规卷曲。
2.4 分子对接分析
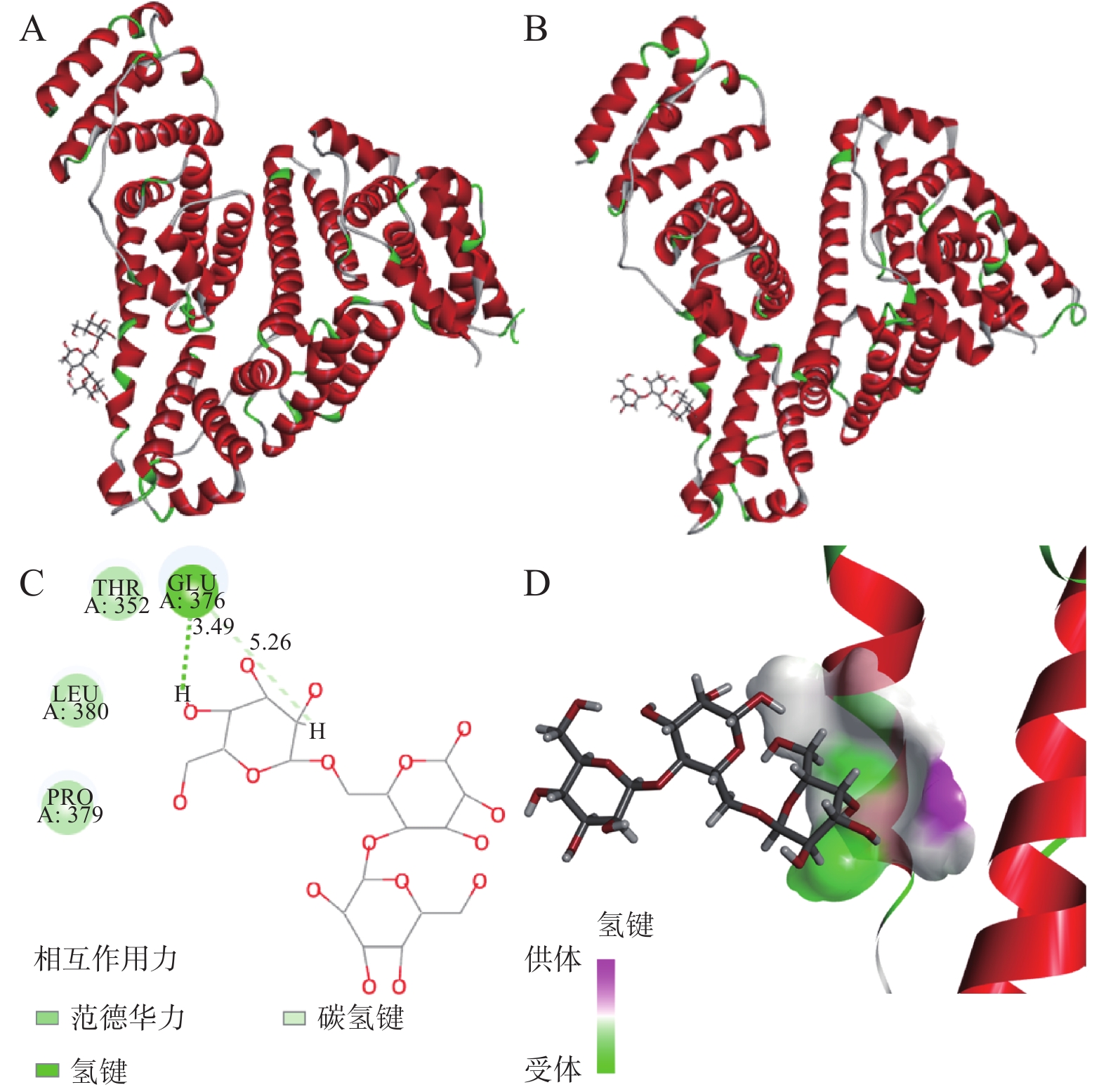
在图6中,分子对接结果表明半乳甘露聚糖结合在HSA的亚结构域IIB的结合口袋内。根据CDOCKER协议,给出最高能量得分(-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY)的姿势被认为是最稳定的构象,半乳甘露聚糖与HSA的最大-CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY为13.3549 kcal/mol。
输出的3D和2D示意图(图6)清楚地表明,半乳甘露聚糖已插入HSA的活性位点并与氨基酸残基相互作用,它与氨基酸残基Pro 379、Leu 380、Thr 352和Glu 376相互作用,这是半乳甘露聚糖与HSA之间的相互作用位点。在半乳甘露聚糖和Glu 376氨基酸残基之间发现了氢键和范德华力,其长度为3.49Å和5.26Å,表明HSA-半乳甘露聚糖主要通过氢键和范德华力(表4)相互作用形成新的稳定配合物。通过图6A~6B,比较结合前后的结构,可以推断半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的构象在相互作用后都发生了不同程度的变化。蛋白质结构的变化与2.2中讨论的热力学参数分析一致。结合Ermakova等[57]、Chugh等[58]的研究以及对接结果的分析,可以得出结论,半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的相互作用发生在HSA亚结构域IIB内,主要结合作用力为氢键和范德华力。
表 4 参与HSA与半乳甘露聚糖分子对接的氨基酸残基以及作用力类型Table 4. Types of molecular docking force and amino acid residue between HSA and galactomannan氨基酸残基 氢键 疏水相互作用 范德华力 Glu 376 1 0 1 3. 结论
本文利用光谱法和分子对接技术,研究了半乳甘露聚糖与HSA的结合机理及HSA构象的变化。结果表明:半乳甘露聚糖的加入会导致HSA的特征吸收峰强度和吸光度发生改变,还伴随着蓝移。半乳甘露聚糖会导致HSA的内源荧光发生静态猝灭,结合比例约为1:1,其结合常数远大于104数量级,说明半乳甘露聚糖能与HSA较好的相互作用。半乳甘露聚糖添加后,HSA的α-螺旋减少,半乳甘露聚糖和HSA的结合改变了蛋白质的二级结构并降低了α-螺旋的稳定性。分子对接进一步验证了光谱实验的结果,并发现半乳甘露聚糖与HSA的最佳结合位点在亚结构域IIB,主要结合作用力为氢键和范德华力,以及参与相互作用的氨基酸残基,使相互作用的过程和结果可视化。本研究为深入理解半乳甘露聚糖在体内的相互作用机理和运输储藏过程奠定了基础,为半乳甘露聚糖在食品化学的发展提供了科学依据和参考价值。
-
表 1 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的猝灭常数KSV、猝灭速率常数Kq
Table 1 Quenching constants KSV, and biomolecular quenching rate constant (Kq) for the interaction of HSA with galactomannan at 4 different temperatures
温度(℃) Ksv×103( L·mol−1) Kq×1011( L·mol−1·s−1) R2 20 7.491±0.063 7.491±0.063 0.9905 25 7.032±0.012 7.032±0.012 0.9594 30 4.889±0.024 4.889±0.024 0.9089 37 3.056±0.003 3.056±0.003 0.9829 表 2 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的结合常数Ka、结合位点数n
Table 2 Binding constants Ka and binding sites n for the interaction of HSA with galactomannan at four different temperatures
温度(℃) Ka×105(L/mol) n R2 20 10.690 ±0.013 1.237±0.061 0.9906 25 3.133±0.067 1.158±0.069 0.9679 30 1.301±0.039 1.054±0.043 0.9931 37 1.191±0.051 1.077±0.047 0.9692 表 3 HSA与半乳甘露聚糖在四种不同温度下相互作用的热力学参数
Table 3 Thermodynamic parameters of the interaction between HSA and galactomannan at 4 different temperatures
