Effects of Oxalic Acid Treatment on Quality and Antioxidant Metabolism of Postharvest Fengtang Plum Fruit
-
摘要: 以蜂糖李果实为试材,经0 mmol/L(对照)以及0.5 mmol/L草酸(Oxalic acid,OA)处理10 min,晾干后贮藏于室温(25±1)℃下,通过测定果实品质、抗氧化物质含量以及抗氧化代谢相关酶活性的变化,研究草酸处理对蜂糖李果实保鲜效果的影响,并从抗氧化代谢角度解析其保鲜机制。结果表明:0.5 mmol/L草酸处理能够有效延缓蜂糖李果实失重率、腐烂率、呼吸速率的上升,推迟贮藏过程中果实呼吸高峰的到来,抑制果实固酸比、可溶性糖含量、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量以及超氧阴离子(
-
Keywords:
- Fengtang plum /
- preservation /
- oxalic acid /
- antioxidation /
- quality
-
蜂糖李(Prunus salicina)是在贵州省安顺市镇宁自治县六马镇发现的地方优良李品种[1],其口感好、甜度高,富含糖、酸、蛋白质、维生素、矿物质以及膳食纤维等多种营养成分[2],深受广大消费者的青睐。蜂糖李属于呼吸跃变型果实,采收期集中在高温季节,采后容易产生变软、腐烂等诸多问题[3]。因此,寻求简单高效的蜂糖李贮藏保鲜技术和方法,减少采后损失,提高商品附加值,是当前急需解决的问题,也是近些年众多学者所关注和研究的热点。
草酸(Oxalic acid)遍布于自然界,是一种可被生物体代谢的安全无毒的有机酸。研究发现,草酸处理能够提高采后果实的抗病性,增强果实的抗氧化能力[4],具有延缓果实采后成熟与衰老、保持果实良好品质的作用[5]。已有研究证明,草酸处理可以延缓香蕉[6]、番荔枝[7]、木瓜[8]等果实的采后成熟衰老进程。Kawaljit[9]等研究表明,草酸处理可有效减少梨果实的失重、腐烂,保持果实的营养和感官品质。Wu等[10]研究发现施用草酸可降低李果实乙烯的生成,延缓果实软化,能有效延长李果实货架期。草酸处理不仅能降低贮藏期间青芒果果实的软化,增强其SOD等抗氧化酶的活性[11],还有助于提高采后芒果果实的抗病性[12],且对于提升采后猕猴桃果实品质和抗病性有着良好的效果[13],同时对降低采后甜瓜果实红粉病病害程度也具有明显效果[14]。此外,草酸处理能有效提高番茄[15]、桃[16]、杏[17]以及哈密瓜[18]等果实的抗冷冻性,缓解果实冷害的发生,是延长果实低温冷藏品质行之有效的方法。草酸处理对抑制荔枝果皮[19]和鲜切莲藕片[20]褐变的效果也极为明显。
但是,关于草酸延迟贵州喀斯特山区地方性李品种蜂糖李采后果实贮藏品质降低、延长果实货架期,还未有过相关的报道。因此,本研究以蜂糖李果实为试材,从果实采后保鲜及抗氧化代谢的角度入手,研究采后使用0.5 mmol/L草酸处理对蜂糖李果实保鲜效果和抗氧化代谢的影响,并对其保鲜、抗氧化代谢的生理机制进行分析和探讨,以期为蜂糖李果实保鲜新技术的开发提供理论依据和技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
蜂糖李果实 于2019年6月16日采摘自贵州省六马蜂糖李种植农民专业合作社的一果园(105.52 E,25.37 N),采后立即运回贵州大学园艺实验室进行处理;草酸、牛血清蛋白质、二硫代硝基苯甲酸、抗坏血酸、红菲咯啉、盐酸羟胺、对氨基苯磺酸、α-萘胺、愈创木酚、核黄素 均为分析纯,贵州省格瑞恩科技有限公司;蔗糖、苯酚、浓硫酸、考马斯亮蓝G-250、无水乙醇、氢氧化钠、三氯乙酸、EDTA-Na2·2H2O、还原型谷胱甘肽、Na2HPO4·12H2O、NaH2PO4·2H2O、硫代巴比妥酸、三氯化铁、磷酸、KNO2、冰醋酸、无水醋酸钠、聚乙二醇6000、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮、TritonX-100、30%H2O2、DTT、PVP、L-蛋氨酸、氮蓝四唑、K2HPO4、KH2PO4、EDTA、PVPP 均为分析纯,贵州省塞兰博科技有限公司。
TEL-7001型呼吸仪 上海金枭仪器有限公司;GY-1型果实硬度计 广州市铭睿电子科技有限公司;移液枪(1000 µL、100 µL) 德国Eppendorf公司;CP213型电子天平 昆山吉和力仪器有限公司;FA-2104型分析天平 上海启闵生物科技有限公司;PAL-BX/ACD1糖酸度计 ATAGO公司;DK-98-II型双列八孔电热恒温水浴锅 天津泰斯特仪器有限公司;YG16W型台式高速冷冻离心机 长沙平凡仪器仪表有限公司;UV752紫外分光光度计 上海佑科仪器有限公司;DW-HL678型超低温冰箱 成都川弘科生物技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
将挑选好的成熟度一致(8成熟)、外观整齐、大小相近、无病虫害、无伤疤、无机械损伤的李果实放入0.5 mmol/L草酸溶液(前期预实验筛选得出的最佳草酸处理浓度)中浸泡处理10 min,自然晾干,置于室温(25±1) ℃下;以蒸馏水处理10 min的果实为空白对照(0 mmol/L),同样自然晾干并置于室温下。自蜂糖李果实采后0 d开始,直至果实采后21 d期间,每3 d测定相关指标并观察记录果实腐烂情况。
1.2.2 果实品质指标
1.2.2.1 失重率测定
采用称重法测定,失重率计算公式为:
式中:M1为采收当天果实的初始重量(g);M2为试验当天果实的重量(g)。
1.2.2.2 腐烂率
以蜂糖李果实出现水渍状褐变斑点、果实软化腐败、果皮皱缩褐变作为果实腐烂的判别依据。记录并统计果实腐烂情况,失重率计算公式为:
腐烂率(%)=(腐烂果实总数/果实总数)×100。
1.2.2.3 呼吸速率测定
