Effects of Storage Methods on the Structure and Solubility of Mung Bean Globulin
-
摘要: 为明确不同贮藏方式对绿豆蛋白质结构和溶解性的影响,以新鲜绿豆和在室温及4 ℃气调贮藏18个月的绿豆为原料,利用傅里叶红外光谱、DTNB比色法、Folin酚法等方法,探究发现室温条件下,绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋结构最大增加4.73%,巯基含量最大降低0.00487、表面疏水性最大降低20.78667,二硫键含量最大升高0.00177;4℃条件下,绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋结构最大增加1.65%,巯基含量最大降低0.00174,表面疏水性最大降低5.48667,二硫键含量最大升高0.00048。经过贮藏后,绿豆球蛋白的溶解性降低,不同贮藏方式变化不同。室温贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白结构和溶解性与新鲜绿豆球蛋白差异显著(P>0.05);而4 ℃气调贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白结构和溶解性与新鲜绿豆差异不显著(P<0.05)。说明4 ℃和气调贮藏可以减少绿豆球蛋白结构的变化与溶解性的变化,从而更好地保持其品质。Abstract: In order to clarify the influence of different storage methods on the protein structure and solubility of mung beans, fresh mung beans and mung beans stored in a gas package at room temperature and 4 °C for 18 months were used as raw materials. Fourier infrared spectroscopy, DTNB colorimetric method and Folin method were used. The investigation found that the maximum α-helical structure of mung bean globulin increased by 4.73%, the maximum sulfhydryl content decreased by 0.00487, the maximum surface hydrophobicity decreased by 20.78667, and the maximum disulfide bond content increased by 0.00177 at room temperature. At 4 °C, the α-helix structure of mungbean globulin increased by 1.65%, the sulfhydryl content decreased by 0.00174, the surface hydrophobicity decreased by 5.48667, and the disulfide bond content increased by 0.00048. The solubility of mung bean globulin decreased after storage, and different storage methods have different changes. The structure and solubility of mung bean globulin after storage at room temperature were significantly different from that of fresh mung bean globulin (P>0.05), while the structure and solubility of mung bean globulin after storage at 4 °C were not significantly different from that of fresh mung bean (P<0.05). It showed that 4 ℃ and controlled atmosphere storage could reduce the changes of mung bean globulin structure and solubility, so as to better maintain its quality.
-
Keywords:
- mung bean globulin /
- modified atmosphere /
- storage /
- protein structure /
- solubility
-
绿豆中含有丰富的蛋白质,其含量高达25%,且绿豆蛋白富含赖氨酸、亮氨酸和苏氨酸3种必需氨基酸[1]。绿豆蛋白中的球蛋白含量高达80%,球蛋白不仅可以促进胆酸胆盐分解,有效降低血脂,还有刺激神经兴奋,增进食欲的功效[2]。随着人们对绿豆的营养作用的重视,其消费量大增,食用的绿豆一般真空包装贮藏一段时间,在贮藏过程中蛋白质的品质变化直接影响了其食用性。蛋白质溶解性与结构直接相关,在贮藏过程中蛋白质的结构会发生变化,使蛋白质溶解性发生改变,尽而降低蛋白质的乳化性、凝胶性和成膜性等加工特性[3],同时降低蛋白的营养特性。研究贮藏技术对绿豆蛋白结构的影响可指导绿豆的贮藏,提高绿豆的加工品质。
已有研究表明贮藏方式对不同来源的植物蛋白质结构、溶解性的变化有很大影响,王炜清等[4]发现,随着贮藏时间的延长,扁桃仁分离蛋白的溶解度和二级结构都发生了明显的变化;赵妍等[5]发现,贮藏时间相同时,低温、低湿度下的小麦蛋白质α–螺旋结构减少最小,小麦品质劣变速度变慢;Hou等[6]发现,较高的温度、湿度条件下贮藏的大豆β-伴球蛋白的结构与溶解度都较低温有明显变化;蔡晓宁等[7]发现,低水分(11.2%)、低温(15 ℃)和气调贮藏更有利于保持绿豆的品质;赵卿宇等[8]发现贮藏后大米蛋白溶解度下降,但低温会促进盐丰大米蛋白溶解。目前植物蛋白贮藏效果的研究主要针对不同温度、湿度下蛋白质二级结构及溶解性的变化,研究的重点也是限于高温条件下的蛋白质结构的变化,在自然温度,不同气调方式下长期贮藏的绿豆蛋白质结构变化研究未见文献,气调与温度相互作用下绿豆蛋白结构与溶解性的变化方面的研究更少。因此,确定不同气调方式及温度对绿豆蛋白结构与溶解性的影响研究对指导绿豆贮藏,保持其品质具有非常重要的意义。
本研究以室温气调贮藏和4 ℃气调贮藏18个月的绿豆为原料,通过与同组新收获的绿豆特性进行比较,分析不同贮藏方式下绿豆球蛋白的二级结构、巯基和二硫键、表面疏水性等结构变化对溶解性的影响,确定最佳的气调方式及贮藏温度,为合理贮藏绿豆、利用绿豆中的营养物质提供数据基础和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
绿豆 取样于黑龙江的绿丰二号品种(水分含量2.6%,蛋白质含量26.5%);NaCl 分析纯,辽宁泉瑞试剂有限公司;石油醚 分析纯,辽宁泉瑞试剂有限公司;NaOH 分析纯,天津永晟精细化工有限公司;HCl 分析纯,天津市大茂化学试剂厂;5,5’-二硫代双(2-硝基苯甲酸) 分析纯,天津永晟精细化工有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;KBr 光谱纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
LGJ-10C冷冻干燥机 北京四环科学仪器厂有限公司;TU-1900型双光束紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;CR22GⅡ/CR21GⅡ高速冷冻离心机 日本日立公司;UDK152自动凯氏定氮仪 意大利VELP公司;RH-KT/C型磁力搅拌器 德国IKA公司;5810R高速冷冻离心机 EPPENDORF公司;TENSORII傅里叶红外光谱仪 德国布鲁克科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
将新鲜的绿豆样品分四组进行包装贮藏,贮藏条件为真空、N2+CO2(比例为1:1,下同)、N2、CO2,分别放在室内避光干燥处与4 ℃冰箱内,贮藏时间为18个月。同一批次的新鲜绿豆立即检测作为对照。
1.2.2 球蛋白提取
采用Osborne分级提取法提取球蛋白[9];将绿豆洗净干燥后进行磨粉、过筛,采用沸程30~60 ℃的石油醚脱脂得到脱脂绿豆粉。取100 g脱脂绿豆粉加入1 L去离子水,在室温条件下搅拌浸提2 h,4 ℃条件下8000 r/min离心20 min取沉淀,继续加500 mL去离子水进行二次水提,取沉淀用l000 mL 1 mol/L NaCl进行浸提,在室温条件下搅拌浸提2 h,4 ℃条件下8000 r/min离心20 min,收集上清液,将沉淀再加500 mL 1 mol/L NaCl进行二次浸提,收集上清液。合并两次上清液,4 ℃透析(MWCO:8000~12000 D)24 h,期间梯度换水,离心获得沉淀,进行冷冻干燥,所得样品即为球蛋白。
1.2.3 结构性质测定
1.2.3.1 二级结构的测定
将冻干样品准确称量1.0 mg,与100 mg烘干的KBr混合充分研磨均匀后,使用压片机压制成透明薄片,随后在干燥室温的环境采集傅里叶红外图谱。采集条件为分辨率4 cm−1,扫描范围400~4000 cm−1,样品扫描次数为32次[10]。
