Effects of Microwave Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Protein Structure Characteristics of Sorghum
-
摘要: 为改善高粱蛋白质理化性质,采用微波技术对三种高粱进行处理,结合扫描电镜和傅里叶变换红外光谱仪等方法,测定微波处理对高粱理化性质及蛋白质结构特性影响。结果表明,微波处理对高粱蛋白质等理化性质具有显著影响。微波处理减小了高粱蛋白粒径,蛋白表面出现缝隙,但处理前后的红外光谱具有相似的结构特征,属于物理变性。微波处理显著提高了三种高粱的总蛋白质含量约0.6%(P<0.05),降低可溶性蛋白质含量0.97~1.87 mg/g,且显著降低体外消化率15.55%~43.63%(P<0.05)。此外,微波处理后,高粱粉的持水力显著提高0.32~0.40 g/g(P<0.05),持油力显著降低0.08~0.18 g/g(P<0.05),表面菌落总数和霉菌数分别显著降低了98.75%和98.94%(P<0.05),色度变暗。本文可为高粱食品的开发及应用提供一定的参考。Abstract: In order to improve the physicochemical properties of sorghum protein, three kinds of sorghum were treated with microwave technology, and the changes of physicochemical properties and protein structural properties of sorghums before and after microwave treatment were measured by scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectrometer. The results showed that microwave treatment had significant effects on the physicochemical and protein structural properties of sorghum. Microwave treatment reduced the grain size of sorghum protein and caused cracks on the protein surface. However, the infrared spectra of sorghum protein before and after treatment had the similar structural characteristics and belonged to physical denaturation. Microwave treatment significantly increased the total protein contents of the three sorghums species by 0.6% (P<0.05), decreased soluble protein contents by 0.97~1.87 mg/g, and significantly decreased in vitro digestibility by 15.55%~43.63% (P<0.05). In addition, after microwave treatment, the water holding capacity of sorghum powder was significantly increased by 0.32~0.40 g/g (P<0.05), the oil holding capacity was significantly decreased by 0.08~0.18 g/g (P<0.05), the total number of bacterial colonies and the number of molds on the surface were significantly decreased by 98.75% and 98.94% (P<0.05), respectively. And the color darkened. The present research can present reference for the development and application of sorghum food.
-
Keywords:
- sorghum /
- protein /
- structural properties /
- physicochemical properties
-
根据现代流行病学研究报道,经常食用全谷物可降低人体患肥胖、心血管疾病和2型糖尿病等慢性疾病风险[1]。高粱(Sorghum bicolor L. Moench)属禾本科,是世界上种植最早和最广泛的农作物之一,也是亚洲和非洲等非半干旱地区主要的主食来源[2]。高粱富含维生素B、赖氨酸、膳食纤维、多酚、矿物质和蛋白质等多种营养成分,是一种重要的粮食原料[3]。
蛋白质作为一种人类生命活动中基本的营养物质,在日常膳食结构中具有重要作用,蛋白质的理化性质对食品的食用品质具有显著影响。近年来,人们研究了各种物理和化学方法来改善蛋白质的溶解性、起泡性及吸油性等性质,以提高食品食用品质[4]。由于高粱蛋白中醇溶蛋白含量较高,因此高粱蛋白具有消化率低、不易溶于水和加工性能差等特点[5]。目前,国内外对高粱蛋白的研究主要集中在提高蛋白提取率、改善蛋白消化率、制备功能性蛋白抑制肽和调控蛋白基因表达等方面[6]。微波技术作为一种新型的热加工技术,具有操作简单、安全和绿色环保等优点,在食品加工领域具有良好的应用前景。研究表明,微波处理可提高青稞蛋白质的提取率[7]。刘海波等[8]研究发现,微波处理可导致小麦面筋蛋白中的巯基和二硫键含量减少,面筋蛋白的网状结构变得疏松。胡方洋等[9]研究发现,微波处理可降低苦荞蛋白的起泡性和乳化性。此外,王娜等[10]研究发现,微波处理可降低小麦醇溶蛋白的抗原性,具有良好的脱敏效果。然而,微波处理对高粱蛋白质的结构特性及其理化性质的研究相对较少。本研究利用扫描电子显微镜(Scanning electron microscopy,SEM)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FT-IR)等方法来探讨微波处理前后高粱理化性质及蛋白质结构的变化情况,旨在为高粱食品的开发和利用提供数据依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱 均由黑龙江省农业科学院提供;考马斯亮蓝试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;光谱级溴化钾 天津市福晨化学试剂厂;胃蛋白酶(活力250 U/mg) 北京博奥拓达科技有限公司;金龙鱼食用大豆油 北京华联超市;平板计数琼脂培养基、马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基 北京博星生物技术有限责任公司;其他试剂 无特殊说明均为分析纯。
755B型紫外可见分光光度计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;DELTA320型pH计 上海珂淮仪器有限公司;S-4800N扫描电子显微镜 日本Hitachi公司;Nicolet 6700型红外光谱仪 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;TDZ5-WS台式低速离心机 上海精若科学仪器有限公司;Beta2-8LD plus冷冻干燥机 德国Christ公司;SL-100型高速多功能粉碎机 浙江省永康市松青五金厂;NH310色差仪 深圳三恩时科技有限公司;M1-211A微波炉 美的集团有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 微波处理
参考姜鹏等[11]方法并稍作改动。取500 g高粱清洗除杂后在室温下浸泡3 h后取出备用,待表面水分自然风干后,在微波600 W的条件下处理6 min,冷却至室温,45 ℃热风干燥,冷却至室温后用组织粉碎机粉碎并过60目筛,置于4 ℃保存;除未经微波处理外,未处理组的前处理步骤均与处理组相同。
1.2.2 高粱蛋白质的提取
根据周剑敏等[12]方法稍作修改。称取500 g过筛后的高粱粉放置于3500 mL石油醚中,在室温下脱脂6 h后,除去石油醚,脱脂后的高粱粉在40 ℃条件下烘干。取200 g的脱脂后的高粱粉于烧杯中,并加入1 mol/L的NaOH溶液(pH=14),搅拌4 h后在4000 r/min条件下离心30 min,取上清液并调节pH至5.0,静置2 h,在4000 r/min条件下离心30 min后取出沉淀,用去离子水清洗并在4000 r/min条件下离心3次,收集沉淀,冷冻干燥后备用。
1.2.3 高粱总蛋白质含量及可溶性蛋白质含量的测定
总蛋白质含量根据GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》。
可溶性蛋白质含量的测定参考方赵志浩等[13]方法并稍作修改。称取高粱粉1.0 g与9 mL生理盐水混匀,在冰浴条件下机械均质2 min后取出,均质液在4000 r/min条件下离心10 min,分离上清液并定容至25 mL。取50 μL定容后的液体于试管中,加入3.0 mL考马斯亮蓝显色液,混匀后静置5 min,在595 nm波长的条件下测定吸光度为A1,用去离子水做空白对照,记录吸光度为A2,以牛血清白蛋标准品(0.563 g/L)作为标准对照,测得吸光度A3。计算公式如式(1):
可溶性蛋质白含量(mg/g)=(A1−A2A3−A2)×0.563×0.025×1000 (1) 1.2.4 SEM分析
在SEM的载物台上贴上一定数量的导电双面胶带,取冷冻干燥后的高粱蛋白质均匀至于双面胶上,用吸耳球吹去多余蛋白质,载物台在镀金仪中镀金120 s后放入SEM中,在电子枪加速电压为10 kV的条件下观察蛋白质形态。
1.2.5 FT-IR分析
在干燥的条件下称取3 mg干燥至恒重后的高粱蛋白质样品和300 mg的溴化钾粉末混合后研磨15 min后过筛,将过筛后的混合粉末压成片后备用,并以溴化钾片作空白,在波数为400~4000 cm−1的条件下进行扫描。
1.2.6 蛋白质体外消化率的测定
采用Mertz等[14]方法测定蛋白质的体外消化率。取高粱粉200.0 mg置于离心管中,加入相当活力为250 U/mg的胃蛋白酶溶液35 mL。溶液在37 ℃水浴中振荡2 h,然后加入2 mLNaOH溶液(2 mol/L)并调节pH至14终止反应。离心后弃上清液,用20 mL磷酸盐缓冲液(pH=7)洗涤沉淀两次,在相同条件下离心后,取出沉淀干燥,测定沉淀中的蛋白质含量。蛋白质体外消化率的计算公式如式(2):
蛋白质体外消化率(%)=M−mM×100 (2) 式中:M为样品消化前的总蛋白含量;m为样品消化后的总蛋白含量。
1.2.7 持水力和持油力的测定
采用Liu等[15]方法并稍作修改。称4.0 g高粱粉与20 mL水或大豆油混合,放入50 mL离心管中,30 ℃条件下放置30 min,每5 min搅拌一次,在3500 r/min条件下离心15 min后,弃去上清液称重,计算公式如(3):
持水(油)力(g/g)=样品被水(油)饱和后湿重−样品干粉重样品干粉重 (3) 1.2.8 色度的测定
采用色度计测定微波处理前后高粱的L*、a*、b*和ΔE值。并按公式(4)计算ΔE值:
ΔE=√(ΔL)2+(Δa)2+(Δb)2 (4) 式中:ΔE表示色差;L*表示黑白值;a*表示红绿值;b*表示黄蓝值。
1.2.9 高粱表面微生物的测定
菌落总数根据GB4789.2-2016《菌落总数测定》;霉菌和酵母菌计数根据GB4789.15-2016《霉菌和酵母总数测定》。
1.3 数据处理
所得数据均测定三次,用平均值±标准差来表示。利用统计学软件SPSS 25.0、Graphpad Prism 8.0和Origin 8.0进行分析作图,采用单因素方差分析比较各组间数据,t检验法分析组间差异显著性,P<0.05表示有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 微波处理影响高粱蛋白质含量结果
蛋白质是高粱中重要的营养物质,常与淀粉等络合的形式存在。微波处理后,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱的总蛋白质含量分别显著(P<0.05)提高了0.60%、0.58%和0.61%(如图1)。这与刘佳男等[16]的研究结果相一致,微波处理后白高粱的总蛋白质含量提高了0.60%,原因可能是由于微波处理破坏了高粱中的蛋白质复合物,使蛋白质充分释放。如图1所示,微波处理前,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱的可溶性蛋白质含量存在显著差异(P<0.05),分别为2.74、3.90和1.97 mg/g。微波处理后,三种高粱的可溶性蛋白质含量显著降低(P<0.05),分别降低至1.56、2.03和1.00 mg/g。这与赵颖等[17]研究的结果相类似,微波处理可使萌芽糙米中的可溶性含量蛋白质降低59.01%。也有研究表明,随着微波比功率(1.4~2.2 W/g)的增加,萌芽糙米中的可溶性蛋白质含量逐渐降低[18]。微波处理导致高粱中可溶性蛋白质含量降低的原因一方面可能与处理过程中蛋白质发生热降解有关,另一方面也有可能是因为微波处理使高粱蛋白质结构遭到破坏,大量的疏水基团外露,蛋白质溶解度降低[19]。
2.2 微波处理改变高粱蛋白质微观结构结果
微波处理前后,高粱蛋白质扫描电镜结果如图2所示。微波处理前,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱等3种高粱的蛋白质均呈块状,表面粗糙,凹凸不平,且粒径较大,但没有孔状结构。微波处理后,3种高粱的蛋白质也均呈块状,粗糙无序,不平整;但与未处理组相比,处理后的高粱蛋白质粒径明显减小,且表面出现明显裂纹。这可能是由于微波处理产生了强烈的热能,从而促进了高粱蛋白质的分解,进而使其粒径减小,表面产生裂纹[20]。因此,微波处理后高粱蛋白质的微观结构发生改变,故其所表现的理化性质也会随之改变。
2.3 高粱蛋白质FT-IR分析结果
高粱蛋白质的FTIR结果如图3所示。微波处理前后,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱等3种高粱的蛋白质红外光谱上的吸收峰波数没有发生明显的蓝移或者红移,未发现新的吸收峰,这表明微波处理并未改变高粱蛋白质分子的化学键组成,且未产生新的化学物质,属于物理变性。但高粱蛋白质的吸收峰强度有所不同,与未处理相比,处理组的吸收峰强度明显强于未处理组。
图3表明,高粱蛋白质在3010~2700 cm−1内有明显的吸收峰,这主要是烃类的氢键或碳碳键伸缩振动峰,在2800 cm−1附近出现的吸收峰主要是-NH和-OH的伸缩振动峰[21],而在1745 cm−1附近出现的伸缩振动峰主要是C=O键的特征峰[22]。在1600 cm−1附近的吸收峰是蛋白质典型的肽键(O=C-N-H)伸缩振动峰[23]。在1300~1200 cm−1范围内的伸缩振动峰主要是由O-H和C-O引起的,而在1150~1000 cm−1范围内的伸缩振动峰则是由碳水化合物产生的[24]。
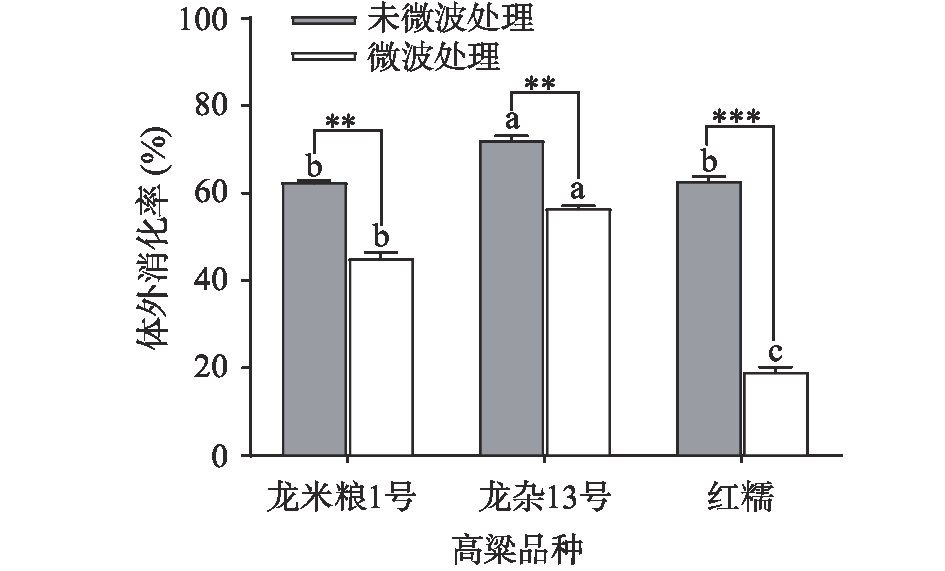
2.4 微波处理降低高粱蛋白质体外消化率结果
如图4所示,微波处理前,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱等3种高粱的蛋白质消化率为60%~70%。龙杂13号高粱的蛋白质消化率显著(P<0.05)高于其他2种高粱。Awika等[25]研究发现,高粱中蛋白质的结合形式及脂类、多酚、膳食纤维、细胞壁等成分均可导致抗酶解复合物的形成,从而影响高粱蛋白质的消化率。因此,本研究中,3种高粱蛋白质的消化率存在差异的原因可能与其自身组成成分有关。微波处理后,3种高粱的蛋白质消化率分别显著降低17.40%、15.55%和43.63%(P<0.05)。这与Duodu等[26]研究结果相类似,高粱在热处理后其蛋白质消化率降低约30%,由于在热处理过程中高粱内部形成大量的含有二硫键的低聚蛋白质,导致其消化率降低。
2.5 微波处理对高粱粉持水力和持油力的影响结果
持水力和持油力是评价谷物食品口感和风味的重要参数。如图5所示,微波处理前,龙米粮1号、龙杂13号和红糯高粱等3种高粱粉的持水力和持油力均存在显著差异(P<0.05),持水力为别1.30、1.35和1.50 g/g,持油力分别为1.27、1.35和1.20 g/g。微波处理后3种高粱的持水力分别提高了0.34、0.40和0.32 g/g,而持油力分别降低了0.11、0.18和0.08 g/g。这与Sharanagat等[27]研究的结果相一致,与对照组相比,随着微波处理时间(5~15 min)的增加,高粱粉的持水力显著提高0.25 g/g,持油力显著降低0.10 g/g。研究表明,微波处理可导致谷物表面出现多孔结构,谷物内部聚合物减少,从而增加谷物粉的持水力;而持油力降低的原因可能与微波处理过程中氨基酸极性的改变有关[28]。
2.6 微波处理对高粱粉色度的影响结果
颜色作为谷物食品的一种重要感官品质,对消费者的接受度有很大的影响。如表1所示,与未处理的高粱相比,微波处理后,高粱龙杂13号和红糯L*值均显著降低(P<0.05),高粱龙米粮1号和红糯a*值均显著升高(P<0.05),高粱龙米粮1号和龙杂13号b*值显著升高(P<0.05),三种高粱的ΔE值均显著升高(P<0.05)。这与Sharanagat等[29]研究的结果相一致,微波处理后高粱的a*、b*和ΔE增加,而L*值降低,原因可能是高粱在微波处理过程中发生了美拉德反应和焦糖化反应。此外,微波处理后龙米粮1号高粱的L*值变化不显著(P>0.05)原因可能是龙米粮1号是白色高粱,而微波处理后龙杂13号高粱的a*值和红糯高粱的b*值变化不显著(P>0.05),可能由于这两种高粱的表皮呈红色,麸皮中含有红色色素,掩盖了微波处理前后色度的变化。
表 1 微波处理对高粱粉色度的影响Table 1. Effect of microwave treatment on sorghum powder chroma样品 L* a* b* ΔE* 龙米粮1号(未处理) 62.98 ± 2.51a 2.63 ± 0.23e 13.05 ± 1.88b 34.13 ± 1.35b 龙米粮1号(处理) 61.22 ± 1.50a 3.50 ± 0.41d 19.21 ± 0.58a 36.60 ± 0.23a 龙杂13号(未处理) 61.37 ± 0.85a 4.38 ± 0.24c 11.01 ± 0.55c 31.26 ± 0.07d 龙杂13号(处理) 53.98 ± 0.81b 4.84 ± 0.10bc 14.60 ± 0.12b 32.57 ± 0.07c 红糯(未处理) 52.75 ± 0.49b 5.35 ± 0.36b 8.25 ± 0.93d 29.11 ± 0.21e 红糯(处理) 40.42 ± 0.74c 8.73 ± 0.55a 8.87 ± 0.37d 30.85 ± 0.18d 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 2.7 微波处理对高粱粉表面微生物的影响结果
微波技术作为一种传统的杀菌技术,因其具有无污染、杀菌速度快等优点,近年来在食品加工中得到了广泛的应用。如表2所示,未处理的高粱中菌落总数和霉菌数量最高,酵母菌数量<10 CFU/g。微波处理前,龙杂13号高粱中菌落总数和霉菌的数量显著(P<0.05)高于龙米粮1号和红糯高粱。推测原因可能是龙杂13号高粱中的含水率高于其他两种高粱,有助于霉菌等微生物的生长繁殖[30]。微波处理后,3种高粱中的菌落总数和霉菌的数量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照组,菌落总数和霉菌的灭菌率分别为98.75%和98.94%。这与Srisang等[31]研究结果相类似,与未处理的谷物相比,微波处理可使谷物表面的微生物数量减少约90%。研究表明,在微波的作用下,微生物会因分子极化而吸收微波能量,从而使其蛋白质变性,失去生物活性,因此微波处理会导致高粱表面微生物数量降低[32]。
表 2 微波处理对高粱粉表面微生物的影响Table 2. Effects of microwave treatment on surface microorganism of sorghum powder样品 菌落总数(CFU/g) 霉菌数量(CFU/g) 酵母菌数量(CFU/g) 龙米粮1号(未处理) 16200 ± 748c 4200 ± 535b <10 龙米粮1号(处理) 73 ± 12d 45 ± 6d <10 龙杂13号(未处理) 17667 ± 984a 11533 ± 704a <10 龙杂13号(处理) 130 ± 29d 117 ± 13d <10 红糯(未处理) 17331 ± 137b 1413 ± 368c <10 红糯(处理) 37 ± 12d 17 ± 3d <10 3. 结论
采用微波处理高粱,并对微波处理前后高粱蛋白和高粱粉的理化性质进行比较分析。结果表明,微波处理后,高粱蛋白质分子表面粗糙、粒径减小,体外消化率降低,然而其化学键及化学基团并未发生改变,为高粱食品原料处理提供物理数据依据。此外,微波处理后高粱粉的蛋白质含量和持水力增加,可溶性蛋白质含量和持油力降低,表面微生物数量减少,色泽变暗,有助于指导高粱食品加工中化学指标调整。因此,微波处理对高粱蛋白和高粱粉的理化性质具有明显影响,可为功能性高粱食品的开发及应用提供一定的参考。
-
表 1 微波处理对高粱粉色度的影响
Table 1 Effect of microwave treatment on sorghum powder chroma
样品 L* a* b* ΔE* 龙米粮1号(未处理) 62.98 ± 2.51a 2.63 ± 0.23e 13.05 ± 1.88b 34.13 ± 1.35b 龙米粮1号(处理) 61.22 ± 1.50a 3.50 ± 0.41d 19.21 ± 0.58a 36.60 ± 0.23a 龙杂13号(未处理) 61.37 ± 0.85a 4.38 ± 0.24c 11.01 ± 0.55c 31.26 ± 0.07d 龙杂13号(处理) 53.98 ± 0.81b 4.84 ± 0.10bc 14.60 ± 0.12b 32.57 ± 0.07c 红糯(未处理) 52.75 ± 0.49b 5.35 ± 0.36b 8.25 ± 0.93d 29.11 ± 0.21e 红糯(处理) 40.42 ± 0.74c 8.73 ± 0.55a 8.87 ± 0.37d 30.85 ± 0.18d 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 微波处理对高粱粉表面微生物的影响
Table 2 Effects of microwave treatment on surface microorganism of sorghum powder
样品 菌落总数(CFU/g) 霉菌数量(CFU/g) 酵母菌数量(CFU/g) 龙米粮1号(未处理) 16200 ± 748c 4200 ± 535b <10 龙米粮1号(处理) 73 ± 12d 45 ± 6d <10 龙杂13号(未处理) 17667 ± 984a 11533 ± 704a <10 龙杂13号(处理) 130 ± 29d 117 ± 13d <10 红糯(未处理) 17331 ± 137b 1413 ± 368c <10 红糯(处理) 37 ± 12d 17 ± 3d <10 -
[1] KAUR K D, JHA A, SABIKHI L, et al. Significance of coarse cereals in health and nutrition: A review[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore,2014,51(8):1429−1441. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0612-9
[2] BELTON P S, DELGADILLO I, HALFORD N G, et al. Kafirin structure and functionality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2006,44(3):272−286. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2006.05.004
[3] TAYLOR J R N, BELTON P S, BETA T, et al. Increasing the utilisation of sorghum, millets and pseudocereals: Developments in the science of their phenolic phytochemicals, biofortification and protein functionality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2014,59(3):257−275. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2013.10.009
[4] 王章存, 康艳玲. 国内外谷物蛋白发展概况[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2006,5:110−113. [WANG Z C, KANG Y L. Status of development on cereal protein[J]. China Food Additives,2006,5:110−113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2006.01.025 [5] STEPHEN G G, RANIL C, DEAN B, et al. Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of citral and quercetin incorporated kafirin-based bioactive films[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,168:341−347. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.077
[6] 戴凌燕, 蔡欣月, 陈卓, 等. 高粱醇溶蛋白的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(3):253−257. [DAI L Y, CAI X Y, CHEN Z, et al. Advance research of sorghum kafirin[J]. Food Industry,2018,39(3):253−257. [7] 霍金杰, 肖志刚, 王娜, 等. 青稞蛋白质的微波辅助提取工艺及性质研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(21):145−153. [HUO J J, XIAO Z G, WANG N, et al. Study on the microwave-assisted extraction technology and properties of barley protein[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(21):145−153. [8] 刘海波, 廖超, 郑万琴, 等. 微波处理小麦面粉对淀粉及蛋白性质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(14):91−97. [LIU H B, LIAO C, ZHENG W Q, et al. Effect of microwave-treated wheat flour on starch and protein properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(14):91−97. [9] 胡方洋, 陈金玉, 王轻, 等. 不同干燥方式对苦荞蛋白功能性质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(1):103−108. [HU F Y, CHEN J Y, WANG Q, et al. Effects of different drying methods on functional properties of tartary buckwheat protein[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(1):103−108. [10] 王娜, 孟利军, 黄忠民, 等. 加工方式对非发酵面团小麦醇溶蛋白致敏性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(9):292−299. [WANG N, MENG L J, HUANG Z M, et al. Effects of different processing on allergenicity of wheat gliadin in non-fermented dough[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(9):292−299. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.09.033 [11] 姜鹏, 李忍, 戴凌燕, 等. 浸泡和微波处理对三种高粱熟化的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(8):70−74. [JIANG P, LI R, DAI L Y, et al. Effects of soaking and microwave treatments on cultivability of three kinds of sorghums[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(8):70−74. [12] 周剑敏, 尹方平, 于晨, 等. 高粱碱溶蛋白ACE抑制肽的制备及其稳定性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2019,34(8):66−72. [ZHOU J M, YIN F P, YU C, et al. Preparation and stability of ACE inhibitory peptides derived from sorghum protein[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2019,34(8):66−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2019.08.012 [13] 赵志浩, 刘磊, 张名位, 等. 预酶解-挤压膨化对全谷物糙米粉品质特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(1):108−116. [ZHAO Z H, LIU L, ZHANG M W, et al. Combined effect of enzymatic pretreatment and extrusion on quality properties of brown rice flour[J]. Food Science,2019,40(1):108−116. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171210-121 [14] MERTZ E T, HASSEN M M, CAIRNS Whittern C, et al. Pepsin digestibility of proteins in sorghum and other major cereals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,1984,81(1):1−2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.1
[15] LIU H, FAN H, CAO R, et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of sorghum starch altered by high hydrostatic pressure[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,92:753−760. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.088
[16] 刘佳男, 于雷, 王婷, 等. 微波处理对白高粱淀粉理化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(5):186−190. [LIU J N, YU L, WANG T, et al. Effect of microwave treatment on physicochemical properties of white sorghum starch[J]. Food Science,2017,38(5):186−190. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201705030 [17] 赵颖, 申莉丽, 姜雯翔, 等. 3种膨化方式处理对萌芽糙米品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2016,42(3):150−155. [ZHAO Y, SHEN L L, JIANG W X, et al. Effects of three different puffing methods on the quality of germinated brown rice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2016,42(3):150−155. [18] 姜雯翔. 萌芽糙米热风微波干燥与焙炒及膨化加工研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. JIANG W X. Study on hot air microwave drying, baking and expansion processing of sprout brown rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014.
[19] 王振宇, 刘欢, 马俪珍, 等. 热处理下的猪肉蛋白质特性[J]. 食品科学,2008,5:73−77. [WANG Z Y, LIU H, MA L Z, et al. Characteristics of porcine proteins by heat treatment[J]. Food Science,2008,5:73−77. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.07.011 [20] LI Y, HU A, ZHENG J, et al. Comparative studies on structure and physiochemical changes of millet starch under microwave and ultrasound at the same power[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,141:76−84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.218
[21] XU B, YUAN J, WANG L, et al. Effect of multi-frequency power ultrasound (MFPU) treatment on enzyme hydrolysis of casein[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2020,63:104930. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104930
[22] SIANO F, SORRENTINO G, RICCARDI M, et al. Chemical, nutritional, and spectroscopic characterization of typical ecotypes of Mediterranean area beans[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2018,244(5):795−804. doi: 10.1007/s00217-017-3004-1
[23] 徐丽. 富含γ-氨基丁酸的小米发芽条件优化及特性分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019. XU L. Optimization of germinating conditions and characteristic analysis of millet rich in γ-aminobutyric acid[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2019.
[24] 曾剑华, 孟妍, 刘琳琳, 等. 基于多光谱技术表征汉麻分离蛋白构象并分析pH对其构象的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(12):3748−3754. [ZENG J H, MENG Y, LIU L L, et al. Characterization and effects of pH on the conformation of hemp protein isolate based on multi-spectroscopic technique[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(12):3748−3754. [25] AWIKA J M, ROONEY L W. Sorghum phytochemicals and their potential impact on human health[J]. Phytochemistry,2004,65(9):1199−1221. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.04.001
[26] DUODU K G, NUNES A, DELGADILLO I, et al. Effect of grain structure and cooking on sorghum and maize in vitro protein digestibility[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2002,35(2):161−174. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.2001.0411
[27] ADEBIYI J A, OBADINA A O, MULABA Bafubiandi A F, et al. Effect of fermentation and malting on the microstructure and selected physicochemical properties of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) flour and biscuit[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2016,70:132−139. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2016.05.026
[28] OBASI N E, UNAMMA N C, NWOFIA G E. Effect of dry heat pre-treatment (toasting) on the cooking time of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp)[J]. Nigerian Food Journal,2014,32(2):16−24. doi: 10.1016/S0189-7241(15)30113-2
[29] HU Z, SHAO Y, LU L, et al. Effect of germination and parboiling treatment on distribution of water molecular, physicochemical profiles and microstructure of rice[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2019,13(3):1898−1906. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00108-5
[30] AUKSORNSRI T, BORNHORST E R, TANG J, et al. Developing model food systems with rice based products for microwave assisted thermal sterilization[J]. LWT- Food Science and Technology,2018,96:551−559. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.05.054
[31] SRISANG N, VARANYANOND W, SOPONRONNARIT S, et al. Effects of heating media and operating conditions on drying kinetics and quality of germinated brown rice[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2011,107(3):385−392.
[32] AUKSORNSRI T, TANG J, TANG Z W, et al. Dielectric properties of rice model food systems relevant to microwave sterilization process[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2018,45:98−105.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 胡泽茜,李洋,崔琢玉,黄碧飞. 冷链物流环境下时间温度指示器的制备与应用. 农业工程学报. 2023(22): 246-257 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 钱艳峰,王娅,张明玥,杜子昂,贾靖璇,万祥龙. 用于监测食品新鲜度的时间-温度指示器研究现状. 食品工业科技. 2022(07): 10-20 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 俞胡斐,钱静. 不可逆变色油墨的配方设计及其制备. 包装工程. 2022(07): 125-131 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙若楠,张敏,夏斯璇,钱静. 胶态酶型时间温度指示器的制备研究. 包装工程. 2022(09): 115-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 俞胡斐,钱静. 不可逆温敏变色油墨的显色动力学探究. 包装工程. 2022(11): 46-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张博云,张宇,李庆山,高雪峰,李娇,寇俊杰,徐凤波. 羧甲基纤维素钠/聚乙烯吡咯烷酮与独活提取物复合涂膜对柑橘果实的保鲜效果. 食品工业科技. 2022(22): 353-364 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 刘冬青,陈朴,臧鹏,杜秉健,徐楠,向红. 时间-温度指示器在食品保质期预测中的应用. 食品工业科技. 2021(22): 1-10 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 康峻菡,胥义. 基于扩散型TTI与鲜银耳品质关联模型的建立及验证. 中国农学通报. 2020(32): 130-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)










 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



