Effect of Calcium Ions on the Freeze-drying Resistance of Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1
-
摘要: 本文以植物乳杆菌LIP-1为研究对象,探讨在培养基中添加不同浓度的钙离子对菌株生长量及抗冷冻干燥性能的影响,在此基础上,研究了不同浓度钙离子对菌体形态、细胞壁及细胞膜结构完整性以及细胞膜脂肪酸构成的影响,以探讨钙离子影响菌株抗冷冻干燥性能的机制。结果表明:当在MRS培养基中添加0.5 mmol/L的钙离子时,与未添加钙离子的对照组相比,菌株的生长量提升了0.717×109 CFU/mL,存活率提升了21.52%(P<0.05);同时与对照组相比,添加钙离子可以使植物乳杆菌LIP-1长度明显变短;菌株的细胞壁与细胞膜的损伤程度降低;细胞膜中不饱和脂肪酸的含量升高,U/S变大;添加钙离子还可以使菌株的常温贮藏稳定性得到提高,第8周时添加钙离子的实验组相较对照组(MRS)活菌数提升了13.65倍。该结果为培养基中添加适量的钙离子促进菌体生长以及提高菌株的抗冷冻干燥性与贮藏稳定性提供了理论参考。Abstract: Taking Lactobacillus Plantarum LIP-1 as a research object, this article explored the growth and the freeze-drying resistance of the strain by adding different concentrations of calcium ions to the culture medium. To understand the mechanism of calcium ions on the freeze-drying resistance of strain, the morphology, cell wall of the bacteria, the structural integrity of cell membrane and the fatty acid composition of cell membrane were studied. The results showed the growth of the strain increased by 0.717×109 CFU/mL and the survival rate increased by 21.52% (P<0.05), when 0.5 mmol/L calcium ions were added to the MRS medium, compared with the control group without calcium ions. Moreover, the length of Lactobacillus Plantarum LIP-1 becomed shorter, the damage to the cell wall and cell membrane of the strain was reduced, the content of unsaturated fatty acids in the cell membrane increased, and the U/S becomed larger. More importantly, the storage stability of the strain at room temperature was improved. We founded that the number of viable bacteria in the experimental group increased by 13.65 times compared with the control group (MRS) at the 8th week. Our result provides a theoretical reference for promoting the growth of bacteria and improving the freeze-drying resistance and storage stability of the strain by adding appropriate amount of calcium ions to the culture medium.