1.2.3.2 紫外吸收光谱的测定
将提取的球蛋白用PH 7.0的磷酸盐缓冲溶液配置成1.0 mg/mL的蛋白质溶液,以相应的缓冲溶液为参比,进行紫外-可见光扫描,扫描范围是200~400 nm,扫描速度 2 nm/s;得到绿豆球蛋白的紫外吸收光谱[11]。
1.2.3.3 巯基、二硫键含量的测定
参照 Huang 等[12]的方法,用DNTB比色法测定巯基和二硫键的含量。即利用5,5’-二硫代-2-硝基苯甲酸(DTNB)与游离SH反应,在波长412nm处生成有最大吸收峰的黄色物质后,采用分光光度法进行吸光度测定而得到。
1.2.3.4 表面疏水性的测定
参照 Arzeni等[13]的方法,用ANS荧光探针测定球蛋白的表面疏水性(H0)。将样品用pH7.0的1 mol/L的磷酸盐缓冲溶液溶解,8000 r/min离心20 min获取上清液,测定上清液的浓度后将其梯度稀释,分别得到浓度为0.05、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4 mg/mL的蛋白质溶液,分别加入20 μL浓度为8.0 mmol/L的ANS试剂,混匀器混匀,避光放置20 min后测定荧光强度。激发波长390 nm,发射波长470 nm,狭缝宽度5 nm,以荧光强度对蛋白浓度作图,曲线的初始斜率即为该蛋白样品的表面疏水性。
1.2.3.5 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(SDS-PAGE)电泳的测定
参照 Moritz 等[14]的方法,利用 SDS-PAGE 对蛋白质分子量变化进行分析。将冻干后的蛋白质溶解于0.1 mol/L的NaOH溶液中,使其最终浓度为0.5 mg/mL,以1:4的比例加入样品与样品缓冲液(0.15 g Tris-HCl,0.02 g溴酚蓝,0.40 g SDS,2 mL 50%甘油,15 mL β-疏基乙醇,混合并用蒸馏水中定容至10 mL)混匀,放入的离心管中,−20 ℃储存,使用时用沸水煮制3~5 min使蛋白质完全变性;上样体积10 μL,浓缩胶与分离胶的质量分数分别为4%,12%,电压80 V恒压,样品下移至分离胶后电压加至120 V,条带接近胶板下边缘时停止电泳,考马斯亮蓝G250染色后进行脱色处理。
1.2.4 溶解性测定
参照 Lemos等[15]的方法,用Folin酚法测定球蛋白的溶解度。用pH7.0的磷酸盐缓冲溶液配制5 mg/mL的蛋白溶液,搅拌30 min后8000 r/min离心10 min,分别将离心后的上清液1 mL碱性铜1 mL和福林酚试剂4 mL加入试管中立即混匀,55 ℃条件下反应5 min,拿出后立即放入冷水静置10 min,除去不溶性残渣,于紫外分光光度计650 nm处测吸光度。按式(2)计算溶解度:
式中;S代表溶解度,%;C1代表可溶性蛋白质量,g;C0代表样品中蛋白质量,g。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据均进行了三次重复测定,测定结果以均值±SD表示。实验数据采用SPSS22.0软件进行统计学分析,使用Origin8.0对数据进行分析和作图,利用Peakfit4.12软件对谱图中1700~1600 cm−1酰胺Ⅰ区分峰处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 贮藏方式对球蛋白结构性质的影响
2.1.1 贮藏方式对球蛋白二级结构的影响变化
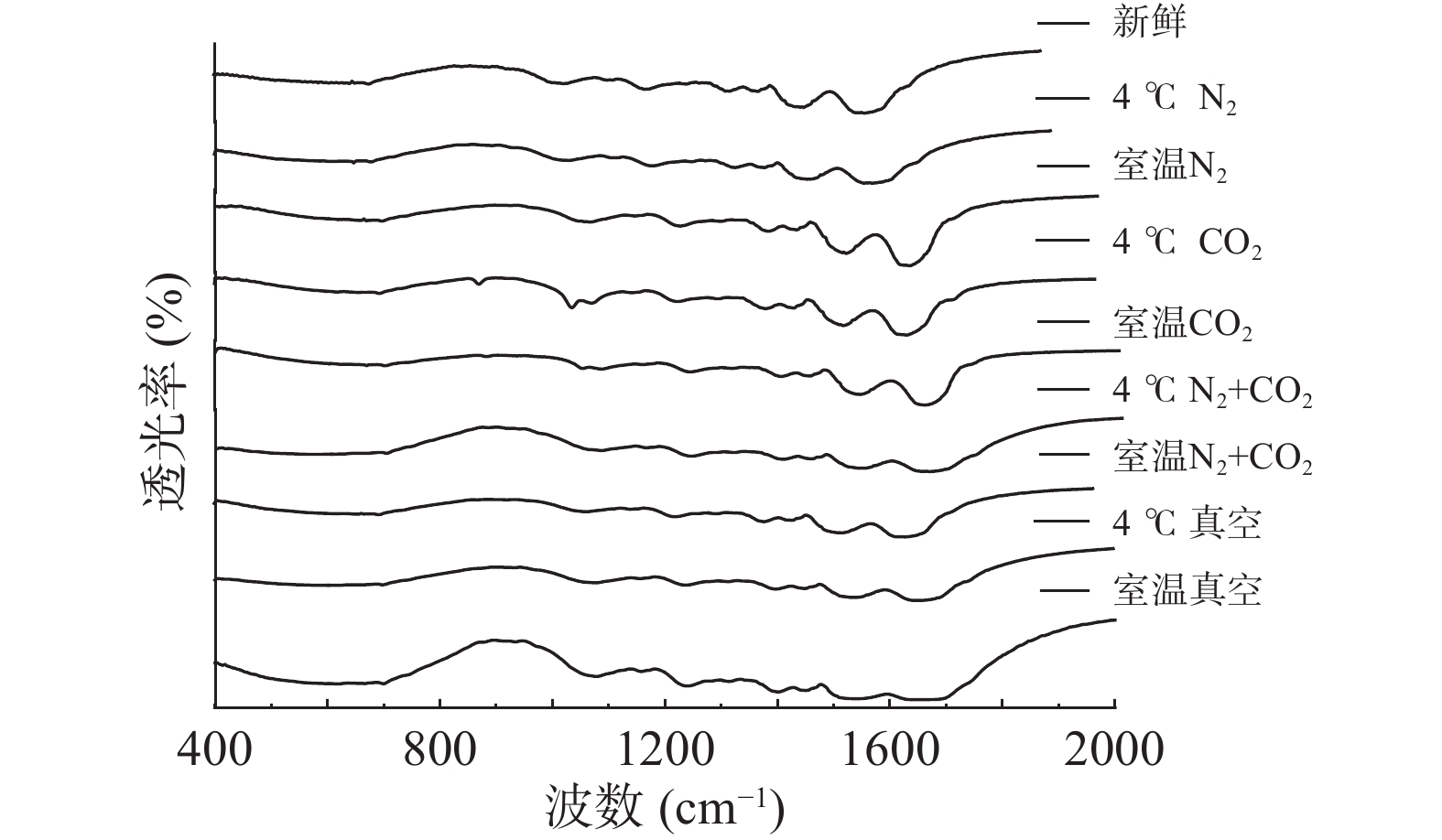
通过傅里叶红外光谱对不同贮藏方式下的绿豆球蛋白进行二级结构的检测,采用OMNIC8.0数据处理软件,原谱进行基线校正,参照去卷积参数,得到去卷积图谱,不同贮藏方式的绿豆球蛋白傅里叶变换红外光谱见图1。
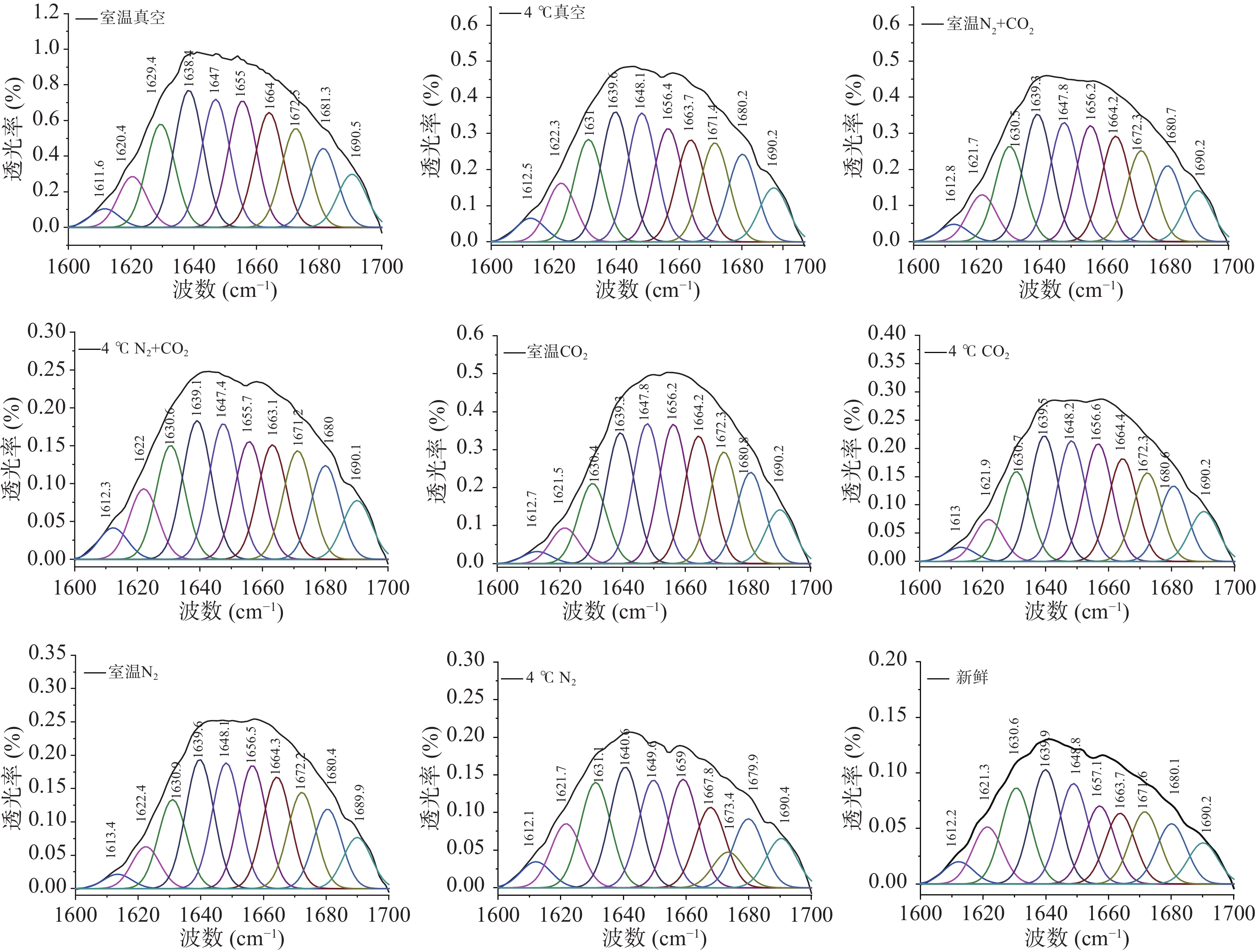
利用Origin8.0软件对图1中球蛋白红外光谱中酰胺Ⅰ区(1700~1600 cm−1)进行拟合,其中,1650~1660 cm−1区为α-螺旋,1610~1642 cm−1区为β-折叠,1642~1650 cm−1区为无规卷曲,1660~1680 cm−1区为β-转角,1680~1700 cm−1区为β-反向[16]。不同贮藏条件的球蛋白样品酰胺Ⅰ带的拟合结果如图2所示,拟合度R2=0.9999,据此计算得出的球蛋白二级结构的各组分含量见表1。
