Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Pulp
-
摘要: 本文研究了菠萝蜜多糖(Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Pulp Polysaccharide, JFP-Ps)的流变学特性,分析浓度、剪切速率、温度、加热时间、pH、冻融变化和盐离子等因素对JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度和粘弹性的影响。结果表明,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度与浓度呈正相关;JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度与剪切速率呈负相关,出现剪切稀释的现象,为“非牛顿流体”,呈现假塑性行为;JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度与温度呈负相关;随加热时间的延长,JFP-Ps的表观粘度先上升后下降;JFP-Ps溶液在pH4~10范围内表观粘度值变化不大;冻融变化可使JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度增大;5%NaCl溶液使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度减小,5% KCl溶液使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度增大;在粘弹性测试中,JFP-Ps的储能G′和损能G″随着频率的增大而增大,且G′始终高于G″,另外,JFP-Ps溶液的储能模量G'和损耗模量G''随着溶液浓度的增大而上升,呈现凝胶性质。研究结果可为菠萝蜜果肉多糖在食品工业中的应用提供一定的理论借鉴。Abstract: The present study was designed to investigate the rheological properties of polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. pulp. The effects of concentration, shear rate, temperature, heating time, pH, freeze-thaw change and salt ions on the apparent viscosity and viscoelasticity of JFP-Ps solution were studied. The results indicated that JFP-Ps as a "non-Newtonian fluid" exhibited pseudoplastic behavior, the apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps solution was positively correlated with the concentration, there existed a negative correlation between the apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps solution and the shear rate, with an emergence of dilution at the sharing mouth. The apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps solution was negatively correlated with temperature; with the extension of heating time, the apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps increased first and then declined; the apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps solution changed a little in the range of pH4~10; freeze thawing changed may cause an increase in the apparent viscosity of JFP-Ps solution; 5% NaCl solution reduced the apparent viscosity of the JFP-Ps solution, while 5% KCl solution increased the apparent viscosity