1H-NMR Fingerprint of Hengshan Astragalus membranaceus
-
摘要: 目的:建立恒山黄芪的氢核磁共振指纹图谱,为恒山黄芪的质量控制提供依据。方法:采用超声波复合酶法提取恒山黄芪化学成分;以氘代氯仿为提取溶剂,在25 ℃下采用标准的预饱和脉冲序列压制水峰建立10批不同来源恒山黄芪的氢核磁共振指纹图谱,通过“加标准品定性”实验、数据库比对和相关文献比对进行信号归属,采用相关系数法计算10批不同来源恒山黄芪1H-NMR指纹图谱的相似度,并进行重复性、精密度及稳定性考察,基于SIMCA软件进行主成分分析,进行药材的质量评价。结果:从恒山黄芪药材中检测分析出24种化合物,包括三萜皂苷、异黄酮、氨基酸、有机酸、糖等。10批恒山黄芪的指纹图谱相似度均>0.9,平均为0.975,与蒙古黄芪和甘肃黄芪对比分析,恒山黄芪的异黄酮含量高于两者。PCA结果显示,前三个主成分的累积贡献率为89.8%,与相似度评价结果基本一致。结论:建立的1H-NMR方法具有快速简便的优点,可为恒山黄芪的质量控制及使用提供参考。Abstract: Objective: To establish a hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) fingerprint of Hengshan Astragalus membranaceus, and provide a basis for its quality control. Method: The chemical components were extracted by ultrasonic assisted enzymatic method. Using deuterated chloroform as the extraction solvent, a standard pre-saturated pulse sequence was used to suppress water peaks at 25 ℃ to establish 1H-NMR fingerprints of 10 batches of
A. membranaceus from different sources. The signal attribution was assigned by the qualitative standard addition test, database comparison and related literature comparison. The correlation coefficient method was used to calculate the similarity of 1H-NMR fingerprints, and the repeatability, precision and stability were investigated. Principal component analysis based on SIMCA was used to evaluate the quality of medicinal materials. Results: 24 compounds were detected and analyzed from Hengshan A. membranaceus, including triterpene saponins, isoflavones, amino acids, organic acids, sugars and so on. The similarities of fingerprints were higher than 0.9 with an average of 0.975. Compared with Mongolian Astragalus membranaceus and Gansu Astragalus membranaceus, the content of isoflavones in Hengshan Astragalus membranaceus was higher than both. PCA results showed that the cumulative contribution rate of the first three principal components was 89.8%, which was basically consistent with the similarity evaluation results. Conclusion: The established 1H-NMR method had the advantages of quickness and simplicity, which could provide reference for the quality control of Hengshan A. membranaceus. -
恒山黄芪,为国家地理标志保护产品,主产于山西省大同市浑源县,在广灵县、灵丘县等地也有分布[1-3]。天然药物研究证实,黄芪的主要药效成分为皂苷类、黄酮类、多糖类等,具有改善人体免疫系统,针对治疗心脑血管疾病和肾脏疾病等的作用[4-6]。伴随着恒山黄芪的市场占有率逐年提升,需要有明确的检测方法,判断恒山黄芪的质量差异性。现行的高效液相色谱技术(High Performance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC)在评定中药材的均一性和差异性时具有检测灵敏度较高[7-9]的特点,但由于中药材具有成分复杂、难分离特点,通过HPLC建立的指纹图谱主要侧重于中药材的相似性评价,难以在差异性方面进行评价,因此需要一种兼顾相似性评价和差异性评价同时能快速检测中药材化学成分的方法。核磁共振(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance,NMR)技术具有分析速度快、无偏向性且对样品依赖较少的特点[10-11],适于分析中药材的复杂成分,是对传统方法的改良。而1H-NMR被应用于天然药物差异性和均一性的评价[12-15],是因为相对于高效液相指纹图谱,氢核磁共振具有更高的灵敏性,更佳的分离性[16-17],因而对天然药物中低含量的药用成分可做更详细的定性和定量分析。同时该技术不需要绘制标准曲线,且对样品要求低,可快速检测天然药物中不稳定的化合物,成为了国内外药材评价的研究方法[18-21]。
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)在进行数据处理时,能有效压缩数据,将分散的信息集合到主成分上,主成分是多个初变量按照不同权重合成的新变量,通过数据组合成新变量不仅可以描述数据集内部的结构,同时还可以对数据进行降维处理[22-23]。通过1H-NMR技术测定天然药物的氢核磁共振指纹图谱,分析图谱,可获得多种有机化学成分的信息,同时结合PCA技术,可得到具有统计学意义的综合数据,再使用软件分析数据,得到直观图形,可达到整体分析药物化学成分的目的。
本研究采用超声波复合酶法提取恒山黄芪化学成分,1H-NMR技术测定恒山黄芪的1H-NMR指纹图谱,并进行重复性、精密度及稳定性考察,进而对其化学成分进行主成分评价。目的是通过该研究建立一种简单准确的恒山黄芪化学成分的评价方法。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
10批恒山黄芪 样品的来源见表1,经山西大同大学生命科学学院周凤教授鉴定均为恒山黄芪(Astragalus membranaceus);对比分析选用的甘肃黄芪和蒙古黄芪 均购自于不同产区(见表1);芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、黄芪皂苷 I、II、III 对照品,上海源叶生物科技有限公司(质量分数>98%);芒柄花素、毛蕊异黄酮苷、黄芪甲苷 对照品,成都瑞芬思生物科技有限公司(质量分数>98%);氘代氯仿(CDCl3) 上海吉至生化科技有限公司;纤维素酶(3 U/mg) 和氏璧生物科技有限公司;果胶酶(30 U/mg) 上海蓝季科技发展有限公司;糖化酶(10 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
表 1 恒山黄芪来源和年限Table 1. Source and age of Hengshan Astragalus membranaceus编号 样品采集地 纬度(°) 经度(°) 海拔(m) 药材年限 采样时间 Am-01 山西浑源县官儿乡穆家庄村 39.46 113.66 1623 3年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-02 山西浑源县官儿乡界板沟村 39.48 113.56 1845 5年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-03 山西浑源县大仁庄乡黄土坡村 39.69 113.83 1728 7年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-04 山西浑源县官儿乡官儿村 39.52 113.65 1689 3年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-05 山西浑源县裴村乡小峪沟 39.54 113.58 1910 5年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-06 山西浑源县东坊城乡龙山村 39.68 113.66 1270 5年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-07 山西浑源县千佛岭乡温庄村 39.45 113.75 1782 7年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-08 山西浑源县千佛岭乡宽坪村 39.48 113.77 1768 5年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-09 山西浑源县千佛岭乡泽青岭村 39.44 113.73 1691 10年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-10 山西浑源县青磁窑乡南张庄村 39.60 113.76 1856 3年恒山黄芪 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-01(购买) 内蒙古自治区赤峰(产地) 3年 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-02(购买) 内蒙古自治区乌兰察布(产地) 3年 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-03(购买) 内蒙古自治区包头(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-01(购买) 甘肃省陇西县(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-02(购买) 甘肃省岷县(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-03(购买) 甘肃省渭源县(产地) 3年 2020.8 Avance Ⅲ 500 MHz型核磁共振波谱仪 德国布鲁克公司;THC-2B超声波提取器 济宁天华超声电子仪器有限公司;XFB-2600小型粉碎机 吉首市中诚制药机械厂;RE-52AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;AXTGL16M微量台式冷冻离心机 上海赵迪生物科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 恒山黄芪化学成分的提取
1.2.1.1 酶制剂的制备
准确称取纤维素酶、果胶酶(质量比1:1)共0.625 g,加少量去离子水,溶解后,定容于25 mL容量瓶中,制成25 mg/mL的复合酶制剂,备用。准确称取糖化酶0.625 g,加少量去离子水后定容于25 mL的容量瓶中,制成25 mg/mL的酶制剂,备用。
1.2.1.2 复合酶超声提取
分别称取10个采样地点的干燥粉碎的黄芪10 g于250 mL三角瓶中,加入复合酶制剂的量分别为2 mL复合酶和2 mL糖化酶溶液,加去离子水46 mL,调节pH缓冲体系至5.5,酶解40 min,温度设置60 ℃,搅拌转速80 r/min,酶解完成后,添加50 mL无水甲醇,设置超声条件:超声功率为200 W,时间45 min,设置相同条件,重复提取一次,过滤合并滤液,90 ℃灭活30 s,减压浓缩后,冷冻干燥。
1.2.2 1H-NMR的测定
1.2.2.1 核磁分析样品的制备
取上述10 mg恒山黄芪提取物,加2 mL氘代氯仿,放入容量为5 mL的离心管中,设置离心条件:转速为13000 r/min,时间为10 min,得上清液,将其转至核磁管中,用于恒山黄芪化学成分的1H-NMR分析。
1.2.2.2 1H-NMR测定条件
测定温度为25 ℃,1H-NMR测定条件设置为:频率500 MHz,扫描次数64次,谱宽为12345.7 Hz,傅里叶变换 0.188 Hz,脉冲间隔D1为1.0 s,延迟时间(RD)为1.0 s。手动进行相位、基线以及峰校正。采用 noesyppr1d 脉冲序列压制水峰,内标为TSP。
1.2.3 方法学考察
1.2.3.1 精密度实验
以3年恒山黄芪(编号Am-01)提取液为标准供试品溶液,在设定的1H-NMR条件下测定5次核磁图谱,用MetreNova软件处理图谱,采用下述核磁数据分析方法,计算5组数据之间的相对峰面积积分值间的相关系数,分析仪器精密度。
1.2.3.2 重复性实验
取3年恒山黄芪(编号Am-01)提取液,进行重复性实验,在设定的1H-NMR条件下连续测定核磁图谱,用MetreNova软件处理图谱,采用下述核磁数据分析方法,计算5组数据之间的相对峰面积积分值间的相关系数,分析实验重复性情况。
1.2.3.3 稳定性实验
取3年恒山黄芪(编号Am-01)提取液,进行稳定性实验,温度条件为25 ℃(即室温条件),分别放置0、4、8、12、24 h后,在设定的1H-NMR条件下分别测定核磁图谱,用MetreNova软件处理图谱,采用下述核磁数据分析方法,计算5组数据之间的相对峰面积积分值间的相关系数,分析实验稳定性情况。
1.3 数据处理
1.3.1 核磁数据分析
将基于MestreNova 8.0分析处理得到的核磁指纹图谱,对其进行定标、相位以及基线校正处理,以0.04 ppm为单位对图谱进行分段积分,位置区间为0~8.5 ppm,设置总峰面积为参照物,对其进行归一化处理,得到各化学位移段对应的信号峰面积值,分析处理得到的数据。在Excel软件中分析处理积分得到的数据用于后续分析。
1.3.2 主成分分析
将上述不同来源的恒山黄芪样品的1H-NMR数据导入SIMCA-P 13.0软件进行主成分分析,进一步评价恒山黄芪的化学成分。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 方法学考察
精密度实验中分段积分法计算相关系数结果分别为0.998、0.996、0.995、0.993和0.992,相关系数都大于0.99,证明仪器精密度高。重复性实验中相关系数计算结果分别为0.997、0.994、0.995、0.998和0.996,从5次相关系数都大于0.99,可以看出该提取方法重复性良好。稳定性实验中相关系数计算结果分别为0.994、0.995、0.996、0.992和0.993,从5次相关系数都大于0.99,可以看出在室温条件下24 h内供试品溶液稳定。
2.2 恒山黄芪1H-NMR的典型信号归属
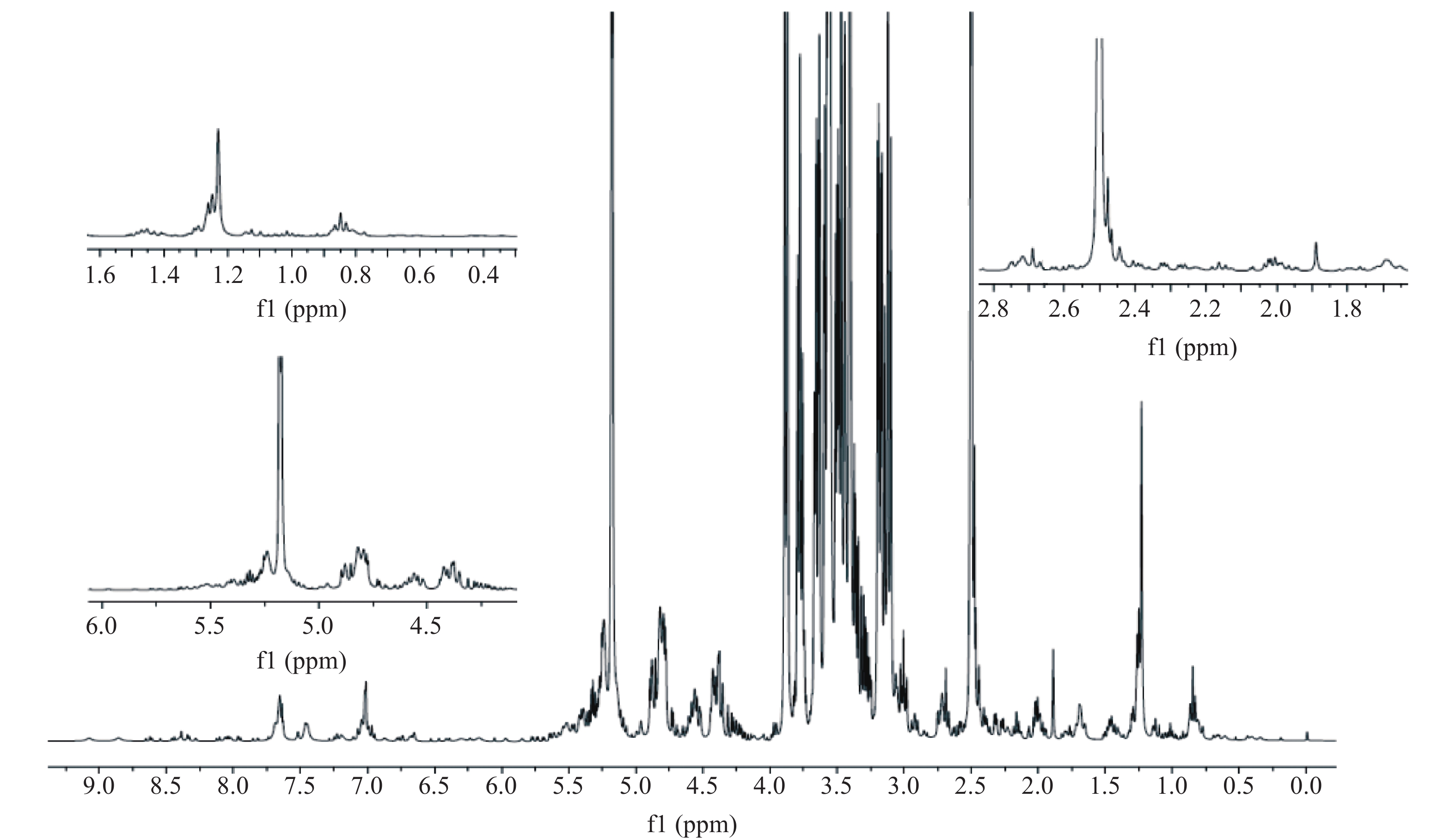
用于1H-NMR指纹图谱研究的提取对象是混合体系,而非单体化合物,因而化合物的鉴定,会有其他成分的干扰,按照文献[20]的报道,在氖代溶剂中加入一定pH范围的缓冲盐(本研究加入pH7.5的磷酸缓冲液),可以有效地缓解各成分化学位移值的漂移,从而降低成分间的干扰,提高NMR分析的准确性。图1为典型的恒山黄芪1H-NMR谱图(500 MHz,CDCl3),采用“加标准品定性”实验进行黄芪皂苷I、II、III、黄芪甲苷、芒柄花素、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、毛蕊异黄酮苷8种成分的1H-NMR信号归属。比对数据库HMDB(www.hmdb.ca)和BMRB(www.bmrb.wisc.edu)及相关文献[1, 24-27]进行其余代谢次级代谢产物、氨基酸、糖类等成分的1H-NMR 信号归属。结果,从恒山黄芪中共鉴定出了24种化合物,其中6个异黄酮类化合物、7个皂苷类化合物(结构见图2)和其他11个初级代谢产物。
为了方便描述,将黄芪1H-NMR谱图分为3个部分:黄酮类成分(主要是芳香区域δ 5.0~9.0)、皂苷类成分(主要是糖区域δ 2.0~5.0)、氨基酸类成分(主要是脂肪区域δ 0.5~2.0),以下分别为3个区域核磁数据分析和化学信号归属。
黄酮类成分:与芒柄花素的相似信号δ 3.78(s),6.86(d,2.0),6.96(2H,d,7.2),6.92(dd,2.0,8.8),7.48(2H,d,8.4);与芒柄花苷相似的信号δ 3.81(s),7.26(s),5.10(d,7.2),7.01(d,8.5),7.16(d,1.5),7.54(d,8.5);与毛蕊异黄酮相似的信号δ 3.78(s),7.04(s),6.84(d,2.4),7.94(d,8.8);与毛蕊异黄酮苷相似的信号δ 3.78(s),6.94(s),7.04(s),5.05(d,5.2),6.84(d,2.4),6.91(d,2.4),7.94(d,8.8);与3-羟基-9,10-二甲氧基紫檀烷相似的信号δ 3.70(s),3.72(s),5.54(s),6.25(s),6.46(dd,8.0,8.4),6.96(d,8.0),7.28(d,8.4);与9,10-二甲氧基紫檀烷-3-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷相似的信号δ 3.73(s),3.74(s),5.56(s),4.85(d,7.5),6.55(d,7.5),6.72(d,2.4),7.01(d,8.5),7.42(d,8.5)。
皂苷类成分:恒山黄芪的核磁数据中与黄芪皂苷I相似的信号(化学位移、耦合常数、裂峰等),包括δ 0.93(s),1.27(s),1.30(s),1.42(s),1.60(s),1.79(s),1.97(s),2.03(s),2.52(d,8.0),3.14(dd,21.0,11.5),3.39(dd,11.5,4.5),3.80(ddd, 8.5,8.5,3.5),4.82(d,7.5),4.93(d,7.5);与黄芪皂苷Ⅱ相似的信号δ 0.93(s),1.27(s),1.31(s),1.41(s),1.58(s),1.80(s),2.04(s),2.51(d,7.5),3.39(dd,11.0,4.0),3.76(ddd,10.0,9.0,3.0),3.88(dd,8.0,5.5),4.77(d,8.0),4.97(dd,14.2,7.2),4.90(d,7.5);与黄芪皂苷III相似的信号δ 1.01(s),1.19(s),1.30(s),1.32(s),1.44(s),1.45(3 s),1.96(s),2.55(d,7.5),3.12(dd,21.4,11.0),3.57(dd,11.5,4.5),3.75(ddd,9.0,9.0,3.5),4.93(d,6.5),5.04(dd,14.0,7.0),5.42(d,7.5);与黄芪甲苷相似的信号δ 0.95(s),1.30(s),1.38(s),1.42(s),1.59(s),2.06(s),2.53(d,9.0),3.14(dd,200,10.5),3.80(ddd,8.5,8.5,4.0),4.88(d,6.5),4.92(d,7.5);与异黄芪苷I相似的信号δ 0.93(s),1.28(s),1.31(s),1.42(s),1.59(s),1.82(s),1.96(s),2.03(s),2.53(d,7.6),3.14(dd,21.0,10.6),3.78(ddd,9.0,9.0,3.8),3.89(dd,9.2,5.2),4.80(d,7.8),4.94(d,7.4),4.99(dd,14.8,7.2);与异黄芪苷II相似的信号δ 1.02(s),1.11(s),1.28(s),1.30(s),1.36(s),1.48(s),1.50(s),2.00(s);2.53(d,7.6),3.14(dd,21.0,10.6),3.39(dd,11.2,4.4),3.78(ddd,9.0,9.0,3.8),3.89(dd,9.2,5.2),4.80(d,7.8),4.94(d,7.4),4.99(dd,14.8,7.2);与环黄芪醇相似的信号δ 1.03(s),1.30(s),1.33(s),1.37(s),1.45(s),1.58(s),1.89(s),1.96(dd,12.0,4.0),2.06(dd,11.5,9.0),2.55(d,7.5),3.12(dd,11.5,9.0),3.66(dd,11.5,4.5),3.80(d,9.5),3.89(dd,9.0,5.5)。
氨基酸类成分:与甘氨酸相似的信号,包括δ 3.60(s);与丙氨酸相似的信号,包括δ 1.49(d,7.2);与缬氨酸相似的信号,包括δ 1.06(d,6.6),1.00(d,7.2);与脯氨酸相似的信号,包括δ 2.08(m),2.36(m),4.16(dd,8.4,6.6);与苏氨酸相似的信号,包括δ 1.33(d,6.6),4.20(m);与天冬酰胺相似的信号,包括δ 2.85(dd,7.8,16.8),2.95(dd,4.2,16.8),4.01(dd,7.8,4.2);与苹果酸相似的信号,包括δ 2.66(d,3.0),2.68(d,3.0);与胆碱相似的信号,包括δ 3.21(s);与尿苷相似的信号,包括δ 5.89(dd,4.2,7.2),7.93(d,7.8),3.85(dd,12.6,3.6);与腺苷相似的信号,包括δ 6.03(d,6.6),8.23(s),8.35(s);与蔗糖相似的信号,包括δ 4.03(t,8.4),4.18(d,9.0),5.40(d,4.2),3.44(t,8.4),3.82(m),3.53(dd,9.9,3.6),3.70(t,9.6)。
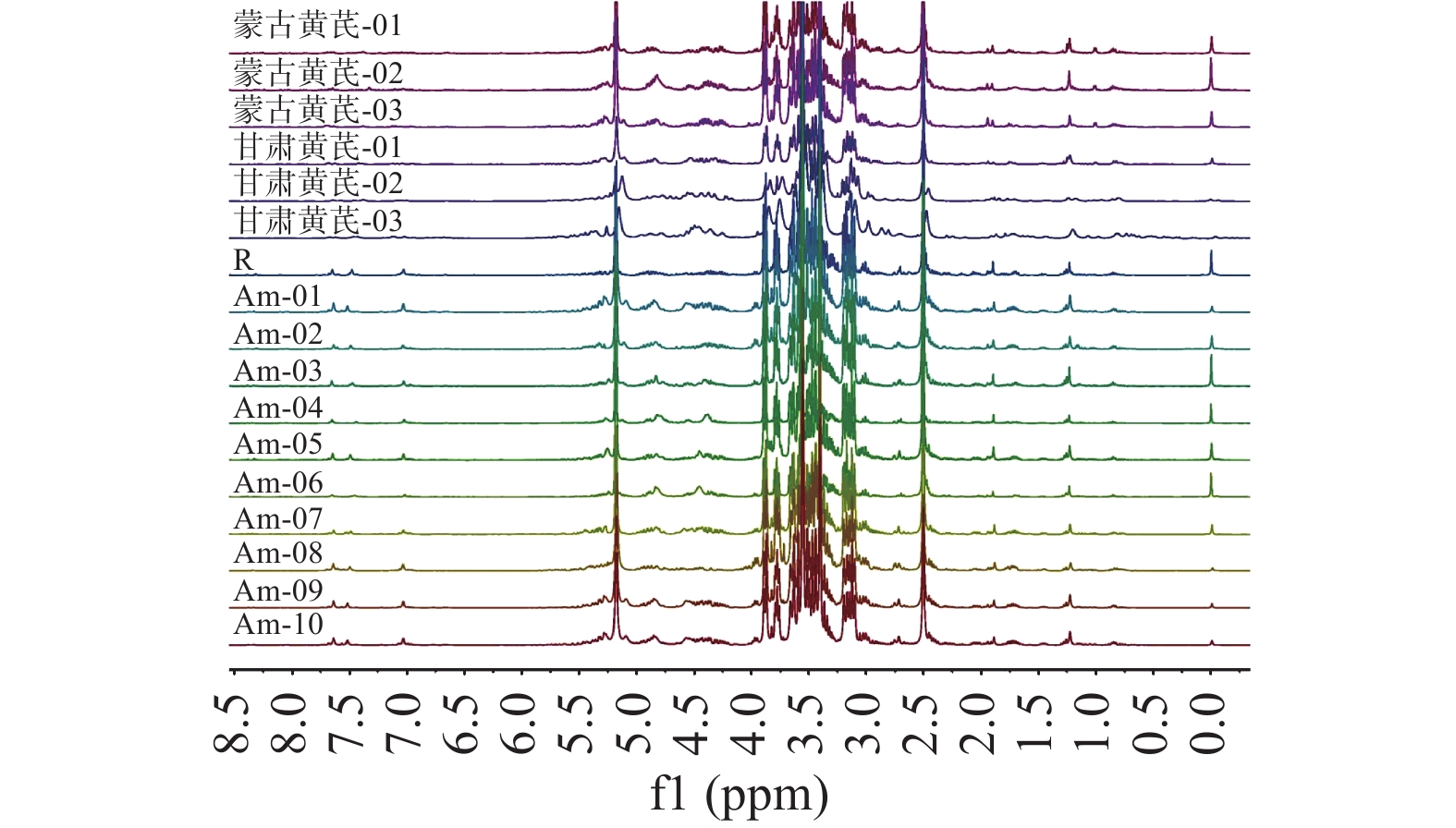
2.3 恒山黄芪典型1H-NMR指纹图谱以及相似度分析
将10批恒山黄芪、3批蒙古黄芪和3批甘肃黄芪的1H-NMR测定数据导入MestReNova软件,通过处理不同年限的恒山黄芪的积分面积,以相关系数为标准,使用中值向量法计算得到10批恒山黄芪不同氢核磁共振指纹图谱的共有模式R(图3中对照图谱R)。通过分析其相同成分(1H-NMR中显示相同信号),确定共有峰,并依据化学位移和耦合常数等,对其化学成分进行鉴定,得到了10批恒山黄芪的1H-NMR特征指纹图谱(见图3)。通过谱图直观分析,可以看到蒙古黄芪(赤峰、乌兰察布、包头)、甘肃黄芪(陇西、岷县、渭源县)、恒山黄芪(山西浑源)3个不同省份产的黄芪的提取物,其1H-NMR谱图峰形以及化学位移、耦合常数等在高中低场区基本相同,证明3个不同省份产的黄芪都含有异黄酮类、皂苷类、氨基酸类等成分。但在部分场区仍有一定差异,如在低场区(δ 7.0~7.7),异黄酮的信号峰的强度存在着一定差异,恒山黄芪的信号峰强度明显高于蒙古黄芪和甘肃黄芪,说明恒山黄芪的异黄酮含量高于蒙古黄芪和甘肃黄芪。而在高场区(δ 0.8~2.0),恒山黄芪、蒙古黄芪、甘肃黄芪的信号峰数量以及峰形有一定的差别,表明它们的氨基酸、脂肪酸类、以及部分糖基等有一定差别。
以共有模式R作为标准,在Excel软件中计算三个不同产地以及不同年限的黄芪的相似度。相似度评价结果见表2。从表中结果中可以看出,10批恒山黄芪的相识度都在0.9以上,而3批甘肃黄芪的相似度分别是0.774、0.753、0.761,3批蒙古黄芪的相似度分别是0.858、0.845、0.833。相识度分析结果与1H-NMR谱图分析结果一致,说明3个不同省份产的黄芪在化学成分上和含量上有明显的差异性。10批恒山黄芪样品的氢核磁共振指纹图谱的平均相似度为0.975,结果表明不同年限恒山黄芪的1H-NMR图谱总体相似,差异较小,同时还可以看到,编号Am-02、Am-05、Am-06、Am-10恒山黄芪相较于其他年限的恒山黄芪相似度相对略低,表明这四批样品相较于其他样品存在一定差异。
表 2 相似度评价结果Table 2. Similarity evaluation result编号 相似度 编号 相似度 Am-01 0.996 Am-06 0.955 Am-02 0.968 Am-07 0.986 Am-03 0.979 Am-08 0.984 Am-04 0.994 Am-09 0.994 Am-05 0.963 Am-10 0.929 甘肃黄芪-01 0.774 蒙古黄芪-01 0.858 甘肃黄芪-02 0.753 蒙古黄芪-02 0.845 甘肃黄芪-03 0.761 蒙古黄芪-03 0.833 2.4 主成分分析
2.4.1 贡献率分析
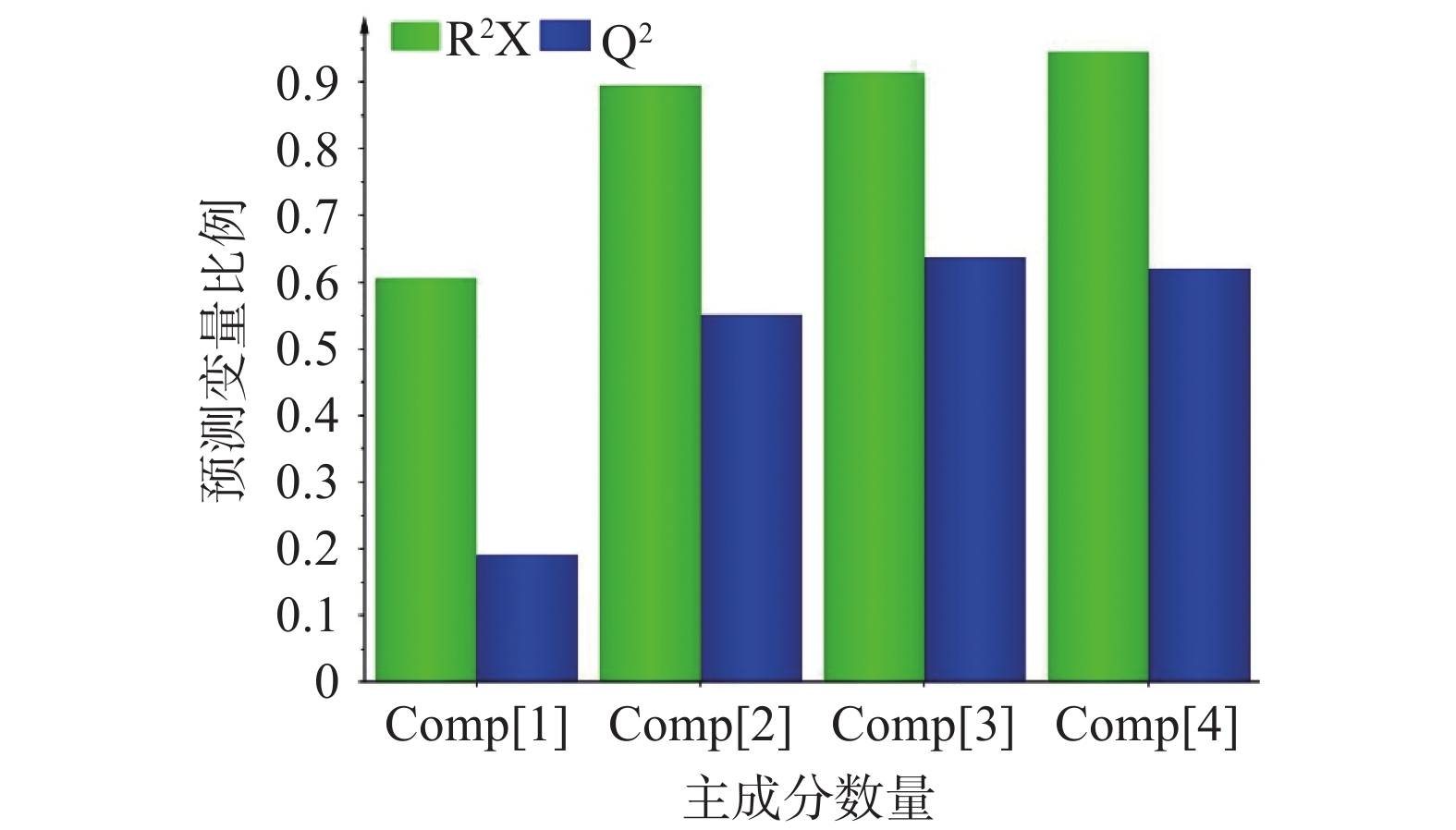
为了进一步评价不同乡村产的恒山黄芪药材的质量差异性,将10批次样品的恒山黄芪的1H-NMR数据导入SIMCA-P 13.0软件进行主成分分析。数据采用中心化方法(Mean-centering and Not Scaling)进行尺度同一化处理。通过主成分分析(见表3),可以看出恒山黄芪中的前4个主成分能够预测95.5%的变量(图4),R2X和Q2分别为0.955和0.629,对于变量具有良好的预测能力。主成分个数的提取原则为其对应的特征值大于1,故取前3个作为主成分,其累计贡献率达到89.8%,它代表了所研究1H-NMR的89.8%的信息量。因为相差越大,贡献率越高,因而从图4中看出,排在第一和第二的主成分对于变量,贡献率分别为51.8%和20.6%,是恒山黄芪最重要的成分群,因此前两个主成分能够预测大部分的变量。
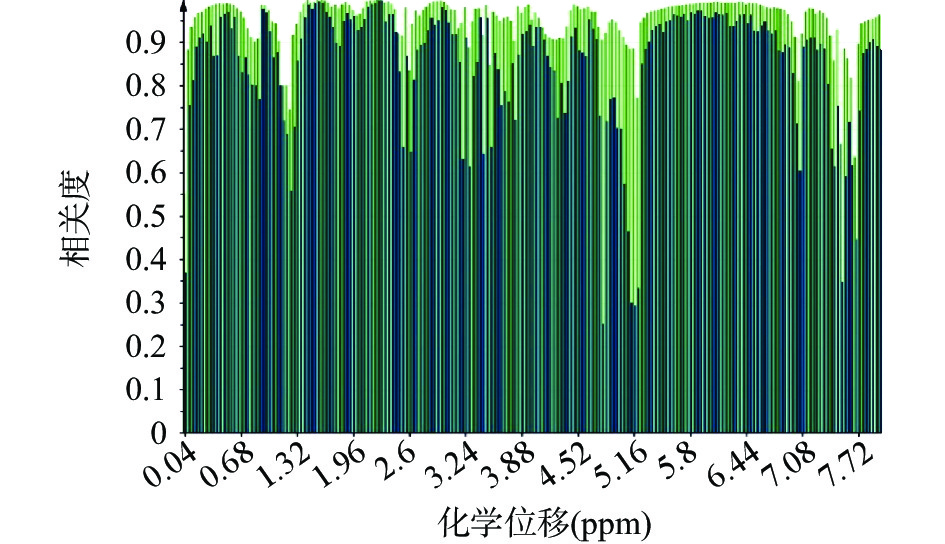
表 3 抽取的主成分特征值及贡献率Table 3. The characteristic value and contribution of principal components主成分因子 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) 1 5.18 51.8 51.8 2 2.06 20.6 72.3 3 1.75 17.5 89.8 4 0.562 5.62 95.5 5 0.218 2.18 97.6 6 0.112 1.12 98.8 7 0.076 0.76 99.5 8 0.0275 0.275 99.8 9 0.0212 0.212 100 由图5主成分因子相关图可以看出,前2个主成分因子与化学位移δ 0.98~1.72,1.84~2.44,2.80~3.12,3.88~4.16,5.36~6.76,7.08~7.32,7.76~7.96这六个分段峰内特征峰高度正相关,说明其对样品的区分评价贡献最大。而根据恒山黄芪1H-NMR的典型信号归属分析,0.98~1.72,1.84~2.44,2.80~3.12,3.88~4.16分段,主要是三萜皂苷特征峰集中的区域,5.36~6.76,7.08~7.32,7.76~7.96分段,主要是异黄酮特征峰集中的区域,中国药典中恒山黄芪的主要药物化学成分也集中体现在这两类物质中,而1H-NMR的PCA分析也证实了其与药典的统一性,上述高度正相关的特征峰在恒山黄芪药材的质量控制中有相对重要的作用,而1H-NMR的快速分析也证实了其广泛有效的应用性。
2.4.2 恒山黄芪的主成分分析
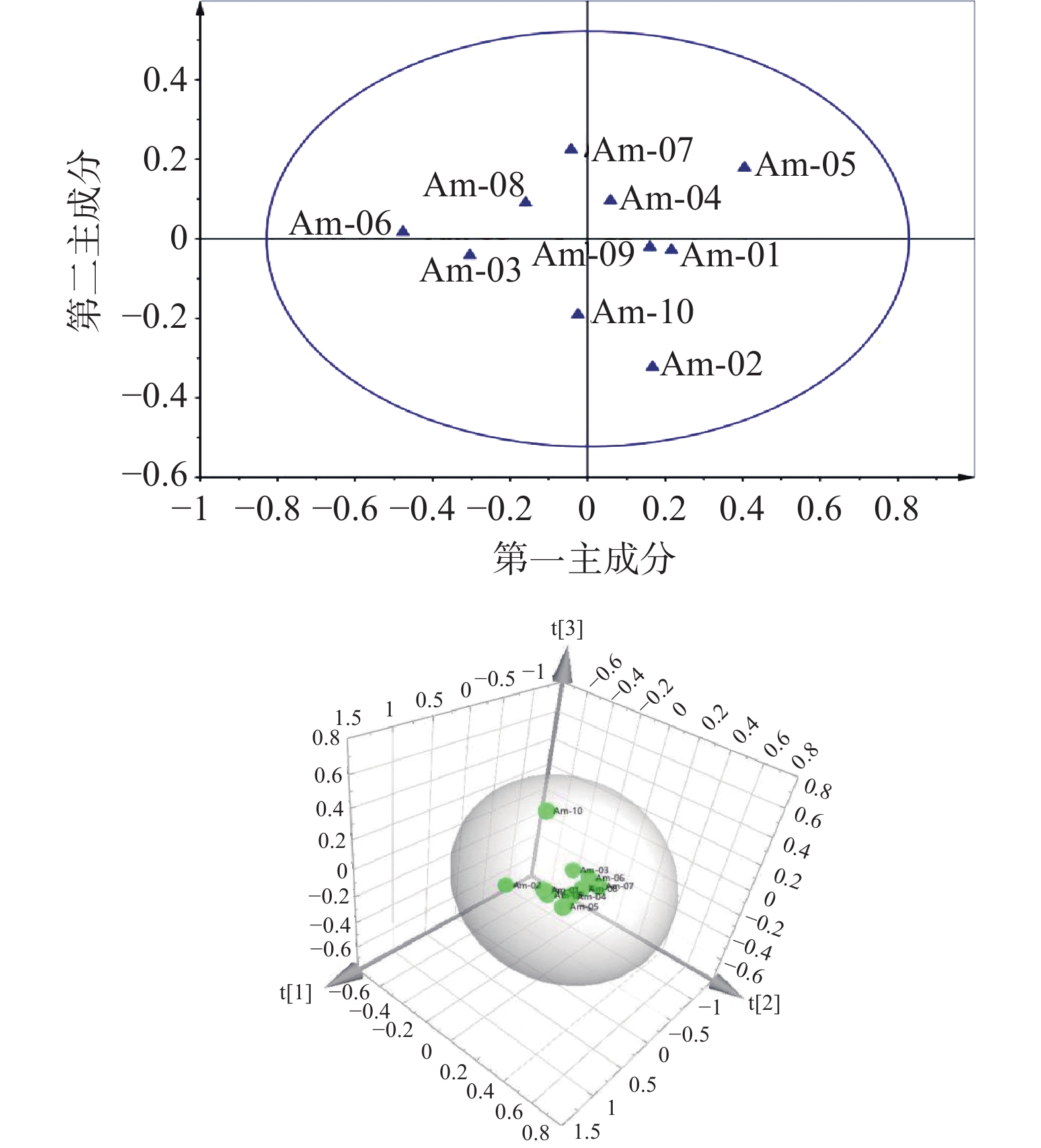
主成分分析研究结果与相似度评价结果基本一致,建立的1H-NMR指纹图谱结合多元统计分析方法可用于恒山黄芪的质量控制和评价。主成分分析的二维得分图和3D图见图6。图6二维得分图显示,不同采样地点的恒山黄芪数据点相互交错,均呈现出较松散的分布,样品离散度相似且化学成分组呈现出一定的变异,然而,10批恒山黄芪在PCA分析聚为2类(样品Am-01、Am-02、Am-04、Am-05、Am-09聚为一类,样品Am-03、Am-06、Am-07、Am-08、Am-10聚为一类),但聚类分组不明显,而样品Am-02、Am-05、Am-06、Am-10距离中心点较远。图6的3D图显示恒山黄芪较为集聚(Am-10远离群落,这与相似性分析结果一致),表明该组内的均一性相对较好,在建立的三维坐标图中,不同来源的恒山黄芪集中在三维的位置,说明10批的恒山黄芪样品化学成分差异较小。综合主成分分析说明浑源县不同地点生长的恒山黄芪,虽然生长环境有所不同,但在化学成分上不存在显著差异,具有很强的相似性。
对比分析Am-02、Am-05、Am-06、Am-10的采样地点,可以得出恒山黄芪主要化学成分与其生态因子,特别是地区海拔有着密切关系。研究已经证实,海拔高度和经纬度是影响植物布局及其生长发育的重要因子,在一定范围内,海拔高度对植物化学成分有显著影响[28-30]。恒山黄芪最适宜生长的海拔高度为1400~1800 m[31],而Am-02、Am-05、Am-06、Am-10的生长海拔分别为1845、1910、1270和1856 m,并且从主成分3D图可以看出Am-02、Am-05、Am-10的成分差异性更大,说明恒山黄芪的主要化学成分随海拔的增高而差异性变大。这一结果,也与胡明勋等[32]基于HPLC-DAD分析环境因素对黄芪的黄酮和皂苷类成分的影响结果一致。
3. 结论与讨论
通过不同来源恒山黄芪的相似度分析和主成分分析,发现浑源县不同地方产的恒山黄芪化学成分不存在明显差异性,建立了典型的恒山黄芪1H-NMR指纹图谱,鉴别其存在24种化合物,包括三萜皂苷、异黄酮、氨基酸、有机酸、糖等,三萜主要有黄芪皂苷Ⅰ、黄芪皂苷Ⅱ、黄芪皂苷III、黄芪甲苷、异黄芪苷I、异黄芪苷II、环黄芪醇;异黄酮主要有芒柄花素、芒柄花苷、毛蕊异黄酮、毛蕊异黄酮苷、3-羟基-9,10-二甲氧基紫檀烷、9,10-二甲氧基紫檀烷-3-O-β-D-葡萄糖苷。
现行的1H-NMR分离技术常用于对中药材进行系统生物分离后再进行NMR分析,本研究未经系统的生物分离过程,也达到了快速分析的目的,和高效液相图谱分析相比,基于氢核磁共振的灵敏性可以更快速的更全面的显示出恒山黄芪中的含量成分。为了更精密的测量恒山黄芪指纹图谱中的信号,可进一步采取将二维核磁共振(2D-NMR)图谱与高分辨质谱结合的方法,可对重叠信号进行一定的分离并提供更多的结构鉴定信息。
PCA相关分析结果表明,恒山黄芪的主要化学成分含量与海拔有一定的相关性,恒山黄芪作为山西地道药材,其表现出的品质优势是恒山地区多种环境因子决定的,是特定的气候条件下,海拔、经纬度、气候、土壤的综合影响的结果。而生态因子对药材品质的影响是多方位的,因此后续研究应采用应用多元统计分析方法,同时分析不同生态因子相互作用的影响,进一步分析生态因子对药材化学成分代谢的关键酶。
-
表 1 恒山黄芪来源和年限
Table 1 Source and age of Hengshan Astragalus membranaceus
编号 样品采集地 纬度(°) 经度(°) 海拔(m) 药材年限 采样时间 Am-01 山西浑源县官儿乡穆家庄村 39.46 113.66 1623 3年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-02 山西浑源县官儿乡界板沟村 39.48 113.56 1845 5年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-03 山西浑源县大仁庄乡黄土坡村 39.69 113.83 1728 7年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-04 山西浑源县官儿乡官儿村 39.52 113.65 1689 3年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-05 山西浑源县裴村乡小峪沟 39.54 113.58 1910 5年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-06 山西浑源县东坊城乡龙山村 39.68 113.66 1270 5年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-07 山西浑源县千佛岭乡温庄村 39.45 113.75 1782 7年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-08 山西浑源县千佛岭乡宽坪村 39.48 113.77 1768 5年恒山黄芪 2020.8 Am-09 山西浑源县千佛岭乡泽青岭村 39.44 113.73 1691 10年恒山黄芪 2020.7 Am-10 山西浑源县青磁窑乡南张庄村 39.60 113.76 1856 3年恒山黄芪 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-01(购买) 内蒙古自治区赤峰(产地) 3年 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-02(购买) 内蒙古自治区乌兰察布(产地) 3年 2020.8 蒙古黄芪-03(购买) 内蒙古自治区包头(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-01(购买) 甘肃省陇西县(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-02(购买) 甘肃省岷县(产地) 3年 2020.8 甘肃黄芪-03(购买) 甘肃省渭源县(产地) 3年 2020.8 表 2 相似度评价结果
Table 2 Similarity evaluation result
编号 相似度 编号 相似度 Am-01 0.996 Am-06 0.955 Am-02 0.968 Am-07 0.986 Am-03 0.979 Am-08 0.984 Am-04 0.994 Am-09 0.994 Am-05 0.963 Am-10 0.929 甘肃黄芪-01 0.774 蒙古黄芪-01 0.858 甘肃黄芪-02 0.753 蒙古黄芪-02 0.845 甘肃黄芪-03 0.761 蒙古黄芪-03 0.833 表 3 抽取的主成分特征值及贡献率
Table 3 The characteristic value and contribution of principal components
主成分因子 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) 1 5.18 51.8 51.8 2 2.06 20.6 72.3 3 1.75 17.5 89.8 4 0.562 5.62 95.5 5 0.218 2.18 97.6 6 0.112 1.12 98.8 7 0.076 0.76 99.5 8 0.0275 0.275 99.8 9 0.0212 0.212 100 -
[1] 卞云云, 管佳, 毕志明, 等. 蒙古黄芪的化学成分研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2006,41(16):1217−1221. [BIAN Y Y, GUAN J, BI Z M, et al. Studies on chemical constituents of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch. ) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge. ) Hsiao[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2006,41(16):1217−1221. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-2494.2006.16.006 [2] LIU R, ZHANG H C, LI H, et al. Obtaining diverse metabolic profiles from endophytic Aspergillus fumigates in Astragalus membranaceus using the one strain-many compounds method[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2021,57:194−196. doi: 10.1007/s10600-021-03317-x
[3] ZHANG H C, LIU R, ZHOU F. Chaetoglobosins in endophytic Chaetomium sp. from Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2021,57:401−403. doi: 10.1007/s10600-021-03374-2
[4] 田华, 邓雁如, 周坤, 等. 蒙古黄芪的化学成分研究[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2016,22(7):70−73. [TIAN H, DENG Y R, ZHOU K, et al. Chemical constituents of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2016,22(7):70−73. [5] 谢静, 龚易昕悦, 丁立生, 等. 黄芪及其活性成分对脓毒症临床和药理作用的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2021,52(8):2502−2510. [XIE J, GONG Y X Y, DING L S, et al. Progress in clinical and pharmacological studies of Astragali Radix and its active components against sepsis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(8):2502−2510. [6] 孔祥琳, 吕琴, 李运伦, 等. 黄芪甲苷对心脑血管疾病的现代药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(2):218−223. [KONG X L, LV Q, LI Y L, et al. Advances in research on pharmacological effect of astragaloside Ⅳ on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2021,27(2):218−223. [7] 易伦朝, 吴海, 梁逸曾. 色谱指纹图谱与中药质量控制[J]. 色谱,2008,26(2):166−171. [YI L Z, WU H, LIANG Y Z. Chromatographic fingerprint and quality control of traditional Chinese medicines[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2008,26(2):166−171. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.02.007 [8] 姚静, 孙欣光, 董蓉, 等. HPLC-CAD一测多评法同时测定黄芪中6种成分含量[J]. 药学学报,2021,56(2):557−564. [YAO J, SUN X G, DONG R, et al. Simultaneous quantitative analyses of six components in Astragalus membranaceus based on HPLC-CAD and quantitative analysis of multi-components with a single-marker[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica,2021,56(2):557−564. [9] 徐翠珊, 陈俭双, 张舒彦, 等. 复方麝香黄芪滴丸HPLC指纹图谱的建立及多成分含量测定[J]. 中国新药杂志,2020,29(16):1894−1901. [XU C X, CHEN J S, ZHANG S Y, et al. Establishment of HPLC fingerprint and determination of multiple components in Compound Shexiang Huangqi Dropping Pills[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs,2020,29(16):1894−1901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2020.16.017 [10] LI A P, LI Z Y, JIA J P, et al. Chemical comparison of coat and kernel of mung bean by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolic fingerprinting approach[J]. Spectroscopy Letters,2016,49(3):217−224. doi: 10.1080/00387010.2015.1133648
[11] LI Z Y, ZHANG Z Z, DU G H, et al. Comparative analysis of Danggui and European Danggui using nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolic fingerprinting[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2015,103:44−51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.10.028
[12] 范刚, 罗尚华, 李艳, 等. 基于1H-NMR 代谢组学技术的中药质量评价[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2013,15(9):1862−1870. [FAN G, LUO S H, LI Y, et al. Quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine by H-NMR-based metabolomics[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2013,15(9):1862−1870. [13] LIU Y, FAN G, ZHANG J, et al. Metabolic discrimination of sea buckthorn from different Hippophaë species by 1H-NMR based metabolomics[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1585−1595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01722-3
[14] FAN G, ZHANG M Y, ZHOU X D, et al. Quality evaluation and species differentiation of Rhizoma coptidis by using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2012,747:76−83. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.038
[15] FAN G, LUO W Z, LUO S H, et al. Metabolic discrimination of Swertia mussotii and Swertia chirayita known a “Zangyinchen” in traditional tibetan medicine by 1H-NMR-based metabolomicsy[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2014,98:364−370. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.06.014
[16] KIM H K, CHOI Y H, VERPOORTE R. NMR-based metabolomic analysis of plant[J]. Nature Protcols,2010,5(3):536−549. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.237
[17] KOOY VDF, MALTESE F, CHOI Y H, et al. Quality control of herbal material and phytopharmaceuticals with MS and NMR based metabolic fingerprinting[J]. Planta Medica,2009,75(7):763−775. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1185450
[18] 吕经纬, 李春楠, 高晓晨, 等. 基于核磁共振氢谱代谢组学结合分子对接技术筛选补肾壮骨汤促睾酮合成活性成分[J]. 分析化学,2021,49(5):779−789,147−151. [LV J W, LI C N, GAO X C, et al. Screening of active ingredients of Bushen Zhuanggu decction for promoting testosterone synthesis based on 1H NMR metabolomics combined with molecular dcking technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2021,49(5):779−789,147−151. [19] 齐彦爽, 李静, 郭冬, 等. 基于核磁共振代谢组学技术的款冬茎和叶的化学成分比较[J]. 中国药学杂志,2019,54(8):608−613. [QI Y S, LI J, GUO D, et al. Chemical comparison of the stems and leaves of Tussilago farfara L. using NMR-based metabolomics[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2019,54(8):608−613. [20] 刘文静, 刘瑶, 宋青青, 等. 利用1H-NMR比较管花肉苁蓉野生品和栽培品的化学成分组[J]. 中国中药杂志,2018,43(17):3506−3512. [LIU W J, LIU Y, SONG Q Q, et al. Chemome comparison between cultivated and wild Cistanche tubulosa using 1H-NMR spectroscopy[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2018,43(17):3506−3512. [21] 李玮, 杨红梅, 王浩, 等. 基于1H-NMR代谢组学初步比较真蜂蜜和掺假蜂蜜差异成分[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(7):218−223,227. [LI W, YANG H M, WANG H, et al. Comparison of chemical constituents in honey and adulterated honey based on 1H-NMR metabonomics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(7):218−223,227. [22] 郭淑娟, 朱晟永, 贾悦, 等. 基于主成分分析微波提取圆头蒿多糖工艺中单糖组分变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(22):267−274. [GUO S J, ZHU S Y, JIA Y, et al. Changes of monosaccharide components in microwave extraction of Artemisia sphaercephala polysaccharides based on principal component analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(22):267−274. [23] 何佳, 黄文康, 马相锋, 等. 基于主成分分析与PLS-DA分析研究浙麦冬道地性与等级评价标准[J]. 中国药学杂志,2021,56(4):285−292. [HE J, HUANG W K, MA X F, et al. Geoherbalism and grand evaluation of Zhejiang Ophiopogon japonicas based on PCA and PLS-DA[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2021,56(4):285−292. [24] 王青虎, 王秀兰, 奥·乌力吉, 等. 蒙古黄芪化学成分的研究[J]. 中国药学杂志,2014,49(5):357−359. [WANG Q H, WANG X L, AO W L J, et al. Chemical constituents of roots of Astragalus membranaceus(Fisch) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge) Hsiao[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2014,49(5):357−359. [25] 孙洁, 张蕾, 张晓拢, 等. 蒙古黄芪的化学成分研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2013,28(2):138−143. [SUN J, ZHANG L, ZHANG X L, et al. Chemical constituents from Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus[J]. Drugs and Clinic,2013,28(2):138−143. [26] ALANIYA M D, KAVTARADZE N S, LAVOIE S, et al. Chemical constituents of the aerial part of Astragalus bungeanus[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2011,46:1001−1003. doi: 10.1007/s10600-011-9811-x
[27] HE Z Q, FINDLAY J A. Constituents of Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Journal of Natural Products,1991,54(3):810−815. doi: 10.1021/np50075a009
[28] SAFFARIHA M, AZARNIVAND H, ZARE CHAHOUKI M A, et al. Changes in the essential oil content and composition of Salvia limbata C. A. Mey at different growth stages and altitudes[J]. Biomedical Chromatography,2021:e5127.
[29] TANG J F, WANG W D, YANG L, et al. Variation in quantity and chemical composition of soil dissolved organic matter in a peri-urban critical zone observatory watershed in Eastern China[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2019,688:622−631. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.270
[30] 沈燕金, 张一扬, 李德青, 等. 文山烟叶主要化学成分与海拔经纬度相关性分析[J]. 湖南农业科学,2015(11):29−31. [SHEN Y J, ZHANG Y Y, LI D Q, et al. Correlation analysis between chemical compositions of flue-cured tobacco leaves and altitude, longitude and latitude in Wenshan[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,2015(11):29−31. [31] 刘瑞. 恒山黄芪内生真菌及其代谢产物研究与应用[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020: 1−12. LIU R. Research and application of metabolites of endophytic fungi from Hengshan Aspergillus fumigatus[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020: 1−12.
[32] 胡明勋, 陈安家, 郭宝林, 等. 影响山西恒山野生蒙古黄芪质量的环境因素研究[J]. 中草药,2005,40(5):984−989. [HU M X, CHEN A J, GUO B L, et al. Effects of environmental factors on quality of wild Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus grown in Hengshan Mountain, Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2005,40(5):984−989. -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 王安婧,朱越,韩诗晴,韩柱,诸葛慧,贾小转,王迎超,杨振中. 基于序贯分析策略的丹红注射液与临床常用输液溶媒配伍稳定性及安全性评价. 药物分析杂志. 2024(03): 493-500 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 彭剑岚,朱永苹,林寿宁,廖冬燕,尹静雯. 黄芪及其活性成分治疗胃癌的作用机制研究进展. 中华中医药学刊. 2023(04): 196-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李建文,郭海波,马婷婷,冯浩彬,靳玲. 核磁共振波谱技术在药品质量与安全方面的应用研究. 广东化工. 2023(10): 195-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 钟勇,刘菡菡,赵永发,谢俊. 注射用红花黄色素的质量控制及安全性研究. 临床医药实践. 2023(07): 509-512 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 梁泰帅,郑淑涵,赵肖琼. 独脚金内酯(SLs)对盐碱胁迫下恒山黄芪种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 种子. 2023(12): 90-95+102 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张弘弛,刘瑞,高志慧,李慧,杨阳. 恒山黄芪毛状根遗传转化体系的建立及活性成分含量测定. 北方园艺. 2022(09): 93-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 姜莉,王成,邢颖,徐怀德. 不同提取方法对黄芪提取液活性成分及抗氧化性的影响. 食品研究与开发. 2022(16): 119-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



