Antioxidant and Anti-bacteria Effects of Acetylated Taraxacum mongolicum Polysaccharide
-
摘要: 目的:以蒲公英多糖为原料,使用乙酸酐法修饰得到乙酰化蒲公英多糖,对其结构特征、体外抗氧化性以及抑菌效果进行研究。方法:采用水提醇沉法等制备蒲公英纯化多糖,选择乙酸酐法修饰得到乙酰化蒲公英多糖。利用红外光谱、扫描电镜、X-射线粉末衍射等测定蒲公英纯化多糖和乙酰化蒲公英多糖的结构特征。在此基础上,应用体外化学模型法评估多糖对清除1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、羟自由基和还原力的能力,并对其通过纸片法进行抑菌试验。结果:蒲公英纯化多糖的多糖含量为68.75%,红外光谱、扫描电镜、X-射线粉末衍射等结构表征证实乙酰化蒲公英多糖修饰成功,而且化学结构修饰后的乙酰化多糖,并未改变结构骨架。在浓度范围0.1~2.0 mg/mL内,改性前后的蒲公英纯化多糖对DPPH自由基IC50值分别为5.393±0.941和2.153±0.093 mg/mL;对超氧阴离子自由基IC50值分别为6.513±0.500和2.092±0.825 mg/mL;对羟自由基IC50值分别为0.626±0.034和0.322±0.010 mg/mL;对还原力最大吸光度值为0.138±0.019和0.239±0.022。随多糖浓度的递增,经修饰后蒲公英纯化多糖的抗氧活性逐渐增强。此外,乙酰化蒲公英多糖抑菌能力强于蒲公英纯化多糖,且随多糖浓度的增加抑菌能力也随之增大。结论:蒲公英多糖经乙酰化修饰后,可显著提高体外抗氧化性和抑菌效果。Abstract: Objective: To prepare acetylated Taraxacum mongolicum polysaccharide from Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz, and study its structural characteristics, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity. Methords: The structure of the polysaccharide extracted by water extraction and then alcohol precipitation method was modified by acetic anhydride method to obtain its acetylated. Infraed spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope and X-ray powder diffraction were used to structural characteristics of the polysaccharide and its acetylated. On the basis, the antioxidant activities were evaluated by 1,1-Dipheny1-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radicals, superoxide anion free radicals, hydroxyl free radicals and reducing power scavenging abilities using chemical model method, and the anti-bacteria tests was evaluated through the paper method in vitro. Results: The extraction yield of purified dandelion polysaccharide was 68.75%. Infraed spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope and X-ray powder diffraction of characterization confirmed the successful synthesis of acetylated. The basic structure framework of polysaccharide was not changed after being modified with acetylated. In the concentration range of 0.1~2.0 mg/mL, IC50 values were 5.393±0.941 and 2.153±0.093 mg/mL for pure polysaccharide and acetylated polysaccharides against 1,1-dipheny1-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) free radicals, respectively, 6.513±0.500 and 2.092±0.825 mg/mL against superoxide anion, respectively, 0.626±0.034 and 0.322±0.010 mg/mL against hydroxyl radical, respectively, and the maximum scanning rates were 0.138±0.019 and 0.239±0.022 reducing power, respectively. As the concentration increased, the antioxidant activity of acetylated polysaccharides increased gradually. In addition, the antibacterial airyctivity of the acetylated polysaccharides was stronger than the unmodified polysaccharides, and the antibaterial activity with the increase of polysaccharide cincentration. Conclusion: The structural stability of purified Taraxacum mongolicum polysaccharide was increased after being modified with acetylated, leading to a significant increase in the antioxidant activity and antibiacterial in vitro.