of the JFP-Ps solution; in the viscoelasticity test, the storage energy G′and loss energy G″of JFP-Ps enlarged with increase of frequency, and G′was always larger than G″. Moreover, the storage modulus G' and loss modulus G'' of JFP-Ps solution enhanced with the increase of the concentration of the solution, showing the properties of gel. The research results can provide certain theoretical reference for the application of jackfruit pulp polysaccharides in food industry.
-
Keywords:
- JFP-Ps /
- apparent viscosity /
- shear rate /
- viscoelasticity /
- rheological properties
-
多糖是一类来源广泛的天然高分子聚合物,由单糖通过糖苷键相互结合而成[1],具有抗氧化、抗病毒、抗疲劳、抑制肿瘤、降血脂、降血糖、保肝、免疫调节等生理活性[2-7]。多糖溶液本身具有一定的粘弹性,此外,多糖的凝胶化对于食品质构和感官特性至关重要,因此可用作食品中的增稠剂、稳定剂、胶凝剂和粘合剂[8]等。
多糖流变学特性对于多糖类的提取工艺、食品设计、感官评价、产品研发、货架期评估等都具有重要意义[9]。在食品加工过程中,浓度、剪切速率、温度、pH、金属离子等因素都影响着多糖的流体特性。IAGHER等[10]发现芒果果肉中多糖溶液浓度为3 g/L时具有假塑性行为并且表现为粘弹性液体;MA等[9]报道了薯蓣粗多糖溶液和浓度为40%、60%的薯蓣多糖溶液的流变性都表现为假塑性和“凝胶状”行为。
菠萝蜜(Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.)是一种木本粮食作物,分布于我国华南地区,种植历史悠久[11],虽易于种植、产量较大但商品化程度不高,经济效益低;大多以鲜果或粗加工产品形式销售,缺乏精深加工限制了菠萝蜜产业价值的提升[12-13]。菠萝蜜多糖(JFP-Ps)具有较强的体外抗氧化活性及免疫调节等活性[2-3];对于人体肠道微生物菌群调节有明显益处[14],是一种具有开发潜力的生物活性物质。目前,对菠萝蜜多糖的流变性仍有待深入研究。本文通过分析浓度、剪切速率、温度、pH、冻融和盐浓度等因素对JFP-Ps表观粘度和粘弹性的影响,考察JFP-Ps溶液的流变学特性,为JFP-Ps在食品工业的研发和生产提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
JFP-Ps(总糖含量为79.12%,主要由鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、木糖和半乳糖醛酸组成,平均分子量为1668 kDa[2]) 由中国热带农业科学院香料饮料研究所提取纯化制得;HCl、NaOH 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;NaCl、KCl 分析纯,西陇化工股份有限公司。
DV2T粘度计 美国博勒飞公司;MCR302流变仪 奥地利安东帕公司;FE20pH计、AL104型电子天平 上海梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;K-98-IIA电热恒温水浴锅 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;Master-s-plus UVF全自动超纯水设备 上海和泰公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 浓度和剪切速率对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
分别称取一定质量的JFP-Ps样品,蒸馏水配制0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%、0.6%、0.7%、0.8%、0.9%、1.0%(w/v,下同)的JFP-Ps溶液,室温(25 ℃)下测定60 r/min下的表观粘度。室温(25 ℃)条件下分别测定0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%和1.0%的JFP-Ps溶液在5、15、30和60 r/min剪切速率条件下的表观粘度。
1.2.2 温度对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
蒸馏水配制0.8% JFP-Ps溶液在30、40、50、60、70、80和90 ℃下恒温保持10 min,分别于60 r/min下测定其表观粘度。
1.2.3 冻融变化对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
蒸馏水配制0.8% JFP-Ps溶液,4 ℃和−20 ℃下保持24 h,解冻至室温(25 ℃),分别于60 r/min下测定其表观粘度,与未处理溶液的表观粘度值进行比较。
1.2.4 加热时间对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
蒸馏水配制0.8% JFP-Ps溶液,60 ℃下分别加热0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5、5 h,冷却至室温(25 ℃)后,分别于60 r/min下测定其表观粘度。
1.2.5 pH对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
蒸馏水配制0.8% JFP-Ps溶液,用1 mol/L HCl溶液和1 mol/L NaOH溶液调节JFP-Ps溶液pH至2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10,分别于60 r/min下测定其表观粘度[15]。
1.2.6 JFP-Ps溶液耐盐性研究
蒸馏水配制0.8% JFP-Ps溶液,室温(25 ℃)下加入NaCl、KCl使溶液中NaCl、KCl的终浓度均为5%,搅拌均匀,加入无机盐后,胶溶液体系不稳定,静置1 d后测量在60 r/min下的表观粘度,连续测定5 d,研究JFP-Ps溶液的耐盐性[16-17]。
1.2.7 JFP-Ps粘弹性的测定
采用MCR302流变仪对样品的流变特性进行研究。采用动态应变扫描法测定应变范围为0.01%~100%的线性粘弹性体系。在控制应变模式下,用振荡法对储能模量G'和损耗模量G''进行动态频率扫描测量。将试样加载到流变仪上,使其平衡至测量温度((25±1)℃, 0.5 min)。频率扫描条件:频率0.1~10 Hz(应变0.01%),记录G随频率变化的曲线图。
1.2.8 抗降解性能
蒸馏水配制0.8%JFP-Ps溶液,室温(25 ℃)下放置3、6、12、24、48、72、96 h,测定JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复三次,使用Excel 2020、SPSS 24.0软件处理数据,实验结果均用平均值±标准差表示,用Origin 2020软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 浓度和剪切速率对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
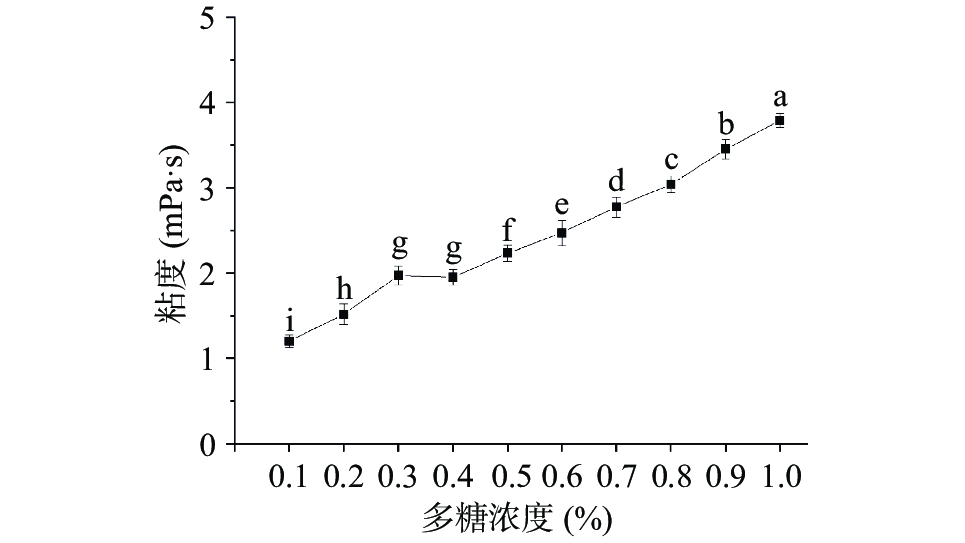
浓度对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响如图1所示,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度与浓度呈正相关,该变化可能是随着溶液浓度的增加,溶液中单位体积内分子数增加,链内、链间相互无顺序的缠绕和链间的相互作用增强,使溶液的流动阻力进一步增加[17-18],多糖浓度为1.0%时,表观粘度基本上达到最大值3.79 mPa·s。ANVARI[19]、WU[20]、CHEN[21]分别研究了Alyssum homolocarpum种子果胶、船果仁酸性多糖和秋葵多糖的表观粘度,溶液的表观粘度随着浓度的增加而增加,与本结果一致。
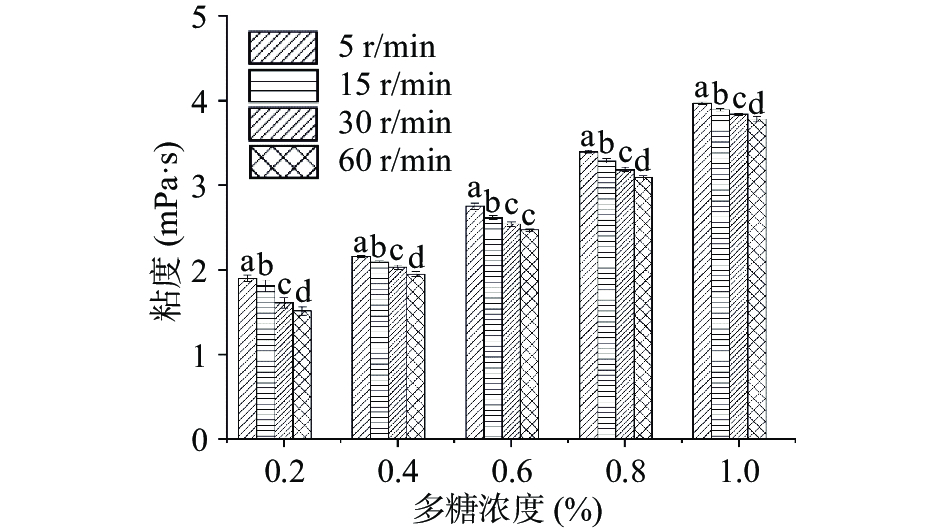
浓度和剪切速率对JFP-Ps表观粘度的影响如图2所示。JFP-Ps溶液浓度在0.2%~1.0%时,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度随剪切速率的增加而降低,呈现剪切稀释现象,说明JFP-Ps为“非牛顿流体”,呈现假塑性行为。在相同浓度下,剪切速率越高,JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度越低,即JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度随剪切速率的增大而减小。相同剪切速率下,浓度越高,JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度越大。当剪切速率增大时,高浓度JFP-Ps溶液(0.6%~1.0%)的表观粘度降低的速率逐渐减慢。可能是由于低剪切速率时,单糖分子链通过静电阻力、氢键等作用形成无规则体系,其分子链相互缠绕,产生很大的粘性阻力。在高剪切速率下,布朗运动随机取向被破坏,倾向于使颗粒沿定向流动[22]。剪切速率增大时,分子间作用力被破坏,分子链的运动阻力降低,由该取向阻力产生的表观粘度随着剪切速率的增加而降低。当剪切速率超出一定范围后,体系的分子链形成比较稳定有序的结构,剪切速率的变化对表观粘度造成的影响不明显[23]。本实验结果与朱会霞[24]、郭守军[18]、XU[25]、STOKES[26]、GALLÃO[27]等研究的樟芝多糖、龙须菜多糖、花菇多糖和铁架木种子多糖等报道结果一致。
2.2 温度对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
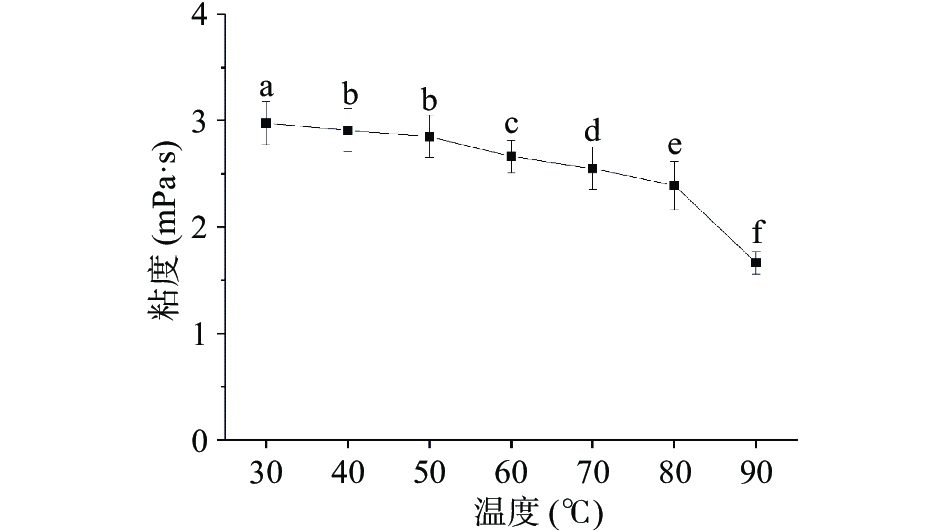
如图3所示,随着温度的上升,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度由2.97 mPa·s逐渐下降至1.66 mPa·s。当体系温度升高时,分子热运动加剧,导致分子链间和链内氢键的断裂[19, 27],削弱了多糖大分子间的缠结[28],使溶液出现了热胀现象,即JFP-Ps溶液产生了“稀释效应”,此效应降低了JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度。研究结果与菅红磊[29]、蒋建新[28]、郭守军[30]等研究的皂荚多糖、塔拉多糖胶、带形蜈蚣藻多糖结果一致。
2.3 冻融变化对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
冻融变化对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响如图4所示,与空白组相比,−20 ℃冷冻处理后的JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度升高了0.78 mPa·s,4 ℃冷藏处理后的JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度升高了0.23 mPa·s,这表明冷冻和冷藏的处理过程中多糖溶液中分子的物理性交联增加,从而升高了JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度。此外,冷冻处理使多糖分子间交联程度增加的幅度较大[17, 28],因而溶液表观粘度有较大幅度的增加。但总体来看,冻融变化对JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度影响较小。研究结果与郭守军[17, 28]研究的龙须菜多糖和带形蜈蚣藻多糖结果一致。
2.4 加热时间对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
加热时间对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度有一定的影响,当加热时间在1.5 h内,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度随时间的延长而增加,当加热至1.5 h时,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度增至最大达到2.98 mPa·s,当加热时间超过1.5 h,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度逐渐减小(图5)。加热增加了JFP-Ps的溶解性和分散性,即相应的增加溶液的表观粘度,但是随着时间的延长,分子热运动加剧,分子间相互作用力减弱,因此溶液的流动阻力下降[18];此外,溶液中的多糖分子可能发生降解,多糖分子链变短,经过长时间的高温加热,溶液出现了热胀现象[29],导致JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度降低。
2.5 pH对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响
pH对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响如图6所示,JFP-Ps溶液在pH4~10区间内表观粘度值为3.05~3.07 mPa·s,未产生较大变化。当溶液pH小于4时,溶液表观粘度随酸性增强而下降,由3.07 mPa·s降至2.92 mPa·s,可能是由于JFP-Ps溶液中,大分子糖呈无规则线团状,彼此交叠,相互缠结,过量的酸根离子起到了静电屏蔽作用而使单个高分子无规线团紧缩[29],从而减弱了缠结程度,导致JFP-Ps表观粘度降低。但总体结果表明JFP-Ps溶液具有良好的耐酸碱稳定性,故JFP-Ps可用于酸性和碱性食品中。
2.6 JFP-Ps溶液耐盐性研究
