Optimization of Preparation Process of Vaterite Calcium Carbonate and Effect of Chitinase on Calcium Carbonate
-
摘要: 为了建立一种以CaCl2为原料碳化合成高产率高纯度球霰石碳酸钙的工艺。通过单因素考察几丁质酶添加、碳化温度、pH、CaCl2浓度和碳化时间等工艺条件对钙离子碳化率的影响,再用正交试验优化工艺,并用扫描电镜(SEM)、红外光谱(IR)等表征考察优化条件下几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型与组成的调控。结果表明,几丁质酶添加基本不影响钙离子碳化率,而碳化温度、pH、CaCl2浓度和碳化时间等对钙离子碳化率存在显著性影响;35 ℃下,以1 L/min气体流速往pH 12.5的1 mol/L CaCl2溶液持续通入CO2碳化6 min,钙离子碳化效果最佳,碳化率达99.88%。SEM和IR等表征结果显示,未加几丁质酶制得由球状颗粒和少部分菱形块状组装形成的直径为2 ~ 8 μm的大小不一的方解石型碳酸钙微球;加入几丁质酶后,菱形块状形貌消失,且随着几丁质酶添加比例增大,碳酸钙微球尺寸逐渐下降;当酶钙质量比为0.01:1时,制备得直径小于1 μm的大小较均一的高纯度蓬松球霰石型碳酸钙微球。结果说明几丁质酶调控下可制备出高产率高纯度球霰石碳酸钙,研究对食药级碳酸钙的仿生制备具有重要意义。Abstract: In order to establish a high-yield and high-purity vaterite calcium carbonate synthesis process, CaCl2 was used as raw material. The effects of chitinase addition, carbonization temperature, pH, CaCl2 concentration and carbonization time on the carbonization rate of calcium ions were investigated through the single factor, and orthogonal experiment was used to optimize the process. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) were applied to investigate the regulation of chitinase on the crystal form and composition of calcium carbonate under optimized conditions. The results showed that the addition of chitinase rarely affected the calcium ion carbonization rate, while the carbonization temperature, pH, CaCl2 concentration and carbonization time had significant effects on the calcium ion carbonization rate. At 35 ℃, the gas flow rate was 1 L/min, the 1 mol/L CaCl2 solution with pH 12.5 was continuously fed with CO2 for 6 min to carbonize, and the effect of calcium ion carbonization was the best, with a carbonization rate of 99.88%. Characterization results such as SEM and IR showed that 2~8 μm calcite-type calcium carbonate microspheres, which assembled from spherical particles and a small part of diamond-shaped blocks, were obtained without chitinase regulation. After adding chitinase, the diamond-shaped block shape disappeared, and the size of calcium carbonate microspheres gradually decreased as the adding proportion of chitinase increased. The high-purity fluffy vaterite-type calcium carbonate microspheres with diameter of less than 1 μm, were obtained with uniform size when the enzyme calcium mass ratio was 0.01:1. The results indicated that high-yield and high-purity vaterite calcium carbonate could be prepared under the control of chitinase. The research was of great significance for the biomimetic preparation of food and pharmaceutical grade calcium carbonate.
-
Keywords:
- carbonization process /
- calcium carbonate /
- chitinase /
- crystal form control
-
碳酸钙是动物贝壳、甲壳、蛋壳、牙齿以及骨头等生物体硬组织的主要成分,在生物体内由蛋白质、多糖等生物大分子调控下矿化形成 [1-4]。碳酸钙主要有方解石、文石、球霰石等3种晶型,不同晶型具有不同形状、性质和功能[5-6]。方解石和文石是单晶体,具有热力学稳定、结构密实的特性,在自然界广泛存在;球霰石是多晶体,一般是由纳米级球形颗粒聚集而成的结构松软的多孔微球,具有密度小、比表面积大、溶解性和分散性好、良好生物安全性及可吸收利用性,被广泛用于食品和医药等行业领域[7-9]。如利用球霰石微球具有促进骨基质形成的特性[10],在增加骨密度的保健食品中,碳酸钙成为使用率最高的补钙配方主成分[11],同时也被用于人工骨和人造牙齿的制备[12];利用其孔隙率高的特性,用作药物、生物标记物、生物传感器等生物医药载体[13-15]。
然而球霰石热力学不稳定,易转化成文石或方解石,自然界中存量稀缺,故如何合成稳定的球霰石碳酸钙越来越受关注[7,9]。目前球霰石碳酸钙的合成方法主要采用碳化法和复分解法,碳化法是直接往Ca2+溶液中通入CO2反应生成碳酸钙,产品纯度较高,但容易受CO2溶解速率影响导致球霰石产率较低;复分解法是利用可溶性钙盐和碳酸盐混合反应制备碳酸钙,反应快产率高,但容易引入杂质;且非仿生体系下,两种方法合成的产品稳定性均较差,易转化成文石与方解石导致产品纯度不高[7,9]。为了提高球霰石稳定性,近年来在碳化法和复分解法合成体系里添加糖、蛋白质等有机分子做为晶型调控剂。仿生合成稳定球霰石的研究报道不少[16-24],但研究内容基本侧重于添加剂对晶型的调控,而关于添加剂对球霰石产率和纯度的影响鲜少研究。
几丁质酶是一种糖苷键水解酶,广泛分布在动物、植物以及微生物等各种生物体内,具有消化几丁质食物、调控形态发育、抗菌防御等功能,在食品、医疗、环保等方面具有广泛应用[25-26]。虾蟹、昆虫等甲壳动物的几丁质酶主要分布在胃肠等内脏和壳膜等组织部位,与围食膜蜕换和周期性蜕壳生长发育密切相关[27-31]。韩晓梅等[2]报道虾蟹壳约含15%~25%的甲壳素和50%矿物质等化合物,其中矿物质主要是碳酸钙,虾蟹壳中碳酸钙生物合成应该与壳膜几丁质酶的调控具有密切关系,但有关几丁质酶对碳酸钙仿生合成调控的研究未见报道。本文优化了钙离子碳化合成碳酸钙的工艺条件,并在优化工艺条件下考察了几丁质酶对钙离子碳化合成碳酸钙的调控,通过扫描电镜(SEM)、红外光谱(IR)等表征分析了产品组成与形貌特征,研究内容对高产率高纯度的球霰石仿生合成和食药级碳酸钙的制备具有重要指导意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
几丁质酶 实验室自制,以凡纳滨对虾内脏为材料,经pH 7.5 Tris-HCl缓冲液抽提、硫酸铵分级沉淀、透析、Sephadex G-100和DEAE-32柱层析制备得电泳纯制剂[26],比活力为14.15 U/mg,备用;99.95% CO2气体 泉州市丰泽区东流焊接材料经营部;无水氯化钙(分析纯) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠(分析纯)、钙羧酸指示剂(分析纯) 北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司;氨水(分析纯) 西陇科学股份有限公司;其它试剂 均为国药集团化学试剂分析纯产品;实验用水 为去离子水。
DGG-9123A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海森信实验仪器有限公司;DF-101S 集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;JY3002电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;AR124CN分析天平 奥豪斯仪器(常州)有限公司;FE28 pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;NICOLET iS 10红外光谱仪 Thermo Fisher SCIENTIFIC;ZEISS MERLIN Compact扫描电镜 德国Zeiss公司;STA 409 PC热重分析仪 NETZSCH。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 碳酸钙碳化制备工艺
用氨水调节CaCl2溶液至合适pH,再加入适量几丁质酶(按不同酶钙质量比或不加),混匀后,在一定温度下通入CO2,使钙离子碳化析出晶体,抽滤、洗涤后烘干得碳酸钙产品。
1.2.2 钙离子浓度测定与碳化率计算
钙离子浓度测定采用EDTA滴定法[17]。取碳化前后(通CO2气体前后)的CaCl2溶液适量,用氢氧化钠溶液调pH至12~13,加入钙羧酸指示剂摇匀,用EDTA标准液滴定,当溶液由玫瑰红变为亮蓝色,终止滴定并记录消耗的EDTA标准液体积,每个样液平行滴定两次,取平均值按公式
cCa2+=cs×V2V1 计算钙离子浓度。式中:cs,EDTA标准溶液浓度,mol/L;V2,滴定消耗的EDTA标准溶液体积,mL;V1,样液体积,mL。
碳化前后溶液体积变化忽略不计,钙离子碳化率计算公式如下:
钙离子碳化率η(%)=(碳化前溶液钙离子浓度-碳化后溶液钙离子浓度)碳化前溶液钙离子浓度×100 1.2.3 碳化工艺的单因素实验
对几丁质酶添加量(按不同酶钙质量比添加)、温度、CaCl2浓度、pH、碳化时间等5个因素进行单因素实验,平行实验3次,分别考察各因素对钙离子碳化率的影响,确定较优工艺条件。
1.2.3.1 几丁质酶对钙离子碳化率的影响
按0:1、0.001:1、0.002:1、0.004:1、0.01:1的酶钙质量比,分别往30 mL pH 12.0的1.00 mol/L的CaCl2溶液中加入不同量的几丁质酶,搅拌混匀后,20 ℃下,按1 L/min气流速度通入CO2碳化5 min后,过滤收集样品,测定分析计算碳化率,考察几丁质酶添加对钙离子碳化率的影响。
1.2.3.2 温度对钙离子碳化率的影响
分别在0、10、20、30、40、50、60 ℃等不同温度下,按1 L/min气流速度,往30 mL pH12.0的1.00 mol/L的CaCl2溶液,通入CO2碳化 5 min后,过滤收集滤液和CaCO3产物,分析滤液残余钙离子浓度,计算碳化率,考察温度对钙离子碳化率影响,确定较佳碳化温度。
1.2.3.3 CaCl2浓度对钙离子碳化率的影响
20 ℃下,按1 L/min气流速度,分别往30 mL pH12.0的0.25、0.50、0.75、1.00、1.25、1.50 mol/L等不同浓度的CaCl2溶液,通入CO2碳化5 min后,过滤收集样品,测定分析计算碳化率,考察CaCl2浓度对钙离子碳化率影响,确定较佳CaCl2浓度。
1.2.3.4 pH对钙离子碳化率的影响
20 ℃下,按1 L/min气流速度,分别往30 mL 用氨水调节至pH 10.5、11.0、11.5、12.0、12.5等不同pH的1.00 mol/L的CaCl2溶液,通入CO2碳化5 min后,过滤收集样品,测定分析计算碳化率,考察pH对钙离子碳化率影响,确定较佳pH。
1.2.3.5 碳化时间对钙离子碳化率的影响
20 ℃下,按1 L/min气流速度,往30 mL pH 12.0的1.00 mol/L的CaCl2溶液,分别通入CO2碳化1、2、3、5、7、9 min后,过滤收集样品,测定分析计算碳化率,考察碳化时间对钙离子碳化率影响,确定较佳碳化时间。
1.2.4 正交试验优化碳化工艺条件
为进一步优化碳化工艺条件,根据单因素实验结果,选取A碳化温度(℃)、B碳化时间(min)、CpH、DCaCl2浓度(mol/L)等4个因素作为试验因素,以钙离子碳化率为指标,按L9(34)正交表制定正交方案并实验,正交试验因素水平见表1。
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal test水平 因素 A 碳化温度(℃) B 碳化时间(min) C pH D/CaCl2浓度(mol/L) 1 25 4 11.5 0.90 2 30 5 12.0 1.00 3 35 6 12.5 1.10 1.2.5 几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型调控的研究
在优化的碳化工艺条件下,分别按0:1、0.002:1、0.004:1、0.01:1酶钙质量比往30 mL的碳化体系中加入几丁质酶,充分搅拌混匀后,以1 L/min气体流速持续通入CO2碳化,碳化结束后过滤收集滤液和CaCO3产物,分析滤液残余钙离子浓度,计算碳化率,洗涤收集CaCO3固体,并置于105 ℃下干燥至恒重,称重并取样分析产品几丁质酶含量及表征产品形貌特征,与同等条件下不加几丁质酶碳化制备的CaCO3形貌比较,考察几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控。
1.2.6 碳酸钙产品表征
1.2.6.1 扫描电镜形貌分析
用直接分散法处理样品:先把裁剪好的尺寸适中的导电胶粘在铜片上,接着将烘干的待测样品借外物直接散落附着于导电胶。进样,观察各样品在放大1000~20000倍下的形貌,晶型及粒径大小。
1.2.6.2 红外光谱定性分析
按50:1~100:1的质量比取适量KBr粉末和少量碳酸钙样品于玛瑙研钵中,研磨后压片,以KBr空白片剂为参照,扫描4000~400 cm−1之间的红外光谱,表征分析产物组成。
1.3 数据处理
所有工艺优化实验均做3个平行,用Excel 2007、SPSS 18.0、Grapher 8.0等软件进行数据处理与分析,实验结果以平均值±标准差表示,单因素方差分析(ANOVA)按P<0.05分析显著性。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 几丁质酶对钙离子碳化率的影响
蛋白质类调控剂的侧链一般都含有—COOH等可解离基团,会与钙离子产生静电与配位作用,影响碳化反应。由图 1 可见,按不同酶钙质量比分别往相同的碳化体系中加入不同量几丁质酶后,钙离子碳化率基本在98.31%~98.54%间波动,对实验数据进行单因素方差分析,P=0.775>0.05,说明几丁质酶添加对钙离子的碳化率不具有显著性影响。
2.1.2 温度对钙离子碳化率的影响
温度会影响化学反应速度和化学反应平衡,温度升高可以提升体系中离子运动速率促进离子之间碰撞结合的机会,有利碳化反应;但温度升高也会降低CO2的溶解度,导致体系中CO32-离子浓度下降,不利钙离子的碳化反应。由图2可见,在固定碳化体系下,温度低于30 ℃时,钙离子碳化率随着温度升高而轻微上升;温度高于30 ℃时,钙离子碳化率随温度升高而出现下降趋势;整体变化趋势显示,低温体系下的钙离子溶液碳化率优于高温体系;说明随着温度升高,CO2的溶解度对碳化率影响渐趋主导,在30 ℃下,具有较好的碳化效果,钙离子碳化率达97.89%;单因素方差分析P=0.00657<0.05,说明温度对钙离子碳化率具有显著性影响。
2.1.3 CaCl2浓度对钙离子碳化率的影响
固定碳化时间、CO2通入流速时,体系CaCl2初始浓度直接影响到CO32−/Ca2+的比例,从而影响钙离子的转化率。图3显示,随CaCl2浓度上升,钙离子碳化率呈现先增大后趋于平稳的趋势。当钙离子浓度小于1.0 mol/L时,体系局部CO32−/Ca2+的比例较高,CO32−过饱和,碳化结束时可能导致碳化成的碳酸钙少量转化成碳酸氢钙,从而导致钙离子碳化率较低;但随着CaCl2浓度上升,体系CO32−/Ca2+比例下降,CO32−过饱和度下降并逐渐趋于稳定,体系钙离子基本都碳化成碳酸钙并稳定存在,故钙离子碳化率随钙离子浓度增大而上升,并趋于稳定;当钙离子浓度为1.00 mol/L时,就具有较佳的碳化效果,碳化率为98.37%。单因素方差分析P=4.56×10−10<0.05,说明CaCl2浓度对钙离子碳化率的影响具有显著性。
2.1.4 pH对钙离子碳化率的影响
碳化体系的pH直接影响二氧化碳的溶解度以及碳酸的解离趋势(碳酸二级解离常数,pKa2=10.2),进而影响着体系钙离子的碳化反应效果。实验采用氨水调节碳化体系pH,考察pH对钙离子碳化率的影响,由图4可知,钙离子碳化率随着体系pH增大呈现先增大后趋于平稳的趋势;pH<12.0,体系钙离子碳化率随着pH增大快速增大;pH>12.0,钙离子的碳化率随pH增大变化不明显;当pH=12.0时,钙离子碳化率为98.14%。单因素方差分析P=1.25×10−17<0.05,说明pH对钙离子碳化率的影响具有显著性。考虑强酸强碱设备成本,确定碳化体系较佳pH为12。
2.1.5 碳化时间对钙离子碳化率的影响
固定碳化体系下,碳化时间直接影响着钙离子与通入的二氧化碳的碳化反应程度。图5显示,随碳化时间延长,钙离子碳化率呈现先增大后趋于平稳的趋势。当碳化时间小于3 min时,碳化率随碳化时间延长而快速上升,说明在这个时间范围内,钙离子不能达到完全的碳化效果;当碳化时间为3、5、7、9 min,体系钙离子碳化率分别达97.60%、98.57%、99.11%、99.22%;即碳化时间大于3 min后,钙离子的碳化率上升缓慢,基本趋于稳定,说明碳化3 min 后体系大部分钙离子已基本完成碳化反应;单因素方差分析P=1.45×10−21<0.05,说明碳化时间对钙离子碳化率具显著性影响。考虑碳化程度,确定较佳碳化时长为5 min。
2.2 正交试验优化碳化工艺条件
2.2.1 正交试验与结果分析
由于添加少量几丁质酶不影响碳化率,故确定A碳化温度(℃)、B碳化时长(min)、C pH、D CaCl2浓度(mol/L)等四因素进行正交试验,根据单因素优化结果,分别在A碳化温度(℃)、B碳化时长)min)、C pH、D CaCl2浓度(mol/L)等4个因素的较佳值周边选择三个水平,按L9(34)正交表设计组合出9个实验方案,以钙离子碳化率为指标,进一步优化碳化工艺条件。具体的实验方案及实验结果极差分析见表2,实验结果的SPSS方差显著性分析见表3。
表 2 钙离子碳化制备碳酸钙的正交实验方案及实验结果Table 2. The schemes and results of orthogonal experiments for the preparation of calcium carbonate by calcium ion carbonization试验号 A B C D 钙离子碳化率(%) 1 1 1 1 1 90.38 2 1 2 2 1 98.80 3 1 3 3 3 99.82 4 2 1 2 3 97.76 5 2 2 3 1 99.04 6 2 3 1 2 99.74 7 3 1 3 2 98.80 8 3 2 1 3 98.91 9 3 3 2 1 99.33 K1 289.00 286.94 289.03 288.75 K2 296.54 296.65 295.89 297.34 K3 297.04 298.89 297.66 296.49 R 2.68 3.98 2.88 2.86 因素主
次关系4 1 2 3 表 3 正交试验结果方差统计分析Table 3. Statistical analysis of variance of orthogonal test results源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 0.028a 8 0.003 2871.510 0.000 截距 34.619 1 34.619 2.866×107 0.000 碳化温度 0.005 2 0.003 2239.609 0.000 碳化时间 0.011 2 0.005 4485.255 0.000 CaCl2浓度 0.006 2 0.003 2470.258 0.000 pH 0.006 2 0.003 2290.917 0.000 误差 3.262×10−5 18 1.208×10−6 总计 34.647 27 校正的总计 0.028 26 注:a. R2 = 0.999(调整 R2 =0.998)。 由表2实验结果可知,按A1B3C3D3组合的工艺条件,即在体系pH12.5,碳化温度25 ℃下,对30 mL 1.1 mol/L CaCl2溶液碳化时间6 min,可取得最佳碳化效果,碳化率达99.82%。但对实验结果进行极差分析,结果显示最佳碳化工艺条件组合应该为A3B3C3D2,即体系pH为12.5、碳化温度为35 ℃、CaCl2浓度为1 mol/L、碳化时间为6 min;通过比较R值可知,四个因素对钙离子碳化率的影响主次顺序为:B>C>D>A,即碳化时间>pH>CaCl2浓度>碳化温度。表3的SPSS统计分析结果显示,四个因素对钙离子碳化率影响均具有显著性,影响主次顺序同极差分析结果基本一致。
2.2.2 钙离子碳化最佳工艺条件验证
由于正交实验结果显示最佳反应条件为A1B3C3D3组合,而正交实验结果极差分析得出的最佳反应条件为A3B3C3D2组合,结果不一致。故在A3B3C3D2组合条件下进行验证实验,平行实验三次,得钙离子碳化率达99.88% ± 0.02%,比A1B3C3D3组合条件下的碳化率99.82%稍高一点,故确定钙离子最佳碳化工艺条件为体系pH为12.5、碳化温度为35 ℃、CaCl2浓度为1 mol/L、碳化时间为6 min。
2.3 几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控
在优化的碳化工艺条件下,分别按0:1、0.002:1、0.004:1、0.01:1的酶钙质量比,往35 ℃、pH 12.5、30 mL的1 mol/L CaCl2溶液中加入几丁质酶,搅拌混匀后,持续通入二氧化碳碳化6 min,碳化结束分析计算钙离子碳化率,不同体系下的碳化率在99.85%~99.92%范围内波动,结果进一步显示几丁质酶的添加确实不影响钙离子的碳化率。产品经洗涤、烘干至恒重后,取适量产品酸溶后,根据蛋白质的紫外特征吸收性质,测定样品液在280 nm的吸光度值判断产品是否夹杂几丁质酶,结果显示不同酶钙质量比的碳化体系制备的产品均无夹杂几丁质酶。在此基础上,取样进行扫描电镜、红外光谱等性能表征测试,进一步了解几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控及产品组成情况。
2.3.1 扫描电镜分析
采用扫描电镜(SEM)测定不同量几丁质酶调控下碳化而成的碳酸钙的形貌和粒径。图6中的a、b、c、d分别是未加酶、按0.002:1、0.004:1、0.01:1的酶钙质量比添加几丁质酶调控碳化形成的碳酸钙的SEM图像。
由图6a可见,未添加几丁质酶调控碳化制备的碳酸钙是由约110 nm的球状颗粒和少部分尺寸近1 μm的菱形块状自组装形成的直径为2 ~ 8 μm左右的大小不一的微球。图6b显示,按0.002:1的酶钙比添加几丁质酶制备得到的碳酸钙微球尺寸变小,且菱形块状形貌消失,碳酸钙基本由80 nm的纳米级球状颗粒团聚而成的粒径约为2 ~ 4 μm的大小较均匀的微球。进一步增大几丁质酶加入量,由图6c、6d可知,碳酸钙基本颗粒和微球粒径随着酶添加量增大而减小,纳米球基本颗粒的团聚由紧密趋向蓬松;按0.004:1的酶钙比添加酶调控,可得到70 nm的纳米颗粒团聚组成的粒径约为1.5 μm的大小均匀的微球;当比例增到0.01:1,得到60 nm的纳米颗粒团聚组成的粒径小于1 μm的蓬松微球。SEM表征结果说明几丁质酶的添加不仅能改变碳酸钙基本颗粒的晶型与尺寸,还会影响碳酸钙颗粒团聚的紧密度与团聚微球粒径,这对食品、保健等轻工业新型钙制剂的制备与应用具有重要意义。几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控效应与高平章等[17]用胰蛋白酶调控碳酸钙晶型的效果类似,肯定了蛋白质类物质对碳酸钙的仿生制备过程具有实际的调控作用。
2.3.2 红外光谱分析
方解石型碳酸钙的红外光谱特征吸收峰为876 cm−1和712 cm−1[4,32]。图7是未加几丁质酶调控CaCl2碳化形成的碳酸钙红外光谱图,由图可见,在3436、1421、875 cm−1和714 cm−1处出现特征吸收峰,与竹文坤等[22]以CaCl2和碳酸钠为原料在纯水体系下复合合成的方解石型碳酸钙的红外谱图基本一致,均具有876 cm−1和712 cm−1的红外特征峰,说明未加几丁质酶调控碳化形成的碳酸钙为方解石型。图中3436 cm−1是H-O键的伸缩振动吸收峰,表明碳酸钙含有水分;而1421 cm−1是方解石型碳酸钙中的C-O键的伸缩振动特征吸收峰;875 cm−1和714 cm−1是方解石型碳酸钙中C-O键的弯曲振动特征吸收峰。目前大部分实验制备的方解石基本是密实菱形,但电镜图显示未加几丁质酶碳化制备的碳酸钙为球形;实验结果与徐焕焕等[32]采用复分解法,用豆腐废水调控制备出球形方解石碳酸钙的形貌相似,表明特定条件下制备的方解石碳酸钙并不完全是菱形。
球霰石型碳酸钙的红外光谱特征吸收峰为876 cm−1和745 cm−1[4]。图8是按0.01:1酶钙质量比加入几丁质酶调控CaCl2碳化形成的碳酸钙红外光谱图,由图可知,在1456~1409 cm−1之间出现了较宽的分裂吸收峰,1089、874 cm−1和745 cm−1处也出现特征吸收峰,特征峰与马晓明等[23]在胃蛋白酶调控下水醇体系中用CaCl2和碳酸氢铵仿生合成的球霰石碳酸钙的红外特征吸收峰基本一致,也与王芬等[33]利用CO2碳化制备的球霰石型碳酸钙的红外特征峰基本吻合。图中1456~1409 cm−1之间的分裂吸收峰是球霰石型碳酸钙中C-O键反对称伸缩振动吸收峰;1089、874 cm−1和745 cm−1分别是球霰石型碳酸钙中C-O键的对称伸缩振动、面外弯曲振动和面内弯曲振动吸收峰。结果说明几丁质酶存在影响了Ca2+碳化形成的碳酸钙的晶型,可调控碳化形成的球霰石型碳酸钙,红外谱图表征结果与SEM观测结果相一致。
几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控机理应该与大部分蛋白质与氨基酸的调控机理类似,借助分子中的—COOH实现,该基团在中性或碱性条件下解离成—COO-,与Ca2+发生静电和配位作用,提高体系局部Ca2+浓度,为碳酸钙结晶提供成核位点,降低成核活化能,调控球霰石型晶体形成[5,17]。目前报道的水体系中蛋白质调控制备的碳酸钙晶型基本以球霰石为主,且晶体中会夹杂有水分和蛋白质[17,22-23],但由图8可见,几丁质酶调控制备的碳酸钙不仅未出现水分子H-O键的伸缩振动峰,也没有出现蛋白质酰胺键的特征峰,说明几丁质酶虽调控碳酸钙晶型,但在晶体生长过程中确实没有夹杂入几丁质酶。
产品未夹杂几丁质酶可能是所用的几丁质酶虽含有较多天冬氨酸、谷氨酸等酸性氨基酸,等电点为5.2[26],在碳化体系下几丁质酶侧链酸性基团基本解离成负离子,加入少量即可与钙离子相互作用起到良好的晶型调控效果,但由于加入量少又可使结合在几丁质酶上的钙离子重新被置换碳化,从而防止碳化过程中的夹杂;故按0.01:1酶钙质量比加入少量几丁质酶调控碳化,既可制出较纯的干燥的球霰石型碳酸钙。
3. 结论
以CaCl2为原料碳化合成碳酸钙,以钙离子碳化率为指标,单因素考察了碳化温度、CaCl2浓度、pH、碳化时间和几丁质酶添加等五个因素对钙离子碳化率的影响,结果显示碳化温度、CaCl2浓度、pH、碳化时间等4个因素对钙离子碳化率有显著性影响,但几丁质酶添加基本不影响钙离子的碳化率。采用正交试验对4个显著影响因素进行优化,确定了最佳碳化工艺条件为:35 ℃下,以1 L/min气体流速往pH 12.5的1.00 mol/L CaCl2溶液持续通入CO2碳化6 min,钙离子碳化成碳酸钙可获最佳效果,碳化率达99.88%。极差分析与SPSS统计分析均显示四个因素对碳化率的影响主次顺序为:碳化时间>pH>CaCl2浓度>碳化温度,四个因素对钙离子碳化率影响均具有显著性。
在优化工艺条件下,分别按0:1、0.002:1、0.004:1、0.01:1的酶钙质量比往体系中加入不同量几丁质酶后,碳化制备碳酸钙,考察几丁质酶对碳酸钙晶型的调控。蛋白成分测定分析显示,碳化过程未夹入几丁质酶;SEM和IR等表征结果显示,未加几丁质酶时,碳化得到的是由球状颗粒和少部分菱形块状组装形成的直径为2 ~ 8 μm的大小不一的方解石型碳酸钙微球;加入几丁质酶后,菱形块状形貌消失,且随着几丁质酶的添加比例增大,碳酸钙微球尺寸逐渐下降;当酶钙质量比为0.01:1时,可制备得直径小于1 μm的大小较均一的高纯度蓬松球霰石型碳酸钙微球。说明几丁质酶调控下可以改变碳酸钙的晶型与尺寸,是高产率高纯度碳化法制备球霰石型碳酸钙仿生合成的良好调控剂。
-
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Factors and levels of orthogonal test
水平 因素 A 碳化温度(℃) B 碳化时间(min) C pH D/CaCl2浓度(mol/L) 1 25 4 11.5 0.90 2 30 5 12.0 1.00 3 35 6 12.5 1.10 表 2 钙离子碳化制备碳酸钙的正交实验方案及实验结果
Table 2 The schemes and results of orthogonal experiments for the preparation of calcium carbonate by calcium ion carbonization
试验号 A B C D 钙离子碳化率(%) 1 1 1 1 1 90.38 2 1 2 2 1 98.80 3 1 3 3 3 99.82 4 2 1 2 3 97.76 5 2 2 3 1 99.04 6 2 3 1 2 99.74 7 3 1 3 2 98.80 8 3 2 1 3 98.91 9 3 3 2 1 99.33 K1 289.00 286.94 289.03 288.75 K2 296.54 296.65 295.89 297.34 K3 297.04 298.89 297.66 296.49 R 2.68 3.98 2.88 2.86 因素主
次关系4 1 2 3 表 3 正交试验结果方差统计分析
Table 3 Statistical analysis of variance of orthogonal test results
源 III 型平方和 df 均方 F Sig. 校正模型 0.028a 8 0.003 2871.510 0.000 截距 34.619 1 34.619 2.866×107 0.000 碳化温度 0.005 2 0.003 2239.609 0.000 碳化时间 0.011 2 0.005 4485.255 0.000 CaCl2浓度 0.006 2 0.003 2470.258 0.000 pH 0.006 2 0.003 2290.917 0.000 误差 3.262×10−5 18 1.208×10−6 总计 34.647 27 校正的总计 0.028 26 注:a. R2 = 0.999(调整 R2 =0.998)。 -
[1] 邓勤, 赖家凤, 梁兴唐, 等. 牡蛎壳制备柠檬酸钙的工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(11):251−254. [Deng Q, Lai J F, Liang X T, et al. Study on the technology of preparation of the calcium citrate from oyster shells[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(11):251−254. [2] 韩晓梅, 王晨笑, 杨鑫, 等. 利用蟹壳制备乳酸钙和甲壳素的技术研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(11):65−70. [Han X M, Wang C X, Yang X, et al. Prepration of vaterite nano-sized CaCO3 with elipse ball-like[J]. Food Research And Development,2018,39(11):65−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.11.013 [3] 刘德婧, 马美湖. 蛋壳源有机钙的研究发展现状[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,39(9):372−376. [Liu D J, Ma M H. Status of research and development of organic calcium from eggshell[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,39(9):372−376. [4] 吴刚, 章守权, 方俊, 等. L-苯丙氨酸为模板碳酸钙纳米晶体的生长[J]. 安徽工业大学学报,2010,27(1):34−37. [Wu G, Zhang S Q, Fang J, et al. Growth of calcium carbonate nano-crystal using L-phenylalanine as a template[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology,2010,27(1):34−37. [5] 徐基贵, 朱军, 史洪伟. L-赖氨酸对CaCO3晶型和形状调控[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2011,34(6):924−926. [Xu J G, Zhu J, Shi H W. Shape and morphology of CaCO3 crystal controlled by L-lysine[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science),2011,34(6):924−926. [6] 张群, 张清. 不同晶型碳酸钙的仿生矿化研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2014,33(5):1236−1240. [Zhang Q, Zhang Q. Study on biomimetic mineralization of calcium carbonate with different crystallines[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2014,33(5):1236−1240. [7] 王宇轩, 徐颖, 王东平, 等. 球霰石的性质及其应用进展[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,37(2):76−80. [Wang Y X, Xu Y, Wang D P, et al. Properties and applications of vaterite[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2017,37(2):76−80. [8] 蒋久信, 吴月, 何瑶. 亚稳态球霰石相碳酸钙的调控制备进展[J]. 无机材料学报,2017,32(7):681−690. [Jiang J X, Wu Y, He Y. Progress in tuning of metastable vaterite calcium carbonate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2017,32(7):681−690. doi: 10.15541/jim20160484 [9] 卓民权, 赵历, 李艳琳, 等. 球霰石碳酸钙宏量制备的研究进展[J]. 化工技术与开发,2020,49(4):25−28. [Zhuo M Q, Zhao L, Li Y L, et al. Research progress of scale preparation of aragonite calcium carbonate[J]. Technology & Development of Chemical Industry,2020,49(4):25−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9905.2020.04.008 [10] Green D W, Bolland B J R F, Kanczler J M, et al. Augmentation of skeletal tissue formation in impaction bone grafting using vaterite microsphere biocomposites[J]. Biomaterials,2009,30:1918−1927. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.052
[11] 萨翼. 增加骨密度保健食品配方规律及对监管研发建议[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(4):314−318. [Sa Y. Increase bone mineral density health food formula rule and recommendations for regulatory and development[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(4):314−318. [12] Tas A C. Use of vaterite and calcite in forming calcium phosphate cement scaffolds[J]. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings,2009,28(9):135−150.
[13] Bukreeva T V, Marchenko I V, Borodina T N, et al. Calcium carbonate and titanium dioxide particles as a basis for container fabrication for brain delivery of compounds[J]. Doklady Physical Chemistry,2011,440(1):165−167. doi: 10.1134/S001250161109003X
[14] Won Y H, Jang H S, Chung D W, et al. Multifunctional calcium carbonate microparticles: Synthesis and biological applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2010,20(36):7728−7733. doi: 10.1039/c0jm01231a
[15] 夏宏宇, 张群, 王刚, 等. 球形和橄榄形球霰石的简易制备研究[J]. 人工晶体学报,2015,44(6):1701−1706. [Xia H Y, Zhang Q, Wang G, et al. Study on facile fabrication of spherical and olivary vaterite[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2015,44(6):1701−1706. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2015.06.048 [16] 程娜, 周梅芳, 陈鹏宇. 碳化法可控制备纳米碳酸钙研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报,2017,17(2):412−419. [Cheng N, Zhou M F, Chen P Y. Controlled synthesis of nano-calcium carbonate via carbonization method: A Review[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering,2017,17(2):412−419. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.216287 [17] 高平章, 艾杨城, 钟榕榕, 等. 牡蛎壳超细球霰石碳酸钙的制备与表征[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(17):151−157. [Gao P Z, Ai Y C, Zhong R R, et al. Preparation and characterization of ultrafine vaterite calcium carbonate from oyster shells[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(17):151−157. [18] 王静梅, 姚松年. 壳聚糖-氨基酸体系中碳酸钙模拟生物矿化的研究[J]. 无机化学学报,2002,18(3):249−254. [Wang J M, Yao S N. The study of mimetic biomineralization of calcium carbonate in some amino acid system[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2002,18(3):249−254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4861.2002.03.005 [19] 尹晓爽, 张慧, 杨文忠, 等. 胞外多糖调控碳酸钙结晶的研究[J]. 人工晶体学报,2010,39(6):1529−1534. [Yin X S, Zhang H, Yang W Z, et al. Investigation of CaCO3 crystallization induced by extracellular polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2010,39(6):1529−1534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2010.06.037 [20] Pérez-Villarejo L, Takabait F, Mahtout L, et al. Synthesis of vaterite CaCO3 as submicron and nanosized particles using inorganic precursors and sucrose in aqueous medium[J]. Ceramics International,2018(44):5291−5296.
[21] 欧阳志远, 杨磊, 刘艳茹, 等. 镁离子/蔗糖体系中碳酸钙结晶的仿生合成初步研究[J]. 电子显微学报,2019,8(3):264−270. [Ouyang Z Y, Yang L, Liu Y R, et al. A preliminary study on biomimetic synthesis of calcium carbonate crystals in magnesium ion /sucrose system[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society,2019,8(3):264−270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2019.03.009 [22] 竹文坤, 罗学刚, 林晓燕, 等. 蛋清蛋白模板法控制合成球形碳酸钙[J]. 人工晶体学报,2010,39(5):1336−1341. [Zhu W K, Luo X G, Lin X Y, et al. Synthesis of CaCO3 crystals using egg white protein as template[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2010,39(5):1336−1341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2010.05.049 [23] 马晓明, 司媛媛, 杨林, 等. 胃蛋白酶指导下水醇体系中碳酸钙的仿生合成与表征[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版),2011,50(4):742−747. [Ma X M, Si Y Y, Yang L, et al. Pepsin-controlled synthesis of sphere-shaped vaterite in ethanol/water mixture solvent[J]. Journal o f Xiamen University (Natural Science),2011,50(4):742−747. [24] Liu Y X, Chen Y P, Huang X C, et al. Biomimetic synthesis of calcium carbonate with different morphologies and polymorphs in the presence of bovine serum albumin and soluble starch[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2017(79):457−464.
[25] 陈茜文, 王佳丽, 许春雨. 克氏原螯虾壳膜几丁质酶的分离纯化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(23):159−163. [Chen X W, Wang J L, Xu C Y. Isolation and purification of chitinase from shellfish of Procambarus clarkia[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(23):159−163. [26] Xie X L, Chen Q X, Lin J C, et al. Purification and some properties of β-N-Acetyl-D-glucosaminidase from prawn (Penaeus vannamei)[J]. Marine Biology, 2004, 146: 143-148.
[27] Buchholz F. Moult cycle and seasonal activities of chitinolytic enzymes in the integument and digestive tract of the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba[J]. Polar Biology,1989,9:311−317. doi: 10.1007/BF00287429
[28] Spindler-Barth M, Van Wormhoudt A, Spindler K D. Chitinolytic enzymes in the integument and midgut-gland of the shrimp Palaemon serratus during the moulting cycle[J]. Marine Biology,1990,106:49−52. doi: 10.1007/BF02114673
[29] Kono M, Wilder M N, Matsui T, et al. Chitinolytic enzyme activities in the hepatopancreas, tail fan and hemolymph of Kuruma prawn Penaeus japonicus during molt cycle[J]. Fisheries Science,1995,61:727−728. doi: 10.2331/fishsci.61.727
[30] Peters G, Saborowski R, Buchholz F, et al. Two distinct forms of the chitin-degrading enzyme N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase in the Antarctic krill: Specialists in digestion and moult[J]. Marine Biology,1999,134:697−703. doi: 10.1007/s002270050585
[31] Kramer K J, Muthukrishnan S. Insect chitinases: Molecular biology and potential use as biopesticides[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,1997,27(11):887−900. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(97)00078-7
[32] 徐焕焕, 华睿清, 吴刚. 球形方解石的合成和表征[J]. 人工晶体学报,2019,48(11):2141−2145. [Xu H H, Hua R Q, Wu G. Synthesis and characterization of spherical-like calcite[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2019,48(11):2141−2145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2019.11.027 [33] 王芬, 余军霞, 肖春桥, 等. CO2碳化法制备微米级球霰石型食品碳酸钙的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报,2017,36(1):43−50, 56. [Wang F, Yu J X, Xiao C Q, et al. Preparation of micro-size food-grade vaterite CaCO3 by CO2 carbonization method[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2017,36(1):43−50, 56. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 吴广武,白蓉,方虎,赵成,陈佩圆. 维生素C调控合成纯球霰石及其形成机理. 硅酸盐通报. 2025(01): 195-201+242 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 范旭,朱迎澳,朱嘉敏,陈倩,王辉. 明胶改善海藻酸钠水凝胶膜的物理性能研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(15): 108-115 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





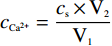
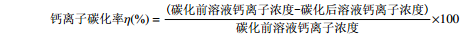
 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:



