Preparation and Emulsifying Properties of Maillard Reaction Products of Soybean Protein Isolate under High Hydrostatic Pressure
-
摘要: 本文研究超高压(High Hydrostatic Pressure,HHP)条件下,不同压力(0.1、100、200、300 MPa)在60 ℃时,对大豆分离蛋白(Soybean Protein Islates,SPI)与果糖(Fructose,Fru)美拉德反应产物的影响。以接枝度及乳化活性为指标,并分析最佳条件下所得产物以及产物乳状液的结构性质。结果表明在压力200 MPa、质量比0.8:1、反应时间24 h、溶液pH 8.0条件下,产物的乳化活性及乳化稳定性均有提升,乳化活性为(85.36±0.04) m2/g,是SPI与Fru混合物的1.71倍,是SPI的2.17倍,乳化稳定性为(27.66±0.03) min,是SPI与Fru混合物的1.15倍,是SPI的1.40倍。凝胶电泳图分析表明糖分子以共价键的形式接入到SPI分子中。圆二色谱图分析得知在200 MPa的条件下改性SPI二级结构发生改变,内源荧光光谱分析表明在200 MPa的压力可以使SPI的空间结构发生改变。粒径、电位和激光共聚焦显微镜微观图均可表明200 MPa的压力对蛋白乳状液稳定性的提升。Abstract: In this paper, the effects of high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) on Maillard reaction products of soybean protein isolate (SPI) and fructose (Fructose, Fru) at 60 ℃ under different pressures (0.1, 100, 200, 300 MPa) were studied. The grafting degree and emulsifying activity were used as indicators, and the structural properties of the products under the optimal conditions were analyzed. The results showed that under the conditions of pressure being 200 MPa, mass ratio 0.8:1, reaction time 24 h, and solution pH8.0, the emulsifying activity and emulsifying stability of the product were improved. The emulsifying activity was (85.36±0.04) m2/g, 1.71 times higher than the SPI and Fru mixture, 2.17 times higher than the SPI, and the emulsifying stability was (27.66±0.03) min, 1.15 times higher than the SPI and Fru mixture, and 1.40 times higher than the SPI. SDS-PAGE indicated that the sugar molecules were inserted into the SPI molecule through covalent bonds. Circular dichroism analysis showed that the secondary structure of modified SPI changed under the condition of 200 MPa. Endogenous fluorescence analysis showed that the spatial structure of SPI could be changed under 200 MPa. The particle size, potential and laser scanning confocal microscope micrographs showed that the stability of protein emulsion was improved by 200 MPa pressure.
-
大豆分离蛋白(Soybean Protein Isolate, SPI)是一种含有多种必需氨基酸及丰富不饱和脂肪酸的植物蛋白,其蛋白含量在90%以上。主要由大豆球蛋白和β-伴大豆球蛋白组成[1]。大豆分离蛋白因其营养价值和表面活性,常作为乳化剂被广泛应用于食品配方中。然而由于一些外界加工条件(如温度、pH、浓度等),蛋白的乳化性质受到了一定影响[2]。随着温度的下降,水相中会形成尖锐的冰晶,穿透油水界面并使乳液变得不稳定[3]。而ZHANG等[4]发现调节pH可以大幅度增强大豆分离蛋白的乳化能力和乳化稳定性。所以为了提高其乳化性以适用于更多的生产,要对大豆分离蛋白进行改性。目前常用的化学改性方法有酸碱化、酰化、脱酰化、磷酸化、糖基化(即美拉德反应)等[5]。
蛋白质的美拉德反应是指碳水化合物和蛋白质的结合物在加热条件下自发产生,不使用对人体害的化学产品。反应可以分为三个阶段:初级、中级和高级。初始阶段包括还原糖的羰基与蛋白质可利用的Ɛ-氨基(赖氨酸是主要的活性氨基)缩合形成席夫碱,以及Amadori化合物的重排[6]。研究证明在初始阶段蛋白质与糖可以通过共价键持久结合,从而使酸碱度、离子强度和温度的变化等对结合产物的影响很小,且功能特性有所改善,包括乳化性质的增强。张志凯等[7]研究大豆分离蛋白与木糖的美拉德反应,得出美拉德反应可以显著增强SPI的乳化活性。左颖昕等[8]将大豆分离蛋白与葡萄糖在55 ℃条件下进行美拉德反应,其产物的乳化性质得到明显改善。但是由于美拉德反应过程复杂,如果控制不当,就会产生醛、杂环胺和晚期糖基化末端终产物等有害致癌物质[9],且到后期产物会发生褐变,不利于蛋白质的感官和营养价值。
超高压(High Hydrostatic Pressure, HHP)处理作为一种新型的加工技术,已经广泛应用于食品杀菌、物理改性以及功能性质强化等食品工业[10-11]。其压力范围为几十到几百兆帕,通过改变反应体系的压力,从而使化学平衡、反应速率以及分子结构发生改变。目前许多研究表明HHP对美拉德反应进程会产生一定影响,ISAACS等[12]指出压力极大抑制了杂环产物、类黑素和挥发物的形成。MA等[13]通过对高压下赖氨酸/精氨酸-葡萄糖/果糖模型的研究,发现高压延缓了美拉德反应的中间和最后阶段。KOBAYASHI等[14]对天冬酰胺-葡萄糖模型在100~300 MPa范围内,于120 ℃处理60 min后测定丙烯酰胺和类黑精的浓度。发现在高压条件下,所有模型系统中丙烯酰胺的生成都被显著抑制。BUCKOW等[15]发现牛血清蛋白与葡萄糖反应速率在0.1~600 MPa压力范围内,随着压力的升高而降低。因此,利用HHP对美拉德反应中后期具有一定的抑制作用,从而控制美拉德反应的进程以获得理想的产物,对超高压联合美拉德反应条件的选择也显得尤为重要。
近几年超高压多用于蛋白质的预处理,在适当的温度和压力下,蛋白质结构展开,有利于蛋白质与糖的共价结合。而对于蛋白与糖在HHP条件下发生美拉德反应,所得产物(Maillard Reaction Products, MRPs)功能性质(例如乳化性质)的研究报道很少见。本文通过测定反应产物的接枝度及乳化性质,确定HHP下美拉德反应的最佳条件,以及在此条件下产物及其乳状液的结构性质。为制备优良性质的SPI乳状液提供新的技术方法,为拓宽SPI作为乳化剂在食品工业中的应用提供了理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆分离蛋白、果糖、半乳糖、葡聚糖、海藻酸钠、魔芋胶 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;九三非转基因大豆油 九三集团哈尔滨惠康食品有限公司;十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)和邻苯二甲醛(OPA) 美国Sigma试剂公司;牛血清蛋白、考马斯亮蓝G-250 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钠等其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
HHP-400高压设备 沈阳人和机电工程设备有限公司;PHS-3C精密pH计 上海雷磁新径仪器有限公司;UV2600紫外-可见光分光光度计 日本岛津有限公司;数显恒温水浴箱 常州丹瑞实验仪器设备有限公司;RET control/t磁力搅拌器、T50高速匀浆机 德国IKA公司;SDS-PAGE电泳仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;CD J-815圆二色谱仪 日本JASCO公司;F4500荧光分光光度计 日本日立有限公司;Malvern激光粒度及ZETA电位仪 英国马尔文公司;SP-2激光共聚焦显微镜 徕卡显微系统贸易有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 MRPs的制备
1.2.1.1 制备工艺
将SPI分别与糖按不同糖-蛋白质量比(0.4:1、0.6:1、0.8:1、1:1、1.2:1, g:g)溶解于0.05 mol/L pH7.0、7.5、8.0、8.5、9.0磷酸盐缓冲液中,室温搅拌2 h后,在4 ℃的条件下水化24 h。置于不同压力条件下(0.1、100、200、300 MPa)反应(12、18、24、30、36、42 h),反应结束后测定所有反应产物的接枝度及乳化活性。
1.2.1.2 糖的选择
将5组含有2%(W/V)的SPI溶于磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.05 mol/L, pH8.0)中,分别向其中加入果糖、半乳糖、葡聚糖、海藻酸钠和魔芋胶,蛋白质与糖的质量比为1:1。磁力搅拌器在室温条件下搅拌2 h,在4 ℃的条件下水化24 h,使蛋白与糖充分接触水合。转移至PVC袋中封口,放入超高压处理腔内,升压至实验所需压力,再使水浴温度达到60 ℃,处理24 h后取出。反应结束后测定5组反应产物的接枝度及乳化活性,确定合适的糖。
1.2.1.3 SPI-糖质量比对美拉德反应的影响
将2%(W/V)的SPI和1.2.1.2中选择的糖与SPI分别按0.4:1、0.6:1、0.8:1、1:1、1.2:1的比例溶于磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.05 mol/L,pH8.0)中配制成混合溶液,磁力搅拌器(1000 r/min)在室温条件下搅拌2 h,在4 ℃的冰箱中水化24 h,使蛋白与糖充分接触水合。转移至PVC袋中封口,将样品放入超高压处理腔中,升压至实验所需压力,再使水浴温度达到60 ℃,处理24 h后取出。处理压力分别为:0.1、100、200、300 MPa,处理时间:24 h。反应结束后测其反应产物的接枝度及乳化活性。
1.2.1.4 反应时间对美拉德反应的影响
将2%(W/V)SPI和糖以质量比(0.8:1)溶于磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.05 mol/L,pH8.0)中配制成混合溶液,其他方法同1.2.1.3,高压处理时间分别为:12、18、24、30、36、42 h,反应结束后测其反应产物的接枝度及乳化活性。
1.2.1.5 缓冲溶液pH对美拉德反应的影响
将2%(W/V)SPI和一定比例的糖分别用0.05 mol/L pH7.0、7.5、8.0、8.5、9.0磷酸盐缓冲溶液配制成混合溶液,其他方法同1.2.1.3。反应结束后测其反应产物的接枝度及乳化活性。
1.2.1.6 接枝度的测定
根据JIANG[16]的方法并稍作改动。将样品浓度调整为2 mg/mL,取200 μL加入到4 mL OPA试剂中,在35 ℃水浴中反应2 min,测定样品在340 nm处的吸光值。空白对照组为4 mL OPA+200 μL去离子水。(OPA试剂的制备:40 mg OPA溶于1 mL甲醇,加入25 mL 0.1 mol/L硼砂溶液,2.5 mL 20%(W/W)SDS溶液,100 μL β-巯基乙醇,用去离子水定容至50 mL。)
接枝度由下式计算:
DG(%)=A0−AtA0×100 式中:At为美拉德反应产物溶液在波长340 nm处的吸光值;A0为未经美拉德反应的蛋白质溶液在波长340 nm处的吸光值。
1.2.1.7 乳化活性的测定
乳化活性(Emulsifying Activity Index, EAI)是根据ZHAO等[17]的方法,稍作改动。反应结束后,用0.1 mol/L pH7.0磷酸盐缓冲液将上述糖基化蛋白与原2% SPI(作为对照)配制成浓度为1 mg/mL的样品溶液15 mL,分别向其中加入5 mL的大豆油,随后在室温下用高速均质机均质在10000 r/min条件下均质1 min,立即从几种乳化液的同一位置取样50 μL,加入到1 mg/mL的SDS溶液中,混匀后测定500 nm处的吸光值。按上述方法测定的吸光值记为A0,用作空白对照组的是0.1%的SDS溶液。
EAI(m2/g)=2×2.303×A0×DFc⋅ϕ⋅θ×104 式中:c为乳化前的蛋白浓度(g/mL);ϕ为代表光学路径(1 cm);θ为油相比例0.25;DF为稀释倍数100。
1.2.2 MRPs的结构分析
1.2.2.1 MRPs的制备
在1.2.1实验中所得的最佳条件下(果糖-蛋白质量比:0.8:1,反应时间:24 h,pH8.0),分别在60 ℃、200 MPa超高压装置及60 ℃常压水浴中制备SPI美拉德反应产物(分别记为200-MRPs及0.1-MRPs)。再将蛋白与糖按质量比0.8:1在常温常压条件下于pH8.0的磷酸盐缓冲液中混合均匀24 h(记为SPI-Fru-Mix)。
1.2.2.2 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分析
根据LAEMMLI等[18]的电泳方法并稍作修改,方法如下:
制胶:配制12%分离胶和5%浓缩胶,小心注入凹型玻璃板与平玻璃板之间,避免产生气泡,插入梳子等待凝胶形成。
样品处理:将1.2.2.1的3种样品(200-MRPs、0.1-MRPs、SPI-Fru-Mix)与2% SPI浓度均调整到2 mg/mL,再加入等体积的样品缓冲液(0.15 mol/L、pH6.8的Tris-HCl溶液中加入4% SDS、2% β-巯基乙醇、20%甘油和0.02%溴酚蓝)。
电泳:样品在水浴中煮沸5 min,冷却后用进样针向孔中注入10 μL。倒入电极缓冲液(pH8.3、0.1% SDS、0.384 mol/L甘氨酸和0.05 mol/L Tris)开始电泳,初始电压为80 V,当样品进入到分离胶后,将电压增大到120 V,当到达距底部还有1 cm时结束。
染色:取出凝胶放入平皿中,在考马斯亮蓝R-250染色液(向100 mL 50%甲醇、6.8%乙酸混合溶液中加入0.1 g R-250考马斯亮蓝)中染色10 min,平皿置于水平摇床上不断摇晃。
脱色:将凝胶放置于脱色液(7.5%冰醋酸,5%甲醇)脱色,直至胶背景透明。
1.2.2.3 圆二色性光谱分析
圆二色性光谱(Circular Dichroism, CD)是根据FU等[19]的方法并稍作改动。用磷酸缓冲液(10 mmol/L,pH7.0)将样品200-MRPs、0.1-MRPs、SPI-Fru-Mix、SPI稀释至浓度为0.1 mg/mL 置于CD J-815圆二色谱仪上进行测定。光谱分析条件:扫描范围:190~250 nm、扫描速度为50 nm/min、光谱间隔1 nm,狭缝宽1 nm、灵敏度20 mdeg。通过仪器提供的软件:the Model JWSSE-480 Protein Secondary Structure Estimation Program,由仪器提供的Reed氏参照CD光谱估算花生球蛋白二级结构中α—螺旋,β—折叠,β—转角和无规卷曲所占的比率。
1.2.2.4 内源荧光光谱分析
参照LI[20]的方法并略作调整。用0.01 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH7.0)将样品稀释至浓度为1 mg/mL。设定参数:荧光光谱激发波长295 nm,扫描发射光谱范围310~450 nm,激发和发射狭缝宽度均5 nm,间隔为0.2 nm,扫描速度为1200 nm/min,光电倍增管负高压400 V。
1.2.3 MRPs乳状液的性质
1.2.3.1 乳状液的制备
参照根据SHI等[21]的方法,稍作改动。取一定量的200-MRPs、0.1-MRPs、SPI-Fru-Mix以及2% SPI,用0.1 mol/L、pH7.0的磷酸盐缓冲液配制为蛋白浓度为1 mg/mL的溶液15 mL,分别向其中加入5 mL的大豆油,随后在室温下用高速均质机均质在10000 r/min条件下均质1 min,均质后加入0.02% NaN3抑菌剂,测定乳状液的乳化活性、乳化稳定性、粒径、电位以及微观特征。
1.2.3.2 乳化活性和乳化稳定性
参照1.2.1.7的方法测定上述乳状液的吸光度A0。乳状液静置10 min后,依照同样的方法测定溶液的吸光值A10。根据下列公式计算乳化稳定性(Emulsifying Stability Index, ESI):
ESI(min)=A0A0−A10×10 1.2.3.3 乳状液的粒径
将1.2.3.1均质后的乳状液,使用Malvern激光粒度分析仪测定几种乳状液的粒度分布。
1.2.3.4 乳状液的电位
将1.2.3.1均质后的乳状液分别用pH7.0、0.01 mol/L的磷酸盐缓冲液调整到合适的浓度[22],注入到毛细管吸收池中,使用Malvern电位仪测定四种乳状液的电势。
1.2.3.5 乳状液微观观察
乳状液中油滴和蛋白质的大小及分布等微观信息可用激光共聚焦显微镜(Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, CLSM)进行观察。荧光染料配制方法如下:油滴染色采用尼罗红无水乙醇溶液(1 mg/mL)为染料,激发波长为488 nm;蛋白质染色采用尼罗蓝异丙醇溶液(1%)为染料,激发波长为633 nm;两种染料均需避光保存。
向1 mL乳状液加入25 μL尼罗红染色液和20 μL尼罗蓝染色液,振荡混匀后避光静置0.5 h。在提前清洁过的载玻片上滴加约5 μL处理好的乳状液,涂布均匀后盖上盖玻片,为防产生气泡要缓慢进行,将制备完成的样品放在载物台上,在较短的时间内用40倍物镜观察乳状液的共聚焦图像。
1.3 数据处理
每组试验进行三次重复独立操作,其结果表示为X±SD。数据分析采用软件Statistix 8.1和Origin 8.0,P<0.05表示差异显著,P>0.05表示差异不显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蛋白质-糖美拉德反应条件的筛选
2.1.1 糖的选择
由图1可知,分别向蛋白溶液中加入等量的不同种类的糖,在200 MPa的高压装置中反应24 h后,半乳糖的接枝度达到最高,为(36.08%±0.021%),其次是果糖,为(32.69%±0.109%)。葡聚糖、海藻酸钠以及魔芋胶的接枝度均较弱。可能由于半乳糖与果糖为单糖反应速度较快,而海藻酸钠及魔芋胶是结构较为复杂的多糖,与蛋白反应的基团可能被埋藏在多糖的内部结构,与蛋白反应的概率降低。并且多糖具有较弱的还原性和较强的分子空间位阻[23],所以接枝度较低。果糖美拉德反应产物的乳化活性(79.33±0.03)m2/g高于半乳糖且高于其他四种糖(P<0.05),比未经任何处理的SPI增加了(39.79±0.024)m2/g。可能由于溶液粘度不同,与SPI共价结合后,较高的溶液粘度会削弱蛋白的界面性质[24]。果糖在该实验中展现出了良好的接枝度及乳化活性,故本试验选择果糖作为还原糖,与SPI进行美拉德反应。
2.1.2 糖-蛋白质质量比对美拉德反应接枝度及乳化性的影响
由图2(a)可知,当压力达到100、200或300 MPa时,SPI-Fru的接枝度在不同质量比条件下均呈下降趋势,低于0.1 MPa(P<0.05)。可推测出SPI-Fru美拉德反应在压力达到或超过100 MPa时,SPI-Fru美拉德反应受到抑制。因为在恒定温度下,此反应的产物体积大于反应物体积,增加压力会使反应速率降低[25]。随着果糖比重的增加,产物接枝度呈现先上升后下降的趋势,与GU等[26]研究所得改性产物接枝度变化趋势相似。可能因为当果糖加入过多时,使空间位阻加大,对果糖-蛋白反应产生阻碍,所以当果糖与蛋白的质量比超过0.8:1后反应接枝度降低。图2(b)当压力为200 MPa时SPI-Fru的乳化活性达到最大,高于其他压力条件下的乳化活性(P<0.05)。推测原因可能是,当压力为0.1 MPa和100 MPa时美拉德反应程度较大,影响了产物的乳化活性。当Fru与SPI的质量达到0.8:1时乳化活性在不同压力作用下同样均达到最大,最大为(85.36±0.04)m2/g。当果糖的添加量过多时乳化活性也逐渐下降,与ZHAO等[17]的研究结果表示一致。引入过量的果糖分子基团,可能会导致蛋白分子在油水界面的吸收速度降低,内部结构的展开和复位也受到影响,从而降低了乳化活性[27]。
2.1.3 高压反应时间对产物接枝度及乳化性的影响
由图3(a)可知,SPI-Fru在0.1 MPa下的接枝度与100 MPa无显著差异(P>0.05),较高的压力对反应有抑制作用。随着反应时间的增加,SPI-Fru的接枝度逐渐上升,24 h后接枝度的增加速率明显减缓。可能由于较长时间的反应导致果糖碱性降解,从而使SPI-Fru相互作用减缓[28]。另一方面,可能由于在有限的反应空间内,赖氨酸容易与果糖迅速结合,而剩余的氨基酸越来越难以接进果糖分子,反应时间增加剩余反应基团的数量也在减少,使反应速率降低[29]。与此同时反应随着时间会产生不理想的颜色和风味,还会增加其他不溶性聚合物生成的可能性。这些不溶性的聚合物是美拉德反应的副产物,对人体健康有害[30]。图3(b)可知,当反应条件为24 h、200 MPa时,反应产物的乳化活性达到最大。且随着时间的延长乳化活性降低,该现象与XU等[24]报导的SPI与葡萄糖反应产物乳化活性结果类似。可能因为SPI-Fru产物的生成降低了分子的流动性,削弱了蛋白在油水界面的吸附作用。所以选择24 h作为反应的最佳时间。
2.1.4 缓冲溶液pH对美拉德反应接枝度及乳化性的影响
如图4(a)所示,反应接枝度随着pH的升高而上升,除0.1 MPa外,其他三种压力的反应速率均在pH8.0时较大,但是并不明显。可能因为碱性条件下有利于美拉德反应的进行,但是反应进行程度较大,颜色和风味不利于加工生产的应用。图4(b)所示,SPI-Fru反应产物的乳化活性在pH<8.0时逐渐增加而在pH>8.0后随着pH的增加没有显著升高(P>0.05),分析原因可能是由于pH在7.0~8.0之间糖基化的SPI溶解度逐渐升高,而pH>8.0后趋于平缓。蛋白的溶解性会对其乳化活性产生一定的影响[31],所以乳化活性也有所改善且在200 MPa条件下效果最好。所以后续试验选择在pH8.0的缓冲溶液中进行。
2.2 MRPs的结构分析
2.2.1 MRPs SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分析
采用聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)来进行蛋白质分子量的分析。蛋白质与糖形成美拉德反应共价交联后其分子量会发生变化。如图5所示,结果与ZHANG等[32]报道的SPI图谱一致。泳道4展示了SPI的β-伴大豆球蛋白(条带α',α,β)和大豆球蛋白(条带A,B)。泳道1与2的顶端都有新的条带产生,说明有较大分子量的聚合物产生。且泳道2顶端比泳道1更深,这表明200 MPa的高压可以抑制美拉德反应的进行,与SPI-F美拉德反应产物接枝度的结果一致。泳道3的条带α',α,β和A几乎没有,可能因为糖包裹在蛋白分子上,使得蛋白分子不能与SDS很好的结合,因此在图中颜色最浅。
2.2.2 圆二色性光谱分析