-
益生菌一词源于希腊语,意思是“对生命有益”。2002年世界粮农组织(FAO)和世界卫生组织(WHO)专家组对益生菌做出了定义,即通过摄取适当的量,对使用者的身体健康能发挥有效作用的细菌[1]。研究发现益生菌制剂中菌株活性对最终产品的益生功效起到至关重要的作用[2]。菌株常通过干粉状态进行运输与贮藏,在一定时期抑制菌株生理活性,从而延长其保质期并节约运输成本[3]。目前工业生产中主要通过真空冷冻干燥法制备乳酸菌制剂,其具有活菌数高、发酵活力强、遗传稳定性好等优点,但也会对菌体造成一定的损伤[4]。因此,保证冷冻干燥存活率至关重要。在早期的研究中,人们通常选用改变保护剂成分以及优化冻干工艺来提高菌株的抗冷冻干燥性能,但近年来研究发现,益生菌在冷冻干燥过程中的存活率与其生长培养基的成分也有着十分密切的联系[5]。
研究表明通过改变如碳源、氮源、生长因子以及微量元素等培养基成分可以提高菌株的冻干存活率[5]。Rault等[6]发现在生长培养基中加入海藻糖可以提高保加利亚乳杆菌Lb6的冷冻存活率。包维臣等[7]将培养基的氮源由酵母浸膏改为动物蛋白胨时,保加利亚乳杆菌ND02在真空冷冻干燥过程的存活率明显升高。Carvalho等[8]发现当甘露糖替代MRS培养基中的葡萄糖时,保加利亚乳杆菌具有更好地抗冷冻干燥性能。张钰等[1]发现钙能够刺激鼠李糖乳杆菌ZY的生长,使其细胞形态由长链变为短链。苏郁文等[9]发现钙离子的添加能够提高鼠李糖乳杆菌GG在喷雾干燥过程中的存活率。除此之外,一些微量元素,如镁离子[10-11]、锰离子[12]和铁离子[4]添加到培养基中时均可促进不同菌株的生长量。由此可知,改变培养基成分,如碳源,氮源,生长因子及微量元素均可有效提高菌株的生长量及冷冻干燥抗性。
虽已有研究表明在培养基中添加钙离子可提高菌株冷冻干燥的抗性[13],但对其作用机制研究尚少。本研究以植物乳杆菌LIP-1为研究对象,在培养基中添加不同浓度的钙离子,探究钙离子对该菌株培养后的活菌数及抗冷冻干燥性能的影响,并通过菌株大小分布、关键酶活以及细胞膜脂肪酸的检测来探讨其内在作用机制,同时通过8周常温贮藏实验评价其贮藏稳定性,以期为今后提升菌株的冷冻干燥抗性提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
植物乳杆菌 LIP-1(Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1)是一株分离自新疆自然发酵酸马奶,拥有较好的耐酸耐胆盐特性及较强的降胆固醇活性的益生菌[14] 由内蒙古农业大学乳品生物技术与工程教育部重点实验室提供;氯化钙(分析纯) 天津永晟精细化工有限公司;正己烷(色谱纯) 福晨(天津)化学试剂有限公司;甲醇(色谱纯) 天津市光复科技发展有限公司;30wt%甲醇钠溶液(色谱纯)、氯仿(色谱纯) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;碱性磷酸酶试剂盒、Na+K+-ATP 酶试剂盒 北京索莱宝试剂公司。
移液枪 德国Eppendorf;MLS-3750型灭菌锅、STAC-S45F型恒温培养箱 日本三洋;Centrifuge-5810R高速离心机 德国艾本德;ZHJH-1214B超净工作台 南京依贝仪器设备有限公司;FD-1A-50真空冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;DW-86L388J医用低温保存箱 青岛海尔特种电器有限公司;SP-650型全自动干热灭菌箱 日本ASVANTEC;ND100-1干式氮吹仪 南京肯凡电子科技有限公司;Technologies 6850气相色谱 上海安捷伦科技(有限)公司;DSM5000 CS显微镜 德国莱卡;细胞破碎仪VCX750 美国Sonics。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 溶液配制[15]
冻干保护剂:蒸馏水82 mL、脱脂乳 10.0 g、蔗糖 8.0 g、L-谷氨酸钠 0.1 g,115 ℃灭菌7 min,灭菌完成后置于冰水混合物中快速冷却,4 ℃保存备用;MRS液体培养基:葡萄糖 20.0 g、大豆蛋白胨 10.0 g、牛肉膏 10.0 g、酵母粉 5.0 g、无水乙酸钠 5.0 g、无水磷酸氢二钾 2.0 g、柠檬酸钠 2.0 g、七水硫酸镁 0.2 g、五水硫酸锰 0.05 g、吐温−80 1 mL。加蒸馏水 1000 mL,121 ℃灭菌 15 min;MRS固体培养基:液体培养基的基础上额外添加琼脂12 g/L,121 ℃灭菌15 min。
1.2.2 菌株活化[15]
将贮藏于−80 ℃冰箱中的植物乳杆菌LIP-1融化,以2%接菌量接种于液体MRS培养基,于37 ℃培养箱中培养18 h,在4 ℃中保存备用。
1.2.3 钙离子对植物乳杆菌生长的影响
将MRS培养基中菌株以2%接菌量分别接种于外加0(对照组)、0.25、0.5、0.75、1、1.5、2 mmol/L氯化钙的液体MRS培养基中,培养18 h后进行稀释平板计数(以后均简称计数)。
1.2.4 钙离子培养后菌株的干燥[15]
将预冻于−80 ℃冰箱中6 h后,添加了保护剂的菌泥,置于真空冷冻干燥机中进行冻干,冻干条件为:冷阱温度−48 ℃,20 Pa,18 h。
1.2.4.1 钙离子培养后菌株的真空冷冻干燥活菌数[15]
将不同培养方式培养出的菌株,冻前计数后,加入2 mL冷冻干燥保护剂,并充分混匀,预冻6 h,后冻干,冻干后计数。
1.2.4.2 存活率的计算[15]
存活率
1.2.5 电镜观察
对(MRS)对照组与添加0.5 mmol/L钙离子的实验组使用光学显微镜拍摄照片,该显微镜配有100倍HCX PL APO物镜。为了更好地观察细胞,细胞使用结晶紫染色。显微镜拍摄后,使用Image J对菌株进行长度统计。
1.2.6 Na+K+-ATP酶活力的测定[16]
将冷冻干燥样品复水离心弃上清,菌泥用 0.85% NaCl 溶液清洗2次后,加入2 mL酶提取液,后进行超声波破碎(超声3 s,间隔10 s,7 min);4 ℃,15000 r/min,离心 10 min 取上清,用于后续相关酶活测定。Na+K+-ATP酶试剂盒分别对组样品进行相关酶活的3次重复测定,酶活的单位用U/g表示。
1.2.7 碱性磷酸酶活检测[16]
取菌泥0.1 g,加入0.05 mL甲苯轻摇15 min;碱性磷酸酶试剂盒分别对样品进行3次重复酶活测定,酶活的单位用U/g表示。
1.2.8 细胞膜脂肪酸的提取及含量测定
1.2.8.1 细胞膜脂肪酸的提取
参考陈境[15]的提取方式。首先,用无菌去离子水对冻前实验组与对照组反复离心洗涤三次(4000 r/min,4 ℃,5 min)。弃上清液后,称取菌泥0.5 g,向其中加入1.9 mL氯仿-甲醇溶液(氯仿:甲醇为1:2制备溶液,V/V),振荡15 min。加入0.625 mL氯仿及0.625 mL无菌去离子水,振荡15 min,离心10 min(4 ℃,8000 r/min)。吸取下层液相,移至无菌离心管。氮吹30 min吹干,加入1 mL甲醇钠-甲醇(1 moL/L),冰浴后振荡5 min。最后加入0.625 mL正己烷,离心5 min(4 ℃,8000 r/min),吸取上清液后经有机过滤器移入气象瓶中。
1.2.8.2 细胞膜脂肪酸含量的测定
同1.2.8.1参考陈境[15]的测定方式。气相色谱条件:DB-WAX毛细管色谱柱(60 m×0.25 μm×0.25 mm);氮气,分流比5:1,流速1 mL/min;进样口250 ℃;检测口260 ℃;柱温程序:初始温度80 ℃,升温速率6.5 ℃/min;170 ℃,升温速率27.5 ℃/min;215 ℃保持2 min;升温速率40 ℃/min,230 ℃保持2 min。进样量3 μL。脂肪酸含量计算采用面积归一法。
1.2.9 菌株的贮藏稳定性
菌株经真空冻冻干燥后,置于25 ℃恒温箱中避光贮藏,每隔一周取出计数。
1.3 数据处理
气相数据为仪器记录数据导出后经Excel处理得出。数据均为3组平行实验得到,应用SPSS26.0软件进行显著性分析,P<0.05为显著性水平,并使用Origin 2018与Excel进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同钙离子浓度对LIP-1真空冷冻干燥存活率的影响
如图1所示,对照组(普通MRS培养基)中,植物乳杆菌LIP-1冻前生长量为(3.30±0.54)×109 CFU/mL;钙离子浓度低于1 mmol/L时,其冷冻干燥存活率逐步提升。但当钙离子浓度为0.75 mmol/L时,菌株冷冻干燥前,培养基已经对菌株的生长出现了抑制作用,造成了冷冻干燥前菌株生长量降低,即使存活率高于其他组,但实际活菌数仅为(3.50±0.33)×109 CFU/mL。钙离子浓度为0.5 mmol/L时,冻前菌株生长量达到了(4.02±0.38)×109 CFU/mL,冻干后菌株存活数相较对照组增长了69.63%,为(3.08±0.27)×109 CFU/mL,其冷干前后活菌数均高于其他组,且冷冻干燥存活率(76.67%±5.00%)相较未添加钙离子的对照组(55.15%±1.50%)显著提高(P<0.05),菌株拥有较高的冷冻干燥抗性,因此选择钙离子浓度为0.5 mmoL/L进行下一步试验。
2.2 钙离子对植物乳杆菌LIP-1细胞形态的影响
如图2所示为植物乳杆菌LIP-1在不同培养条件下的显微电镜下的长度分布图。由图2可知,对照组(普通MRS培养基)培养下植物乳杆菌LIP-1的长度范围集中在1.1 ~1.7 μm之间,而添加了0.5 mmoL/L钙离子培养出的植物乳杆菌LIP-1则集中分布于0.8~1.4 μm之间。经含有钙离子的MRS培养基(对照组)培养出的植物乳杆菌LIP-1平均长度相较于普通MRS(实验组)培养基培养出的植物乳杆菌LIP-1长度缩短了约0.4 μm,这一实验结果与张钰[1]研究相同。相关文献表明,短杆相较于长杆更具稳定性[10],因此当植物乳杆菌LIP-1加入0.5 mmoL/L的钙离子后具有较高的冷冻干燥抗性。
2.3 细胞壁损伤评价
如图3所示为植物乳杆菌LIP-1在不同培养条件下,经真空冷冻干燥前后菌株的碱性磷酸酶变化。碱性磷酸酶(AKP)存在于细胞壁和细胞膜之间,正常情况下细菌培养液中只能检测到少量的AKP,只有当细胞壁通透性增大或损坏时,指示液中AKP含量才会增加,所以可以通过检测AKP活性来反映细胞壁损伤的情况[16]。由图3可知,冷冻干燥处理前对照组和实验组AKP的酶活无显著差异(P>0.05)。经冷冻干燥处理后,对照组与实验组AKP的含量均显著增加(P<0.05),说明菌体经冻干处理后,菌体的细胞壁受到损伤,且对照组AKP的含量(595.45±3.55)U/g显著高于实验组(543.75±2.50)U/g(P<0.05)。结果表明,适当的添加钙离子可提高菌体细胞壁的稳定性。
2.4 细胞膜损伤评价
如图4所示为植物乳杆菌LIP-1在不同培养条件下,经真空冷冻干燥前后菌株的Na+K+-ATP酶活性变化。Na+K+-ATP酶是一种生物膜酶,存在细胞膜的磷脂双分子层中,通过催化ATP水解提供能量,驱动Na+向细胞外和K+向膜内进行运输,维持细胞膜两侧的膜电位及乳酸菌菌体细胞的正常生理功能。所以Na+K+-ATP 酶可以在一定程度上反映细胞膜的通透性[16]。在真空冷冻干燥前实验组与对照组酶活性无显著差异,分别为(19.32±0.12) U/g与(19.41±0.22)U/g。经冷冻干燥后对照组与实验组出现了显著差异(P<0.05),对照组酶活为(10.65±0.15)U/g,实验组是(16.85±0.26)U/g,这说明经实验组培养出的菌株相较于对照组(普通MRS组)有效的提升了菌株的抗冷冻干燥性。
2.5 钙离子对植物乳杆菌LIP-1细胞膜脂肪酸的影响
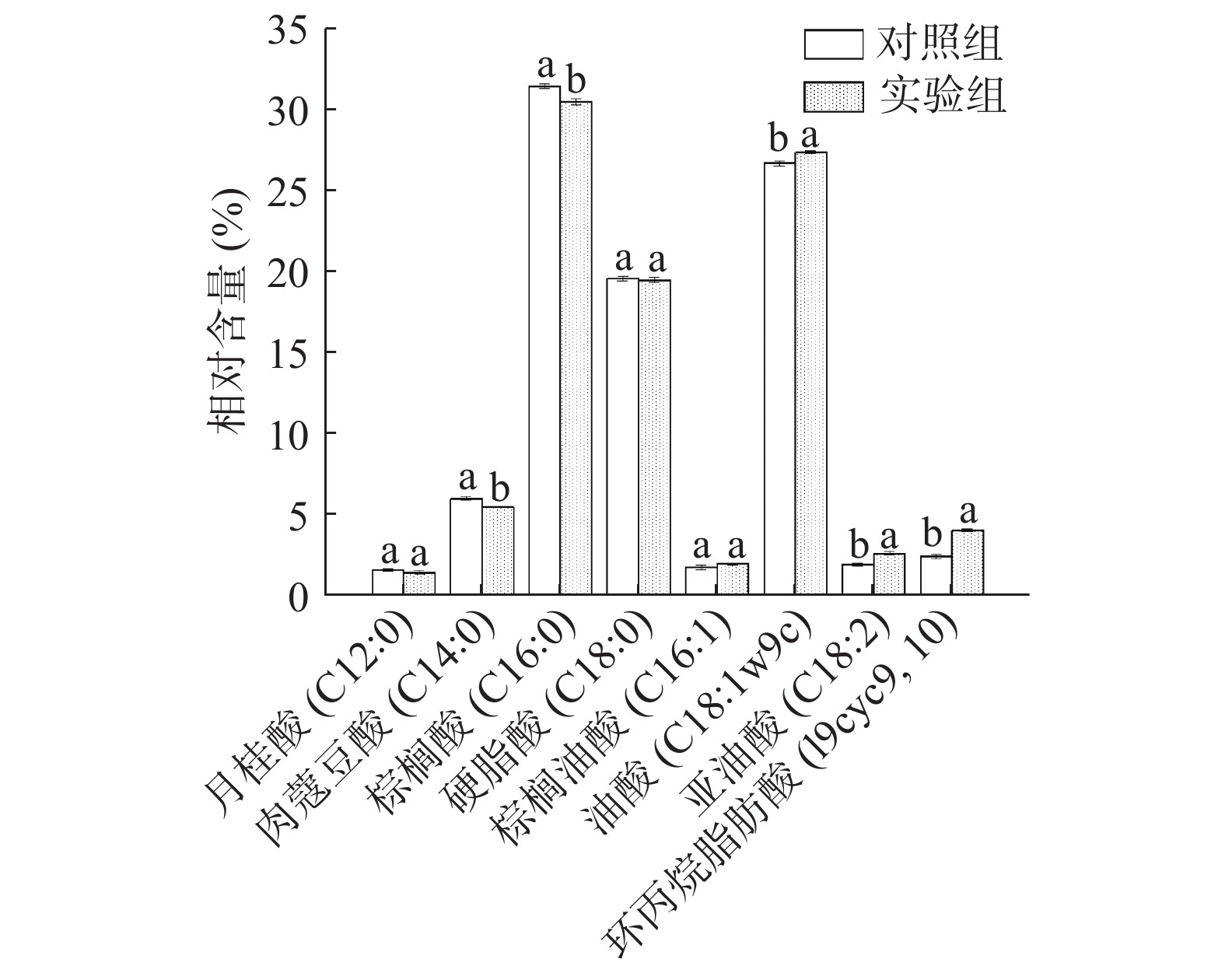
细胞膜脂肪酸组成成分是影响菌株抗冷冻干燥性能的重要指标。在冷冻干燥过程中,乳酸菌可以通过脂肪酸脱氢酶调节饱和/不饱和脂肪酸的比例。饱和/不饱和脂肪酸的比例决定了细胞膜的流动性和完整性,不饱和脂肪酸相对含量高的菌株具有较好的细胞膜流动性和完整性,从而提高菌体对冻干的抵抗能力[5,13]。通过对细胞膜脂肪酸的测定发现(如图5所示),细胞膜中主要包含8种细胞膜脂肪酸,分别为月桂酸(C12:0)、肉蔻豆酸(C14:0)、棕榈酸(C16:0)、棕榈油酸(C16:1)、硬脂酸(C18:0)、油酸(C18:1w9c)、亚油酸(C18:2)及环丙烷脂肪酸(19cyc9,10);实验组与对照组脂肪酸的相对含量存在显著性差异,其中,棕榈酸(C16:0)和肉蔻豆酸(C14:0)两种饱和脂肪酸占总脂肪酸比例显著降低(P<0.05),而油酸(C18:1w9c)、环丙烷脂肪酸(19cyc)以及亚油酸(C18:2)占比却显著提升(P<0.05)。并且实验组中不饱和度(U/S)为0.6312明显高于对照组(0.5587)。因此,在培养基中适当的添加Ca2+可使细胞膜的不饱和脂肪酸含量增加,不饱和度(U/S)的比值升高,提高了细胞膜的流动性和完整性,从而明显提高了菌体的冷冻干燥抗性。
有研究报道,细胞中蛋白酶、脂肪酶、ATP酶等多种酶,均与钙离子的作用相关[17]。Heibrunn等[18]报道,Ca2+具有影响酶活性、调节细胞膜的透性、控制代谢等功能[19]。由此我们推测Ca2+可能通过调节脂肪酸脱氢酶的活性从而调节细胞膜饱和/不饱和脂肪酸的比例,进而提高了菌株的冷冻干燥抗性。
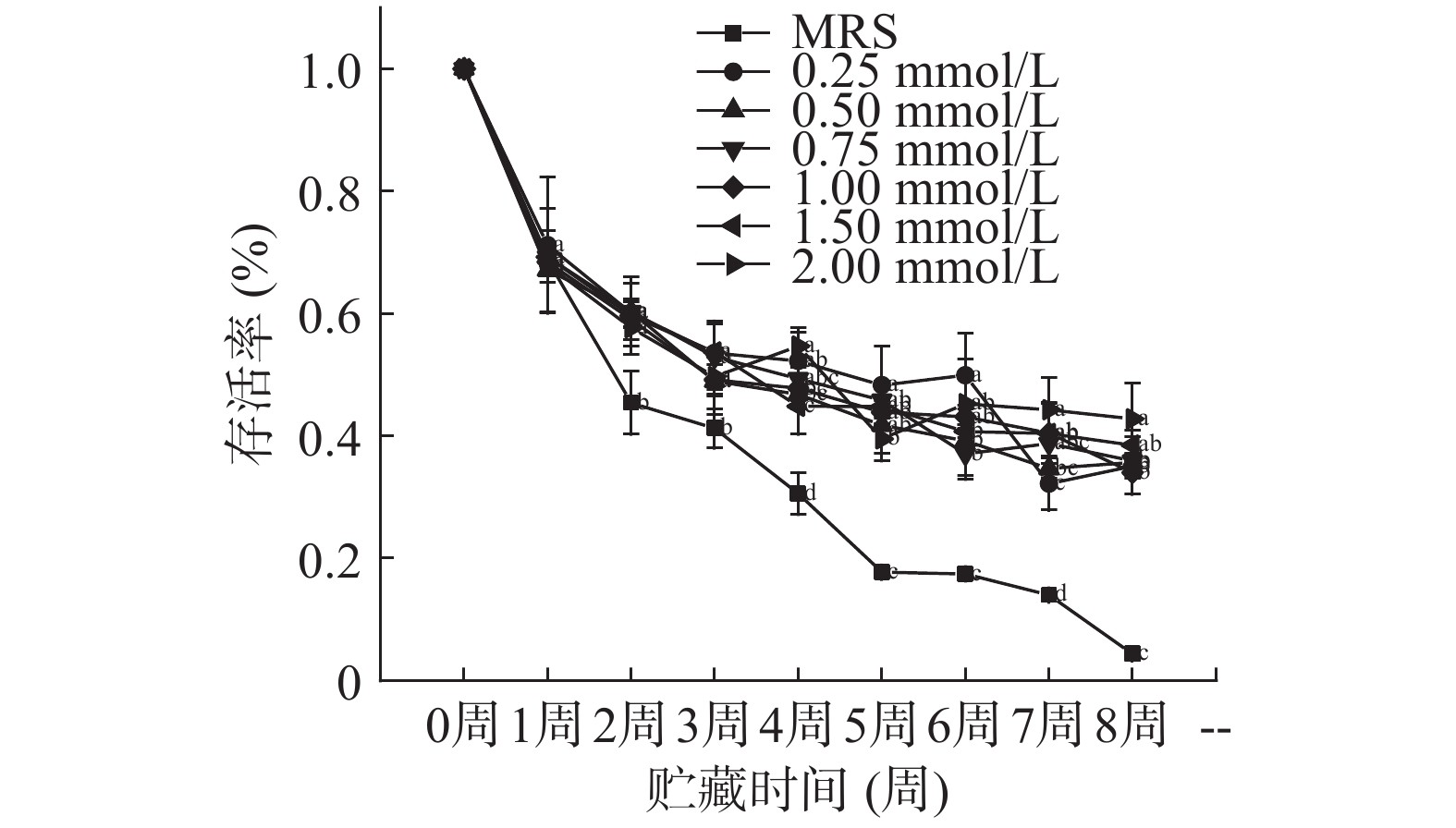
2.6 不同浓度钙离子对菌株冷冻干燥后常温贮藏稳定性的影响
如图6、图7所示,本研究通过检测真空冷冻干燥后植物乳杆菌LIP-1在25 ℃环境下贮藏8周的活菌数反映其贮藏稳定性,同时通过存活率变化评价其下降幅度。由图6可知,菌株在贮藏2~8周时,在培养基中添加了钙离子可显著提升菌株活菌数且存活率降幅较小,从而提高了菌株的贮藏稳定性(P<0.05)。随着钙离子浓度的增加,菌株贮藏稳定性提高。由于当钙离子浓度过高时菌株生长会受到抑制,影响了贮藏初始菌株密度,从而造成了第8周时2 mmoL/L钙离子虽然拥有较高的存活率,但是实际活菌数仅为(8.7±0.11)×108 CFU/mL,低于添加钙离子培养基的其他组。这表明,钙离子的加入可以有效地提高植物乳杆菌LIP-1的贮藏稳定性,并且随着钙离子浓度升高,贮藏稳定性随之升高[20]。钙离子对细胞壁、细胞膜的保护作用[13]可提高菌株的冷冻干燥抗性及贮藏稳定性。普通MRS培养基中,初始菌浓度为(2.31±0.18)×109 CFU/mL,当贮藏8周后,活菌数为(1.9±0.14)×108 CFU/mL,存活率仅为8.06%。综上所述,当钙离子浓度为0.5 mmoL/L时,菌株生长情况良好,8周内贮藏稳定性较高,经8周贮藏后的活菌数仍有(1.09±0.11)×109 CFU/mL。
3. 讨论
不同培养基成分会造成菌株形态和生理上的改变,进而导致了其对外界不良环境的抗性不同。首先从形态上,在培养基中添加例如猪源蛋白胨[21]和钙离子[22-23]等会缩短菌株形态,此时菌体表面积减小,在冷冻过程中形成的冰晶对其细胞膜的机械损伤减少,从而菌体的冷冻干燥抗性提高。在本实验中,当培养基中添加0.5 mmoL/L的钙离子时,菌株形态由长杆转变为短杆,且菌株的生长量由(3.3±0.54)×109 CFU/mL增加到(4.02±0.38)×109CFU/mL,冻干存活率提高了21.52%,这一结果再次验证在冻干过程中,钙离子可以通过改变菌株形态减少其在冷冻过程中所受到的损伤。
对于细菌而言,细胞壁与细胞膜至关重要。其中,细胞壁是位于细胞膜外的一层较厚、较坚韧并略具弹性的结构,使细菌既能适应多变的环境,又能维持细菌的结构[11]。本研究通过对AKP酶的泄漏量的测定来评估细胞壁的损伤程度,发现钙离子的加入有效保护了植物乳杆菌LIP-1的细胞壁完整性,降低了其在冷冻干燥中受到的损伤,这是由于钙离子可通过电荷作用来维持细胞壁的完整性[24]。
细胞膜可以使菌体与外部环境隔离,是保护乳酸菌的主要屏障。在冷冻干燥过程中,细胞膜受损也是导致细菌死亡的主要原因之一[25]。Na+K+-ATP酶可以使横跨膜产生电势,从而起到维持细胞内外pH动态平衡的作用。冷冻干燥过程会使得Na+K+-ATP酶活性降低甚至失活[26],从而细胞膜完整性受损,细菌的冻干存活率降低。因此可以通过测定Na+K+-ATP酶活性来评价细胞膜的损伤程度。本研究发现钙离子的加入有效保护了植物乳杆菌LIP-1的细胞膜,降低了其在冷冻干燥中受到的损伤。这与细胞膜脂肪酸成分的改变有密切联系。菌株在冷冻干燥后,其细胞膜结构受损,其中的不饱和脂肪酸相对含量是评估冷冻干燥过程细胞膜流动性与完整性的重要指标[27]。Li等[28]发现不饱和脂肪酸含量高的菌株,在冷冻干燥过程中会有更大的存活率。并且,适当改变培养基成分可使细胞膜上饱和脂肪酸向不饱和脂肪酸转变速率加快,从而有助于保持膜在冻干过程中的流动性[29]。但目前关于添加钙离子对经冻干处理后菌株细胞膜的变化尚未报道。本研究通过对Na+K+-ATP酶活性以及脂肪酸含量变化的检测,评价了钙离子对细胞膜的保护作用。结果表明,钙离子的加入提高了Na+K+-ATP酶的活性,进而更好地维持了细胞膜的通透性,降低了细胞膜的损伤程度;同时,细胞膜中不饱和脂肪酸的含量升高,U/S变大,细胞膜流动性增强,提高了菌株的冷冻干燥存活率。综上所述,在培养基中添加钙离子可有效保护菌株的细胞壁、细胞膜,提高了细胞膜的流动性,从而使菌株具有较强的冷冻干燥抗性及贮藏稳定性。但本研究并未结合基因组学,蛋白组学,代谢组学等对细胞的变化进行深入探讨,只是基于表观特征初步的探讨了钙离子对菌株的影响,还需进一步研究。
4. 结论
在培养基中添加适当浓度的钙离子(0.5 mmoL/L),可以促进植物乳杆菌LIP-1的生长量,相较于未添加钙离子的培养基活菌数增长了0.717×109 CFU/mL,并且显著提高其冷冻干燥存活率。经电镜实验发现添加钙离子使菌株形态由长杆向短杆转变,平均长度缩短0.4 μm;通过关键酶活的检测发现实验组有效的保护了菌株的细胞壁与细胞膜;通过对其脂肪酸成分的测定发现细胞膜中不饱和脂肪酸的含量升高,U/S变大(实验组(0.6312)明显高于对照组(0.5587)),致使细胞膜流动性增强,进而显著的增加了植物乳杆菌LIP-1的冷冻干燥存活率。
-
-
[1] 张钰. 鼠李糖乳杆菌胁迫应答机制的研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2014. Zhang Yu. Study on the stress response mechanism of Lactobacillus rhamnosus[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2014.
[2] 益生菌的科学共识(2020年版)[J]. 中国食品学报, 2020, 20(5): 303−307. The scientific consensus of probiotics (2020 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2020, 20(5): 303−307.
[3] 陈胜杰, 高翔, 袁戎宇. 真空冷冻干燥法制备益生菌粉的冻干保护剂配方优化[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−15[2020-11-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1759.TS.20200615.1458.032.html. Chen Shengjie, Gao Xiang, Yuan Rongyu. Optimization of freeze-dried protective agent formula for preparing probiotic powder by vacuum freeze-drying method[J/OL]. Food Industry Technology: 1−15[2020-11-09]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1759.TS.20200615.1458.032.html.
[4] 李明慧, 尚一娜, 霍麒文, 等. 真空冷冻干燥对乳酸菌损伤机制的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(19):273−279. [Li Minghui, Shang Yina, Huo Qiwen, et al. Research progress on the damage mechanism of lactic acid bacteria by vacuum freeze drying[J]. Food Science,2018,39(19):273−279. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201819042 [5] 岳林芳, 王俊国, 萨如拉, 等. 培养条件对乳酸菌发酵剂抗冷冻干燥性能影响的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2016(11):270−276. [Yue Linfang, Wang Junguo, Sa rula, et al. Research progress on the influence of culture conditions on the freeze-drying resistance of lactic acid bacteria starter[J]. Food Science,2016(11):270−276. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201611047 [6] Rault A, Bouix M, Catherine B. Cryotolerance of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus CFL1 is influenced by the physiological state during fermentation[J]. International Dairy Journal,2010,20(11):792−799. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2010.05.002
[7] 包维臣. 保加利亚乳杆菌高密度培养及冷冻保护的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2012. BaoWeichen. Research on high-density cultivation and cryoprotection of Lactobacillus bulgaricus[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2012.
[8] Carvalho A S, Silva J, Ho P, et al. Effects of various sugars added to growth and drying media upon thermotolerance and survival throughout storage of freeze-dried Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus[J]. Biotechnol Prog,2010,20(1):248−254.
[9] Su Y, X Zheng, Qiang Z, et al. Spray drying of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG with calcium-containing protectant for enhanced viability[J]. Powder Technology,2018:358.
[10] Yang Y, Huang S, Wang J, et al. Mg2+ improves the thermotolerance of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, Lactobacillus casei Zhang and Lactobacillus plantarum P-8[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,2017,64(4):283. doi: 10.1111/lam.12716
[11] Johnson M, Berger J. The enzymatic properties of peptidases[M]. Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, Volume 2. John Wi ley & Sons, Inc. 2006.
[12] 高洪波. Ca2+和钙调素拮抗剂对茄子幼苗抗冷性的影响[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2002. Gao Hongbo. Effect of Ca2+ and calmodulin antagonist on cold resistance of eggplant seedlings[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2002.
[13] Wright C T, Klaenhammer T R. Survival of Lactobacillus bulgaricus during freezing and freeze-drying after growth in the presence of calcium[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,48(3):773−777.
[14] 尚一娜. 培养基成分对植物乳杆菌LIP-1抗冷冻活性影响及其蛋白组学研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2018. ShangYina. The effect of medium components on the antifreeze activity of Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 and its proteomics study[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018.
[15] 陈境. 不同初始pH值对植物乳杆菌LIP-1抗冷冻干燥性能的影响及作用机制[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2019. Chen Jing. The effect of different initial pH valueson the anti-freeze drying performance of Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 and its mechanism[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2019.
[16] 公丕民. 保加利亚乳杆菌喷雾干燥过程中损伤机制及保护方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. Gong Pimin. Research on damage mechanism and protection methods of Lactobacillus bulgaricus during spray drying process[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
[17] 宋剑武, 吴永继, 孙燕杰, 等. 救必应水提取物对产 ESBLs 细菌的抑菌机理研究[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2016,43(6):1536−1543. [Song Jianwu, Wu Yongji, Sun Yanjie, et al. Study on the antibacterial mechanism of the water extract of Jiubiying on ESBLs producing bacteria[J]. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2016,43(6):1536−1543. [18] 贺怀贞. 新型Ca2+荧光探针的设计合成及胞内信使作用研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2009. He Huaizhen. Design and synthesis of a novel Ca2+ fluorescent probe and its intracellular messenger function[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2009.
[19] Velly H, Bouix M, Passot S, et al. Cyclopropanation of unsaturated fatty acids and membrane rigidification improve the freeze-drying resistance of Lactococcuslactis subsp. lactis TOMSC161[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,2015,99(2):907−918. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6152-2
[20] Song H, Dong C. Significant effect of Ca2+ on improving the heat resistance of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Fems Microbiology Letters,2013,344(1).
[21] Senz M, Lengerich B, Bader J, et al. Control of cell morphology of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus for enhanced cell stability during industrial processing[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2015,192:34−42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.09.015
[22] Wright C, Klaenhammer T. Survival of Lactobacillus bulgaricus during freezing and freeze-drying after growth in the presence of calcium[J]. Journal of Food ence,2010,48(3):773−777.
[23] Beal C, Fonseca F, Corrieu G. Resistance to freezing and frozen storage of Streptococcus thermophilus is related to membrane fatty acid composition[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2001,84(11):2347−2356. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)74683-8
[24] Yan W, Fan H, Wenjie L, et al. Enhanced thermal stability of lactic acid bacteria during spray drying by intracellular accumulation of calcium[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2020,279:109975. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.109975
[25] Jingjing E, Lili M, Zichao, C, et al. Effects of buffer salts on the freeze-drying survival rate of Lactobacillus plantarum, LIP-1 based on transcriptome and proteome analyses[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,326:126849. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126849
[26] Soukoulis C, Solmaz, Behboudi J. Impact of milk protein type on the viability and storage stability of microencapsulated Lactobacillus acidophilus NCIMB 701748 using spray drying[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2014,7(5):1255−1268. doi: 10.1007/s11947-013-1120-x
[27] Zhang G, Fan M, Lv Q, et al. The effect of cold, acid and ethanol shocks on synthesis of membrane fatty acid, freeze-drying survival and malolactic activity of Oenococcus oeni[J]. Annals of Microbiology,2013,63(2):477−485. doi: 10.1007/s13213-012-0492-x
[28] Li C, Zhao J, Wang Y, et al. Synthesis of cyclopropane fatty acid and its effect on freeze-drying survival of Lactobacillus bulgaricus L2 at different growth conditions[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology,2009,25(9):1659−1665.
[29] Hansen M, Petersen M, Risbo J, et al. Implications of modifying membrane fatty acid composition on membrane oxidation, integrity, and storage viability of freeze-dried probiotic, Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2015,31(3):799−807. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2074
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 刘荣倩,杨申明,李新会,王振吉,彭润,解健翠. 百香果壳总三萜提取工艺优化及抗氧化性能评价. 饲料工业. 2025(01): 118-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 景炳年,李宁洁,魏磊,谢晓阳,刘雨晴,王学方,王韬,王伟. 连翘三萜酸提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2025(03): 64-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄瑜,张锡宇,赵海桃,石统帅,邱隽蒙,符群. 沙棘叶提取物的体外抗氧化及乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制能力. 精细化工. 2024(02): 391-400 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 温舒然,马占山,詹冬玲. 灵芝三萜提取工艺的优化. 吉林大学学报(理学版). 2024(02): 452-463 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 岳洪霞,胡娜,隆海燕,王洪伦,栾广祥. 响应面法优化超声辅助提取蕨麻总三萜工艺研究. 中国野生植物资源. 2024(03): 28-33+66 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨洪飞,卢雨菲,葛婷婷,王洁琼,陈祺,孟丽媛,要辉,闵清. 星点设计-效应面法优化超声提取桂籽中三萜化合物的工艺研究. 湖北科技学院学报(医学版). 2024(03): 214-220 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 曹柏营,杨海蛟,侯宇,王家利,乔新宇,陈英伟,刘馨阳. 蓝靛果花青素抗氧化作用及机制. 食品研究与开发. 2024(19): 53-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张剑林,张亮亮,姜露熙,裴龙英,王寒博,孙博,梁睿武,房丹丹. 基于人工神经网络优化黑木耳红枣发酵乳及其抗氧化分析. 食品研究与开发. 2023(05): 141-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 沈柯辰,宋亚茹,高琳,张仁堂. 红枣固态发酵黑化前后苯甲酸及农药残留含量比较分析. 食品研究与开发. 2023(05): 177-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘树萍,陆家慧,张佳美,彭秀文,苏晓文,石长波. 奇亚籽胶提取工艺优化及其理化性质. 食品研究与开发. 2023(22): 53-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 林瑞,杜秋旻,李永春,闫美霖,何家丽,苗晶囡,徐丹,邱军强. 黄药子中黄独乙素提取工艺研究. 吉林医药学院学报. 2022(02): 91-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 李金金,孟琦,崔馨燕,石汝杰,吴应梅,杨玲,周浓. 响应面法优化地参三萜酸提取工艺及抗氧化活性分析. 南方农业学报. 2022(08): 2261-2271 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 刘嘉鑫,陈小梅,曾慧,王淑美,向丽敏. 响应面法优化蒲桃籽中三萜类化合物的提取工艺及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2022(23): 192-199 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 周海旭,苏同超,李姝,冉军舰,李波,高晗,余梦薇,薛静丽,李婧瑜,李晓晴,李忠海. 樟叶木脂素的提取纯化及其抗氧化性、抗癌活性. 食品工业科技. 2021(13): 170-178 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. 王吉宇,李成文,徐彦靖,于青,刘楠,刘东春. 响应面法优化藏红花素碱水解制备反式藏红花酸工艺. 食品工业科技. 2021(23): 176-183 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(9)







 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
