Research Progress on the Relationship between Intestinal Flora and Extreme Environment
-
摘要: 肠道菌群的动态平衡是维持人体健康的重要标志之一,许多疾病证实与肠道菌群失调有关。环境是影响肠道菌群的重要因素,进一步可分为常规环境和特殊环境,其中关于特殊环境与肠道菌群之间相互联系的研究少之又少,而两者之间的相互作用对在特殊环境下工作的特殊人群健康具有十分重要的意义。因此,本文从特殊环境入手,重点探讨高原、航空航天、航海等几类特殊环境下人体肠道菌群的变化以及通过饮食干预调节肠道菌群,以期为适应特殊环境,改善特殊人群健康提供参考。Abstract: The dynamic balance of intestinal flora is one of the important signs of maintaining human health, and the development of many human diseases have been confirmed to be closely related to intestinal flora disorders. Environment is a crucial factor affecting intestinal flora, which can be further divided into conventional environment and extreme environment, however there are few studies on the interrelationship between the extreme environment and the intestinal flora, which is of great significance for the special crowds who work under special environment. Therefore, this article focuses on extreme environment, exploring the changes of human intestinal flora in the plateau, aerospace, navigation and other environments, as well as the regulation of intestinal flora through dietary intervention, in order to provide references for adapting to extreme environments and improving the health of special populations.
-
Keywords:
- extreme environment /
- intestinal flora /
- diet intervention /
- research progress
-
肠道菌群的稳态是维持人体健康的重要标志之一,其与人体健康之间的联系一直都是研究的热点问题。近年来随着对肠道微生物研究的深入,人们发现肠道菌群与多种疾病的发生有着密切的联系,但肠道菌群与这些疾病相互之间的关系以及相关机制尚未完全清楚,而环境因素作为联系两者之间的桥梁在其中发挥着重要作用。越来越多的研究表明,环境因素是影响肠道菌群组成和结构的关键因素[1]。近年来,研究者们已经对一些普通环境因素有了较为成熟的研究,从而将目光转向了特殊环境特殊人群肠道菌群的变化,旨在探究特殊环境对人体健康和肠道菌群的影响以及三者之间的相互作用机理。
一般来说,特殊环境包括高温、低温、缺氧环境、有毒物质、噪声、辐射和微重力等非常规环境[2]。在此环境下长期工作的人被称为特殊环境人群,如运动员、战士、航海员、宇航员等等。与处于一般生活和工作环境的健康成人比较,他们长期处于物理或化学因素的刺激下以及高强度的体力或脑力应激状态中,在生理或机体代谢方面往往会发生不正常的变化,对健康十分不利,极易发生各种疾病。肠道菌群作为参与机体代谢,维持生理功能的物质,在特殊环境下势必会发生变化:一方面,肠道菌群的种类和丰度受环境的影响而发生改变,这种变化可能会导致机体生理功能受损但也可能适应这些不利环境;另一方面,通过有效的方式调节肠道菌群同样也可以抵御恶劣条件所带来的种种问题。因此,探究在这些环境下肠道菌群如何改变显得尤为关键,研究两者之间的关联对特殊工作人群健康具有非常重要的意义和价值。
肠道菌群结构受到内外环境的影响,其中饮食因素发挥着重要作用[3]。研究证实,肠道微生物参与了碳水化合物和氨基酸等营养物质的代谢过程并且能够发酵人体不能消化的多糖、蛋白质和脂肪产生多种代谢物,包括短链脂肪酸(SCFAs)、支链脂肪酸、胺和多酚类化合物[4],这些代谢物可以促进肠道功能成熟、调节免疫以及机体脑部功能,从而进一步影响人体的健康状况。不论是在一般环境还是在特殊环境下,饮食因素都是最容易改变和控制的因素且对人体安全无害。通过科学合理的膳食来调节肠道菌群结构以避免和改善由肠道菌群紊乱引起的各种疾病是一种行之有效的手段。同时也为特殊工作人群科学设计营养膳食以调节其肠道健康提供了新的思路。
本文总结了肠道与人体健康的关系及影响因素,重点探讨特殊环境(高原、航海与潜水、航空与航天)对肠道菌群的影响以及如何通过饮食营养干预调节肠道菌群以尽量减少或避免环境或职业不利因素对健康造成的损害,以期为开发特殊人群膳食或微生态制剂的相关研究提供依据和参考。
1. 肠道菌群与人体健康
随着微生物学科的发展和现代科技手段的进步,使现阶段人们对肠道菌群与人体健康具有重要联系的认知越来越高,肠道菌群也一直是科研工作者热衷研究的问题之一。据报道,婴儿自诞生数小时就有微生物在肠道定植并相伴终生[5]。人类肠道中有超过100万亿种微生物,包括大量细菌、病毒、真菌和原生动物,其中既包括对人体有益的益生菌,如乳酸菌(Lactobacillus)、双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium)等,也包括能够引起肠道疾病的有害菌,如大肠杆菌(Escherichia)、沙门氏菌(Salmonella)等,其基因数量是整个人类基因组的150倍[6]。科学家意识到仅有人类基因组信息是不够的,不能完全解决人的健康问题,由此逐渐拉开了了人类肠道元基因组学的序幕[7]。基因测序手段、生物信息学和宏基因组技术为研究和阐明微生物在人体中的作用打开了大门并取得了重要进展,进一步从分子手段揭示肠道菌群与人体健康的关系。
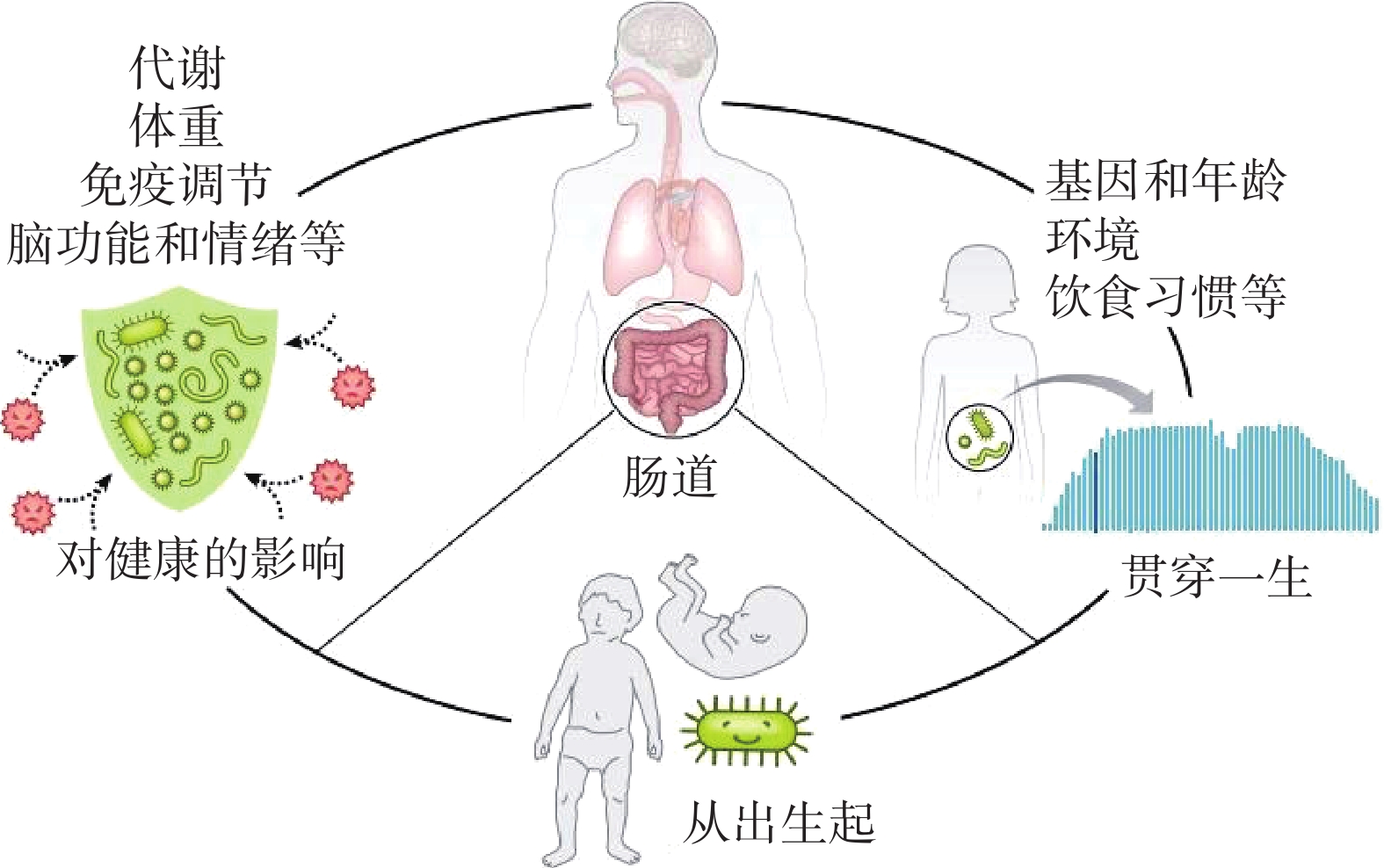
在人类以往的认知中,肠道菌群与消化系统密切相关,菌群紊乱可能会导致腹泻腹痛等消化道症状。但随着研究的不断深入,人们发现肠道微生物参与许多基本的生物学过程,包括上皮细胞发育,调节新陈代谢和刺激先天免疫等并且通过改变生理系统(如免疫系统发育,内分泌,代谢调节,甚至是体内的基因)而影响宿主的健康[8](图1)。肠道菌群被证实与多种疾病的发生和发展密切相关,甚至与人的情绪、精神状态和性格也是密不可分的[9]。如与代谢相关的疾病:糖尿病、肥胖等;神经系统及精神类疾病:精神分裂症、帕金森症和抑郁症等;与心血管系统相关的疾病:高血压、心力衰竭和动脉粥样硬化等[10]。此外,肠道菌群还与肿瘤、癌症及酒精性肝病、非酒精性脂肪性肝病等肝脏疾病有着千丝万缕的联系[11]。通过分子手段使肠道菌群对于人体各系统的影响机理逐渐被挖掘出来并且对不同疾病的干预机制也取得了重大进展。研究表明,失衡的肠道菌群会从多种途径如内毒素血症、能量吸收、胆碱、SCFAs、脑肠轴、胆汁酸代谢等影响宿主的健康[12]。因此研究肠道菌群对于疾病的预防与治疗,维护人类健康具有重大意义。
2. 影响肠道菌群的因素
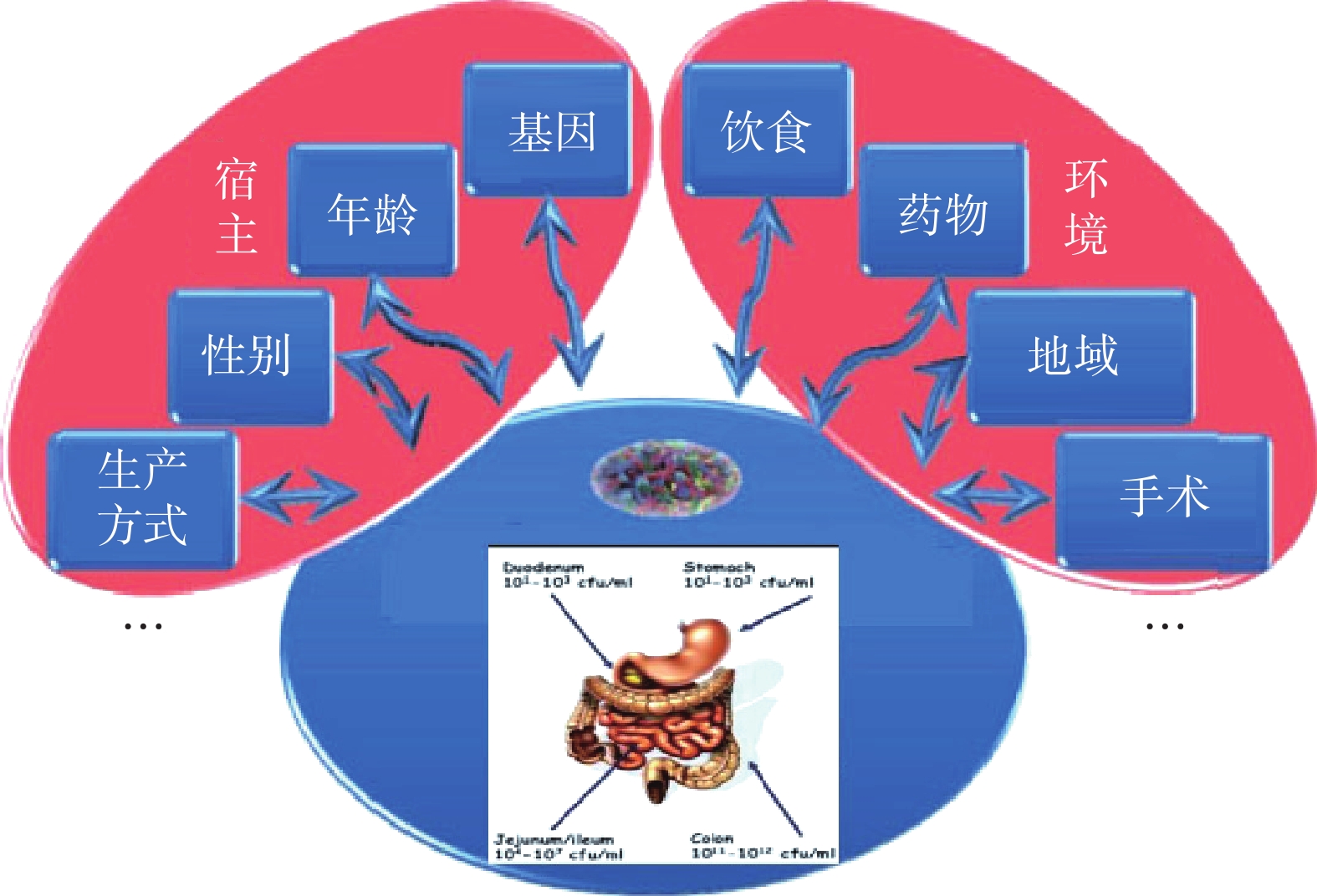
人们日益意识到肠道菌群在人类健康中所发挥的作用,与此同时也面临着一个挑战:肠道微生物受到哪些因素的影响以及它们如何随这些因素发生改变。就现有的研究来看可以总结为两大因素:内因和外因,都会对微生物群产生影响,具体来说既包括遗传、民族、内分泌、年龄、性别差异等宿主因素,也包括饮食、地理、生活方式、卫生条件、手术、抗生素使用等环境因素[13](图2)。2017年Nature上的一篇文章报道在对肠道菌群影响的因素中环境因素大于宿主基因。文中提到肠道菌群没有显著的家族遗传倾向,遗传因素对肠道菌群的影响甚微。而没有血缘的人群长期居住在一起,肠道菌群结构却表现为高度相似。在各类影响因素中,饮食、药物和生活方式等相关因素所占比重最大,影响了超过20%人群个体间菌群差异[14]。尤其是饮食因素,对于肠道菌群的定植、成熟和稳态发挥着重要的作用。
影响肠道菌群的各因素并不是独立存在的,往往是多种因素共同作用的结果。比如研究发现各民族间肠道菌群存有一定差异,但藏族与蒙族、壮族与汉族、白族与哈萨克族和维族肠道菌群具有相似性[15]。一方面是由于不同民族间的遗传因素,如长期生活在低氧低压高辐射环境致使藏族人民形成适应了这种恶劣的生活环境的基因;另一方面不同民族生活的地域不同,有各自地方性的特征,包括生活方式、饮食习惯、文化传统等。正是这些因素的相互作用导致了肠道菌群的相似或不同。此外,年龄、运动等都会影响肠道菌群的组成和功能,而药物、食品添加剂、抗生素和杀虫剂则可能对肠道菌群产生不良影响[16]。由于肠道菌群影响因素的复杂性和多样性,所以在研究时不能只考虑单一因素,更要考虑各因素间的交互作用,以此能够更加透彻地研究并加以利用肠道菌群,从而调节机体生理功能促进人体健康。
3. 特殊环境对肠道菌群的影响
特殊环境通常包括高温、严寒、低氧、强辐射等非常规理化环境。研究证实在一些极端特殊环境下,肠道菌群平衡会被打破,其组成与在正常条件下有很大差异,严重影响特殊人群的身心健康,而肠道菌群又具有适应特殊环境的潜力。因此,可以说特殊环境影响着肠道菌群的变化但同时它的改变又可以帮助人类适应这些特殊条件。由此可见,研究两者之间的相互作用和关系对于维持人体健康和适应特殊环境至关重要。
3.1 高原环境对肠道菌群的影响
3.1.1 高原环境特点及对机体的影响
高原环境主要有以下特点:低压缺氧是最显著的特征,大气压随着海拔的升高而降低,海拔越高,空气越稀薄;气候寒冷干燥,高原气温低,昼夜温差大;太阳辐射强,日照时间长。另外,强紫外线、风沙、气流快及自然灾害多等多种环境因素对高原环境人群的日常生活和健康状况有十分显著的影响。已有研究显示,人初入高原身体会出现一系列的变化,如心率增加、血压升高、头痛、厌食、失眠和脑水肿等,而当地人则不受这些高原环境因素的影响。研究表明高原民族(如藏族人、安第斯人和埃塞俄比亚人等)对高原环境的适应能力是经过长期进化而来的[17]。虽然随着生活时间的延长,人体能够依靠机体自身的调节适应能力慢慢适应高原环境,但大部分人由于不能立即适应,会出现一些高原反应或高原疾病,以胃肠道反应最为强烈,如呕吐、腹泻等[18]。同时,肠粘膜屏障功能下降,肠道菌群也出现结构性变化进而引发相关肠道疾病。韩天雨等[19]通过实地调研考察高原训练中运动员腹泻发生率,研究高原训练过程中运动员肠道菌群变化,证实了肠道菌群的改变与高原腹泻具有高度相关性。
3.1.2 高原环境人群肠道菌群特点
关于在不同海拔高度下肠道菌群组成不同,最早是通过研究高原动物如高原鼠兔、高原牦牛[20-21]的肠道菌群结构发现的。相似地,研究报道居住在平原的汉族和居住在高原的藏族婴人肠道菌群组成大不相同。Zhang等[22]通过高通量测序对藏族和汉族的婴儿肠道菌群的组成及丰度进行分析发现藏族和汉族纯母乳喂养婴儿的肠道菌群存在显著差异,前者菌群多样性高于后者,而且前者主要以厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)为主,后者以放线菌门(Actinobacteria)为主。相似地,在成人的研究中,Li等[23]也发现藏汉两个民族人群的肠道菌群存在着明显的不同。具体而言,门水平上,生活在青藏高原不同地区的藏族人肠道优势菌为拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes),Firmicutes,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)和Actinobacteria,同时兼性厌氧菌在肠道内也普遍存在;属水平上,藏民的肠道菌群普氏杆菌(Prevolla)较为丰富,汉族人群则是拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)。在Jia等[24]的研究中,系统地分析了393例健康成人(包括在高原生活不同时间的汉族人和长期在高原生活的藏族人)的肠道菌群和73项血液临床指标。结果发现随着高原生活时间的延长,汉族人群的肠道菌群的特征和血液临床指标与藏族人群越来越相似,即使在几个月后从高原地区返回平原地区,其肠道微生物群和血液临床指标也没有恢复到非高原状态时,这表明高原缺氧环境可以迅速而持久地影响人体肠道菌群和血液临床指标。
3.1.3 高原环境对肠道菌群影响机制的研究进展
为了解释肠道菌群的差异,阐明高原环境的影响,探究肠道菌群与高原环境的相互作用关系,以及肠道菌群变化在高原适应中的作用。研究者们又进一步做了大量的试验。基于海拔梯度肠道微生物的研究表明越来越多的节能细菌富集在高海拔组,厌氧菌数量增加,高原中的低氧可能是造成这种原因的主要因素[25]。肠道菌群中生成SCFAs如Prevolla等相关菌群种类和丰度显著增加,这些菌属能够促进SCFAs生成,也能更好的利用SCFAs生成乙酸、丙酸等小分子代谢物为机体提供能量,同时可能也参与了维生素B6和酮体的代谢,有利于在缺氧条件下人体能够高效利用能量而适应高原环境[26]。高原的地理环境特点造就了高原人群与平原人群生活方式的差异。Li等[27]通过膳食结构分析发现当地藏人通常会消耗更多的肉和乳制品,而汉族则消耗更多的小麦、大米和蔬菜,也就是说在饮食方面藏族人通常以富含蛋白质的食物为主,而汉族人则更喜欢摄入碳水化合物含量高的食物,在对能源利用的过程中涉及的菌属差异逐渐显现出来,饮食习惯的不同可能是导致肠道菌群种类和丰度差异的重要原因。此外,还有学者认为城市化或工业化水平的不同,可能也会影响高原居民肠道菌群的多样性和组成[28]。
由于受外部环境影响较大,人们关于高原等极端环境对肠道菌群影响的认知还远远不够。近年来,越来越多的研究证实肠道菌群受高原环境的影响较大,海拔高度可以塑造肠道微生物群落,改变肠道菌群的组成和结构。同时低气压、低温和高辐射条件是影响生物体生存和繁殖的生理应激源,会导致体内发生多种生理变化而引发高原反应或高原疾病,同样也会引发机体肠道菌群失衡。现阶段的研究表明,肠道菌群与高原红细胞增多症、高原血压异常等慢性高原疾病的发生密切相关[29],可以说高原环境和肠道菌群共同影响着人类的生理和心理健康。但肠道菌群如何变化,有什么变化趋势,与各类高原疾病是否存在关联及其机制有待于进一步探索。因此,如何调节肠道菌群结构以提高对环境的适应性对于维护初入高原甚至是长期生活或驻守在高原的非土著特殊人群的健康具有重要的意义。虽然目前对其作用机制尚不清楚,但是我们对高原环境改变人体肠道菌群组成和结构的信息已有了较为深入的了解并且掌握了一定的信息,这将对未来更好地研究高原环境适应性打下了坚实的基础,提供了新的思路。
3.2 航空与航天环境对肠道菌群的影响
3.2.1 航空与航天环境特点及对机体的影响
航空航天事业的蓬勃发展使得人类在太空中生存和生活成为了现实,但空间环境较高原和海洋环境要更加复杂。缺氧、低气压、加速度、噪声和振动等飞行因素对人体的影响是同时发生的综合作用,可对机体多个系统造成不良影响,产生健康风险。另有研究结果表明,航空作业环境还可影响认知功能。微重力是航天所特有的特殊环境,已有大量资料表明失重对人体的功能和代谢有显著影响[30]。在失重条件下,人体胃肠道的功能发生变化,影响机体营养素的需要量和机体的营养状态。多项研究表明,航天对人类和动物都有短期和长期的生理影响,这些影响包括骨质流失、心脏萎缩和心律改变、肌肉流失和免疫功能障碍等[31]。航空肮天环境的复杂性使得肠道菌群受到影响的因素也更多,这些不利因素联合作用导致宇航员或飞行员肠道微生态发生显著变化,肠道菌群失调,对机体健康构成潜在威胁。
3.2.2 航空航天环境下人群肠道菌群特点
早就有研究报道,空间环境对微生物生长有显著的影响,进一步可导致肠道菌群失调,益生菌数量减少,有害菌占比增加[32]。Liu等[33]对2次执行航天任务(分别为15和35 d)的5名宇航员在执行飞行任务前后肠道菌群进行对比分析,研究表明:航天飞行对肠道菌群的组成及功能具有显著影响,飞行后Bacteroidetes菌属的丰度增加,而Lactobacillus和Bifidobacterium丰度下降,且肠道菌群的毒力基因总数增加,有害细菌的毒力和感染机会增加。另外发现抗生素的合成功能发生显著变化,航天飞行对一些抗生素的耐药基因和可移动遗传元件也有一定影响。Voorhies等[34]调查了长期(6~12个月)在国际空间站执行任务的宇航员体内微生物群的组成。结果发现宇航员的胃肠道、皮肤、口腔的微生物结构在太空执行任务期间均发生了明显的变化。在太空中,宇航员肠道微生物群的组成变得更加相似,主要是一些细菌类群(Bifidobacterium、Pseudobutyrivibrio)的丰度下降。
3.2.3 航空航天环境对肠道菌群影响机制
肠道菌群的改变致使肠道免疫功能受损,免疫功能的下降会导致宇航员出现肠胃不适、呼吸系统疾病、皮肤刺激和感染等一系列症状。Mccarville等[35]证实,太空飞行通过改变细胞因子的产生和淋巴细胞数量,特别是T细胞来改变免疫系统,而肠道菌群在微重力作用下的变化会影响免疫系统,具体的机制还有待研究。此外,还有研究表明肠道菌在航天员之间可相互传播,增加了空间肠道疾病散播的风险[36]。Garrett-Bakelman等[37]曾研究过一名双胞胎宇航员的肠道微生物组,并发现了他在国际空间站(ISS)进行为期一年的飞行任务时所发生的变化,而在同一时期他的双胞胎弟弟并未观察到这种变化。基于此,该团队继续分析了在国际空间站常规饲养的小鼠的粪便菌群组成,进一步探究太空飞行给小鼠肠道菌群带来的变化,结果表明太空飞行使小鼠肠道菌群α多样性升高、组成结构改变,这些变化与之前报道的太空飞行小鼠相似,不同于在地球上进行的模拟太空辐射引起的小鼠肠道菌群变化,揭示了太空飞行队小鼠肠道菌群的影响具有可重复性,微重力(而非辐射)是影响菌群的组成和代谢功能的主要因素,而菌群的变化反过来对宿主代谢产生影响[38]。相似地,Jin等[39]用后肢去负荷大鼠模型模拟分析发现失重是肠道菌群变化的主要原因。男性和女性在许多方面存有差异,在太空中对某些条件的适应也是不同的。Urbaniak等[40]首次提出了长时间航天飞行对女性宇航员微生物群以及在太空中患病风险的影响。尿路感染(UTIs)是在太空飞行中普遍出现的问题,与男性相比,女性宇航员的发病率更高,可能的原因是在微重力作用下致病菌的毒力因子增加,粘附性增强。而太空辐射和航天飞行期间睡眠模式改变导致的昼夜节律的变化使女性患癌症的风险比男性高20%。
由此可见,空间环境中的微重力和辐射是引发肠道菌群结构改变的主要因素,破坏了肠道菌群之间的动态平衡,这些变化对宇航员健康的影响不可忽视。因此,迫切需要科研工作者了解和探索空间环境对肠道菌群的影响机制并急需寻找其防治方法。虽然近年来相关的研究和文献越来越多,并且上述这些发现也有助于理解太空生活对宇航员肠道菌群和健康的作用,对菌群的变化规律和机制有了一定认知,科学家们也在根据这些研究结果试图寻找一些调节方式和预防措施。但由于条件限制,目前大部分报道都存在样本小并且都是基于模拟实验,缺乏长期在空间真实环境的系统性研究等问题,这也是当前研究面临的难题和挑战。相信随着航天事业的进步,空间环境的复杂性不再是制约肠道菌群研究的瓶颈,通过对肠道菌群的干预可以更好地保障宇航员的肠道健康和生命安全。
3.3 航海与潜水环境对肠道菌群的影响
3.3.1 航海与潜水环境特点及对机体的影响
航海环境主要有以下特点:由于风浪或浪涌的作用导致舰船在航行或泊锚时出现摇摆等复杂而不规则的运动或使船体发生局部振动;舰船舱室的机械、空调通风系统、局部气流引起的噪声、螺旋桨及水动力产生的一系列噪声;舰船上的核动力装置会产生一定量的辐射;潜航时长时间处于密闭环境;潜水员时常面临高氧和高压的海底作业环境。除此之外,与陆地隔离的单调环境、昼夜节律的改变、睡眠不足以及新鲜水果和蔬菜供应不足,会使人体的免疫功能和消化系统受损,严重威胁船员的生理和心理健康[41]。人体肠道的微生物菌群是保持人体免疫系统正常、维持人体健康的基础,由此可见,正常的肠道微生物菌群结构对于维持长途海上航行船员的健康至关重要。但目前对于航海与潜水环境与肠道菌群的结构和功能关系的研究少之又少。
3.3.2 航海与潜水环境下人群肠道菌群特点
近年来,肠道菌群与航海或潜水环境相互影响的研究被相继报道。吕伟[42]通过高通量测序技术分析了29名官兵执行长远航任务中(出发前,45、90和135 d)肠道菌群结构变化和多样性特征。结果表明长远航过程中官兵的肠道菌群结构和多样性均发生了显著的变化,结构差异主要表现为Bacteroidetes、Firmicutes门类有益菌低于健康人群,且菌群多样性随着航行时间的延长不断降低,但在远航任务结束时又逐渐恢复。同时远航后肠道致病菌的数量多于健康人群且出现了水生环境中的菌属分布。在最近的研究中,Zheng等[43]研究表明,在长时间的海上航行过程中,益生菌可通过改善水手肠道健康抑制肠道菌群组成及功能实现缓解水手的航海压力及焦虑。研究团队利用深度宏基因组测序技术和相关性分析首先证实了长途航行前后(0、30 d)不仅扰乱了船员肠道菌群平衡,而且还减少了肠道菌群功能特征的多样性,增加了压力和焦虑感。进一步比较益生菌组受试者与安慰剂组在航行前后肠道菌群结构的变化。研究发现:与安慰剂组相比,益生菌的干预可以有效维护远航船员肠道微生态平衡,其中长双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium longum)、动物双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium animalis)和植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillu plantarum)的丰度持续增加,而肺炎克雷白杆菌(Klebsiella pneumoniae)、人体普氏菌(Prevotella)的丰度显著降低。同时,益生菌的干预可有效缓解由远航造成的船员肠道微生物碳水化合物-活性酶基因多样性锐减。此外,柔嫩梭菌(Clostridium leptum)、沙氏别样杆菌(Alistipes shahii)和Klebsiella pneumoniae等有害菌株和船员焦虑程度呈正相关,Bifidobacterium等有益菌株和船员焦虑程度呈负相关,表明益生菌可通过调节特定肠道菌群缓解船员的焦虑症状。Yuan等[44]通过采集47名潜水员在饱和潜水之前、期间和之后这三个时间段的粪便样品采用16S rDNA和Illumina测序技术分析了商业氦氧饱和度潜水对潜水员肠道菌群的影响,结果显示尽管肠道菌群的α和β多样性没有明显改变,但发现在高压的氦氧饱和环境作业会降低潜水员体内肠道菌群的丰度,Bifidobacterium的丰度下降最为显著。此外,一些产SCFAs的细菌,如Fusicatenibacter、费氏细菌(Faecalibacterium)等在整个过程中丰度也呈下降趋势。相反,诸如艰难梭菌(Peptoclostridium difficile),变形链球菌(Streptococcus mutans)等大部分病原细菌的丰度提高。
3.3.3 航海与潜水环境对肠道菌群影响机制
目前对航海和潜水环境与肠道菌群相互作用的认识还比较少,但通过上述研究可以发现肠道菌群结构与多样性的变化是航行过程中多种因素共同作用的结果。在长航过程中,饮食常以高脂低纤维的食物为主,研究表明高脂低纤维膳食可以促进肠道促炎性细菌的生长[45];昼夜节律的改变、睡眠不足、生活单调,容易引起焦虑甚至抑郁,而焦虑以及抑郁已被证实与肠道菌群存在相关性[46];高温高湿的海洋环境可能会使船员的肠道菌群中出现水源性微生物的生长繁殖,肠道菌群的多样性发生改变。另外高压的氦氧饱和度环境和潜水员摄入的高蛋白饮食是影响肠道菌群丰度的主要原因。作为陆地生活的人类来说,水面和水下航行,尤其是长航,机体势必会出现一系列反应,这些反应是不利于机体健康的。与高原环境不同的是,暂未有研究证明机体对海上环境具有适应性。微生态学研究表明航行条件可以引起微生态的改变造成肠道菌群紊乱甚至影响船员的心理健康。但航行条件复杂多变,各种因素之间相互影响导致肠道菌群失调各有特点,需要具体研究,但可以肯定的是这些变化为寻找应对海上或水下不良环境的措施提供了有效的依据和方向,有助于预防疾病的发生,改善海上船员或水下潜水员的生活质量和机体健康。
3.4 其他特殊环境对肠道菌群的影响
除以上三种特殊环境外,还存在一些其他极端的环境,如高温、寒冷、低照度、辐射、有毒有害化学物等,在这些特殊工作环境中从事作业的人群或多或少都有特殊职业性疾病,严重时可危及生命。而关于这些特殊环境对人体肠道菌群的影响的报道很少且机理不清甚至是空白。仅有少数研究仅限于动物或昆虫[47-49],对于人体的研究试验尚未见报道。其原因推测如下:一方面人体在极端温度条件下有自我调节机制;另一方面,在极端环境工作的人群数量较少,取样困难。最关键的因素是这些环境中常存在一些对人体健康不利的物理或化学因素,进行人体试验可能会对机体造成损害,所以导致一些试验研究停留在动物模型阶段。虽然我们对于这些极端条件如何影响肠道菌群及机制仍然知之甚少,通过少数动物实验的报道,可以确定的是肠道菌群在这些环境下势必会发生变化,相信随着科技的发展,两者之间的关系在不久后将会取得突破。
4. 营养干预
特殊环境可导致机体生理功能和营养代谢出现显著变化,进一步发展引发一些疾病。而这些疾病往往都是在症状出现后采用抗生素来治疗,但长期使用药物来调节和治疗由特殊环境引发的健康问题不仅会或多或少带来一些副作用和临床问题,而且会导致肠道菌群改变,降低菌群的丰富度[50]。目前大量的研究表明,通过改善饮食结构或服用微生态制剂,进而调整肠道菌群的结构和数量是提高机体健康状况一条有效的途径[51]。对于特殊环境人群来说,营养需求与正常情况下存有极大差异,特殊营养学应运而生,目前主要的应用领域如军用食品、航天食品,主要是通过强化部分营养素或添加功能因子及微生态制剂来调节肠道菌群结构。
4.1 调整膳食结构
为使特殊人群能够适应特殊环境,改善或调节机体的不适、亚健康甚至治疗和预防可能出现的疾病,最直接也是较科学的方式就是平衡膳食和合理营养。基于各种特殊环境的复杂因素考虑,调整膳食结构是能够调节肠道菌群又对人体健康无副作用的重要抓手。饮食对于人体健康的重要性显而易见,而肠道微生物则是联系二者之间的关键。大量的实验研究证实饮食的改变可以影响肠道微生物的组成、结构和功能,而肠道微生物通过调节肠道中营养物质的代谢来影响宿主的生理状态[52]。从前面的研究来看,藏族等高原土著人群与汉族等平原地区人群的膳食结构不同,Xu等[53]报道发现谷氨酰胺干预有助于改善高原环境下机体肠道菌群的失调,可在膳食中补充这种物质。针对航海过程中新鲜果蔬供应不足,可以通过保鲜技术或在膳食中增加维生素供给量,从而来避免因为营养缺乏导致肠道微生态的紊乱。不同于一般膳食,航天飞行中的航天食品通常会添加低聚肽、抗氧化植物提取物、活性多糖等功能因子,能够有效提高人体防疫酶系活性水平,增强机体免疫功能,降低辐射损伤,同时这些功能因子也能刺激肠道益生菌的增殖,有效改善菌群结构[54]。但需要注意的是,膳食对于肠道菌群的影响具有两面性,膳食纤维有益于肠道菌群,而蛋白质会促进有害副产物的积累等[55]。因此,通过膳食干预的方法不仅为特殊人群肠道微生物的调控和重构提供了新的方向和思路,也为预防和治疗特定的特殊环境疾病提供了可能性。差异化和个性化的精准营养也是未来关于特殊人群膳食结构的研究重点。
4.2 添加益生元或益生菌
研究证实,饮食调节是一个长期的过程,短期的饮食改变并不能改变肠道菌群结构[56]。最有效的方式就是摄入益生菌,益生菌同样对人体安全无害,但相较单纯的膳食能够高效快速地调节肠道微生物,同时还具有促健康作用。益生菌主要包括乳酸菌和双歧杆菌,是人体肠道微生物的重要组成部分,且具有一定的益生作用,摄入外源益生菌可以直接或间接地对宿主肠道微生物产生影响[57]。研究证实,外源益生菌的摄入不仅可以改变宿主肠道内原有菌群的种类和结构,而且会对SCFA代谢水平、总胆汁酸代谢水平、肠道内矿物质的吸收和肠道内酶活力均产生显著影响,主要是通过抑制有害菌定植,分泌酶、产生抗菌物质和产酸、激素等多种途径来调控肠道菌群和人体健康[58]。摄入益生菌的方式有两种,一种是将益生菌添加到食品中;另一种则是直接口服微生态制剂。前者虽具有食品的属性,但活性低,后者活性较高但没有营养物质。所以如何完美地将两者整合、保持益生菌稳定,并使益生菌达到足够量是发挥其益生作用的关键。在前面的研究中,科研工作者利用深度宏基因组测序技术研究了益生菌对航天员[34]、船员[43]、潜水员[44]以及在高原环境[24]居住或工作等的特殊人群肠道菌群的调控作用,揭示了有助于改善这些特殊环境下作业适应度的可能机制,为维护特殊环境下工作的人群中肠道微生态健康和缓解精神焦虑提供了一种有效解决方案,并为益生菌个性化选择提供了新的视野。另外,益生元可以促进益生菌对营养物质的利用,并被代谢成乙酸盐、丁酸盐等短链脂肪酸,同时还能够抑制有害菌的生长[59]。下一步的工作就是将益生菌或益生元完美地添加到食品中,以供特殊人群需要时食用。
5. 结论
极端的恶劣环境条件影响着特殊工作人群的健康,但我们对太空、航海、高原等特殊环境的认识还远远不够。不可否认的是,特殊环境同样对肠道菌群具有显著的影响,这种改变是一个复杂且相互关联的过程。随着特殊营养学的发展以及肠道菌群与人体健康关系的深入认知,特殊环境下的特殊人群逐渐成为研究人员关注的焦点。越来越多的研究证据表明特殊环境与肠道菌群两者之间相互联系,互相影响,通过调整肠道菌群来缓解恶劣环境对机体的损伤以及改善处于不利环境人群的营养状况,增加其在特殊环境习服适应中的能力是一条值得深入研究的新途径和新思路,同时对于肠道微生态健康也提供了一种有效的解决方案,最好的方式就是膳食调节,如当下十分热门的益生菌和益生元。就目前来看,虽然关于特殊环境对肠道菌群结构和组成影响的研究已经取得了一些进展,但仅仅只是一小部分,由于这些环境自身的复杂性、研究方法的局限性以及研究技术上的不足,导致具体的机制还不是十分清楚,并且这类的研究虽然每年都有报道但总体来说也比较少,导致研究数据缺乏,加之我们对太空、高原等极端环境的认知还远远不够,还有许多基础的工作要去做。另外,相较于正常条件,营养干预在特殊环境下是否仍继续有效还存在着大量的实验数据要去证明。相信随着研究的继续深入,未来对于特殊环境下的特殊人群肠道菌群-营养干预-人体健康三者之间的关系会愈发明朗,如何通过饮食与营养调节和平衡肠道菌群是未来特殊营养学研究的重中之重,同时也为精准营养提供了新的视野。
-
[1] EISENSTEIN M. The hunt for a healthy microbiome[J]. Nature,2020,577(7792):S6−S8. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00193-3
[2] TIGHE S, AFSHINNEKOO E, ROCK T M, et al. Genomic methods and microbiological technologies for profiling novel and extreme environments for the extreme microbiome project (XMP)[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Techniques Jbt,2017,28(1):31−39. doi: 10.7171/jbt.17-2801-004
[3] DAVID L A, MAURICE C F, CARMODY R N, et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome[J]. Nature,2013,505(7484):559−563.
[4] OLIPHANT K, ALLEN-VERCOE E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health[J]. Microbiome,2019,7(1):1−15. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0604-3
[5] ASHLEY Y. Delivery of the gut microbiome[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2018,16(9):520−521.
[6] SALAZAR N, VALDÉS-VARELA L, GONZÁLEZ S, et al. Nutrition and the gut microbiome in the elderly[J]. Gut Microbes,2017,8(2):82−97. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2016.1256525
[7] BOUCHIE A. White house unveils national microbiome initiative[J]. Nature Biotechnology,2016,34(6):580.
[8] WU Y B, WAN J W, CHOE U, et al. Interactions between food and gut microbiota: Impact on human health[J]. Annual Review of Food Science and Technology,2019,10(1):389−408. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-032818-121303
[9] JOHNSON V A. Gut microbiome composition and diversity are related to human personality traits[J]. Human Microbiome Journal,2020,15:1−15.
[10] CAITRÍONA LONG-SMITH, O'RIORDAN K J, CLARKE G, et al. Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: New therapeutic opportunities[J]. Annual Review of Pharmacology,2020,60(1):1−26. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-082719-110050
[11] ADOLPH T E, GRANDER C, MOSCHEN A R, et al. Liver–Microbiome axis in health and disease[J]. Trends in Immunology,2018,39(9):712−723. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.05.002
[12] VALDES A M, JENS W, ERAN S, et al. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health[J]. BMJ,2018,361(1):36−44.
[13] NIE P, LI Z, WANG Y, et al. Gut microbiome interventions in human health and diseases[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews,2019,39(6):1−28.
[14] DAPHNA R, OMER W, ELAD B, et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota[J]. Nature,2018,555(7695):210−215. doi: 10.1038/nature25973
[15] KWOK LAI-YU, ZHANG J C, GUO Z, et al. Characterization of fecal microbiota across seven Chinese ethnic groups by quantitative polymerase chain reaction[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(4):e93631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093631
[16] CAO Y, LIU H, QIN N, et al. Impact of food additives on the composition and function of gut microbiota: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,99(4):295−310.
[17] ZHANG W, JIAO L F, LIU R X, et al. The effect of exposure to high altitude and low oxygen on intestinal microbial communities in mice[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(9):e0203701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203701
[18] MAZEL F. Living the high life: Could gut microbiota matter for adaptation to high altitude?[J]. Molecular Ecology,2019,28(9):2119−2121. doi: 10.1111/mec.15093
[19] 韩天雨, 胡扬, 张玮佳, 等. 高原训练中运动员腹泻发生状况及肠道菌群的变化[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2018,18(10):1909−1915. [HAN T Y, HU Y, ZHANG W J, et al. Athletes' diarrhea occurrence and changes of intestinal microbial flora in high altitude gtraining[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine,2018,18(10):1909−1915. [20] YAN M, SHUANG M, LAN C C, et al. Gut microbiota adaptation to high altitude in indigenous animals[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2019,516(1):120−126. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.085
[21] LI H, LI T T, BEASLEY D E, et al. Diet diversity is associated with beta but not alpha diversity of pika gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2016,7(758):1169−1178.
[22] ZHANG Q X, SHANG J C, ZHU D Q, et al. Structural segregation of the gut microbiome between Chinese Han and Tibetan infants[J]. Food Science,2019,40(24):128−135.
[23] LI K, DAN Z, GESANG L, et al. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota of native Tibetan and Han populations living at different altitudes[J]. Plos One,2016,11(5):e0155863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155863
[24] JIA Z L, ZHAO X J, LIU X S, et al. Impacts of the plateau environment on the gut microbiota and blood clinical indexes in Han and Tibetan individuals[J]. mSystems, 2020, 5(1): e00660.
[25] QUAGLIARIELLO A, PAOLA M D, FANTI S D, et al. Gut microbiota composition in Himalayan and Andean populations and its relationship with diet, lifestyle and adaptation to the high-altitude environment[J]. Journal of Anthropological Sciences,2019,97:189−208.
[26] 陈郁, 罗勇军. 肠道菌群调控高原习服适应过程及其机制研究进展[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志,2020,38(4):70−72,76. [CHEN Y, LUO Y J. Research progress on the regulation of intestinal flora on the adaptation process of plateau acclimatization and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Preventive Medicine of Chinese People's Liberation Army,2020,38(4):70−72,76. [27] LI K, PENG W, ZHOU Y, et al. Host genetic and environmental factors shape the composition and function of gut microbiota in populations living at high altitude[J]. BioMed Research International,2020,2020:1−10.
[28] LI H, LI T T, LI X Z, et al. Gut microbiota in Tibetan herdsmen reflects thedegree of urbanization[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,9(1745):1−14.
[29] SUN S, LULLA A, SIODA M, et al. Gut microbiota composition and blood pressure[J]. Hypertension,2019,73(5):998−1006. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.12109
[30] VOORHIES A A, LORENZI H A. The challenge of maintaining a healthy microbiome during long-duration space missions[J]. Frontiers in Astronomy & Space Sciences,2016,3(23):1−7.
[31] ALAUZET C, CUNAT L, WACK M, et al. Hypergravity disrupts murine intestinal microbiota[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):9410−9422. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45153-8
[32] LAUREN E R, STELLA S T, BRAD R W, et al. Space environmental factor impacts upon murine colon microbiota and mucosal homeostasis[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(6):e0125792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125792
[33] LIU Z Z, LUO G, DU R K, et al. Effects of spaceflight on the composition and function of the human gut microbiota[J]. Gut Microbes,2020,11(4):1−13.
[34] VOORHIES A A, OTT C M, MEHTA S, et al. Study of the impact of long-duration space missions at the international space station on the astronaut microbiome[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):9911−9928. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46303-8
[35] MCCARVILLE J L, CLARKE S T, PADMAJA S, et al. Spaceflight influences both mucosal and peripheral cytokine production in PTN-Tg and wild type mice[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(7):e68961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068961
[36] 徐绸, 何平, 刘长庭. 空间环境对肠道菌群的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程,2016,29(4):297−300. [ XU C, HE P, LIU C T. Effects of space environment on intestinal flora[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering,2016,29(4):297−300. [37] GARRETT-BAKELMAN F E, DARSHI M, GREEN S J, et al. The NASA twins study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight[J]. Science,2019,364(6436):1−23.
[38] JIANG P, STEFAN J G, GEORGE E C, et al. Reproducible changes in the gut microbiome suggest a shift in microbial and host metabolism during spaceflight[J]. BioMed Central,2019,7(113):1−18.
[39] JIN M L, ZHANG H, ZHAO K, et al. Responses of intestinal mucosal barrier functions of rats to simulated weightlessness[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2018,9(729):1−13.
[40] URBANIAK C, REID G. The potential influence of the microbiota and probiotics on women during long spaceflights[J]. Womens Health,2016,12(2):193−198.
[41] O’HALLORAN C L, SILVER M W, COLFORD J M. Acute stress symptoms among US ocean lifeguards[J]. Wilderness & Environmental Medicine,2015,26(3):442−443.
[42] 吕伟. 海军长远航官兵肠道菌群多样性研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2017. LV W. Diversisy of gut flora in navy officers and soldiers involved in long voyage[D]. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University, 2017.
[43] ZHENG W, ZHANG Z, LIU C, et al. Metagenomic sequencing reveals altered metabolic pathways in the oral microbiota of sailors during a long sea voyage[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):9131−9142. doi: 10.1038/srep09131
[44] YUAN Y, ZHAO G, JI H, et al. Changes in the gut microbiota during and after commercial helium–oxygen saturation diving in China[J]. Occupational and Environmental Medicine,2019,76(11):801−807. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2019-106031
[45] DONJETE S, A MÒNICA, JOHN M S, et al. The impact of western diet and nutrients on the microbiota and immune response at mucosal interfaces[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2017,8(838):1−21.
[46] KACZMAREK J L, THOMPSON S V, HOLSCHER H D. Complex interactions of circadian rhythms, eating behaviors, and the gastrointestinal microbiota and their potential impact on health[J]. Nutrition Reviews,2017(9):673−682.
[47] HENRY Y, COLINET H. Microbiota disruption leads to reduced cold tolerance in Drosophila flies[J]. The Science of Nature,2018,105(9-10):59−64. doi: 10.1007/s00114-018-1584-7
[48] BO T B, ZHANG X Y, WEN J, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain interaction in regulating host metabolic adaptation to cold in male Brandt's voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii)[J]. The ISME Journal,2019,13(12):1−17.
[49] KANAKO Y, TAKAKIYO T, YAMATO S, et al. Short-term follow-up of intestinal flora in radiation-exposed mice[J]. Journal of Radiation Research,2019,60(3):328−332. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrz002
[50] SAVAGE N. The complex relationship between drugs and the microbiome[J]. Nature,2020,577(7792):S10−S11. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00196-0
[51] FRAGIADAKIS G K, WASTYK H C, ROBINSON J L, et al. Long-term dietary intervention reveals resilience of the gut microbiota despite changes in diet and weight[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2020:1−10.
[52] ZMOR A, SUEZ J, ELINAV E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2018,16(1):35−56.
[53] XU C L, SUN R, QIAO X J, et al. Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2014,20(16):4662−4674. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662
[54] HWK A, MSR B. Space food and bacterial infections: Realities of the risk and role of science[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,106:275−287.
[55] FRAME L A, ELISE C, JACKSON S A. Current explorations of nutrition and the gut microbiome: A comprehensive evaluation of the review literature[J]. Nutrition Reviews,2020:1−50.
[56] DERRIEN M, VEIGA P. Rethinking diet to aid human-microbe symbiosis[J]. Trends in Microbiology,2016,25(2):110−112.
[57] GOWRI R S, MEENAMBIGAI P, PRABHAVATHI P, et al. Probiotics and its effects on human health-A review[J]. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences,2016,5(4):384−392. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2016.504.046
[58] KUNDU P, BLACHER E, ELINAV E, et al. Our gut microbiome: The evolving inner self[J]. Cell,2017,171(7):1481−1493. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.024
[59] SANDERS M E, MERENSTEIN D J, REID G, et al. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2019,16(Suppl.1):1−12.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