温度(K) ΔH(kJ/mol) ΔS(J/mol·K−1) ΔG(kJ/mol) 293.15 −97.831 −221.061 −33.027 298.15 −31.922 303.15 −30.816 310.15 −29.269 表 4 参与HSA与半乳甘露聚糖分子对接的氨基酸残基以及作用力类型
Table 4 Types of molecular docking force and amino acid residue between HSA and galactomannan
氨基酸残基 氢键 疏水相互作用 范德华力 Glu 376 1 0 1 -
[1] SITTIKIJYOTHIN W, TORRES D, GONÇALVES M P. Modelling the rheological behaviour of galactomannan aqueous solutions[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2005,59(3):339−350. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.10.005
[2] LOSER Ú, ITURRIAGA L, RIBOTTA P D, et al. Combined systems of starch and Gleditsia triacanthos galactomannans: Thermal and gelling properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106378. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106378
[3] LIU L, LI M, YU M, et al. Natural polysaccharides exhibit anti-tumor activity by targeting gut microbiota[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:743−751. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.083
[4] SINDHU R K, GOYAL A, DAS J, et al. Immunomodulatory potential of polysaccharides derived from plants and microbes: A narrative review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications,2021,2:100044. doi: 10.1016/j.carpta.2021.100044
[5] BEUTLER B. Innate immunity: An overview[J]. Molecular Immunology,2004,40(12):845−859. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2003.10.005
[6] PANTOSTI A, TZIANABOS A O, ONDERDONK A B, et al. Immunochemical characterization of two surface polysaccharides of Bacteroides fragilis[J]. Infection and Immunity,1991,59(6):2075. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2075-2082.1991
[7] SHI L. Bioactivities, isolation and purification methods of polysaccharides from natural products: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,92:37−48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.100
[8] ZHANG G, MA Y. Mechanistic and conformational studies on the interaction of food dye amaranth with human serum albumin by multispectroscopic methods[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,136(2):442−449. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.026
[9] CIEPLAK M, SZWABINSKA K, SOSNOWSKA M, et al. Selective electrochemical sensing of human serum albumin by semi-covalent molecular imprinting[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2015,74:960−966. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.061
[10] PENG X, WANG X, QI W, et al. Affinity of rosmarinic acid to human serum albumin and its effect on protein conformation stability[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,192:178−187. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.109
[11] 肖建波. 多酚类化合物与血清白蛋白相互作用的结构—结合力关系、理论模型和应用研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009. XIAO J B. Structure-affinity relationship, theory model and application of interaction between polyphenols and serum albumin[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009.
[12] MANJUSHREE M, REVANASIDDAPPA H D. Evaluation of binding mode between anticancer drug etoposide and human serum albumin by numerous spectrometric techniques and molecular docking[J]. Chemical Physics,2020,530:110593. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphys.2019.110593
[13] LIU T, LIU M, GUO Q, et al. Investigation of binary and ternary systems of human serum albumin with oxyresveratrol/piceatannol and/or mitoxantrone by multipectroscopy, molecular docking and cytotoxicity evaluation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2020,311:113364. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113364
[14] MUSA K A, NING T, MOHAMAD S B, et al. Intermolecular recognition between pyrimethamine, an antimalarial drug and human serum albumin: Spectroscopic and docking study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2020,311:113270. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113270
[15] NERUSU A, VAIKUNTAPU P R, CHINTHAPALLI D K, et al. Truncated domains of human serum albumin improves the binding efficiency of uremic toxins: A surface plasmon resonance and computational approach[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,155:1216−1225. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.089
[16] LI J, REN C, ZHANG Y, et al. Human serum albumin interaction with honokiol studied using optical spectroscopy and molecular modeling methods[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2008,881(1):90−96.
[17] KHAN I M, SHAKYA S, AKHTAR R, et al. Exploring interaction dynamics of designed organic cocrystal charge transfer complex of 2-hydroxypyridine and oxalic acid with human serum albumin: Single crystal, spectrophotometric, theoretical and antimicrobial studies[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2020,100:103872. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103872
[18] JALALVAND A R, GHOBADI S, AKBARI V, et al. Mathematical modeling of interactions of cabergoline with human serum albumin for biosensing of human serum albumin[J]. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research,2019,25:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.sbsr.2019.100297
[19] BOURASSA P, DUBEAU S, MAHARVI G M, et al. Binding of antitumor tamoxifen and its metabolites 4-hydroxytamoxifen and endoxifen to human serum albumin[J]. Biochimie,2011,93(7):1089−1101. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.03.006
[20] DING F, LIU W, ZHANG L, et al. Sulfometuron-methyl binding to human serum albumin: Evidence that sulfometuron-methyl binds at the sudlow's site I[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2010,968(1):59−66.
[21] KIM H S, HAGE D S. Chromatographic analysis of carbamazepine binding to human serum albumin[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2005,816(1):57−66.
[22] KALANUR S S, SEETHARAMAPPA J, KALALBANDI V K A. Characterization of interaction and the effect of carbamazepine on the structure of human serum albumin[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2010,53(3):660−666. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2010.05.025
[23] BOURASSA P, HASNI I, TAJMIR RIAHI H A. Folic acid complexes with human and bovine serum albumins[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,129(3):1148−1155. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.094
[24] SARZEHI S, CHAMANI J. Investigation on the interaction between tamoxifen and human holo-transferrin: Determination of the binding mechanism by fluorescence quenching, resonance light scattering and circular dichroism methods[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2010,47(4):558−569. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.08.002
[25] MATEI I, HILLEBRAND M. Interaction of kaempferol with human serum albumin: A fluorescence and circular dichroism study[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2010,51(3):768−773. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.09.037
[26] TAYYAB S, SAM S E, KABIR M Z, et al. Molecular interaction study of an anticancer drug, ponatinib with human serum albumin using spectroscopic and molecular docking methods[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2019,214:199−206. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.02.028
[27] MOHAMMADZADEH AGHDASH H, AKBARI N, ESAZADEH K, et al. Molecular and technical aspects on the interaction of serum albumin with multifunctional food preservatives[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,293:491−498. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.119
[28] 申炳俊, 柳婷婷. 光谱法和分子对接技术研究胡桃醌与人血清白蛋白的相互作用[J]. 分析化学,2020,48(10):1383−1391. [SHEN B J, LIU T T. Study on the interaction between juglone and human serum albumin by spectroscopy and molecular docking technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2020,48(10):1383−1391. [29] 李楠, 曾观娣, 孙正华, 等. 光谱法结合分子对接研究普罗帕酮与牛血清白蛋白的相互作用[J]. 分析试验室,2020,39(10):1148−1154. [LI N, ZENG G D, SUN Z H, et al. Study on the interactions of propafenone with bovine serum albumins using multi-spectroscopy and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2020,39(10):1148−1154. [30] 赵旭红, 夏彩芬, 周紫薇, 等. 花青素对牛血清白蛋白的光谱特性及构象的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(7):57−62. [ZHAO X H, XIA C F, ZHOU Z W, et al. Study on spectral properties and conformation of bovine serum album by anthocyanin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(7):57−62. [31] 裘兰兰, 李金贵, 李芳. 分子对接技术与光谱法分析薯蓣皂苷和人血清白蛋白的相互作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(10):93−99. [QIU L L, LI J G, LI F. Interaction between dioscin and human serum albumin analyzed by molecular docking technique and spectroscopy[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(10):93−99. [32] 吕艳芳, 梁倩倩, 郭雨晴, 等. 分子对接和光谱法研究原儿茶醛和阿魏酸与牛血清白蛋白的互作机理[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(14):24−31. [LV Y F, LIANG Q Q, GUO Y Q, et al. Studies on the interactions of protocatechuic aldehyde and ferulic acid with bovine serum albumin by molecular docking and spectroscopy[J]. Food Science,2021,42(14):24−31. [33] 何文妮, 陈开意, 邵波. 对氨基苯甲酸与牛血清白蛋白相互作用的荧光分析[J]. 河南化工,2020,37(9):23−28. [HE W N, CHEN K Y, SHAO B. Fluorescence analysis on the interaction between p-aminobenzoic acid and bovine serum albumin[J]. Henan Chemical Industry,2020,37(9):23−28. [34] 张保林, 王文清, 袁荣尧. 蒽醌及黄酮类化合物与牛血清白蛋白结合的反应研究[J]. 化学学报,1994(12):1208−1212. [ZHANG B L, WANG W Q, YUAN R Y. Binding of anthraqulnones and flavonoids to bovine serum albumin[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,1994(12):1208−1212. [35] WANG W, GAN N, SUN Q, et al. Study on the interaction of ertugliflozin with human serum albumin in vitro by multispectroscopic methods, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2019,219:83−90. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.04.047
[36] 豆换敬. 分子光谱法研究血红蛋白和小分子的相互作用[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2014. DOU H J. Studies on the interaction between hemoglobin and small molecule by molecular spectrometry[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2014.
[37] 陈蓉蓉. 光谱法研究四种青蒿素类抗疟药与人血清白蛋白的相互作用[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2013. CHEN R R. Spectrometric studies on the interaction between four anti-malarial drugs of the artemisinins and human serum albumin[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2013.
[38] CHAVES O A, FERNANDES T V A, De MELOS J L R, et al. Elucidation of the interaction between human serum albumin(HSA) and 3, 4-methylenedioxyde-6-iodo-benzaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone, a potential drug for leishmania amazonensis: Multiple spectroscopic and dynamics simulation approach[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2020,310:113117. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113117
[39] ZHU G, WANG Y, XI L, et al. Spectroscopy and molecular docking studies on the binding of propyl gallate to human serum albumin[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2015,159:188−196. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.11.020
[40] 张丽娇. 光谱法和分子对接技术研究FTO蛋白与小分子的相互作用[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2017. ZHANG L J. Studying on the interaction of FTO protein with small molecules by spectroscopy and molecular docking[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2017.
[41] GEHLEN M H. The centenary of the stern-volmer equation of fluorescence quenching: From the single line plot to the sv quenching map[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews,2020,42:100338. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2019.100338
[42] CIOTTA E, PROSPOSITO P, PIZZOFERRATO R. Positive curvature in stern-volmer plot described by a generalized model for static quenching[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2019,206:518−522. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.10.106
[43] TAYEH N, RUNGASSAMY T, ALBANI J R. Fluorescence spectral resolution of tryptophan residues in bovine and human serum albumins[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2009,50(2):107−116. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.03.015
[44] MEMARPOOR YAZDI M, MAHAKI H. Probing the interaction of human serum albumin with vitamin B2 (riboflavin) and L-arginine (L-arg) using multi-spectroscopic, molecular modeling and zeta potential techniques[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2013,136:150−159. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.11.016
[45] WANG Q, SUN Q, MA X, et al. Probing the binding interaction of human serum albumin with three bioactive constituents of Eriobotrta japonica leaves: Spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B:Biology,2015,148:268−276. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.04.030
[46] AFRIN S, RIYAZUDDEEN, RABBANI G, et al. Spectroscopic and calorimetric studies of interaction of methimazole with human serum albumin[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2014,151:219−223. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.02.028
[47] PARVEEN I, KHAN P, ALI S, et al. Synthesis, molecular docking and inhibition studies of novel 3-n-aryl substituted-2-heteroarylchromones targeting microtubule affinity regulating kinase 4 inhibitors[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2018,159:166−177. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.030
[48] EFTINK M R, GHIRON C A. Fluorescence quenching studies with proteins[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1981,114(2):199−227. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90474-7
[49] DING F, LIU W, ZHANG X, et al. Fluorescence and circular dichroism studies of conjugates between metsulfuron-methyl and human serum albumin[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2010,76(2):441−448. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.12.003
[50] BI S, DING L, TIAN Y, et al. Investigation of the interaction between flavonoids and human serum albumin[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2004,703(1):37−45.
[51] KOLAWOLE A O, KOLAWOLE A N, OLOFINSAN K A, et al. Kolaflavanone of kolaviron selectively binds to subdomain 1b of human serum albumin: Spectroscopic and molecular docking evidences[J]. Computational Toxicology,2020,13:100118. doi: 10.1016/j.comtox.2020.100118
[52] LI J, ZHANG Y, HU L, et al. Binding of carbendazim to bovine serum albumin: Insights from experimental and molecular modeling studies[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2017,1139:303−307. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.03.048
[53] ISHTIKHAR M, RABBANI G, KHAN R H. Interaction of 5-fluoro-5'-deoxyuridine with human serum albumin under physiological and non-physiological condition: A biophysical investigation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2014,123:469−477. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.09.044
[54] SHAHABADI N, MAGHSUDI M, ROUHANI S. Study on the interaction of food colourant quinoline yellow with bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic techniques[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,135(3):1836−1841. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.095
[55] XIAO D, ZHANG L, WANG Q, et al. Investigations of the interactions of peimine and peiminine with human serum albumin by spectroscopic methods and docking studies[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2014,146:218−225. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.09.067
[56] DING F, ZHANG L, DIAO J, et al. Human serum albumin stability and toxicity of anthraquinone dye alizarin complexone: An albumin-dye model[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2012,79:238−246. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.01.009
[57] ERMAKOVA E A, DANILOVA A G, KHAIRUTDINOV B I. Interaction of ceftriaxone and rutin with human serum albumin. Waterlogsy-NMR and molecular docking study[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,2020,1203:127444. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127444
[58] CHUGH H, KUMAR P, TOMAR V, et al. Interaction of noscapine with human serum albumin(HSA): A spectroscopic and molecular modelling approach[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:Chemistry,2019,372:168−176. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.12.001
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 刘帅,荣晓辉,张书锋,屈磊,刘芳,井娟. 纳豆激酶递送系统研究进展. 中国现代应用药学. 2024(09): 1295-1302 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 施雅,朱佳妮,赵博,米飞,顾然. 常见发酵食品中生物活性物质对心脏功能影响的研究进展. 食品与发酵科技. 2024(03): 92-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 祁红兵,宋军霞,毛艳红. 纳豆固体发酵抗氧化功能研究. 农产品加工. 2024(18): 1-4+9 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 屈家亮,柳惠平,张佑红. 纳豆激酶研究进展. 武汉工程大学学报. 2024(05): 527-533 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴丹,杨苗苗,杜小平,祁蒙,杨水云. 依赖于豆粕原材料的纳豆激酶制备和纯化工艺研究. 中国调味品. 2023(03): 79-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. Chunfang Wang,Jinpeng Chen,Wenguo Tian,Yanqi Han,Xu Xu,Tao Ren,Chengwang Tian,Changqing Chen. Natto: A medicinal and edible food with health function. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 2023(03): 349-359 .  必应学术
必应学术
7. 王刚,王芝玉,安荣荣,滕玉婷,古梅,刘霞,高慧娟,董瑞丽. 固态发酵条件对纳豆激酶活性的影响及发酵条件的优化. 粮食加工. 2023(05): 33-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 任莉莉,张胜海,程昆木,杨凌鉴,黄九林. 模拟体内环境下血栓形成及药物溶栓作用. 粘接. 2022(02): 1-5 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 潘钰,夏海华,叶阳,曲晓军,于冲. 纳豆软胶囊功效成分安全性及免疫功能研究. 中国调味品. 2022(06): 84-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 洪奕,夏海华,田洁萍,张淑梅,于冲,田缘,闫更轩,潘钰. 响应面法优化豆粕固体发酵产纳豆激酶培养条件. 中国调味品. 2022(08): 41-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 樊璐,李宏梁,吕名蕊,严烨,黄峻榕. 纳豆糕点的制备及活菌数变化特性的研究. 农产品加工. 2022(15): 15-17+21 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 高梦迪,苏钱琙,李杰,樊学晶,王朝阳,邓立高,李坚斌. 纳豆激酶微生物生产研究进展. 大豆科学. 2022(06): 740-746 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



