Effect of Air-conditioned Refrigerated Container on Preservation of Vegetables
-
摘要: 为探讨气调冷藏集装箱的保鲜效果,以常见蔬菜小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜为试材,在1 ℃条件下,分别用气调冷藏集装箱与普通冷库贮藏,气调环境为5%±1% O2、95%±1% N2,相对湿度为90%±5%,乙烯脱除模块每天凌晨脱除0.5 h,臭氧杀菌模块每天灭菌一次,浓度2 g·min−1,时间是10 min,而普通冷库除冷藏外不再增加其他措施。通过测定贮藏期间蔬菜的失重率、可溶性固形物、可滴定酸、抗坏血酸、呼吸强度、丙二醛、叶绿素指标,评价设备保鲜性能。结果表明,与普通冷库相比,在45 d贮藏期内,气调冷藏集装箱明显能有效防止蔬菜水分的散失,维持较高的可溶性固形物、可滴定酸含量,在一定程度上抑制了果蔬的呼吸作用,降低抗坏血酸、叶绿素的消耗,减轻叶片细胞膜质过氧化的程度,能有效延缓蔬菜腐烂变质的时间,保持蔬菜较好的贮藏品质。因此,气调冷藏集装箱对大批量蔬菜的贮藏具有良好的应用前景。Abstract: In order to study the fresh-keeping effect of air-conditioned refrigerated container, both the air-conditioned refrigerated container and common cold storage were used to preserve fresh vegetables (pakchoi, leaf lettuce, celery and spinach) under 1 ℃. The controlled atmosphere was 5%±1% O2, 95%±1% N2, and the relative humidity was 90%±5%. The ethylene removal module runned for half an hour every morning, and the ozone sterilization module worked for 10 minutes once a day, with the concentration of 2 g·min−1. While, there were no other measures for common cold storage in addition to cold storage. The indicators of the weight loss rate, soluble solids content, titratable acid content, VC, respiration intensity, MDA and chlorophyll content were investigated to evaluate the preservation performance of the equipment. The results showed that during 45 d storage period, the air-conditioned refrigerated container performed better on effectively preventing vegetables weight loss, maintaining high soluble solids and titratable acid content, inhibiting the respiration intensity of vegetables, reducing the consumption of VC and chlorophyll, also relieving the degree of cell membrane peroxidation in leave. Furthermore, it can effectively retard the corruption of vegetable and maintain the fresh quality of vegetables. In conclusion, air-conditioned refrigerated container has a better application prospect for storage of large quantities of vegetables.
-
现今,随着大量开发海岛、沙漠、边疆等荒芜地区,驻扎人员越来越多,其物资的供应显得越发重要[1]。这些地区植被的恢复和改造进行缓慢,不可能单纯依靠种植出来的果蔬来满足驻扎人员的饮食需求。此外,环境条件恶劣,许多保鲜设备使用受限[2];果蔬品种也应多样化,只可考虑多品种混合贮藏。因此,如何为驻岛人员保质保量的提供新鲜果蔬,对保鲜技术和设备都提出了很高的要求。
气调保鲜技术在国外已经有数十年的研究历史,在国内也有了一定研究基础[3],一些大中型气调库在很多地方使用,主要用于果蔬的长周期储存,具有较好保鲜效果,技术也比较完善,然而气调冷藏集装箱却仍停留于设计或初步试用的阶段,杨双桥等[4]设计了船舶用气调保鲜集装箱,为海上蔬果运输提供了新思路。王默晗[5]指出气调冷藏集装箱的发展不仅要提升数量,还要提高集装箱设备的技术水平,加快农产品的储藏、加工、运输等物流设施建设。韩志等[6]在其研究中综述了国内外气调冷藏集装箱的食品保鲜效果,并对其发展进行了前景展望。可见,气调冷藏集装箱在果蔬贮运保鲜领域中具有较好的潜力。现阶段,市场上可接触到的气调冷藏集装箱虽装载量大、灵活便捷、能同时满足运输和贮藏两方面的要求[7],但其保鲜技术大多落后、功能单一、库容利用率不高。本研究探讨的气调冷藏集装箱为一款复合多种保鲜技术的新型保鲜设备[8],通过将冷藏、气调、加湿、乙烯脱除、臭氧杀菌结合于一体,革新了现有的集装箱保鲜技术,从温度、气体组分、湿度、微生物的角度,全方位的为果蔬贮藏提供一个适宜的环境。该设备的研发成型,也推动了保鲜类集装箱产业的发展,探讨其保鲜效果也十分有必要的。
本研究以小白菜(Brassica chinensis L.)、油麦菜(Lactuca sativa L.)、菠菜(Spinacia oleracea L.)、芹菜(Apium graveolens L.)4种气调贮藏要求相近的当季绿叶蔬菜为试材,将其贮藏进气调冷藏集装箱中,利用蔬菜品质作为考察指标,评价设备的保鲜性能,以期为果蔬贮运保鲜提供一种高效、便捷的形式,同时向今后的应用提供理论基础和参考借鉴。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
小白菜、油麦菜、菠菜、芹菜试验当天从无锡万亩良田蔬菜基地采购,采收前3 d不浇水,去掉泥沙黄叶后,立即4 ℃冷链运输至试验厂区,在冷库内1 ℃预冷12 h;镂空蔬菜筐(规格为600 mm×400 mm×280 mm)江苏轩盛塑业;聚乙烯保鲜袋(规格为700×500 mm,厚度为0.04~0.05 mm) 北京崇高纳米科技有限公司;氢氧化钠、酚酞、无水乙醇、邻菲罗啉、草酸、硫代巴比妥酸、磷酸 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;三氯乙酸、碳酸钙 分析纯,上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司;丙酮、三氯化铁 分析纯,上海沃凯生物技术有限公司。
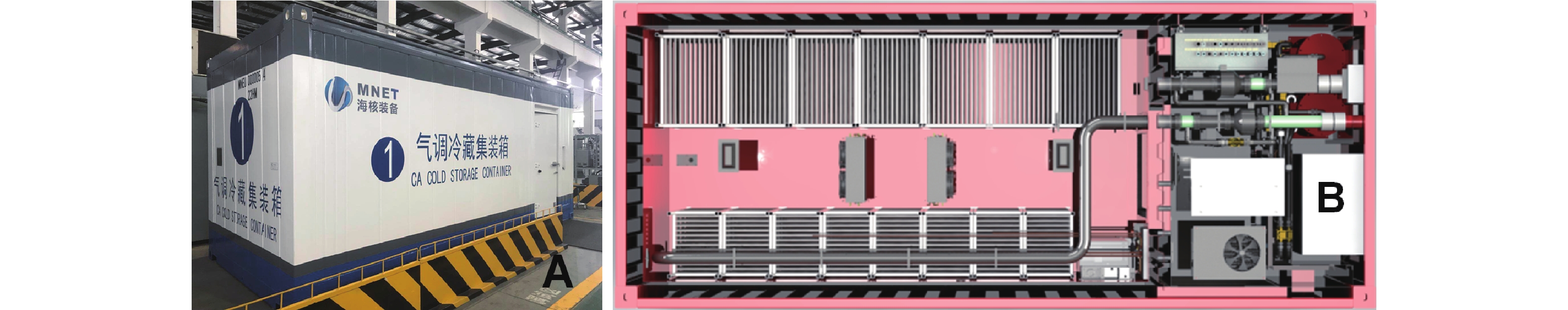
CLC-PLD-20气调冷藏集装箱(见图1) 无锡海核装备科技有限公司;CTB-PLF冷藏库 无锡海核装备科技有限公司;Metrohm877Titrino plus 自动滴定仪 瑞士万通公司;电子秤 上海精科天美贸易有限公司;电子天平 上海浦春计量仪器有限公司;紫外分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;手持式折光仪 艾普计量仪器有限公司;离心机 美国Beckman公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 贮藏保鲜工艺
提前将气调冷藏集装箱和普通冷库降温至贮藏温度1±1 ℃。分别挑选新鲜、无机械损伤、无病虫害、大小接近的小白菜、油麦菜、菠菜、芹菜装入镂空蔬菜筐,并且在外套上一层透气PE塑料薄膜,不挽口,小白菜每筐净重约11 kg,油麦菜每筐约7 kg,菠菜每筐约8 kg,芹菜每筐约8 kg,四种菜每种各44筐,其中,22筐装入集装箱内,另22筐装入普通冷库内,使两设备均为满库装载,普通冷库为对照。每层货架上筐与筐之间的距离在10~15 cm左右保持气体流通。入库完毕后,集装箱设定气体成分5%±1% O2、95%±1% N2,控制相对湿度为90%±5%,乙烯脱除模块每天凌晨脱除0.5 h,臭氧杀菌模块每天灭菌一次,浓度2 g·min−1,时间是10 min,而普通冷库除冷藏外不再增加其他措施。前15 d不开库,后30 d每5 d开一次库,并取样测定相关指标。
1.2.2 测定指标及方法
1.2.2.1 失重率的测定
采用称重法[9]。重量采用电子秤称量,精度为0.1 g。
失重率(%)=初始重量−贮藏后重量初始重量×100 1.2.2.2 可溶性固形物的测定
采用NY/T2637-2014[10]折光仪法测定。将蔬菜样品切碎,研磨混匀,用四层纱布过滤得到匀浆液。使用手持式折光仪前进行调零,调零后,把匀浆过滤的样品滴2滴在折光仪盖板上,盖上盖板进行读数,读数即为可溶性固形物含量。
1.2.2.3 可滴定酸的测定
参考GB/T 12456-2008采用氢氧化钠滴定法[11]测定。
1.2.2.4 抗坏血酸的测定
参考曹建康法[12]测定。结果用mg·100 g−1表示。取1 g液氮研磨好的样品,加入5 mL 50 g·L−1三氯乙酸,10000 r·min−1,离心20 min,取0.5 mL上清液于试管中,加入1.5 mL上述三氯乙酸、1 mL无水乙醇、0.5 mL 0.4%磷酸-乙醇溶液、1 mL 5 g·L−1邻菲罗啉-乙醇溶液、0.5 mL 0.3 g·L−1三氯化铁-乙醇溶液,并将其置于30 ℃下反应60 min,用蒸馏水代替上清液为对照,测定534 nm处的吸光值。
1.2.2.5 呼吸强度的测定
参考静置法[13]测定。结果用mg·kg−1·h−1表示。取10 mL 0.4 mol·L−1的氢氧化钠溶液于50 mL烧杯中,放入干燥器的底部,置于隔板上,装入300 g左右的蔬菜,封盖,静置30 min后取出小烧杯,将碱液移入250 mL锥形瓶中,用蒸馏水冲洗4~5次,加入饱和BaCl2溶液5 mL,酚酞2滴,用0.2 mol·L−1草酸滴定,同时进行空白对照。
1.2.2.6 丙二醛的测定
采用硫代巴比妥酸法[14]。结果用μmol·g−1Fw表示。取1 g液氮研磨好的样品,加5 mL的磷酸缓冲液(pH=6.8)。离心后,取1.0 mL上清液,加入3.0 mL 0.5%硫代巴比妥酸(TBA),沸水浴下反应20 min,迅速冷却,分别于450、532、600 nm处测定吸光值。
1.2.2.7 叶绿素的测定
参照分光光度法[15]测定。结果用 mg·g−1表示。取 2.0±0.1 g 蔬菜样品,去除叶脉,加入适量的碳酸钙与石英砂和少量的 80%(体积分数)的丙酮溶液,将蔬菜研磨成匀浆状态,继续加入80%的丙酮溶液,继续研磨至组织变白。将溶液避光静置3~5 min,随后过滤,润洗滤渣并再次过滤,将2次滤液均转入容量瓶中,定容至25 mL。在645 nm 和663 nm处测定吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2016进行数据的整理,并用Origin 8.5对数据进行拟合及作图。采用SPSS 18.0软件对数据进行方差分析,用最小显著性差异法进行差异显著性分析,P<0.05表示差异性显著。所测样品均进行3次以上重复实验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜失重率的影响
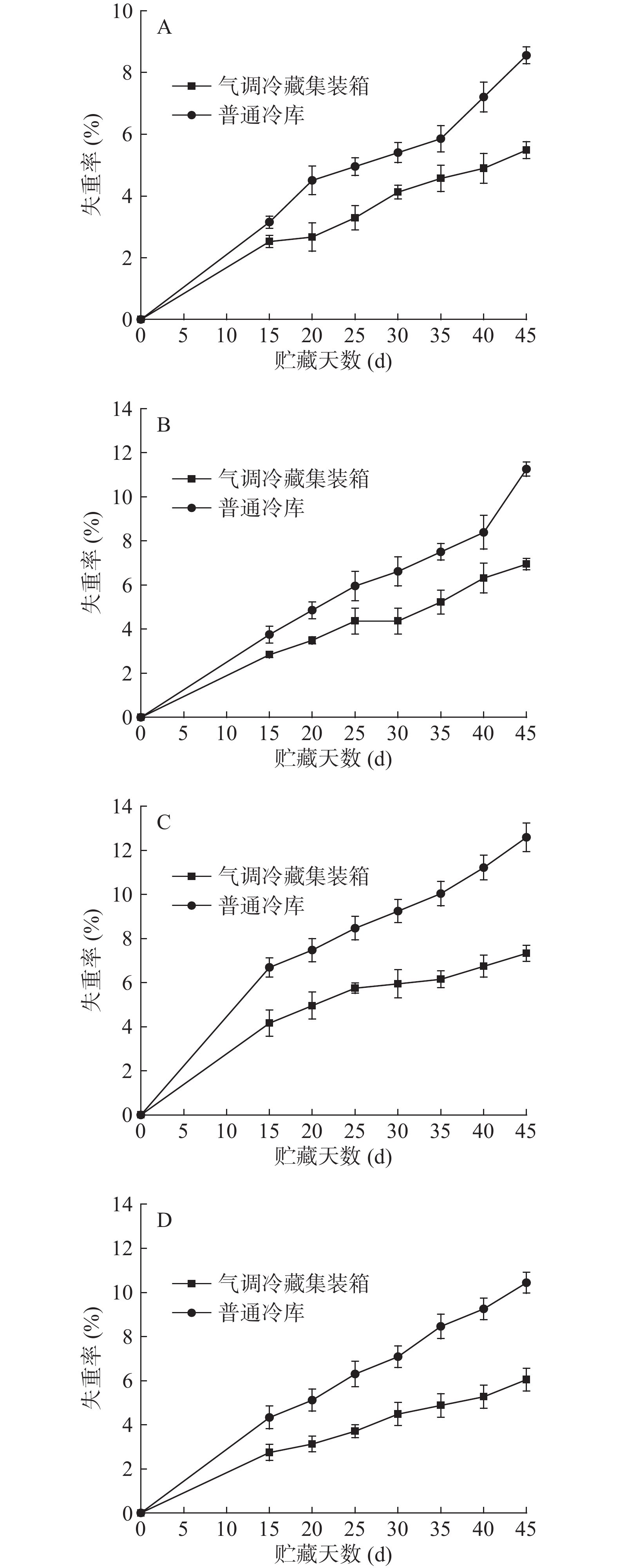
随着贮藏时间的延长,水分流失会使得蔬菜萎蔫、皱缩,缩短贮藏期,失去食用价值。失重率是反映果蔬新鲜度的主要指标之一[16]。由图2可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜的失重率均呈上升趋势,但气调冷藏集装箱的失重率整体上都低于普通冷库,在贮藏末期时,气调冷藏集装箱内小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜的失重率分别为5.49%、6.94%、7.33%、6.05%,均较好的保持了蔬菜的水分,这可能与气调能抑制呼吸,从而减轻了蔬菜的蒸腾作用与生理代谢有关;另外,气调冷藏集装箱内加装了加湿措施,也有利于蔬菜水分的保持。四种蔬菜中,芹菜失重率较高,小白菜失重率最低,这主要是由于蔬菜种类不同,其结构不同,组织保水力有差异[17],芹菜失水较多的原因可能是,其根、茎上分布有大量皮孔[18],细胞间隙与外界接触流通多,导致水分散失较快。
2.2 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜可溶性固形物含量的影响
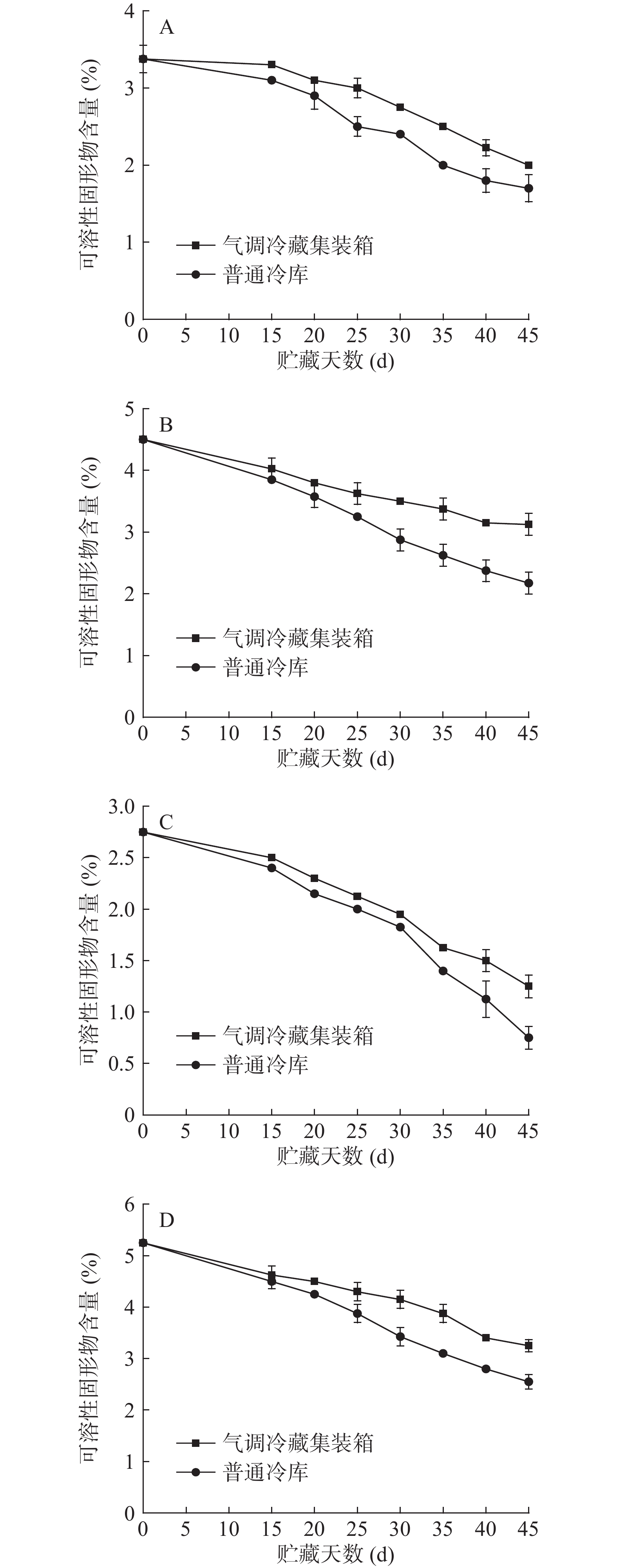
可溶性固形物(TSS)与蔬菜的风味有关,也是呼吸作用的主要代谢底物,含量的变化能反映蔬菜的衰老情况[19]。由图3可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜TSS含量呈下降趋势,这是由于果蔬采后分解大于合成,TSS作为呼吸底物被消耗。气调冷藏集装箱中TSS下降较普通冷库缓慢,在贮藏末期小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜其含量下降均小于2%,而普通冷库均下降了2.0%以上,可见,气调冷藏集装箱能保持较稳定的可溶性固形物含量,这可能是由于气调作用能降低果蔬的生理活动,从而减少了组织内消耗。
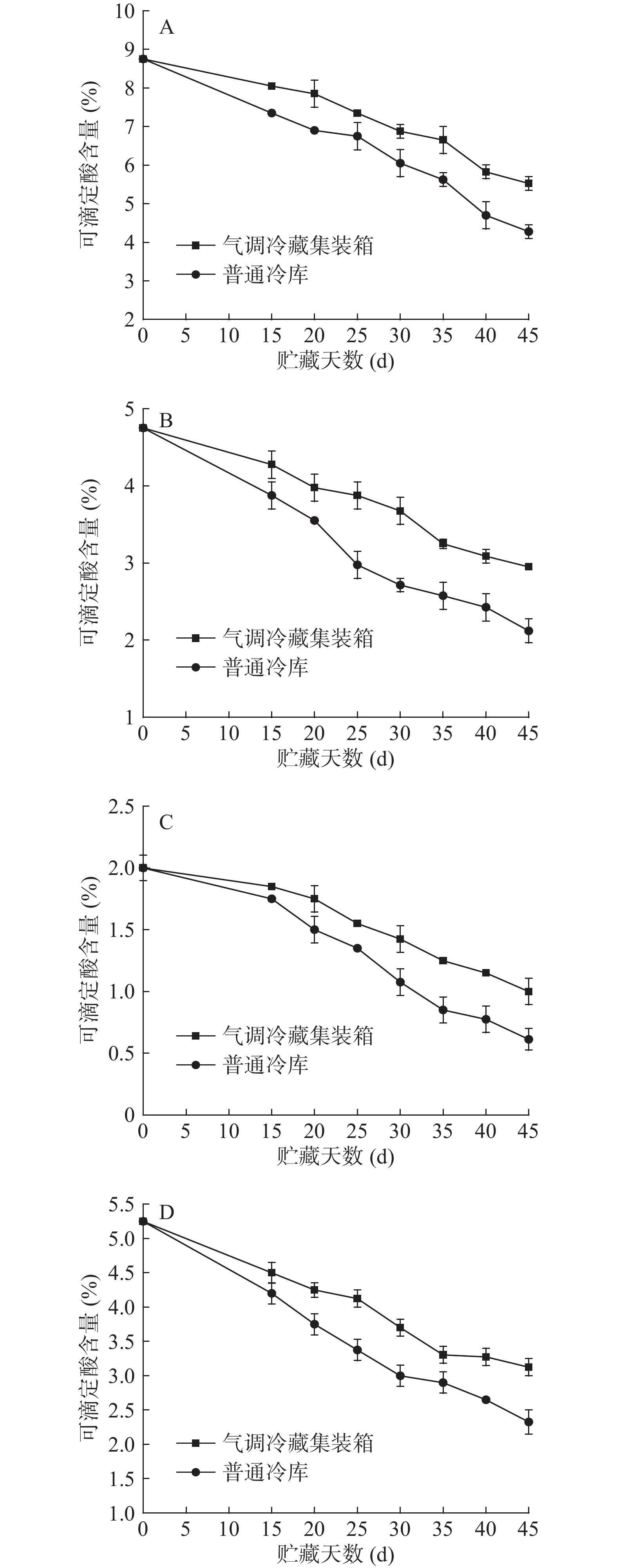
2.3 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜可滴定酸含量的影响
可滴定酸(TA)是衡量蔬菜口感的一个指标,能间接反映蔬菜的成熟度和内在品质情况[20]。由图4可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜可滴定酸含量均呈下降趋势,在贮藏结束时气调冷藏集装箱内小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜的可滴定酸含量分别为5.53%、2.95%、1%、3.13%,相较于普通冷库分别高了1.25%、0.83%、0.39%、0.8%,各处理组均大于对照组。可见,气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜TA具有较好保持作用,分析原因可能是气调冷藏集装箱减弱了蔬菜的新陈代谢,乙烯的脱除延缓了蔬菜的后熟及衰老,降低了有机酸的消耗。
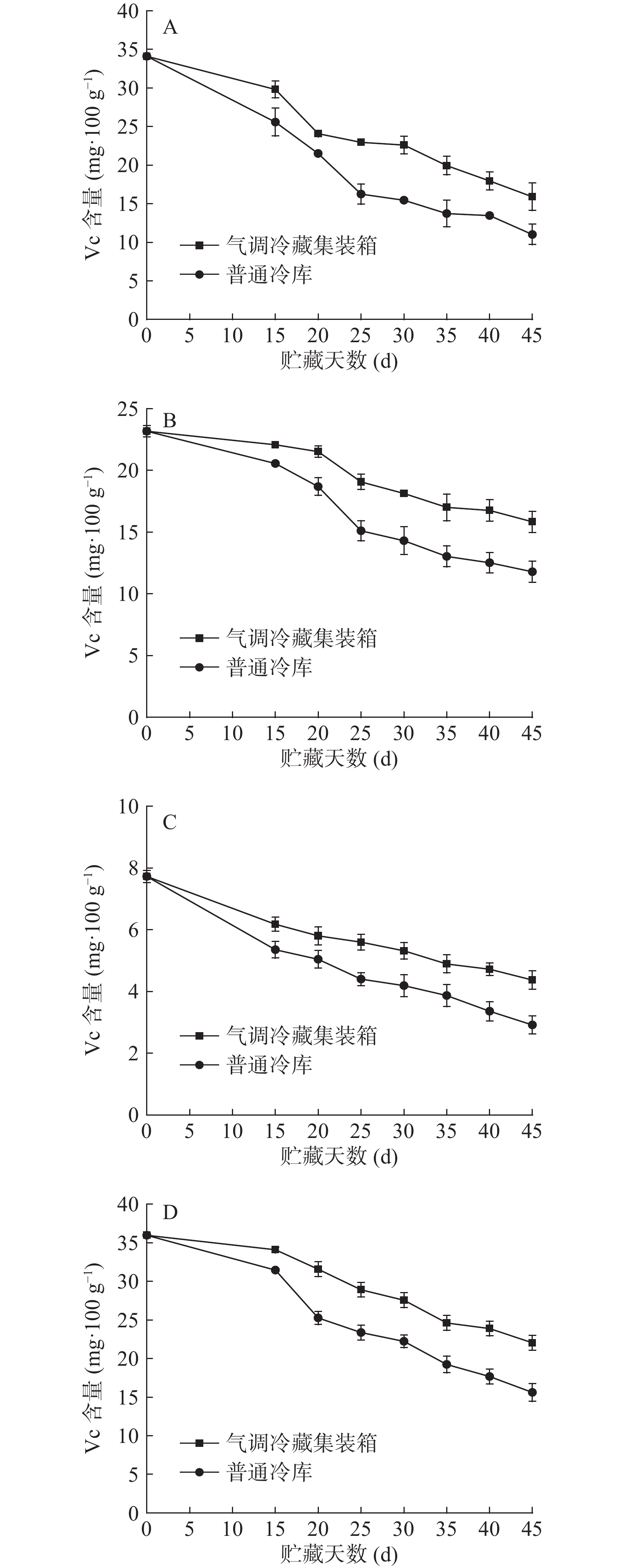
