Fungal Diversity of Natural Fermented Soybean Curd in Rural Areas
-
摘要: 为探究乡村豆腐乳内真菌的多样性,本研究以江西上饶市乡村自然发酵豆腐乳为对象,采用稀释平板培养方法,结合形态特征和LSU序列测序进行菌株鉴定、研究自然发酵豆腐乳真菌多样性。结果表明:从上饶市八个采样地24份豆腐乳样品中分离出277株菌株,鉴定出9个属26个种。根据分离频率,青霉属Penicillium(29.04%)、曲霉属Aspergillus(24.65%)、蓝状菌属Talaromyces (22.88%)、镰刀菌属Fusarium(10.57%)是鉴定出所有菌株中的优势属,不同来源地的真菌优势属具有明显差异;多样性指数(H)结果表明,铅山县石塘周边的多样性指数(H=1.92)是八个地区最高,菌群丰富度较高,而德兴市红山生活区的多样性指数(H=0.74)是最低,其菌群丰富度低。相似性指数(Cj)结果表明,铅山县石塘周边与广丰区小康城安利小区中豆腐乳的真菌的相似性系数为1.00,两地菌群相似程度较高,而铅山县紫溪乡文山村与玉山县樟树镇中豆腐乳的真菌相似程度极低,相似性系数为0.29。该研究结果将对提高豆腐乳的品质与安全性提供理论基础。Abstract: In order to explore the diversity of fungi in rural fermented bean curd, in this study, natural fermented bean curd in rural areas of Shangrao city, Jiangxi province was taken as the object. Strain identification and fungal diversity of natural fermented bean curd were conducted by dilution plate culture method, combined with morphological characteristics and LSU sequence sequencing. The results showed that 277 strains were isolated from 24 samples of fermented bean curd from eight sampling sites in Shangrao, and 26 species from 9 genera were identified. According to the separation frequency, Penicillium (29.04%), Aspergillus (24.65%), Talaromyces (22.88%) and Fusarium (10.57%) were the dominant genus of all the isolates, and there were significant differences among the dominant genera from different sources. The results of diversity index (H) showed that the diversity index (H=1.92) around Shitang in Yanshan County was the highest and the flora richness was high, while the diversity index (H=0.74) in Hongxing living area of Dexing city was the lowest and the flora richness was low. The results of similarity index (Cj) showed that the similarity coefficient of the fungi in fermented bean curd around Shitang in Yanshan County and Xiaokang city Anli community of Guangfeng area was 1.00, and the similarity degree of the fungi in the fermented bean curd was relatively high, while the similarity degree of the fungi in Wenshan Village of Zixi Township and Zhangshu Town of Yushan County was extremely low, with the similarity coefficient of 0.29. The results would provide a theoretical basis for improving the quality and safety of fermented bean curd.
-
Keywords:
- fermented bean curd /
- fungi /
- dominant genus /
- diversity /
- similarity
-
豆腐乳是中国流传数千年的汉族传统民间美食,豆腐乳以它的口味鲜美、风味独特、质地细腻、营养丰富而著称,被称之为“东方奶酪”,是我国著名的传统发酵豆制调味品之一。发酵豆制品的整个生产过程被认为是一个开放的、传统的过程,整个发酵过程中有多种微生物共同参与,不同微生物所起的作用可能各不相同。
豆腐乳作为发酵食品,目前研究发现豆腐乳中真菌有毛霉属(Mucor)[1-2]、曲霉属(Aspergillus)、青霉属(Penicillium)、根霉属(Rhizopus)[3]、地霉属(Geotrichum)、镰刀孢属(Fusarium)、毛孢子菌属(Trichosporon)、毕赤酵母属(Pichia)、假丝酵母属(Candida)、酵母属(Saccharomyces)、耶罗维亚酵母属(Yarrowia)等微生物[4-6];微生物在豆腐乳的生产、挥发性风味、品质等方面具有影响,国内外不同地方[7-9]以及不同风味的豆腐乳中微生物多样性研究[10-12]表明,豆腐乳中具有丰富的真菌资源,如低盐[13-14]、红豆腐乳[15]、传统发酵的豆腐乳[16-17]中的真菌资源均很丰富。
上饶位于江西省东北部,气候温湿,适合真菌的生存。由于当地的风俗习惯,每年春节将近家家户户都会制作豆腐乳。相对于工厂里具有严格的安全管理,家庭自制发酵豆腐乳具有更高的危害性,由于自制豆腐乳开放式的制作环境,豆腐乳中其它杂霉菌和细菌存在的几率很高。这些霉菌的存在对于豆腐乳风味的形成可能具有一定的有益作用,同时也可能是有害菌株,在发酵过程中产毒,造成多种微量毒素共存的现象[18-22]。因此,为了让百姓了解自制发酵豆腐乳的危害性,更好地改善自制豆腐乳的品质,本文以自然发酵豆腐乳为材料,采用稀释平板培养方法,结合形态特征和LSU序列测序进行菌株鉴定探究上饶不同地区豆腐乳真菌的多样性。研究结果将有助于进一步了解家庭自制自然发酵豆腐乳真菌毒素的检测,为家庭自制豆腐乳安全性提供科学的理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料和仪器
自然发酵豆腐乳 来自江西上饶市的八个乡村;分离培养基 虎红培养基(蛋白胨5 g、葡萄糖10 g、磷酸二氢钾1 g、硫酸镁0.5 g、琼脂19 g、孟加拉红0.033 g、氯霉素0.1 g、蒸馏水1000 mL);纯化、保种培养基 PDA培养基。
LT302电子天平、DYY-2C型电泳仪 北京市六一仪器厂;紫外分析仪、HH-4数显恒温水浴锅、基因扩增仪 上海启前电子科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 材料采集和处理
于2018年4月分别在江西上饶市八个乡村进行了自然发酵豆腐乳样本采集(具体采样地点为:A:婺源县溪头乡呈川村;B:广丰区洋口镇;C:铅山县紫溪乡文山村;D:玉山县樟村镇;E:德兴市红山生活区;F:上饶县田墩镇;G铅山县石塘周边;H:广丰区小康城安利小区。在文中图表用不同英文字母来表示不同采样点)。在每个采样点分别采集3家自然发酵豆腐乳放入无菌瓶中(每瓶150 g),并用无菌自封袋密封带回实验室于4 ℃保存,对样品进行处理培养。
1.2.2 真菌分离纯化
采用稀释涂布平板法。样品稀释液的制备:准确称取待测样品l0 g,放入研钵中,加入90 mL蒸馏水,进行研磨,使微生物细胞分散,再在虎红培养基上进行涂布,将平板倒置,进行标号,放入25 ℃恒温培养箱培养5~7 d,每天观察。做三个平行实验,每一个平行实验中每个稀释浓度涂布五个平板。
当培养基上长出菌丝后,通过不同菌落的形态特征进行区分,用无菌接种针分别挑取不同菌落的菌丝接到PDA培养基上,继续25 ℃恒温培养箱中培养3~5 d,进行纯化培养,直到获得单一的菌种[23]。纯化得到的菌株进行分离鉴定,并采用甘油管保藏法置于−20 ℃于保存。
1.2.3 真菌的鉴定
1.2.3.1 形态学鉴定
根据菌落的形态、颜色、菌丝和产孢器结构的形态查阅《真菌鉴定手册》[24]、Barnett & hunter(1998)和Seifert et al.(2011)的分类系统鉴定到属。
1.2.3.2 分子生物学鉴定
根据菌落的培养特征及微观特征进行形态型的划分合并,通过选取具有代表性的形态型菌株,分别刮取在PDA上培养成熟的菌丝,利用氯化苄法提取DNA[25]。采用真菌引物LR0R(5’-GTACCCGCTGAACTTAAGC-3’)和LR5(5’-TTAAAAAGCTCGTAGTTGAAC-3’)对菌株进行PCR扩增LSU片段[26],获得的扩增产物送北京擎科生物科技有限公司进行序列测定。测得序列经峰图检查并在NCBI中进行同源性比对[27]。确保序列准确性后,将本研究获得序列和从GenBank数据库中下载的相关序列利用MEGA 10.1软件构建系统发育树。
1.2.4 实验数据公式
1.2.4.1 菌落总数(colonies number)的计算
每克样品中的菌落总数(CFU/g)=(C/m)×M (1) 式中:C表示某一稀释度下平板上生长的平均菌落数;m表示涂布平板时所用豆腐乳的质量,g;M表示稀释倍数。
1.2.4.2 分离频率(isolation frequency,IF)的计算
分离频率IF(%)=分离得到的某一个属(种)真菌的菌株数分离得到的所有真菌菌株总数×100 (2) 1.2.4.3 Shannon-Wiener指数(H)的计算
H=−∑ni=1[pilnpi] (3) 式中:pi表示为种i真菌菌株数目与全部真菌菌株数目的比值。
1.2.4.4 Jaccard相似性指数(Cj)的计算[28]
Cj=ca+b−c (4) 式中:a表示一个地区豆腐乳分离的真菌的属数;b表示另一个地区豆腐乳分离的真菌的属数;c表示两个地区豆腐乳具有的相同真菌属数;Cj表示两个地区豆腐乳之间真菌的属组成的相似程度。
1.3 数据处理
运用Origin75汉化版软件进行数据统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 豆腐乳中菌落数的比较
豆腐乳中每样品中的菌落数(表1),豆腐乳中的真菌数量较多。在同一稀释浓度下,不同的地区的豆腐乳中真菌数有较大的差异,在稀释浓度为10−3时,铅山县紫溪乡文山村、广丰区洋口镇、婺源县溪头乡呈川村每克样品中的菌落数明显高于其他五个地区;在稀释浓度为10−4时,铅山县紫溪乡文山村、上饶县田墩镇、广丰区小康城安利小区、婺源县溪头乡呈川村的每克样品中的菌落数明显高于其他四个地区;在稀释浓度为10−5时,铅山县紫溪乡文山村、广丰区洋口镇、铅山县石塘周边的每克样品中的菌落数明显高于其他五个地区;说明铅山县紫溪乡文山村、广丰区洋口镇、铅山县石塘周边三个地区的菌株丰富度较高。
表 1 每克样品中的菌落数Table 1. Number of colonies per gram of sample采样地点 每克样品中的菌落数/稀释浓度(CFU/g) 10−3 10−4 10−5 A 4.90×103 4.50×104 2.70×105 B 6.40×103 2.70×104 6.40×105 C 2.71×104 1.58×105 1.33×106 D 2.70×103 3.70×104 3.70×105 E 2.80×103 1.20×104 1.1×105 F 3.30×103 5.10×104 3.40×105 G 3.50×103 2.60×104 5.30×105 H 4.00×103 4.50×104 4.30×105 注:A:婺源县溪头乡呈川村;B:广丰区洋口镇;C:铅山县紫溪乡文山村;D:玉山县樟村镇;E:德兴市红山生活区;F:上饶县田墩镇;G:铅山县石塘周边;H:广丰区小康城安利小区;表2、表3、图2同。 2.2 豆腐乳中真菌主要类群组成
从上饶市八个地区自制豆腐乳样品中共分离227个菌株,根据形态特征,形态型菌株LSU序列的相似性比较和分子发育分析将227株菌株划分Aspergillus、Penicillium、Talaromyces等26个分类单元(表2)。从属级水平的分离频率来看,以Penicillium(29.04%)、Aspergillus(24.65%)、Talaromyces(22.88%)、Fusarium(10.57%)为优势菌群;同时可知Penicillium为婺源县溪头乡呈川村、铅山县石塘周边、广丰区洋口镇的共同优势菌群,Talaromyces为广丰区小康城安利小区和上饶县田墩镇的共同优势菌群,而德兴市红山生活区的优势菌群为Penicillium和Aspergillum,铅山县紫溪乡文山村的优势菌群为Aspergillus,玉山县樟树镇的优势菌群为Fusarium。
表 2 上饶地区自制豆腐乳真菌菌群组成Table 2. Composition of fermented soybean curd fungus in Shangrao area分类单元 真菌分离 不同地区 A B C D E F G H 总株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) Penicillium brasilianum 19 8.36 5 2.20 3 1.32 6 2.64 4 1.76 1 0.44 Penicillium pulvillorum 25 11.00 7 3.08 8 3.52 4 1.76 5 2.20 1 0.44 Penicillium simplicissimum 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium citrimum 18 7.92 6 2.64 9 3.96 1 0.44 2 0.88 Penicillium oxalicum 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium mariae-crucis 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium sp. 1 0.44 1 0.44 小计(Penicillium) 66 29.04 Aspergillus niger 29 12.77 5 2.20 10 4.41 5 2.20 7 3.08 2 0.88 Aspergillus restrictus 17 7.48 3 1.32 3 1.32 6 2.64 5 2.20 Aspergillus flavus 7 3.08 5 2.20 2 0.88 Aspergillus novoparasiticus 2 0.88 2 0.88 Aspergillus flavusvar 1 0.44 1 0.44 小计(Aspergillus) 56 24.65 Talaromyces verruculosus 12 5.28 2 0.88 4 1.76 6 2.64 Talaromyces albobiverticillius 23 10.12 2 0.88 5 2.20 3 1.32 5 2.20 3 1.32 5 2.20 Talaromyces amestolkiae 10 4.40 5 2.20 2 0.88 3 1.32 Talaromyces allahabadensis 3 1.32 3 1.32 Talaromyces aculeatus 1 0.44 1 0.44 Talaromyces purpureogenus 3 1.32 3 1.32 小计(Talaromyces) 52 22.88 Fusarium flocciferum 14 6.17 10 4.41 4 1.76 Fusarium tricinctum 2 0.88 2 0.88 Fusarium oxysporum 8 3.52 4 1.76 4 1.76 小计(Fusarium) 24 10.57 Bionectria sp. 16 7.04 2 0.88 3 1.32 4 1.76 3 1.32 4 1.76 Clonstachys rosea 7 3.08 3 1.32 1 0.44 1 0.44 2 0.88 Fungal sp. 3 1.32 3 1.32 Trematosphaeria biappendiculate 2 0.88 2 0.88 Meyerozyma guilliermondii 1 0.44 1 0.44 总计 227 100 30 13.22 33 14.54 35 15.42 34 14.98 10 4.41 34 14.98 33 14.54 18 7.93 从种级水平的分离频率来看:在八个地区中,以Aspergillus niger(12.77%)、Penicillium pulvillorum(11.00%)、Talaromyces albobiverticillius(10.12%)为优势菌群;在各个地区的优势类群也有一定的差异,在婺源县溪头乡呈川村以Penicillium pulvillorum(3.08%)、Penicillium citrimum(2.64%)、Fusarium oxysporum(1.76%)为优势菌群,在广丰区洋口镇以Penicillium citrimum(3.96%)、Talaromyces albobiverticillius(2.20%)、Aspergillus niger(2.20%)为优势菌群,在铅山县紫溪乡文山村以Aspergillus niger(4.41%)、Penicillium pulvillorum(3.52%)、Talaromyces amestolkiae(2.20%)为优势菌群,在玉山县樟村镇以Fusarium flocciferum(4.41%)、Aspergillus restrictus(2.64%)、Fusarium oxysporum(1.76%)、Bionectria sp.(1.76%)为优势菌群,在德兴市红山生活区以Penicillium brasilianum(1.32%)、Aspergillus flavus(0.88%)、Fusarium tricinctum(0.88%)优势菌群,在上饶县田墩镇以Penicillium brasilianum(2.64%)、Talaromyces verruculosus(2.64%)、Aspergillus restrictu(2.20%)为优势菌群,在铅山县石塘周边以Aspergillus niger(2.20%)、Penicillium pulvillorum(2.20%)、Penicillium brasilianum(1.76%)、Fusarium flocciferum(1.76%)为优势菌群,在广丰区小康城安利小区以Talaromyces albobiverticillius(2.20%)、Bionectria sp.(1.76%)、Talaromyces allahabadensis(1.32%)为优势菌群;其中Aspergillus novoparasiticus、Trematosphaeria biappendiculate为婺源县溪头乡呈川村特有菌株,Fungal sp.为铅山县紫溪乡文山村特有菌株,Penicillium oxalicum、Penicillium mariae-crucis、Penicillium sp.、Talaomyces aculeatus为玉山县樟村镇特有菌株,Aspergillus flavusvar、Fusarium tricinctum、Meyerozyma guilliermondii为德兴市红山生活区特有菌株,Talaromyces purpureogenus为上饶县田墩镇特有菌株,Penicillium simplicissimum、Penicillium mariae-crucis、Talaromyces allahabadensis为广丰区小康城安利小区特有菌株,说明每个地区的环境不同导致了菌落的差异性。
2.3 系统发育树的构建
从图1中可以看出明显分为三个进化分支,其自展值各为99%;其中菌株D011与Meyerozyma guilliermondii KY108543单独划为一支,两者的自展值为99%,具有较高的相似性。菌株D001、Y007、Y036聚集在一支归属于Fusarium,另外菌株Y042与Bionectria sp. DQ327624.1具有99%的自展值;Aspergillus、Penicillium、Talaromyces、Trematosphaeria划为一支,均属于散囊菌目的丝孢发菌科mitosporic Trichocomaceae;其中菌株R007、R001、Y009、Y019、1K004以及W009聚集为一支归属于Talaromyces,菌株1K004与Talaromyces albobiverticillius MH869906具有99%的自展值,较高的相似性;菌株D004、Q026、D005、W041聚集为一支归属于Aspergillus,该四株菌种为Aspergillus的可信度较高,菌株G038与Aspergillus restrictus JF922028的自展值达到99%;菌株2Y019、K009、K006、Y014、T018等聚集为一支,归属于Penicillium,其中菌株G033与Penicillium citrinum MH665234的自展值为99%。
2.4 豆腐乳中真菌相似性及多样性分析
2.4.1 上饶地区豆腐乳中真菌菌群组成的多样性
从Shannon-Wiener指数(H)来看(图2),铅山县石塘周边(H=1.92)>广丰区小康城安利小区(H=1.57)>婺源县溪头乡呈川村(H=1.56)>玉山县樟村镇(H=1.50)>广丰区洋口镇(H=1.42)>铅山县紫溪乡文山村(H=1.28)>上饶县田墩镇(H=1.26)>德兴市红山生活区(H=0.74),可以看出铅山县石塘周边的豆腐乳中的真菌多样性较高,而德兴市红山生活区的豆腐乳中的真菌多样性是八个地区中最低的,该地区的豆腐乳中的真菌种类相当于其他七个地区更单调。
2.4.2 上饶地区豆腐乳中真菌菌群组成的相似性
从相似性系数来看(表3),铅山县石塘周边和广丰区小康城安利小区豆腐乳的真菌的相似性系数(Cj)为1.00,而铅山县紫溪乡文山村和玉山县樟村镇中豆腐乳的真菌的相似性系数(Cj)为0.29,并且Fungal只出现在铅山县紫溪乡文山村、Trematosphaeria只出现在婺源县溪头乡呈川村、Meyerozyma只出现在德兴市红山生活区,说明铅山县紫溪乡文山村与玉山县樟树村镇的豆腐乳中的真菌相似性不高,具有一定的差异性,铅山县石塘周边和广丰小康城安利小区的豆腐乳中的真菌的属相似度很高,并且以上一些菌株只在个别地区存在,因此八个地区豆腐乳中的真菌类群存在一定的差异性和专一性。
表 3 不同地区豆腐乳真菌的相似性指数Table 3. Similarity index of soybean curd fungi in different regions采样地 A B C D E F G H A 1.00 0.57 0.43 0.36 0.50 0.57 0.71 0.83 B 1.00 0.50 0.43 0.60 0.80 0.83 0.83 C 1.00 0.29 0.75 0.60 0.43 0.43 D 1.00 0.33 0.50 0.57 0.57 E 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.50 F 1.00 0.67 0.67 G 1.00 1.00 H 1.00 3. 结论
本研究从上饶市中八个地区豆腐乳中共分离了227个菌株,鉴定出26个分类单元:Penicillium、Aspergillus、Talaromyces、Fusarium等9个属26种。研究发现不同地区豆腐乳中的真菌种群数量和群落结构存在较大差异性与专一性,个别地区具有特殊的菌株,如婺源县溪头乡呈川村豆腐乳中的真菌(Aspergillus novoparasiticus、Trematosphaeria biappendiculate)为该地区的特有菌株,Fungal sp.为铅山县紫溪乡文山村豆腐乳中的特有菌株,Penicillium oxalicum、Penicillium mariae-crucis、Penicillium sp.、Talaromyces aculeatus为玉山县樟村镇豆腐乳中的特有菌株。八个地区豆腐乳中分离得到的菌株多样性系数和相似性系数结果表明,铅山县石塘周边的豆腐乳真菌多样性系数(H=1.92)最高,该地环境中能侵入豆腐乳的真菌相当于其他地区种类更多;而德兴市红山生活区的豆腐乳真菌为多样性系数(H=0.74),是八个地区中最低,该地豆腐乳中的真菌比其他七个地区种类更少;由相似性系数分析可知,铅山县石塘周边和广丰区小康城安利小区豆腐乳的真菌的相似性系数(Cj)为1.00,而铅山县紫溪乡文山村和玉山县樟村镇中豆腐乳的真菌的相似性系数(Cj)为0.29,不同两个地区的菌株相似性系数不相同,说明不同地区自然发酵豆腐乳的真菌具有一定的差异性。影响八个地区豆腐乳中真菌多样性的因素很多,如温度、湿度、季节、覆盖的稻草环境因素等[29-30],而有关影响豆腐乳中真菌多样性的具体机制有待进一步探究。
-
表 1 每克样品中的菌落数
Table 1 Number of colonies per gram of sample
采样地点 每克样品中的菌落数/稀释浓度(CFU/g) 10−3 10−4 10−5 A 4.90×103 4.50×104 2.70×105 B 6.40×103 2.70×104 6.40×105 C 2.71×104 1.58×105 1.33×106 D 2.70×103 3.70×104 3.70×105 E 2.80×103 1.20×104 1.1×105 F 3.30×103 5.10×104 3.40×105 G 3.50×103 2.60×104 5.30×105 H 4.00×103 4.50×104 4.30×105 注:A:婺源县溪头乡呈川村;B:广丰区洋口镇;C:铅山县紫溪乡文山村;D:玉山县樟村镇;E:德兴市红山生活区;F:上饶县田墩镇;G:铅山县石塘周边;H:广丰区小康城安利小区;表2、表3、图2同。 表 2 上饶地区自制豆腐乳真菌菌群组成
Table 2 Composition of fermented soybean curd fungus in Shangrao area
分类单元 真菌分离 不同地区 A B C D E F G H 总株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) 株数 分离频率(%) Penicillium brasilianum 19 8.36 5 2.20 3 1.32 6 2.64 4 1.76 1 0.44 Penicillium pulvillorum 25 11.00 7 3.08 8 3.52 4 1.76 5 2.20 1 0.44 Penicillium simplicissimum 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium citrimum 18 7.92 6 2.64 9 3.96 1 0.44 2 0.88 Penicillium oxalicum 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium mariae-crucis 1 0.44 1 0.44 Penicillium sp. 1 0.44 1 0.44 小计(Penicillium) 66 29.04 Aspergillus niger 29 12.77 5 2.20 10 4.41 5 2.20 7 3.08 2 0.88 Aspergillus restrictus 17 7.48 3 1.32 3 1.32 6 2.64 5 2.20 Aspergillus flavus 7 3.08 5 2.20 2 0.88 Aspergillus novoparasiticus 2 0.88 2 0.88 Aspergillus flavusvar 1 0.44 1 0.44 小计(Aspergillus) 56 24.65 Talaromyces verruculosus 12 5.28 2 0.88 4 1.76 6 2.64 Talaromyces albobiverticillius 23 10.12 2 0.88 5 2.20 3 1.32 5 2.20 3 1.32 5 2.20 Talaromyces amestolkiae 10 4.40 5 2.20 2 0.88 3 1.32 Talaromyces allahabadensis 3 1.32 3 1.32 Talaromyces aculeatus 1 0.44 1 0.44 Talaromyces purpureogenus 3 1.32 3 1.32 小计(Talaromyces) 52 22.88 Fusarium flocciferum 14 6.17 10 4.41 4 1.76 Fusarium tricinctum 2 0.88 2 0.88 Fusarium oxysporum 8 3.52 4 1.76 4 1.76 小计(Fusarium) 24 10.57 Bionectria sp. 16 7.04 2 0.88 3 1.32 4 1.76 3 1.32 4 1.76 Clonstachys rosea 7 3.08 3 1.32 1 0.44 1 0.44 2 0.88 Fungal sp. 3 1.32 3 1.32 Trematosphaeria biappendiculate 2 0.88 2 0.88 Meyerozyma guilliermondii 1 0.44 1 0.44 总计 227 100 30 13.22 33 14.54 35 15.42 34 14.98 10 4.41 34 14.98 33 14.54 18 7.93 表 3 不同地区豆腐乳真菌的相似性指数
Table 3 Similarity index of soybean curd fungi in different regions
采样地 A B C D E F G H A 1.00 0.57 0.43 0.36 0.50 0.57 0.71 0.83 B 1.00 0.50 0.43 0.60 0.80 0.83 0.83 C 1.00 0.29 0.75 0.60 0.43 0.43 D 1.00 0.33 0.50 0.57 0.57 E 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.50 F 1.00 0.67 0.67 G 1.00 1.00 H 1.00 -
[1] 赵玉莲, 郑学翔. 豆腐乳生产用微生物(一)[J]. 中国调味品,1998,23(12):5−7. [Zhao Y L, Zheng X X. Microorganism for production of bean curd milk (1)[J]. Chinese Condiment,1998,23(12):5−7. [2] 赵玉莲, 郑学翔. 豆腐乳生产用微生物(二)[J]. 中国调味品,1999,24(2):5−9. [Zhao Y L, Zheng X X. Microorganism for production of bean curd milk (2)[J]. Chinese Condiment,1999,24(2):5−9. [3] 秦恩华. 根霉发酵豆腐乳蛋白酶活性动态变化研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2006,27(11):101−102. [Qin E H. Study on dynamic changes of protease activity in fermented bean curd by Rhizopus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2006,27(11):101−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2006.11.030 [4] 李幼筠. 中国豆腐乳的现代研究[J]. 中国酿造,2006,25(1):4−7. [Li Y Y. Modern research on chinese bean curd[J]. China Brewing,2006,25(1):4−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2006.01.003 [5] 李理, 罗立新, 梁世中. 腐乳的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2002,28(10):70−74. [Li L, Luo L X, Liang S Z. Research progress of fermented bean curd[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2002,28(10):70−74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2002.10.017 [6] 万红芳. 生产菌种及环境微生物与豆腐乳品质关系研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(6):255−261. [Wan H F. Research progress on the relationship between production strains and environmental microorganisms and the quality of bean curd[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(6):255−261. [7] 王瑞芝, 郑建远. 豆腐乳毛霉菌种的选育[J]. 中国酿造,1993,12(4):17−25. [Wang R Z, Zheng J Y. Breeding of Mucor lactobacilli from bean curd[J]. Brewing in China,1993,12(4):17−25. [8] 杜鹏, 包媛媛, 杨明, 等. 结合云南牟定豆腐乳探究传统发酵豆制品豆腐乳的研究现状[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(11):242−247. [Du P, Bao Y Y, Yang M, et al. Research status of traditional fermented bean curd with Mouding bean curd[J]. The Food Industry,2019,40(11):242−247. [9] Xie C, Zeng H, Qin L. Physicochemical, taste, and functional changes during the enhanced fermentation of low-salt Sufu paste, a Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2018,21(1):2714−2729. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2018.1560313
[10] Han B Z, Rombouts F M, Nout M. A Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2001,65(1):1−10.
[11] Yang B, Tan Y, Kan J Q. Regulation of quality and biogenic amine production during sufu fermentation by pure Mucor strains[J]. LWT,2020,52(10):123−128.
[12] Xie C, Zeng H, Wang C, et al. Volatile flavour components, microbiota and their correlations in different sufu, a Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2018,125(6):1761−1773. doi: 10.1111/jam.14078
[13] 喻世哲, 范熠, 韩北忠, 等. 低盐豆腐乳生产过程及加工环境中的微生物分析[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(12):18−22. [Yu S Z, Fan Y, Han B Z, et al. Microbial analysis of low salt bean curd production process and processing environment[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(12):18−22. [14] 杨智慧, 张军伟, 魏冠棉, 等. 云南豆腐乳发酵菌种的分离鉴定及其低盐豆腐乳的品质分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(1):62−68. [Yang Z H, Zhang J W, Wei G M, et al. Isolation and identification of strains from sufu and quality analysis of low-salt sufu fermented using isolated strains[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(1):62−68. [15] Tang T, Qian K, Shi T, et al. Monitoring the contents of biogenic amines in sufu by HPLC with SPE and pre-column derivatization[J]. Food Control,2011,22(8):1203−1208. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.01.018
[16] 张鹏飞, 乌日娜, 武俊瑞. 传统发酵大豆制品挥发性成分和微生物多样性的研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(12):1−6. [Zhang P F, Wu R N, Wu J R. Research progress on volatile components and microbial diversity of traditional fermented soybean products[J]. China Brewery,2018,37(12):1−6. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.12.001 [17] 张雅婷, 孙娜, 于寒松, 等. 红豆腐乳发酵过程中菌群结构与风味相关性研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(1):287−294. [Zhang Y T, Sun N, Yu H S, et al. Advances in research on correlation between flora structure and product flavor during red sufu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(1):287−294. [18] 丁松乔, 肖志刚. 乳制品中黄曲霉毒素M1的常用检测方法比较分析[J]. 中国乳品工业,2016,44(5):36−39. [Ding S Q, Xiao Z G. Comparative analysis analysis of common detection methods for aflatoxin M1 in dairy products[J]. China Dairy Industry,2016,44(5):36−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2230.2016.05.009 [19] S Tusgul, G Prod'hom, L Senn, et al. Bacillus cereus bacteraemia: Comparison between haematologic and non-haematologic patients[J]. New Microbes and New Infec-tions,2017,15(3):65−71.
[20] Han B Z, Beume R R R, Rombouts F M, et al. Microbiological safety and quality of commercial sufu-A Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. Food Control,2001,12(8):541−547. doi: 10.1016/S0956-7135(01)00064-0
[21] 陈兴林. 发酵豆制品中黄曲霉毒素的控制[J]. 现代食品,2017,22(14):87−89. [Chen X L. Control of aflatoxin in fermented soybean products[J]. Modern Food,2017,22(14):87−89. [22] 刘琪, 陈静, 张佩娜, 等. 发酵豆制品中蜡样芽孢杆菌的调查分析[J]. 农产品加工,2018,17(4):57−59. [Liu Q, Chen J, Zhang P N, et al. Investigation and analysis of Bacillus cereus in fermented soybean products[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products,2018,17(4):57−59. [23] 张丽英, 沈微, 等. 一株豆腐乳生产菌的筛选、鉴定及其生理特征[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2007,26(9):116−120. [Zhang L Y, Shen W, et al. Screening, identification and physiological characteristics of a bean curd milk producing bacteria[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology,2007,26(9):116−120. [24] 魏景超. 真菌鉴定手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1979. Wei J C. Fungi identification manual[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1979.
[25] 朱衡, 瞿峰, 朱立煌. 利用氯化节提取适于分子生物学分析的真菌DNA[J]. 真菌学报,1994,13(1):34−40. [Zhu H, Qu F, Zhu L H. Extraction of fungal DNA suitable for molecular biological analysis by chlorination[J]. Journal of Fungi,1994,13(1):34−40. [26] White T J, Bruns T, Lee S, et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1990: 315-322.
[27] 燕勇, 李卫平, 高雯洁, 等. rDNA-ITS序列分析在真菌鉴定中的应用[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2008,18(10):1958−1961. [Yan Y, Li W P, Gao W J, et al. Application of rDNA-ITS sequence analysis in fungal identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Inspection,2008,18(10):1958−1961. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8685.2008.10.007 [28] 马克平. 生物群落多样性的测度方法. 生物多样性研究的原理与方法[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版, 1994: 141-165. Ma K P. A method for measuring the diversity of biological communities. Principles and methods of biodiversity research[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Publishing, 1994: 141-165.
[29] Han B Z, Wang J H, Rombouts F M, et al. Effect of NaCl on textural changes and protein and lipid degradation during the ripening stage of sufu a Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2003,83(9):899−904. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.1425
[30] Liu L B, Chen X Q, Hao L L, et al. Traditional fermented soybean products: Processing, flavor formation, nutritional and biological activities[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020,40(23):1−19.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 邓晓茜,符漫,杨甜甜,张彦,郭壮,王玉荣. 大竹米酒真菌群落研究及酵母菌分离鉴定. 中国酿造. 2023(03): 78-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





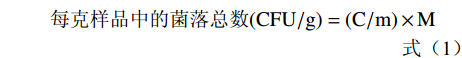
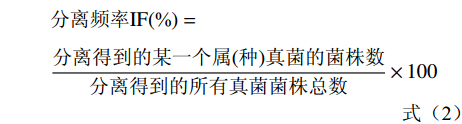


 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



