Studies on Changes of Physicochemical Properties in Shuidouchi before and after Fermentation and the Inhibitory Effect of Its Extracts on Prostate Cancer Cells
-
摘要: 目的:为研究水豆豉发酵前后理化特性变化,并初步探讨水豆豉提取物对去势抵抗前列腺癌细胞(CRPC)的抑制作用。方法:使用三株高产蛋白酶菌株发酵制备水豆豉,参照国家标准方法检测水豆豉发酵前后氨基酸态氮、总酸、pH、还原糖及大豆异黄酮的含量,化学法检测总酚及总黄酮的含量,并测定水豆豉提取物的抗氧化能力。最后,观察最优发酵菌株制备的水豆豉提取物对CRPC细胞的抑制作用。结果:高产蛋白酶菌株发酵水豆豉后,其氨基酸态氮、还原糖、大豆异黄酮含量及抗氧化能力指标均比蒸熟黄豆有所提高(P<0.05),其中B19菌株发酵水豆豉的效果最佳。使用B19菌株发酵制备的水豆豉提取物对CRPC细胞有选择性杀伤作用,并能促进其凋亡,同时对前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)、雄激素睾酮(T)和二氢睾酮(DHT)分泌有抑制作用。结论:高产蛋白酶菌株发酵水豆豉后能改变其理化特性,并增强其营养活性。且B19菌株发酵的水豆豉对CRPC细胞有抑制作用。本研究为水豆豉相关保健功能食品的研发提供了数据参考及理论支撑。Abstract: Objective: To study the changes of physicochemical properties in Shuidouchi before and after fermentation, and to preliminarily explore the inhibitory effect of its extracts on castration-resistant prostate cancer cells (CRPC). Methods: Shuidouchi was fermented using three high-yielding protease strains. With reference to the national standard methods, contents ofamino nitrogen, total acid, pH, reducing sugar and soybean isoflavones in Shuidouchi before and after fermentation were tested, and total phenol and flavonoids were examined by chemical method. And the antioxidant capacity of Shuidouchi extracts was also determined. Finally, the inhibitory effect of Shuidouchi extracts fermented with the optimal strain was observed. Results: Fermented by high-yielding protease strains, the contents of amino nitrogen, reducing sugar, isoflavone and antioxidant capacity of soybean were all improved compared with steamed soybean, among which B19 strain fermented Shuidouchi had the best effect. And the extract of Shuidouchi fermented by B19 strain could selectively kill CRPC cells and promote their apoptosis, and inhibit the secretion of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), androgen (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Conclusion: Fermentation by high-yielding protease strains of Shuidouchi can change the physicochemical properties, and enhance its nutritional activities. Moreover, the extract of Shuidouchi fermented with B19 strain has an inhibitory effect on CRPC cells. This study provides data references and theoretical support for the research and development of health functional foods related to Shuidouchi.
-
水豆豉(Shuidouchi, SDC),一种中国传统的发酵豆制品,具有独特的风味与较高的营养价值。在微生物发酵过程中,大豆蛋白被分解成小分子的氨基酸和多肽,以及发酵后的总酸、pH、还原糖等理化特性是评价水豆豉成熟和营养价值的主要参考指标。此外,发酵后的大豆中大豆异黄酮、大豆皂苷、豆豉溶纤酶等生物活性成分的存在,进一步增加了大豆发酵产物的保健功能[1]。迄今为止,我国水豆豉的生产多以自然发酵为主[2],因而发酵微生物种类不受人为控制,从而无法保证市售水豆豉的营养价值和品质,存在一定的食用安全隐患。因此,通过单菌发酵水豆豉,并研究其发酵后的生物活性物质、理化特性、抗氧化能力,对保障并提高水豆豉食用的安全性尤为重要,且目前对单菌发酵水豆豉类似的相关研究鲜有报道。
已有研究证实发酵大豆的主要活性成分是大豆异黄酮[3],具有抗自由基、抗氧化、抗溶血、抗肿瘤等生物活性,其抗肿瘤活性受到国内外学者的广泛关注,主要表现在抗乳腺癌、结直肠癌、前列腺癌等方面[4-6]。前列腺癌是一类雄激素依赖性肿瘤,目前雄激素剥夺治疗是一线治疗方法,但只在前列腺癌早期有效,大多数患者在治疗14~30个月后,肿瘤局部复发,同时对内分泌治疗产生抵抗,进而便进入“去势抵抗”阶段,发展成为去势抵抗前列腺癌(castration-resistant prostate cancer, CRPC)[7-8],且CRPC患者的生存期通常小于24个月。目前,在前列腺癌的治疗中除了雄激素剥夺疗法,还主要有化疗和放射治疗。当疾病发展成为CRPC后,这些方法都存在起效慢、副作用大等缺点,因此,寻找安全有效的抗CRPC策略成为亟待解决的公共卫生问题。国内外学者在这方面不断探索,特别是近年来有研究提示[9-10],膳食中摄入大豆异黄酮能够降低罹患前列腺癌的风险,并且流行病学研究也证实[11],亚洲人群前列腺癌的低发生率与膳食中豆类食品或豆制品的较高摄入量相关。生活方式中膳食的调节作用越来越引起人们的关注,所以,通过食疗的方式预防并延缓CRPC发生与发展具有重要的应用价值。同时,寻找一种富含大豆异黄酮的食品也成为研究CRPC的热点。水豆豉,作为富含大豆异黄酮的发酵豆制品,是否能抑制前列腺癌的发生与发展,目前还未见报道。
因此,本研究采用从市售水豆豉中筛选出的3株高产蛋白酶菌株发酵黄豆,测定发酵前后氨基酸态氮、总酸、pH、还原糖含量变化,比较6种大豆异黄酮、总酚、总黄酮含量和抗氧化能力的差异,并初步探讨水豆豉提取物对人去势抵抗前列腺癌细胞Vcap、22RV1的抑制作用。一方面,为水豆豉的保健功能价值评价提供了一定的实验数据;另一方面,为水豆豉相关健康产品的研发、以及深入探讨水豆豉抗前列腺癌可能的分子机制提供实验依据和理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
实验菌株和细胞株 选择从市售水豆豉中筛选出的3株高产蛋白酶菌株,编号为B19、B20、B61,经鉴定,B19和B20菌株为枯草芽孢杆菌,B61菌株为贝莱斯芽孢杆菌[12-13];人去势抵抗前列腺癌细胞(Vcap) 中国科学院上海细胞库;人正常前列腺上皮细胞(RWPE-1)和人去势抵抗前列腺癌细胞(22RV1) 重庆医科大学生命科学院感染实验室赠送;总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(ABTS法、FRAP法) 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;DPPH、Hoechst染色试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;人特异性抗原(PSA)、人睾酮(T)、人二氢睾酮(DHT)ELISA检测试剂盒 武汉伊莱瑞特生物科技股份有限公司
6种大豆异黄酮标准品(大豆苷、染料木苷、黄豆黄苷、大豆黄素、染料木素、黄豆黄素) 成都德思特生物科技有限公司;绿原酸标准品、芦丁标准品 大连美仑生物技术有限公司;UltiMate3000 HPLC仪(色谱柱RPC18柱:柱长250 nm,柱内径4.6 mm,柱填料粒径5 μm) 美国戴安公司;multiskan GO 1510全波长酶标仪 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;ECLIPSE Ti荧光倒置显微镜 日本尼康公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 水豆豉的制备
水豆豉的制备如流程图1所示,具体操作要点如下。
挑选:选择完整、均匀大小的黄豆,除去腐烂、发霉的黄豆和其他杂质。
浸泡:称取30 g黄豆于250 mL锥形瓶中,加入90 mL蒸馏水后浸泡12 h。沥干水后称量,并记录黄豆湿重重量。
蒸煮:将沥干后的黄豆置于高压蒸汽灭菌锅内121 ℃高压30 min。
接种菌液:蒸熟黄豆待自然冷却后接种B19、B20、B61菌株菌液,接菌量为3.00%。
恒温发酵:接种菌液摇匀后置于35 ℃恒温培养箱中培养,发酵时间为4 d,将其他条件相同,不加入菌液发酵的黄豆(蒸熟黄豆)作为对照组。
1.2.2 理化特性的测定
氨基酸态氮、总酸、pH、还原糖的测定方法分别参照国家标准《GB 5009.235-2016 食品中氨基酸态氮的测定》[14]、《GB 12456-2008 食品中总酸的测定》[15]、《GB 5009.237-2016 食品pH的测定》[16]、《GB 5009.7-2016 食品中还原糖的测定》[17]。
1.2.3 大豆异黄酮的测定
参照国家标准GB/T 26625-2011《粮油检验大豆异黄酮含量测定高效液相色谱法》进行测定[18]。检测指标包括大豆苷、染料木苷、黄豆黄苷、大豆黄素、染料木素、黄豆黄素6种大豆异黄酮类物质。
1.2.4 总酚、总黄酮及抗氧化能力的测定
1.2.4.1 水豆豉提取物中总酚含量的测定
参照HE等[19]的实验方法,用蒸馏水将绿原酸标准品配制成1 mg/mL的储备液,再将其稀释成0.00~0.20 mg/mL标准溶液,将不同浓度的绿原酸标准溶液和提取物溶液混合,依次经福林酚试剂、20%碳酸钠溶液处理后于760 nm处测定吸光度值,以标准品绿原酸浓度为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,制作标准曲线计算水豆豉提取物中总酚含量。
1.2.4.2 水豆豉提取物中总黄酮含量的测定
参照劳佳丽等[20]的实验方法,用70%乙醇将芦丁标准品配制1 mg/mL的储备液,再将其稀释成0~200 μg/mL芦丁标准溶液,以不同浓度的芦丁标准溶液和提取物溶液混合,依次经5%亚硝酸钠溶液、10%硝酸铝溶液、4%氢氧化钠溶液处理后于510 nm处测定吸光度值,以芦丁标准品浓度为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,制作标准曲线计算水豆豉提取物中总黄酮含量。
1.2.4.3 抗氧化能力的测定
参照ERCAN等[21]的实验方法,用蒸馏水将10 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液稀释至0~2.0 mmol/L,取不同浓度标准系列溶液及提取物溶液经DPPH 乙醇溶液处理后,混匀后避光放置30 min,于517 nm处测定吸光度值;ABTS自由基阳离子清除实验按照试剂盒操作说明进行测定,以Trolox标准品浓度为横坐标,清除率为纵坐标,制作标准曲线计算水豆豉提取物清除DPPH和ABTS自由基的能力;FRAP法总抗氧化能力测定实验按照试剂盒操作说明进行测定,以FeSO4·H2O标准品浓度为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,制作标准曲线测定总抗氧化能力。
1.2.5 水豆豉提取物对CRPC细胞的抑制作用
1.2.5.1 水豆豉提取物制备
在本课题组前期确定的水豆豉纯种发酵的最优条件下[22],即采用B19菌株发酵、发酵温度40 °C、发酵时间4 d、接菌量3.00%。称取最优条件下发酵的黄豆发酵物,置于超声波清洗器中60 ℃提取30 min,重复2次提取,合并提取液,用布氏漏斗抽滤后,浓缩蒸发溶解后,得到1 g/mL(以提取物净重计)的黄豆发酵提取物,过0.22 μm滤膜,分装后于−80 ℃保存。
1.2.5.2 细胞培养
DMEM完全培养液(含5%胎牛血清、1%青、链霉素)用于培养Vcap细胞、RPMI-1640培养液(含5%胎牛血清、1%青、链霉素)用于培养RWPE-1和22RV1细胞,置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱内培养。
1.2.5.3 水豆豉提取物作用浓度及时间筛选
对数生长期的Vcap、22RV1及RWPE-1细胞制成细胞悬液,将细胞数调节至5×104个/mL后接种于96孔板,置于37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养12 h。水豆豉提取物设置为0.125、0.25、0.5、1、2、4、8、16、32、64 mg/mL系列浓度,同时设置空白组(只含完全培养基)和对照组(只含细胞和完全培养基),于37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养12、24、48 h。CCK8法测定细胞存活率,细胞存活率(%)=(A实验组−A空白组)/(A对照组−A空白组)×100,根据结果筛选出对正常细胞RWPE-1无明显毒性的水豆豉提取物作用浓度和时间。
1.2.5.4 Hoechst染色观察CRPC细胞形态
根据筛选出水豆豉提取物的有效浓度和作用时间,对干预后的Vcap、22RV1细胞进行Hoechst染色,置于倒置荧光显微镜下观察细胞凋亡情况。
1.2.5.5 ELISA检测培养基中PSA、DHT及T的含量
对PSA、T及DHT含量的检测,参照PSA、DHT及T ELISA检测试剂盒操作说明书进行。
1.3 数据分析
组间对比采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用SNKq检验,均采用双侧检验,当P<0.05时,差异具有统计学意义,所有数值均由均数±标准差(Mean±SD)表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 水豆豉发酵前后理化特性与活性成分的变化
2.1.1 理化特性分析
样品中氨基酸态氮、总酸、pH、还原糖的测定含量如表1所示。B19、B20、B61号菌株发酵的水豆豉中氨基酸态氮、总酸、还原糖含量均高于蒸熟黄豆,其中B19号菌株发酵的水豆豉中氨基酸态氮、还原糖含量最高。B19菌株发酵水豆豉的氨基酸态氮含量最高(7.76 g/kg),高于同属细菌发酵的日本纳豆中平均氨基酸态氮含量(6.0 g/kg)[23],但低于曲霉发酵的浏阳豆豉中氨基酸态氮(13.7 g/kg)[24],这可能与发酵选用菌种及其产蛋白酶特性有关[25]。样品均为弱酸性或中性,其pH大小差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),本研究发酵品总酸的含量均低于别的产品,可能由发酵不完全导致。
表 1 样品中理化成分的检测结果Table 1. Test results of physicochemical components in samples2.1.2 大豆异黄酮变化分析
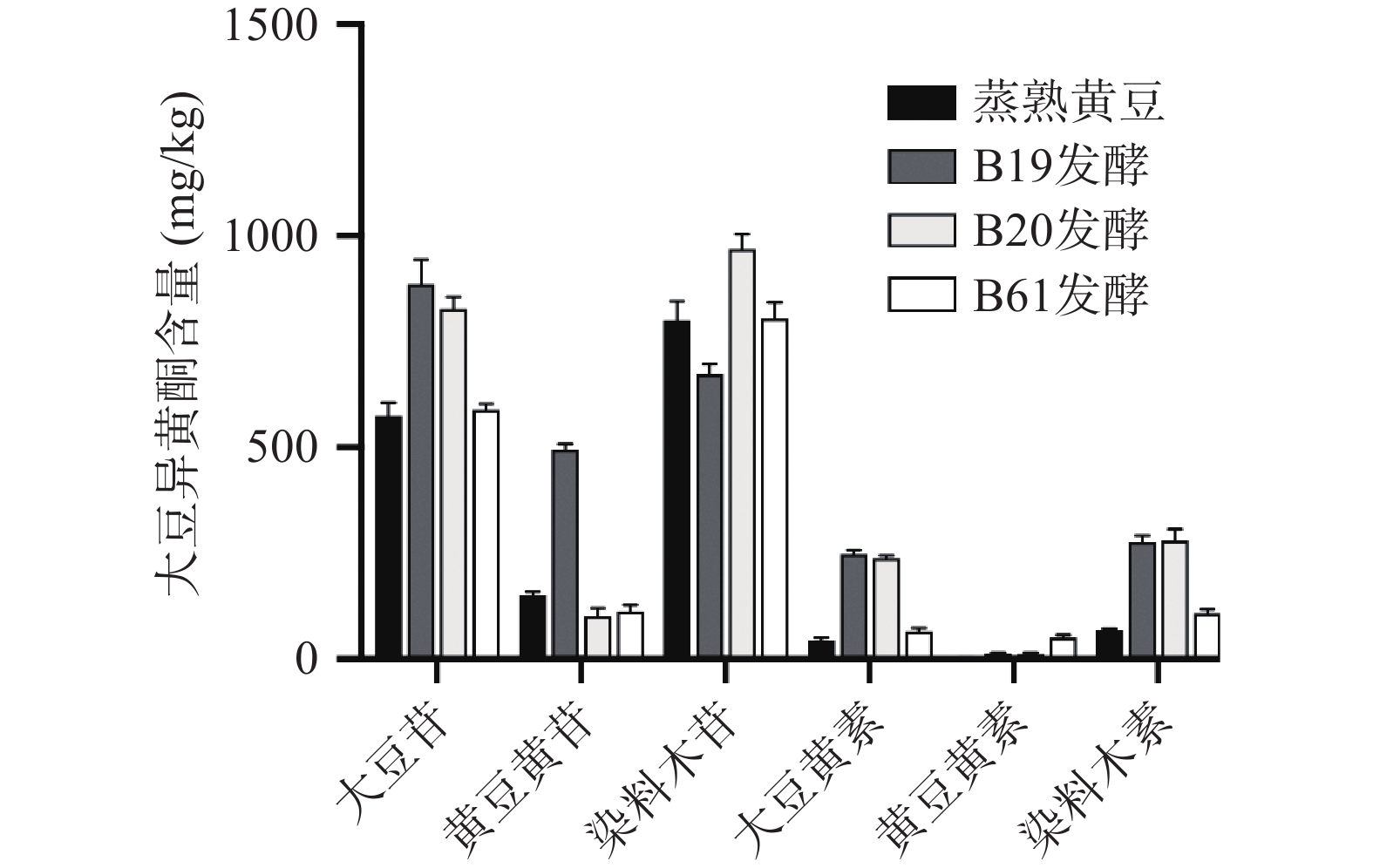
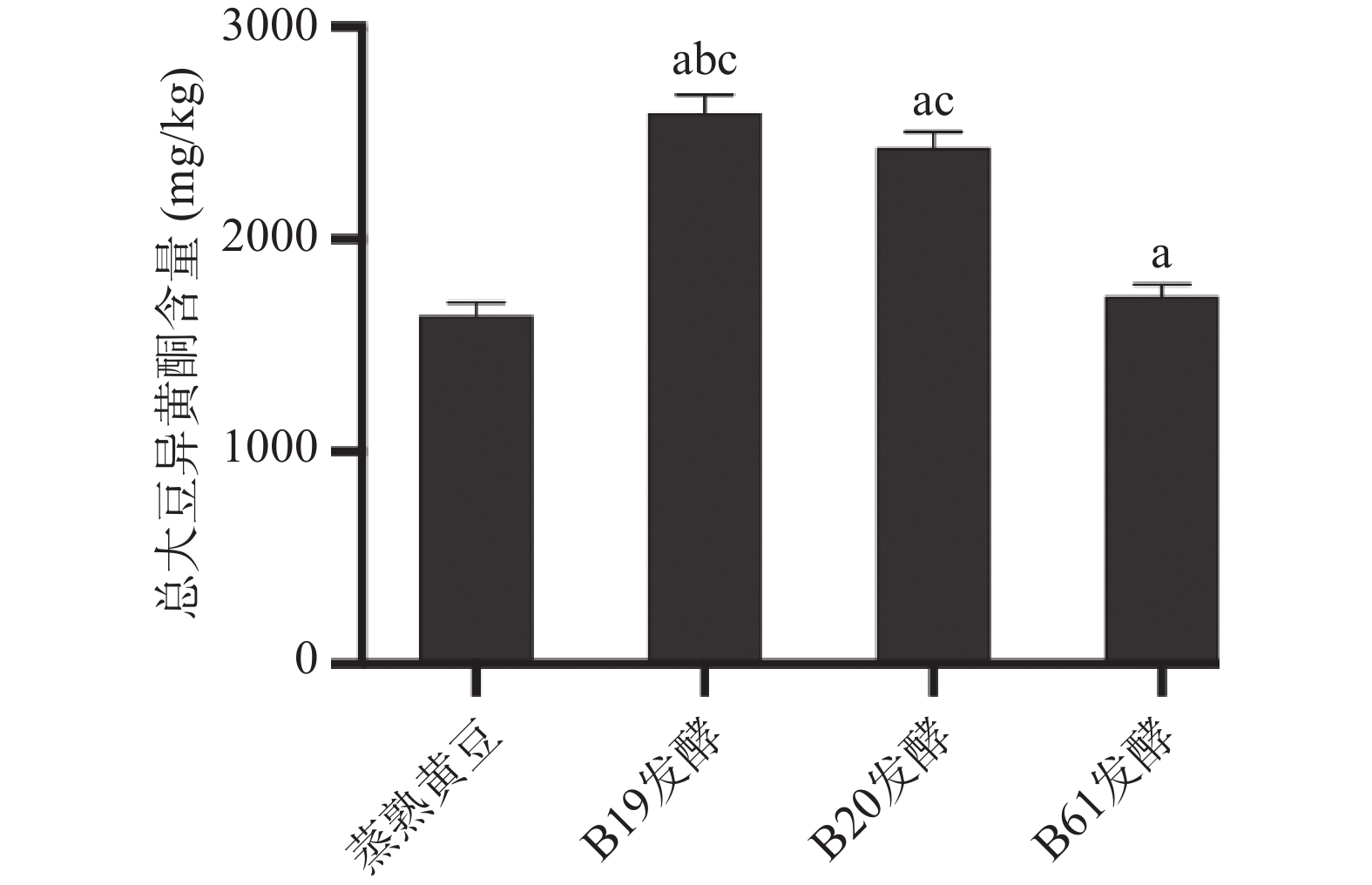
根据国标方法测定水豆豉中大豆异黄酮含量,6种大豆异黄酮色谱峰形及分离效果较好,如图2所示,方法的灵敏度和特异度均满足实验要求,加标回收实验结果显示回收率均在(100%±10%)之间。样品中6种大豆异黄酮均有检出,含量如图3所示。总大豆异黄酮的比较如图4所示,B19、B20、B61号菌株发酵的水豆豉中总大豆异黄酮均高于蒸熟黄豆,三株菌中,B19号菌株发酵的水豆豉中总大豆异黄酮含量最高。发酵水豆豉中总大豆异黄酮总含量均>1000 mg/kg,高于其他豆类食品(嫩豆腐、腐乳等)(100~600 mg/kg)[26]。但值得注意的是,与其他研究报道的发酵豆豉如永川豆豉、浏阳豆豉不同[27],这些豆豉在发酵过程中其总大豆异黄酮含量呈下降趋势,提示发酵菌种和加工工艺等因素对豆豉的营养活性成分有重要的影响[28]。
2.1.3 总酚、总黄酮含量分析
不同菌株发酵水豆豉总酚、总黄酮测定实验结果见表2。B19、B20、B61号菌株发酵后总黄酮含量均高于蒸熟黄豆,三株菌中B19、B61菌株发酵后总黄酮含量高于B20号;总酚含量测定显示,B19、B61号菌株发酵后总酚均高于蒸熟黄豆,其中B19号菌株发酵后总酚含量最高。
表 2 不同菌株发酵水豆豉的总酚、总黄酮含量结果Table 2. Experimental results of the contents of total phenols and flavonoids in SDC fermented by different strains样品 总黄酮
(mg RT/g)总酚
(mg CAE/g)蒸熟黄豆 45.23±1.33 133.10±3.72 B19发酵 148.34±5.34ab 168.54±4.13abc B20发酵 107.40±3.81ac 112.94±4.56c B61发酵 146.73±4.48a 155.70±6.45a 2.1.4 抗氧化能力的测定
FRAP实验,DPPH、ABTS自由基清除实验结果如表3所示。B19、B61号菌株发酵的水豆豉抗氧化能力均强于蒸熟黄豆;而B20号菌株发酵后水豆豉DPPH自由基清除能力与蒸熟黄豆相比无统计学差异。发酵后总酚、总黄酮含量及抗氧化能力明显提高,而抗氧化能力的提高可能与发酵后总酚含量增加,或是与增加的游离氨基酸和多肽相关[29]。后者提示发酵过程中游离氨基酸和多肽的增加或对豆制品抗氧化活性提升具有重要意义。但在不同豆制品理化特性与活性成分的比较中,大豆种类、发酵菌种、加工工艺等因素的影响是多样性的,需综合评价。
表 3 不同菌株发酵水豆豉抗氧化能力实验结果Table 3. Experimental results of antioxidant capacity of SDC fermented by different strains样品 FRAP
(μmol Fe(II)/g)DPPH
(μmol Tolox/g)ABTS
(μmol Trolox/g)蒸熟黄豆 219.98±6.52 91.15±3.15 94.35±2.08 B19发酵 383.66±12.18abc 122.57±2.14ab 118.11±5.16a B20发酵 286.40±7.25ac 106.74±5.21c 120.84±7.11a B61发酵 252.31±3.17a 125.68±6.04a 115.48±4.26a 2.2 B19菌株发酵水豆豉提取物对CRPC细胞的抑制作用
2.2.1 提取物中大豆异黄酮的测定
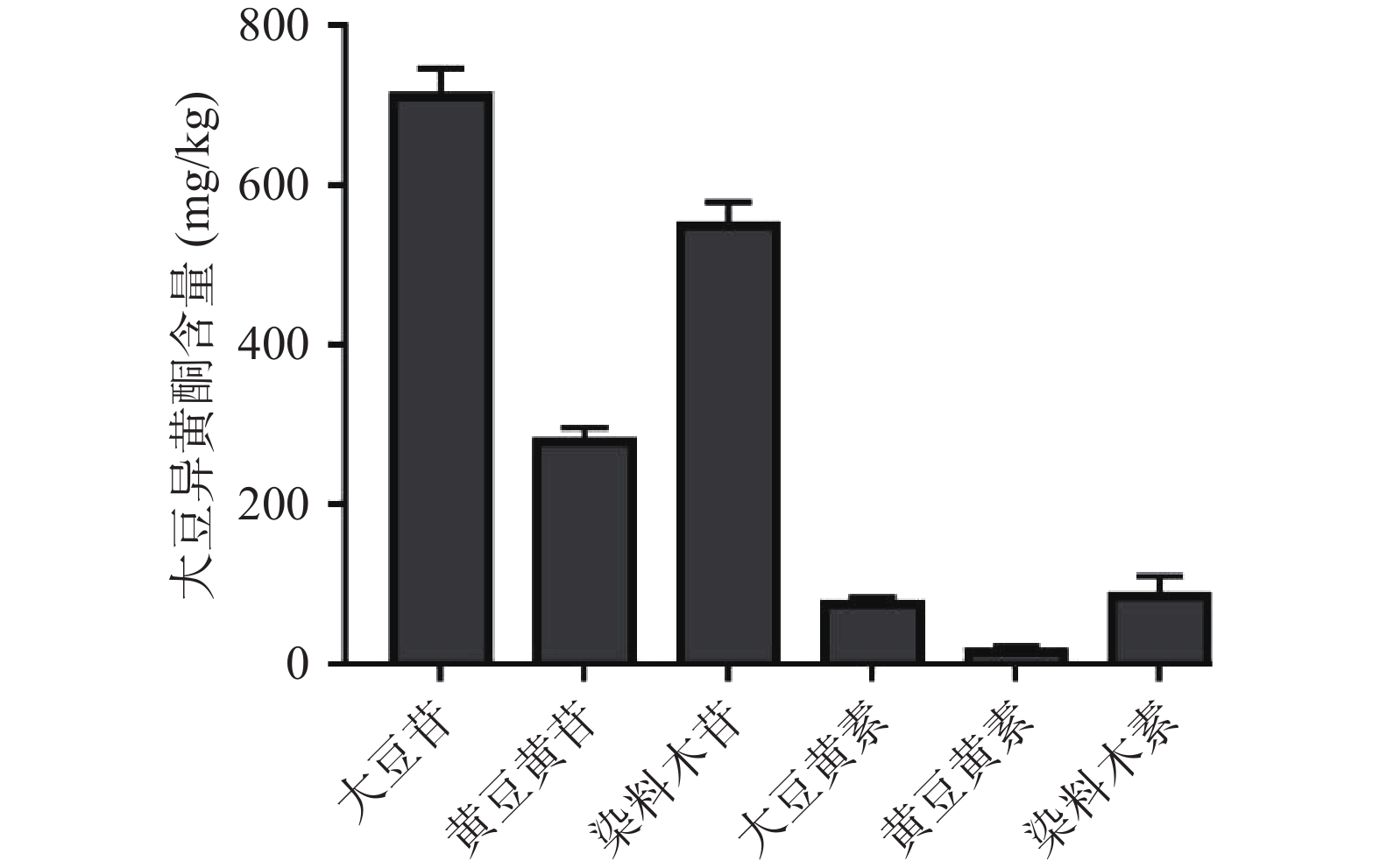
水豆豉提取物中大豆异黄酮的含量如图5所示,6种大豆异黄酮均有检出,总大豆异黄酮含量为(1713.25±75.38) mg/kg(以黄豆干重计)。其中,在糖苷型中,大豆苷含量最高,为(711.15±35.21) mg/kg;在苷元型中,染料木素含量最高,为(86.17±25.17) mg/kg。
2.2.2 提取物作用浓度及时间筛选
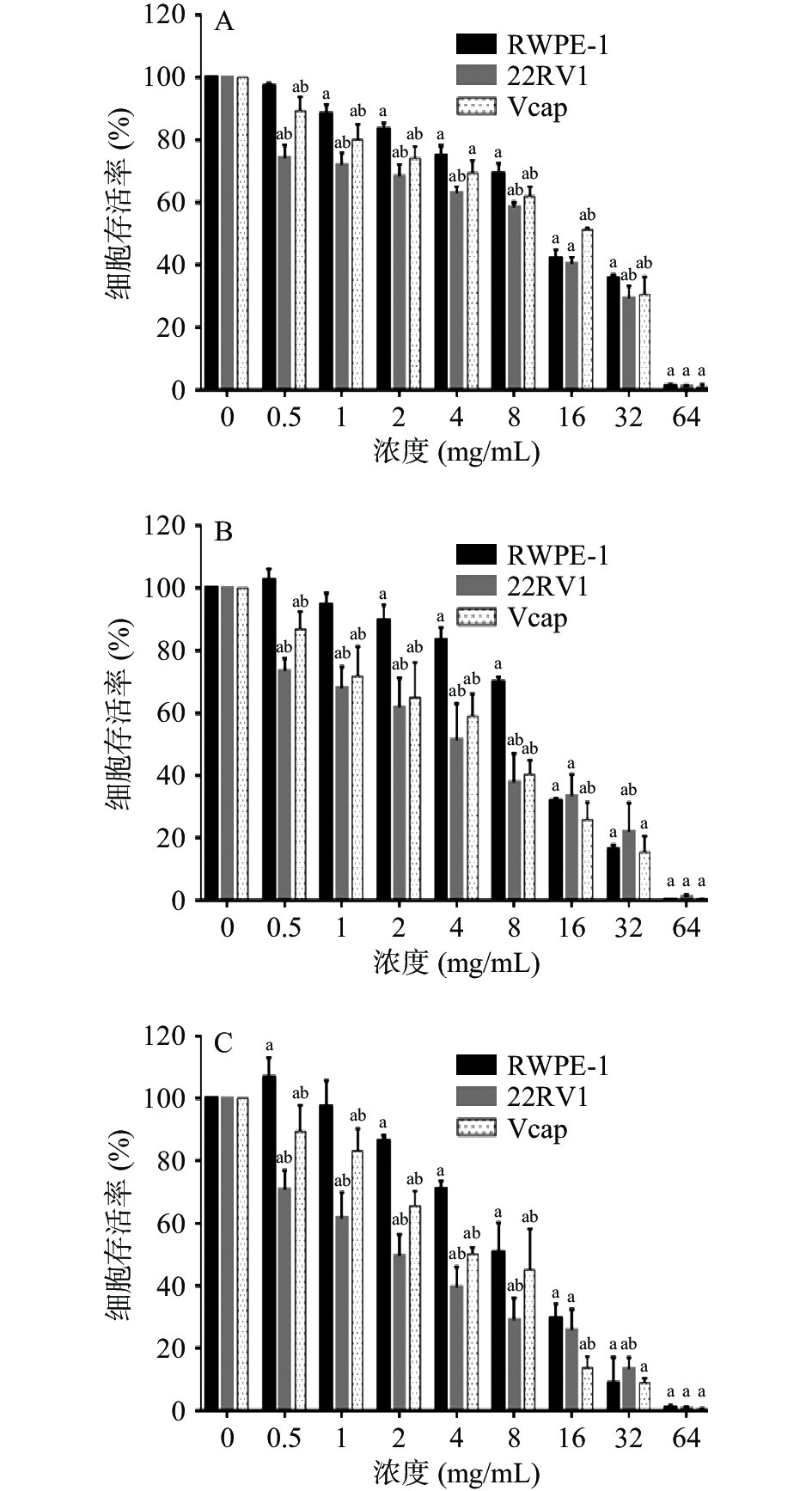
作用时间为12、24、48 h时,RWPE-1、22RV1和Vcap细胞的存活率均随提取物浓度增大而降低,呈现剂量-反应关系。在不同作用时间、浓度下,细胞存活率:RWPE-1>Vcap>22RV1细胞。当作用浓度为64 mg/mL时,三种细胞存活率均低于2%。22RV1细胞随着作用时间的增加,细胞存活率逐渐降低,呈现出时间-反应关系;而RWPE-1和Vcap细胞在作用浓度大于2 mg/mL时呈时间-反应关系,在作用浓度小于2 mg/mL时,细胞存活率反而随作用时间的增加而有上升趋势。因此,为保证水豆豉提取物对前列腺正常细胞RWPE-1无明显损伤作用,又能保证对前列腺癌细胞22RV1和Vcap细胞的杀伤作用,故选择水豆豉提取物浓度为2、4、8 mg/mL,作用时间为24 h进行后续实验(图6)。
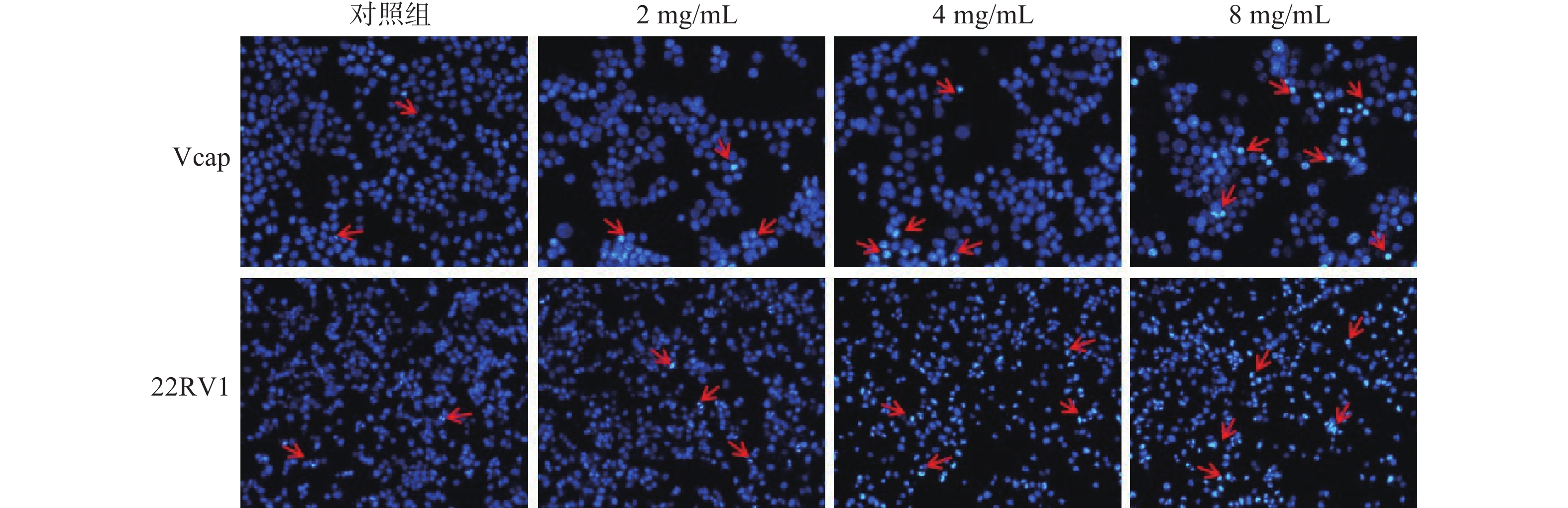
2.2.3 提取物对CRPC细胞形态的影响
经筛选出的2、4、8 mg/mL水豆豉提取物干预22RV1和Vcap细胞24 h后,Hoechst染色对CRPC细胞进行凋亡检测,于倒置荧光显微镜下观察实验结果,如图7所示。随着作用浓度的增加,凋亡细胞明显增多,且凋亡细胞的细胞核呈致密浓染或呈块状致密浓染,并可见凋亡小体。提示其对22RV1、Vcap细胞具有选择性杀伤作用,并能促进细胞凋亡。细胞的增殖是通过周期来实现的,而调控细胞周期主要依靠细胞周期蛋白和周期素依赖性激酶,其过表达导致肿瘤的发生。李飞等[30]的研究表明,染料木黄酮能抑制周期蛋白的表达,且能阻滞CRPC细胞于G2/M期,从而抑制细胞进行分裂,最终导致细胞凋亡。而细胞凋亡可能是抑制细胞增殖的原因之一,细胞凋亡在抑制肿瘤发展中起重要作用。提示大豆异黄酮可能是水豆豉提取物中促进细胞凋亡的关键活性成分。
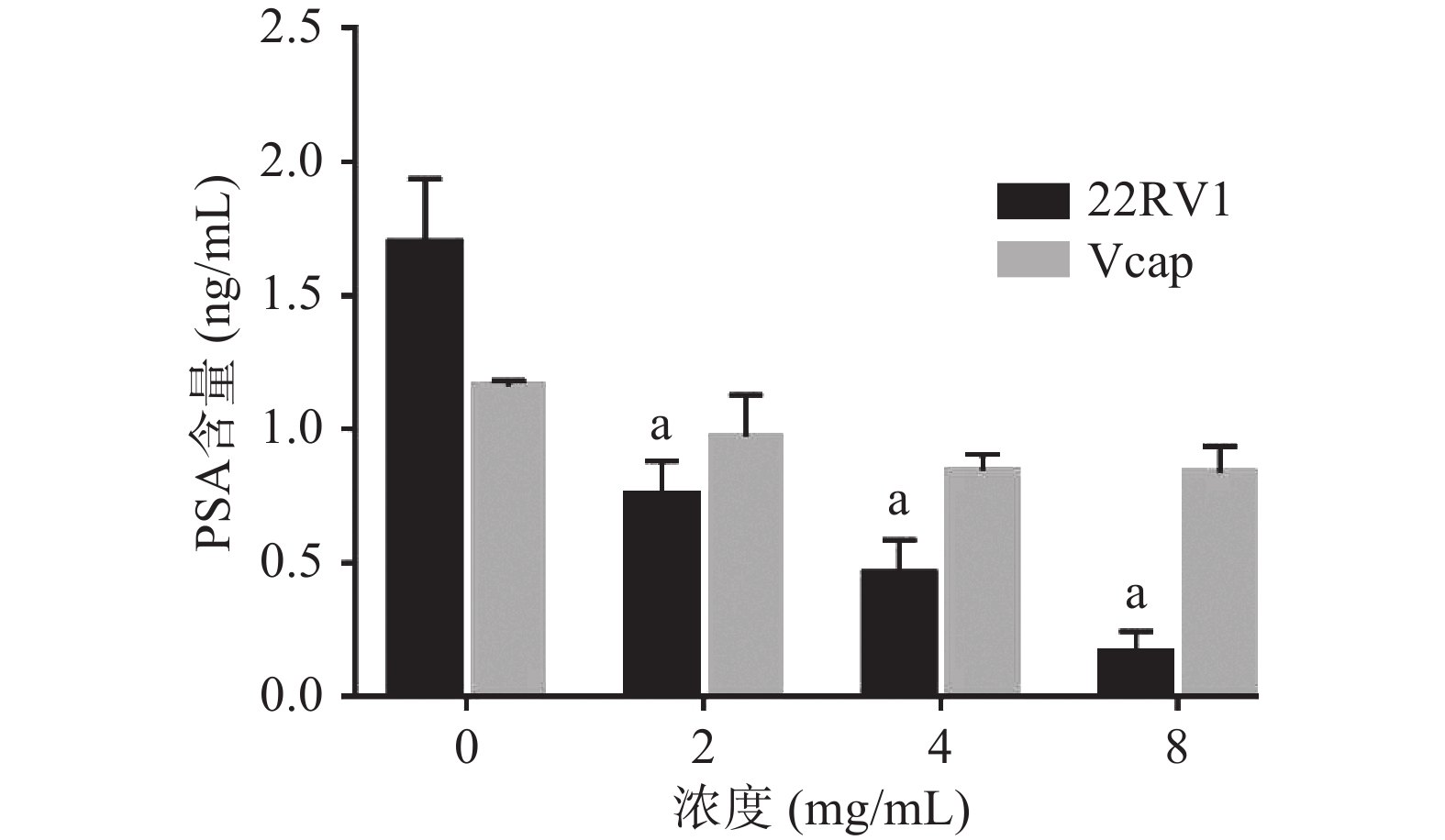
2.2.4 提取物对CRPC细胞中PSA含量的影响
与对照组相比,各剂量组均能抑制22RV1细胞中PSA的分泌,但水豆豉提取物对Vcap细胞中PSA的分泌没有抑制作用。PSA作为前列腺癌特异性标志物,其含量与疾病的发展息息相关,可及时反映前列腺癌患者的治疗情况。在本研究中,水豆豉取物能够抑制22RV1细胞PSA的分泌, CRPC细胞拥有雄激素合成所需的酶及调节蛋白,可以通过从头合成途径将胆固醇合成雄激素,从而激活 AR信号通路,但该提取物是否是通过作用于AR信号通路进而抑制其分泌还需进一步研究(图8)。
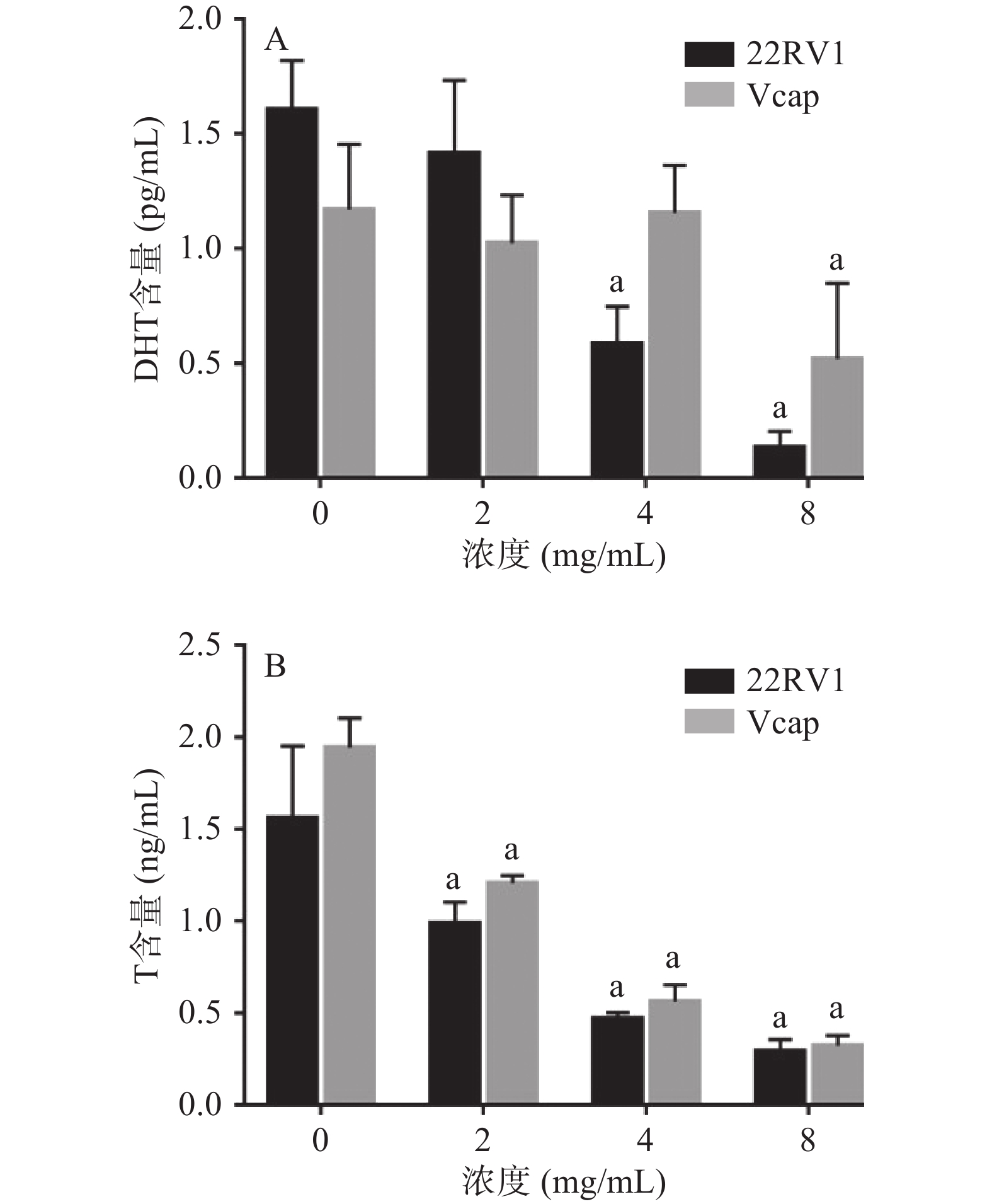
2.2.5 提取物对CRPC细胞中DHT及T含量的影响
提取物浓度≥4 mg/mL时抑制22RV1细胞DHT的合成,提取物浓度≥8 mg/mL时抑制Vcap细胞DHT的合成。各剂量组的提取物均能抑制22RV1和Vcap细胞T的合成。DHT是前腺癌细胞通过从头合成途径合成的最终产物,水豆豉提取物能下调CRPC细胞DHT的表达水平,这提示水豆豉提取物能够有效的抑制CRPC细胞雄激素的合成,但其抑制机制还需进一步研究(图9)。
3. 结论
比较3株高产蛋白酶菌株单菌发酵水豆豉后理化特性、活性成分及抗氧还能力的改变,发现均有不同程度地改变和提升,并筛选出一株具有较好理化特性及抗氧化活性的B19菌株,为进一步研发水豆豉健康相关产品提供理论依据;以B19菌株在前期确定的最佳发酵条件下发酵制备水豆豉,发现其水提物对CRPC细胞具有选择性杀伤作用,并能促进其凋亡,同时对前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)、雄激素睾酮(T)和二氢睾酮(DHT)分泌有抑制作用,为后续探讨水豆豉对前列腺癌作用的相关机制提供思路和数据参考,水豆豉提取物抑制CRPC细胞的潜在机制值得进一步深入研究。
-
表 1 样品中理化成分的检测结果
Table 1 Test results of physicochemical components in samples
表 2 不同菌株发酵水豆豉的总酚、总黄酮含量结果
Table 2 Experimental results of the contents of total phenols and flavonoids in SDC fermented by different strains
样品 总黄酮
(mg RT/g)总酚
(mg CAE/g)蒸熟黄豆 45.23±1.33 133.10±3.72 B19发酵 148.34±5.34ab 168.54±4.13abc B20发酵 107.40±3.81ac 112.94±4.56c B61发酵 146.73±4.48a 155.70±6.45a 表 3 不同菌株发酵水豆豉抗氧化能力实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results of antioxidant capacity of SDC fermented by different strains
样品 FRAP
(μmol Fe(II)/g)DPPH
(μmol Tolox/g)ABTS
(μmol Trolox/g)蒸熟黄豆 219.98±6.52 91.15±3.15 94.35±2.08 B19发酵 383.66±12.18abc 122.57±2.14ab 118.11±5.16a B20发酵 286.40±7.25ac 106.74±5.21c 120.84±7.11a B61发酵 252.31±3.17a 125.68±6.04a 115.48±4.26a -
[1] 吴易武, 吴小刚, 蒋先志, 等. 发酵大豆制品的药理作用研究进展[J]. 广东药科大学学报,2020,36(5):743−746. [WU Y W, WU X G, JIANG X Z, et al. Advances in pharmacological effects of fermented soybean products[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University,2020,36(5):743−746. [2] 黄晓润, 郭娅, 黎忠杰, 等. 自然发酵型水豆豉细菌菌群的动态监测研究[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(6):103−106,110. [HUANG X R, GUO Y, LI Z J, et al. Natural fermentation type dynamic monitoring of natto bacteria flora research[J]. Chinese Seasoning,2020,45(6):103−106,110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.06.022 [3] PIAO Y Z, EUN J B. Physicochemical characteristics and isoflavones content during manufacture of short-time fermented soybean product (cheonggukjang)[J]. J Food Sci Technol,2020,57(6):2190−2197. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04255-2
[4] NACHVAK S M, MORADI S, ANJOM-SHOAE J, et al. Soy, soy isoflavones, and protein intake in relation to mortality from all causes, cancers, and cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. J Acad Nutr Diet,2019,119(9):1483−1500. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2019.04.011
[5] TAKAGI A, KANO M, KAGA C. Possibility of breast cancer prevention: Use of soy isoflavones and fermented soy beverage produced using probiotics[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2015,16(5):10907−10920.
[6] PABICH M, MATERSKA M. Biological effect of soy isoflavones in the prevention of civilization diseases[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(7):1660. doi: 10.3390/nu11071660
[7] ADASHEK J J, JAIN R K, ZHANG J S. Clinical development of PARP inhibitors in treating metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Cells,2019,8(8):860. doi: 10.3390/cells8080860
[8] CHOWDHURY S, BJARTELL A, LUMEN N. Real-world outcomes in first-line treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: The prostate cancer registry[J]. Targeted Oncology,2020,15(3):301−315. doi: 10.1007/s11523-020-00720-2
[9] APPLEGATE C C, ROWLES J L, RANARD K M, et al. Soy consumption and the risk of prostate cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutrients,2018,10(1):40. doi: 10.3390/nu10010040
[10] SAWADA N, IWASAKI M, YAMAJI T, et al. Soy and isoflavone consumption and subsequent risk of prostate cancer mortality: The japan public health center-based prospective study[J]. International Journal of Epidemiology,2020,49(5):1553−1561. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyaa177
[11] MCTIERNAN A, IRWIN M, VONGRUENIGEN V. Weight, physical activity, diet, and prognosis in breast and gynecologic cancers[J]. J Clin Oncol,2010,28(26):4074−4080. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.27.9752
[12] 庞钰鑫, 刘雪薇, 黄嘉玲, 等. 市售川产水豆豉分离株中高产蛋白酶与β-葡萄糖苷酶菌株的菌属鉴定与产酶能力评价[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2019,50(5):714−719. [PANG Y X, LIU X W, HUANG J L, et al. Identification of strains with high yield of protease and β-glucosidase in commercial fermented soya bean isolates from Sichuan[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Science),2019,50(5):714−719. [13] 董科, 陈宇航, 沈丹芸, 等. 水豆豉中高产豆豉纤溶酶的菌株筛选、鉴定及生长性能研究[J]. 中国调味品,2019,44(9):85−89. [DONG K, CHEN Y H, SHEN D Y, et al. Isolation, identification and growth performance of high yield tempeh fibrinolytic enzyme from tempeh[J]. China Condiments,2019,44(9):85−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2019.09.017 [14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB5009.235-2016食品中氨基酸态氮的测定[S]. 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB5009.235-2016 Determination of amino acid nitrogen in food[S]. 2016.
[15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB12456-2008食品中总酸的测定[S]. 2008. National Health and Family Planning Commission of thePeople's Republic of China. GB 12456-2008 Determination of total acid in food[S]. 2008.
[16] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.237-2016食品pH的测定[S]. 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB5009.237-2016 Determination of pH of food[S]. 2016.
[17] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB5009.7-2016食品中还原糖的测定[S]. 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB5009.7-2016Determination of reducing sugar in food[S]. 2016
[18] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB/T26625-2011 粮油检验大豆异黄酮含量测定高效液相色谱法[S]. 2011. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. Determination of isoflavone content in soybean by high performance liquid chromatography[S]. 2011.
[19] HE F, CHEN J, DONG K, et al. Multi-technical analysis on the antioxidative capacity and total phenol contents of 94 traditional Chinese dietary medicinal herbs[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2018,6(6):1358−1369.
[20] 劳佳丽, 高丽玉, 陈丽珍, 等. 冰糖草茎叶总黄酮测定及其清除亚硝酸盐的作用[J]. 当代化工,2019,48(10):2202−2205. [LAO J L, GAO L Y, CHEN L Z, et al. Determination of total flavonoids in stems and leaves of Schistodontgrass and its scavenging effect on nitrite[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry,2019,48(10):2202−2205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.10.009 [21] ERCAN B, ABDULMELIK A, ÖMER K, et al. Chemical constituent and radical scavenging antioxidant activity of Anthemis kotschyana Boiss[J]. Natural product research, 2020: PP 1−4.
[22] 沈丹芸, 董科, 范紫玮, 等. 响应面法优化水豆豉纯种发酵产大豆异黄酮的条件[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(6):31−36. [SHEN D Y, DONG K, FAN Z W, et al. Optimization of soybean isoflavone production by pure fermentation of tempeh by response surface methodology[J]. China Condiments,2020,45(6):31−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.06.008 [23] 齐凤元, 毕海燕, 邵悦, 等. 花生纳豆与传统纳豆营养成分含量对比[J]. 中国调味品,2017,42(5):99−102. [QI F Y, BI H Y, SHAO Y, et al. Comparison of nutrient content of peanut natto and traditional natto[J]. China Condiment,2017,42(5):99−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2017.05.021 [24] 谢靓, 蒋立文, 龚彩姣, 等. 浏阳豆豉生产过程中理化性质的变化研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(8):225−32,122. [XIE L, JIANG L W, GONG C J, et al. Study on the change of physical and chemical properties during the production of Liuyang black bean[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(8):225−32,122. [25] 李婷婷, 程江华, 张焕焕, 等. 现代传统发酵豆制品中微生物资源的挖掘与应用[J]. 农产品加工,2021(6):63−69. [LI T, CHENG J, ZHANG H H, et al. Mining and application of microbial resources in modern traditional fermented soybean products[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2021(6):63−69. [26] 高丽英, 聂少平, 邱奇琦, 等. 豆类食品中4种大豆异黄酮的含量分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2011,11(4):211−217. [GAO L Y, NIE S P, QIU Q Q, et al. Analysis of four kinds of soybean isoflavones in legumes[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2011,11(4):211−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2011.04.031 [27] FAN J, ZHANG Y, CHANG X, et al. Changes in the radical scavenging activity of bacterial-type douchi, a traditional fermented soybean product, during the primary fermentation process[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2009,73(12):2749−2753. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90361
[28] 陈怡, 刘洋, 蒋立文, 等. 浏阳豆豉发酵过程中抗氧化成分及活性变化研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(19):273−278. [CHEN Y, LIU Y, JIANG L W, et al. Study on the changes of antioxidant components and activity in the fermentation process of Liuyang black bean[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(19):273−278. [29] 索化夷, 骞宇, 卢露, 等. 永川豆豉传统发酵过程中的大豆异黄酮变化[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(8):270−273. [SUO H Y, QIAN Y, LU L, et al. Changes of soybean isoflavones during traditional fermentation of Yongchuan tempeh[J]. Food Science,2012,33(8):270−273. [30] 李飞, 朱彦锋, 陈静瑶, 等. 染料木黄酮对去势抵抗性前列腺癌VCaP细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中华男科学杂志,2016,22(12):1065−1070. [LI F, ZHU Y F, CHEN J Y, et al. Effects of genistein on VCAP cell proliferation in castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Andrology,2016,22(12):1065−1070. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 宋露露,李云飞,刘鑫源,徐睿绮,郑郭芳,秦楠. 阿胶中驴血清白蛋白的提取纯化、功能特性及抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 179-188 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘贵涛,权煜,饶欢,赵丹丹,赵霞,郝建雄,刘学强. 亚麻籽粕蛋白多肽的制备及其抗氧化性. 食品研究与开发. 2024(24): 84-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