表 1 不同贮藏方式的球蛋白二级结构变化Table 1. Changes in the secondary structure of globulins in different storage methods条件 α-螺旋结构(%) β-折叠结构(%) β-转角结构(%) 无规卷曲结构(%) 新鲜 10.96±0.78a 41.28±0.37h 20.09±0.04a 15.19±0.02e 4 ℃N2+CO2 11.99±0.58ab 36.08±0.08f 22.70±0.05b 13.80±0.04a 4 ℃C O2 12.24±0.36ab 32.87±0.20c 23.18±0.03c 14.61±0.04d 4 ℃真空 12.61±0.71bc 35.02±0.12e 22.36±0.59b 14.33±0.04c 4 ℃N2 12.17±0.41c 40.70±0.39g 24.19±0.08d 14.07±0.04b 室温N2+CO2 13.91±1.56c 33.97±0.10d 23.26±0.32c 14.10±0.03b 室温CO2 13.73±0.85c 28.07±0.04a 25.96±0.08e 14.11±0.02b 室温真空 15.69±0.28d 34.07±0.13d 23.50±0.17c 14.08±0.03b 室温N2 13.97±0.22d 31.87±0.13b 24.20±0.04d 14.60±0.03d 注:同一列中的不同字母表示在P<0.05水平上有显著差异。 由表1可知,经18个月的贮藏,不同贮藏方式下的绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋与β-转角结构均呈增长趋势,分别最大增长了4.73%与5.87%;无规则卷曲与β-折叠结构均呈下降趋势,分别最大下降了1.39%与13.21%。不同贮藏温度下,室温四种贮藏方式(真空、N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,球蛋白α-螺旋结构含量分别增加了4.73%、2.95%、2.77%、3.01%,差异显著(P<0.05),原因可能是贮藏中球蛋白发生氧化,使得球蛋白中无序的无规则卷曲结构向有序的α-螺旋结构转变,蛋白质的结构收缩,形成更多的螺旋结构[17],叶林等[18]研究发现,蛋白质发生氧化会导致花生分离蛋白大分子聚集体的形成。氧化发生的条件是有适宜的温度与充足的氧气,气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋结构差异显著(P<0.05),可能是真空条件下,蛋白质网格结构变小,但因结合室温贮藏,仍会发生氧化[19]。而气调贮藏下,有适宜的温度,球蛋白氧化程度小于真空贮藏,说明气体延缓了球蛋白结构的氧化,对其结构有保护作用。4 ℃条件贮藏下的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,气调贮藏(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋结构含量差异不显著(P>0.05),且相比室温贮藏,4 ℃贮藏后绿豆球蛋白的α-螺旋结构增量较小,说明4 ℃条件会延缓球蛋白的氧化,减少结构转变;气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋结构差异显著(P<0.05),说明4 ℃与气调条件都有保护球蛋白结构,延缓氧化的作用。两种贮藏温度下,三种气调贮藏之间差异不显著(P>0.05),说明充气包装中的气体种类并不影响气体作用。
2.1.2 贮藏方式对球蛋白紫外吸收光谱的影响变化
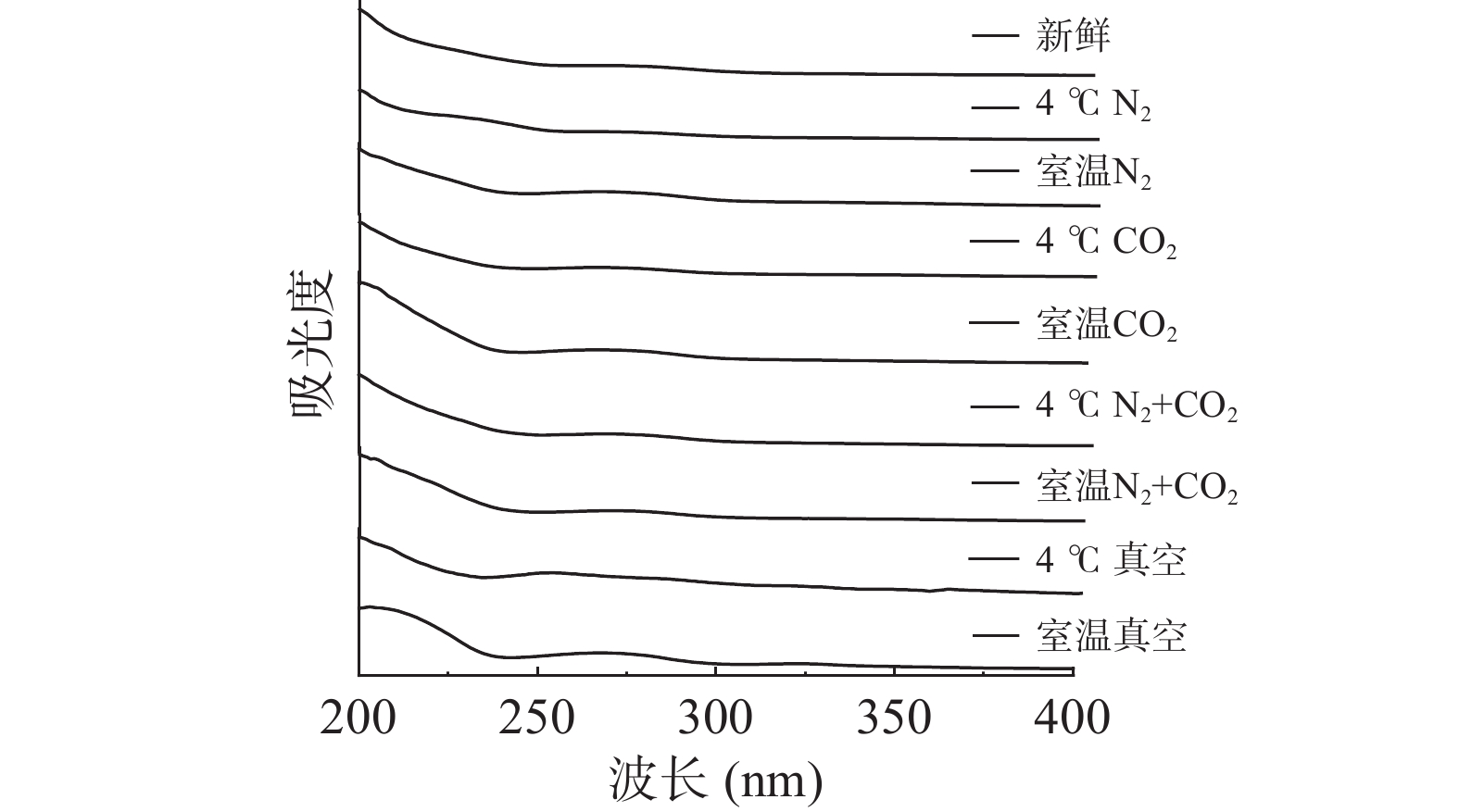
为了进一步揭示贮藏方式对绿豆球蛋白二级结构的影响,对其进行紫外-可见光扫描,得到不同贮藏方式下球蛋白的紫外吸收光谱如图3所示。
由图3可知,在260~280 nm附近,不同贮藏条件的绿豆球蛋白均出现最大吸收峰,这是由于芳香族氨基酸的紫外吸收作用,其中起主要作用的酪氨酸的最大吸收波长为Tyr 275 nm,色氨酸的最大吸收波长为Trp 280 nm,和苯丙氨酸的最大吸收波长为Phe 257 nm[18]。由图可知,根据贮藏方式的不同,紫外扫描图谱的变化趋势是类似的,新鲜绿豆球蛋白在263~264 nm处出现最大吸收峰,4 ℃气调条件(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)贮藏下的绿豆球蛋白最大吸收峰也出现在264 nm附近,而除此之外,其他贮藏条件下的绿豆球蛋白出峰位置均发生改变,且最大吸收峰也出现不同程度的红移。室温N2以及室温N2+CO2贮藏下的绿豆球蛋白出峰位置发生改变,峰强度也明显增加。管斌等[20]发现,通过紫外吸收光谱的变化可以推断出蛋白质构象的变化。贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白最大吸收峰红移,从溶剂效应来分析,表明经贮藏处理后,生色团微环境由极性向非极性转变,由此可知,不同方式贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白,结构发生聚集,芳香族氨基酸残基被包埋,球蛋白的表面疏水性也降低[21],同时,球蛋白的二级结构中的α-螺旋结构含量增加,发生聚集,这一结论也从前文中红外光谱研究得到证实。
2.1.3 贮藏方式对球蛋白巯基和二硫键的影响变化
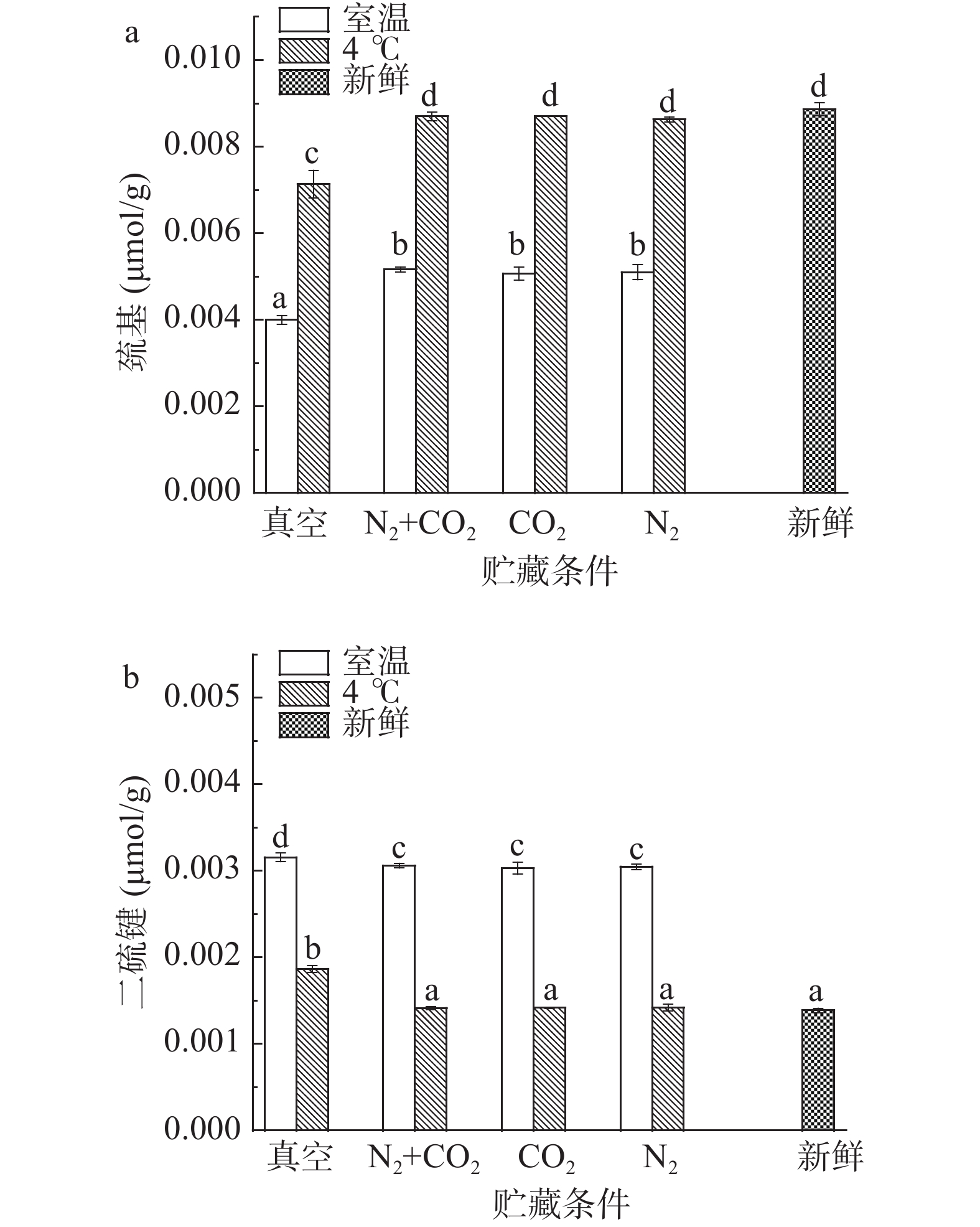
通过DTNB比色法对不同贮藏方式下绿豆球蛋白巯基和二硫键的变化进行测定,不同贮藏方式对绿豆球蛋白巯基和二硫键的影响变化如图4a~图4b所示。由图4a可知,不同贮藏温度下,室温四种方式(真空、N2+CO2、CO2、N2) 贮藏后的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,球蛋白巯基含量差异显著(P<0.05),可能是长期室温条件贮藏,酶活性相对较高,蛋白质的新陈代谢加快,巯基被氧化,从而含量降低[22],真空与气调贮藏绿豆球蛋白巯基含量差异显著(P<0.05),真空条件会抑制酶的生理活动进行,延缓球蛋白的巯基氧化,而气调贮藏下球蛋白巯基氧化程度低于真空条件,可能是气体的存在降低绿豆球蛋白与空气的接触,起到了保护巯基不被氧化的作用[22],这也与前文中α-螺旋结构的变化相对应。4 ℃条件贮藏下的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,气调贮藏(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆球蛋白巯基含量差异不显著(P>0.05),且相比室温贮藏,4 ℃贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白巯基含量下降较小,原因是由于4 ℃贮藏不利于酶的生理活动,从而对球蛋白的氧化也有延缓的作用;气调与真空贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白巯基含量差异显著(P<0.05),说明贮藏过程中4 ℃和气调贮藏都有延缓巯基氧化的作用。
由图4b可知,不同贮藏温度下,室温四种贮藏方式(真空、N2+CO2、CO2、N2)的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,球蛋白二硫键含量差异显著(P<0.05),原因是长期室温条件加速巯基氧化,巯基发生脱氢反应,大量的分子间二硫键生成,从而二硫键的含量上升;真空与气调贮藏的绿豆球蛋白二硫键含量差异显著(P<0.05),原因是由于真空条件贮藏的巯基氧化程度大于气调贮藏,二硫键的生成也差异显著(P<0.05)。4 ℃条件贮藏下的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,气调贮藏(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)的绿豆球蛋白二硫键含量变化不显著(P>0.05),且相较室温贮藏,4 ℃贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白二硫键含量上升较小,原因是4 ℃贮藏球蛋白的巯基氧化会受到抑制,导致二硫键的生成也受到影响;真空与气调贮藏的绿豆球蛋白二硫键含量均差异显著(P<0.05),说明4 ℃和气调贮藏都会延缓巯基的氧化,抑制二硫键的生成。张来林等[22]研究发现,稻谷巯基含量随贮藏时间的延长而降低,温度越高降低得幅度越大,而气调贮藏下降幅度较小,本研究通过对球蛋白巯基与二硫键的变化研究得到,4 ℃和气调贮藏会延缓巯基的氧化,减少二硫键的生成,这与文献结果一致。而贮藏过程中巯基的变化刚好与二硫键相反,证明在贮藏过程中,蛋白质巯基和二硫键呈现一定程度的转化;从实验结果可以看出,不同条件贮藏下球蛋白的变性聚集机制与巯基、二硫键的变化密切相关,球蛋白的二级结构被重新排列,分子结构发生聚集[21]。
2.1.4 贮藏方式对球蛋白表面疏水性的影响变化
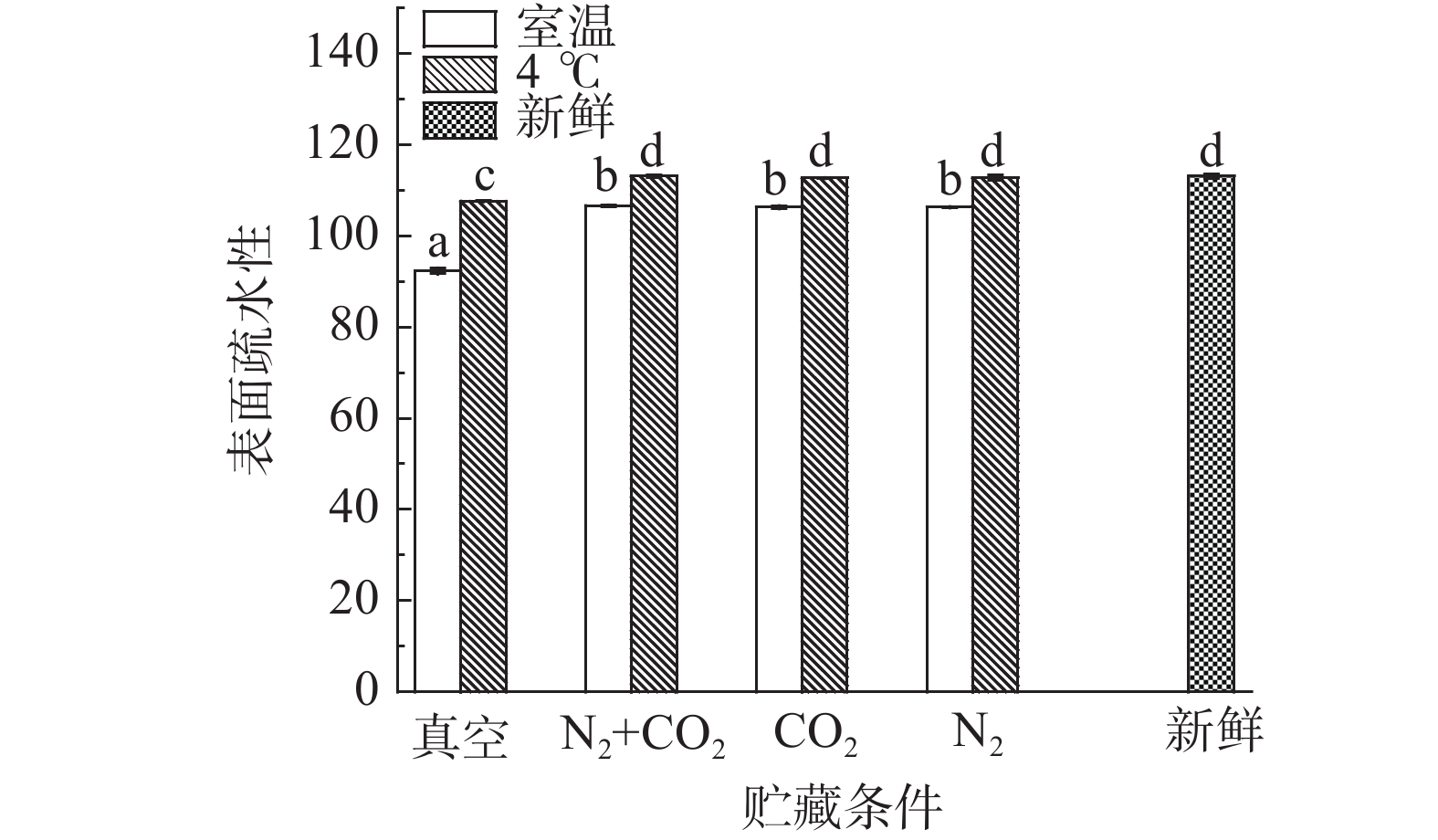
蛋白质分子的表面疏水性可以反映其表面疏水基团的相对含量,是维持蛋白质结构的重要特性[23],与蛋白质的溶解性有很大关系。不同贮藏方式对球蛋白表面疏水性的影响变化如图5所示。
由图5可知,不同贮藏温度下,室温四种贮藏方式(真空、N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,球蛋白表面疏水性差异显著(P<0.05),原因是球蛋白发生氧化后,其α-螺旋增加,球蛋白结构发生收缩,形成了不溶的聚集体,使暴露的疏水性基团被掩埋[24];气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白表面疏水性差异显著(P<0.05),原因是气调贮藏对球蛋白结构有保护作用,而真空条件下球蛋白氧化程度大于气调条件,球蛋白分子内部形成的不溶性聚集体增加,导致其表面疏水性也差异显著(P<0.05)。