2.4 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜抗坏血酸含量的影响
抗坏血酸又称VC,是蔬菜中的抗氧化活性成分,也与蔬菜的营养价值相关,在贮藏过程中受周围环境的影响和自身代谢作用,极易分解[21]。由图5可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜VC含量均呈下降趋势,气调冷藏集装箱下降较为平缓,普通冷藏下降剧烈,在贮藏中期25 d时,四种菜普通冷藏已平均下降41.1%,而气调冷藏集装箱平均下降24.2%;到贮藏末期时,四种菜普通冷藏平均下降50.3%,而气调冷藏集装箱平均下降32.6%。这可能原因是冷库中为常氧环境,氧气使VC氧化降解,导致普通冷库中的VC下降更快;气调冷藏集装箱抑制VC的降解。4种蔬菜下降速率差异不大,可见对蔬菜均有较好效果。
2.5 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜呼吸强度的影响
呼吸强度表示了呼吸作用强弱,是衡量蔬菜新陈代谢进程的一个关键指标,呼吸作用越强,衰老越快[22]。由图6可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜呼吸强度均呈下降趋势,气调冷藏集装箱下降较快,而普通冷库下降较慢,在贮藏末期时,气调冷藏集装箱内小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜相较于普通冷库分别低了2、1.7、3.5、2.05 mg·kg−1·h−1。这可能与两方面有关,一是气调冷藏集装箱通过调节气体成分,低氧环境能有效降低果蔬的呼吸作用;二是普通冷库内单一的低温保鲜技术对蔬菜的呼吸作用控制效果不佳。
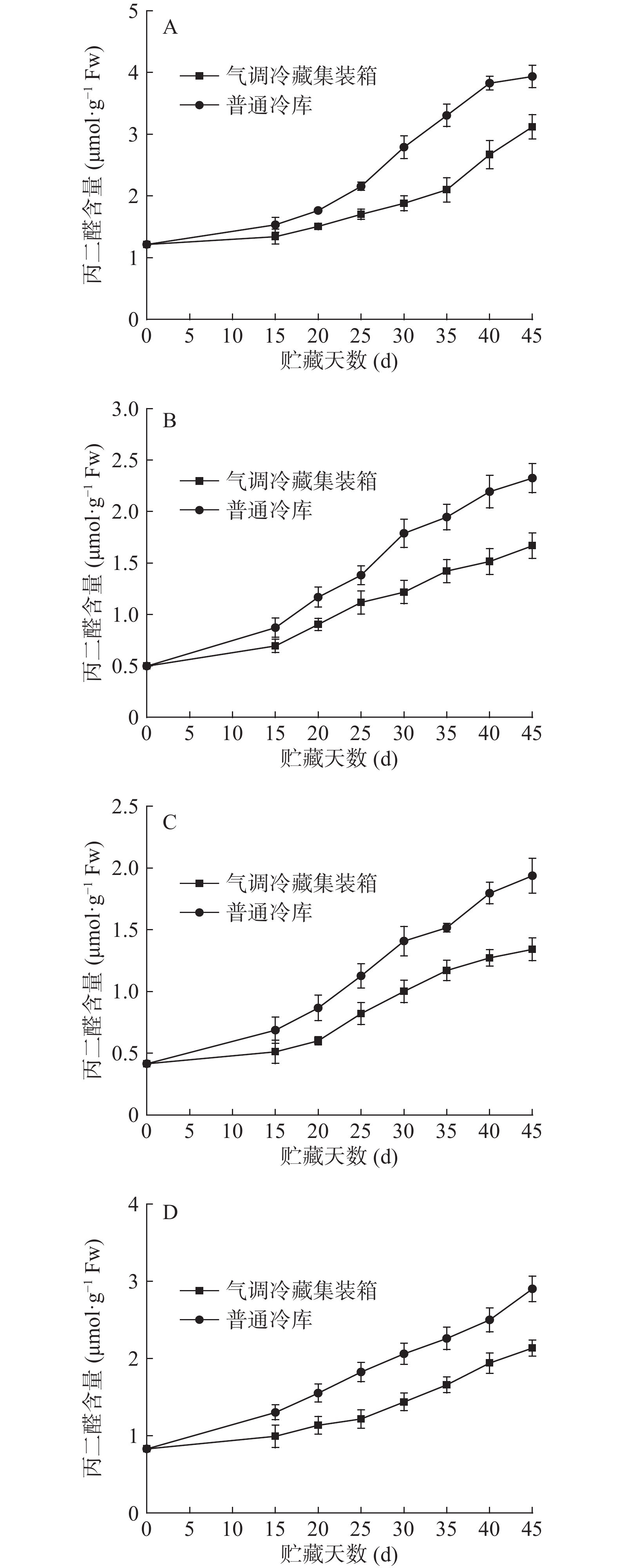
2.6 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜丙二醛含量的影响
丙二醛(MDA)是细胞膜质过氧化的产物,其产量的变化表征了膜系统受损害程度[23]。由图7可见,不同贮藏条件下小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜的丙二醛浓度,随着贮藏时间的延长,丙二醛含量逐渐升高,前25 d四种菜的上升较为缓慢,后20 d上升有明显的加快。这表明了在贮藏后期各项生理活动能力下降,活性氧清除机能降低,致使细胞膜上的膜质成分被氧化。气调冷藏集装箱中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜前25 d较普通冷库分别低了0.46、0.26、0.31、0.38 μmol·g−1Fw,后20 d分别低了0.81、0.66、0.59、0.77 μmol·g−1Fw,气调贮藏下四种菜MDA的浓度整体低于普通冷藏贮藏下MDA的浓度,说明了气调贮藏下叶菜的细胞膜系统受损度更小,也可能与臭氧杀菌抑制微生物的侵染有关,延缓叶片腐烂变质的时间。
2.7 气调冷藏集装箱对蔬菜叶绿素含量的影响
叶绿素与绿叶菜感官品质相关,其分解快慢能直接体现叶菜的黄化速率[24]。由图8可见,不同贮藏设备中小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜叶绿素含量均呈下降趋势,从整体上看,前15 d下降较慢,第15 d时,气调冷藏集装箱内的小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜叶绿素分别仅下降了2.7%、5.6%、7.2%、6.9%,后30 d下降较快,普通冷库内蔬菜更为明显,在贮藏末期时小白菜、油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜叶绿素仅为1.22、0.80、0.52和0.80 mg·g−1。可见,气调冷藏集装箱对抑制叶绿素的下降具有一定作用。油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜三种菜下降程度接近,而小白菜下降最少,主要原因可能是小白菜为较耐贮藏品种,其叶绿素酶、脱镁螯合酶等叶绿素降解相关酶活性较低[25-26]。
3. 讨论
温度、气体组分、湿度、微生物是影响蔬果贮藏的重要外界因素[27]。低温可以抑制果蔬呼吸和其它的代谢过程,从而延缓衰老,在不发生冷害的前提下,应尽可能地采用低的温度来延长贮藏期[28]。气体组分对果蔬保鲜也有重要影响,例如降低氧气含量、增加二氧化碳含量可以减慢新陈代谢速度,减少乙烯的含量可以延缓果蔬的成熟、衰老[29]。采收后的果蔬停止吸收吸收植物根部水分,这可以引起结构、质地和表面的变化,果蔬因此保持一定的湿度,减少水分损失,这对于保持果蔬鲜度和质量同样起着关键的作用[30];此外,有害微生物的侵染能引起果蔬的变质、腐败,对贮藏产生不利影响[31],控制环境中微生物的生长也是十分有必要的。本装置复合了多项保鲜技术,通过将冷藏、气调、加湿、乙烯脱除、臭氧杀菌结合于一体,从温度、气体组分、湿度、微生物多角度调控,旨在为果蔬贮藏提供一个适宜的环境。
试验结果表明,气调冷藏集装箱对4种常见蔬菜均有较好保鲜效果,45 d贮藏期内,4种蔬菜的失重率最高不超过7.5%,其中小白菜失重率最低,仅为5.49%,可见与油麦菜、芹菜、菠菜相比,该气调环境更适宜小白菜的贮藏。这也与高春霞等[32]学者的研究结果一致。TSS和TA是判断果蔬采后品质的重要指标,早有学者[33]提出以杨桃、砀山梨、黄瓜、小麦草为试材,气调包装对混合贮藏的鲜切果蔬TSS、TA含量的下降均具有减缓的作用,而在本项试验中,气调冷藏集装箱与普通冷库相比,能保持更高的TSS、TA含量,也是对这一结论的肯定。此外,从VC含量和叶绿素这两项指标可以看出,气调冷藏集装箱不仅具有减少VC氧化的作用,护绿效果也较好,使得蔬菜保持着较高的食用价值和商品价值,在濮艳清[34]及Dong等[35]的研究结论中也有相似观点。在抑制呼吸强度方面,气调冷藏集装箱的效果明显优于普通冷库,证实了低温结合气体环境调控对减弱果蔬呼吸的显著作用[36],温度为1 ℃与气体配比为5% O2、95% N2的组合已能满足需求。对绝大多数绿叶菜来说,叶片为其直接裸露部分,减少细胞膜系统损伤也是十分有必要的。丙二醛含量的测定可以看出,气调冷藏集装箱能够减少细胞膜氧化,延缓叶片衰老,对为维持蔬菜新鲜具有促进作用,这可能不光与冷藏、气调技术有关,臭氧杀菌及乙烯脱除也有增进意义。臭氧处理在一定程度上可降解果蔬表面微生物及其分泌的毒素,乙烯脱除能够削弱果蔬自身进一步的成熟。耿玉秋[37]在其文章中也有相关表述。
4. 结论
综上,复合冷藏、气调、加湿、乙烯脱除、臭氧杀菌多项保鲜技术于一体的气调冷藏集装箱对小白菜、油麦菜、菠菜、芹菜4种常见蔬菜均具有较好保鲜效果。它能够有效防止蔬菜水分的散失,失重率均小于7.5%;维持较高的可溶性固形物、可滴定酸含量,在整个贮藏周期中可溶性固形物含量下降均不超过2%,可滴定酸含量均高于对照组;同时,在一定程度上抑制果蔬的呼吸作用,与普通冷藏相比,贮藏末期时四种菜的呼吸速率均能低2 mg·kg−1·h−1以上;此外,对降低VC、叶绿素的消耗及减轻叶片细胞膜脂过氧化的程度有促进意义,从而延缓了蔬菜腐烂变质的时间,将蔬菜保鲜期延长至45 d,保持较好的贮藏品质。本试验探究的复合保鲜技术效果明显、实用性强、创新度高,对果蔬贮运保鲜行业具有一定推动意义。今后可考虑在长时间、远距离的海运、陆运及贮藏上做进一步应用。
-
-
[1] 赵锦霞, 张志卫, 王晶, 等. 浅谈我国生态岛礁分类建设[J]. 海洋开发与管理,2016(S2):21−25. [2] 林伟, 刘立洁. 岛礁运输补给方式研究[J]. 中国储运,2016(8):132−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0434.2016.08.049 [3] 孙长江, 李冠伦, 朱春来, 等. 船舶氮氧气体制备工艺[J]. 舰船科学技术,2012,34(2):129−132. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2012.02.028 [4] 杨双桥, 于献榕, 马丽君, 等. 船舶用气调保鲜集装箱的设计[J]. 舰船科学技术,2017,39(3):82−86. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7619.2017.03.017 [5] 王默晗. 气调保鲜集装箱的发展状况[J]. 制冷与空调,2006(1):88−89. [6] 韩志, 张柔佳, 沈雅钧, 等. 气调冷藏集装箱的食品保鲜研究[J]. 中国水运,2012,12(5):81−82. [7] 刘芳, 周子京, 郜丽芹. 果蔬储藏和运输冷链特性及影响因素[J]. 中国果菜,2013(3):42−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1038.2013.03.019 [8] 无锡海核装备科技有限公司. 一种用于极地环境的气调冷藏集装箱: 中国, 201820828651.3[P]. 2019-01-08. [9] 陈少霞, 周丹丹, 潘磊庆. 不同包装材料对娃娃菜贮藏过程中品质指标的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(3):270−284. [10] 全国果品标准化技术委员会(SAC/TC510). NY/T 2637-2014水果和蔬菜可溶性固形物含量的测定折射仪法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014. [11] 中华人民共和国卫生部. GB/T 12456-2008食品中总酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [12] 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2007: 28-30. [13] 张桂. 果蔬采后呼吸强度的测定方法[J]. 理化检验(化学分册),2005,41(8):596−597. [14] 程春梅. 1-MCP和减压处理对翠冠梨贮藏效果的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2007. [15] 王宁芳. 蔬菜中叶绿素的提取和检测[J]. 河北农业科学,2009,13(1):166−168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1088-1631.2009.01.063 [16] 董朝贤. 船用混合蔬菜的气调低温贮藏研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2016. [17] Hempel A, O’Sullivan M G, Pankovsky D B, et al. Nondestructive and continuous monitoring of oxygen levels in modified atmosphere packaged ready-to-eat mixed salad products using optical oxygen sensors, and its effects on sensory and microbiological counts during storage[J]. Journal of Food Science,2013,78(7):57−62.
[18] Miguel-Pintado C, Resende M, Rodrigues I, et al. Improvement of ‘Sweetheart’ cherry quality by modified atmosphere packaging (MAP)[J]. Acta horticulturae,2017(1161):549−554.
[19] Tian W N, Lv Y C, Cao J K, et al. Retention of iceberg lettuce quality by low temperature storage and postharvest application of 1-methylcyclopropene or gibberellic acid[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology-Mysore,2014,51(5):943−949. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0587-6
[20] Sandhya M. Modified atmosphere packaging of fresh produce: current status and future needs[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2010,43(3):381−392. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2009.05.018
[21] Lin Y F, Lin H T, Lin Y X, et al. The roles of metabolism of membrane lipids and phenolics in hydrogen peroxide-induced pericarp browning of harvested longan fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2016,111:53−61. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.07.030
[22] 袁芳, 邱诗铭, 李丽, 等. 异抗坏血酸与氯化钙联合处理对鲜切芒果的保鲜效果[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(1):272−278. [23] 康慧芳, 乔勇进, 刘晨霞, 等. 气调贮藏对"徐香"猕猴桃采后保鲜效果影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(2):285−293. [24] 朱军伟. 菠菜低温保鲜关键技术的研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2013. [25] Rai D R, Balasubramanian S. Qualitative and textural changes in fresh okra pods (Hibiscus esculentus L.) under modified atmosphere packaging in perforated film packages[J]. Food Science and Technology International,2009,15(2):131−138. doi: 10.1177/1082013208106206
[26] Rivera M C V, Martin A, D E Herrera S R M S, et al. Effect of modified atmosphere packaging on the antioxidant activity and total phenolic content in ‘Albacor’ figs[J]. Acta horticulturae,2015,1079(1079):573−579.
[27] 包骞, 孙企达, 兰秀凯, 等. 远洋蔬果保鲜特性分析及复合气调保鲜的应用研究[J]. 农产品加工,2009(8):67−70. [28] Li T H, Zhang M, Wang S J. Effects of modified atmosphere packaging with a silicon gum film as a window for gas exchange on agrocybe chaxingu storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2007,43(3):343−350. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.10.006
[29] Thompson A K. Controlled atmosphere storage of fruits and vegetables[M]. UK: MPG Books Group, 2010: 172-173.
[30] 张慜, 高中学, 过志梅. 生鲜果蔬食品保鲜品质调控技术专论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 14−16. [31] Yousuf B, Qadri O S, Srivastava A K. Recent developments in shelf-life extension of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables by application of different edible coatings: A review[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018(89):198−209.
[32] 高春霞, 乔勇进, 甄凤元, 等. 气调贮藏对小白菜品质及生理生化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2017,53(1):1−5, 73. [33] 徐春蕾, 王佳, 李长洪, 等. 气调包装对混合鲜切果蔬保鲜效果的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(7):131−135. [34] 濮艳清, 卢立新, 潘嘹, 等. 预处理结合气调包装对混合鲜切果蔬品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(6):114−120. [35] Dong S C, Seok H O P, Seung R C, et al. The combined effects of ultraviolet-C irradiation and modified atmosphere packaging for inactivating salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and extending the shelf life of cherry tomatoes during cold storage[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2015,3:19−30. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2014.10.005
[36] 方宗壮, 何艾, 窦志浩, 等. 不同气调包装结合低温处理对鲜切菠萝贮藏品质的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(4):102−107. [37] 耿玉秋. 臭氧处理对甘薯采后生理生化的影响[D]. 大连: 大连轻工业学院, 2007. -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王若彤,秦小勤,何小宇,夏宁. 基于响应面法的沃柑果酱工艺优化. 农产品加工. 2025(03): 49-52+57 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任二芳,韦志福,庞成友,罗朝丹,黄燕婷,罗文彬,李建强. 不同产地沃柑品质差异分析. 食品研究与开发. 2024(12): 150-155 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙建城,王登亮,马创举,刘丽丽,陈骏,刘春荣,吴群. 不同采收期对华柑4号柑橘果实品质的影响. 中国果树. 2024(07): 67-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 谢林君,成果,张劲,张瑛,王海军,何洁,庞丽婷,周咏梅. 基于电子鼻和GC-IMS解析‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄成熟过程香气特征差异. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒. 2024(04): 14-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 段敏仙,张碧蓉,史文斌,闫素云,唐少平,李雪佳,周先艳. 云南沃柑果实发育成熟过程中品质变化规律分析. 云南农业科技. 2024(06): 14-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 荣传胜,姜永峰,陆玉卓,张婷婷,郝义. 不同采收期对油桃果实采后贮藏品质的影响. 中国果树. 2023(09): 86-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘征,何仁春,黄光云,黄香,黄丽霞,李绍波,王启芝,肖正中. 沃柑次果、落果发酵饲料对富凤麻鸡养分表观消化率、生长性能及肉品质的影响. 饲料研究. 2023(19): 30-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 郑芳玲,甘诗雅,赵蕾,陈颖琦,赵潇奕,姜青,邱桐,张莹,郑鹏程,夏涛,戴前颖. 基于GC-MS/GC-O的不同地区红茶特征香气及分子感官分析. 食品科学. 2023(24): 262-268 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
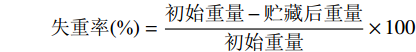


 下载:
下载:



