Analysis of Biogenic Amines and Related Quality Indexes of Commercial Dry Salted Fish in the East China Sea
-
摘要: 为研究零售期东海鱼鲞的生物胺潜在风险及生物胺与品质指标的相关性,以浙江地区的4种鱼鲞(鳗鱼、大黄鱼、鲳鱼和马鲛鱼)为研究对象,对理化指标(水分含量、NaCl、pH、TVB-N和POV)、微生物指标(菌落总数)和8种生物胺进行测定分析。结果表明,4类鱼鲞的理化、微生物和生物胺指标各不相同。水分含量为25.6%~59.7%,NaCl含量为3.4%~24.1%,pH为6.08~6.97,TVB-N为7.7~56.4 mg/100 g,菌落总数为3.43~5.67 lg CFU/g,POV为0.04~1.76 g/100 g,其中50%样品超过水产干制品POV限值。鱼鲞样品的主要生物胺为亚精胺、组胺、尸胺和腐胺。15%的样品组胺含量>100 mg/kg,超过FDA和/或欧盟的限量标准,其中黄鱼鯗B4的组胺含量达到了1405.88 mg/kg。全部样品的酪胺含量均<100 mg/kg,符合FDA限量标准。生物胺总量在96.05~2164.64 mg/kg之间,其中15%的样品>1000 mg/kg,超过FDA限量标准。相关分析表明,部分生物胺指标与菌落总数和NaCl含量呈中度或高度相关(P<0.05),相关系数r分别为0.727~0.975和−0.828~−0.970。综上,东海鱼鯗,包括以非高组胺鱼为原料的产品,可能存在生物胺超标风险及其他质量问题。本研究为鱼鲞类水产干制品的品质评价和安全控制提供了基础数据和参考依据。Abstract: In order to study the potential risk of biogenic amines and the correlation between biogenic amines and quality indexes of dry salted fish from East China Sea during retail period, the physical and chemical indexes (water content, NaCl, pH, TVB-N and POV), microbial index (aerobic plate count) and eight biogenic amines of four species of dry salted fish (sea eel, large yellow croaker, pomfret and mackerel) in Zhejiang province were determined and analyzed. The results showed that the physicochemical indexes, microbial index and biogenic amines of the four dry salted fish were different. The water content was 25.6%~59.7%, the NaCl content was 3.4%~24.1%, pH was 6.08~6.97, TVB-N content was 7.7~56.4 mg/100 g, POV was 0.04~1.76 g/100 g, the total bacterial count was 3.43~5.67 lg CFU/g, and 50% of the samples exceeded the POV limit of dried aquatic products. Spermidine, histamine, cadaverine and putrescine were the main biogenic amines in dry salted fish. 15% of the samples contained histamine more than 100 mg/kg, which exceeded the limit standards of FDA and EU. The histamine content of B4 reached 1405.88 mg/kg. The tyramine content of all samples was less than 100 mg/kg, which met the limit of FDA. The total amounts of biogenic amines ranged from 96.05 mg/kg to 2164.64 mg/kg, and 15% of the samples were more than 1000 mg kg, which exceeded the limit standards of FDA. Correlation analysis showed that some biogenic amines indexes were moderately or highly correlated with aerobic plate count and NaCl content(P<0.05), and the correlation coefficients were 0.727~0.975 and −0.828~0.970, respectively. In conclusion, dry slated fish from the East China Sea, including products made from non high histamine fish, might have the risk of excessive biogenic amines and other quality problems. This study provides basic data and reference for quality evaluation and safety control of dry slated fish products.
-
鲞,本义为剖开晾干的鱼,现泛指成片的腌腊食品,按动物来源可分为海水鱼类、淡水鱼类和头足类制品。在东海水产干制品中,除了常见的黄鱼鲞、鳗鱼鲞、马鲛鱼鲞之外,还有鲳鱼鲞、玉秃鱼鲞、橡皮鱼鲞、鱿鱼鲞、墨鱼鲞等多个加工品种。按照GB 10136-2015《动物性水产制品》的要求[1],鲞类制品属于预制水产干制品,检测项目包括过氧化值、污染物和添加剂等,对这类产品的其他理化、微生物、生物胺等指标未作强制性要求。但在鱼鲞的实际生产中,由于原料特性复杂、加工周期长,往往存在危害因子如亚硝酸盐、脂质过氧化物和生物胺等[2]。因此,有必要对影响工艺条件和质量安全的因素进行深入考察,以促进行业的健康发展,增强市场竞争力,保障消费者的饮食安全和身体健康。
近年来,生物胺对于高蛋白易腐水产品的品质和安全的影响越来越受到重视[3-4]。过量的生物胺往往与生产、运输和贮藏环节中的污染微生物相关,因此生物胺不仅被作为潜在的毒性成分,也被作为衡量生产过程卫生条件、判断食品新鲜程度的指标[5-6]。由于组胺是毒性最大的生物胺,高组胺鱼类(如青皮红肉海水鱼)和发酵水产品中的组胺变化规律一直是研究的热点[7]。而随着研究范围的拓宽,非高组胺鱼类(如白肉鱼)以及不同加工状态的水产品也逐渐受到关注[8]。东海鱼鲞是浙江地区的传统水产干制品,主要生产环节包括腌渍和干制,由于多使用自然晾晒,处于开放式的加工环境,易受微生物污染并产生生物胺。一旦在加工和贮藏过程中形成生物胺,除挥发性胺外,高温和高酸条件均不能将其降解,存在一定的食品安全风险[9]。但目前对于东海鱼鲞的生物胺质量指标还缺乏有效的监测和监督。
因此,本研究选择了4种常见的东海鱼鲞加工制品,包括3种非高组胺鱼(黄鱼、鳗鱼和鲳鱼)和1种高组胺鱼(马鲛鱼),对不同鱼鲞的理化、微生物指标,特别是生物胺的种类和含量变化进行测定,探讨生物胺指标与其他品质指标的相关性,以期为东海鱼鲞产品的现代化加工和质量安全控制提供数据基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鱼鲞 宁波当地超市,产地均为浙江地区,包括:鳗鱼鲞,编号A1~A8,原料为海鳗(Muraenesox cinereus);黄鱼鲞,编号B1~B6,原料为大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea);鲳鱼鲞,编号C1~C6,原料为金鲳鱼(Trachinotus ovatus);马鲛鱼鲞,编号D1~D6,原料为马鲛鱼(Scomberomorus niphonius);所有产品均属于预制水产干制品,不可直接食用。原料分别为上述四种水产品,辅料为食盐,具体规格、产地等信息见表1;精胺、亚精胺、腐胺、尸胺、组胺、2-苯乙胺、酪胺、色胺等生物胺标准品(≥98%)、1,7-二氨基庚烷(≥98%) 美国Sigma公司;乙醇、乙腈、正己烷、二氯甲烷、甲酸、乙酸、七氟丁酸、乙酸铵 色谱纯,德国Merck公司;其他试剂 均为国产分析纯;水 为超纯水。
表 1 东海鱼鲞的产品信息Table 1. Product information of dry salted fish from the East China Sea编号 大小规格(g) 来源产地 零售包装贮藏方式 A1 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A2 1000 宁波 预包装、冷藏 A3 1000 宁波 预包装、冷藏 A4 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A5 1500 温州 预包装、冷藏 A6 1500 温州 预包装、冷藏 A7 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A8 1000 杭州 预包装、冷藏 B1 500 宁波 预包装、冷藏 B2 500 宁波 预包装、冷藏 B3 450 舟山 散装、室温 B4 550 温州 散装、室温 B5 500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 B6 500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C1 350 象山 预包装、冷藏 C2 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C3 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C4 400 温州 预包装、冷藏 C5 350 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C6 300 温州 预包装、冷藏 D1 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 D2 350 舟山 预包装、冷藏 D3 450 温州 预包装、冷藏 D4 400 象山 预包装、冷藏 D5 350 象山 预包装、冷藏 D6 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 Alliance e2695/Xevo TQ MS液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱联用仪 美国Waters公司;色谱柱ACQUITY HSS T3(100 mm×2.1 mm, 1.8 μm) 美国Waters公司;UV-2600紫外可见分光光度计 尤尼柯(上海)仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 理化指标测定
理化指标测定主要参照GB 10136-2016[1],其中水分含量测定采用直接干燥法[10],pH测定采用玻璃电极法[11],NaCl含量测定采用滴定法[12],过氧化值(Peroxide value,POV)测定采用直接法[13],挥发性盐基氮(Total volatile basic nitrogen,TVB-N)测定采用半微量定氮法[14],菌落总数测定采用平板计数法[15]。
1.2.2 生物胺测定
1.2.2.1 样品制备
取鱼鲞样品可食部分,以1:10(W:V)比例与水混合,浸泡30 min后匀浆。取匀浆液20 mL,加入1 mL内标使用液(1.0 mg/mL 1,7-二氨基庚烷),充分混匀。加入20 mL乙腈、3 mL乙醇、5 mL正己烷,涡旋振荡1 min,5000 r/min离心5 min。取下层清液16 mL,加入2 mL二氯甲烷,涡旋振荡1 min,5000 r/min离心5 min。弃去上层,下层试样溶液加入1 mL二氯甲烷,涡旋振荡1 min,5000 r/min离心5 min。取上清液稀释一定倍数,用0.22 μm滤膜针头滤器过滤至进样瓶中,待测定。
1.2.2.2 检测条件
色谱柱:ACQUITY HSS T3 (100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 μm);流动相:2 mmol/L乙酸铵(A)-含0.1%甲酸的甲醇(B);梯度洗脱:0~0.10 min,95%A;0.10~9.85min,95%~0%A;9.85~11.40 min,0%A;11.40~11.50 min,0%~95%A;11.50~14 min,95%A;柱温:30 ℃;流速:0.20 mL/min;进样量:5 µL。质谱条件:ESI离子源(正离子模式);离子喷雾电压(3500 V);锥孔电压(15 V);脱溶剂温度(500 ℃);脱溶剂流量(1100 L/Hr);锥孔气流量(100 L/Hr);碰撞气流量(0.15 mL/min)。
1.2.2.3 生物胺相关指标
生物胺指数(biogenic amine index,BAI)=组胺+酪胺+腐胺+尸胺。
质量指数(quality index,QI)=(组胺+腐胺+尸胺)/(1+亚精胺+精胺)。
总生物胺(Total biogenic amine,TBA)=组胺+酪胺+腐胺+尸胺+色胺+苯乙胺+精胺+亚精胺[16]。
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin2018进行绘图,利用SPSS17.0统计软件进行Shapiro-Wilk检验和相关性分析,检验的显著水平为P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 常规质量指标统计
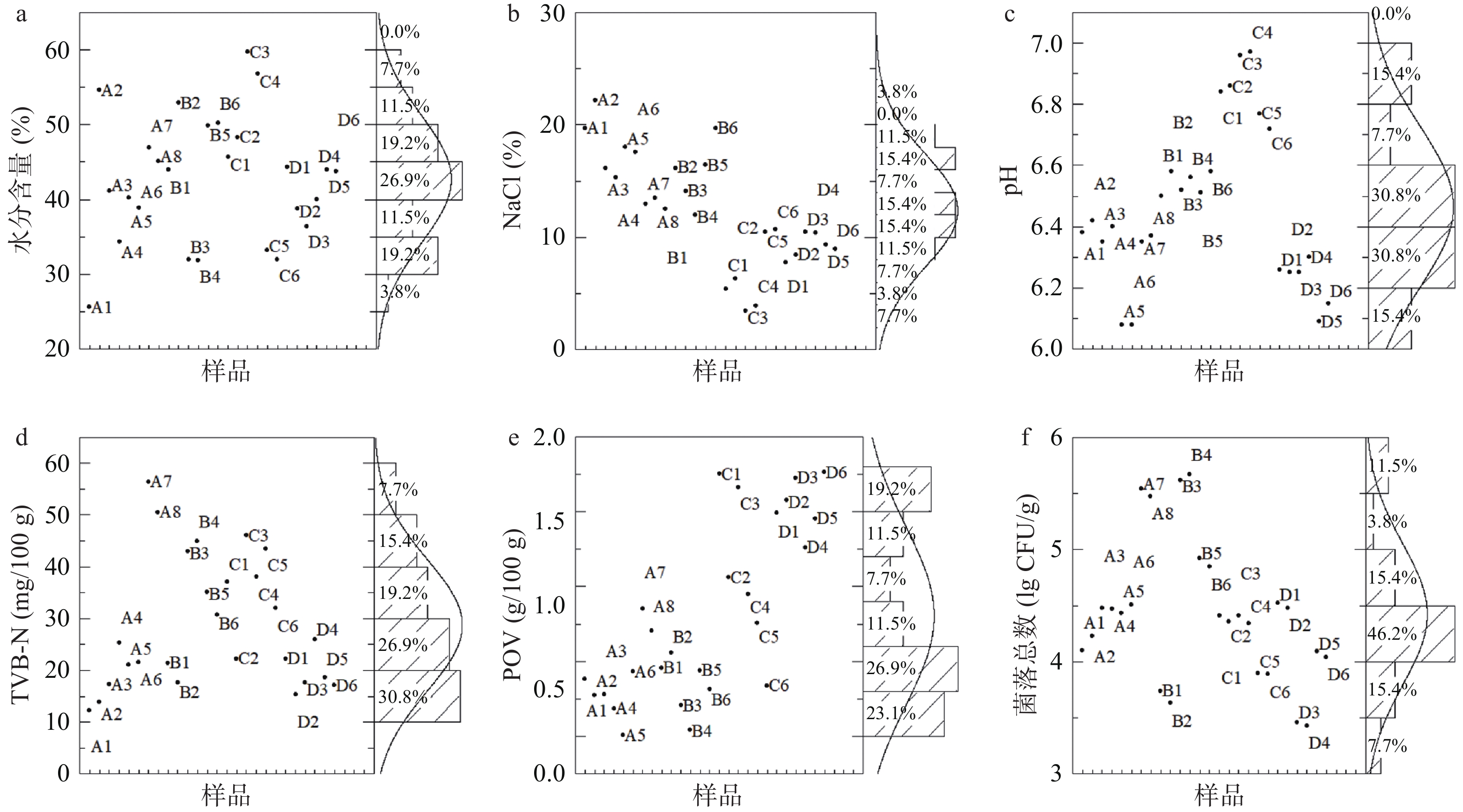
本文采集的26份鱼鲞样品,产自舟山、象山、温州等地区。均在保质期内,感官质量正常,具有产品应有的色泽、滋味、形状和组织状态,无异味、酸败味、霉变和虫蛀等问题[1]。使用边际直方图表示各理化及微生物指标的分布(图1),图中散点表示每个样品对应的指标变量数值,右侧的矩形表示指标变量的分布频数,曲线表示指标变量的正态分布规律。使用Shapiro-Wilk检验对各指标进行正态性检验,除POV值外,其他5项指标的P值均大于0.05,满足正态分布,说明样本选择具有一定代表性。
2.1.1 水分含量
水分含量是控制鱼鲞制品质量的重要参数,主要取决于晾晒的条件和时间,按企业工艺一般小于50%或60%。26份样品的水分含量分布在25.6%~59.7%之间(图1a),符合工艺要求。四个种类的鱼鲞数据分布均比较分散,可见由于加工方式和干燥时间不同,同一种类的鱼鲞水分含量的差异也可能较大。同时,零售阶段的保存方式也可能产生影响,本实验中散装的B3和B4样品暴露于卖场中,水分含量低于其他密封包装的冷藏黄鱼鯗样品。此外,80%鱼鲞样品的水分含量小于50%,为半干水产品。通常水分含量较高的干制品,品质下降和腐败的速度较快,如张晓艳等[17]研究25 ℃贮藏下黄鱼鲞的货架期时发现,50%水分含量的样品可比60%的延长一倍以上。
2.1.2 NaCl含量
盐渍是鱼鲞生产的重要工序之一,通过加入食盐,使水分渗出、盐分透入,从而使鱼体的水分活度降低,抑制微生物的活动,降低并延缓腐败程度。适量的腌渍不但提高了保藏效果的,同时可增加鱼肉风味[18]。传统鱼鲞加工一般采用高盐工艺,用盐量为鱼重的10%~17%,产品含盐量一般<20%。26份鱼鲞样品的NaCl含量范围为3.4%~24.1%(图1b),其中30%样品的含盐量较低,NaCl含量<10%,均为马鲛鱼鲞和鲳鱼鲞。而鳗鱼鲞和黄鱼鲞的平均NaCl含量为17.6%,高于马鲛鱼鲞和鲳鱼鲞的8.0%,可能是腌制过程用盐量不同且腌制时间不同造成的。
2.1.3 pH
本文鱼鲞样品的pH为中性偏酸,范围在6.08~6.97之间(图1c),平均pH为6.47。各种类鱼鲞的pH数据分布均比较集中,其中鲳鱼鲞的pH偏中性,而鳗鱼鲞和马鲛鱼鲞稍偏酸性。Wu等[19]调查中国南部沿海地区的43份盐干鱼,品种包括丁香鱼、帝王鲑鱼、金线鱼、鲭鱼、小黄鱼和大眼鱼,平均pH为6.39,与本文结果相近。而Köse等[20]调查欧洲地区的78份腌渍鱼和盐干鱼,平均pH为5.80~5.90,较本文结果更偏酸。据报道,水产干制品的贮藏期内,pH先上升后下降,前期微生物的生长分解蛋白质生成氨类等碱性物质,造成pH升高,后期可能由产酸微生物发酵生产酸性物质,使pH下降[17]。
2.1.4 TVB-N值
26份鱼鲞样品的TVB-N值分布在7.7~56.4 mg/100 g(图1d),鳗鱼鲞、黄鱼鲞和鲳鱼鲞的TVB-N值较分散,马鲛鱼鲞较集中。TVB-N是水产品新鲜度和食品安全评价的重要监测指标,表示腐败过程中蛋白质分解产生的氨与含氮胺类物质的总量,其浓度与品种来源、贮存温度和时间等有关,如Lin等[21]检测台湾地区盐干沙丁鱼和盐干丁香鱼,TVB-N值为21.9~182 mg/100 g,赵延宁等[22]检测青岛地区咸干鲅鱼,TVB-N值为10~50 mg/100 g。一般认为TVB-N值越低,水产品的新鲜度越高,如规定冰鲜、冻鲜及预制动物性水产制品(不含干制品和盐渍制品)的安全限值为30 mg/100 g[1]。本文中鳗鱼鲞、黄鱼鯗和马鲛鱼鲞的平均TVB-N值分别为27.3、28.3和19.5 mg/100 g。鲳鱼鲞的平均值最高,达到36.5 mg/100 g。黄鱼鯗中,散装样品B3和B4的TVB-N值为42.0和45.9 mg/100 g,高于其他黄鱼鯗样品(17.6~35.1 mg/100 g)。
2.1.5 POV
POV是油脂酸败的早期指标,随着酸败加剧,POV先升后降,是表示食品中油脂氧化变质程度的重要指标之一。鳗鱼和黄鱼的脂肪含量较高,脂肪氧化是感官质量下降的重要原因之一[17,23]。26份鱼鲞样品的POV分布在0.04~1.76 g/100 g(图1e),黄鱼鲞和马鲛鱼鲞的POV值较集中,鳗鱼鲞和鲳鱼鲞较分散。马鲛鱼鲞的平均值最高,达1.54 g/100 g。马鲛鱼属于多脂鱼,在水产干制品加工中,多脂鱼的脂肪氧化比较常见。按GB 10136-2015,预制水产干制品的POV应小于等于0.6 g/100 g,而50%样品超过限值,是影响鱼鲞质量安全的重要因素。脂肪的水解和氧化是脂肪腐败的两个主要途径,赵延宁等[22]检测发现市售咸干鲅鱼POV全部超标,并指出了脂肪氧化对咸干鱼质量安全的重要性。
2.1.6 菌落总数
菌落总数代表食品被细菌污染的程度。四种鱼鲞的菌落总数平均值为4.42 lg CFU/g(图1f),高于其他学者调研的结果,如中国大陆地区43份盐干鱼的菌落总数平均值3.74 lg CFU/g[19]、台湾地区32份盐干鱼的3.14 lg CFU/g[21]。菌落总数范围在3.43~5.67 lg CFU/g之间,46.2%的样品集中在4.00~4.50 lg CFU/g之间。马鲛鱼鲞的平均值较低,黄鱼鲞的平均值较高。散装样品的菌落总数最高,黄鱼鯗B4和B3分别达到5.67和5.62 lg CFU/g。在零售阶段,大型超市一般采用立式冷藏柜售卖鱼鲞产品,而小型超市和农贸市场,常以无包装非冷藏的方式销售鱼鲞产品,更易造成微生物污染和繁殖,需引起重视。鱼鲞一般经热加工后食用,国标中未对此类产品的微生物指标进行限定,但是较高的菌落总数可能反映食品在生产和贮运过程中未符合卫生要求,并进一步促进腐败变质等问题。
2.2 生物胺的比较与分析
水产品中的生物胺主要由细菌对游离氨基酸脱羧而形成,监测其种类和含量,具有指示腐败程度和防止食用潜在毒性的重要意义[19]。26份样品的生物胺含量差异较大,TBA在96.05~2164.64 mg/kg之间(表2)。亚精胺、组胺、尸胺和腐胺是鱼鲞中的优势生物胺,精胺、酪胺、β-苯乙胺和色胺的含量则较低。其中70%的样品未检测到色胺,27%未检测到β-苯乙胺。相关研究表明,生物胺的种类和含量受污染微生物、原料品种、加工贮藏条件等因素影响,与腐败有关的海产品中最常见的生物胺是组胺、酪胺、腐胺和尸胺[24]。Wu等[19]检测中国南部沿海地区的43份盐干鱼,生物胺总量为17.18~4148.79 mg/kg,尸胺和腐胺占比较高,80%样品的色胺和β-苯乙胺含量较低,与本文部分结果相似;而赵延宁等[22]检测的8份市售咸干鲅鱼,生物胺总量为13.66~45.79 mg/kg,色胺含量最高。BAI和QI在鲜鱼和水产加工品的新鲜度研究中,表现了与产品品质变化的相关性[16]。本文鱼鲞样品的BAI范围在44.62~1923.14 mg/kg之间,QI范围在0.22~7.83之间。但由于原料种类和加工贮运条件对生物胺的形成有较大影响,BAI和QI不是评价鱼肉新鲜度的绝对指标,目前尚无一致的评价范围[16]。
表 2 26种市售东海鱼鲞的生物胺含量Table 2. Biogenic amines content of 26 commercial dry salted fish in the East China Sea序号 含量(mg/kg) BAI QI TBA(mg/kg) 尸胺 组胺 苯乙胺 酪胺 亚精胺 色胺 精胺 腐胺 A1 132.04±9.40 14.95±1.69 2.53±0.34 4.50±0.41 108.43±12.12 − 12.70±2.09 43.34±3.26 194.83 1.56 318.49 A2 192.28±8.67 34.29±3.07 8.68±1.36 7.53±1.23 162.48±4.44 − 16.91±1.30 59.85±3.57 293.95 1.59 482.02 A3 53.82±6.57 5.36±0.72 0.13±0.00 1.10±0.16 215.25±26.03 − 60.05±6.20 32.77±3.69 93.05 0.33 368.48 A4 51.76±2.44 5.16±0.62 0.14±0.01 0.76±0.04 169.09±32.41 − 29.87±3.79 32.36±2.33 90.04 0.45 289.14 A5 170.20±15.89 37.46±2.55 0.41±0.02 4.76±0.85 177.15±7.36 − 13.99±0.22 78.59±2.03 291.01 1.49 482.56 A6 141.00±12.30 24.90±3.51 0.53±0.07 5.52±0.86 136.54±9.77 − 23.21±4.54 91.44±14.84 262.86 1.60 423.14 A7 243.81±32.35 89.49±11.40 0.56±0.09 11.00±0.55 285.34±34.88 − 11.89±0.51 165.89±14.58 510.19 1.67 807.98 A8 242.04±28.86 51.69±4.45 0.35±0.02 6.31±0.17 182.75±16.88 − 13.73±0.38 118.34±8.44 418.38 2.09 615.21 B1 241.16±24.12 188.23±18.97 18.40±0.96 21.57±3.70 590.59±89.40 1.50±0.08 90.49±2.03 178.21±15.50 629.17 0.89 1330.15 B2 180.96±4.95 156.81±14.34 16.23±1.51 13.57±1.24 539.29±18.38 1.10±0.10 80.10±10.84 151.50±23.77 502.84 0.79 1139.56 B3 229.76±38.49 1277.50±51.96 1.83±0.16 47.48±6.84 229.11±28.18 8.06±3.54 40.78±4.73 164.06±6.41 1718.80 6.17 1998.58 B4 252.56±5.61 1405.88±18.36 2.30±0.11 68.26±6.99 206.90±20.31 3.36±1.29 28.94±1.82 196.44±30.00 1923.14 7.83 2164.64 B5 5.75±0.09 15.97±1.28 0.03±0.00 0.13±0.01 227.81±46.82 − 12.36±0.39 30.60±2.12 52.45 0.22 292.65 B6 4.84±0.06 13.78±2.55 − 0.11±0.02 219.13±20.44 − 15.90±1.18 25.89±1.84 44.62 0.19 279.65 C1 10.87±0.48 69.82±1.60 − 0.06±0.01 215.10±32.39 − 10.78±1.23 36.20±3.10 116.95 0.52 342.83 C2 8.56±1.12 67.73±3.37 − − 204.39±18.01 − 9.97±0.94 29.83±3.84 106.12 0.49 320.48 C3 233.21±45.67 95.71±9.72 2.66±0.07 28.42±0.73 144.56±12.70 0.42±0.02 11.03±2.38 102.60±8.17 459.94 2.76 618.61 C4 191.81±12.04 74.46±5.41 0.33±0.04 9.10±0.49 97.81±15.09 − 10.96±0.38 90.04±6.51 365.41 3.25 474.51 C5 13.95±2.41 1.06±0.04 − 0.20±0.04 43.60±5.10 0.33±0.03 8.08±1.06 39.36±8.82 54.57 1.03 106.58 C6 8.19±0.59 − − − 112.30±5.73 0.25±0.01 10.29±0.34 39.45±1.08 47.64 0.39 170.48 D1 263.61±33.96 13.44±1.43 0.58±0.02 27.12±3.43 308.69±8.78 − 11.59±1.79 166.80±32.26 470.97 1.38 791.83 D2 205.64±20.79 12.50±2.77 0.84±0.05 26.32±2.33 258.04±22.16 − 10.85±0.89 160.36±9.46 404.82 1.40 674.55 D3 12.69±0.45 18.81±1.51 − 0.12±0.01 273.85±24.01 − 12.00±1.35 32.19±4.14 63.81 0.22 349.66 D4 7.39±0.91 20.51±4.06 − 0.25±0.02 307.85±13.33 − 17.08±2.64 32.51±5.55 60.66 0.19 385.59 D5 5.48±1.11 − 0.24±0.04 0.23±0.01 42.14±5.28 0.31±0.01 8.10±0.79 39.55±5.43 45.26 0.88 96.05 D6 11.19±1.48 − 0.28±0.02 − 34.23±2.07 − 9.59±0.12 47.74±7.54 58.93 1.31 103.03 注:−表示未检出。 生物胺中组胺毒性最大,酪胺次之。各国对于鱼鲞类产品的生物胺安全限量有不同的要求。我国GB 10136-2015对盐渍鱼产品规定了组胺安全限量,高组胺鱼类和非高组胺鱼类分别为40和20 mg/kg,而对预制水产干制品(包括鱼鲞、虾类和贝类及其他干制品)未作要求;美国FDA对进出口水产品中生物胺的容许残留限量为组胺≤50 mg/kg,酪胺≤100 mg/kg,生物胺总量≤1000 mg/kg[25];欧盟规定鲭科鱼类中组胺≤100 mg/kg,经盐水酶熟化处理或发酵的鱼类产品≤200 mg/kg[26]。本文中31%的鱼鲞样品组胺含量大于50 mg/kg,包括鳗鱼鲞A7和A8、黄鱼鲞B1、B2、B3和B4以及鲳鱼鲞C1、C2、C3和C4,均为非高组胺鱼类。其中,黄鱼鲞B1、B2、B3和B4的组胺含量大于100 mg/kg,且TBA大于1000 mg/kg,占样品总数的15%。属于高组胺鱼类的马鲛鱼鲞,组胺含量均未超标,最高为样品D4(20.51 mg/kg)。从酪胺的检测数据来看,最高为黄鱼鲞B4(68.26 mg/kg),全部样品均小于100 mg/kg的安全限值。在各国报道的水产品组胺中毒事件中,高组胺鱼类更受到关注,如检出马鲛鱼(1539 mg/kg)、剑鱼(2937 mg/kg)、异鳞蛇鲭(3800 mg/kg)和冷熏三文鱼(>7000 mg/kg)等[27]。一般认为食品中组胺含量超过500 mg/kg是有毒的,并对人体健康造成危害[28]。而本实验中,非高组胺鱼类的黄鱼鲞B3和B4,组胺含量分别达到1277.50和1405.88 mg/kg,远超过容许残留限量水平。同时,B3和B4也是所有样品中仅有的散装商品(无包装、未冷藏)。可见,非高组胺鱼加工制品以及不当的保存条件可能引起组胺超标风险,有必要对非高组胺鱼类的预制干制品进行生物胺安全风险评估,从而警示其加工和贮藏卫生链中产胺微生物的污染或不当的保存条件。
除组胺外,亚精胺、尸胺和腐胺也均为本文鱼鲞样品中的主要生物胺。尸胺、腐胺、精胺和亚精胺均为中等毒性的生物胺,不但可与硝酸盐生成致癌的亚硝基胺,而且对组胺毒性具有增强作用。按形成机制,亚精胺由腐胺通过亚精胺合成酶产生[24]。本文中亚精胺含量(34.23~590.59 mg/kg)远高于其他报道,如盐干银鱼(22.03 mg/kg)[19]和热烟熏鲣鱼(79.1 mg/kg)[20]等,有待于进一步研究。尸胺和腐胺在新鲜鱼体中含量较低,在死后迅速积累,是表示水产品新鲜度与加工卫生条件优劣的重要指标,特别是非高组胺鱼类产品[27]。本文鱼鲞中尸胺(4.84~263.61 mg/kg)和腐胺(25.89~196.44 mg/kg)在四种鱼鲞中均广泛分布,与部分报道结果相似[21]。
2.3 生物胺指标与质量指标的相关性
在鱼鲞生产贮运过程中,生物胺的增加是不断累积的,受到水分、pH、微生物和温度等因素的影响[29]。由于品种、产地、腌制工艺和干燥方法的不同,鱼鲞的理化性质、微生物和生物胺有一定的差异,因此分别对四种鱼鲞的生物胺与其他品质指标进行Pearson相关性分析,从而评价生物胺与理化指标和菌落总数的相关关系。由表3可见,四种鱼鲞受各项指标的影响程度并不相同。鳗鱼鲞的生物胺数据主要与菌落总数、POV和TVB-N指标显著相关(P<0.05),黄鱼鲞主要与水分含量、NaCl含量和菌落总数显著相关(P<0.05),鲳鱼鲞主要与水分含量、pH和NaCl相关,马鲛鱼鲞主要与pH、NaCl含量和菌落总数显著相关(P<0.05)。
表 3 鱼鲞中生物胺与理化指标和菌落总数的相关性Table 3. Correlation among biogenic amines and physicochemical properties, aerobic plate count in dry salted fish指标 尸胺 组胺 苯乙胺 酪胺 亚精胺 色胺 精胺 腐胺 BAI QI TBA 鳗鱼鲞 水分含量 0.539 0.531 0.469 0.544 0.519 / −0.062 0.439 0.526 0.265 0.617 pH −0.033 −0.019 0.368 −0.009 0.163 / 0.108 −0.167 −0.074 −0.192 0.004 NaCl −0.158 −0.430 0.78* −0.082 −0.655 / −0.103 −0.547 −0.340 0.049 −0.494 菌落总数 0.727* 0.856** −0.284 0.656 0.694 / −0.359 0.875** 0.827* 0.486 0.888** POV 0.674 0.755* −0.03 0.722* 0.544 / −0.279 0.804* 0.779* 0.530 0.813* TVB-N 0.648 0.816* −0.397 0.574 0.701 / −0.331 0.863** 0.774* 0.407 0.846** 黄鱼鲞 水分含量 −0.669 −0.957** 0.287 −0.929** 0.391 −0.948** 0.117 −0.637 −0.944** −0.946** −0.868* pH −0.163 −0.032 −0.094 −0.032 −0.122 0.003 −0.14 −0.113 −0.060 0.006 −0.094 NaCl −0.871* −0.642 −0.343 −0.778 −0.246 −0.628 −0.432 −0.871* −0.741 −0.644 −0.828* 菌落总数 0.465 0.966** −0.532 0.885* −0.634 0.975** −0.382 0.449 0.903* 0.968** 0.760 POV −0.221 −0.807 0.650 −0.631 0.714 −0.796 0.476 −0.184 −0.709 −0.782 −0.541 TVB-N 0.08 0.764 −0.812* 0.632 −0.871* 0.792 −0.708 0.058 0.643 0.775 0.428 鲳鱼鲞 水分含量 0.826* 0.957** 0.651 0.737 0.242 −0.179 0.695 0.767 0.844* 0.750 0.945** pH 0.855* 0.902* 0.604 0.714 0.105 −0.174 0.6 0.802 0.866* 0.825* 0.915* NaCl −0.737 −0.981** −0.565 −0.646 −0.372 0.295 −0.747 −0.679 −0.761 −0.658 −0.904* 菌落总数 0.629 0.987** 0.464 0.538 0.488 −0.414 0.735 0.559 0.656 0.549 0.837* POV 0.362 0.81 0.514 0.487 0.64 −0.11 0.465 0.322 0.405 0.219 0.604 TVB-N 0.544 0.069 0.57 0.59 −0.482 0.637 −0.046 0.609 0.539 0.552 0.355 马鲛鱼鲞 水分含量 0.155 −0.700 0.206 0.09 −0.535 0.412 −0.423 0.156 −0.159 0.121 0.514 pH 0.379 0.937** 0.034 0.376 0.952** −0.781 0.839* 0.316 0.396 −0.199 0.709 NaCl −0.836* 0.363 −0.873* −0.817* 0.049 0.055 0.456 −0.864* −0.823* −0.97** −0.547 菌落总数 0.949** −0.121 0.942** 0.951** 0.197 −0.109 −0.323 0.970** 0.946** 0.915* 0.744 POV −0.031 −0.229 0.037 −0.050 −0.192 −0.238 0.279 −0.003 −0.032 0.207 −0.105 TVB-N −0.055 0.473 −0.428 −0.124 0.451 −0.105 0.757 −0.159 −0.07 −0.412 0.160 注:*表示有显著性差异(P<0.05);**表示有极显著差异(P<0.01)。 菌落总数是重要的影响指标之一,与各生物胺指标呈正相关,相关系数r在0.727~0.975之间。在黄鱼鯗中,组胺(r=0.966)、色胺(r=0.975)和QI(r=0.968)与菌落总数呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),酪胺(r=0.885)和BAI(r=0.903)与菌落总数呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。其他三种鱼鲞的组胺指标也均与菌落总数呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),相关系数r在0.856~0.987之间。同时,鳗鱼鲞中的尸胺、腐胺、BAI和TBA,鲳鱼鲞中的TBA,以及马鲛鱼鲞中的尸胺、苯乙胺、酪胺、腐胺和QI,均与菌落总数呈显著(P<0.05)或极显著(P<0.01)正相关。此外,菌落总数与理化指标中的NaCl含量、TVB-N和POV有一定相关性。虽然本实验中四种鱼鲞的含盐量有一定差距,但菌落总数与NaCl含量均呈显著负相关,相关系数r分别为−0.629、−0.756、−0.945和−0.942,符合盐渍可抑制微生物生长和繁殖的食品保藏原理。同时,在黄鱼鲞、鳗鱼鲞中,菌落总数与TVB-N呈显著正相关(P<0.05);在鲳鱼鲞中,菌落总数与POV呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。研究表明,食品中的生物胺主要由其丰富的蛋白质和微生物分泌的外源氨基酸脱羧酶作用而产生[29]。本实验中,鱼鲞中生物胺的产生,特别是组胺的产生,与微生物指标紧密相关,有必要严格控制鱼鲞的加工和保存等条件,避免因微生物的大量生长繁殖而导致的生物胺不断累积。
除鳗鱼鲞外,其他鱼鲞的NaCl含量基本与各生物胺指标呈负相关,相关系数r在−0.828~−0.970之间。食品中加入NaCl可以降低水分活度,提高渗透压,从而抑制微生物的生长。也有研究表明,NaCl可通过破坏位于细菌细胞膜上的氨基酸脱羧酶来降低生物胺的产生[30]。鱼鯗生产是在水产中加入食盐腌渍晾晒的贮藏方法,成本低廉,风味独特。虽然黄鱼鲞的含盐量比鲳鱼鲞高12%,但两类鱼鲞的TBA指标与NaCl的相关性规律相似,均为显著负相关(P<0.05),r值分别为−0.828和−0.904。可见,在同类原料的鱼鲞中,提高食盐加入量,显著降低了生物胺水平。当然,现代营养健康提倡低盐饮食,世界卫生组织推荐成人一天食用不超过5 g盐,可以适当控制鱼鲞等盐渍食品的使用量。此外,水分含量、pH、POV和TVB-N等理化指标对不同的鱼鲞产品生物胺指标表现出不同的相关性,如鳗鱼鲞的POV与组胺、酪胺、腐胺、BAI和TBA均为显著正相关(P<0.05),相关系数r在0.722~0.813之间,而其他三种鱼鲞的POV与生物胺指标没有表现出相关性。总的来说,菌落总数越低、盐分越高的鱼鲞产品在生物胺方面的安全性越高。今后的研究可适当增加样本的数量和范围,拓展考察因素,更全面地探究鱼鲞中生物胺的控制规律。
3. 结论
本文研究了26份零售阶段东海鱼鲞样品的理化、微生物及生物胺指标,发现在理化指标(水分含量、NaCl、pH、TVB-N和POV)中,50%的样品出现了POV超标的问题;在微生物指标(菌落总数)中,无包装非冷藏散装样品的菌落总数明显高于冷藏包装的鱼鲞样品;在生物胺指标中,虽然样品的酪胺含量均低于限量要求,但31%的样品组胺含量超过FDA允许的限量水平,15%的样品组胺含量超过欧盟规定的不可接受水平。值得注意的是,样品中以高组胺鱼类为原料的马鲛鱼鲞未出现组胺超标情况,但以非高组胺鱼类为原料的鳗鱼鲞、黄鱼鲞和鲳鱼鲞出现了组胺超标问题,其中黄鱼鲞还出现了组胺含量大于1000 mg/kg的情况。因此,不仅应关注青皮红肉鱼为原料的鱼鲞产品,也应重视以非高组胺类的白肉鱼为原料的鱼鲞产品的生物胺安全性。通过相关性分析发现,菌落总数和NaCl含量与鱼鲞的生物胺含量存在显著相关性,特别是组胺指标,说明菌落总数越高、盐分越低的鱼鲞产品可能存在更大的组胺安全性风险。本文为鱼鲞的加工贮藏中的生物胺安全控制提供了一定的理论参考依据。
-
表 1 东海鱼鲞的产品信息
Table 1 Product information of dry salted fish from the East China Sea
编号 大小规格(g) 来源产地 零售包装贮藏方式 A1 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A2 1000 宁波 预包装、冷藏 A3 1000 宁波 预包装、冷藏 A4 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A5 1500 温州 预包装、冷藏 A6 1500 温州 预包装、冷藏 A7 1500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 A8 1000 杭州 预包装、冷藏 B1 500 宁波 预包装、冷藏 B2 500 宁波 预包装、冷藏 B3 450 舟山 散装、室温 B4 550 温州 散装、室温 B5 500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 B6 500 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C1 350 象山 预包装、冷藏 C2 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C3 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C4 400 温州 预包装、冷藏 C5 350 舟山 预包装、冷藏 C6 300 温州 预包装、冷藏 D1 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 D2 350 舟山 预包装、冷藏 D3 450 温州 预包装、冷藏 D4 400 象山 预包装、冷藏 D5 350 象山 预包装、冷藏 D6 400 舟山 预包装、冷藏 表 2 26种市售东海鱼鲞的生物胺含量
Table 2 Biogenic amines content of 26 commercial dry salted fish in the East China Sea
序号 含量(mg/kg) BAI QI TBA(mg/kg) 尸胺 组胺 苯乙胺 酪胺 亚精胺 色胺 精胺 腐胺 A1 132.04±9.40 14.95±1.69 2.53±0.34 4.50±0.41 108.43±12.12 − 12.70±2.09 43.34±3.26 194.83 1.56 318.49 A2 192.28±8.67 34.29±3.07 8.68±1.36 7.53±1.23 162.48±4.44 − 16.91±1.30 59.85±3.57 293.95 1.59 482.02 A3 53.82±6.57 5.36±0.72 0.13±0.00 1.10±0.16 215.25±26.03 − 60.05±6.20 32.77±3.69 93.05 0.33 368.48 A4 51.76±2.44 5.16±0.62 0.14±0.01 0.76±0.04 169.09±32.41 − 29.87±3.79 32.36±2.33 90.04 0.45 289.14 A5 170.20±15.89 37.46±2.55 0.41±0.02 4.76±0.85 177.15±7.36 − 13.99±0.22 78.59±2.03 291.01 1.49 482.56 A6 141.00±12.30 24.90±3.51 0.53±0.07 5.52±0.86 136.54±9.77 − 23.21±4.54 91.44±14.84 262.86 1.60 423.14 A7 243.81±32.35 89.49±11.40 0.56±0.09 11.00±0.55 285.34±34.88 − 11.89±0.51 165.89±14.58 510.19 1.67 807.98 A8 242.04±28.86 51.69±4.45 0.35±0.02 6.31±0.17 182.75±16.88 − 13.73±0.38 118.34±8.44 418.38 2.09 615.21 B1 241.16±24.12 188.23±18.97 18.40±0.96 21.57±3.70 590.59±89.40 1.50±0.08 90.49±2.03 178.21±15.50 629.17 0.89 1330.15 B2 180.96±4.95 156.81±14.34 16.23±1.51 13.57±1.24 539.29±18.38 1.10±0.10 80.10±10.84 151.50±23.77 502.84 0.79 1139.56 B3 229.76±38.49 1277.50±51.96 1.83±0.16 47.48±6.84 229.11±28.18 8.06±3.54 40.78±4.73 164.06±6.41 1718.80 6.17 1998.58 B4 252.56±5.61 1405.88±18.36 2.30±0.11 68.26±6.99 206.90±20.31 3.36±1.29 28.94±1.82 196.44±30.00 1923.14 7.83 2164.64 B5 5.75±0.09 15.97±1.28 0.03±0.00 0.13±0.01 227.81±46.82 − 12.36±0.39 30.60±2.12 52.45 0.22 292.65 B6 4.84±0.06 13.78±2.55 − 0.11±0.02 219.13±20.44 − 15.90±1.18 25.89±1.84 44.62 0.19 279.65 C1 10.87±0.48 69.82±1.60 − 0.06±0.01 215.10±32.39 − 10.78±1.23 36.20±3.10 116.95 0.52 342.83 C2 8.56±1.12 67.73±3.37 − − 204.39±18.01 − 9.97±0.94 29.83±3.84 106.12 0.49 320.48 C3 233.21±45.67 95.71±9.72 2.66±0.07 28.42±0.73 144.56±12.70 0.42±0.02 11.03±2.38 102.60±8.17 459.94 2.76 618.61 C4 191.81±12.04 74.46±5.41 0.33±0.04 9.10±0.49 97.81±15.09 − 10.96±0.38 90.04±6.51 365.41 3.25 474.51 C5 13.95±2.41 1.06±0.04 − 0.20±0.04 43.60±5.10 0.33±0.03 8.08±1.06 39.36±8.82 54.57 1.03 106.58 C6 8.19±0.59 − − − 112.30±5.73 0.25±0.01 10.29±0.34 39.45±1.08 47.64 0.39 170.48 D1 263.61±33.96 13.44±1.43 0.58±0.02 27.12±3.43 308.69±8.78 − 11.59±1.79 166.80±32.26 470.97 1.38 791.83 D2 205.64±20.79 12.50±2.77 0.84±0.05 26.32±2.33 258.04±22.16 − 10.85±0.89 160.36±9.46 404.82 1.40 674.55 D3 12.69±0.45 18.81±1.51 − 0.12±0.01 273.85±24.01 − 12.00±1.35 32.19±4.14 63.81 0.22 349.66 D4 7.39±0.91 20.51±4.06 − 0.25±0.02 307.85±13.33 − 17.08±2.64 32.51±5.55 60.66 0.19 385.59 D5 5.48±1.11 − 0.24±0.04 0.23±0.01 42.14±5.28 0.31±0.01 8.10±0.79 39.55±5.43 45.26 0.88 96.05 D6 11.19±1.48 − 0.28±0.02 − 34.23±2.07 − 9.59±0.12 47.74±7.54 58.93 1.31 103.03 注:−表示未检出。 表 3 鱼鲞中生物胺与理化指标和菌落总数的相关性
Table 3 Correlation among biogenic amines and physicochemical properties, aerobic plate count in dry salted fish
指标 尸胺 组胺 苯乙胺 酪胺 亚精胺 色胺 精胺 腐胺 BAI QI TBA 鳗鱼鲞 水分含量 0.539 0.531 0.469 0.544 0.519 / −0.062 0.439 0.526 0.265 0.617 pH −0.033 −0.019 0.368 −0.009 0.163 / 0.108 −0.167 −0.074 −0.192 0.004 NaCl −0.158 −0.430 0.78* −0.082 −0.655 / −0.103 −0.547 −0.340 0.049 −0.494 菌落总数 0.727* 0.856** −0.284 0.656 0.694 / −0.359 0.875** 0.827* 0.486 0.888** POV 0.674 0.755* −0.03 0.722* 0.544 / −0.279 0.804* 0.779* 0.530 0.813* TVB-N 0.648 0.816* −0.397 0.574 0.701 / −0.331 0.863** 0.774* 0.407 0.846** 黄鱼鲞 水分含量 −0.669 −0.957** 0.287 −0.929** 0.391 −0.948** 0.117 −0.637 −0.944** −0.946** −0.868* pH −0.163 −0.032 −0.094 −0.032 −0.122 0.003 −0.14 −0.113 −0.060 0.006 −0.094 NaCl −0.871* −0.642 −0.343 −0.778 −0.246 −0.628 −0.432 −0.871* −0.741 −0.644 −0.828* 菌落总数 0.465 0.966** −0.532 0.885* −0.634 0.975** −0.382 0.449 0.903* 0.968** 0.760 POV −0.221 −0.807 0.650 −0.631 0.714 −0.796 0.476 −0.184 −0.709 −0.782 −0.541 TVB-N 0.08 0.764 −0.812* 0.632 −0.871* 0.792 −0.708 0.058 0.643 0.775 0.428 鲳鱼鲞 水分含量 0.826* 0.957** 0.651 0.737 0.242 −0.179 0.695 0.767 0.844* 0.750 0.945** pH 0.855* 0.902* 0.604 0.714 0.105 −0.174 0.6 0.802 0.866* 0.825* 0.915* NaCl −0.737 −0.981** −0.565 −0.646 −0.372 0.295 −0.747 −0.679 −0.761 −0.658 −0.904* 菌落总数 0.629 0.987** 0.464 0.538 0.488 −0.414 0.735 0.559 0.656 0.549 0.837* POV 0.362 0.81 0.514 0.487 0.64 −0.11 0.465 0.322 0.405 0.219 0.604 TVB-N 0.544 0.069 0.57 0.59 −0.482 0.637 −0.046 0.609 0.539 0.552 0.355 马鲛鱼鲞 水分含量 0.155 −0.700 0.206 0.09 −0.535 0.412 −0.423 0.156 −0.159 0.121 0.514 pH 0.379 0.937** 0.034 0.376 0.952** −0.781 0.839* 0.316 0.396 −0.199 0.709 NaCl −0.836* 0.363 −0.873* −0.817* 0.049 0.055 0.456 −0.864* −0.823* −0.97** −0.547 菌落总数 0.949** −0.121 0.942** 0.951** 0.197 −0.109 −0.323 0.970** 0.946** 0.915* 0.744 POV −0.031 −0.229 0.037 −0.050 −0.192 −0.238 0.279 −0.003 −0.032 0.207 −0.105 TVB-N −0.055 0.473 −0.428 −0.124 0.451 −0.105 0.757 −0.159 −0.07 −0.412 0.160 注:*表示有显著性差异(P<0.05);**表示有极显著差异(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 10136-2015动物性水产制品[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 10136-2015 Animal aquatic products[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015.
[2] 赵延宁, 王玉, 王睿迪, 等. 咸干鱼中危害因子分析及其控制的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(14):320−324. [ZHAO Y N, WANG Y, WANG R D, et al. Research progress on hazards factor analysis and control of salted dry fish[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(14):320−324. [3] 丁海燕, 孙晓杰, 宁劲松, 等. 储藏温度对3种海水鱼产生生物胺的规律影响研究[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(9):177−182. [DING H Y, SUN X J, NING J S, et al. Study on the regular of biogenic amines from three marine fish stored at different temperature[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(9):177−182. [4] 常娅妮, 马俪珍, 杨梅, 等. 不同冷冻方式对调味鱼贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(2):137−143. [CHANG Y N, MA L Z, Yang M, et al. Effects of different freezing methods on the storage quality of seasoned channel catfish[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(2):137−143. [5] LALY S J, ANUPAMA T K, KUMAR K A, et al. Quality and freshness of fish available in supermarkets of Cochin, India based on biogenic amine content[J]. Fishery Technology,2019,56(1):212−220.
[6] COSTA C, GRAZHDAN D, FIUTOWSKI J, et al. Meat and fish freshness evaluation by functionalized cantilever-based biosensors[J]. Microsystem Technologies,2020,26(4):1−5.
[7] HE S, CHEN Y N, YANG X Q, et al. Determination of biogenic amines in chub mackerel from different storage methods[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85(6):1699−1706. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15146
[8] 朱作艺, 张玉, 王君虹, 等. 不同贮藏条件下大黄鱼生物胺变化[J]. 浙江农业学报,2018,30(9):1592−1598. [ZHU Z Y, ZHANG Y, WANG J H, et al. Changes of biogenic amines in large yellow croaker stored at different conditions[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2018,30(9):1592−1598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2018.09.21 [9] SUN Y Y, GAO P, XU Y S, et al. Effect of storage conditions on microbiological characteristics, biogenic amines, and physicochemical quality of low-salt fermented fish[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2020,83(6):1057−1065. doi: 10.4315/JFP-19-607
[10] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.237-2016 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.237-2016 Determination of pH value in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.42-2016 食盐指标的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.42-2016 Determination of salt index[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准GB 5009.227-2016 食品中过氧化值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.227-2016 Determination of peroxide value in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 5009.228-2016食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 5009.228-2016 Determination of total volatile basic nitrogen in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[15] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 GB 4789.2-2016食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. National food safety standard. GB 4789.2-2016 Microbiological examination: aerobic plate count[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[16] 杨春婷, 赵晓娟, 白卫东. 肉类中的生物胺形成及其在肉类新鲜度评价中的应用研究进展[J]. 肉类研究,2017,31(1):55−59. [YANG C T, ZHAO X J, BAI W D, et al. Formation of biogenic amines during meat storage and their application in assessment of meat freshness[J]. Meat Research,2017,31(1):55−59. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-201701010 [17] 张晓艳, 杨宪时, 郭全友, 等. 水分含量对淡腌大黄鱼贮藏性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(9):364−366, 375. [ZHANG X Y, YANG X S, GUO Q Y, et al. Effect of moisture content on storage properties in light salted Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(9):364−366, 375. [18] 吴燕燕, 钱茜茜, 李来好, 等. 基于Illumina MiSeq技术分析腌干鱼加工过程微生物群落多样性[J]. 食品科学,2016,38(12):8−15. [WU Y Y, QIAN X X, LI L H et al. Microbial community diversity in dried-salted fish during processing revealed by illumina MiSeq sequencing[J]. Food Science,2016,38(12):8−15. [19] WU Y Y, CHEN Y F, LI L H, et al. Study on biogenic amines in various dry salted fish consumed in China[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China,2016,15(4):681−689. doi: 10.1007/s11802-016-2958-0
[20] KÖSE S, KORAL S, TUFAN B, et al. Biogenic amine contents of commercially processed traditional fish products originating from European countries and Turkey[J]. European Food Research & Technology,2012,235(4):669−683.
[21] LIN C S, LIU, F L, LEE Y C, et al. Histamine contents of salted seafood products in Taiwan and isolation of hatotolerant histamine-forming bacteria[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,131(2):574−579. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.027
[22] 赵延宁, 王玉, 王睿迪, 等. 市售咸干鲅鱼的安全性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(14):215−220. [ZHAO Y N, WANG Y, WANG R D, et al. Safety analysis of commercially available salted and dried Spanish markerel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(14):215−220. [23] 陈申如, 张其标, 胡阳, 等. 温度对液熏鳗鱼质量特性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(7):95−99. [CHEN S R, ZHANG Q B, HU Y, et al. The effect of temperature on the quality characteristics of liquid-smoked eel[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(7):95−99. [24] LEHANE L, OLLEY J. Histamine fish poisoning revisited[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2000,58(1-2):1−37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00296-8
[25] US FDA. Fish and fishery products hazards and controls guide. 3rd ed. Scombrotoxin (histamine) formation[S]. Washington: Food and Drug Administration, 2001.
[26] European Commission (EC). Commission recommendation of 10 January 2003 concerning a coordinated programme for the official control of foodstuffs for 2003 (2003/10/EC)[S]. Brussels: Official Journal of the European Communities, 2003.
[27] PRESTER L. Biogenic amines in fish, fish products and shellfish: A review[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants,2011,28(11):1547−1560.
[28] TEN B B, DAMINK C, JOOSTEN H M, et al. Occurrence and formation of biologically active amines in foods[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,1990,11(1):73−84. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(90)90040-C
[29] 陈玉峰, 吴燕燕, 李来好, 等. 腌干鱼贮藏过程生物胺的变化及其货架期研究[J]. 核农学报,2016,30(8):1548−1557. [CHEN Y F, WU Y Y, LI L H, et al. Study on the change of biogenic amines and its shelf life of dried-salted fish at storage[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2016,30(8):1548−1557. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2016.08.1548 [30] 景智波, 田建军, 杨明阳, 等. 食品中与生物胺形成相关的微生物菌群及其控制技术研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(15):272−278. [JING Z B, TIAN J J, YANG M Y, et al. Progress in understanding and controlling the microbial community involved in biogenic amine production[J]. Food Science,2018,39(15):272−278. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陆健航,李瑞琳,陈凤美,刘宇,姜维. 东海区市售大黄鱼鲞的品质分析研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(11): 159-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗振玲,高海波,杨挺,付余. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定小黄花鱼中9种生物胺. 食品工业科技. 2023(05): 251-257 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王梅英,吴若玫,黄琳杉,陈慧斌. 黄鱼鲞加工中感官品质和挥发性风味成分分析. 闽南师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 79-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