-
蒲公英(Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz)作为一种多年生菊科草本植物,可称婆婆丁、奶汁草、华花郎等,性味苦、甘、寒,归肝、胃经,具有清热解毒、消肿散结、利尿通淋之功效[1]。蒲公英可生长在各种类型的土壤中,且在沙质土壤里生长能力最为茁壮[2]。国家卫健委于2002年将蒲公英收录在药食同源目录中药品名单列表内[3]。近年来研究发现,蒲公英富含有效活性成分如黄酮、香豆素、三萜、多糖等。其中,多糖类化合物作为蒲公英的主要有效成分之一,其具有良好的解热镇痛、抗菌消炎、保肝利胆、降血糖、抗肿瘤等多种药理功效[4-10]。
多糖分子的改性修饰多指通过物理、化学、生物等改变多糖结构的手段。近年来许多报道表明,多糖的化学修饰相比于相应的天然多糖具有较好的生物活性[11]。对多糖结构上的化学修饰多根据其结构上的活性基团(如羟基、羧基、氨基等)在化学反应下引入新的官能团(如硫酸衍生化、硒化、羧甲基化等)[12]。对多糖进行乙酰化修饰是一种常见的改性方法。乙酰基取代多糖链上的羟基,改变多糖的分子结构与形态,改变多糖的溶解性,对多糖的生物活性产生影响[13-17]。经研究表明,对马齿苋多糖通过对其引入乙酰官能团后,可增强其抗氧化活性;另外,在乙酰化修饰后的金针菇多糖的抑菌活性变化与浓度相关。目前文献关于蒲公英多糖的研究仅限于提取、纯化、结构解析等方面的研究[18-19],在此基础上对其经化学反应得到的乙酰化蒲公英多糖结构、抗氧化性及抑菌能力等的研究未见报道。
因此,本文利用乙酸酐作为反应试剂,对蒲公英多糖纯化后进行乙酰化修饰,通过红外光谱、扫描电镜、X-射线粉末衍射等对蒲公英纯化多糖(Polysaccharides from Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz,TMP)和乙酰化蒲公英多糖(Actylated polysaccharides from Taraxacum mongolicum Hand.-Mazz,Ac-TMP)结构进行表征与分析,并评价其体外抗氧化性及抑菌性,为蒲公英多糖修饰乙酰化后效果进行研究和产品利用提供参考价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
蒲公英干燥全草 批号为:170801,2019年9月购自黑龙江省同仁堂大药房;透析袋分子量截留为3000 Da 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;葡萄糖、氯化乙酰胆碱、DPPH 美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;苯酚、氢氧化钠、浓盐酸、盐酸羟胺、三氯化铁、三氯甲烷、正丁醇、浓硫酸、乙酸酐、铁氰化钾、三氯乙酸 分析纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;金黄色葡萄球菌,菌种编号:LWCC1002(CMCC(B)26003)、大肠杆菌,菌种编号:LWCC1033(ATCC25922) 上海鲁微科技有限公司;普通肉汤培养基、Mueller-Hinton琼脂 青岛高科技工业园海博生物技术有限公司。
FA2004型电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;DL-5-B低速多管离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;FDU-1200冷冻干燥机 日本东京理化;RE-2000A旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;Vortex-1/2涡旋混合器 上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司;765紫外可见分光光度计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;FTIR-650傅里叶交换红外光谱仪 天津港东科技股份有限公司;Rigaku Mini Flex600粉末衍射仪 日本理学公司;Phenom Pro X扫描电镜 荷兰飞纳公司;LDZF-30L立式高压蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蒲公英多糖的提取
称取1 kg蒲公英干燥全草,加入2 L的超净水,浸泡2 h后,在90 ℃加热提取3次,每次2 h,在减压浓缩条件下合并3次滤液,与最终体积的80%乙醇放置24 h,以4500 r/min离心10 min,收集沉淀物,在水中复溶沉淀物,在130 Pa、45 ℃真空干燥,得到蒲公英粗多糖[20]。
1.2.2 蒲公英多糖的脱蛋白与纯化
取蒲公英粗多糖溶于超净水中,准备10%的多糖溶液,将Sevage试剂(氯仿:正丁醇=4:1)加入为1/4体积比的多糖溶液中,在超声条件下完全振荡30 min,4500 r/min离心10 min,弃去下层蛋白,保留上清液,并透析(分子透过率为3000 Da)48 h,过程重复3~5次。然后用80%乙醇沉淀除蛋白后的多糖,4500 r/min离心10 min,冷冻干燥后即得脱蛋白蒲公英多糖[21]。
将得到已除去蛋白的蒲公英多糖溶解至超净水中配制成浓度为4 mg/mL溶液,通过AB-8大孔树脂对多糖溶液进行脱色的氢键吸附作用,使用超净水进行洗脱并调节流速为1 mL/min,收集流出液,减压浓缩冷冻干燥,得到蒲公英纯化多糖[22]。
1.2.3 蒲公英纯化多糖的含量测定
精准称量105 ℃干燥至恒重的10 mg葡萄糖标准品,在100 mL容量瓶内加超净水溶解标准品并定容,得到0.1 mg/mL的葡萄糖标准品溶液。移取0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 mL标准品溶液置于具塞刻度试管中,依次加入超净水,使最终体积为2.0 mL。分别向各浓度具塞刻度试管中精密移取量为1 mL的5%苯酚溶液并涡旋1 min。再立刻移取5 mL浓硫酸混匀,在90 ℃水浴锅内15 min热浴,取出冷却至25 ℃。在490 nm波长下测量吸光度并绘制标曲,得到回归方程y=19.673x+0.219,R2=0.9996。并配制浓度为0.1 mg/mL的TMP多糖溶液,同上述操作测得吸光度值,将结果代入回归方程计算出浓度和TMP的糖含量,计算公式如下:
糖含量(%)=x0.1×100 式中:x为通过回归方程计算出的浓度,mg/mL。
1.2.4 蒲公英多糖的乙酰化修饰
采用乙酸酐法制备[23-24],称取0.5 g干燥的TMP溶解在30 mL超净水,超声充分振荡5 min直至获得均匀溶液。移取0.5 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液调节反应液pH为9.0,在30 ℃水浴条件下,交替加入2 mL乙酸酐和2 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液,消耗氢氧化钠溶液,保证2 mL乙酸酐量用尽,控制反应溶液pH维持在7.0~9.0。维持30 ℃水浴锅热浴反应3 h,反应溶液稳定在pH8.0以终止反应。在温度为25 ℃条件下反应结束后,用0.5 mol/L盐酸改变反应液pH为7.0。在饮用水流水状态下透析(分子透过率为3000 Da)24 h,然后在超净水流下透析24 h,通过减压浓缩反应液,在冷冻干燥条件下,得到乙酰化蒲公英多糖。
1.2.5 乙酰基取代度的测定
1.2.5.1 绘制标准曲线
采用羟胺比色法[25]检测,配制0.001 mol/L的乙酸钠溶液,称取0.0182 g氯化乙酰胆碱标准品,将标准品溶解于乙酸钠溶液中使之成为标准溶液,精密移取氯化乙酰胆碱标准溶液0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 mL于具塞刻度试管中,补水至2 mL。向试管内先移取2 mL临用现配的碱性羟胺溶液,在涡旋混匀10 s,于25 ℃条件下放置4 min,再移取4 mol/L盐酸溶液1 mL和0.37 mol/L三氯化铁-盐酸溶液1 mL,完全反应后,在540 nm波长下测量吸光度,绘制标准曲线。计算横坐标为氯化乙酰胆碱标准溶液得到的不同浓度乙酰基与纵坐标为其吸光度值回归方程y=0.206x+0.0221,R2=0.9989。
1.2.5.2 取代度的计算
精密称取干燥的乙酰化蒲公英多糖溶解在超净水中得到0.5 mg/ mL乙酰化蒲公英多糖溶液,同1.2.5.1步骤的操作方法进行实验。代入标曲得到乙酰化蒲公英多糖的乙酰基质量M1,按照下述公式计算到乙酰化蒲公英多糖的乙酰基取代度。
乙酰基百分含量(W,%)=M1M2×100 取代度(DS)=162×W4300−(43−1)×W 式中:M1为乙酰化蒲公英多糖中乙酰基的质量,mg;M2为乙酰化蒲公英多糖的质量,mg;162为多糖中葡萄糖的相对分子质量;43为乙酰基的相对分子质量;1为氢原子的相对分子质量。
1.2.6 蒲公英纯化多糖及乙酰化多糖结构表征测定
1.2.6.1 红外光谱(FI-IR)分析
精密称取TMP与Ac-TMP各2 mg,与干燥溴化钾粉末以1:50的比例混匀,通过研磨与压片的过程,采用傅里叶交换红外光谱仪经红外光谱扫描,确定扫描范围在4000~400 cm−1之间。
1.2.6.2 扫描电镜(SEM)分析
称取适量干燥TMP和Ac-TMP样品,分别于载物台上粘贴导电胶,涂一层导电的金属薄膜,将其导电过的样品放置于离子溅射仪内,实验在15 kV加速电压下扫描电子显微镜下进行,观察,并拍照记录以供分析多糖样品表面特征。
1.2.6.3 X-射线粉末衍射(XRD)分析
将干燥TMP和Ac-TMP样品分别均匀分布在样品板上,并充分压实在载玻片后,置放于X-射线粉末衍射仪中,使石墨单色化高强度具有Cu-Kα辐射光线下,RS为0.3 mm,测量角度为2 θ,测量范围在 5°~50°,扫描速度为5 °/min。
1.2.7 体外抗氧化测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除活性的测定
参考文献[26]报道加以修改,称取1 mg DPPH溶解在10 mL无水乙醇中,移取浓度为0.1 mg/mL临用现配的DPPH-无水乙醇溶液2 mL。分别精密转移TMP与Ac-TMP溶液(不同浓度0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mg/mL)2 mL置于具塞刻度试管中,在涡旋混合器混匀20 s,在室温阴暗处静置反应5 min,于517 nm处波长测定吸光度。分别使用超净水调零,以抗坏血酸溶液作为阳性组对照,以DPPH·溶液作为空白组对照。按照下述公式进行计算DPPH自由基清除活性。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 式中:A0空白组对照溶液的吸光度值;A1样品的吸光度值。
1.2.7.2 超氧阴离子自由基清除活性的测定
采用邻苯三酚自氧法[27]加以修改,精密移取TMP与Ac-TMP溶液(不同浓度0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mg/mL)2 mL,在具塞刻度试管中加入3 mL Tris-HCl溶液(0.05 mmol/L,pH=8.2),涡旋混合10 s,在25 ℃水浴锅中维持10 min,同时迅速加入已预热过200 μL的15 mmol/L邻苯三酚溶液,室温反应4 min。在320 nm波长下测量吸光度。使用超净水调零,Tris-HCl溶液作为空白组对比和抗坏血酸溶液作为阳性组对比。按照下述公式计算超氧阴离子自由基清除活性。
超氧阴离子自由基清除率(%)=A0−A1A0−A2×100 式中:A0为空白对照溶液的吸光度值;A1为样品的吸光度值;A2为Tris-HCl液吸光度值。
1.2.7.3 羟自由基(·OH)清除活性的测定