远紫外区域圆二色光谱(Far-UV CD)用于研究蛋白的二级结构[33]。根据样品的圆二色性光谱,可计算出SPI-Fru二级结构种类的相对含量。蛋白质的主要二级结构是有序结构如α-螺旋和β-折叠,以及非有序结构如β-转角和无规则卷曲。这些结构的含量变化可以反映蛋白质分子的疏松程度。如表1和图6可知,与SPI相比,SPI-Fru-Mix二级结构的数值变化较小,这说明糖与蛋白简单混合对蛋白质结构影响弱于美拉德反应,与前人用葡聚糖与荞麦分离蛋白混合物与荞麦分离蛋白的对比结果一致[34]。改性后SPI的二级结构发生了变化,大豆分离蛋白的β-转角和无规则卷曲含量增加,α-螺旋和β-折叠含量减少,经过200 MPa高压处理产物结构的含量变化更显著(P<0.05)(表1)。这表明在反应过程中,蛋白质分子被糖分子完全延伸,内部基团暴露,这导致α-螺旋和β-折叠结构分解[35]。并且样品200-MRPs中α-螺旋含量最少以及无规则卷曲含量最多说明HHP可以进一步促进SPI结构的展开,使SPI结构由紧密变得松散,提高蛋白质的柔韧性,改性效果最好。α-螺旋在HHP和美拉德反应处理过程中被破坏,这也被ZHENG等[36]研究证实。
表 1 MRPs的二级结构组成Table 1. Secondary structure composition of MRPs样品 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规则卷曲(%) 200-MRPs 9.56±0.01d 16.36±0.02d 17.05±0.02b 57.03±0.02a 0.1-MRPs 10.63±0.03c 20.05±0.04c 22.36±0.03a 46.96±0.02d SPI-Fru-Mix 14.15±0.02b 26.38±0.05b 11.45±0.01c 48.02±0.04c SPI 14.60±0.01a 27.03±0.02a 10.22±0.02d 48.69±0.03b 注:不同小写字母表示样品间差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.2.3 内源荧光光谱分析
内源荧光光谱可用来获取蛋白质的结构信息。蛋白质分子中内源荧光主要来自芳香族氨基酸:色氨酸(Trp)、酪氨酸(Tyr)以及苯丙氨酸(Phe)。因为这两种氨基酸残基Trp及Tyr残基对环境变化较敏感,所以多用Trp的荧光强度来研究蛋白接构象的变化[37]。当Trp残基处在偏极性的微环境时,其最大内源荧光强度会减小并且出现红移[38]。如图7所示,原始蛋白样品SPI和简单混合物SPI-Fru-Mix的荧光强度相差不大,说明简单混合对大豆分离蛋白的空间结构影响不大。而200-MRPs与0.1-MRPs产物的荧光强度显著低于两者的混合物且发生了不同程度的红移,混合物SPI-Fru-Mix的最大扫描波长(λmax)为334.8 nm,而0.1-MRPs移至340.8 nm,200-MRPs移至339.2 nm。这种现象说明美拉德反应及HHP处理的产物200-MRPs与0.1-MRPs中Trp残基周围微环境的极性变大,亲水性增加[39],200-MRPs强于0.1-MRPs。并且改变了SPI及SPI-Fru混合物的结构,使其结构变得松散[37]。HHP可以延缓美拉德反应的进程,所以200-MRPs的荧光强度及λmax均小于0.1-MRPs。
2.3 MRPs乳状液的性质
2.3.1 乳化活性及乳化稳定性
如图8所示,在超高压作用下,果糖与SPI进行美拉德反应所得产物的EAI及ESI显著提高(P<0.05)。果糖与SPI混合后,形成的SPI-Fru-Mix为非共价结合,其乳化性有所提升。将混合物在常压及200 MPa下加热反应,使果糖与SPI进行共价结合,其乳化活性分别比混合物提高了43.08%、70.79%。大部分研究表明,蛋白质与糖类共价交联所得产物的功能性质优于非共价结合,共价交联既可以不破坏糖类的原始特性又可以提高蛋白质的功能特性[40]。引入糖使得亲水基团引入到SPI上,形成的产物结合了蛋白质在油水界面上强烈的吸附特性和糖在水相介质中溶解特性,增加了界面活性,所以乳化活性提高。
SPI与Fru共价或非共价结合后,ESI也得到显著提升(P<0.05)。研究表明,将糖作为稳定剂引入水相,增加乳化系统的黏度和油-水界面稳定层的厚度,可以显著提高乳液的稳定性[41]。SPI-Fru-Mix乳液与MRPs乳液进行比较,MRPs的乳化稳定性得到得到改善。由上述2.2.3结论得知,MRPs的亲水性增强,而且与糖的结合使其空间位阻增大,油-水界面张力降低,可以有效的减少油滴之间的碰撞,以阻碍油滴絮凝,从而提高了SPI的乳化稳定性[42]。同时,可能由于与果糖反应使SPI带电荷数增多,由于静电排斥力使SPI不易聚集,乳液体系相对稳定,乳化稳定性相对提高。
由上述2.2.2得知HHP可以进一步促进SPI结构的展开,且通过2.1.2可知HHP处理后的蛋白质不会连接过多的还原糖分子,从而影响其界面活性和内部结构伸展[43],所以经处理后的MRPs乳化性显著提升(P<0.05)。与此同时HHP会抑制美拉德反应进程,使美拉德反应不会过度使破坏蛋白质的功能性质,从而降低其乳化活性及乳化稳定性。所以HHP处理后MRPs的两个性质较处理前均有所提(P<0.05)。
2.3.2 乳状液的粒径
图9(a)所示的是四种乳状液的粒度分布,用来评价乳液的乳化稳定性。SPI-Fru-Mix出现双峰而其他三个乳状液显示为单峰。呈单峰的乳状液属于单分散体系,其中粒子较小而均匀且分布在一定的尺寸范围内。呈双峰的乳状液属于多分散体系,其粒子大小不同且分布在不同的尺寸范围内[44]。与未经任何处理的SPI相比,0.1-MRPs和200-MRPs的乳液出现向较小粒度分布的方向移动,与LI等[45]研究结果相似。且经HHP处理后的MRPs乳液移动范围最大,说明其液滴粒径更小更均匀,乳化稳定更好。如图9(b)所示,SPI与果糖MRPs和Mix稳定的乳液相比,MRPs乳液的平均粒径和粒径分布(PDI)均减小,且经过高压处理的MRPs平均粒径和PDI显著小于常压下的乳状液(P<0.05)。RIES等[46]提出,与较大的液滴尺寸乳液相比,粒径较小的乳液会更稳定。可以证明,美拉德反应可以使更多的蛋白质的疏水残基暴露于油滴的表面,导致其颗粒尺寸减小,从而提供更好的乳液稳定性[47]。高压可以使蛋白质的颗粒尺寸变得更小,获得更稳定的乳状液。
2.3.3 乳状液的电位
乳状液的Zeta电位反映了乳状液颗粒表面的带电性质,粒子所带电荷越多其静电斥力越强,静电斥力可以有效防止分子的聚集,进而可以反映出乳状液的乳化稳定性[48]。由图10可以看出,在pH7.0的条件下,SPI所带电荷为负电荷,SPI与果糖混合溶液的电位为(−10.2±0.03)mV,二者在0.1 MPa发生美拉德反应后,其电位的绝对值增加了(3.66±0.04)mV,在200 MPa下的MRPs电位绝对值增加了(4.85±0.04)mV。SPI与Fru结合后乳状液电位有所降低,充分说明了带有负电荷的果糖分子与蛋白结合使其负电荷增多,在200 MPa的HHP条件下,乳状液表现出更低的Zeta电位,其乳化稳定性增强。
2.3.4 乳状液的微观观察
本实验使用激光共聚焦显微镜更直观地观察蛋白油脂所形成的乳状液的微观形态,分别使用尼罗红和尼罗蓝对油脂和蛋白进行染色,结果如图11所示,图中红色表示油脂,绿色表示蛋白。未经任何处理的SPI乳液中存在液滴的聚集和蛋白沉淀,加入糖后的SPI-Fru-Mix乳状液颗粒的分布较为均匀,但是仍有聚集和沉淀产生。经过美拉德反应的蛋白,不但油脂液滴直径减小而且蛋白与油脂分布均匀。经过HHP处理的MRPs乳状液的蛋白和油脂呈现出最佳的大小和分布,所以说明经过HHP处理的MRPs乳化性能最好。
3. 结论
本研究通过对SPI与Fru的美拉德反应条件优化,以接枝度及乳化性为指标,结果表明:200 MPa的压力对SPI-Fru的乳化性可以显著提升且接枝度较低,可以抑制美拉德反应的进行。当压力为200 MPa、质量比为0.8:1、反应时间为24 h、溶液pH为8.0时,反应的乳化活性及乳化稳定性达到最佳,乳化活性为(85.36±0.04) m2/g,是SPI-Fru-Mix的1.71倍,是SPI的2.17倍,乳化稳定性为(27.66±0.03) min,是SPI-Fru-Mix的1.15倍,是SPI的1.40倍。还通过在此条件下所制得200-MRPs与0.1-MRPs、SPI-Fru-Mix以及SPI的结构及其乳状液的结构对比,圆二色性光谱图以及内源荧光光谱图表明200 MPa下的HHP影响美拉德反应产物的结构,使其变得松散且亲水性增强。200-MRPs的乳状液的粒径变小,电位的绝对值增大且激光共聚焦呈现出粒子均匀分布。说明HHP对美拉德反应产物的乳化性质有明显的改善。本实验优化出HHP作用下,SPI与Fru的美拉德反应最佳条件,提高了SPI的乳化性质并改变其结构,是改善SPI乳化性质的有效方法。同时为SPI美拉德反应提供新的技术,使美拉德反应得到更广泛的应用。
-
表 1 MRPs的二级结构组成
Table 1 Secondary structure composition of MRPs
样品 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规则卷曲(%) 200-MRPs 9.56±0.01d 16.36±0.02d 17.05±0.02b 57.03±0.02a 0.1-MRPs 10.63±0.03c 20.05±0.04c 22.36±0.03a 46.96±0.02d SPI-Fru-Mix 14.15±0.02b 26.38±0.05b 11.45±0.01c 48.02±0.04c SPI 14.60±0.01a 27.03±0.02a 10.22±0.02d 48.69±0.03b 注:不同小写字母表示样品间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 涂宗财, 段邓乐, 王辉, 等. 微波处理对固相合成大豆分离蛋白-乳糖糖基化接枝物的影响[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(13):32−36. [TU Z C, DUAN D L, WANG H, et al. Effect of microwave treatment on solid-phase synthesis of soy protein isolate-lactose graft[J]. Food Science,2015,36(13):32−36. [2] 贾聪. 大豆蛋白及其酶解产物复合阿拉伯胶的乳化性质研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. JIA C. Study on the emulsdifying properties of soy protein and its enzymatic hydrolysates complexed with gum arabic[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[3] 王玉莹, 张安琪, 周国卫, 等. 大豆分离蛋白与单糖、双糖、多糖共价复合物的冻融特性及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):28−35. [WANG Y Y, ZHANG A Q, ZHOU G W, et al. Freeze-thaw properties and structural characterization of covalent complexes of soy protein isolate with monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):28−35. [4] ZHANG X, LUO X, WANG Y, et al. Concentrated O/W Pickering emulsions stabilized by soy protein/cellulose nanofibrils: Influence of pH on the emulsification performance[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,108:106025.
[5] KASRAN M, CUI S W, GOFF H D. Covalent attachment of fenugreek gum to soy whey protein isolate through; natural Maillard reaction for improved emulsion stability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,30(2):552−558.
[6] 樊雪静. 大豆分离蛋白—寡糖复合体系乳化性及乳化稳定性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2018. FAN X J. Research of emulsification and emulsification stability of soybean protein isolate-oligosaccharide complex system[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018.
[7] 张志凯, 肖军霞, 牟瑶瑶, 等. 大豆分离蛋白超声处理对其与木糖美拉德反应及产物乳化能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,589(24):48−54. [ZHANG Z K, XIAO Z X, MU Y Y, et al. Effect of ultrasonication of soybean protein on its Maillard reaction with xylose and emulsifying property of the resultant products[J]. Food Science,2018,589(24):48−54. [8] 左颖昕, 布冠好. 葡萄糖接枝对大豆分离蛋白功能特性和结构的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(2):58−64,71. [ZUO X Y, BU G H. Effect of glucose grafting on the functional properties and structure of soy protein isolate[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,39(2):58−64,71. [9] LASEKAN O, TEOH L S. Contribution of aroma compounds to the antioxidant properties of roasted white yam (Dioscorea rotundata)[J]. BMC Chemistry,2019,13(1):133.
[10] SONOIKE Koichiro. High pressure sterilization technology-subject for the application to food[J]. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi,1997,44(7):522−530.
[11] STADLER R H, ROBERT F, RIEDIKER S, et al. In-depth mechanistic study on the formation of acrylamide and other vinylogous compounds by the maillard reaction[J]. J Agriculture Food Chemistry,2004,52(17):5550−5558.
[12] ISAACS N S,COULSON M . Effect of pressure on processes modelling the Maillard reaction[J]. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry,1996,9(9):639−644.
[13] MA X J, GAO J Y, TONG P, et al. Tracking the behavior of Maillard browning in lysine/arginines-ugar model systems under high hydrostatic pressure: High pressure affects Maillard reaction in model systems[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2017,97(15):5168−5175.
[14] KOBAYASHI A, GOMIKAWA S, OGURO A, et al. The effect of high hydrostatic pressure on acrylamide generation in aqueous reaction systems using asparagine and glucose[J]. Food Science and technology research,2019,25(4):587−596.
[15] BUCKOW R, WENDORFF J, HEMAR Y. Conjugation of bovine serum albumin and glucose under combined high pressure and heat[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2011,59(8):3915−3923.
[16] JIANG Z, WANG L, WU W, et al. Biological activities and physicochemical properties of Maillard reaction products in sugar-bovine casein pepride model system[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(4):3837−3845.
[17] ZHAO N, ZOU H N, SUN SHUANG, et al. The interaction between sodium alginate and myofibrillar proteins: The rheological and emulsifying properties of their mixture[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,161(8):1545−1551.
[18] LAEMMLI U K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4[J]. Nature,1970,227(5259):680−685.
[19] FU L, WANG C, WANG J, et al. Maillard reaction with ribose, galacto-oligosaccharide or chitosan-oligosaccharide reduced the allergenicity of shrimp tropomyosin by inducing conformational changes[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,274(FEB.15):789−795.
[20] LI C, XUE H, CHEN Z, et al. Comparative studies on the physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate-polysaccharide conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment or classical heating[J]. Food Research International,2014,57(12):1−7.
[21] SHI Y, RONG L, LING C, et al. The antioxidant mechanism of Maillard reaction products in oil-in-water emulsion system[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,87:582−592.
[22] ZHANG X Y, WANG Q S, WU Z X, et al. An experimental study on size distribution and zeta potential of bulk cavitation nanobubbles[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials,2020,27(2):152−161.
[23] Oliveira, Fabíola C, Coimbra, et al. Food protein-polysaccharide conjugates obtained via the Maillard reaction: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2016,56(7):1108−1125.
[24] XU Z Z, HUANG G Q, XU T C, et al. Comparative study on the Maillard reaction of chitosan oligosaccharide and glucose with soybean protein isolate[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,131:601−607.
[25] CONSIDINE T, PATEL H A, ANEMA S G, et al. Interactions of milk proteins during heat and high hydrostatic pressure treatments-a review[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2007,8(1):1−23.
[26] GU F L, ABBAS S, ZHANG X M. Optimization of Maillard reaction products from casein–glucose using response surface methodology[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2009,42(8):1374−1379.
[27] 夏秀芳, 洪岩, 郑环宇, 等. 湿法糖基化改性对大豆分离蛋白溶解性和乳化能力的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(1):167−172. [XIA X F, HONG Y, ZHENG H Y, et al. Effect of wet glycosylation modification on sobubility and emulsifying activity of soybean protein isolate[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2016,16(1):167−172. [28] YANG B Y, MONTGOMERY R. Alkaline degradation of glucose: Effect of initial concentration of reactants[J]. Carbohydrate Research,1996,280(1):27−45.
[29] DARIA, TROFIMOVA, HARMEN, et al. Modification of β-lactoglobulin by oligofructose: Impact on protein adsorption at the air-water interface[J]. Langmuir:The Acs Journal of Surfaces & Colloids,2004,20(13):5544−5552.
[30] 曾稳稳, 刘玉环, 阮榕生, 等. 美拉德反应所引起的食品安全问题的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(7):447−450,454. [ZENG W W, LIU Y H, RUAN R S, et al. Research proqress in food safety issue caused by Maillard reaction[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(7):447−450,454. [31] LIU D, ZHANG L, WANG Y, et al. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on solubility and conformation changes of soybean protein isolate glycated with flaxseed gum[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,333:127530.
[32] ZHANG J, WU N, LAN T, et al. Improvement in emulsifying properties of soy protein isolate by conjugation with maltodextrin using high-temperature, short-time dry-heating Maillard reaction[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2014,49(2):460−467.
[33] BAJOVIC B, BOLUMAR T, HEINZ V. Quality considerations with high pressure processing of fresh and value added meat products[J]. Meat Science,2012,92(3):280−289.
[34] 曹丽霞. 荞麦分离蛋白-葡聚糖共价复合物的制备及乳化性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2014. CAO L X. Study of preparation and emulsifying properity of buckwheat protein isolate-dextran cojugates[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2014.
[35] DAREWICZ M, DZIUBA J. The effect of glycosylation on emulsifying and structural properties of bovine beta-casein[J]. Die Nahrung,2001,45(1):15−20.
[36] ZHENG J X, YIN H, SHEN C C, et al. Functional and structural properties of Spirulina phycocyanin modified by ultra-high-pressure composite glycation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,306:125615.
[37] 葛伟. 超声预处理对酪蛋白美拉德反应及其产物功能特性的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2015. GE W. The Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on Maillard reaction and functional properties of Maillard reaction products of casein[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2015.
[38] ZHOU T, ROSEN B P. Tryptophan fluorescence reports nucleotide-induced conformational changes in adomain of the ArsA ATPase[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1997,272(32):19731−19737.
[39] TANG C H, SUN X, FOEGEDING E A. Modulation of physicochemical and conformational properties of kidney bean vicilin (phaseolin) by glycation with glucose: Implications for structure-function relationships of legume vicilins[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(18):10114−10123.
[40] CHEN W, MA X, WANG W, et al. Preparation of modified whey protein isolate with gum acacia by ultrasound maillard reaction[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,95:298−307.
[41] DIFTIS N, KIOSSEOGLOU V. Improvement of emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate by conju-gation with carboxymethyl cellulose[J]. Food Chemistry,2003,81(1):1−6.
[42] DICKINSON E. Mixed biopolymers at interfaces: Competitive adsorption and multilayer structures[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(8):1966−1983.
[43] 薛路舟, 陈淑花, 夏远景, 等. 超高压处理对生物大分子的影响研究进展[J]. 食品工程,2009(1):20−23. [XUE L Z, CHEN S H, XIA Y J, et al. Advances of effect on ultra-high pressure treatment on biomacromolecules[J]. Food Engineering,2009(1):20−23. [44] 李媛媛, 刘骞, 汪海棠, 等. 不同质量分数阿拉伯树胶-肌原纤维蛋白共建乳状液体系的物理稳定性[J]. 食品科学,2016(11):189−196. [LI Y Y, LIU Q, WANG H T, et al. Physical stability of arabic gum at differentconcentrations-myofibrillar protein complex emulsion system[J]. Food Science,2016(11):189−196. [45] LI W, MIN W, LIU H M. Emulsifying and physicochemical properties of soy hull hemicelluloses-soy protein isolate conjugates[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,163(1):181−190.
[46] RIES D, YE A, HAISMAN D, et al. Antioxidant properties of caseins and whey proteins in model oil-in-water emulsions[J]. International Dairy Journal,2010,20(2):72−78.
[47] LI K, MENG W W, PATEL H, et al. Enhancing the stability of protein-polysaccharides emulsions via Maillard reaction for better oil encapsulation in spray-dried powders by pH adjustment[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,69(1):121−131.
[48] 柴智. 纳米营养载体中食品多糖与蛋白质复合壁材的协同稳定及控释机理[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. CHAI Z. Stabilization and controlled release mechanism of nutrients nanocarriers prepared with synergistic food polysaccharides-protein complex[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2015.





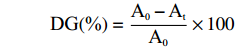
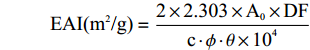
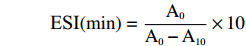

 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:
