Enhanced Detection of Uric Acid through Fe3O4@Au Based Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Biosensor
-
摘要: 本文通过自组装方法合成金磁微粒(Fe3O4@Au),并利用透射电子扫描电镜(TEM)对其结构和形貌进行表征。基于金磁微粒催化H2O2氧化分解体系,构建快速、灵敏、低成本的新型电化学传感器。研究结果表明,氨基化的Fe3O4可以有效固载金纳米粒子。检测最佳体系组合为:温度为60 ℃,金磁微粒添加量为1.20 mg/mL,扫描速率为0.1 V/s,缓冲溶液pH=5.5;在最佳试验条件下,所构建的尿酸传感器具有较高的灵敏度,在尿酸浓度为0.1~10 mmol/L范围内提供良好的线性电化学响应,线性方程为:y=13.267x+6.044,决定系数R2为0.9952,最低检出限为0.087 μmol/L;对现有市售新鲜牛奶进行加标回收试验,加标回收率在97.9%~110.2%以上。因此,该方法对检测尿酸具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract: In this paper, we reported an electrochemical biosensor based on Fe3O4@Au nanocomposite for the detection of uric acid (UA). The nanocomposite was prepared by self-assembling technique and the characterisation was carried out using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A highly sensitive and selective enzyme-free electrochemical based on peroxidemimetic enzyme activity of composite nanoparticles was prepared for the detection uric acid. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was used to assess the electrocatalytic response of Fe3O4@Au towards uric acid, and then the Fe3O4@Au exhibited high electrocatalytic response which was attributed to the increased surface area and conductivity of the nanocomposite. The results showed that Fe3O4 functionalized with amino groups could be effectively loaded with gold nanoparticles. The optimum detection conditions were as follows: Amount of temperature 60 ℃, Fe3O4@Au suspension 1.20 mg/mL, scanning rate was 0.1 V/s, and the electrolyte pH was 5.5. The novel electrochemical detection method showed an extremely high sensitivity towards uric acid under the optimized conditions, with a good linear relationship between the current response and the concentration of uric acid in the range of 0.1~10 mmol/L, and then the equation was y=13.267x+6.044 (R2=0.9952), with the corresponding limit of detection of 0.087 μmol/L. The recoveries ranged from 97.9%~110.2%%, recycling was very well and the accuracy of method was very high. The sensor showed excellent sensitivity for uric acid with good stability and selectivity. Thus, these results implied that the electrochemical sensor provided a popular price and simple method for the reliable analysis of uric acid.
-
尿酸(2,6,8-三羟基嘌呤,UA)是人体内最重要的生物分子,为嘌呤和核苷酸代谢的终产物,在人体中发挥着重要的抗氧化作用,可以清除体内的氧自由基,阻止人体走向衰老,并提高机体的免疫力[1]。由于其在水中的溶解度偏低(约6 mg/L),容易在人体和体液中积累形成固态尿酸,导致痛风和肾结石等疾病[2]。高尿酸血症是由尿酸分泌过多所致,尿酸分泌过多已被判定为痛风的主要原由。且高尿酸血症常伴有高血压、糖尿病、肾病、肥胖、冠心病等疾病[3]。因此,准确分析和检测UA水平是临床诊断的必要条件。目前,常用于检测UA的方法主要有高效液相色谱(HPLC)法[4]、比色法[5]、荧光法[6]、毛细管电泳法[7]、酶传感器法[8]以及磷钨酸还原法[9]等。由于荧光法和色谱方法耗时,设备昂贵,易受干扰且不方便操作等缺点限制了这些方法在检测尿酸方面的应用。近年来,电化学方法因其灵敏度高、检测范围广、检测速度快、操作简单和低消耗引起了广泛关注[10-12]。因此,电化学方法已成为分析化学的重要组成部分,并已广泛应用于环境、生物和医学领域。
天然酶因其稳定性差、制备成本高等缺陷使其应用范围逐渐缩小[13-15],纳米模拟酶在许多方面具有独特的优势,如稳定性好、成本低、易于长期储存和催化活性强等[16-17]。纳米Fe3O4粒子的尺寸小于某一临界值时,会呈现出超顺磁性、高矫顽力、高磁化率等特性[18-19]。同时,金纳米粒子(AuNPs)也表现出高导电率,高稳定性和优良的生物相容性等优点[20-21],因而在生物传感[22]、药物传输[23]、医学诊断[24]中得到了广泛的应用。通过静电自组装技术[25]所制备的磁性纳米复合金磁微粒(Fe3O4@Au)分布均匀,吸附性强,比表面积大,可以良好的改善电催化性能,从而增强电化学传感器的电化学响应[26]。本研究采用自组装法制备Fe3O4@Au,将其与电化学相结合,利用Fe3O4@Au过氧化物模拟酶活性,促进H2O2分解形成羟基自由基(·OH),催化UA在电极表面发生氧化反应,并产生大量电子转移[27],从而增加电极表面电子的转移,增强电流响应信号,建立检测UA含量的新型电化学方法,以期对临床诊断尿酸方法进行改进。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
FeCl3·6H2O、APTES 国药集团化学试剂有限公司生产;HAc-NaAc缓冲液、NaAc·3H2O、HAc-乙醇溶液、H2O2、尿酸、乙醇、PEG-4000、氯金酸 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;所有试验中所用试剂 均为分析纯。
YZHR-25型水热反应釜 上海耀冠仪器有限公司;H-7500型透射电子显微镜 日本电子株式会社;KQ 3200型超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;VSM LDJ 9600型振动磁强计 北京翠海佳诚磁电科技有限责任公司;FC204型电子天平 沈阳龙腾电子有限公司;PHS-3C型pH计 上海雷磁精密科学仪器有限公司;CH1660E型电化学工作站 上海辰华仪器有限公司;HWS24型电热恒温水浴锅 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验原理
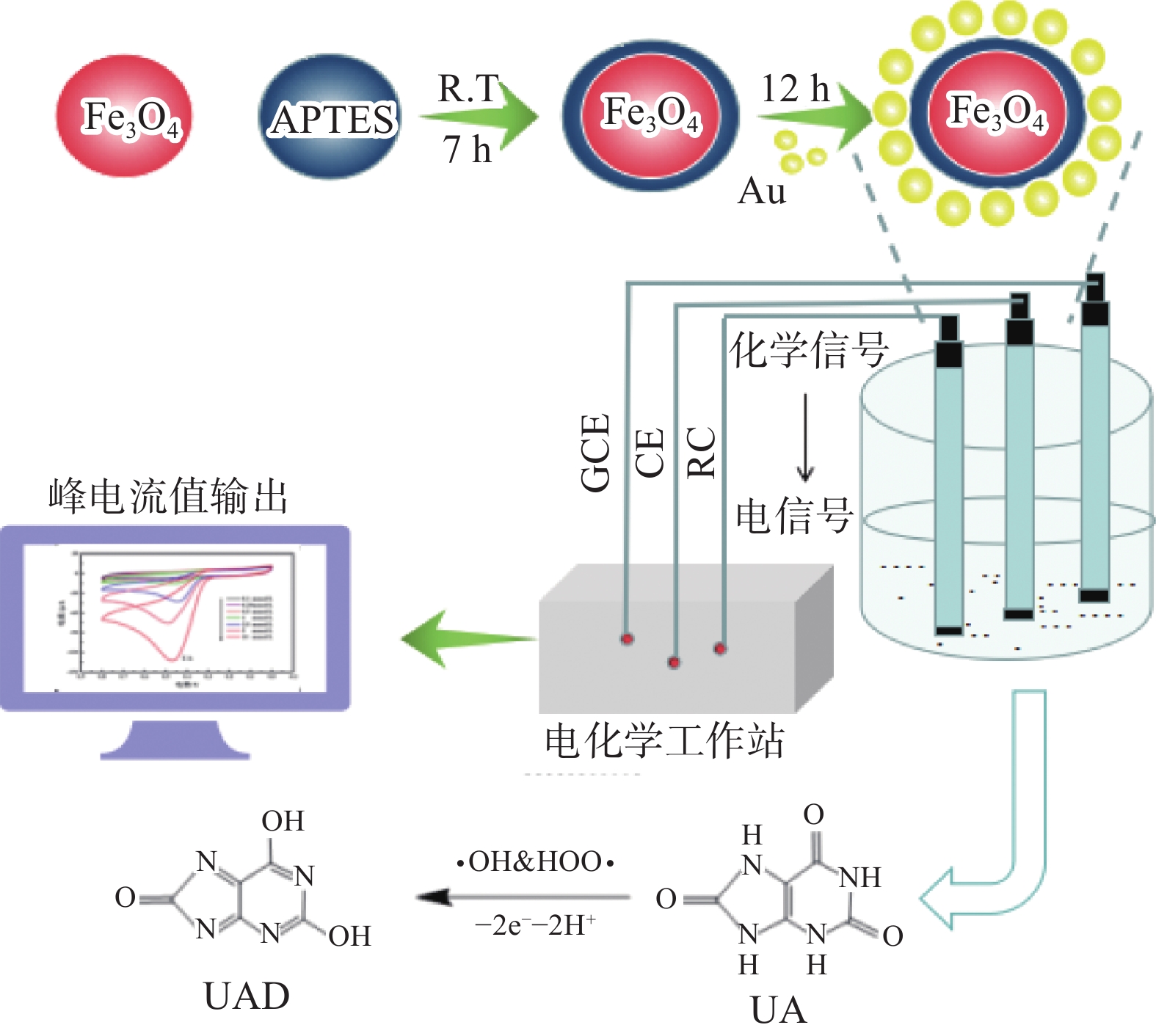
本研究中的所有反应均利用三电极系统,在室温下进行。使用CH1660E电化学工作站进行检测,工作原理如图1所示。当检测体系中加入纳米Fe3O4@Au时,Fe3O4@Au能够有效催化H2O2分解形成大量的氧化活性物质(主要为·OH和HOO·)[28],可进一步催化UA在电极附近发生氧化反应,UA氧化为脱氧尿酸(Dehydrourate,UAD),产生的电子积聚在电极表面,增强电化学响应,改善电化学检测尿酸的灵敏度。
1.2.2 Fe3O4@Au微粒的制备
准备60 mL乙二醇,2.0 g的FeCl3·6H2O,1.2 g的PEG-4000,4.2 g的NaAc·3H2O,依次加入100 mL烧杯中,加入搅拌子,通过使用磁力搅拌器得到均匀的混合溶液,迅速转移到水热反应釜中,在180 ℃条件下加热反应10 h后,室温下自然冷却,结果产物用无水乙醇和去离子水洗涤,重复三次。洗涤后干燥备用。
首先,烧杯中加入200 mL 80 ℃蒸馏水,精确称量80 g新鲜葡萄皮,并将其浸入烧杯中20 min,将浸泡液离心(3000 r/min)并分离5 min。取上清液200 mL作为工作液体。然后将烧杯于4 ℃条件下提前预冷却,分别取25 mL HAuCl4和6 mL工作液于烧杯中,通过使用恒温磁力搅拌器低速混合来观察溶液的颜色变化,当出现酒红色时,迅速加快搅拌速度,30 min后,所得溶液于4 ℃条件下保存备用。
称取4 g上述制备的Fe3O4NPs颗粒,并将其加入到60 mL 乙醇溶液(20%)中,利用超声使其在溶液中分散均匀,再缓慢加入2 mL 3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES),摇匀,将此体系置于恒温摇床中,调节振荡速度为150 r/min,持续10 h后,观察溶液颜色为浅棕色,即得到氨基化Fe3O4NPs磁性颗粒。将所得产物用0.1 mol/L HAc-乙醇溶液清洗,重复三次,清洗后放入60 ℃真空干燥箱,干燥备用。制备好的氨基化磁性纳米颗粒Fe3O4 3 g加入到烧杯中,然后将金纳米粒子溶液缓慢加入到烧杯中,在加入过程中不断地搅拌,之后将烧杯置于搅拌器台上,调节为低速状态,搅拌12 h后,即可得到磁性纳米颗粒Fe3O4@Au混悬液,烘干备用。
1.2.3 Fe3O4@Au微粒的表征
将制备的磁性材料粉末置于100 mL蒸馏水中,40 kHz 超声振荡使其均匀分散,然后将少量分散在蒸馏水中的样品滴铸在碳包覆的铜网格上制备。利用透射电子显微镜(TEM)观察材料的形态和粒径,工作电压为80 kV。
1.2.4 检测条件的单因素实验
反应温度对电化学体系的影响:配制pH为5.0的HAc-NaAc缓冲液10 mL,加入纳米Fe3O4@Au颗粒0.96 mg/mL,再加入200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2标准液,采用电热恒温水浴锅将该体系加热至恒定温度(20、30、40、50和60 ℃),反应15 min后,再加入200 μL的尿酸标准溶液(1 mmol/L)。调节电化学工作站扫描速率为0.06 V/s,考察反应温度对电化学体系的影响。
Fe3O4@Au添加量对电化学体系的影响:配制pH为5.0的HAc-NaAc缓冲液10 mL,加入纳米Fe3O4@Au颗粒(0.24、0.48、0.72、0.96和1.20 mg/mL),再加入200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2标准液,反应温度40 ℃,反应时间15 min,再加入200 μL的尿酸标准溶液(1 mmol/L)。调节电化学工作站扫描速率为0.06 V/s,考察Fe3O4@Au添加量对电化学体系的影响。
扫描速率对电化学体系的影响:配制pH为5.0的HAc-NaAc缓冲液10 mL,加入纳米Fe3O4@Au颗粒0.96 mg/mL,再加入200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2标准液,反应温度40 ℃,反应时间15 min,再加入200 μL的尿酸标准溶液(1 mmol/L)。调节电化学工作站扫描速率(0.02、0.04、0.06、0.08和0.10 V/s),考察扫描速率对电化学体系的影响。
pH对电化学体系的影响:配制不同pH(pH=5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5和7.0)HAc-NaAc缓冲液10 mL,加入纳米Fe3O4@Au颗粒0.96 mg/mL,再加入200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2标准液,反应温度40 ℃,反应时间15 min,再加入200 μL的尿酸标准溶液(1 mmol/L)。调节电化学工作站扫描速率0.06 V/s,考察pH对电化学体系的影响。
1.2.5 正交设计优化试验
将一定浓度的纳米Fe3O4@Au颗粒和200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2标准溶液加入到10 mL一定pH的HAc-NaAc缓冲液中,加热反应15 min后,加入浓度为1 mmol/L的尿酸标准溶液。采用三电极系统,调节电化学工作站不同扫描速率,利用循环伏安法检测体系中的尿酸浓度,考察氧化峰电流绝对值的变化,重复实验3次,确定因素影响主次顺序及优选方案,详情见表1。
表 1 试验因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface experiment水平 因素 A(反应温度,℃) B(添加量,mg/mL) C(扫描速率,V/s) D(pH) 1 40 0.72 0.06 5.0 2 50 0.96 0.08 5.5 3 60 1.20 0.10 6.0 1.2.6 尿酸电化学检测体系工作曲线的测定
在最适添加量、最适温度、pH和扫描速率体系下,向小烧杯中准确量取10 mL HAc-NaAc缓冲液,加入200 μL 50 mmol/L的H2O2溶液,再加入一定质量的金磁微粒纳米颗粒,恒温水浴15 min后,分别加入200 μL(0.1、0.25、0.50、1、2.5、5和10 mmol/L)尿酸标准溶液,连接好三电极系统,调节电化学工作站扫描速率,通过CV法检测氧化峰电流绝对值,重复实验3次。根据不同尿酸浓度与氧化峰电流绝对值绘制工作曲线。
1.2.7 检出限及回收率的测定
根据不同尿酸浓度与氧化峰电流绝对值绘制工作曲线,根据方程计算最低检测限。选择不同浓度0.5、2.5和10 mmol/L的尿酸标准液,检测其氧化峰电流绝对值,重复实验6次,将结果代入工作曲线回归方程,评价其回收率和精密度。
1.2.8 抗干扰性的测定
采用正交优化设计获得的优选方案,分别加入K2SO4、NaCl、CuCl2、AlCl3、蔗糖和甘氨酸等食品中常见物质,浓度均为0.1 mol/L,通过考察反应过程中氧化峰电流绝对值的变化,对其抗干扰性能进行监测。
1.2.9 实际样品检测
为验证本研究所构建的新型电化学检测方法在实际样品中的可实用性,选择正规超市购买的纯牛奶作为样品,将其与1.12%偏磷酸溶液(1:1)混合,以沉淀乳蛋白。并于2000 r/min离心15 min后,提取上清液,以1:1的比例加入氯仿(95%),以溶解乳脂。涡旋1 min后,以2000 r/min离心20 min,取其上清液,加入尿酸标准液,得到牛奶工作溶液。按照优选方案检测体系,检测3种不同浓度牛奶样品溶液的氧化峰电流绝对值,重复实验3次,计算加标回收率并评价该检测体系的精确度。
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin 8.0软件处理数据作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 金磁微粒的表征
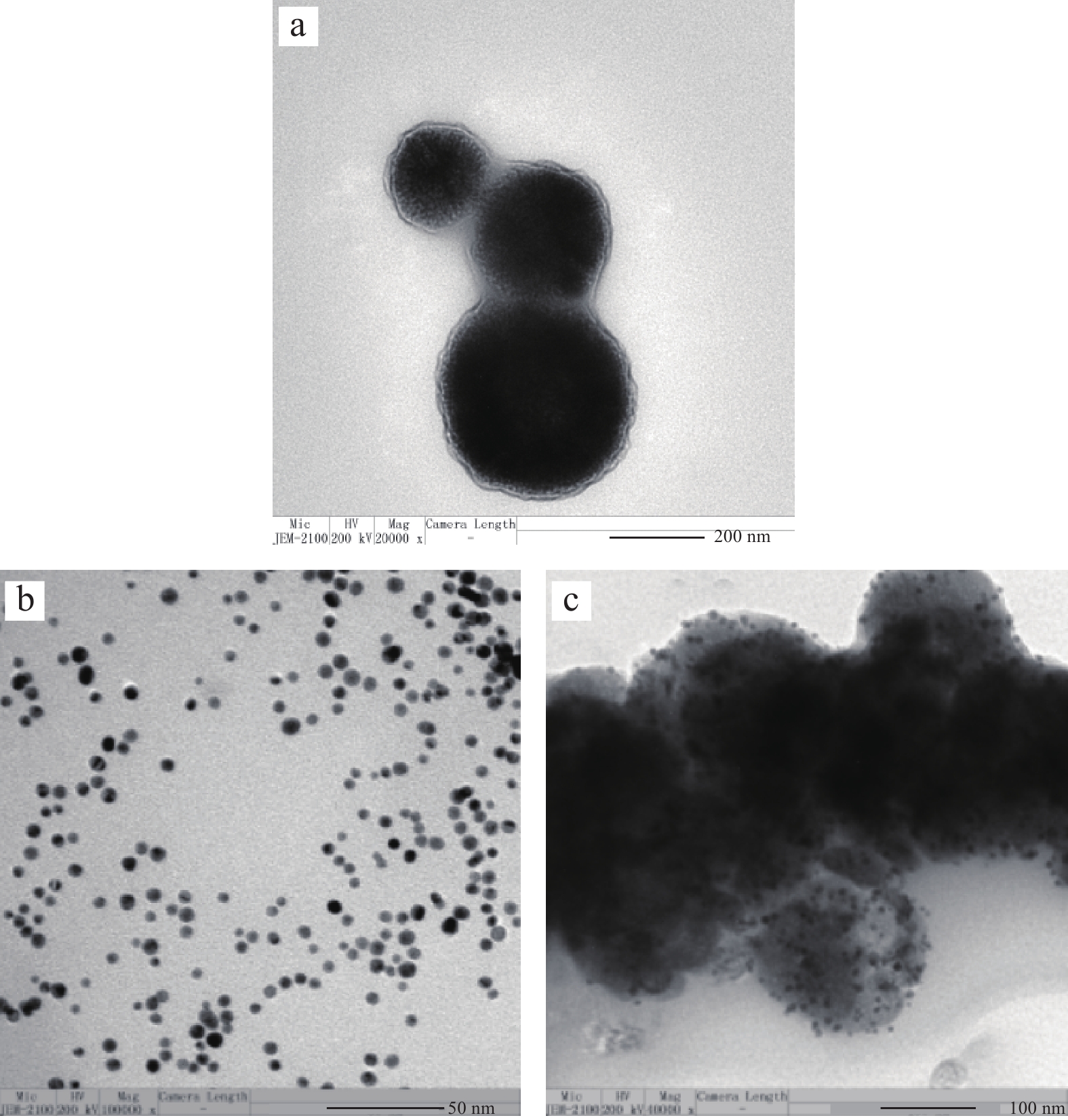
利用透射电子扫描电镜(TEM)对所制备的磁性纳米Fe3O4@Au结构和形貌进行表征,结果如图2所示。由图2a可以看出,Fe3O4纳米粒子结构多为球形,且聚集在一起,粒径较小,约为130 nm。由图2b可以看出,所制备的金纳米粒子结构为圆球形,且大小较为一致,分散度良好,平均粒径约为7~9 nm。由图2c可以看出,Fe3O4纳米粒子表面积聚了大量的金纳米粒子,表明经氨基化的磁性Fe3O4可以大量覆载金纳米粒子,该方法已成功制备出磁性纳米复合材料Fe3O4@Au。
2.2 电化学检测尿酸单因素试验
2.2.1 反应温度对电化学体系的影响
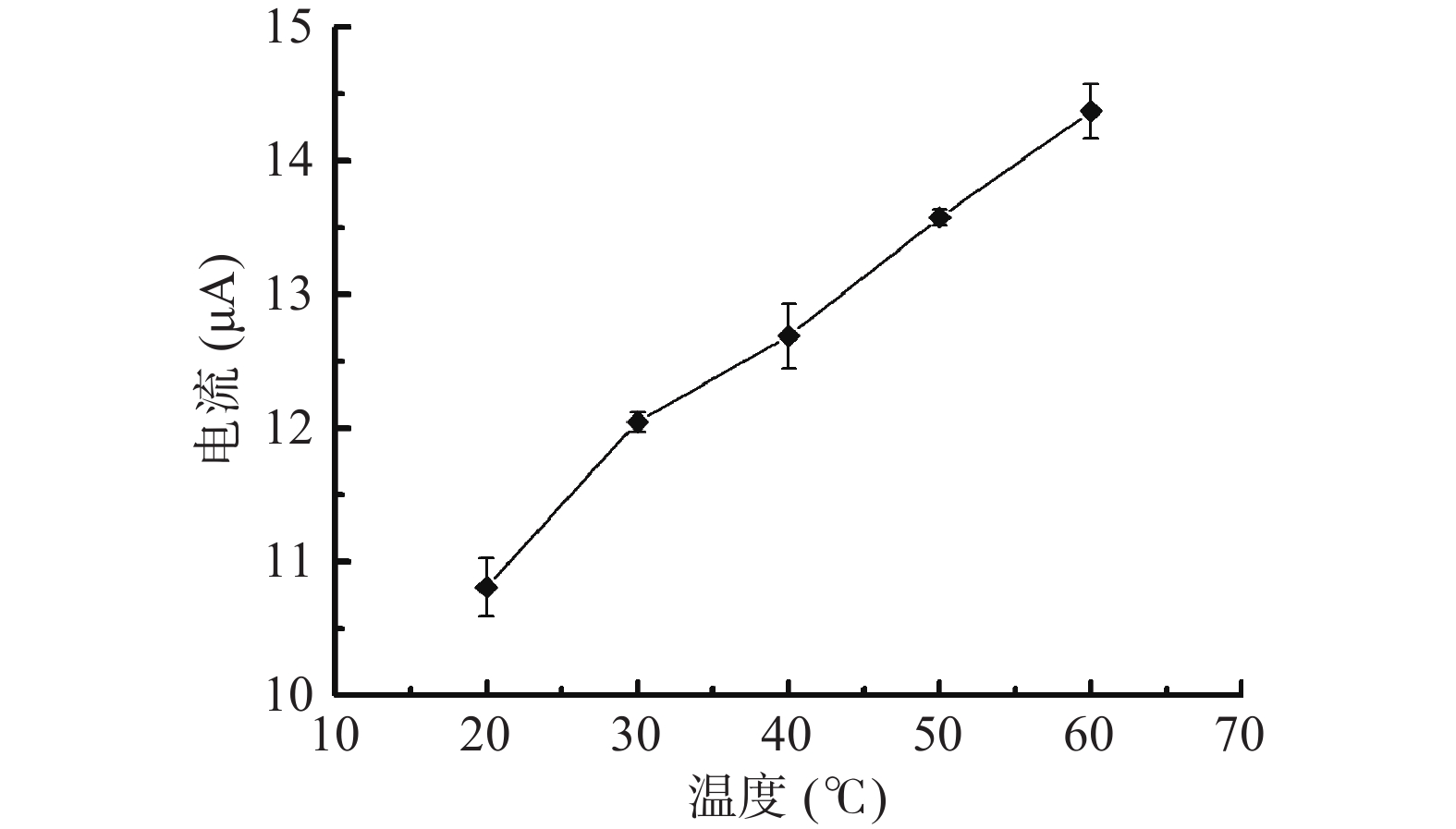
反应温度对电化学检测体系有直接影响,结果如图3所示。由图3可知,氧化峰电流绝对值随反应温度不断上升而逐渐增大,当温度在20~30 ℃区间内时,反应速率迅速增加,电极表面的电荷数量增加,电子转移速度加快,电流响应信号增强,氧化峰电流绝对值快速升高;当温度在30~60 ℃区间内时,随温度的不断升高,检测体系中Fe3O4@Au模拟酶活性增强,H2O2不断被氧化分解产生大量氧化活性自由基,从而加快了尿酸的电催化氧化,电极表面的电子转移数目不断增多,增强了电化学响应信号,氧化峰电流绝对值随之变大,考虑到该电化学传感系统的实用性,反应温度过高不利于其即时检测。因此,在进行正交优化试验设计中,选择反应温度为40、50和60 ℃。
2.2.2 Fe3O4@Au添加量对电化学体系的影响
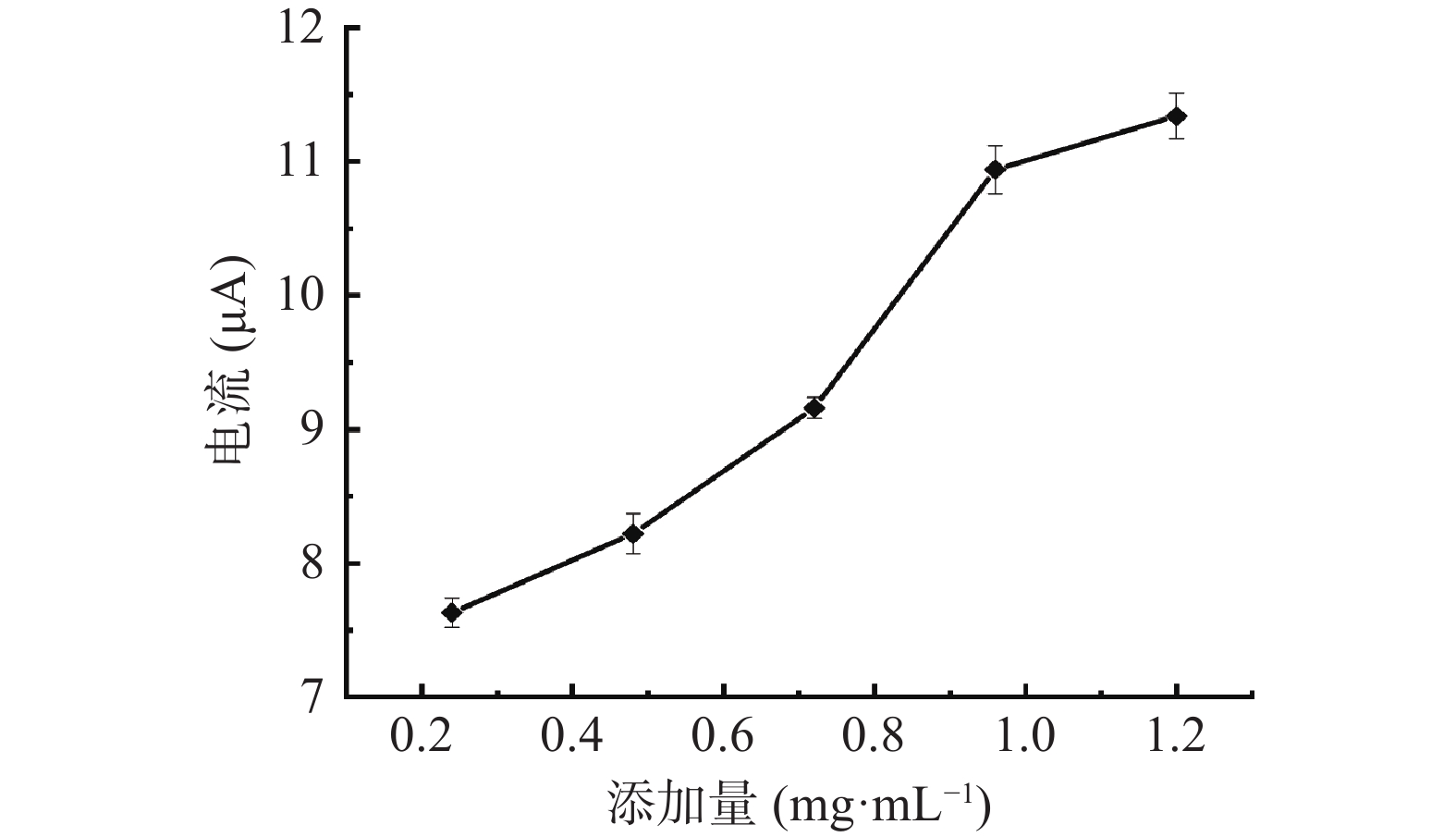
由图4可知,氧化峰电流绝对值随检测体系中Fe3O4@Au添加量的不断增加而稳定升高,当Fe3O4@Au添加量在0.24~0.48 mg/mL区间内时,反应速率开始变大,氧化峰电流绝对值随之增加;当Fe3O4@Au添加量在0.48~0.96 mg/mL区间内时,反应速率继续变大,氧化峰电流绝对值持续增加,说明随着电化学检测体系中Fe3O4@Au添加量的增加,增强了检测体系中模拟酶催化活性,促进H2O2氧化分解产生更多的羟基自由基;当Fe3O4@Au添加量在0.96~1.20 mg/mL区间内时,氧化峰电流绝对值的上升趋势变得缓慢,反应速率随之减小,说明随着纳米Fe3O4@Au在电化学检测体系中不断添加,产生团聚现象,比表面积减小,导致其模拟酶活性降低,体系中电子转移量随之减少。因此,在进行正交优化试验设计中,选择Fe3O4@Au添加量为0.72、0.96和1.20 mg/mL。
2.2.3 扫描速率对电化学体系的影响
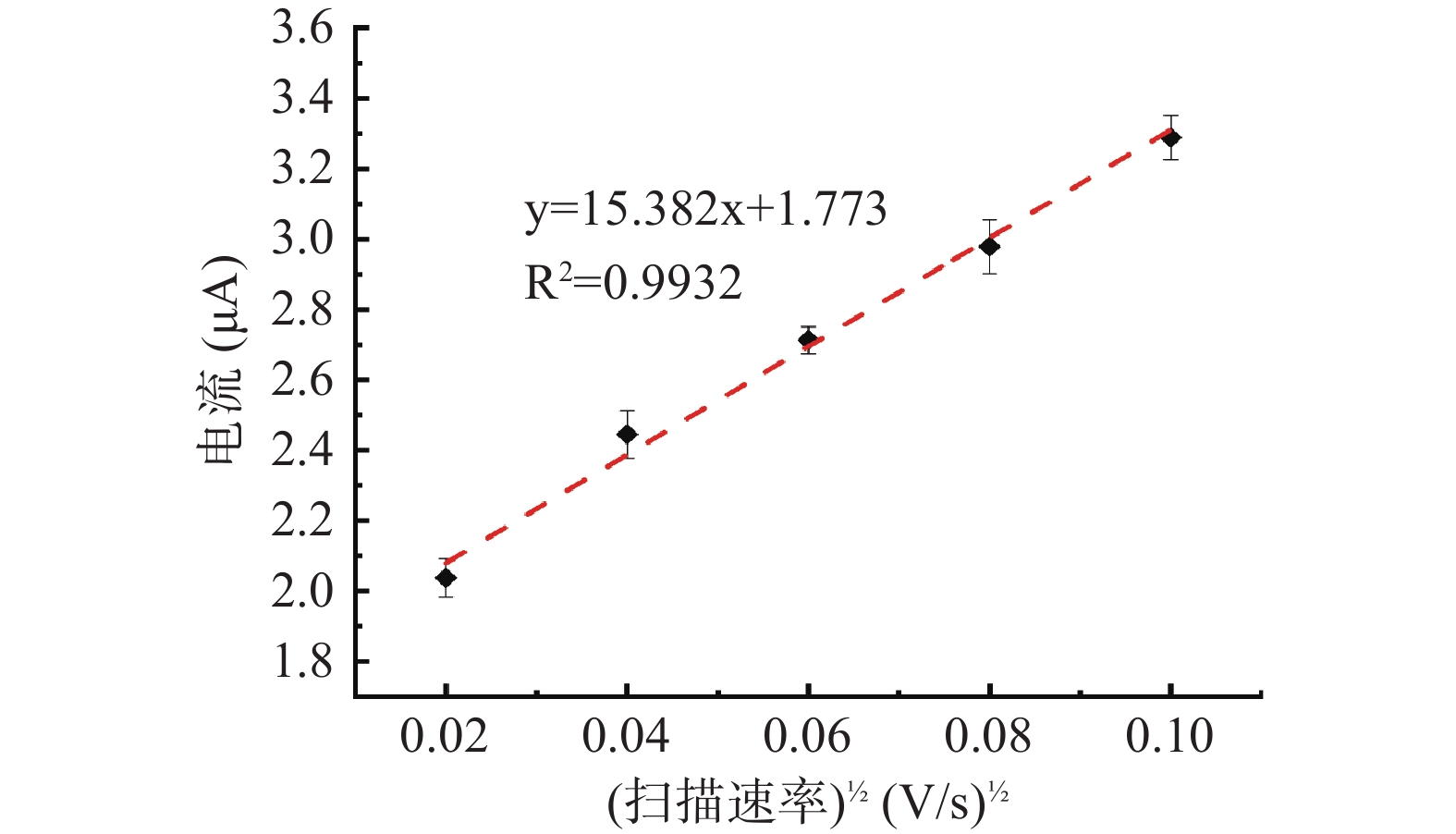
扫描速率对电化学检测体系的影响结果如图5所示。由图5可知,尿酸检测过程中氧化峰电流绝对值随扫描速率v的增大而增大,由氧化峰电流值与扫描速率平方根的线性曲线关系可知,氧化峰电流值|ipa(μA)|与扫描速率平方根在0.02~0.10 V/s范围内时表现出良好的线性关系,回归方程为:|ipa(μA)|=15.3821/2(V/s)1/2+1.773(R2=0.9932),表明尿酸在玻碳电极表面发生的氧化反应过程受表面吸附控制,可以更好地增强电化学响应信号[29]。由于扫描速率过大会影响尿酸电化学检测体系的稳定性,因此,在进行正交优化试验设计中,选择电化学检测体系的扫描速率为0.06、0.08和0.10 V/s。
2.2.4 pH对电化学体系的影响
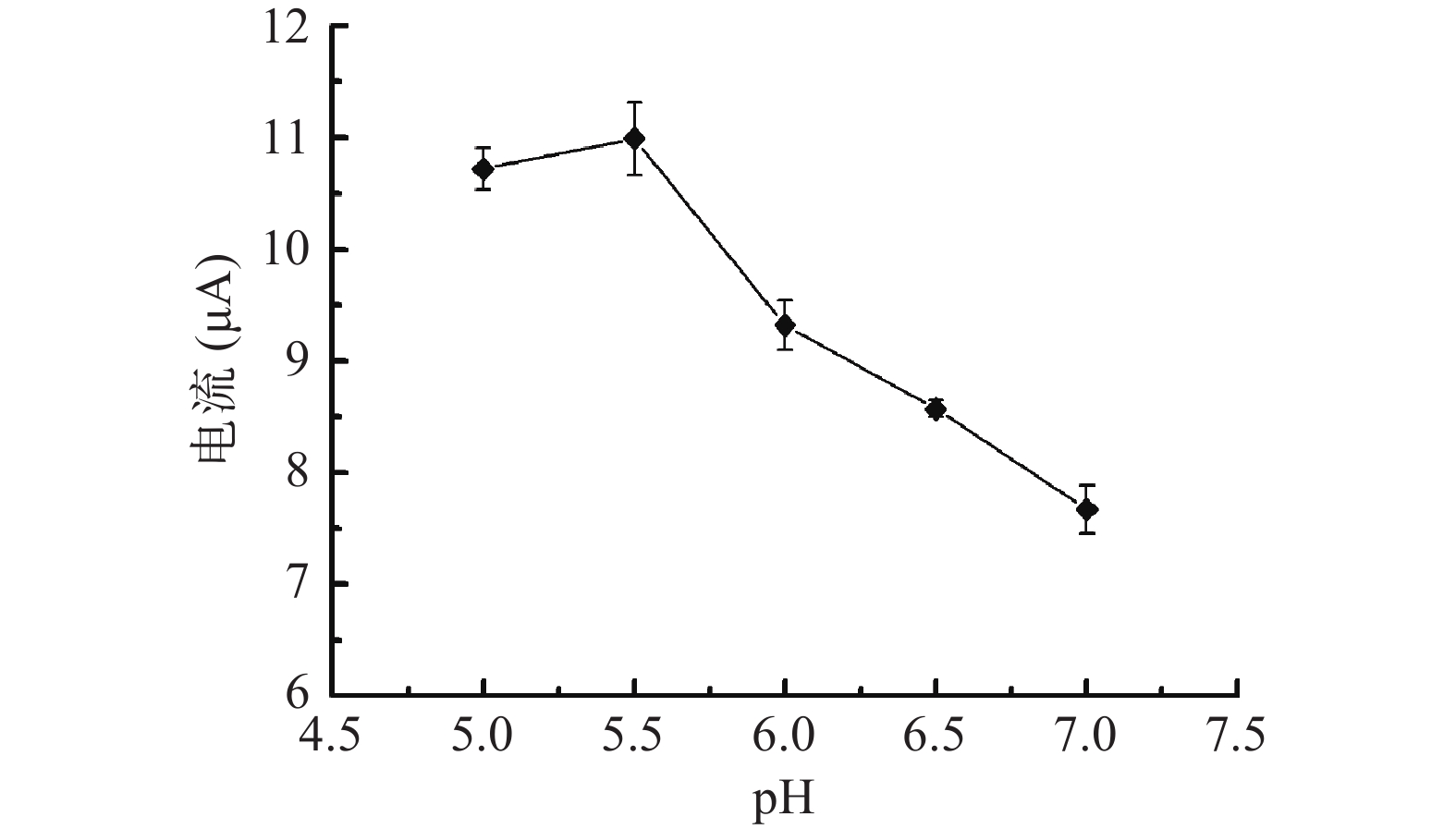
缓冲液的pH对电化学检测体系的影响结果如图6所示。氧化峰电流绝对值随缓冲液pH的增大先升高后减小,当缓冲液pH在5.0~5.5区间内时,氧化峰电流值变大,且到达最高点,说明此时纳米Fe3O4@Au模拟酶催化效果最显著,当pH在5.5~6.0范围内时,氧化峰电流绝对值大幅度减小,而pH在6.0~7.0范围内时,氧化峰电流绝对值持续减小,说明缓冲液的pH对尿酸检测体系的电子转移有明显的影响,首先,pH=5.5时,纳米Fe3O4@Au的电催化性能被激发到最大;其次,尿酸的氧化反应过程有质子的参与[30],质子覆盖了从尿酸中产生的电子,抑制了电极表面电子的转移,电流强度值明显下降。因此,在进行正交优化试验设计中,选择缓冲液pH为5.0、5.5和6.0。
2.3 正交设计优化电化学检测尿酸体系
结果如表2所示,实验中各因素对尿酸检测体系的主次顺序为:C>A>B>D,即扫描速率>温度>Fe3O4@Au添加量>pH。通过极差分析确定的最优方案组合为:A3B3C3D2,即温度为60 ℃,金磁微粒添加量为1.20 mg/mL,扫描速率为0.1 V/s,缓冲溶液pH=5.5。因此,说明扫描速率是影响Fe3O4@Au模拟酶催化体系的最主要因素,温度、醋酸缓冲溶液pH及Fe3O4@Au添加量对模拟酶检测尿酸浓度也有相应的影响。以最优方案对1 mmol/L尿酸进行3次独立平行试验,得到氧化峰电流绝对值平均值约为14.56 μA,相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.45%,表明该尿酸传感器检测体系精密度良好。
表 2 正交试验结果分析Table 2. Result of orthogonal experiment实验号 A B C D 氧化峰电流值(μA) 1 1 1 1 1 8.646 2 1 2 2 2 9.363 3 1 3 3 3 11.730 4 2 1 2 3 9.645 5 2 2 3 1 10.410 6 2 3 1 2 9.530 7 3 1 3 2 13.357 8 3 2 1 3 9.449 9 3 3 2 1 10.753 K1 29.739 31.647 27.625 29.809 K2 29.585 29.222 29.761 32.250 K3 33.559 32.014 35.497 30.823 k1 9.913 10.549 9.208 9.936 k2 9.862 9.741 9.920 10.750 k3 11.186 10.671 11.832 10.274 R 3.974 2.792 7.872 2.441 因素主次:C>A>B>D
最优组合条件:A3B3C3D22.4 尿酸检测体系的电化学响应效果
2.4.1 模拟酶电化学检测体系的工作曲线、最低检出限和回收率测定
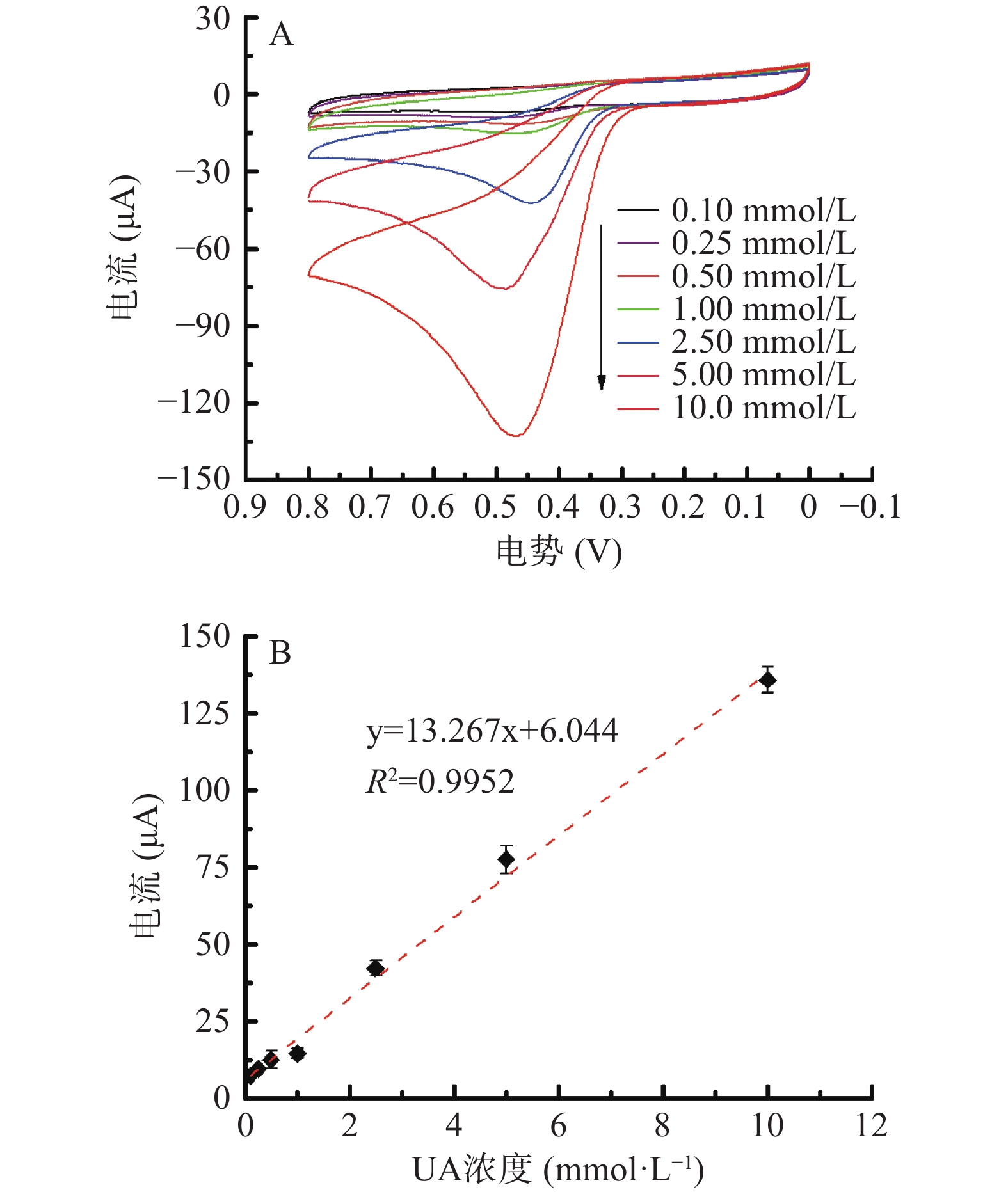
如图7A所示,在0.1~10 mmol/L范围内,氧化峰电流绝对值随尿酸浓度的增加而增大。采用循环伏安法考察不同浓度的尿酸标准溶液与氧化峰电流绝对值的线性效果,结果如图7B所示,尿酸在0.1~10 mmol/L范围内呈良好的线性关系,回归方程为y=13.267x+6.044,R2=0.9952。根据方程计算最低检出限为0.087 μmol/L(3s/b)。分别检测0.5、2.5和10 mmol/L的尿酸标准液,根据工作曲线回归方程,对该电化学检测体系进行回收率评价,回收率分别为105.30%、104.15%和96.17%,说明基于Fe3O4@Au模拟酶电化学检测尿酸的方法具有良好的准确度。
2.4.2 电化学检测体系抗干扰性能
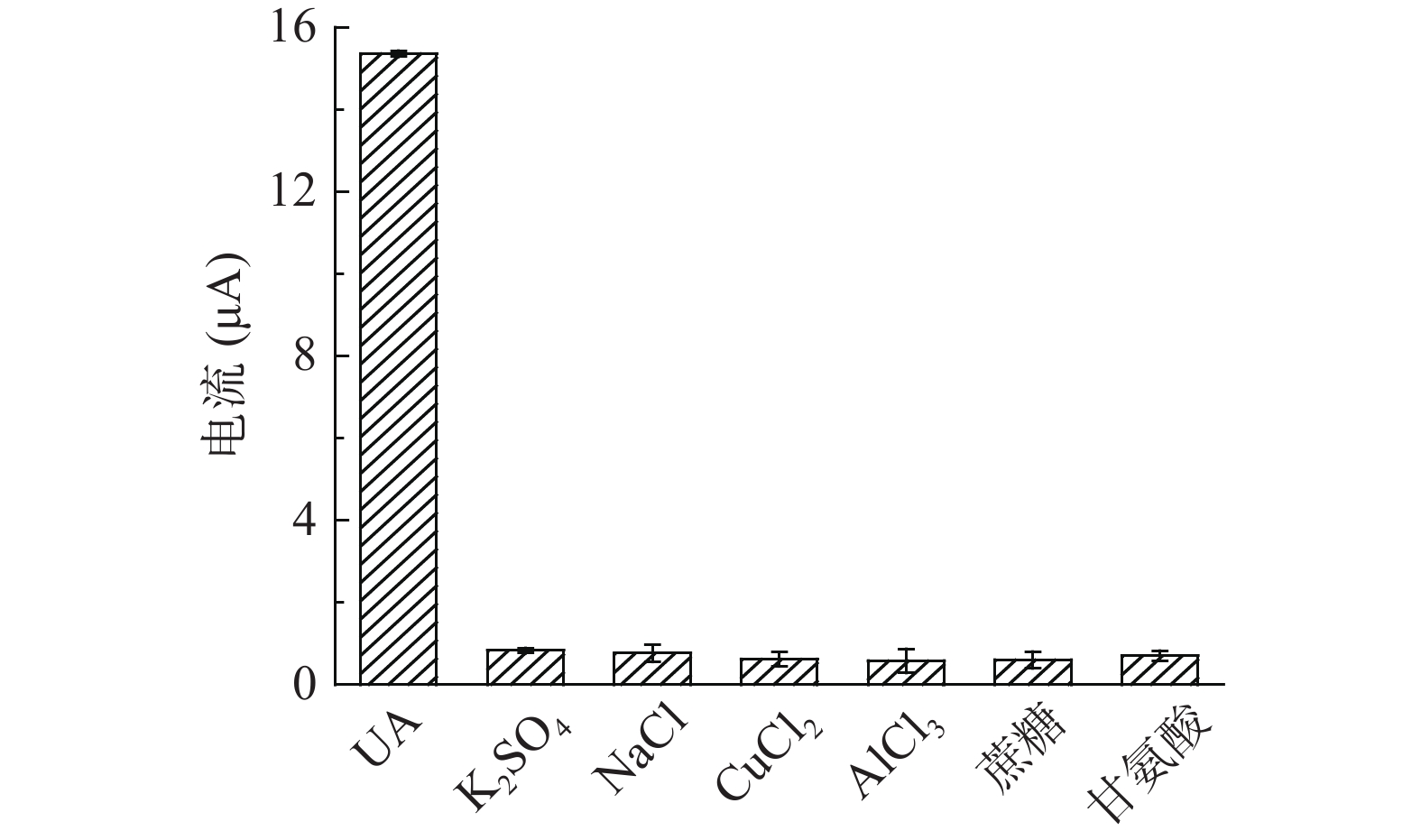
根据所构建的尿酸检测电化学传感器,考察氧化峰电流绝对值的变化,评估该检测方法的抗干扰性能。向检测体系中分别添加浓度为0.1 mol/L的K2SO4、NaCl、CuCl2、AlCl3、蔗糖和甘氨酸这些食品中常见干扰物质(每种添加物的浓度均为尿酸浓度的100倍)获得氧化峰电流绝对值,以1 mmol/L尿酸的体系作为参照,从而评估其抗干扰性能,结果如图8所示,电化学催化检测体系中加入0.1 mol/L的K2SO4、NaCl、CuCl2、AlCl3、蔗糖和甘氨酸均没有较强的电化学响应,而尿酸标准液具有明显的电化学响应信号。综上所述,该电化学检测方法对尿酸有较高的选择性。
2.5 实际样品检测
在相同体系下检测含有0.042、0.42和0.84 g/L浓度UA的牛奶标准溶液的氧化峰电流绝对值,带入工作曲线回归方程,评价其加标回收率。结果如表3所示,该电化学检测体系加标回收率分别为110.2%、97.9%和101.2%。重复测定3次,RSD分别为0.73%、1.84%和3.42%,均小于4%,说明该电化学检测体系具有良好的加标回收率和精密度,可实现对实际样品中UA的检测。
表 3 检测实际样品中不同浓度尿酸的加标回收率和精密度Table 3. Recovery rate and precision of real sample on different concentrations of uric acid样品 加标质量浓度(g/L) 测定值(g/L) 回收率(%) 相对标准偏差(%) 纯牛奶 0.042 0.0463 110.2 0.73 0.42 0.4111 97.9 1.84 0.84 0.8498 101.2 3.42 3. 结论
基于Fe3O4@Au纳米复合材料催化H2O2体系,构建了一种快速、灵敏、低成本的尿酸电化学传感器。该方法在UA浓度为0.1~10 mmol/L时具有明显的线性动态范围,检出限低至0.087 μmol/L,该电化学检测体系加标回收率分别为110.2%、97.9%和101.2%。该类传感器在潜在干扰物质存在下具有较高的选择性,并且成功应用于牛奶样品中的尿酸检测。本研究将为实际样品中尿酸的检测提供基础资料。
-
表 1 试验因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface experiment
水平 因素 A(反应温度,℃) B(添加量,mg/mL) C(扫描速率,V/s) D(pH) 1 40 0.72 0.06 5.0 2 50 0.96 0.08 5.5 3 60 1.20 0.10 6.0 表 2 正交试验结果分析
Table 2 Result of orthogonal experiment
实验号 A B C D 氧化峰电流值(μA) 1 1 1 1 1 8.646 2 1 2 2 2 9.363 3 1 3 3 3 11.730 4 2 1 2 3 9.645 5 2 2 3 1 10.410 6 2 3 1 2 9.530 7 3 1 3 2 13.357 8 3 2 1 3 9.449 9 3 3 2 1 10.753 K1 29.739 31.647 27.625 29.809 K2 29.585 29.222 29.761 32.250 K3 33.559 32.014 35.497 30.823 k1 9.913 10.549 9.208 9.936 k2 9.862 9.741 9.920 10.750 k3 11.186 10.671 11.832 10.274 R 3.974 2.792 7.872 2.441 因素主次:C>A>B>D
最优组合条件:A3B3C3D2表 3 检测实际样品中不同浓度尿酸的加标回收率和精密度
Table 3 Recovery rate and precision of real sample on different concentrations of uric acid
样品 加标质量浓度(g/L) 测定值(g/L) 回收率(%) 相对标准偏差(%) 纯牛奶 0.042 0.0463 110.2 0.73 0.42 0.4111 97.9 1.84 0.84 0.8498 101.2 3.42 -
[1] DONG W Y, HU X J, CHEN Z C, et al. An innovative bio-tissue network signal amplifier activated by high-N-doped carbon for uric acid detection[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2020:254.
[2] WANG Q W, WEN X, KONG J M, et al. Recent progress on uric acid detection: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry,2020,50(4):1−17.
[3] PATIL ANIRUDDHA B, ZHENG CHUANBAO, MA LIYUN, et al. Flexible and disposable gold nanoparticles-N-doped carbon-modified electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid[J]. Nanotechnology,2021,32(6):065502. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/abc388
[4] 依力哈木·扎依尔, 杨艳伟, 朱英, 等. 自动固相萃取-气相色谱-质谱法测定生活饮用水中60种半挥发性有机物[J]. 环境卫生学杂志,2020,10(1):81−88. [YILIHAMU Z, YANG Y W, ZHU Y, et al. Determination of 60 semi-volatile organic compounds in drinking water using automatic solid phase extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Environmental Hygiene,2020,10(1):81−88. [5] ZHANG Y M, HUANG H P, XU L. A novel electrochemical sensor based on Au-Dy 2 (WO 4 3 nanocomposites for simultaneous determination of uric acid and nitrite[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2019,48(3):e20032−e20037.
[6] WANG H Y, HUI Q S, XU L X, et al. Fluorimetric determination of dopamine inpharmaceutica products and urine using ethylene diamine as the fluorigenic reagent[J]. Anal Chim Acta,2020,497(1−2):93−99.
[7] WANG X, LU J J, TANG X M, et al. Colorimetric detection of uric acid with high sensitivity using Cu2O@Ag nanocomposites[J]. Chemistry Afric,2020,3:749−758. doi: 10.1007/s42250-020-00122-x
[8] LI N I, CHEN Y T, HU Y P, et al. Mobile healthcare system based on the combination of a lateral flow pad and smartphone for rapid detection of uric acid in whole blood[J]. Biosensors & bioelectronics,2020:164.
[9] 何云清. 紫外分光光度法与磷钨酸还原法测定尿酸浓度对比研究[J]. 广东化工,2017,44(9):250−251. [HE Y Q. A comparative study on the measurement of uric acid using ultraviolet spectrophotometry and phospho-tungstic acid deoxidizing method[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2017,44(9):250−251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2017.09.111 [10] KURBANOGLU S, OZKAN S A, MERKOÇI A. Nanomaterials-based enzyme electrochemical biosensors operating through inhibition for biosensing applications[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2017,89(2):886−898.
[11] MALLIKARJUNA K, VEERA M R Y, BATHINAPATLA S, et al. Simple synthesis of biogenic PdAg bimetallic nanostructures for an ultra-sensitive electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of uric acid[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2018,822:163−170. doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.05.019
[12] PARVANEH R, YVONNE J. Enzyme-based biosensors for choline analysis: A review[J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2018,110:367−374.
[13] 钟青梅, 黄欣虹, 覃庆敏, 等. 以碳量子点为过氧化物模拟酶的葡萄糖测定方法[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(7):1062−1068. [ZHONG Q M, HUANG X H, QIN Q M, et al. Determination of glucose based on carbon quantum dots as peroxidase mimetic enzyme[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2018,46(7):1062−1068. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.171396 [14] CHENG H, WANG X, WEI H. Ratiometric electrochemical sensor for effective and reliable detection of ascorbic acid in living brains[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2015,87(17):8889−8895. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02014
[15] LIU J, ZHAO Z, DING Z, et al. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol in fentonr-like system using Au-Fe omagnetic nanocompositesas the heterogeneous catalyst at near neutral condition[J]. RSC Adv,2016(6):53080−53088.
[16] 王鸿, 刘旭挺, 黄园, 等. 抗生素功能化金磁纳米探针的制备及其过氧化物模拟酶性能研究[J]. 中国科学:化学,2019,49(2):391−398. [WANG H, LIU X T, HUANG Y, et al. Preparation of antibiotic functionalized gold-magnetic nanoprobes and the study of their mimic peroxidase properties[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica),2019,49(2):391−398. [17] 李铸衡, 高晶清, 简明红, 等. 构建金纳米粒子标记的凝集素芯片应用于抗生素与金黄色葡萄球菌相互作用研究[J]. 分析化学,2018(12):1904−1912. [LI Z H, GAO J Q, JIAN M H, et al. Fabrication of lectin microarray for studying interactions of antibiotics with staphylococcus aureus by gold nanoparticle probes[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2018(12):1904−1912. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.181570 [18] LEONEL ALICE G, MANSUR ALEXANDRA A P, MANSUR HERMAN S. Advanced functional nanostructures based on magnetic iron oxide nanomaterials for water remediation: A review[J]. Water Research, 2020, 190: 116693−116697.
[19] 王文姣, 庄钊, 白瑞钦, 等. 四氧化三铁(Fe3O4)磁性复合材料在废水处理中的研究进展[J]. 胶体与聚合物,2020,38(4):186−190. [WANG W J, ZHUANG Z, BAI R Q, et al. Research progress of ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) magnetic composite materials in wastewater treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Colloid & Polymer,2020,38(4):186−190. [20] TAVALLAIE R, CARROLL J M, GRAND M L, et al. Gooding, nucleic acid hybridization on an electrically reconfigurable network of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles enables microRNA detection in blood[J]. Nature Nanotechnol,2018,13(38):1066−1071.
[21] WANG W W, HAO C L, SUN M ZH, et al. Spiky Fe3O4@Au supraparticles for multimodal in vivo imaging[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(22):1800310. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201800310
[22] LIU Y M, YANG J J, CAO J T, et al. An electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on CdSe/ZnS functionalized MoS and enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation for sensitive detection of immunoglobulin E[J]. Sensors and Actuators B Chemical,2016,232:538−544. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.165
[23] SHEN G Y, ZHANG S B, SHENG G L, et al. Development of an electrochemical aptasensor for thrombin based on aptamer/Pd-AuNPs/HRP conjugates[J]. Anal. Methods,2016,8(10):2150−2155.
[24] AFSHARANN H, KHALILZADEH B, TAJALLI H, et al. A sandwich type immunosensor for ultrasensitive electrochemical quantification of p53 protein based on gold nanoparticles/graphene oxide[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2016,188:153−164. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2015.11.133
[25] 韩博林, 关桦楠. 金磁微粒的制备及其催化性能[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(20):1−5, 10. [HAN B L, GUAN H N. Preparation and catalytic performance of gold magnetic particles[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(20):1−5, 10. [26] SUN D F. Fabrication of one-dimensional nanomaterials and their electrochemistry properties based on electrospinning[D]. Hebei: Yanshan University, 2011.
[27] Oliveira G C M D, Carvalho J, Brazaca L C, et al. Flexible platinum electrodes as electrochemical sensor and immunosensor of Parkinson’s disease biomarkers[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics,2020,152(3):112016.
[28] HUANG Y, XUE Y W, ZENG J X, et al. Non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on reduction graphene oxide-persimmon tannin-platinum nanocomposite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C,2018,92:590−598. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.07.021
[29] 牛博怀, 王文廉. 活化碳布电化学传感器对尿酸的检测研究[J]. 分析科学学报,2020,36(3):400−404. [NIU B H, WANG W L. Detection of uric acid by activated carbon cloth electrochemical sensor[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2020,36(3):400−404. [30] 张英, 张智彦, 马华, 等. 电化学方法快速测定尿酸的应用研究[J]. 四川理工学院学报(自然科学版),2009,22(4):85−87. [ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z Y, MA H, et al. Application of electrochemical method for rapid determination of uric acid[J]. Journal of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering(Natural Science Edition),2009,22(4):85−87.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