JFP-Ps溶液的耐盐性如图7所示,5% NaCl溶液和5% KCl溶液对JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度的影响存在差异。Na+的加入使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度随着时间的延长而减小,放置3 d后的表观粘度变化量(0.23 mPa·s)大于放置1~ 2 d的表观粘度变化量(0.09 mPa·s),原因可能是Na+与JFP-Ps分子上的羟基反应生成钠盐[28],阻碍了分子间缔合氢键的形成,造成表观粘度的下降。K+的加入使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度随着时间的延长而增大,加入KCl的JFP-Ps溶液放置4 d时,JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度升高了0.22 mPa·s,说明K+与JFP-Ps分子间可能发生了交联反应[31],可能是K+减少了JFP-Ps分子的电荷,促使可溶性分子配合物的产生[32],掩盖了半乳糖醛酸残基之间的静电作用,溶液的聚合更加灵活[33],从而使表观粘度增大。溶液在放置4 d后表观粘度变化不大,说明JFP-Ps有良好的耐盐特性,可应用于高盐食品中。
2.7 JFP-Ps粘弹性测量分析
储能模量G'指粘弹性材料在交变应力作用下一个周期内储存能量的能力,通常指弹性;耗能模量G''指在一个变化周期内所消耗能量的能力,通常指粘性。本实验用频率振荡测试JFP-Ps溶液的粘弹特性,不同浓度JFP-Ps振荡测试结果如图8所示。JFP-Ps溶液的储能模量G'和损耗模量G''随着溶液浓度的增大而上升,这是由于在低浓度下不能参与非共价交叉连接的分子间带,在较高的浓度下可以形成结合带[19],使分子间网络增多。浓度为0.4%、0.8%和1%的JFP-Ps溶液的储能G′和损能G″随着频率的增大而增大,且G′一直高于G″,表明在0.1~10 Hz整个频率范围内,JFP-Ps仍表现出弹性行为,呈现凝胶性质。此时高浓度下的JFP-Ps溶液可能会形成凝胶网络[31],其凝胶的稳定与其浓度有一定的依赖性,呈现的凝胶性质可能与其具有的三维网状结构、官能团、交联程度及聚合度等相关[34]。
2.8 JFP-Ps溶液的抗降解性能
如图9所示,JFP-Ps溶液在放置0~12 h时,多糖溶液表观粘度逐渐由3.16 mPa·s下降至2.49 mPa·s,可能是多糖自身带有的α-半乳糖苷酶和β-甘露聚糖酶起到降解作用,以及其他微生物的侵蚀作用导致表观粘度降低[35]。12~48 h时,多糖溶液表观粘度下降速率变慢,变化量为0.3 mPa·s,放置超过48 h后,溶液表观粘度基本不变,表明JFP-Ps具有良好的抗降解性能。郭守军[30]和朱科学等[32]研究结果表明带形蜈蚣藻多糖溶液和苦丁茶冬青多糖溶液均具有良好的抗降解性能,本实验研究结果与之相一致。
3. 结论
JFP-Ps为“非牛顿流体”,呈现假塑性行为,具有良好的抗降解性能;JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度与浓度呈正相关,随剪切速率的增加呈现剪切稀释现象;随着温度的升高,JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度降低;冷冻(−20 ℃)和冷藏(4 ℃)均能使JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度增加;JFP-Ps溶液表观粘度随加热时间的增加而增大,当加热时间超过1.5 h时,JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度逐渐减小;JFP-Ps溶液在pH4~10范围内表观粘度值变化不大;Na+的加入使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度减小,K+的加入使JFP-Ps溶液的表观粘度增大;在粘弹性测试中,JFP-Ps的储能G′和损能G″随着频率的增大而增大,且G′始终高于G″,另外,JFP-Ps溶液的储能模量G'和损耗模量G''随着溶液浓度的增大而上升,呈现凝胶性质;研究表明,JFP-Ps具有良好的酸碱稳定性、耐盐稳定性和良好的抗降解性能,可广泛应用于酸性或碱性食品、高盐食品、冷冻冷藏食品等食品中。本研究为JFP-Ps在食品工业中的功能食品、食品感官评价及天然增稠剂的选择提供了一定的理论支持。
-
-
[1] HU Q B, HU S Q, FLEMING E, et al. Chitosan-caseinate-dextran ternary complex nanoparticles for potential oral delivery of astaxanthin with significantly improved bioactivity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020:151.
[2] ZHU K X, ZHANG Y J, NIE S P, et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro antioxidant activities of polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. pulp[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,155:354−361. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.074
[3] 朱科学, 王颖倩, 张彦军, 等. 菠萝蜜多糖对脾淋巴细胞抗氧化作用及免疫功能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(23):207−212. [ZHU K X, WANG Y Q, ZHANG Y J, et al. Antioxidant and immunoenhancing activity of polysaccharide from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. on spleen lymphocytes[J]. Food Science,2017,38(23):207−212. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201723033 [4] 张婷. 紫芝菌丝体多糖的分离纯化、结构鉴定及生物活性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. ZHANG T. Extraction, purification, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum Mycelium [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[5] 刘袆帆. 兜唇石斛免疫活性多糖及抗氧化肽的结构鉴定及功能表征[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. LIU Y F. The identification of structure and characterization of immunoregulatory polysaccharide and antioxidative peptides isolated from Dendrobium aphyllumin[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
[6] 刘瑶. 玫瑰花多糖的提取及功能性饮料的制备[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2017. LIU Y. Study on extraction of rose polysaccharide and preparation of functional beverage [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2017.
[7] 吴少微. 鸡骨草多糖的生物活性、结构解析及快速制备活性多糖的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016. WU S W. Biological activities and structural characteristics of polysaccharides from Abrus cantoniensis and the rapid preparation for the bioactive polysaccharide [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016.
[8] BAO H, YOU S G, CAO L K, et al. Chemical and rheological properties of polysaccharides from fruit body of Auricularia auricular-judae[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,57:30−37. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.12.031
[9] MA F Y, ZHANG Y, LIU N H, et al. Rheological properties of polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb[J]. 2017, 227: 64−72.
[10] IAGHER F, REICHER F, GANTER J. Structural and rheological properties of polysaccharides from mango (Mangifera indica L.) pulp[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2002,31(1-3):9−17. doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00044-2
[11] 张彦军, 王少曼, 左慧玉, 等. 菠萝蜜主要功能活性成分及其研究进展[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2019,37(6):16−22. [ZHANG Y J, WANG S M, ZUO H Y, et al. Research progress on main functional components of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2019.06.003 J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,37(6):16−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2019.06.003
[12] 梁裕崴. 菠萝蜜果酒酵母的选育及发酵工艺的研究[D]. 湛江: 广东海洋大学, 2019. LIANG Y W. Study on the yeast breeding and fermentation technology of jackfruit fruit wine[D]. Zhanjiang: Guangdong Ocean University, 2019.
[13] 刘学敏, 李宗锴, 高梅, 等. 菠萝蜜良种“马来西亚一号”在滇东南热区的引种推广与发展对策[J]. 热带农业科技,2018,41(2):18−23. [LIU X M, LI Z K, GAO M, et al. The status of Malaysian Latex-free Jackfruit No. 1 in Yunnan southeast tropical zone[J]. Tropical Agricultural Science & Technology,2018,41(2):18−23. [14] 姚思雯, 何佳丽, 朱科学, 等. 菠萝蜜多糖体外酵解特征研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(3):87−94. [YAO S W, HE J L, ZHU K X, et al. In vitro fermentation characteristics of polysaccha- rides from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. pulp[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(3):87−94. [15] CALVO C, FERRER M R, MARTINEZ-CHECA F, et al. Some rheological properties of the extracellular polysaccharide produced by volcaniella eurihalina F2-7[J]. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology,1995,55(1):45−54.
[16] B Q G A, B S W C, B Q W, et al. Microstructure and rheological properties of psyllium polysaccharide gel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2009,23(6):1542−1547. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.10.012
[17] 杨永利, 郭守军, 何都能, 等. 鹿角海萝多糖的流变性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2007(7):103−106. [YANG Y L, GUO S J, HE D N, et al. Rheological study of polysaccharides from Gloiopeltis tenax[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2007(7):103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2007.07.029 [18] 郭守军, 杨永利, 林杜鑫. 龙须菜多糖的流变性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2009,25(4):23−27. [GUO S J, YANG Y L, LIN D X. Study on rheological properties ofGracilaria lamaneiformis polysaccharide[J]. Food & Machinery,2009,25(4):23−27. [19] ANVARI M, TABARSA M, CAO R A, et al. Compositional characterization and rheological properties of an anionic gum from Alyssum homolocarpum seeds[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52:766−773. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.07.030
[20] WU Y, CUI S W, WU J H, et al. Structure characteristics and rheological properties of acidic polysaccharide from boat-fruited sterculia seeds[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,88(3):926−930. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.01.035
[21] CHEN Y, ZHANG J G, SUN H J, et al. Pectin from Abelmoschus esculentus: Optimization of extraction and rheological properties[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,70:498−505. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.07.024
[22] ZISENIS M. Correlation of molecular orientation and shear viscosity of high molar mass polymers in dilute solution[J]. European Polymer Journal,1997,33(5):773−780. doi: 10.1016/S0014-3057(96)00150-4
[23] 刘楠华. 怀山药多糖铁补血活性及怀山药多糖乳化和流变性研究[D]. 开封: 河南大学, 2016. LIU N H. Antanemic activities of Huaishanyao(Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) polysacc- haride iron complex and the emulsification & rheology study on polysaccharide [D]. Kaifeng: Henan University, 2016.
[24] 朱会霞, 孙金旭, 王灿. 樟芝多糖流变特性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2011,32(1):10−13. [ZHU H X, SUN J X, WANG C. The rheology study for antrodia camphorate[J]. Food Research and Development,2011,32(1):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2011.01.005 [25] XU J L, ZHANG J C, LIU Y, et al. Rheological properties of a polysaccharide from floral mushrooms cultivated in Huangshan Mountain[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,139:43−49. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.12.011
[26] STOKES J R, MACAKOVA L, CHOJNICKA-PASZUN A, et al. Lubrication, adsorption, and rheology of aqueous polysaccharide solutions[J]. Langmuir,2011,27(7):3474−3484. doi: 10.1021/la104040d
[27] GALLAO M I, NORMANDO L D O, VIEIRA I G P, et al. Morphological, chemical and rheological properties of the main seed polysaccharide from Caesalpinia ferrea Mart[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2013,47:58−62. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.02.035
[28] 蒋建新, 朱莉伟, 张卫明, 等. 塔拉多糖胶的研究[J]. 西南林学院学报,2003(4):12−16. [JIANG J X, ZHU L W, ZHANG W M, et al. Study on properties of Caesalpinia spinosa polysaccharide gum[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry College,2003(4):12−16. [29] 菅红磊, 朱莉伟, 张卫明, 等. 两种皂荚多糖胶流变性质的表征[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(17):68−72. [JIAN H L, ZHU L W, ZHANG W M, et al. Rheological characteristics of gums from Gleditsia sinensis Lam. seeds with different Shapes[J]. Food Science,2010,31(17):68−72. [30] 郭守军, 杨永利, 谢泳娴, 等. 带形蜈蚣藻多糖的流变性研究[J]. 广东农业科学,2014,41(16):112−115. [GUO S J, YANG Y L, XIE Y X, et al. Study on the rheological properties of polysaccharides from Centipede algae[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2014,41(16):112−115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.16.024 [31] 查春节. 龙眼多糖的流变性、结构鉴定及其清除自由基活性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2013. CHA C J. Rheological properties, Structure identification and the activity of scavenging radicals of polysaccharide extracted from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.)[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013.
[32] 朱科学, 赵书凡, 朱红英, 等. 苦丁茶冬青多糖流变学特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(22):61−65, 70. [ZHU K X, ZHAO S F, ZHU H Y, et al. Rheological properties of polysaccharide isolated from Ilex Kudingcha C. J. Tseng[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(22):61−65, 70. [33] KONTOGIORGOS V, MARGELOU I, GEORGIADIS N, et al. Rheological characterization of okra pectins[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,29(2):356−362. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.04.003
[34] 林丽华. 凉粉草多糖提取优化、理化性质及流变胶凝特性研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2017. LIN L H. Polysaccharide from Mesona chinensis: Extraction optimization, physicochemical characterizations, rheological and gelling properties[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2017.
[35] 蒋建新, 朱莉伟, 安鑫南. 植物多糖胶流变性质的研究[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2003,22(5):29−32. [JIANG J X, ZHU L W, AN X N. Studies on rheologies of plant polysaccharide gum[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources,2003,22(5):29−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9690.2003.05.011 -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 马金花,马紫荆,王晓雨,常晨光,黄文书. 超高压均质对非浓缩还原甜瓜汁的流变学特性研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(04): 171-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾凤娟,高世伟,黄姗,冯莉莉,杨耀红. 菠萝蜜果皮废弃生物质的多糖提取工艺及其絮凝效果研究. 环境科学与管理. 2024(11): 100-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 魏团团,王慧蕊,孙闫小凡,柯悦,郑扬,刘舒,何云海,任丹丹,汪秋宽. γ射线辐照降解多糖研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨静兰,蔡燕雪,王弘,王际辉,杨金易. 超声波-微波处理条件对西兰花泥总酚含量及其品质的影响. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(20): 287-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘艺珠,刘佩冶,赵玉梅,曹建康. 黄花菜多糖的表征与抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2022(12): 54-61 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王自凡,卢永仲,张振. 响应面优化白芨多糖提取工艺及流变性研究. 中国调味品. 2022(07): 58-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘荣柱,郭东东,潘旭,常明昌,孟俊龙,耿雪冉,程艳芬,徐丽婧. 超声辅助低共熔溶剂提取鳞杯伞多糖工艺优化及结构和流变学特性. 食用菌学报. 2022(06): 67-77 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



