Effects of Different Lactic Acid Bacteria on Fermentation Characteristics and Metabolites of Grape Jiaosu
-
摘要: 以葡萄为原料,通过研究6株不同乳酸菌接种发酵过程中的发酵特性(还原糖、可溶性固形物、pH、总酸)、代谢产物(有机酸、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力、SOD酶活力)及生长情况(菌落总数)来筛选出适合葡萄酵素发酵的乳酸菌。结果表明:ACCC 11095在低pH的条件下生长情况优于其它菌株;ACCC 11095在发酵4 d后,还原糖、可溶性固形物趋于稳定;ACCC 11095、ATCC 14917和GDMCC 1.380于第5 d发酵结束后pH为3.33~3.35,总酸含量为11.07~12.74 g/L,显著高于其它三株菌(P<0.05);发酵结束后GDMCC 1.380的超氧化物歧化酶活力最高,为37.50 U/mL,其次是ATCC 14917,而ACCC 11095的发酵液呈现出最高的β-葡萄糖苷酶活力,为400.70 µU/mL;ACCC 11095产乳酸能力是其它菌株的1.2~30倍,6株菌均能代谢苹果酸且不产生乙酸;ACCC 11095和GDMCC 1.380的葡萄酵素液发酵5 d后,活菌数明显增加,分别为8.42和8.50 lg cfu/mL。综上所述,植物乳杆菌ACCC 11095产乳酸和产酶能力相对较强,具有更大的发酵潜力和应用于葡萄酵素生产的价值。Abstract: Grape Jiaosu was fermented by using grape as raw material. In order to screen suitable lactic acid bacteria(LAB) for grape Jiaosu, the fermentation properties (reducing sugar, the soluble solid content, pH, total acid), metabolites (organic acid, β-glucosidase activity, super oxide dismutase activity) and growth condition of six kinds of LAB during fermentation process was compared. The results showed that the growth of ACCC 11095 was better than that of other strains in low pH medium. Reducing sugar and soluble solids of ACCC 11095 tended to be stable on the fourth day. The pH of ACCC 11095, ATCC 14917 and GDMCC 1.380 was 3.33~3.35 at the end of the fifth day and the total acidity was 11.07 ~ 12.74 g/L, which was significantly higher than other strains (P<0.05). After fermentation, GDMCC 1.380 appeared at the highest superoxide dismutaseactivity, which was 37.50 U/mL, followed by ATCC 14917. While ACCC 11095 grape Jiaosu appeared at the highest β-glucosidase activity, which was 400.70 µU/mL. The lactic acid production capacity of ACCC 11095 was 1.2~30 folder higher than that of other strains. All six strains could degrade malic acid and not promote the formation of acetic acid. After 5 days of fermentation, the viable counts of ACCC 11095 and GDMCC 1.380 were 8.42 and 8.50 lg cfu/mL, respectively. In conclusion, Lactobacillus plantarum ACCC 11095 showed high lactic acid production capacity and relatively strong enzyme production capacity, which had greater potential for fermentation and application in grape Jiaosu production.
-
Keywords:
- grape /
- Jiaosu /
- lactic acid bacteria /
- superoxide dismutase activity /
- organic acid
-
食用酵素是以动物、植物、菌类等为原料,添加或不添加辅料,经微生物发酵制得的含有特定生物活性成分可供人类食用的酵素产品[1]。近年来,由于人们保健意识加强,越来越多的酵素产品受到消费者的欢迎。葡萄(Vitis vinifera),属葡萄科,落叶藤本植物,是世界栽培面积最大的水果,也是世界上产量仅次于柑橘的第二大水果,遍及亚洲,欧洲和美洲[2]。作为季节性较强的浆果,葡萄贮藏期短,需进行深加工。目前市场上葡萄制品主要有鲜食葡萄、葡萄酒、葡萄汁、葡萄干和葡萄果醋等。因此,开发新型葡萄酵素有利于丰富葡萄深加工产品类型,延长葡萄产业链。葡萄富含膳食纤维、维生素、矿物质、酚酸、类黄酮和花青素等,将葡萄通过微生物发酵制成葡萄酵素,基质中的糖类、维生素和花色苷等营养成分转变为小分子活性物质如有机酸、酶类和单体酚,不仅保留了天然果香还增加了营养密度[3-4]。
酵素中微生物由于酵素原料的不同,在发酵过程中微生物类型也不相同,果蔬酵素的微生物主要是酵母菌、醋酸菌和乳酸菌[5-7]。乳酸菌,作为益生菌被广泛的研究,对维持人体肠道菌群平衡、提高免疫力具有重要作用。除了益生功能,乳酸菌在酵素发酵过程中主要包括同型乳酸发酵和异型乳酸发酵,同型乳酸发酵通过分解糖类产生乳酸,而异型乳酸发酵产物除了乳酸之外还有乙醇、乙酸、琥珀酸和二氧化碳等,通过发酵,乳酸菌产生大量乳酸,使得发酵液pH降低,较高的酸度能抑制微生物的增长,保护发酵液不腐败变质,延长保质期。此外,乳酸发酵过程中产生的风味更加柔和、不酸涩,且也产生的一些醇、醛、酮等物质,使得发酵产品风味更加浓郁[8-9]。
目前,酵素在日本和台湾地区研究较多,我国大陆地区处于初始发展阶段,相关研发企业还比较少,市场上的酵素产品大多采用自然发酵,但该方法耗时长,微生物群落不稳定,发酵过程不易控制,易污染杂菌,其所导致的产品品质不稳定,不利于工业化生产[10-11]。因此本文以葡萄为原料,通过跟踪监测不同的乳酸菌对葡萄酵素发酵过程中总糖、总酸、pH、可溶性固形物、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活力、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力和有机酸的变化情况来研究乳酸菌对葡萄酵素发酵的影响,旨在筛选出适合葡萄酵素发酵的乳酸菌,以期为葡萄酵素的开发提供相关理论依据,这对葡萄的深加工具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
夏黑葡萄(Summer Black) 购于河南省南阳市某超市;植物乳杆菌ATCC 14917(Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14917)、植物乳杆菌ACCC 11095(Lactobacillus plantarum ACCC 11095)、植物乳杆菌GDMCC 1.380(Lactobacillus plantarum GDMCC 1.380)、干酪乳杆菌ATCC 334(Lactobacillus casei ATCC 334)、类干酪乳杆菌CICC 20109(Lactobacillus paracasei)、短乳杆菌GDMCC 1.288(Lactobacillus breris GDMCC 1.288) 北京微生物保藏中心;果胶酶(酶活力500 U/mg) 诺维信有限公司;草酸、酒石酸、苹果酸、丙酮酸、乳酸、乙酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸 色谱纯,美国Sigma公司;磷酸 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;对硝基苯酚、邻苯三酚、4-硝基苯基-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 分析纯,麦克林生化科技有限公司;乳酸菌通用培养基(MRS)、琼脂粉 北京奥博星生物技术有限公司。
Neofuge 15R高速冷冻离心机 上海力申科学仪器有限公司;SPX生化培养箱 宁波东南仪器有限公司;PHS-3C精密酸度计 杭州齐威仪器有限公司;UV752N紫外可见分光光度计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;QL-861涡旋机 海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司;1260安捷伦高效液相色谱(配备有四元泵,自动进样器,DAD检测器) 安捷伦科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 葡萄酵素的制备
取20 μL保藏在甘油管的乳酸菌菌液于MRS固体平板上,培养2~3 d,待长出单菌落后,挑取单菌落于已灭菌的液体培养基中进行扩大培养,37 ℃培养至对数生长期,即得到菌种活化液[12]。
挑选完好无破损的葡萄洗净、晾干,并用搅拌机打浆。用盐酸调pH为3.6,加入75 mg/mL的果胶酶酶解40 min,之后进行巴氏灭菌(60 ℃灭菌30 min)。待灭菌后的原料冷却,分别接3%的培养至对数生长期的乳酸菌于葡萄基质中,30 ℃下发酵5 d[13]。每隔1 d取样,对发酵液的还原糖、可溶性固形物、pH、可滴定酸、β-葡萄糖苷酶、SOD酶、有机酸、活菌数进行测定。
1.2.2 乳酸菌生长曲线的测定
将活化好的6株乳酸菌菌的菌液(菌液浓度>106 cfu/mL)以3%的接种量接入MRS液体培养基,置于37 ℃恒温摇床培养24 h,于0、2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20、22、24 h取样,测定OD600 nm值,以不加菌的MRS培养液为空白对照。
1.2.3 pH对乳酸菌生长的影响
根据食用酵素生化指标规定,食用酵素pH不应高于4.0[14],因此需要考察pH对不同乳酸菌生长的影响。活化后的菌液以(菌液浓度>106 CFU/mL) 1%的接种量接入MRS液体培养基(分别用盐酸调配pH至3.0、3.5、4.0、4.5、5.0)中,混合均匀,置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中培养48 h,测定OD600 nm,以不加菌的各pH的MRS培养液为空白对照。
1.2.4 不同乳酸菌发酵性能测定
还原糖采用3, 5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS)法测定[15],即取稀释一定倍数的样品1 mL与1.5 mL的DNS混合,沸水浴显色5 min,待冷却后将体积定容到10 mL,550 nm处测定吸光值,以1 mL蒸馏水做空白对照。可溶性固形物的测定参照NY/T 2637-2014《水果和蔬菜可溶性固形物含量的测定》,结果以Brix°表示。使用pH计测定葡萄酵素发酵过程中样品的pH,可滴定酸含量的测定参照GB/T 12456-2008,结果以乳酸质量浓度计。
1.2.5 SOD和β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的测定
SOD活力按照邻苯三酚自氧化法GB/T 5009.171-2003《保健食品中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性的测定》操作;β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的测定参照文献中的方法[16]。
1.2.6 有机酸含量的测定
取2.5 mL的样品于50 mL的容量瓶中,加入1 mL10.6%的亚铁氰化钾溶液和1 mL 30%的硫酸锌溶液,用去离子水定容,静置30 min,之后取上清液离心,离心后的液体经0.45 μm膜和C18柱过滤,上HPLC分析。
检测条件:色谱柱Eclipse XDB-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);流动相:0.02 mol/L 磷酸二氢钠,用磷酸调pH至2.1;流速:0.9 mL/min;柱温:30 ℃;进样量:10 μL;检测波长:210 nm;检测器:二极管阵列检测器[17]。
1.2.7 活菌数的测定
为了考察不同乳酸菌在葡萄基质中的生长情况,对乳酸菌在基质中发酵5 d后的活菌数进行测定。乳酸菌活菌数的测定按照平板计数法GB 4789.35-2016操作。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据以平均值±标准差表示。采用Origin软件进行图形绘制,利用SPSS 20.0软件进行单因素方差分析(Duncan’s test),P<0.05为显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同乳酸菌的生长曲线
采用比浊法对6株不同的乳酸菌的生长进行了测定并绘制生长曲线,确定菌株的最佳接种时间,生长曲线如图1所示。
由图1可知GDMCC 1.288和ATCC 334在6 h左右进入对数生长期,菌株生长较为平缓,且都在20 h进入对数生长稳定期。ATCC 14917、GDMCC 1.380、ACCC 11095和CICC 20109在4 h左右进入对数生长期,随后菌数呈指数上升。GDMCC 1.380、ATCC 14917和ACCC 11095在22 h进入对数生长稳定期,而CICC 20109在18 h进入对数生长稳定期。
2.2 pH对乳酸菌生长的影响
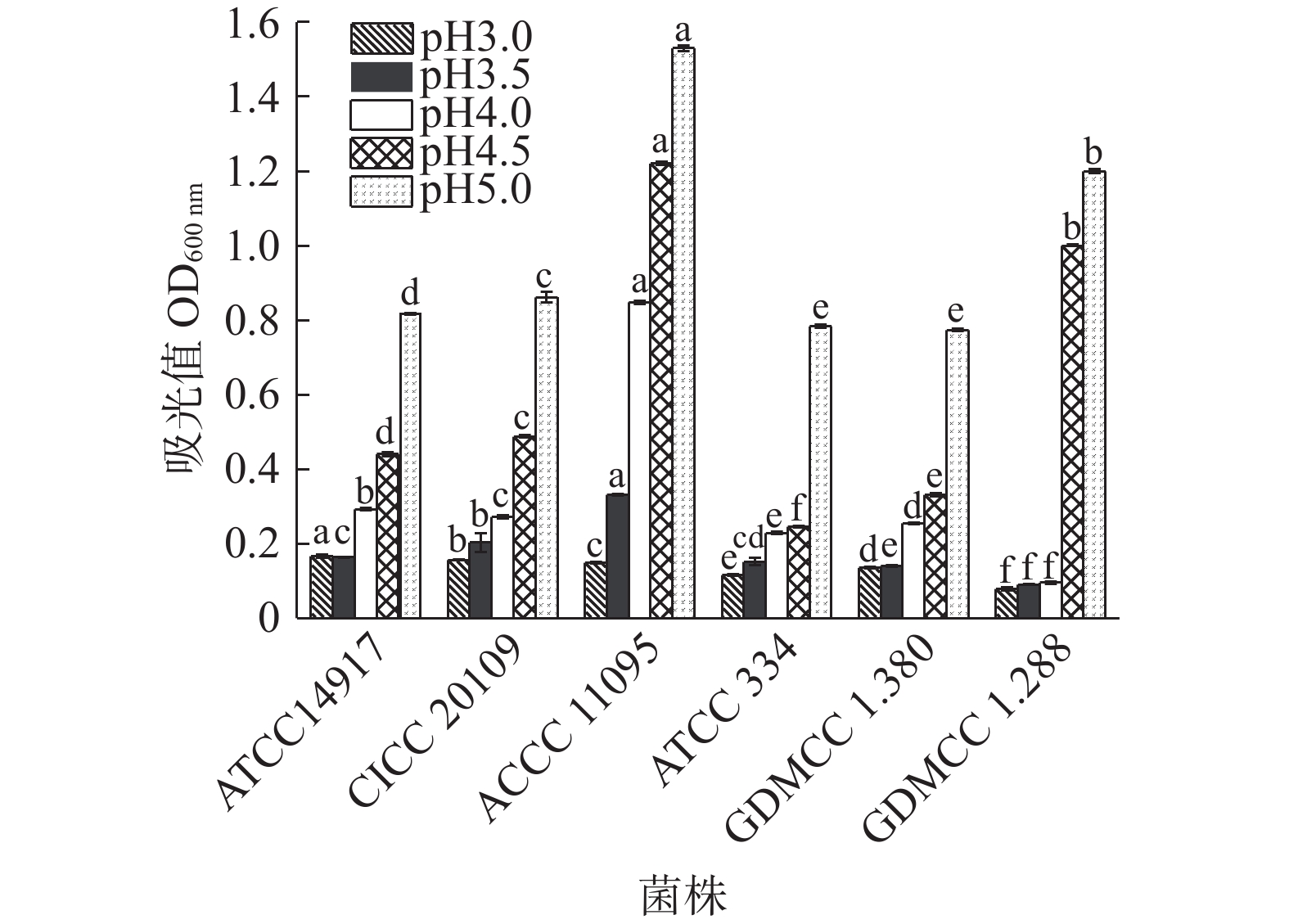
通过测定6株乳酸菌在不同pH条件下的OD600 nm,考察乳酸菌在不同pH条件下的生长情况,结果如图2所示。
由图2可知,pH越低,6种菌株的生长情况越差,不同菌株在同一pH的条件下生长情况存在显著差异(P<0.05),且低pH(3.0、3.5、4.0)显著抑制了菌体生长(P<0.05),GDMCC 1.288的抑制作用尤为明显。当pH为3时,ATCC 14917的生长情况相对较好,OD600 nm最大,为0.172。随着pH的增大,不同菌株的OD600 nm有不同程度的增加,ACCC 11095的增长趋势最大。CICC 20109和ATCC 14917在不同pH条件下变化趋势基本一致,ATCC 334和GDMCC 1.380的生长情况也基本相似。因此6株乳酸菌中耐酸性较好的是ACCC 11095,其次为CICC 20109和ATCC 14917,然后是ATCC 334和GDMCC 1.380,最后是GDMCC 1.288。
2.3 不同乳酸菌发酵葡萄酵素理化性质变化
2.3.1 还原糖动态变化
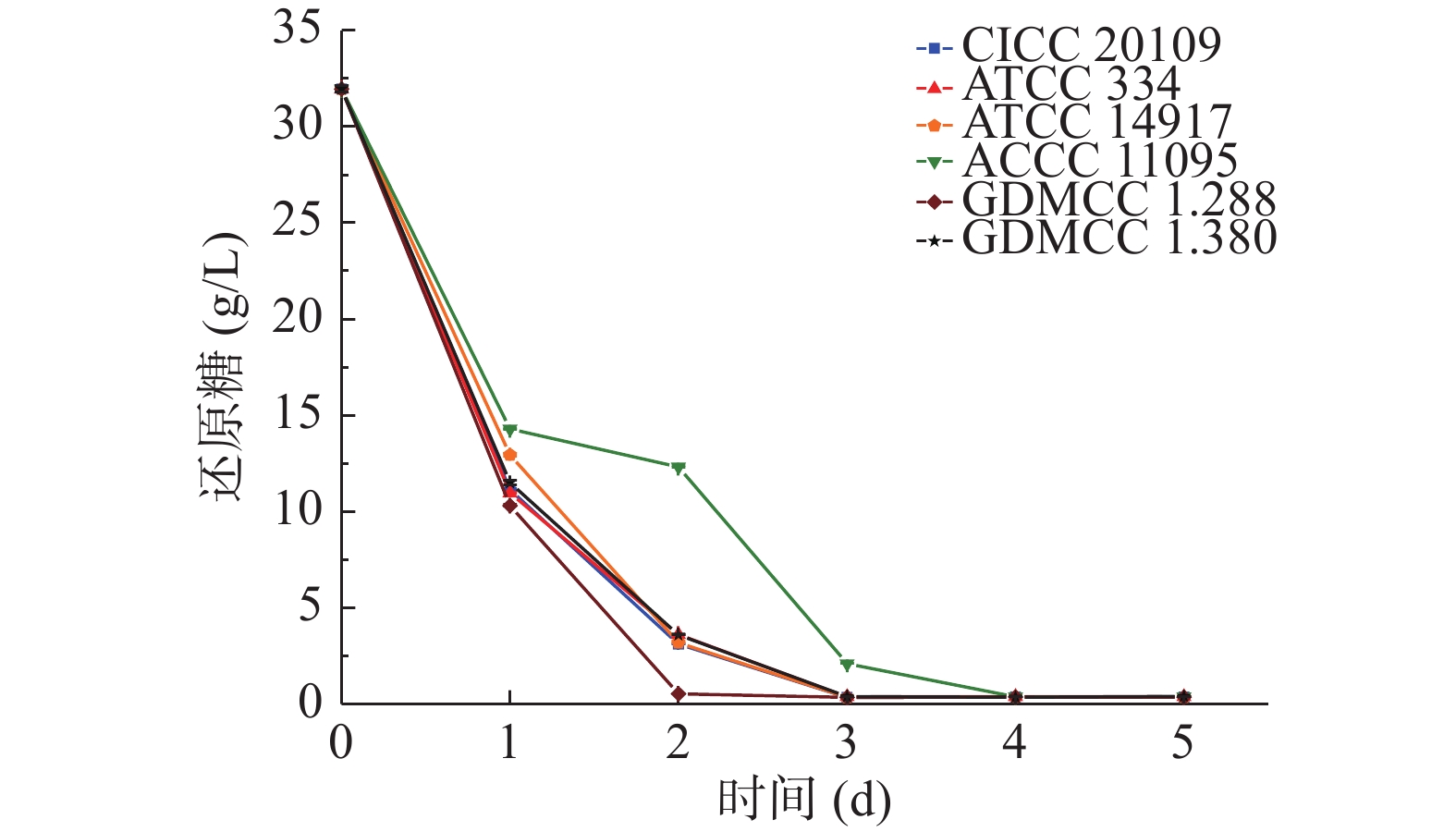
通过测定6株乳酸菌发酵过程中的还原糖含量,考察不同菌株的糖代谢能力,如图3所示。
由图3可知,6株乳酸菌发酵过程中还原糖的含量呈逐渐下降趋势,表明6株菌均有代谢糖的能力。初始葡萄汁中的还原糖含量为32.06 g/L,发酵第1 d,不同菌株的发酵液还原糖含量降低了55%~68%,存在显著差异(P<0.05),发酵第2 d,GDMCC 1.288的残糖量趋于0,ACCC 11095 残糖量为13.32 g/L,其余菌株残糖量在3.11~3.58 g/L之间,ACCC 11095显著高于其它菌株(P<0.05),发酵3 d后除ACCC 11095之外,其余菌株还原糖含量趋于0。综上所述,GDMCC 1.288降解糖的能力最强,CICC 20109、ATCC 334、ATCC 14917和GDMCC 1.380降解糖的能力类似,其次是ACCC 11095。
2.3.2 可溶性固形物动态变化
由图4可知,不同菌株发酵过程中的可溶性固形物呈逐渐下降的趋势,最后趋于5左右,这与陈华丽等[18]的研究结果类似。葡萄基质中初始可溶性固形物为15.43 Brix°,发酵1 d后,ACCC 11095降低了4%,其余菌株降低了15%~20%,发酵第2 d,ACCC 11095降低了26.6%,其余菌株下降了34%~59%,发酵第3 d,ACCC 11095发酵液的可溶性固形物为6.23 Brix°,其余菌株下降至5 Brix°左右,随后保持稳定,不同菌株发酵过程中可溶性固形物存在显著差异。
2.3.3 pH动态变化
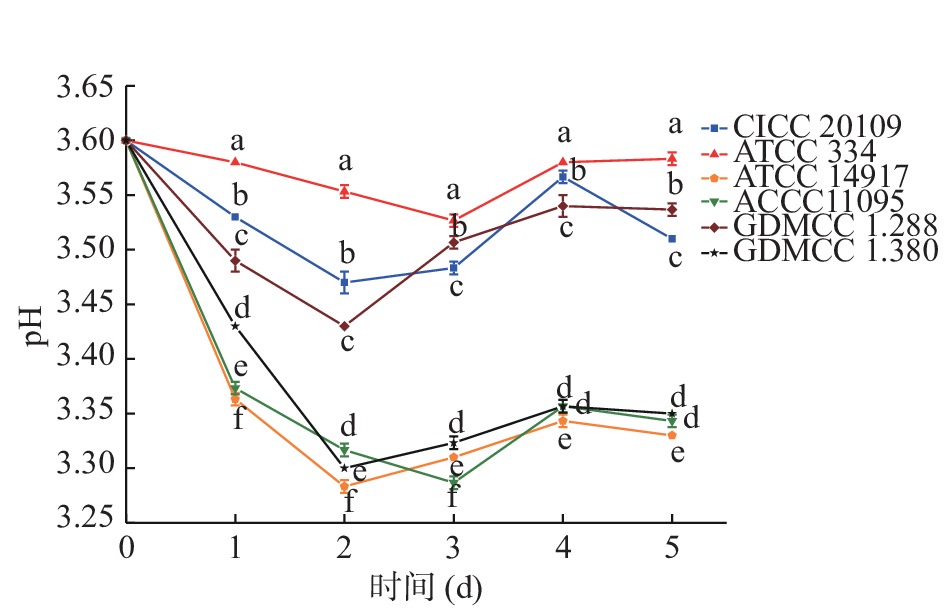
pH在一定程度上可以反映微生物是否正常生长。不同菌株发酵过程中pH的动态变化趋势如图5所示,发酵过程中pH呈先降低再升高后趋于稳定的趋势,不同菌株发酵过程中pH差异显著(P<0.05)。由图5可知,初始pH3.6,发酵第1 d,pH迅速下降,ATCC 14917发酵液显著降低(P<0.05),为3.37,发酵第2 d,所有菌株发酵液的pH持续降低,ATCC 14917的发酵液达到了最低值,为3.28,其次是GDMCC 1.380,发酵第3~4 d,不同菌株发酵液的pH呈上升趋势,这可能是由于微生物的作用,发酵基质发生了物质转变,如酚类物质[19],发酵第4~5 d,不同菌株发酵液pH逐渐趋于平稳。ATCC 14917、ACCC 11095和GDMCC 1.380发酵结束时pH为3.33~3.35,而CICC 20109、ATCC 334和GDMCC 1.288发酵结束时pH为3.51~3.58,表明前者产酸能力比后者更强。
![]() 图 5 不同菌株发酵过程中pH的变化注:当pH时间时,不同小写字母根据Duncan测验有显著性差异,P<0.05;图6同。Figure 5. Changes of pH value of different strains during fermentation
图 5 不同菌株发酵过程中pH的变化注:当pH时间时,不同小写字母根据Duncan测验有显著性差异,P<0.05;图6同。Figure 5. Changes of pH value of different strains during fermentation2.3.4 总酸含量的动态变化
总酸在一定程度上可以反映微生物生长代谢情况,由图6可知,总酸含量为11.07~12.74 g/L,与pH变化趋势相反,不同菌株发酵过程中总酸含量呈先升高后降低的趋势。发酵第1 d,不同菌株发酵液总酸含量由5.69 g/L上升到5.78~8.40 g/L,这是由于基质中碳源充足,乳酸菌迅速消耗碳源生成乳酸。随着发酵的进行,乳酸菌经历对数平稳期到衰亡期,基质中的总酸含量缓慢上升,发酵第2~4 d,总酸含量略有下降,到发酵后期,乳酸菌逐渐衰亡,酸度趋于稳定。由图6可知,不同菌株产酸能力存在显著差异(P<0.05),其中ACCC 11095 产酸能力显著高于其它菌株(P<0.05)。
2.4 不同乳酸菌发酵葡萄酵素酶活力变化
2.4.1 SOD活力的动态变化
由于食用酵素是一个多元复杂发酵体系,原料经过微生物发酵后,获得一些代谢产物,如功能性酶类物质,目前研究最多的主要是SOD,它是一种以超氧阴离子为底物的金属酶,是体内O2-的天然清除剂[20-21]。因此对葡萄酵素发酵过程中的SOD活力进行了监测,考察乳酸菌是否对SOD活力有影响,不同菌株发酵过程中SOD活力的变化如表1所示。
表 1 不同菌株发酵过程中SOD活力的变化(U/mL)Table 1. Changes of SOD activity of different strains during fermentation(U/mL)菌株 0 d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d CICC20109 9.68±4.19a 25.00±8.33b 22.88±7.62b 13.33±5.20b 37.50±7.50a 20.5±5.76bc ATCC334 9.68±4.19a 11.11±4.82b 10.16±4.41c 19.17±3.82b 9.83±4.04b 19.17±3.82bc ATCC14917 9.68±4.19a 11.84±4.32b 46.94±5.95a 37.50±7.50a 30.00±7.50a 30.00±7.50ab ACCC 11095 9.68±4.19a 16.67±8.34b 11.07±3.86c 37.50±7.50a 37.5±7.50a 15.00±7.50c GDMCC1.288 9.68±4.19a 16.67±8.34b 17.79±4.41bc 10.00±4.33b 10.00±4.33b 10.00±4.33c GDMCC1.380 9.68±4.19a 58.33±8.34a 11.17±3.84c 19.28±3.86b 37.50±7.50a 37.50±7.50a 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株SOD活力有显著差异(P<0.05)。 由表1可知,CICC 20109、ATCC 334和ACCC 11095的发酵液在发酵过程中SOD活力呈先波动上升后下降的趋势,这与之前的报道趋势相近[22-23]。而ATCC14917、GDMCC 1.380和GDMCC 1.288这三个发酵组在发酵过程中SOD活力呈先上升后下降最后趋于平稳的趋势。不同菌株发酵过程中的SOD活力存在显著差异(P<0.05)。未接种前,葡萄汁中的SOD活力为9.68 U/mL,发酵第1 d,CDMCC 1.380的发酵液SOD活力最先达到了最大值为58.33 U/mL,发酵第2 d,ATCC 14917和GDMCC 1.288的发酵液SOD活力达到了最大值,分别为46.94和17.79 U/mL。发酵第3 d,ACCC 11095和ATCC 334 的发酵液SOD活力达到了最大值,分别为37.50和19.17 U/mL,发酵第4 d,接种CICC 20109的酵素SOD活力达到了最大值,为37.50 U/mL,由于菌株产酸能力不同,因此SOD活力达到最高点所需时间不同,且后期乳酸的积累,达不到SOD的最适pH,导致酶活力有不同程度的降低。乳酸菌发酵结束时,GDMCC 1.380的发酵液酶活最高,为37.50 U/mL,其次是ATCC 14917,为30.00 U/mL。
2.4.2 β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的动态变化
β-葡萄糖苷酶能催化烷基糖苷、芳基糖苷、纤维素和纤维低聚糖等结合于糖链末端非还原性的β-D-葡萄糖苷键水解,使其释放出具有香气的游离糖苷配体[24-25],因此β-葡萄糖苷酶对葡萄酵素的香气形成有重要的作用。Marta等[26]报道了乳酸杆菌属和双歧杆菌属可以通过β-葡萄糖苷酶水解蔬菜中的β-糖苷,这种酶也被认为是酚类化合物结构中糖苷键断裂的第一步,而葡萄中含有丰富的酚类物质,因此有必要考察不同乳酸菌对β-葡萄糖苷酶产生的影响。
由表2可知,除GDMCC 1.288外,其它菌株的发酵液在发酵过程中β-葡萄糖苷酶活力呈先上升后下降的趋势,而接种GDMCC 1.288的发酵液β-葡萄糖苷酶仅在最后1 d被检测到,为10.52 µU/mL。不同菌株产生的β-葡萄糖苷酶在10.52~501.29 µU/mL之间,曾子毅等人比较了5株植物乳杆菌产β-葡萄糖苷酶的特性,结果表明植物乳杆菌产生的β-葡萄糖苷酶在4.630~14.168 U/g[27]。这可能是由于菌株及生长基质的差异。在发酵第2 d,ATCC 14917,β-葡萄糖苷酶活力显著高于其它菌株(P<0.05),为501.29 µU/mL,发酵结束后,ACCC 11095发酵液的β-葡萄糖苷酶活力最高,为400.70 µU/mL。
表 2 不同菌株发酵过程中β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的变化(µU/mL)Table 2. Changes of β-glucosidase activity of different strains during fermentation (µU/mL)菌株 0 d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d CICC20109 0±0 26.72±4.34a 125.55±17.36b 216.28±19.3a 65.39±12.3c 31.85±5.04b ATCC334 0±0 15.02±2.00a 26.33±4.13d 48.62±10.02b 36.00±5.57cd 21.67±3.51b ATCC14917 0±0 31.85±5.04a 501.29±29.04a 266.57±50.30a 132.45±19.04b 48.62±12.08b ACCC 11095 0±0 31.85±5.04a 82.15±15.04bc 216.28±20.37a 300.10±24.03a 400.70±29.04a GDMCC1.288 0±0 0±0a 0±0d 0±0b 0±0d 10.52±2.63b GDMCC1.380 0±0 0±0a 31.85±4.04cd 31.85±4.04b 65.39±12.3c 31.85±4.04b 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株β-葡萄糖苷酶活力差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.5 不同乳酸菌发酵葡萄酵素有机酸含量变化
益生菌可以通过发酵分解糖,形成有机酸,这些有机酸是许多微生物属在食品发酵过程中大量繁殖的重要二级碳源[28]。不同菌株发酵过程中有机酸含量的变化如表3所示。乳酸的产生是发酵是否成功的标志。不同菌株发酵后乳酸含量都有不同程度的增加,发酵后乳酸的含量在0.38~11.72 g/L,这与之前的报道相一致[29]。其中ACCC 11095发酵产生的乳酸含量最多,是其它菌株的1.2~30倍,其次是ATCC 14917、GDMCC 1.380和CICC 20109,GDMCC 1.288发酵产生的乳酸含量最少。乳酸和低酸碱度会破坏细胞壁和细胞膜,改变膜电位和主动运输,从而导致能量消耗和细胞死亡,因此产乳酸能力较高的乳酸菌对酵素的保存可能是有利的[30]。
表 3 不同菌株发酵过程中有机酸含量的变化Table 3. Changes of organic acid of different strains during fermentation有机酸(g/L) 菌株 发酵时间(d) 0 1 2 3 4 5 草酸 CICC20109 0.39±0.05a 0.69±0.08a 0.26±0.03c 0.37±0.03a 0.39±0.04ab 0.18±0.02a ATCC 334 0.39±0.05a 0.35±0.04c 0.28±0.04bc 0.35±0.04a 0.36±0.02b 0.18±0.02a ATCC 14917 0.39±0.05a 0.36±0.04c 0.33±0.03b 0.39±0.05a 0.44±0.04a 0.18±0.02a ACCC11095 0.39±0.05a 0.49±0.05b 0.4±0.06a 0.33±0.02a 0.41±0.03ab 0.20±0.03a GDMCC1.288 0.39±0.05a 0.33±0.03c 0.17±0.01d 0.35±0.05a 0.17±0.02c 0.18±0.01a GDMCC1.380 0.39±0.05a 0.36±0.03c 0.17±0.02d 0.4±0.04a 0.18±0.02c 0.19±0.01a 酒石酸 CICC20109 2.56±0.18a 2.13±0.21ab 1.24±0.21b 1.46±0.23b 2.3±0.18ab 2.31±0.18b ATCC 334 2.56±0.18a 2.45±0.20a 1.22±0.22b 1.32±0.16b 2.18±0.16abc 2.09±0.24bc ATCC 14917 2.56±0.18a 1.57±0.23c 2.29±0.25a 1.92±0.22a 1.49±0.24bc 2.3±0.19b ACCC11095 2.56±0.18a 1.09±0.15d 1.28±0.23b 1.22±0.21b 2.15±0.21abc 1.89±0.17c GDMCC1.288 2.56±0.18a 1.8±0.21bc 1.23±0.20b 1.36±0.18b 1.36±0.21c 3.82±0.35a GDMCC1.380 2.56±0.18a 1.98±0.22b 1.56±0.20b 1.27±0.12b 2.51±0.20a 2.38±0.21b 苹果酸 CICC20109 1.82±0.20a 1.72±0.20a 1.54±0.21a 1.29±0.20a 1.24±0.12b 1.73±0.21a ATCC 334 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.10b 0.65±0.12b 0.66±0.11b 0.66±0.10c n.d ATCC 14917 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.11b 0.66±0.11b 0.67±0.09b 0.79±0.10c n.d ACCC11095 1.82±0.20a 0.66±0.11b 0.66±0.11b 0.68±0.09b 0.67±0.09c n.d GDMCC1.288 1.82±0.20a 1.83±0.10a 1.78±0.10a 1.27±0.13a 1.68±0.12a 1.77±0.10a GDMCC1.380 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.11b 0.65±0.10b 0.67±0.10b n.d n.d 丙酮酸 CICC20109 0.56±0.13a 0.69±0.11a 0.72±0.11b 0.33±0.09c 0.33±0.03d 1.12±0.12a ATCC 334 0.56±0.13a 0.58±0.11ab 0.66±0.11bc 0.7±0.11a 0.71±0.06ab 0.7±0.06b ATCC 14917 0.56±0.13a 0.39±0.09c 0.46±0.06d 0.55±0.06ab 0.5±0.06c 0.52±0.06c ACCC11095 0.56±0.13a 0.41±0.09bc 0.44±0.06d 0.5±0.08b 0.53±0.05c 0.5±0.05c GDMCC1.288 0.56±0.13a 0.73±0.10a 1.17±0.11a 0.3±0.04c 0.81±0.09a 1.04±0.10a GDMCC1.380 0.56±0.13a 0.49±0.08bc 0.52±0.11cd 0.59±0.05ab 0.56±0.05bc 0.59±0.04bc 乳酸 CICC20109 n.d 0.21±0.03e 0.25±0.03e 0.38±0.04e 0.38±0.02e 0.45±0.03e ATCC 334 n.d 2.32±0.23d 2.9±0.30d 2.9±0.30d 2.83±0.25d 3.04±0.42d ATCC 14917 n.d 7.09±0.80b 9.44±0.94b 10.18±1.89b 9.77±1.46b 9.94±1.40b ACCC11095 n.d 9.05±1.02a 10.18±1.8a 11.37±2.34a 11.56±2.41a 11.72±2.38a GDMCC1.288 n.d 0.1±0.01e 0.25±0.02e 0.34±0.04e 0.35±0.03e 0.38±0.02e GDMCC1.380 n.d 5.51±0.50c 7.99±0.75c 8.7±1.02c 8.37±0.84c 8.65±0.74c 乙酸 CICC20109 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ATCC 334 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ATCC 14917 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ACCC11095 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d GDMCC1.288 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d GDMCC1.380 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d 柠檬酸 CICC20109 0.55±0.10a 1.55±0.10b 0.46±0.03c 1.82±0.25a 1.84±0.17a 1.51±0.13b ATCC 334 0.55±0.10a 0.5±0.03c 0.52±0.04c 0.5±0.03b 0.51±0.03c 1.54±0.11b ATCC 14917 0.55±0.10a 1.57±0.10b 1.38±0.20b 0.59±0.02b n.d 1.4±0.10b ACCC11095 0.55±0.10a 2.47±0.26a 2.2±0.24a 0.64±0.03b 0.57±0.02c 2.14±0.26a GDMCC1.288 0.55±0.10a 1.68±0.13b 1.55±0.14b 1.59±0.23a 1.58±0.15ab 1.58±0.12b GDMCC1.380 0.55±0.10a 1.66±0.12b 1.53±0.16b 0.61±0.03b 1.48±0.11b 1.51±0.11b 琥珀酸 CICC20109 0.91±0.11a 1.56±0.18a 1.67±0.22a 0.32±0.05b 0.33±0.05c 0.33±0.03c ATCC 334 0.91±0.11a 1.41±0.20a 1.6±0.15a 1.25±0.20a 1.21±0.15b 1.14±0.20b ATCC 14917 0.91±0.11a 0.47±0.13b 0.54±0.05c 0.32±0.05b n.d n.d ACCC11095 0.91±0.11a 0.31±0.05b 0.49±0.04c 0.33±0.02b 0.32±0.04c n.d GDMCC1.288 0.91±0.11a 1.59±0.25a 1.29±0.16b 0.31±0.06b 1.49±0.22a 1.51±0.11a GDMCC1.380 0.91±0.11a 0.54±0.07b n.d 0.3±0.04b n.d n.d 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株之间有显著差异(P<0.05),n.d:未检出。 苹果酸是乳酸菌发酵过程中重要的有机酸,因为苹果酸也可被代谢为乳酸。发酵结束后,与未发酵的基质相比,苹果酸含量下降了5%~100%,尤其是ATCC 14917、ACCC 11095和ATCC 334完全转化了苹果酸,Markkinen等[31]用乳酸菌发酵火龙果、沙棘中也有类似的结果。这主要是在苹果酸脱羧酶的作用下,乳酸菌能够依赖NAD+和Mn2+通过脱羧作用代谢苹果酸[32]。
柠檬酸是葡萄浆果中重要的有机酸,第0 d时,柠檬酸含量为0.55 g/L,不同菌株发酵过程中柠檬酸波动变化。除ATCC 334外,发酵第2 d柠檬酸含量突然增多,随着发酵时间的延长,柠檬酸含量有不同程度的下降,但是发酵结束后柠檬酸累积,含量为1.4~2.4 g/L。柠檬酸和苹果酸都可以用作第二碳源被乳酸菌利用,通常,柠檬酸的代谢与糖或其它能源的消耗相结合,在本研究中使用的乳酸菌似乎更倾向于使用苹果酸,焦媛媛等[33]用干酪乳杆菌和植物乳杆菌发酵梨汁中也有类似的结果。
酒石酸是葡萄中的特征酸,未接种时,酒石酸含量为2.56 g/L,Xu等[28]用益生菌发酵果蔬汁初始酒石酸浓度为3.09 g/L,这主要是由于原料的差异。随着发酵的进行,不同菌株的酒石酸含量略有降低,但是发酵结束时酒石酸含量与初始含量相比,没有显著的降低,含量为1.89~3.82 g/L。只有两种乳酸杆菌(植物乳杆菌和短乳杆菌)可将酒石酸代谢为乳酸、乙酸、琥珀酸和二氧化碳[34]。然而在本研究中,发酵结束后,酒石酸没有被代谢。乙酸在所有样品中都未检测到,表明这几株乳酸菌均进行同型乳酸发酵,减少乙酸的产生对最终酵素产品的风味也有重要的作用。
2.6 不同菌株发酵葡萄酵素前后活菌数的变化
酵素发酵到后期pH较低,而乳酸菌达到一定的数量级才可发挥益生功能,因此需要考察接种发酵后乳酸菌的活菌数。经过5 d的发酵后,不同乳酸菌的活菌数如图7所示。
由图7可知,接种发酵后不同菌株的生长情况存在显著差异(P<0.05)。ACCC 11095和GDMCC 1.380在发酵结束后活菌数增加,且二者没有显著差异(P<0.05),分别为(8.42±0.11)、(8.51±0.01)lg cfu/mL,表明这两株菌能很好地适应发酵基质。表明这两株菌对外界的应激影响小于其它菌株。ATCC 14917、CICC 20109和ATCC 334在接种发酵后,活菌数分别降低了1、1 lg cfu/mL和0.66 lg cfu/mL,这可能归因于低pH和酚类物质的影响[35]。而GDMCC 1.288在发酵前后总菌数基本一致。
3. 结论
通过比较6株乳酸菌发酵葡萄果浆的发酵特性、代谢产物及生长情况后得出,植物乳杆菌ACCC 11095能很好地适应发酵基质,耐酸能力强,接种发酵启动速度快,发酵1 d后,还原糖和可溶性固形物迅速降低,并于第5 d葡萄糖消耗完毕;发酵结束后细胞总数上升,能够产生丰富的SOD和β-葡萄糖苷酶;产酸能力强,能够累积大量的乳酸和柠檬酸,完全消耗苹果酸,不产生乙酸,表明该菌株具有提升葡萄酵素的功能及改善其风味潜力;综上,确定植物乳杆菌ACCC 11095为葡萄酵素发酵的优选菌株,这为葡萄酵素的制备提供了理论基础,对葡萄的深加工有重要意义。
-
图 5 不同菌株发酵过程中pH的变化
注:当pH时间时,不同小写字母根据Duncan测验有显著性差异,P<0.05;图6同。
Figure 5. Changes of pH value of different strains during fermentation
表 1 不同菌株发酵过程中SOD活力的变化(U/mL)
Table 1 Changes of SOD activity of different strains during fermentation(U/mL)
菌株 0 d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d CICC20109 9.68±4.19a 25.00±8.33b 22.88±7.62b 13.33±5.20b 37.50±7.50a 20.5±5.76bc ATCC334 9.68±4.19a 11.11±4.82b 10.16±4.41c 19.17±3.82b 9.83±4.04b 19.17±3.82bc ATCC14917 9.68±4.19a 11.84±4.32b 46.94±5.95a 37.50±7.50a 30.00±7.50a 30.00±7.50ab ACCC 11095 9.68±4.19a 16.67±8.34b 11.07±3.86c 37.50±7.50a 37.5±7.50a 15.00±7.50c GDMCC1.288 9.68±4.19a 16.67±8.34b 17.79±4.41bc 10.00±4.33b 10.00±4.33b 10.00±4.33c GDMCC1.380 9.68±4.19a 58.33±8.34a 11.17±3.84c 19.28±3.86b 37.50±7.50a 37.50±7.50a 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株SOD活力有显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 不同菌株发酵过程中β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的变化(µU/mL)
Table 2 Changes of β-glucosidase activity of different strains during fermentation (µU/mL)
菌株 0 d 1 d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d CICC20109 0±0 26.72±4.34a 125.55±17.36b 216.28±19.3a 65.39±12.3c 31.85±5.04b ATCC334 0±0 15.02±2.00a 26.33±4.13d 48.62±10.02b 36.00±5.57cd 21.67±3.51b ATCC14917 0±0 31.85±5.04a 501.29±29.04a 266.57±50.30a 132.45±19.04b 48.62±12.08b ACCC 11095 0±0 31.85±5.04a 82.15±15.04bc 216.28±20.37a 300.10±24.03a 400.70±29.04a GDMCC1.288 0±0 0±0a 0±0d 0±0b 0±0d 10.52±2.63b GDMCC1.380 0±0 0±0a 31.85±4.04cd 31.85±4.04b 65.39±12.3c 31.85±4.04b 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株β-葡萄糖苷酶活力差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同菌株发酵过程中有机酸含量的变化
Table 3 Changes of organic acid of different strains during fermentation
有机酸(g/L) 菌株 发酵时间(d) 0 1 2 3 4 5 草酸 CICC20109 0.39±0.05a 0.69±0.08a 0.26±0.03c 0.37±0.03a 0.39±0.04ab 0.18±0.02a ATCC 334 0.39±0.05a 0.35±0.04c 0.28±0.04bc 0.35±0.04a 0.36±0.02b 0.18±0.02a ATCC 14917 0.39±0.05a 0.36±0.04c 0.33±0.03b 0.39±0.05a 0.44±0.04a 0.18±0.02a ACCC11095 0.39±0.05a 0.49±0.05b 0.4±0.06a 0.33±0.02a 0.41±0.03ab 0.20±0.03a GDMCC1.288 0.39±0.05a 0.33±0.03c 0.17±0.01d 0.35±0.05a 0.17±0.02c 0.18±0.01a GDMCC1.380 0.39±0.05a 0.36±0.03c 0.17±0.02d 0.4±0.04a 0.18±0.02c 0.19±0.01a 酒石酸 CICC20109 2.56±0.18a 2.13±0.21ab 1.24±0.21b 1.46±0.23b 2.3±0.18ab 2.31±0.18b ATCC 334 2.56±0.18a 2.45±0.20a 1.22±0.22b 1.32±0.16b 2.18±0.16abc 2.09±0.24bc ATCC 14917 2.56±0.18a 1.57±0.23c 2.29±0.25a 1.92±0.22a 1.49±0.24bc 2.3±0.19b ACCC11095 2.56±0.18a 1.09±0.15d 1.28±0.23b 1.22±0.21b 2.15±0.21abc 1.89±0.17c GDMCC1.288 2.56±0.18a 1.8±0.21bc 1.23±0.20b 1.36±0.18b 1.36±0.21c 3.82±0.35a GDMCC1.380 2.56±0.18a 1.98±0.22b 1.56±0.20b 1.27±0.12b 2.51±0.20a 2.38±0.21b 苹果酸 CICC20109 1.82±0.20a 1.72±0.20a 1.54±0.21a 1.29±0.20a 1.24±0.12b 1.73±0.21a ATCC 334 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.10b 0.65±0.12b 0.66±0.11b 0.66±0.10c n.d ATCC 14917 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.11b 0.66±0.11b 0.67±0.09b 0.79±0.10c n.d ACCC11095 1.82±0.20a 0.66±0.11b 0.66±0.11b 0.68±0.09b 0.67±0.09c n.d GDMCC1.288 1.82±0.20a 1.83±0.10a 1.78±0.10a 1.27±0.13a 1.68±0.12a 1.77±0.10a GDMCC1.380 1.82±0.20a 0.65±0.11b 0.65±0.10b 0.67±0.10b n.d n.d 丙酮酸 CICC20109 0.56±0.13a 0.69±0.11a 0.72±0.11b 0.33±0.09c 0.33±0.03d 1.12±0.12a ATCC 334 0.56±0.13a 0.58±0.11ab 0.66±0.11bc 0.7±0.11a 0.71±0.06ab 0.7±0.06b ATCC 14917 0.56±0.13a 0.39±0.09c 0.46±0.06d 0.55±0.06ab 0.5±0.06c 0.52±0.06c ACCC11095 0.56±0.13a 0.41±0.09bc 0.44±0.06d 0.5±0.08b 0.53±0.05c 0.5±0.05c GDMCC1.288 0.56±0.13a 0.73±0.10a 1.17±0.11a 0.3±0.04c 0.81±0.09a 1.04±0.10a GDMCC1.380 0.56±0.13a 0.49±0.08bc 0.52±0.11cd 0.59±0.05ab 0.56±0.05bc 0.59±0.04bc 乳酸 CICC20109 n.d 0.21±0.03e 0.25±0.03e 0.38±0.04e 0.38±0.02e 0.45±0.03e ATCC 334 n.d 2.32±0.23d 2.9±0.30d 2.9±0.30d 2.83±0.25d 3.04±0.42d ATCC 14917 n.d 7.09±0.80b 9.44±0.94b 10.18±1.89b 9.77±1.46b 9.94±1.40b ACCC11095 n.d 9.05±1.02a 10.18±1.8a 11.37±2.34a 11.56±2.41a 11.72±2.38a GDMCC1.288 n.d 0.1±0.01e 0.25±0.02e 0.34±0.04e 0.35±0.03e 0.38±0.02e GDMCC1.380 n.d 5.51±0.50c 7.99±0.75c 8.7±1.02c 8.37±0.84c 8.65±0.74c 乙酸 CICC20109 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ATCC 334 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ATCC 14917 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d ACCC11095 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d GDMCC1.288 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d GDMCC1.380 n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d n.d 柠檬酸 CICC20109 0.55±0.10a 1.55±0.10b 0.46±0.03c 1.82±0.25a 1.84±0.17a 1.51±0.13b ATCC 334 0.55±0.10a 0.5±0.03c 0.52±0.04c 0.5±0.03b 0.51±0.03c 1.54±0.11b ATCC 14917 0.55±0.10a 1.57±0.10b 1.38±0.20b 0.59±0.02b n.d 1.4±0.10b ACCC11095 0.55±0.10a 2.47±0.26a 2.2±0.24a 0.64±0.03b 0.57±0.02c 2.14±0.26a GDMCC1.288 0.55±0.10a 1.68±0.13b 1.55±0.14b 1.59±0.23a 1.58±0.15ab 1.58±0.12b GDMCC1.380 0.55±0.10a 1.66±0.12b 1.53±0.16b 0.61±0.03b 1.48±0.11b 1.51±0.11b 琥珀酸 CICC20109 0.91±0.11a 1.56±0.18a 1.67±0.22a 0.32±0.05b 0.33±0.05c 0.33±0.03c ATCC 334 0.91±0.11a 1.41±0.20a 1.6±0.15a 1.25±0.20a 1.21±0.15b 1.14±0.20b ATCC 14917 0.91±0.11a 0.47±0.13b 0.54±0.05c 0.32±0.05b n.d n.d ACCC11095 0.91±0.11a 0.31±0.05b 0.49±0.04c 0.33±0.02b 0.32±0.04c n.d GDMCC1.288 0.91±0.11a 1.59±0.25a 1.29±0.16b 0.31±0.06b 1.49±0.22a 1.51±0.11a GDMCC1.380 0.91±0.11a 0.54±0.07b n.d 0.3±0.04b n.d n.d 注:同列不同字母表示不同菌株之间有显著差异(P<0.05),n.d:未检出。 -
[1] 中国生物发酵产业协会. T/CBFIAO8001-2016酵素产品分类导则[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. China Biological Fermentation Industry Association. T/CBFIAO8001-2016 Jiaosuproduct classification guidelines[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[2] Aubert C, Chalot G. Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, and volatiles of six table grape varieties (Vitisvinifera L.)[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,240(1):524−533.
[3] 洪厚胜, 朱曼利, 李伟, 等. 葡萄果渣酵素的发酵工艺优化及其理化特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(8):63−72. [Hong HS, Zhu ML, Li W, et al. Optimization of fermentation process and physicochemical properties of probiotic fermented grape pomace[J]. Food Science,2019,40(8):63−72. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180510-166 [4] 杨培青, 李斌, 颜廷才, 等. 蓝莓果渣酵素发酵工艺优化[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(23):205−210. [Yang P Q, LiB, Yan T C et al. Fermentation of blueberry pomace for the production of biomass and protease activity[J]. Food Science,2016,37(23):205−210. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201623034 [5] 张巧, 柯博芳, 唐小闲, 等. 不同发酵菌种对大果山楂酵素品质的影响[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(6):162−166. [Zhang Q, Ke B F, Tang XX, et al. Effects of different fermentation strains on the quality of Malusdomeri (Bois) Chev. enzyme drink[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(6):162−166. [6] 王瑜, 李立郎, 张洁, 等. 野木瓜酵素发酵过程中活性成分的变化[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(10):125−130. [Wang Y, LI LL, Zhang J, et al. Changes in active components in stauntoniachinensis ferment during fermentation[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(10):125−130. [7] 李建强, 温立香, 罗小杰, 等. 酵素三级发酵与自然发酵过程中SOD活性变化的研究[J]. 轻工科技,2016,32(1):4−5, 33. [LiJ Q, WenL X, LuoX J, et al. Study on SOD activity changes during three-stage fermentation and natural fermentation[J]. Light Industry Technology,2016,32(1):4−5, 33. [8] Flach J, MarkVD W, Maurits V D N, et al. The underexposed role of food matrices in probiotic products: Reviewing therelationship between carrier matrices and product parameters[J]. Crit Rev Food Nutr,2018,25(15):2570−2582.
[9] Garbetta A, D"Antuono I, Sisto A, et al. Effect of artichoke fermentation by probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei LMG P-22043 andof digestion process on polyphenols and antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018:S1756464618300653.
[10] 李凡. 滨海白首乌酵素的制备及其功效性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2019. Li F. Preparation of cynanchumauriculatumroyle ex wight ferment and its research on efficacy[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019.
[11] 韩齐, 赵金敏, 高小琴, 等. 功能性酵素发展研究现状[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(1):337−340, 345. [Han Qi, Zhao J M, Gao X Q, et al. Development status of functional fermented enzymes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(1):337−340, 345. [12] 侯周超. 家用酵素机的研发与桑葚酵素发酵工艺的研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2019. Hou Z C. Research and development of domestic enzyme machine and study on Mulberry fermentation technology[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2019.
[13] 韦仕静. 桑葚酵素发酵工艺及花青素生物转化的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. Wei S J. The research on fermentation process of Mulberry Jiaosu and biotransformation of anthocyanins[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
[14] 中国生物发酵产业协会. QB/T 5323-2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. China Biofermentation Industry Association. QB/T 5323-2018[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018.
[15] Miller G L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagentfor determination of reducing sugar[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1959,31(3):426−428. doi: 10.1021/ac60147a030
[16] 侯晓瑞, 王婧, 杨学山, 等. 甘肃河西走廊葡萄酒产区高产β-葡萄糖苷酶酵母菌株筛选[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(23):139−143. [Hou X R, Wang J, Yang X S, et al. Screening of yeast strains producing β-glucosidase from Hexi corridor wine-producing regions of Gansu province[J]. Food Science,2014,35(23):139−143. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201423028 [17] 雷艳, 廖雯意, 叶帆. 高效液相色谱法同时测定果醋饮品中7种有机酸的含量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(17):5857−5861. [Lei Y, Liao W Yi, Ye F. Simultaneous determination of 7 organic acids in fruit vinegar drinks by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2019,10(17):5857−5861. [18] 陈华丽. 复合果汁混菌发酵特性及贮藏过程中的品质变化研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2019. Chen H L. Study on fermentation characteristics of mixed bacteria in compound juice and quality change during storage[D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2019.
[19] Cho K M, Lee J H, Yun H D, et al. Changes of phytochemical constituents (isoflavones, flavanols, and phenolic acids) during cheonggukjang soybeans fermentation using potential probiotics Bacillus subtilis CS90[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2011,24(3):402−410. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2010.12.015
[20] 丁楠, 何美珊, 戈子龙, 等. 果蔬发酵制品的功效及应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(7):332−336. [Ding N, He M S, Ge Z L, et al. Functions and applications of the fermented products of fruits and vegetables[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(7):332−336. [21] 高庆超, 常应九, 马蓉, 等. 微生物酵素的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(2):190−195. [Gao Q C, Chang Y J, et al. Ma R, et al. Research progress on microbial ferment[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(2):190−195. [22] 白琳, 茹先古丽·买买提依明, 王旭光, 等. 五种不同的乳酸菌对库车小白杏发酵液的理化性质及感官评价的影响[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−9[2020−10−07]. http://kns. cnki.net/ kcms/detail/ 11.2206.ts.20200924.1647.103.html.Bai L, Ruxianguli·M M T Y M, Wang X G, et al. Effects of five different lactic acid bacteria on thephysicochemical properties and sensory evaluation of the Kuche small white apricot juice [J/OL]. Food Science: 1−9[2020−10−07]. http://kns. cnki.net/ kcms/detail/ 11.2206.ts.20200924.1647.103.html. [23] 李豆. 新型水果酵素的研制及生物活性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2018. Li D. Study on the development of a new type of fruit enzyme and its biological activity[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2018.
[24] Maria Arevalo V, Juan F U I, Gundllapalli S B, et al. Characterization of an exocellular β-glucosidase from Debaryomycespseudopolymorphus[J]. Enzyme & Microbial Technology,2006,39(2):229−234.
[25] Ma D, Yan X, Wang Q, et al. Performance of selected P. fermentans and its excellular enzyme in co-inoculation with S. cerevisiaefor wine aroma enhancement[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,86:361−370. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.018
[26] Marta A, Maria H, Concepcio SM, et al. Bioconversion of anthocyanin glycosides by Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus[J]. Food Research International,2009,42(10):1453−1461. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.07.026
[27] 曾子毅, 丁诗瑶, 卢向阳, 等. 几株植物乳杆菌β-葡萄糖苷酶的特性研究[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(01):75−79. [Zeng Z Y, Ding S Y, Lu X Y, et al. Characteristics of β-glucosidase from Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(01):75−79. [28] Xu X X, Bao Y J, Wu B B, et al. Chemical analysis and flavor properties of blended orange, carrot, apple and Chinese jujube juice fermented by selenium-enriched probiotics[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,289:250−258. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.068
[29] Cirlini M, Ricci A, Galaverna G, et al. Application of lactic acid fermentation to elderberry juice: Changes in acidic and glucidic fractions[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,118:108779.
[30] Davidson P M, Taylor T M. Chemical preservatives and natural antimicrobial compounds[J]. Food Microbiology Fundamentals & Frontiers,2013.
[31] Markkinen N, Laaksonen O, Nahku R, et al. Impact of lactic acid fermentation on acids, sugars, and phenolic compounds in black chokeberry and sea buckthorn juices[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,286:204−215. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.189
[32] Jyoti B D, Suresh A K, Venkatesh K V. Effect of preculturing conditions on growth of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on medium containing glucose and citrate[J]. Microbiological Research,2004,159(1):35−42. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2004.01.008
[33] 焦媛媛, 杜丽平, 孙文, 等. 优良梨汁发酵乳酸菌的筛选与发酵性能分析[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(2):149−153. [Jiao YY, DU L P, Sun W, et al. Screening and fermentation characteristics of lactic acid bacteria for fermentation of pear juice[J]. Food Science,2019,40(2):149−153. [34] Saad S M I. Lactic acid bacteria: Microbiological and functional aspects[J]. Revista Brasileira de Ciências Farmacêuticas,2006,42(3).
[35] Suenia GG M, Borgess G D S C, Lima M D S, et al. Effects of probiotics on the content and bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds in red pitayapulp[J]. Food Research International,2019,126:108681. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108681
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 霍善琴,赵新楠,林怡辰,王腾,谭志军,彭吉星. 食品中维生素B分析方法研究进展. 食品与药品. 2025(01): 112-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 于瑞莉,任静,华佳淼,邹凤,黄丽俊. 国标法测定特医食品中叶酸的方法研究. 中国标准化. 2024(15): 251-256 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陆伟,王俊,靳利军,熊菲菲,晏永球,贾福怀. 高效液相色谱法测定复合营养素补充剂中叶酸含量. 山东化工. 2023(04): 127-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 于瑞莉,冯永巍,黄丽俊,杨婷. 特殊食品中3种B族维生素检测方法的研究进展. 食品与药品. 2022(01): 91-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王养平,焦建军. 运动营养饼干品质指标的主成分分析及聚类分析. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(05): 1405-1413 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 苏妙仪,严家俊,张娟. 微生物法检测乳粉中叶酸的优化研究. 中国乳业. 2021(02): 81-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 涂宏建,陆伟,贾福怀,谢承群,雷蕾,王鹏泽. 涡旋振荡提取-高效液相色谱-紫外检测法测定铁叶酸片中的叶酸含量. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2021(09): 3721-3726 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 吴思敏,严家俊,黄钟标. 微生物法测定婴幼儿配方乳粉中叶酸含量不确定度评估. 中国乳业. 2021(07): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 霍艳杰,雷浩,高勤叶,曹晓洁,张晓英,贺习文. 分光光度法测定饲料添加剂叶酸含量的方法研究. 粮油与饲料科技. 2021(05): 30-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



