Effect of Portulaca oleracea L. on Lowering Uric Acid and Protecting Kidney
-
摘要: 目的:研究马齿苋降尿酸和肾脏保护作用,为临床研究提供参考。方法:将雄性ICR小鼠随机分为5组,空白组(CON)、模型组(HUA)、别嘌呤醇阳性药对照组(ALLOP,0.02 g/kg/d)、马齿苋高剂量组(PO-H,1.48 g/kg/d)、马齿苋低剂量组(PO-L,0.5 g/kg/d)。每组按相应给药剂量连续灌胃21 d,第7 d开始,除空白组外,每组腹腔注射次黄嘌呤(HX,0.3 g/kg)联合氧嗪酸钾(OAPS,0.3 g/kg)以建立高尿酸血症模型。观察小鼠血清尿酸值(SUA)、丙二醛(MDA)水平;收集肝脏检测黄嘌呤氧化酶(XOD)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)水平;收集肾脏检测谷胱甘肽(GSH)、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶(GSH-PX)水平;实验结束前一天收集24 h尿液检测尿尿酸(UUA)、尿肌酐(UCr)水平;对小鼠肾脏HE染色进行病理学观察。结果:与CON组比较,HUA组极显著(P<0.01)升高MDA、SUA、XOD水平,极显著(P<0.01)降低SOD、GSH、GSH-PX、UUA、UCr水平,说明高尿酸血症建模成功。与HUA组比较,PO-H组可极显著(P<0.01)降低SUA、MDA、XOD水平,极显著(P<0.01)升高SOD、GSH、GSH-PX、UCr水平;PO-L组可显著(P<0.05或P<0.01)降低SUA、MDA、XOD水平,显著(P<0.05或P<0.01)升高GSH、GSH-PX、UCr水平;HE染色结果显示PO可明显改善HUA小鼠肾组织的病理变化。结论:马齿苋提取物对高尿酸血症小鼠具有一定的降尿酸和肾保护功能。Abstract: Objective: To study the uric acid-lowering and renal protective effects of Portulaca oleracea to provide reference for clinical research. Methods: Male ICR mice were randomly divided into 5 groups. Blank group (CON), model group (HUA), allopurinol positive drug control group (ALLOP, 0.02 g/kg/d), purslane high-dose group (PO-H, 1.48 g/kg/d), Portulaca low-dose group (PO-L, 0.5 g/kg/d). Each group was given the corresponding dose for 21 d continuously, starting from the 7th day, except for the blank group, each group was intraperitoneally injected with hypoxanthine (HX, 0.3 g/kg) combined with potassium oxazine (OAPS, 0.3 g/kg) to establish a hyperuricemia model. Observe serum uric acid (SUA) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in mice, collect liver to detect xanthine oxidase (XOD) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels, collect kidney to detect glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) level. 24 hours urine was collected the day before the end of the experiment to detect urine uric acid (UUA) and urine creatinine (UCr) levels, pathological observation of mouse kidney HE staining was performed. Results: Compared with the CON group, the HUA group significantly (P<0.01) increased the levels of MDA, SUA, and XOD, and significantly (P<0.01) decreased the levels of SOD, GSH, GSH-PX, UUA, and UCr, indicating that hyperuricemia was a cause of hyperuricemia. The model was successful. Compared with HUA group, PO-H group could significantly (P<0.01) reduce SUA, MDA, XOD (levels, significantly (P<0.01), increase SOD, GSH, GSH-PX, UCr levels. PO-L group could significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01) reduce the levels of SUA, MDA, XOD, and significantly (P<0.05 or P<0.01) increase the levels of GSH, GSH-PX, UCr. HE staining results showed that PO could significantly improve the kidneys of HUA mice tissue pathological changes. Conclusion: Portulaca oleracea extract would have certain uric acid-lowering and renal protective functions on hyperuricemia mice.
-
Keywords:
- Portulaca /
- hyperuricemia /
- uric acid reduction /
- xanthine oxidase /
- urine creatinine
-
高尿酸血症(Hyperuricemia,HUA)是一种常见的代谢性疾病,最常见的病因是尿酸(Uric acid,UA)分泌过多和(或)排泄不足[1]。众所周知,高尿酸血症是痛风的潜在危险因素,也是糖尿病[2]、高血压[3]、动脉粥样硬化[4]和肾脏疾病[5]等多种代谢疾病的危险因素。近年来,由于过量食用富含嘌呤的食物,高尿酸血症和痛风的发病率在全球范围内上升。美国健康与营养调查(NHANES)在2015~2016年进行的研究显示,美国男性和女性高尿酸血症的患病率分别为20.2%和20.0%[6]。据报导,中国大陆高尿酸血症患病率为17.4%[7]。因此,高尿酸血症已成为严重的公共卫生问题,严重影响患者的生活,造成严重的社会经济负担,值得全球关注。临床常用的治疗高尿酸血症的药物多为西药,如果长期服用会导致胃肠道损伤、肝肾损伤等副作用[8]。因此研发安全、有效、副作用小,可长期服用的中药迫在眉睫。
马齿苋(Portulaca oleraeea,PO)别名五行草、长寿菜,是我国101种药食同源的野生植物之一[9]。具有食用和药用双重价值[10]。有相关研究证实马齿苋具有降血糖、抑菌、抗氧化、增强免疫力等多种功能[11],而对高尿酸血症的研究却未见报道。痛风在中医属“痹症”范畴[12],本课题在前期工作中拟以筛选清热利湿化瘀的中药,发现了PO的降尿酸作用,因此以PO为研究对象,对PO进行提取及纯化,考察PO的降尿酸作用,进而发掘PO对高尿酸血症的治疗作用,为PO后续研究及成药提供了基础理论以及科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
马齿苋中药饮片 保康中药饮片加工公司;SPF级雄性ICR小鼠 体重20.0±2.0 g,50只,实验动物许可证编号为SCXK(吉)-2016-0003,长春市亿斯实验动物技术有限责任公司;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶(glutathioneperoxidase,GSH-PX)试剂盒 南京建成生物制品研究所;血尿酸(serum uric acid,SUA)、尿尿酸(urine uric acid,UUA)、尿肌酐(urine creatinine,UCr)试剂盒 上海酶联生物科技有限公司;次黄嘌呤、氧嗪酸钾、别嘌呤醇 美国Sigma公司;多聚甲醛、苏木素精、硫酸铝钾、伊红、冰醋酸、丽春红G、酸性品红、中性树胶、磷钼酸 上海化学试剂公司;其他化学试剂 均为分析纯。
AL204电子天平 梅特勒-托利多有限公司;Milli-Q纯水机 美国Millipore公司;RE-52A旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;THC-20B超声波提取机 济宁天华超声电子仪器有限公司;SHB-B型循环水式多用真空泵 郑州长城科工贸有限公司;UV-2550型紫外可见分光光度计 岛津国际贸易有限公司;GZX-9140ME数显鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司;光学显微镜 日本 Olympus公司;5430R低温高速离心机 美国Eppendorf公司;电热恒温水浴锅 北京长安科学仪器厂;THZ-C恒温振荡器 太仓市实验设备厂;Infinite M200型全波段酶标仪 瑞士Tecan 公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 马齿苋提取物的制备
称量5 kg马齿苋干品,粉碎,料液比1:10加入pH=5盐酸溶液,利用超声波提取器,温度50 ℃提取,每次100 min[13]。抽滤,合并提取液,加氨水调pH=8~9,得碱水层石油醚萃取3次,每次30 min。将碱水层石油醚挥干,利用旋转蒸发仪挥去3/4水分,进行干燥,得马齿苋粗提取物,保存备用。
1.2.2 动物饲养条件及高尿酸血症模型的建立
饲养于北华大学动物房清洁笼中。室内温度22±3 ℃,湿度50%±10%。
选取18~22 g健康雄性小鼠50只,随机分为5组:空白组(CON)、高尿酸血症模型组(hyperuricemia,HUA)、别嘌呤醇组(allopurinol,ALLOP,0.02 g/kg/d)、马齿苋高剂量组(PO-H,1.48 g/kg/d);马齿苋低剂量组(PO-L,0.74 g/kg/d)。给药方式为预防性给药,除CON组和HUA组外,每组按相应剂量连续灌胃给药21 d。从第7 d开始,除CON组外,各组小鼠腹腔注射次黄嘌呤(hypoxanthine,HX,0.3 g/kg/d)和氧嗪酸钾(oxonic acid potassium salt,OAPS,0.3 g/kg/d),CON组注射等量生理盐水[14]。
1.2.3 肾脏指数测定
摘取肾脏。使用0.9%的氯化钠溶液冲洗后用滤纸吸干称重,右侧肾脏投入4%多聚甲醛溶液中固定,左侧肾脏置于−80 ℃冻存备用[15]。
肾脏指数(PI,%)=双侧肾重(g)/体重(g)×100 (g) 1.2.4 血清SUA、MDA含量测定
末次给药1 h后每只小鼠眼球取血,静置 1 h,离心(4 ℃,3500 r/min,20 min),吸取上层血清用于试剂盒检测血清中SUA、MDA水平。
1.2.5 肝脏XOD、SOD含量测定及肾脏GSH、GSH-PX含量测定
称取适量肝脏组织,加入9倍质量分数的生理盐水,冰水中匀浆,制成 10%的匀浆液并离心(4 ℃,3500 r/min,10 min),取上清液,按相关试剂盒说明书检测小鼠肝脏XOD、SOD活性。
取小鼠肾组织适量,加入9倍质量分数的生理盐水,冰水中匀浆,制成10%的肾组织匀浆液并离心(4 ℃,3500 r/min,10 min)。取上清液,按相关试剂盒说明书检测小鼠肾脏GSH、GSH-PX活性。
1.2.6 尿液UUA、UCr含量测定
实验结束前1 d,将小鼠置于代谢笼中,禁食不禁水,收集24 h尿液并记录。将尿液离心(4 ℃,1200 r/min,15 min),取清液按相关试剂盒说明书测定UUA、UCr水平。
1.2.7 肾脏病理学检查
参考HE染色方法[16],观察小鼠肾脏病理变化。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据采用SPSS17.0软件进行统计学分析,GraphPad Prism5软件进行图表分析。数据均以平均值±标准差(
ˉX ±SD)的形式表示,每组中的样品数目表示“n”。以P<0.05时,表示差异显著;以P<0.01时,表示差异极显著。2. 结果与分析
2.1 对小鼠肾脏指数的影响
脏器的肿大或萎缩体现脏器的损伤情况,脏器与体重的比值减小说明脏器有可能出现一定程度的萎缩,增加说明脏器有可能有增生和水肿的情况[17]。如表1所示。HUA组小鼠肝脏指数、脾脏指数和肾脏指数均极显著(P<0.01)高于CON组,说明腹腔注射HX和OAPS可以引起小鼠的肝脏、脾脏和肾脏肿大,即高尿酸血症模型建立成功。与HUA组比较,PO-H和PO-L组小鼠肾脏指数均极显著(P<0.01)降低,说明马齿苋提取物对HX和OAPS引起的肾脏肿大有一定的抑制作用。但与HUA组比较,给药组的脾脏指数和肝脏指数差异不显著,说明ALLOP与马齿苋提取物对高尿酸小鼠模型肝脏和脾脏指数没有影响。
表 1 对小鼠脏器指数的影响Table 1. Effect on organ index of mice组别 n 肝脏指数(%) 脾脏指数(%) 肾脏指数(%) CON 10 4.87±0.69 0.39±0.09 1.52±0.26 HUA 10 6.56±0.77** 0.63±0.19** 2.29±0.39** ALLOP 10 6.83±0.74 0.61±0.11 1.82±0.31## PO-H 10 6.16±0.26 0.59±0.1 1.93±0.08## PO-L 10 6.27±0.12 0.54±0.1# 2.01±0.17## 注:与CON比较,*代表差异显著P<0.05,**代表差异极显著P<0.01;与HUA组比较,#代表差异显著P<0.05,##代表差异极显著P<0.01。 2.2 对小鼠血清SUA、MDA水平的影响
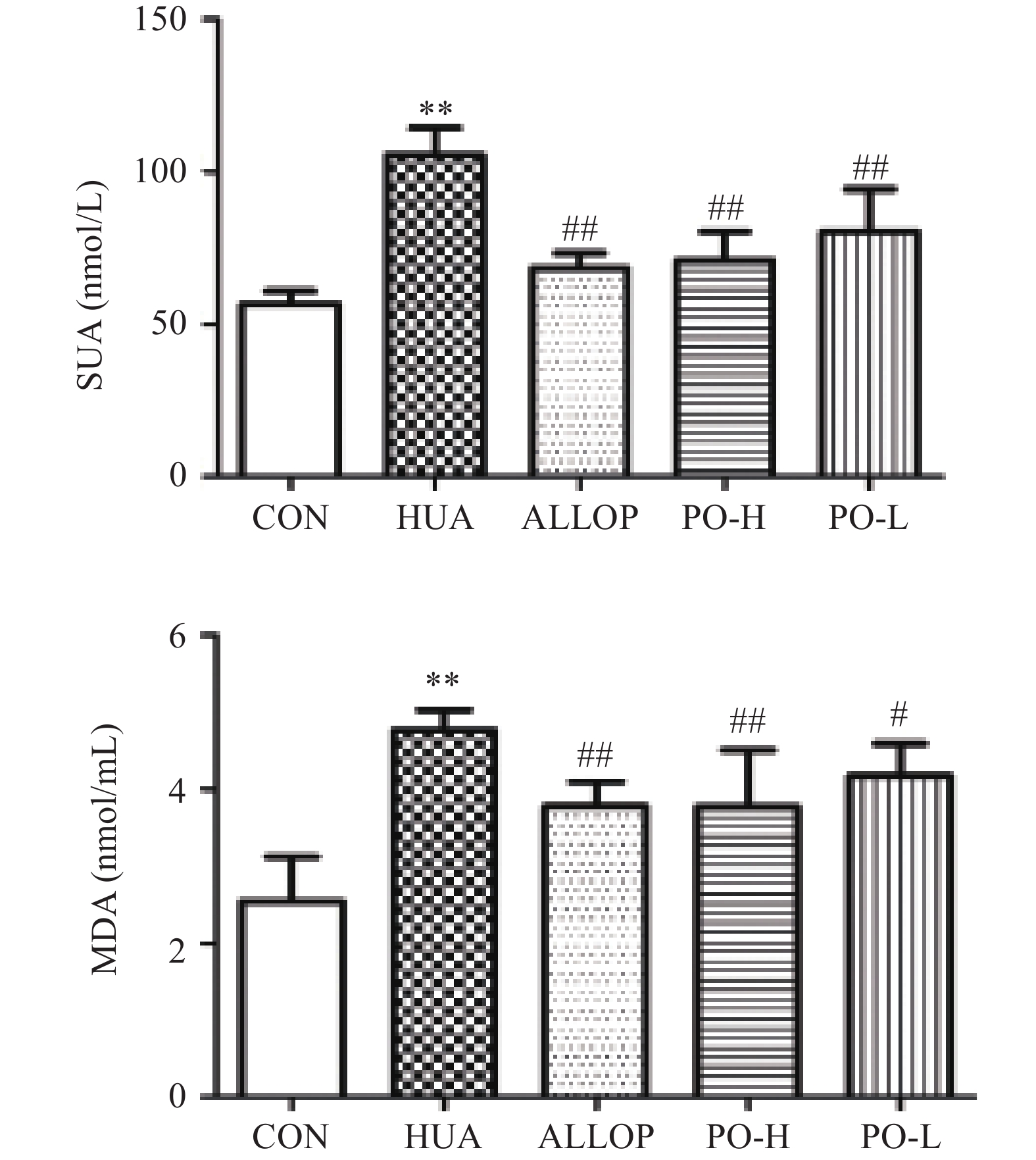
在正常饮食状态下,体内生成尿酸过多或排泄过低,都会引起血尿酸的升高,从而导致高尿酸血症[18]。因此通过在饮食上的调整和使用降低血清尿酸的药物将SUA水平降低至正常值是治疗HUA的主要目标[19]。MDA水平的高低可以反映机体内自由基代谢的情况[20-21]。如图1所示。与CON组比较,HUA组小鼠SUA浓度和MDA水平极显著升高(P<0.01)。说明成功建立了HUA模型。和HUA组比较,PO-H组和PO-L组SUA、MDA水平显著下降(P<0.01或P<0.05)。说明马齿苋提取物可有效降低患病小鼠的SUA水平,且随着剂量的增加,效果增强。
2.3 对小鼠肝脏XOD、SOD及肾脏GSH、GSH-PX水平的影响
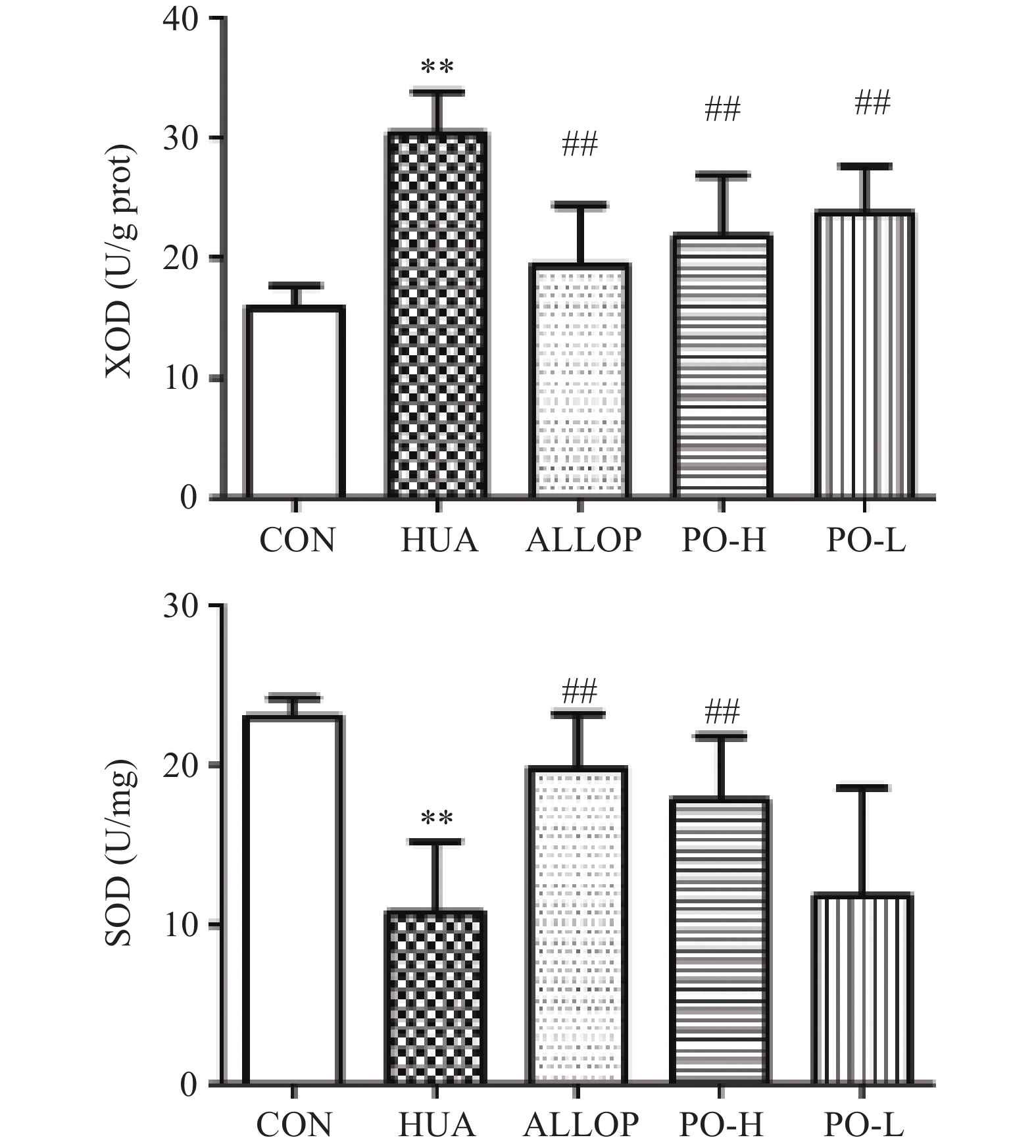
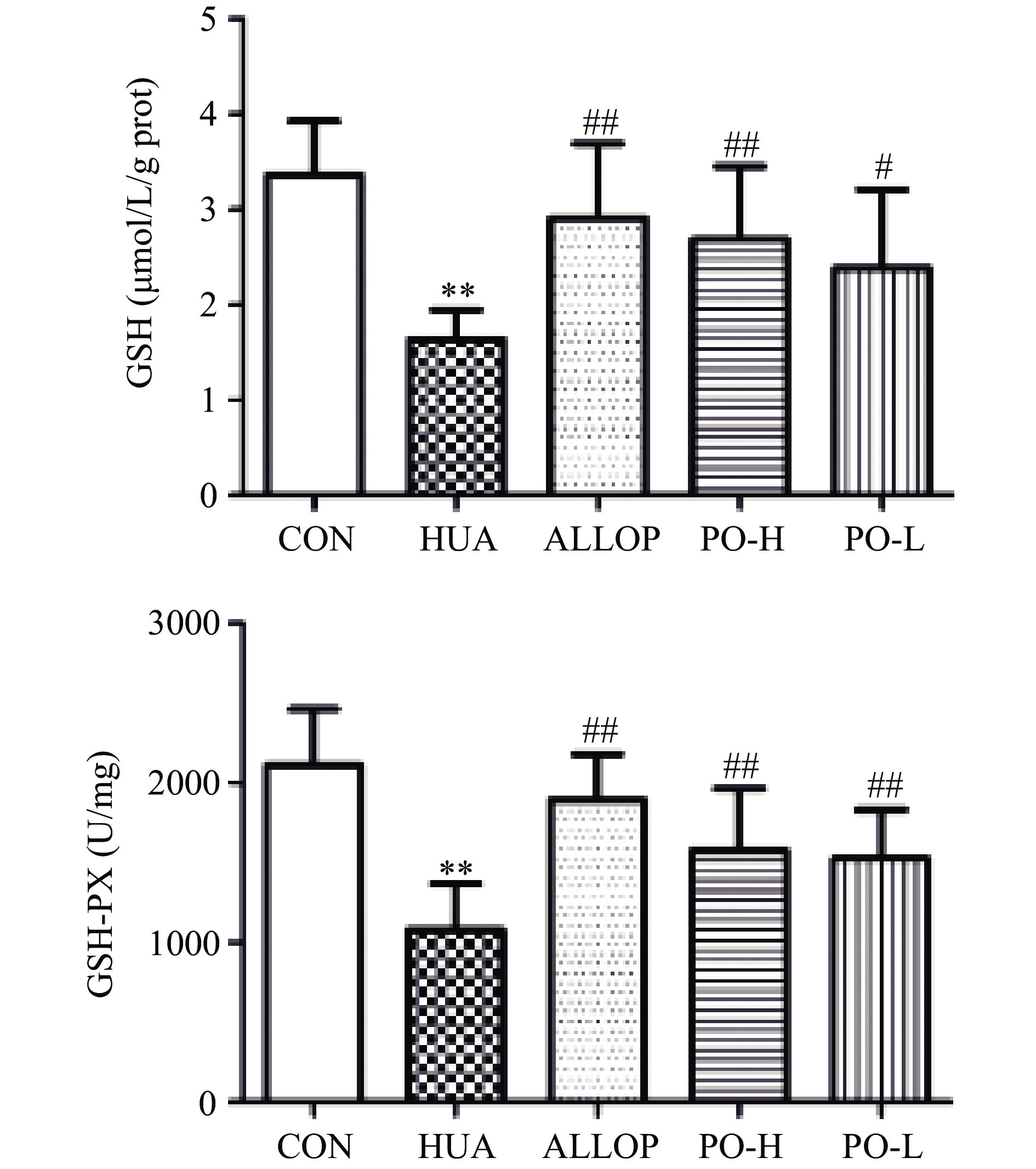
XOD是一种与嘌呤代谢有关的酶[22]。XOD在体内水平的升高引起嘌呤分解代谢的增强,最终导致SUA水平升高[23]。 SOD在人体内普遍存在,是一种天然的抗氧化酶,可以保护细胞免受损伤[24]。有研究发现,血尿酸升高是肾脏疾病发生独立危险因素[25]。而GSH-PX可以催化GSH参与过氧化反应,清除生物体内活性氧自由基[26],提高机体抗氧化能力。如图2所示。与CON组比较,HUA组肝脏XOD水平极显著升高(P<0.01),SOD水平极显著降低(P<0.01);与HUA组比较,PO-H组肝脏XOD水平极显著降低(P<0.01),SOD水平极显著升高(P<0.01);PO-L组肝脏XOD水平极显著降低(P<0.01),SOD水平无统计学意义(P>0.05)。由图3所示。与CON组比较,HUA组肾脏GSH、GSH-PX水平极显著降低(P<0.01);与HUA组比较,PO-H组、PO-L组肝脏GSH、GSH-PX水平均显著升高(P<0.01或P<0.05)。马齿苋提取物可显著降低HUA小鼠血清中XOD、MDA水平,提高SOD、GSH、GSH-PX水平。
2.4 对小鼠尿液UUA、UCr水平的影响
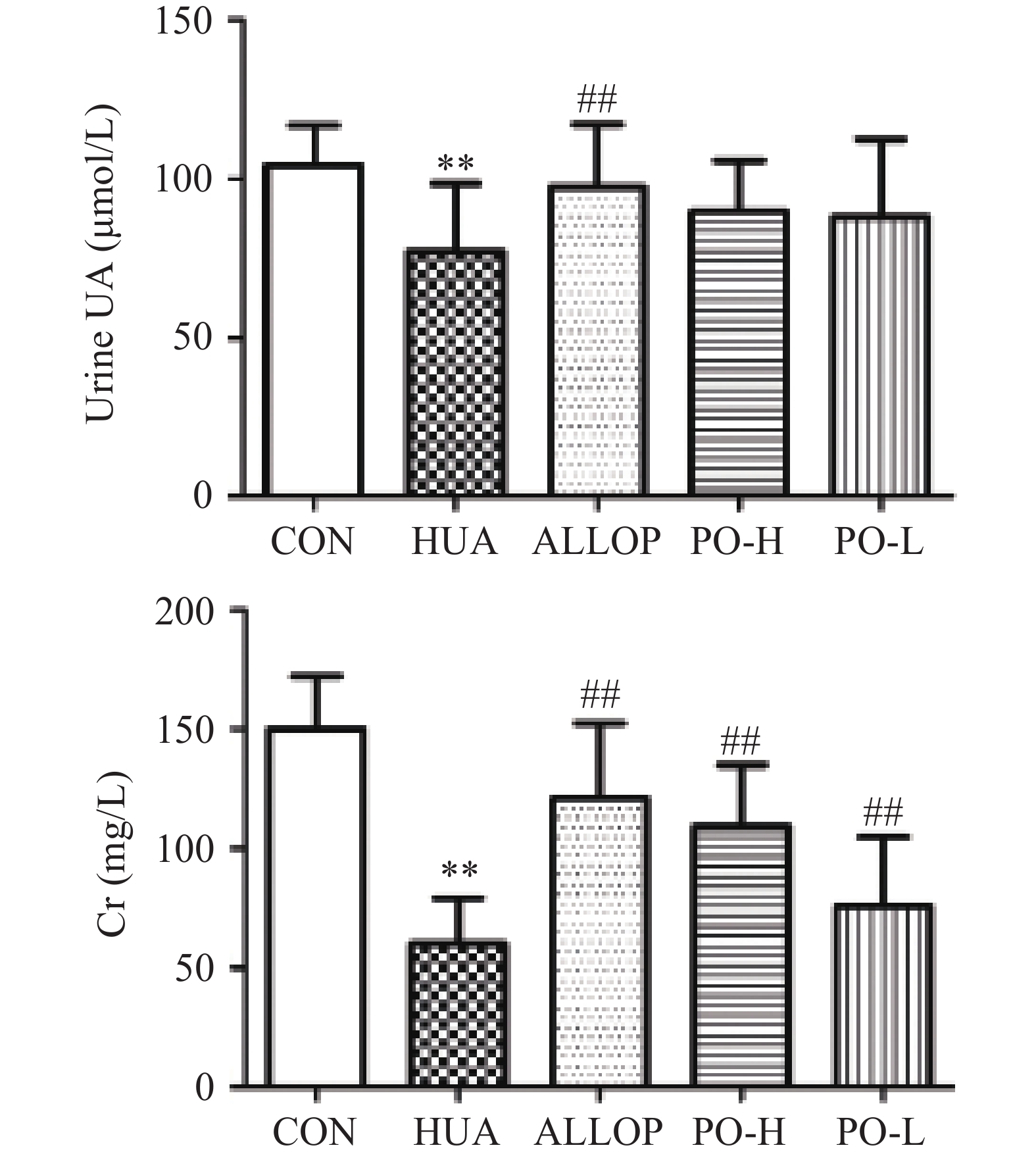
尿液中Cr的变化可以作为肾脏损害的标志[27]。如图4所示。与CON组比较,HUA组小鼠UUA、UCr水极显著降低(P<0.01);表明已出现初始肾功能损害。与HUA组比较,PO-H组和PO-L租UCr水平极显著升高(P<0.01),且两组小鼠UUA浓度与HUA组比较无显著性差异(P>0.05)。PO组尿液中Cr水平升高,提示通过马齿苋提取物的治疗,改善了次黄嘌呤和氧嗪酸钾所致的早期肾功能损害。
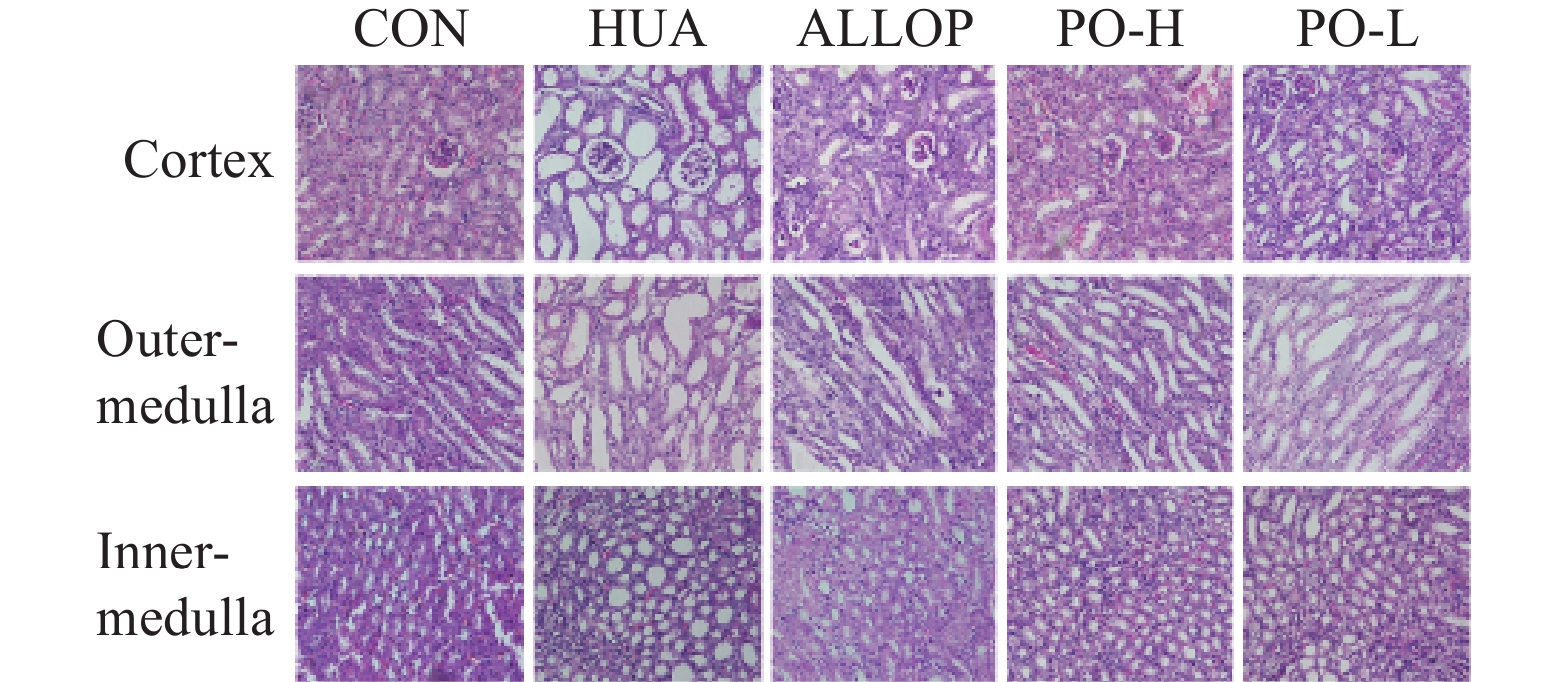
2.5 肾病理形态学观察
2.5.1 肾组织外观形态
CON组小鼠肾脏的大小正常。颜色为深红色。质地柔软按压时有弹性,表面光滑均匀。HUA组肾脏明显肿大,颜色发白。质地变硬,按压时无弹性。表面粗糙不平,有颗粒感。PO组肾脏外观与CON组接近,肾脏颜色呈淡红色,未见出血点。表面光滑,没有出现变白变硬情况。已知高尿酸血症会加重肾脏疾病的发生,而PO组小鼠肾脏指数相比HUA组有所下降,且双肾外观接近正常组,说明马齿苋提取物延缓了肾脏病变的进程。
2.5.2 光镜下观察肾组织病理表现
在400倍光镜下观察结果如图5所示,CON组小鼠具有清晰完整的细胞结构。细胞间隙正常,没有明显的病理改变。HUA组小鼠肾小球结构紊乱,肾小管明显扩张,且管腔形态排列杂乱不规则。肾间质宽度明显增加,被大量炎症细胞浸润,产生黏液。部分上皮细胞有水肿、坏死的现象。说明HUA组小鼠肾脏有病理性损伤。而当给予马齿苋提取物治疗后,肾小球形态接近正常。肾小管扩张减少,炎性细胞浸润减轻。提示马齿苋提取物可以明显改善HUA小鼠肾脏的病理变化。
3. 结论
本实验研究中,采用HX联合OAPS腹腔注射建立HUA模型,发现马齿苋提取物可有效降低效患病小鼠的SUA水平,且随着剂量的增加,效果增强,但对患病小鼠尿液UUA水平影响较小,其机制可能是通过在体内抑制尿酸的生成,从而起到降低血清尿酸的作用。马齿苋提取物可显著降低HUA小鼠血清中 XOD 、MDA水平,提高SOD、GSH、GSH-PX水平,表明马齿苋提取物可以减少脂质氧化代谢产物的生成,增强机体抗氧化能力。
实验结果表明,马齿苋提取物能够显著降低高尿酸血症小鼠血尿酸水平,其机制可能是通过降低小鼠肝脏XOD活性从而减少尿酸生成。有效延缓小鼠肾脏病变进程。这充分证明了中药在提高机体抗病能力、增强免疫力及毒副作用小等方面的优势,对于马齿苋用于高尿酸血症的治疗提供了参考。
-
表 1 对小鼠脏器指数的影响
Table 1 Effect on organ index of mice
组别 n 肝脏指数(%) 脾脏指数(%) 肾脏指数(%) CON 10 4.87±0.69 0.39±0.09 1.52±0.26 HUA 10 6.56±0.77** 0.63±0.19** 2.29±0.39** ALLOP 10 6.83±0.74 0.61±0.11 1.82±0.31## PO-H 10 6.16±0.26 0.59±0.1 1.93±0.08## PO-L 10 6.27±0.12 0.54±0.1# 2.01±0.17## 注:与CON比较,*代表差异显著P<0.05,**代表差异极显著P<0.01;与HUA组比较,#代表差异显著P<0.05,##代表差异极显著P<0.01。 -
[1] XU Lieqiang, LIN Guoshu, YU Qiuxia, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of dihydroberberine in potassium oxonate- and hypoxanthine-induced hyperuricemic mice[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:804.
[2] LV Q, MENG X F, HE F F, et al. High serum uric acid and increased risk of type 2 diabetes: A systemic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(2):e56864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056864
[3] DE BECKER B, BORGHI C, BURNIER M, et al. Uric acid and hypertension: A focused review and practical recommendations[J]. J Hypertens,2019,37(5):878−883. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001980
[4] LIU Z, CHEN T, NIU H, et al. The establishment and characteristics of rat model of atherosclerosis induced by hyperuricemia[J]. Stem Cells Int,2016,2016:1365257.
[5] RODENBACH K E, SCHNEIDER M F, FURTH S L, et al. Hyperuricemia and progression of CKD in children and adolescents: The chronic kidney disease in children (CKiD) cohort study[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2015,66(6):984−92. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.06.015
[6] CHEN X M, YOKOSE C, RAI S K, et al. Contemporary prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the united states and decadal trends: The national health and nutrition examination survey, 2007-2016[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol,2019,71(6):991−999. doi: 10.1002/art.40807
[7] HUANG J, MA Z F, ZHANG Y, et al. Geographical distribution of hyperuricemia in mainland China: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Glob Health Res Policy,2020,5(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s41256-020-00178-9
[8] FEIG D I, KANG D H, JOHNSON R J. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk[J]. N Engl J Med,2008,35(9):1811−2110.
[9] 崔旻, 尹苗, 安利国, 等. 马齿苋多糖的抗肿瘤活性[J]. 山东师大学报,2002,17(1):73−76. [CUI Y, YI M, AN LI G, et al. Anti-tumor activity of Portulaca oleracea polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Shandong Normal University,2002,17(1):73−76. [10] 陈国妮. 马齿苋黄酮类化合物的提取及抗菌特性研究[D]. 西安: 西安工程大学, 2016. CHEN G N. Study on extraction and antibacterial properties of flavonoids from Portulaca oleracea[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Polytechnic University, 2016.
[11] 舒成闯. 马齿苋多糖改善HepG2细胞胰岛素抵抗的研究[D]. 南昌: 江西科技师范大学, 2016. SHU C C. Study on the effect of Portulaca oleracea polysaccharide on improving insulin resistance of HepG2 cells[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, 2016.
[12] 陈绍华, 赵啸, 徐浩, 等. 痛风的中西医研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(4):1220−1227. [CHEN SHAO H, ZHAO X, XU H, et al. Research progress of gout in traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2021,23(4):1220−1227. [13] 马志宏, 党岩, 苟想珍, 等. 红茂草总生物碱酸水提取工艺试验[J]. 中国兽医杂志,2019,55(4):107−110. [MA Z H, DANG Y, GOU X Z, et al. Test on the extraction technology of total alkaloids from red grass[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2019,55(4):107−110. [14] MENG X, MAO Z, LI X, et al. Baicalein decreases uric acid and prevents hyperuricemic nephropathy in mice[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8:40305−40317. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16928
[15] 朱煜冬. 芡实超微粉对2型糖尿病小鼠的降血糖与肾脏功能调节作用[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2020. ZHU Y D. Gorgon superfine powder reduces blood sugar and regulates kidney function in type 2 diabetic mice[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2020.
[16] 吕静. 愈肾颗粒对肾纤维化模型大鼠影响机制的实验研究[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁中医药大学, 2008. LV J. Experimental study on the effect mechanism of yushen granules on renal fibrosis model rats[D]. Liaoning: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2008.
[17] 刘青, 王俊杰, 易果. 泼尼松对小鼠胸腺、脾脏、肝脏脏器指数及肝脏形态学的影响[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版),2019,21(3):14−17. [LIU Q, WANG JUN J, YI G. Effects of prednisone on thymus, spleen, liver organ index and liver morphology in mice[J]. Journal of Xiangnan University(Medical Sciences),2019,21(3):14−17. [18] 李静. 高尿酸血症的流行病学研究[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2016,21(2):83−86. [LI J. Epidemiological study of hyperuricemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine,2016,21(2):83−86. [19] PITTMAN J. Diagnosis and management of gout[J]. Am Fam Physician,1999,59(7):1799−1806.
[20] 关婷, 刘佳馥, 王思思. 丹参川芎嗪注射液治疗脑血栓患者的临床疗效及SOD、MDA、LPA和内皮素的作用分析[J]. 世界中医药,2019,14(9):2309−2312. [GUAN T, LIU J F, WANG S S. Clinical efficacy of Danshen Ligustrazine Injection in the treatment of cerebral thrombosis and analysis of the effects of SOD, MDA, LPA and endothelin[J]. World Chinese Medicine,2019,14(9):2309−2312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.09.018 [21] 李金儒. 愈溃方对实验性溃疡性结肠炎大鼠SOD、MDA、NO及iNOS、MPO影响[D]. 辽宁: 辽宁中医药大学, 2019. LI JIN R. Effect of Yukui Recipe on SOD, MDA, NO, iNOS, MPO in experimental ulcerative colitis rats[D]. Liaoning: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[22] 孙海滨. 上中下通用痛风方对高尿酸血症小鼠尿酸及尿α1微球蛋白的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江省中医药科学院, 2019. SUN H B. Effect of Shangzhongxiatongfeng recipe on uric acid and urine α1 microglobulin in hyperuricemia mice[D]. Harbin: Heilongjiang Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[23] 刘佳, 李玲. 高尿酸血症的发病机制与药物治疗研究进展[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2010,37(1):24−28. [LIU J, LI L. Research progress on the pathogenesis and drug treatment of hyperuricemia[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research,2010,37(1):24−28. [24] 张帅, 殷国泉, 于春晓, 等. 超氧化物歧化酶检测辅助诊断2型糖尿病肾病[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报,2019,40(6):18−21. [ZHANG S, YIN GUO Q, YU CHUN X, et al. Superoxide dismutase test assists in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic nephropathy[J]. Journal of Mudanjiang Medical College,2019,40(6):18−21. [25] MEHMET K, YALCIN S, BARIS A, et al. Serum uric acid and risk for acutekidney injury following contrast[J]. Angiology,2017,68(2):132−144. doi: 10.1177/0003319716644395
[26] 余玲, 包春燕, 宁苗, 等. 麦角新碱联合米索前列醇治疗前置胎盘的临床疗效及对血清ROS、SOD、GSH-px水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2019,19(14):2712−2715. [YU L, BAO CHUN Y, NING M, et al. The clinical efficacy of ergonovine combined with misoprostol in the treatment of placenta previa and its effect on serum ROS, SOD and GSH-px levels[J]. Modern Biomedicine Progress,2019,19(14):2712−2715. [27] 郭诗韵. 糖肾通络方对脾肾气虚型糖尿病肾病Ⅲ期患者疗效研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学 , 2019. GUO S Y. Effect of Tangshen Tongluo Recipe on diabetic nephropathy with deficiency of spleen and kidney qi[D]. Urumqi: Xingjiang Medical College, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 常逍柯,田潇凌,林顺顺,李梦琴,田争争,高恩红. 不同制粉方式对黑小麦全麦粉及饼干品质影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(21): 266-272 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王冬,任健,王志鹏,宋春丽. 酶预处理对黑珍珠糯玉米粉分散性的影响研究. 齐齐哈尔大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 69-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