4 ℃条件贮藏下的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,气调贮藏(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆球蛋白表面疏水性差异不显著(P>0.05),且相较室温贮藏,4 ℃贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白表面疏水性下降较小,原因是4 ℃贮藏有延缓氧化的作用,球蛋白内大分子聚集体的生成减少,也会影响其表面疏水性的降低;气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白表面疏水性差异显著(P<0.05),说明4 ℃和气调贮藏都起保护球蛋白结构的作用,减少了球蛋白分子内部形成的不溶性聚集体,从而减小对暴露的疏水性基团作用。Ye等[25]研究发现,花生蛋白发生氧化,其表面疏水性逐渐下降,本研究通过对绿豆球蛋白溶解性及表面疏水性的变化研究,得到球蛋白氧化程度增加,溶解度降低,表面疏水性也降低,与文献中结果一致。
2.1.5 贮藏方式对球蛋白SDS-PAGE的影响变化
本文在制备绿豆球蛋白过程中没有采用色谱分离技术进一步纯化,所以球蛋白电泳图中可能含有少量清蛋白、谷蛋白和醇溶蛋白的亚基条带,不同贮藏条件球蛋白的SDS-PAGE电泳图如图6所示。
由图6可知,不同贮藏方式的电泳图中亚基数目没有变化,表明不同贮藏方式下的绿豆球蛋白亚基数目没有改变,但是由于贮藏条件的不同,绿豆球蛋白的亚基条带都发生了不同程度的变化。泳道1、3、5在40 kDa出现明显的条带,推测的原因是蛋白质分子之间的二硫键具有一定程度的聚集和交联[26];泳道1、3、5、7的14 kDa条带颜色变浅模糊,其中泳道7整个条带变浅,这可能是因为在还原态电泳中,β-巯基乙醇的加入打断了大分子蛋白聚集体中的二硫键[16],此时球蛋白发生变性;且与对照组相比,所有泳道顶端浓缩胶颜色有不同程度的加重,宽窄也有不同变化,说明不同贮藏方式下大分子物质均发生了聚集;同时,蛋白质氧化的加深也会引起某些蛋白质分子发生降解,从而在低分子量区域产生离散不均匀的条带[27]。吴伟等[28]研究发现,米糠在贮藏过程中蛋白质氧化形成聚集体,并且二硫键和非二硫共价键共同参与其形成。泳道4、6、8与对照组条带相似;说明此三种贮藏条件下,绿豆球蛋白结构变化较小,与前文结果相同。
2.2 贮藏方式对球蛋白溶解性的影响变化
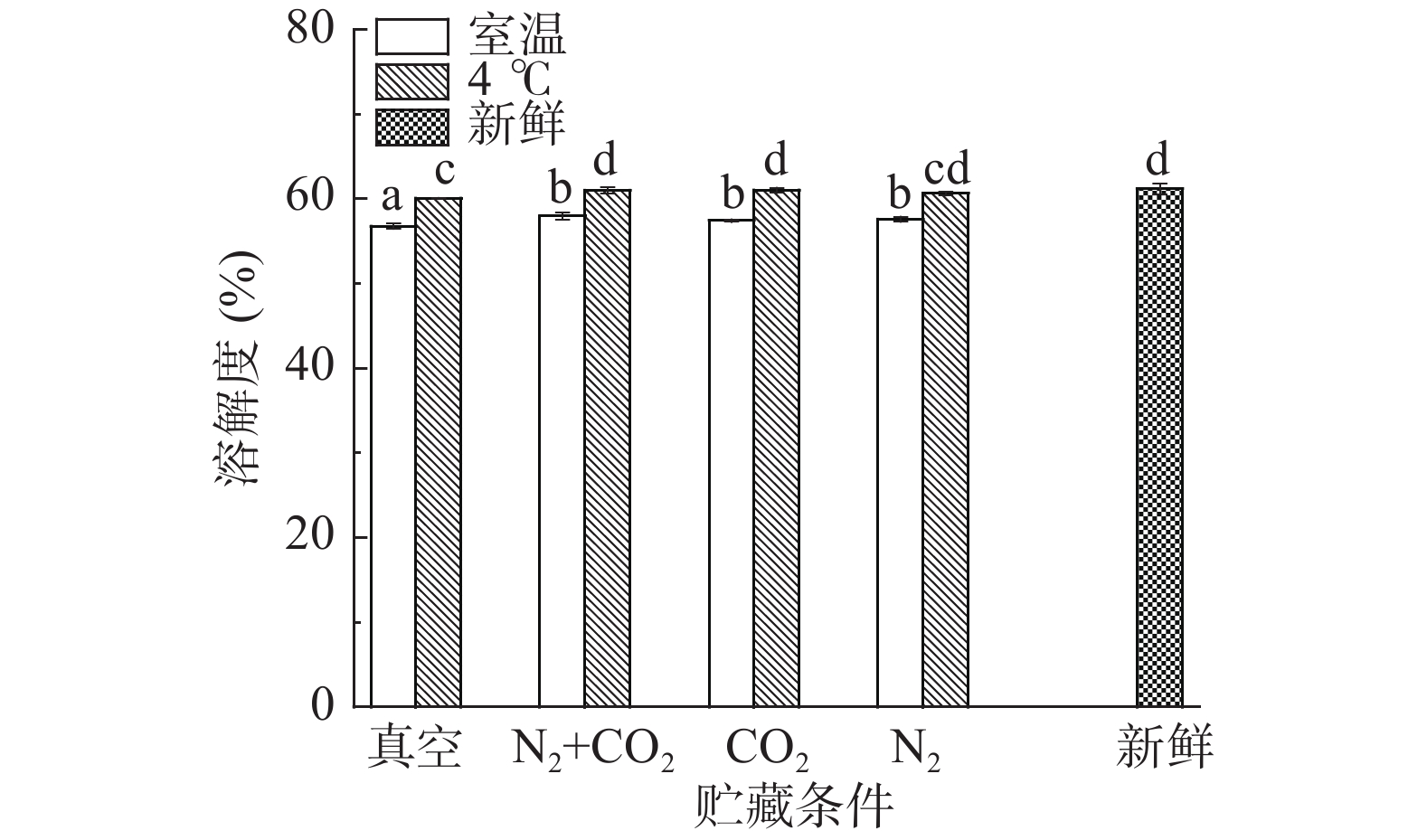
溶解度是表征蛋白质质变的重要特征。通过对球蛋白溶解度的变化明确其结构品质的变化带动功能性质的变化。采用Folin酚法对不同贮藏方式下绿豆球蛋白的溶解度进行分析测定,测定结果变化如图7所示。
由图7可知,不同贮藏温度下,室温四种贮藏方式(真空、N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,球蛋白溶解度差异显著(P<0.05),原因是贮藏中球蛋白的氧化作用使球蛋白分子之间发生交联,球蛋白内部形成较大分子量的聚集体,导致其溶解性下降[29] ,气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白溶解性差异显著(P<0.05),原因是真空条件下球蛋白结构氧化更严重,大分子聚集体生成更多。4 ℃条件贮藏下的绿豆与新鲜绿豆相比,气调贮藏(N2+CO2、CO2、N2)后的绿豆球蛋白溶解度差异不显著(P>0.05),且相较室温贮藏,4 ℃贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白溶解度下降较小,原因是4 ℃贮藏有延缓球蛋白氧化的作用,抑制球蛋白不溶性聚集体的生成,从而减少溶解度的下降;气调与真空贮藏的绿豆球蛋白溶解性差异显著(P<0.05),说明绿豆在经4 ℃和气调贮藏后,球蛋白的氧化作用都受到抑制,球蛋白结构收缩变少,导致溶解性下降不显著(P>0.05)。研究[16]发现,大米谷蛋白中α-螺旋含量的变化与谷蛋白的溶解性呈现显著的负相关(P<0.05),根据本研究对绿豆球蛋白α-螺旋和溶解性的研究,得到α-螺旋结构含量增加,溶解度降低,与报道中相同。
2.3 球蛋白结构与溶解性的相关性分析
学者对大豆vicilin球蛋白研究发现,球蛋白的结构特征和理化功能性质之间存在一定的相关性[29-30]。不同贮藏方式下,绿豆球蛋白的结构与溶解性均发生了变化,利用Pearson相关系数分析了两者之间的相关性如表2所示,由表2可知,球蛋白二级结构中α-螺旋结构与球蛋白的溶解性呈现显著的负相关(P<0.05);β-折叠结构与溶解性呈现显著的正相关(P<0.05);β-转角结构与球蛋白溶解性呈显著的正相关(P<0.05);而无规则卷曲结构与球蛋白的功能性质没有相关性;巯基与球蛋白溶解性呈显著的正相关(P<0.05);二硫键与球蛋白溶解性呈显著的负相关(P<0.05);表面疏水性与溶解性呈显著的正相关(P<0.05)。研究表明大多数蛋白质二级结构的变化,可归因于α-螺旋的增加或减少,因为α-螺旋主要起到维持蛋白质天然结构的作用[27]。
表 2 贮藏过程中球蛋白结构与溶解性的相关性Table 2. Correlation between globulin structure and solubility during storage溶解性 α-螺旋 −0.839* β-折叠 0.649* β-转角 −0.586* 无规则卷曲 0.282 巯基 0.977* 二硫键 −0.974* 表面疏水性 0.820* 注:*,在P<0.05水平上显著相关。 3. 结论
经过不同温度与方式贮藏的绿豆,其球蛋白结构及溶解性都发生了变化,不同贮藏方式引起的变化也有所不同。经4 ℃气调贮藏后绿豆,其球蛋白α-螺旋结构、巯基、二硫键、表面疏水性、溶解性与新鲜绿豆球蛋白相比差异均不显著(P>0.05),且变化都较室温贮藏后的绿豆球蛋白变化幅度小,并且球蛋白的结构与其溶解性具有极显著的相关性(P<0.01),由此4 ℃气调贮藏会相对减少绿豆球蛋白的结构变化与性质变化,是绿豆球蛋白的理想保存方式。本研究对于真空贮藏与气调贮藏的区别没有得到满意的答案,而贮藏过程中气体对于绿豆球蛋白结构所起的作用也未有明确的研究结果,因此关于贮藏过程中气体对球蛋白的保护作用机制还有待进一步研究。
-
表 1 不同贮藏方式的球蛋白二级结构变化
Table 1 Changes in the secondary structure of globulins in different storage methods
条件 α-螺旋结构(%) β-折叠结构(%) β-转角结构(%) 无规卷曲结构(%) 新鲜 10.96±0.78a 41.28±0.37h 20.09±0.04a 15.19±0.02e 4 ℃N2+CO2 11.99±0.58ab 36.08±0.08f 22.70±0.05b 13.80±0.04a 4 ℃C O2 12.24±0.36ab 32.87±0.20c 23.18±0.03c 14.61±0.04d 4 ℃真空 12.61±0.71bc 35.02±0.12e 22.36±0.59b 14.33±0.04c 4 ℃N2 12.17±0.41c 40.70±0.39g 24.19±0.08d 14.07±0.04b 室温N2+CO2 13.91±1.56c 33.97±0.10d 23.26±0.32c 14.10±0.03b 室温CO2 13.73±0.85c 28.07±0.04a 25.96±0.08e 14.11±0.02b 室温真空 15.69±0.28d 34.07±0.13d 23.50±0.17c 14.08±0.03b 室温N2 13.97±0.22d 31.87±0.13b 24.20±0.04d 14.60±0.03d 注:同一列中的不同字母表示在P<0.05水平上有显著差异。 表 2 贮藏过程中球蛋白结构与溶解性的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between globulin structure and solubility during storage
溶解性 α-螺旋 −0.839* β-折叠 0.649* β-转角 −0.586* 无规则卷曲 0.282 巯基 0.977* 二硫键 −0.974* 表面疏水性 0.820* 注:*,在P<0.05水平上显著相关。 -
[1] 胡广甫. 杂粮谷物营养成分分析及杂粮复合营养面条预混合粉研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2018. HU G F. The analysis of the nutritional components of cereals and cereals and the research on the premixed flour of mixed nutritious noodles [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2018.
[2] 段佐萍. 绿豆的营养价值及综合开发利用[J]. 农产品加工,2005(2):58−60. [DUAN Z P. The nutritional value of mung bean and its comprehensive development and utilization[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2005(2):58−60. [3] 赵新淮, 徐红华, 姜毓君. 食品蛋白质[M]. 科学出版社, 2009: 122−125. ZHAO X H, XU H H, JIANG Y J. Food protein[M]. Science Press, 2009: 122−125.
[4] 王炜清, 李秀婷, 周彬等. 贮藏条件对扁桃仁分离蛋白理化特性及消化特性的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(8):102−108. [WANG W Q, LI X T, ZHOU B. et al. Effects of storage conditions on the physical and chemical properties and digestion properties of almond protein isolate[J]. Food and Machinery,2020,36(8):102−108. [5] 赵妍, 刘晓林, 王若兰等. 贮藏微环境对小麦蛋白质二级结构影响[J]. 粮食与油脂,2014,27(1):36−38. [ZHAO Y, LIU X L, WANG R L, et al. The influence of storage microenvironment on the secondary structure of wheat protein[J]. Cereals & Oils,2014,27(1):36−38. [6] HOU H J, CHANG K C. Structural characteristics of purified glycinin from soybeans stored under various conditions[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2004,52(12):7931.
[7] 蔡晓宁, 张来林, 陶琳岩. 不同贮藏条件下绿豆品质变化规律研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,37(2):16−21. [CAI X N, ZHANG L L, TAO L Y. Study on the quality change of mung bean under different storage conditions[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,37(2):16−21. [8] 赵卿宇, 林佳慧, 沈群. 贮藏温度对大米蛋白功能特性的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(13): 200-207. ZHAO Q Y, LIN J H, SHEN Q. The effect of storage temperature on the functional properties of rice protein[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(13): 200-207.
[9] 乔宁, 张坤生, 任云霞. 绿豆中四种蛋白质的分级提取与功能性质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(17):83−87. [QIAO N, ZHANG K S, REN Y X. Study on fractional extraction and functional properties of four proteins in mung bean[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(17):83−87. [10] 朱明华, 胡坪. 仪器分析. 第4版[M]. 高等教育出版社, 2008: 245−268. ZHU M H, HU O. Instrumental analysis. 4th edition[M]. Higher Education Press, 2008: 245−268.
[11] 陈曦. 脂肪氧合酶诱导氧化对大豆分离蛋白结构和消化性的影响研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. CHEN X. The effect of lipoxygenase-induced oxidation on the structure and digestibility of soy protein isolate[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[12] HUANG Y, HUA Y, QIU A. Soybean protein aggregation induced by lipoxygenase catalyzed linoleic acid oxidation.[J]. Food Research International,2006,39(2):240−249. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2005.07.012
[13] ARZENI C, PEREZ O E, PILOSOF A. Functionality of egg white proteins as affected by high intensity ultrasound[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,29(2):308−316. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.03.009
[14] MORITZ LASSÉ, SANTANU DEB-CHOUDHURY, STEPHEN HAINES, et al. The impact of pH, salt concentration and heat on digestibility and amino acid modification in egg white protein[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2015:38.
[15] LEMOS D, LAWRENCE A L, III A. Prediction of apparent protein digestibility of ingredients and diets by in vitro pH-stat degree of protein hydrolysis with species-specific enzymes for juvenile Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Aquaculture,2009,295(1):233−241.
[16] XING F X, WEI L, CHENG M L, et al. Effect of limited enzymatic hydrolysis on structure and emulsifying properties of rice glutelin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016:61.
[17] 石嘉怿, 张太, 梁富强, 等. 大米谷蛋白储藏过程中结构与功能性质变化的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(6):29−34. [SHI J Y, ZHANG T, LIANG F Q, et al. Study on the changes of structure and functional properties of rice gluten during storage[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(6):29−34. [18] 叶林, 廖钰, 赵谋明. 花生分离蛋白氧化过程中的结构变化[J]. 食品与机械,2015,31(2):3−6. [YE L, LIAO Y, ZHAO M M. Structural changes during the oxidation of peanut protein isolate[J]. Food and Machinery,2015,31(2):3−6. [19] 丁磊博. 储藏条件对蔬菜面硝酸盐含量及其品质的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2020. DING L B. The effect of storage conditions on the nitrate content and quality of vegetable noodles[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2020.
[20] 管斌, 林洪, 王广策. 食品蛋白质化学[M]. 化学工业出版社, 2005: 314−327. GUAN B, LIN H, WANG G C. Food Protein Chemistry[M]. Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 314−327.
[21] 郭丽萍. 超高压结合热处理对猪肉蛋白质氧化、结构及特性的影响[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2016. GUO L P. The effect of ultra-high pressure combined heat treatment on the oxidation, structure and characteristics of pork protein[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[22] 张来林, 黄文浩, 肖建文, 等. 不同贮藏条件对大豆、稻谷蛋白中巯基和二硫键的影响研究[J]. 粮食加工,2012,37(3):67−70. [ZHANG L L, HUANG W H, XIAO J W, et al. Effects of different storage conditions on sulfhydryl and disulfide bonds in soybean and rice gluten[J]. Cereal Processing,2012,37(3):67−70. [23] 刘洪洪. 储藏条件对SPI功能特性影响的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨商业大学, 2010. LIU H H. Research on the influence of storage conditions on the functional characteristics of SPI[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2010.
[24] WU W, ZHANG C M, KONG X, et al. Oxidative modification of soy protein by peroxyl radicals[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,116(1):295−301. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.049
[25] YE L, LIAO Y, ZHAO M, et al. Effect of protein Oxidation on the conformational properties of peanut protein isolate[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2013:1−6.
[26] 尤翔宇. 过氧自由基和丙二醛氧化对米糠蛋白结构、功能性质和消化性质的影响[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2019. YOU X Y. Effects of peroxy free radicals and malondialdehyde oxidation on the structure, functional properties and digestion properties of rice bran protein[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2019.
[27] MEHDI A, JOHN A, NILS-GUNNAR C, et al. Effect of stabilization method and freeze/thaw-aided precipitation on structural and functional properties of proteins recovered from brown seaweed (Saccharina latissima)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019:96.
[28] 吴伟, 叶建芬, 蔡勇建等. 贮藏过程中酸败引起的米糠谷蛋白功能性质变化[J]. 食品与机械,2015,31(5):165−168. [WU W, YE J F, Cai Y J. et al. Changes in the functional properties of rice bran gluten caused by rancidity during storage[J]. Food & Machinery,2015,31(5):165−168. [29] AMRO B HASSAN, DIETER von HOERSTEN, ISAM A MOHAMED AHMED. Effect of radio frequency heat treatment on protein profile and functional properties of maize grain[J]. Food Chemistry,2019:271.
[30] KIMURA A, TANDANG-SILVAS M, FUKUDA T, et al. Carbohydrate moieties contribute significantly to the physicochemical properties of french bean 7s globulin phaseolin[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2010,58(5):2923.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 尚学钰,美合日班,苏玲,王琦. 黑木耳可溶性膳食纤维功能特性和降脂活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2025(02): 112-121 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张潇予,王丹妮,柴欣,于卉娟,崔英,王跃飞. 补骨脂的质量特征解析及其在减毒工艺中的应用. 中草药. 2024(08): 2784-2791 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马力亚,李梅梅,黄玉卓,舒劲. 四神丸治疗溃疡性结肠炎的研究概况. 中医药临床杂志. 2024(05): 987-994 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 徐波,陈天天,杜薛平,张海峰,陈伟,黄凯健,董大勇. 益肾化痰祛瘀方治疗绝经后骨质疏松症(肾虚血瘀型)的效果及对氧化应激的影响. 中医药学报. 2024(09): 60-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 钟婉滢,苗建银,叶灏铎,马凤,胡一晨. 藜麦蛋白肽的酶解制备及体外降血脂与降尿酸活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(23): 156-166 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