根据文献[28]的方法,精密吸取TMP与Ac-TMP溶液(不同浓度0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mg/mL)2 mL,先移取2 mL 0.6 mmol/L硫酸亚铁溶液,再加2 mL 0.6 mmol/L水杨酸-乙醇溶液和2 mL 0.6 mmol/L过氧化氢溶液于具塞刻度试管中,为保证混合均匀选用涡旋20 s,37 ℃反应35 min,在510 nm波长下测量吸光度。使用超净水调零,抗坏血酸溶液作为阳性组对比。按照下述公式计算羟自由基(·OH)清除活性。
羟自由基清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 式中:A0空白对照溶液的吸光度值;A1样品的吸光度值。
1.2.7.4 还原力实验
参考文献[29]方法加以修改,精密移取TMP与Ac-TMP溶液(不同浓度0.1、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mg/mL)1.5 mL,先加入磷酸溶液(0.2 mol/L,pH=6.0)1.5 mL,再加入1%铁氰化钾1.5 mL,在50 ℃水浴加入保持30 min,取出冷却至室温后,加入10%三氯乙酸1.5 mL,涡旋混匀10 s,放置3 min后,移取2 mL 0.1%三氯化铁溶液,充分反应10 min,在700 nm处波长测定吸光度。
1.2.8 抑菌实验
采用滤纸片药敏实验法[30],打孔器制备直径在6 mm的圆形无菌滤纸片,在高压灭菌(125 ℃,30 min)条件下处理,放置于超净操作台备用。在紫外光照射下,将滤纸片浸于多糖浓度分别为25、50、100、200 mg/mL的TMP与Ac-TMP溶液中及空白对照的生理盐水溶液中。大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌在活化条件下,分别于琼脂固体培养基上使用无菌三角挂铲涂布,放置5 min后,在无菌条件下将多糖滤纸片取2~3张附着于固体培养基表面,同时设置3个平行试验组,在调节至37 ℃的恒温培养箱将其放入,设置时间12 h,取出附着多糖样品的固体培养基并利用游标卡尺测量抑菌圈直径。
1.3 数据处理
上述实验所得数据用Origin Pro 2021处理作图,使用SPSS进行试验数据相对标准偏差,并进行差异的显著性分析,P<0.05表示为显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蒲公英纯化多糖的含量测定及乙酰化蒲公英多糖取代度测定
经大孔树脂AB-8洗脱后得到蒲公英纯化多糖,多糖含量测定结果为68.75%。通过计算得到经修饰后的蒲公英多糖乙酰基取代度为0.227。
2.2 蒲公英纯化多糖及乙酰化多糖结构表征
2.2.1 FT-IR结果分析
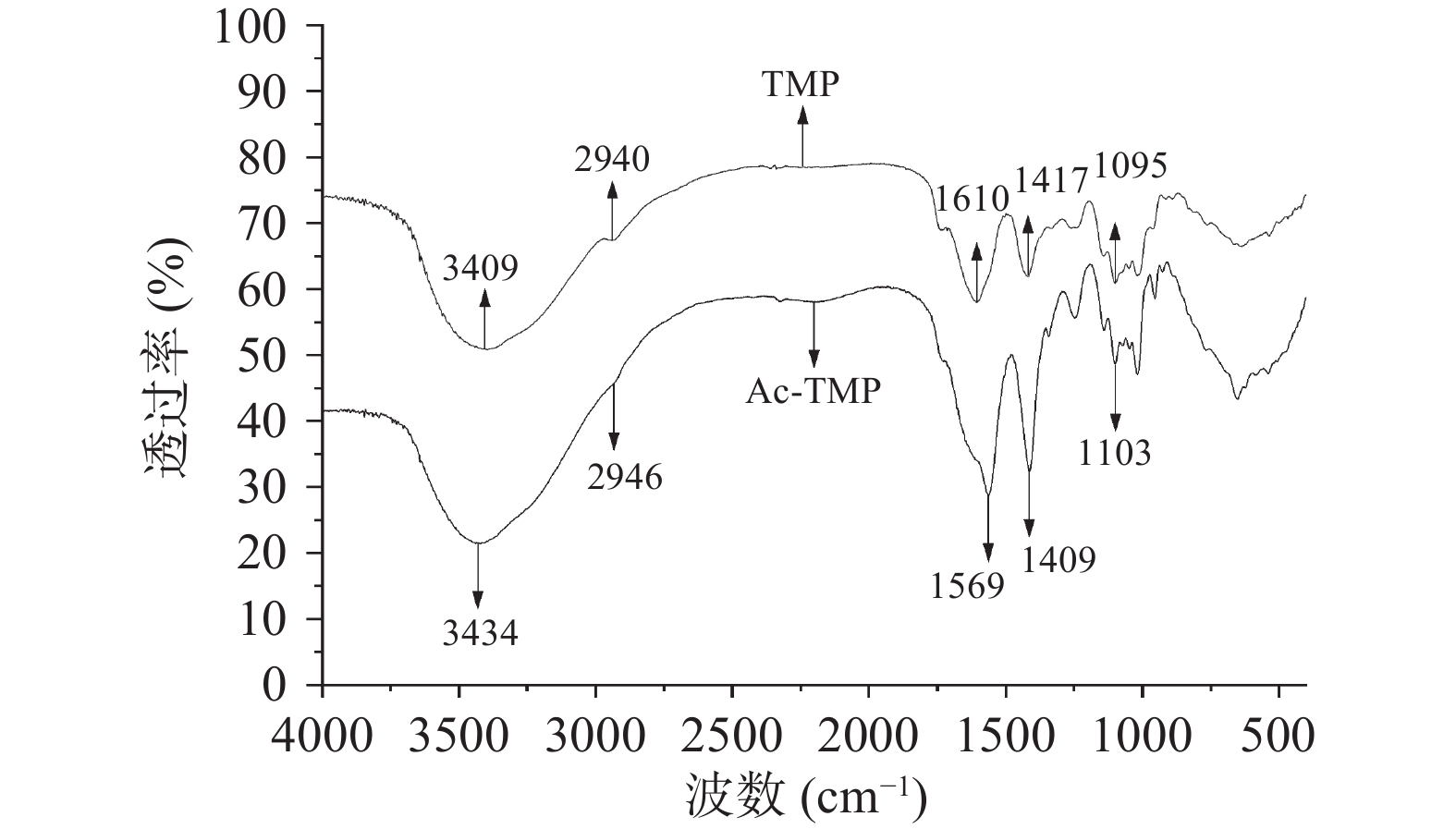
由图1可知,乙酰化修饰前的蒲公英多糖均具有多糖成分红外特征吸收峰:峰形呈强且宽的分子内或分子间氢键显现的O-H伸缩振动峰在3409 cm−1附近出现;基团为甲基(-CH3)、次甲基(-CH2-)C-H伸缩振动峰的峰形较强在2940 cm−1附近出现;官能团为甲基(-CH3)、次甲基(-CH2-)的C-H变形振动峰在1417 cm−1处出现;1095 cm−1附近处存在吡喃环吸收峰。乙酰化修饰后的蒲公英多糖在1103 cm−1处有酯基(-COOR)较强的C-O单键伸缩振动峰;官能团为酯基(-COOR)的C=O双键伸缩振动峰在1569 cm−1处存在,为较强峰形,说明蒲公英纯化多糖引入乙酰基官能团成功。
2.2.2 SEM结果分析
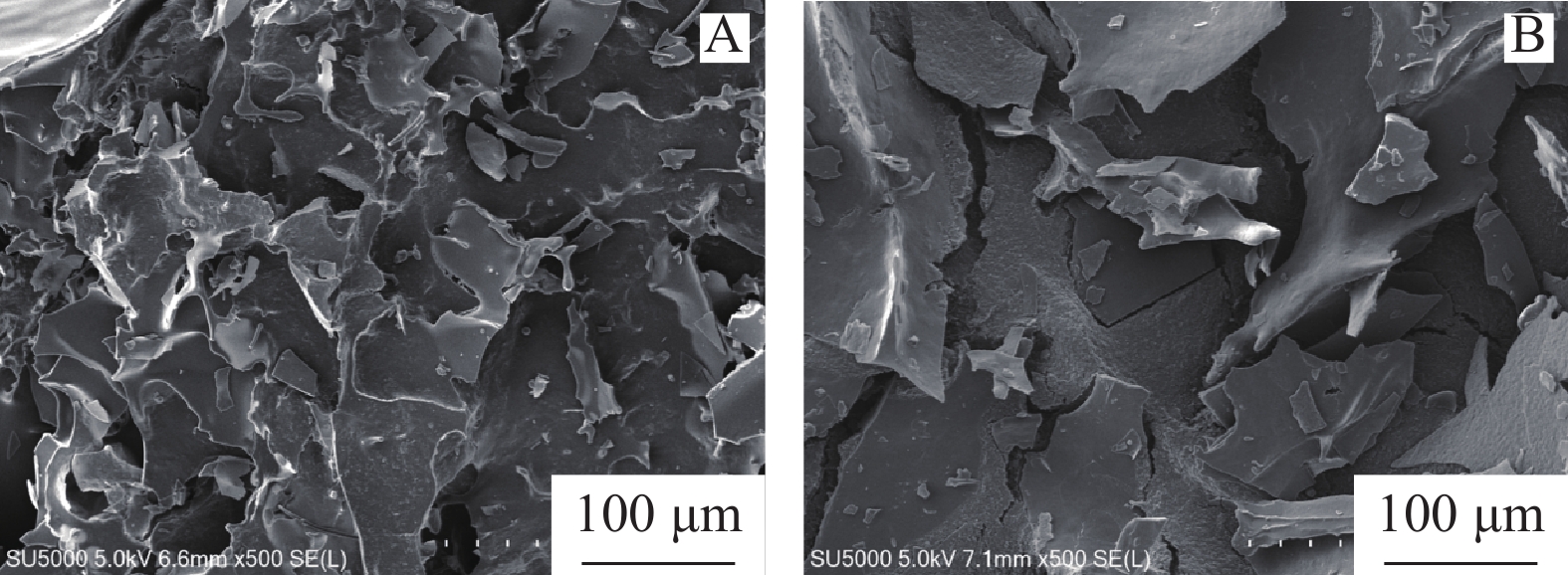
由图2显示,从表面状态观察得到,蒲公英纯化多糖表面粗糙,附着纹裂清晰,排列不规律、大小不均一,存在较大间隙;乙酰化修饰后,Ac-TMP呈片状,附着裂纹平滑,排列严密紧实、大小较为均一,中间间隙较小。由于TMP属于高分子碳水化合物,结构上是通过氢键交联糖苷键结合的糖链[31],在通过乙酰化修饰后,极有可能造成糖苷键上的氢键断裂,被酯基取代,导致糖链间的氢键密度变大,增加表面光滑度,则说明TMP在结构修饰后可形成乙酰化结构的复合物。
2.2.3 XRD结果分析
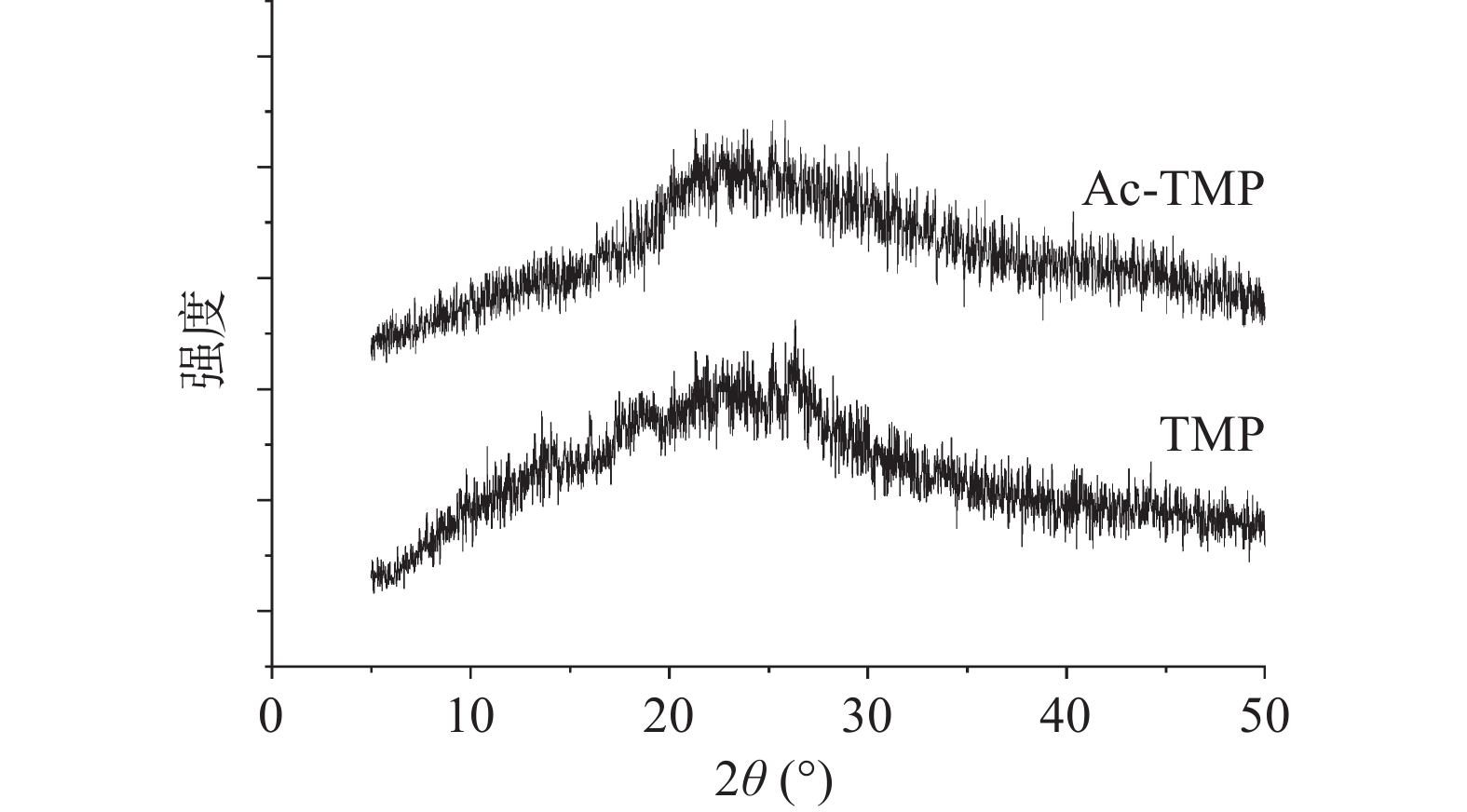
由图3可知,修饰前后的多糖结构在XRD图谱基本相同,仅在峰强上略显不同,说明对其结构修饰后,并未破坏多糖结构的基本骨架,XRD显示结果与FT-IR显示结果差别不大。TMP整个衍射图谱出现一个峰,样品在入射角处出现少量的晶体衍射峰,TMP在2θ范围为17.86°~26.40°入射时出现微量晶体衍射峰外,几乎为无定型区。同样的,Ac-TMP在衍射图上也出现一个峰,在2θ范围为18.36°~27.64°入射时出现少量的晶体衍射峰,为无定型特征。总的来说,TMP与Ac-TMP未呈现较大的晶体构造趋势,仅为微量结晶形态,属无定型粉末结构。
2.3 体外抗氧化测定
2.3.1 DPPH自由基清除活性的测定结果
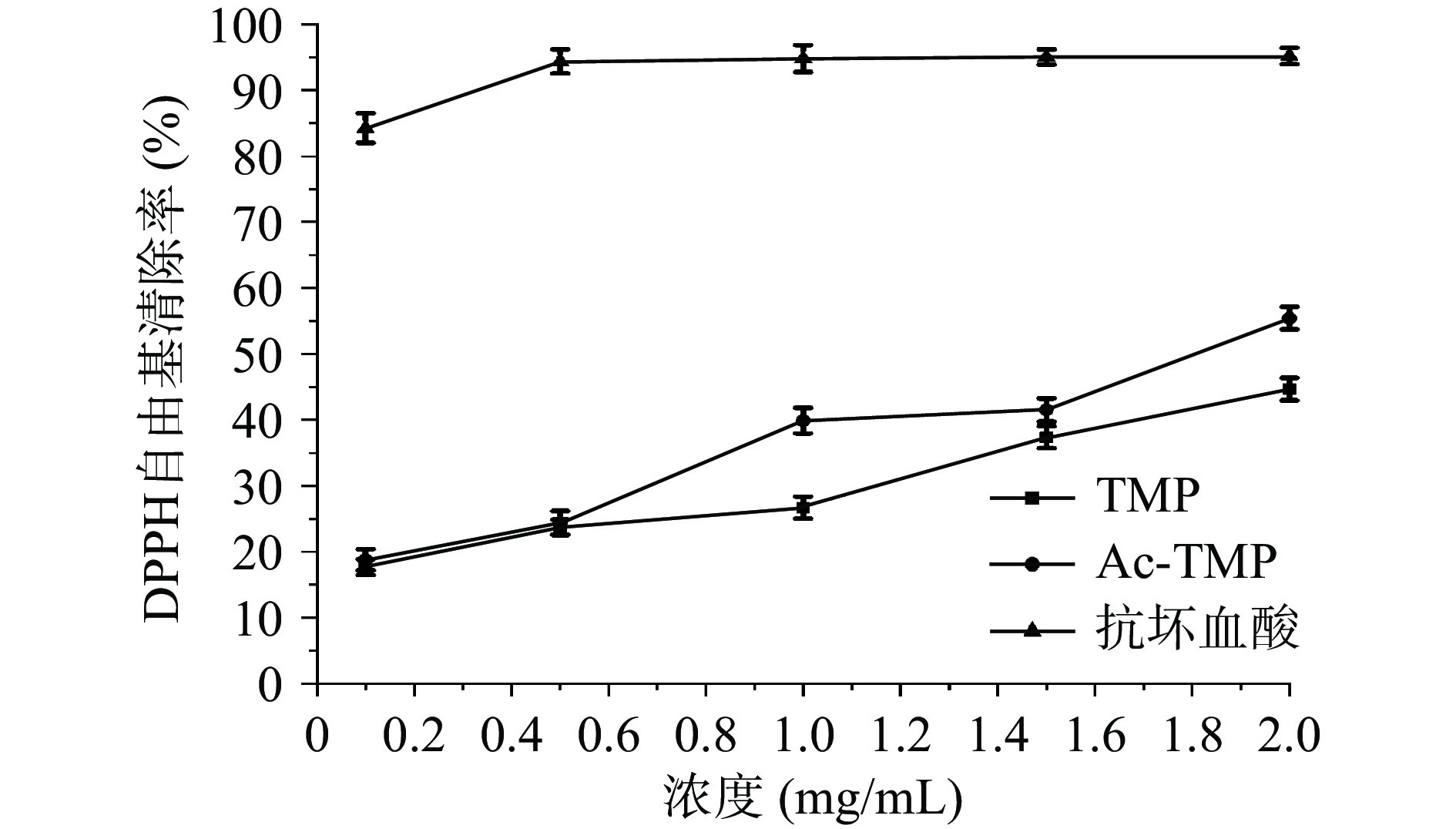
由图4可知,在0.1~2.0 mg/mL的质量浓度之间,抗坏血酸对DPPH自由基清除效果最佳,Ac-TMP对DPPH自由基清除相对于TMP清除效果显著(P<0.05)。两者的清除率随质量浓度的增加呈量效关系,质量浓度在2 mg/mL时,TMP和Ac-TMP清除率分别为44.64%±1.71%和55.41%±1.72%,其IC50值分别为5.393±0.941和2.153±0.093 mg/mL。由此表明,乙酰基团的引入对DPPH自由基清除力能有显著性(P<0.05)的增强作用。
2.3.2 超氧阴离子自由基清除活性的测定结果
由图5可知,各浓度抗坏血酸对超氧阴离子自由基清除率较高,不同浓度的TMP和Ac-TMP均具有清除超氧阴离子自由基的作用。总的来说,随着多糖浓度的递增,超氧阴离子自由基的去除率有明显的升高趋势。此外,Ac-TMP清除超氧阴离子自由基的能力明显优于TMP,在浓度为2 mg/mL时,Ac-TMP对超氧阴离子自由基清除率可达55.45%±1.55%,其IC50值为2.092±0.825 mg/mL。
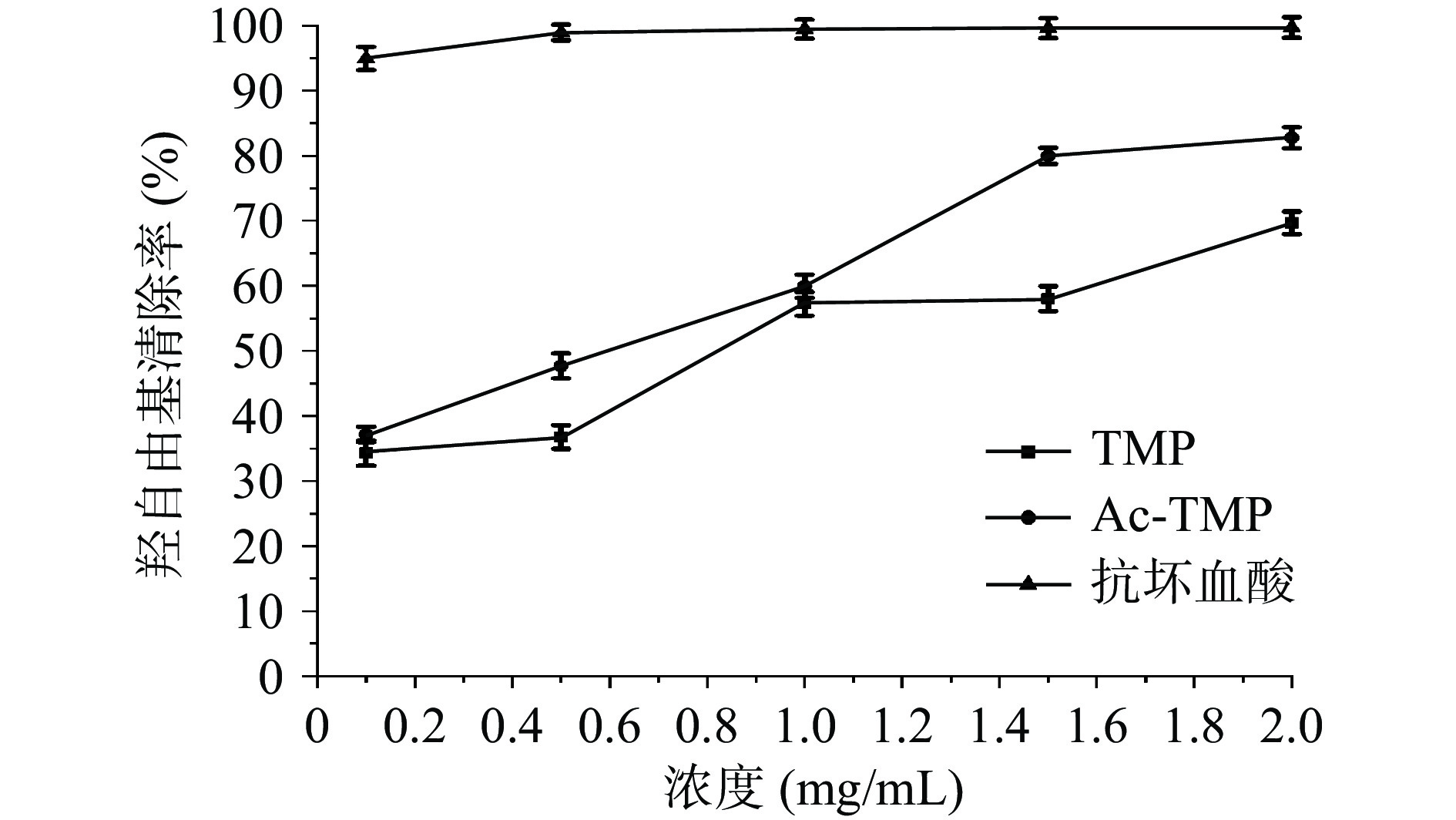
2.3.3 羟自由基(·OH)清除活性的测定结果
由图6结果表明,Ac-TMP和TMP对羟自由基清除活性相当,两者均表现出较强的清除能力,前者略高于后者;抗坏血酸对羟自由基的清除率明显优于Ac-TMP和TMP。当质量浓度为2.0 mg/mL时,Ac-TMP和TMP的清除率分别为82.76%±1.63%、69.69%±1.74%。抗坏血酸的IC50值为0.005±0.017 mg/mL,TMP和Ac-TMP的IC50值分别为0.626±0.034和0.322±0.010 mg/mL。说明对羟自由基的作用强弱顺序为抗坏血酸、Ac-TMP、TMP。
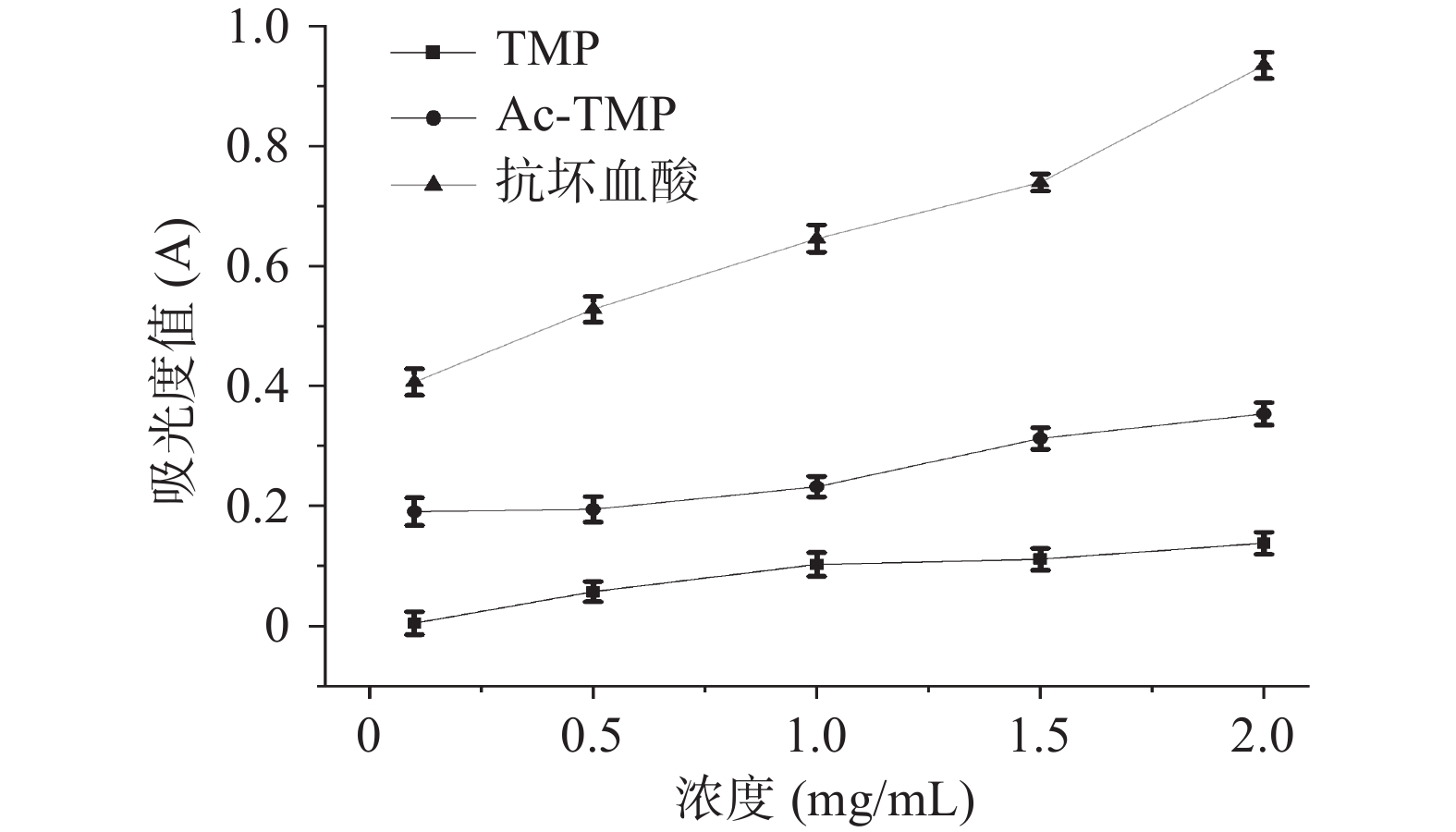
2.3.4 还原力测定结果
由图7可知,TMP与AC-TMP均具有还原能力,在质量浓度0.1~2.0 mg/mL之间,还原力均呈显著的量效关系。TMP还原力与Ac-TMP相比存在显著性(P<0.05)差异,在最大浓度为2.0 mg/mL时,其还原力分别为0.138±0.019和0.239±0.022。
2.4 抑菌试验结果
结合图8和表1结果显示,除修饰前后多糖浓度为25 mg/mL组别,其余各组对金黄色葡萄球菌TMP相对于Ac-TMP的抑菌圈直径具有差异性;TMP与Ac-TMP对大肠杆菌的抑菌圈直径表现出显著性(P<0.05)差异。不仅如此,在浓度为50 mg/mL时,TMP对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌圈直径为6.5 mm呈不敏感,Ac-TMP抑菌直径为8.0 mm呈低度敏感; TMP对于大肠杆菌的抑菌圈直径为7.3 mm呈低度敏感,Ac-TMP抑菌圈直径为10.6 mm呈中度敏感。在浓度达到200 mg/mL时,TMP和Ac-TMP对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌圈直径分别为7.8和10.2 mm;对于大肠杆菌的抑菌圈直径值分别为9.6 和13.0 mm。结合结果观察可知,随浓度的增加乙酰化蒲公英多糖对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌抑制效果均优于蒲公英纯化多糖,且抑菌强度随之增加。
表 1 TMP和Ac-TMP抑菌结果Table 1. Bacteria results of TMP and Ac-TMP
所选菌种多糖溶液 多糖溶液(25 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(50 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(100 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(200 mg/mL) TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP 大肠杆菌 − 6.2 mm 7.3 mm 10.6 mm 8.4 mm 11.9 mm 9.6 mm 13.0 mm 金黄色葡萄球菌 − − 6.5 mm 8.0 mm 6.9 mm 9.8 mm 7.8 mm 10.2 mm 注:数据为抑菌实验三次平均值,符号“−”表示为抑菌圈直径小于6.0 mm;根据判抑菌圈直径判定抑菌程度标准[32]:>20 mm为极度敏感、15~20 mm为高度敏感、11~14 mm为中度敏感、7~10 mm为低度敏感、<7 mm为不敏感。 实验表明,大多数多糖均具有一定的抗氧化活性和抑菌活性。经乙酰化改性前后的多糖,抗氧化性能和抑菌性能比较未修饰前发生明显变化,修饰前后多糖抑菌性均高于空白对照的生理盐水,修饰后的多糖抑菌效果较修饰前的多糖有所提高。在体外抗氧化性能比较中,乙酰化修饰前后多糖均低于阳性对照的抗坏血酸对DPPH自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、羟自由基的清除率,抗坏血酸的还原能力相较乙酰化改性前后多糖吸光度值变化较强,修饰后的多糖对DPPH自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、羟自由基的清除率及还原性的表现均高于修饰前多糖。巩丽虹等[33]在对药材防风进行乙酰化修饰后,对其修饰前后多糖进行抗氧化实验,得到经修饰后的防风多糖抗氧化活性提高,与本实验结果一致。可能由于多糖的抗氧化活性来源于糖链上的游离羟基,在乙酰化结构修饰后使糖链的空间位阻发生变化,暴露出更多的羟基,可以结合更多的自由基,从而提高抗氧化性。李晓丽[34]在对牡丹籽提取物进行结构修饰,对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抑制作用进行研究,得到经修饰后的多糖对细菌菌株具有有效的抑制作用,与本实验结果一致。可能由于多糖的糖链结构对细菌的细胞膜产生破坏作用,可使细胞内容物渗透压升高代谢紊乱细菌死亡,在结构修饰后多糖的糖链结构会将乙酰基交联在游离基团上,增加多糖的脂溶性,可以更快的穿透细胞膜从而导致细菌死亡。
3. 结论
本实验以药食同源的蒲公英全草为原料,通过水提醇沉法等方式得到TMP的多糖含量为68.75%,采用乙酸酐为乙酰化试剂,对TMP进行乙酰化的改性修饰,得到取代度为0.227的Ac-TMP。经红外光谱、扫描电镜和X-射线粉末衍射等表征证实乙酰化蒲公英多糖修饰成功,并证明化学结构修饰得到的乙酰化多糖,并未改变结构骨架,对其进行体外抗氧化实验表明,经乙酰化改性后的蒲公英多糖相较于蒲公英纯化多糖更加能够清除DPPH自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、羟自由基和还原能力。此外,乙酰化蒲公英多糖抑菌能力强于蒲公英纯化多糖,且随多糖浓度的增加抑菌效果递增,显现出经乙酰化改性过的蒲公英多糖对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌作用影响更大。综上所述,TMP经化学修饰引入乙酰基官能团,可提高结构稳定性、抗氧化性和抑菌能力。
有研究发现,通过乙酰化修饰多糖进行改性不仅对多糖结构的分子量、单糖组成、结构形态产生影响,而且对多糖的抗氧化、降血糖、抗肿瘤、抗衰老、提升免疫力等作用增大。针对本实验中的抗氧化性和抑菌能力结构修饰改性后的多糖相较于一般多糖能力增强,分析原因可能为未改性前的多糖结构呈团聚形态,在乙酰化修饰后呈现舒展状态,增加了结构中羟基对乙酰化基团的结合能力。故为研究蒲公英多糖的结构活性关系提供了新的研究方向,为蒲公英多糖的化学改性修饰、抗氧化性和抑菌作用提供了重要的参考。
-
表 1 TMP和Ac-TMP抑菌结果
Table 1 Bacteria results of TMP and Ac-TMP
所选菌种多糖溶液 多糖溶液(25 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(50 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(100 mg/mL) 多糖溶液(200 mg/mL) TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP TMP Ac-TMP 大肠杆菌 − 6.2 mm 7.3 mm 10.6 mm 8.4 mm 11.9 mm 9.6 mm 13.0 mm 金黄色葡萄球菌 − − 6.5 mm 8.0 mm 6.9 mm 9.8 mm 7.8 mm 10.2 mm 注:数据为抑菌实验三次平均值,符号“−”表示为抑菌圈直径小于6.0 mm;根据判抑菌圈直径判定抑菌程度标准[32]:>20 mm为极度敏感、15~20 mm为高度敏感、11~14 mm为中度敏感、7~10 mm为低度敏感、<7 mm为不敏感。 -
[1] 于伯健. 蒲公英的营养与药用价值及开发和利用[J]. 林区教学,2007(10):124−125. [YU B J. Nutritional and medicinal value of dandelion and development and utilization[J]. Teach Forestry Region,2007(10):124−125. [2] 易思荣, 黄亚. 蒲公英属植物的研究概况[J]. 时珍国医国药,2002,6(2):108−111. [YI S R, HUANG Y. A survey of studies on the genus Taraxacum mongolicum[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Reasearch,2002,6(2):108−111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2002.02.034 [3] 付晨青, 何立威, 王秀萍. 药食同源蒲公英的开发应用研究现状与展望[J]. 陕西农业科学,2021,67(5):86−88. [FU C Q, HE L W, WANG X P. Research status and pospect of development and application of medicinal and edible dandelion[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2021,67(5):86−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2021.05.022 [4] LI F, FENG K L, YANG J C, et al. Polysaccharides from dandelion (Taraxacum mongolicum) leaves: Insights into innovative drying techniques on their structral characteristics and biological activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macronmolecules,2021,167(15):995−1005.
[5] BERNADETTA L, BEATA O. Pro-health activity of dandelion (Taraxacum officinale L.) and its food products-history and present[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,59(10):40−48.
[6] 刘炜熹, 陈帅, 刘磊, 等. 蒲公英多糖的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(10):214−219. [LIU W X, CHEN S, LIU L, et al. Research progress on dandelion polysaccharides[J]. Food Reseach and Deveopment,2020,41(10):214−219. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.10.035 [7] NIU H, FAN J W, WANG G P, et al. Anti-tumor effect of polysaccharides isolated from Taraxacum mongolicum Hand-Mazz on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells[J]. Trop J Pharm Res,2017,16(1):83−89. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v16i1.11
[8] DING A G, WEN X H. Dandelion root extract protects NCM460 colonic cells and relieves experimental mouse colitis[J]. J Nat Med,2018,72(4):857−866. doi: 10.1007/s11418-018-1217-7
[9] YU M, JI Y B, QI Z, et al. Anti-tumor activity of sulfated polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme[J]. Saudi Pharmaceutucal Journal,2017,25(4):464−468. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2017.04.007
[10] DENG Y, LI M, CHEN L X, et al. Chemical character and immunomodulatory activity of acetylated polysaccharides from Dendrobium devonianum[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2018, 180: 238-245.
[11] LIU J, LUO J G, YE H, et al. Preparation antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro of different derivatives of levan from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50:767−772. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.016
[12] 梁少茹, 肖霄, 肖斌. 绿茶多糖的乙酰化修饰及清除自由基、NO2−活性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(11):85−99. [LIANG S R, XIAO X, XIAO B. Study on acetylated modification and scavenging effect on free radicals, NO2− of green tea polysaccharides[J]. Science and Techology of Food Industry,2015,36(11):85−99. [13] 邵珠领, 吴艳丽, 张宇, 等. 桦褐孔菌多糖的乙酰化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(9):73−77. [SHAO Z L, WU Y L, ZHANG Y, et al. Acetylated modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides[J]. Science and Techology of Food Industry,2019,40(9):73−77. [14] 贾红倩, 刘嵬, 颜军, 等. 杏鲍菇多糖的分离纯化、乙酰化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(3):39−44. [JIA H Q, LIU W, YAN J, et al. Isolation and purification, acetylation modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides of Pleurotus eryngii Quel[J]. Science and Techology of Food Industry,2018,39(3):39−44. [15] ZHAO M, HAN Y, LI J G, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of acetlated Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharide(Ac-CPP0.1)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,171(28):112−122.
[16] CHEN H L, TAN H L, YANG J, et al. Inhibitory effect of polysaccharide of Sargassum weizhouence on PCV2 induced inflammation in mice by suppressing histone acetylatio[J]. Biomedicine and Macromolecules,2019,112(7):108741.
[17] YANG Y X, CHEN J L, LEI L, et al. Acetylation of polysaccharide from Morchella angusticeps peck enhances its immune activation and anti-inflammatory activies in macrophage RAW264.7 cells[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2019,125(6):38−45.
[18] 肖潮勇, 张宇, 王宇亮. 蒲公英总多糖的提取、纯化及其体外抗炎活性分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2016,22(6):25−28. [XIAO C Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y L. Extraction and purification of total polysaccharides in Taraxaci Herba and its anti-inflammatory activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2016,22(6):25−28. [19] GUO H J, ZHANG W D, JIANG Y, et al. Physicochemical, structural, and biological prooerties of polysaccharides from dandelion[J]. Molecules,2019,24(12):1−14.
[20] REN F, WU K, YANG Y, et al. Dandelion polysaccharide exerts anti-angiogenesis effect on hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating VEGF/HIF-1α expression[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020,11:460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00460
[21] 侯京玲, 周霄楠, 赵兴华. 几种蒲公英成分的提取及体外抑菌效果试验[J]. 中国兽医杂志,2016,52(12):53−55. [HOU J L, ZHOU X N, ZHAO X H. Research on antibacterial activity of different Herba Taraxaci extracts in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2016,52(12):53−55. [22] 郭慧静, 张伟达, 陈国刚. 蒲公英多糖脱色脱蛋白方法及其降血糖活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(3):24−28. [GUO H J, ZHANG W D, CHEN G G. Decoloration and deproteinization of polysaccharides from dandelion and its hypoglycemic acivity[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(3):24−28. [23] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, WANG Y X. et al. Acetylation and carboxymethylation of the polysaccharide from Ganoderma atrum and their antioxidant and immunomodulating activities[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,156:279−288. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.111
[24] 李瑾, 张婷婷, 蒲定涛, 等. 乙酸酐法合成乙酰化熟地黄多糖工业及其对抗氧化活性的影响[J/OL]. 中国中药杂志: 1−9 [2021-03-28]. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210310.302. LI J, ZHANG T T, PU D T, et al. Acetylization derivatives synthesis and antioxidant active of polysaccharides from Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch[J/OL]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica: 1−9 [2021-03-28]. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210310.302.
[25] WANG X M, ZHANG Z S, WU Y, et al. Synthesized sulfated and acetyated derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis and their potenial antioxidant and immunological activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,124(1):568−572.
[26] HUA J, ZHANG X F, WANG Z J, et al. Preparation, characterization and antioxidant activities of acetylated polysaccharides from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,31(7):1−18.
[27] 张曼, 张宇, 徐少博, 等. 平贝母多糖铁配合物的合成、结构特征及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2019,12(7):36−42. [ZHANG M, ZHANG Y, XU S B, et al. Preparation, structural characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide-iron complex from Fritillaria ussuriensis[J]. Food Science,2019,12(7):36−42. [28] ZHANG M, ZHAO H, SHEN Y, et al. Preparation, characterization and antioxidant activity evaluation in vitro of Fritillaria ussuriensis polysaccharide-zinc complex[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,7(1):462−474.
[29] CHEN S H, HUANG H L, HUANG G L. Extraction, derivatization and antioxidant activity of cucumber polysaccharide[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,140(1):1047−1053.
[30] WANG S N, YAO J Y, ZHOU B, et al. Bacteriostatic effect of quercetin as an antibiotic alternative in vivo and its antibacterial mechanism in vitro[J]. Research Paper,2018,81(1):68−78.
[31] 秦利鸿, 曹建波, 易伟松. 绿茶多糖的扫描电镜制样新方法及原子力显微镜观察[J]. 电子显微学报,2009,28(2):162−167. [QIN L H, CAO J B, YI W S. A new methord for scanning electron microscope samples of polysaccharudes distilled from green tea and the observation of ultrafine structure of them with atomic force microscope[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society,2009,28(2):162−167. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2009.02.014 [32] 李凡, 徐志凯. 医学微生物学(第九版)[M]. 人民卫生出版社, 2018. LI F, XU Z K. Medical microbiology(The ninth edition)[M]. People’s Medical Publishing House, 2018.
[33] 巩丽虹, 徐红纳, 刘嘉祺, 等. 防风多糖USPS乙酰化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(10):200−203. [GONG L H, XU H N, LIU J Q, et al. Acetylation modification and antioxidant activity of a polysaccharide USPS from Radix saposhnikoviae[J]. Food Industry,2019,40(10):200−203. [34] 李晓丽. 牡丹籽粕多糖的化学修饰及其抗氧化和抑菌能力的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. LI X L. Chemical modifications of polysaccharides extracted from peony seed dreg and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity in vitro[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(18)
1. 宫益霞,孔凡星,卢玉婷,任杰,谢炜康,王丽红. 辽东楤木芽多糖乙酰化修饰工艺及其抗氧化活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(01): 162-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 牛航迪,马迎红,谢青贵,马玉花. 藏菖蒲提取工艺优化及抑菌和抗氧化活性研究. 中南药学. 2024(03): 654-659 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 牛亦婷,刘子彰,包怡红,李芳菲,于莹. 蒲公英多糖提取技术及生物活性的研究进展. 食品研究与开发. 2024(07): 204-209 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘子怡,李仪晴,张仁群,叶靖宇,张涛. 天然植物多糖抗氧化活性的研究进展. 中国食物与营养. 2024(08): 40-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 朱星枚,郭凯丽,袁盼盼,姜宇,姚琳,张东旭,刘继平,王斌,蔡盈盈,张美文,张兵兵. 一种拉帕替尼衍生物的合成及抗HER2阳性乳腺癌作用研究. 中南药学. 2024(09): 2261-2265 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孙寒,刘松,宁紫月,玉杏珊,王雅,吴昊卓,藏颖,李媚,梁钟文,刘红全. 几种化学修饰的三角褐指藻胞内多糖对宫颈癌Hela细胞增殖的抑制效果比较. 现代食品科技. 2024(07): 8-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 魏鑫鑫,沈柯辰,姚俊修,吴德军,张仁堂. 超声辅助接骨木多糖提取工艺优化及其结构特性分析. 中国食物与营养. 2024(09): 45-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 何袅袅,陈雅鑫,蔡树芸,施丽君,陈伟珠,陈晖,洪专,张怡,张怡评. 铜藻多酚的分离纯化及抗氧化活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(03): 183-191 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 单舒萱,于洋,李敬双,成雨欣,许诺,刘思含,刘熙荣,屈影. 蒲公英多糖对肉仔鸡免疫功能、血清生化指标和生长性能的影响. 饲料研究. 2023(03): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 程广东,汪梓晗,夏秋博,周清波,孙宏莱,张春悦,夏俊,刘德江. 响应面法优化柞蚕蛹多糖的提取工艺及其抑菌活性研究. 中国饲料. 2023(06): 19-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘燕婷,吴迪,王占琴,武辉. 腰腿痛贴膏联合温针对关节型银屑病患者中医症候评分、Th17细胞因子及生活质量的影响. 海南医学. 2023(07): 933-937 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 徐光沛,李涵涛,邓奇元,刘昌利,蒋平,何燕飞. 环磷酰胺对小鼠血常规、血液生化指标的影响及构树叶多糖的干预作用. 安徽科技学院学报. 2023(03): 76-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 刘晓伟,王萌蕾,牛恒林. 观赏海棠果多糖的乙酰化修饰及其对油脂抗氧化研究. 食品科技. 2023(05): 185-191 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 王薇,曹雯. 沙棘果渣多酚、多糖及黄酮抑菌性及对葡萄保鲜研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2023(11): 12-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 张泽岩,张康,王磊,张小丽,马小军,李建喜. 乳宁散对隐性乳房炎奶牛产奶性能影响和防治效果的评价. 甘肃农业大学学报. 2023(05): 32-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 周彤,闫寒汐,朱李想,张睿,胡佳悦,吴萧. 不同方法对蒲公英多糖脱色工艺条件优化的研究. 农产品加工. 2023(22): 29-35+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 郑毅,苟海芹,常贺,王璐,周雪艳,杨亚慧,王子朝. 药用植物多糖在家禽养殖中的应用研究进展. 现代牧业. 2023(04): 13-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 朱巧玲,邹宇晓,廖森泰,孙远明,黎尔纳. 桑枝低聚糖抑制变异链球菌工艺优化及其抗氧化活性. 食品研究与开发. 2022(10): 85-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(14)











 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