参考董晓庆等[21]方法。用CO2分析仪测定:将干燥器放入(25±1)℃的环境下,每个处理随机取10个蜂糖李(单果质量48 g左右),放入9.4 L的干燥器中,同时放入CO2分析仪,密封,每隔10 min读数1次,读数3次。结果以CO2计,单位mg/(kg·h)。
1.2.2.4 硬度测定
参考曹建康等[22]方法。每个重复随机选取6个果实,在每个果实赤道部位两侧对称取2个点,去皮(厚约1 mm),用硬度计(探头直径3.5 mm,测定深度10 mm)测定,结果以kg/cm2表示。
1.2.2.5 SSC、TA含量测定以及固酸比的计算
采用PAL-BX/ACD1糖酸度计进行果实SSC含量(%)和TA含量(%)的测定;固酸比=SSC/TA。
1.2.2.6 叶绿素含量测定
参考曹建康等[22]方法测定果实中叶绿素的含量。
1.2.2.7 可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白含量测定
参考曹建康等[22]的方法,采用苯酚-硫酸法测定果实可溶性糖;参考曹建康等[22]的方法,采用考马斯亮蓝染色法测定可溶性蛋白含量。
1.2.3 果实抗氧化代谢相关物质指标
1.2.3.1 MDA含量的测定
参考曹建康等[22]方法测定果实中MDA的含量。
1.2.3.2
参考曹建康等[22]利用羟胺氧化的方法测定果蔬组织中
1.2.3.3 GSH、VC含量测定
参考曹建康等[22]方法测定果实中GSH、VC的含量。
1.2.4 果实抗氧化代谢相关酶活性指标
POD、SOD、CAT、APX活性测定 参考曹建康等[22]方法进行果实POD、SOD、CAT、APX等酶活性的测定。
1.3 数据处理
使用软件Microsoft Excel 2013对所获得的实验数据进行整理计算并绘图。同时,在Microsoft Excel 2013数据分析模块中采用t检验:平均值的成对二样本分析对实验结果进行差异显著性分析。
2. 结果与分析
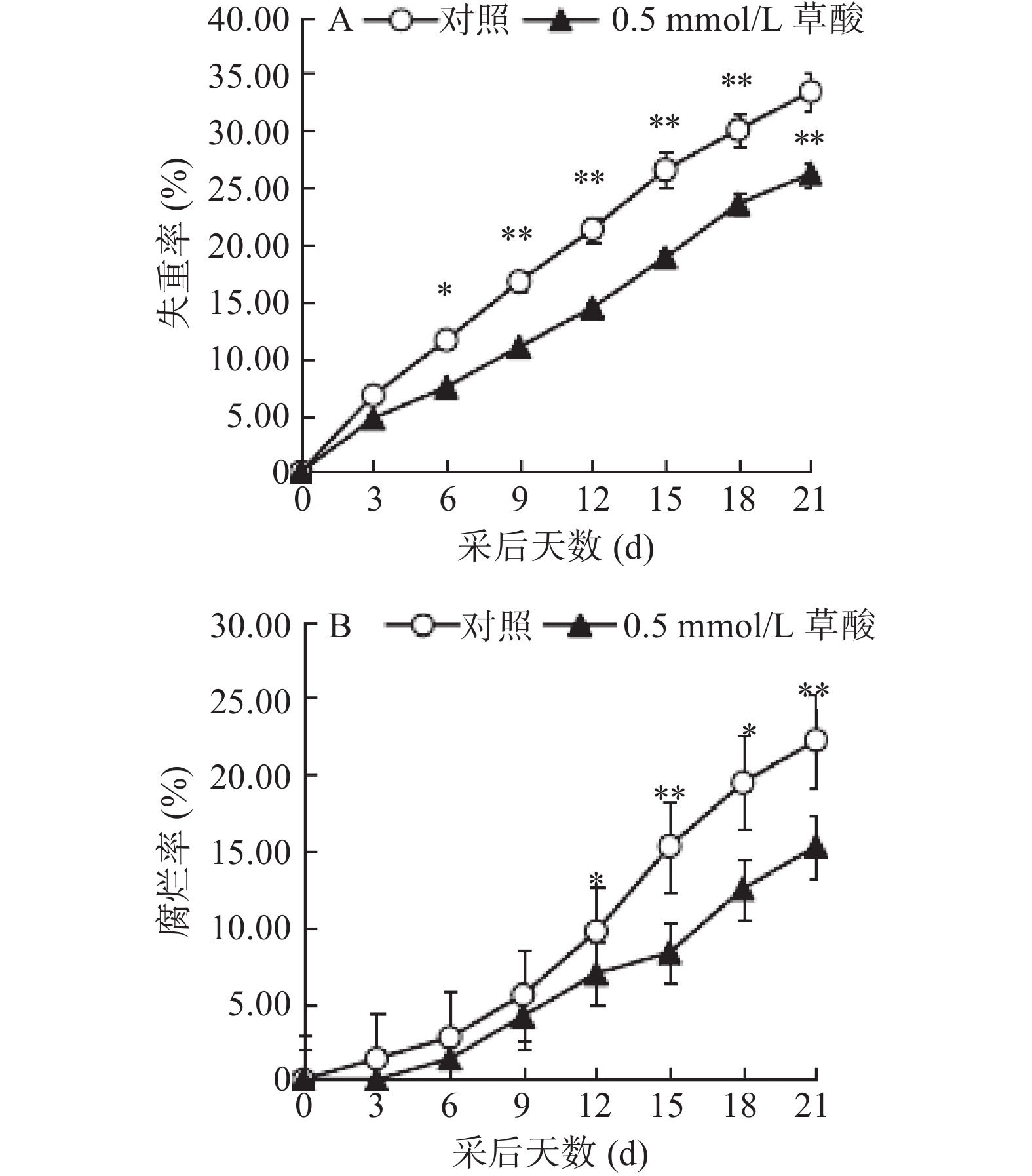
2.1 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实失重率、腐烂率的影响
由图1-A可以看出,整个采后贮藏期间,经草酸处理的蜂糖李果实失重率低于对照组果实。至21 d贮藏结束时,处理组失重率为26.22%,而对照组则达到了33.42%,果实经处理后9~21 d期间,处理组和对照组果实之间失重率存在极显著差异(P<0.01),草酸处理可抑制贮藏期间蜂糖李果实的失重。
如图1-B所示,采后蜂糖李果实腐烂率呈上升趋势。在经过处理后,对照组果实腐烂率总是高于处理组。到第21 d时,对照组果实腐烂率为22.22%,处理组果实腐烂率为15.28%,处理组腐烂率比对照组低6.94%,两者差异极显著(P<0.01)。
果实失重率、腐烂率是衡量采后果实成熟衰老程度的重要指标。试验结果显示,草酸处理明显抑制了蜂糖李果实失重率和腐烂率的上升。这说明草酸处理减少了贮藏过程中蜂糖李果实水分以及营养物质的损失,延缓了果实成熟衰老的进程。这与草酸处理在猕猴桃[5]和青芒果[11]上的研究结论相一致。
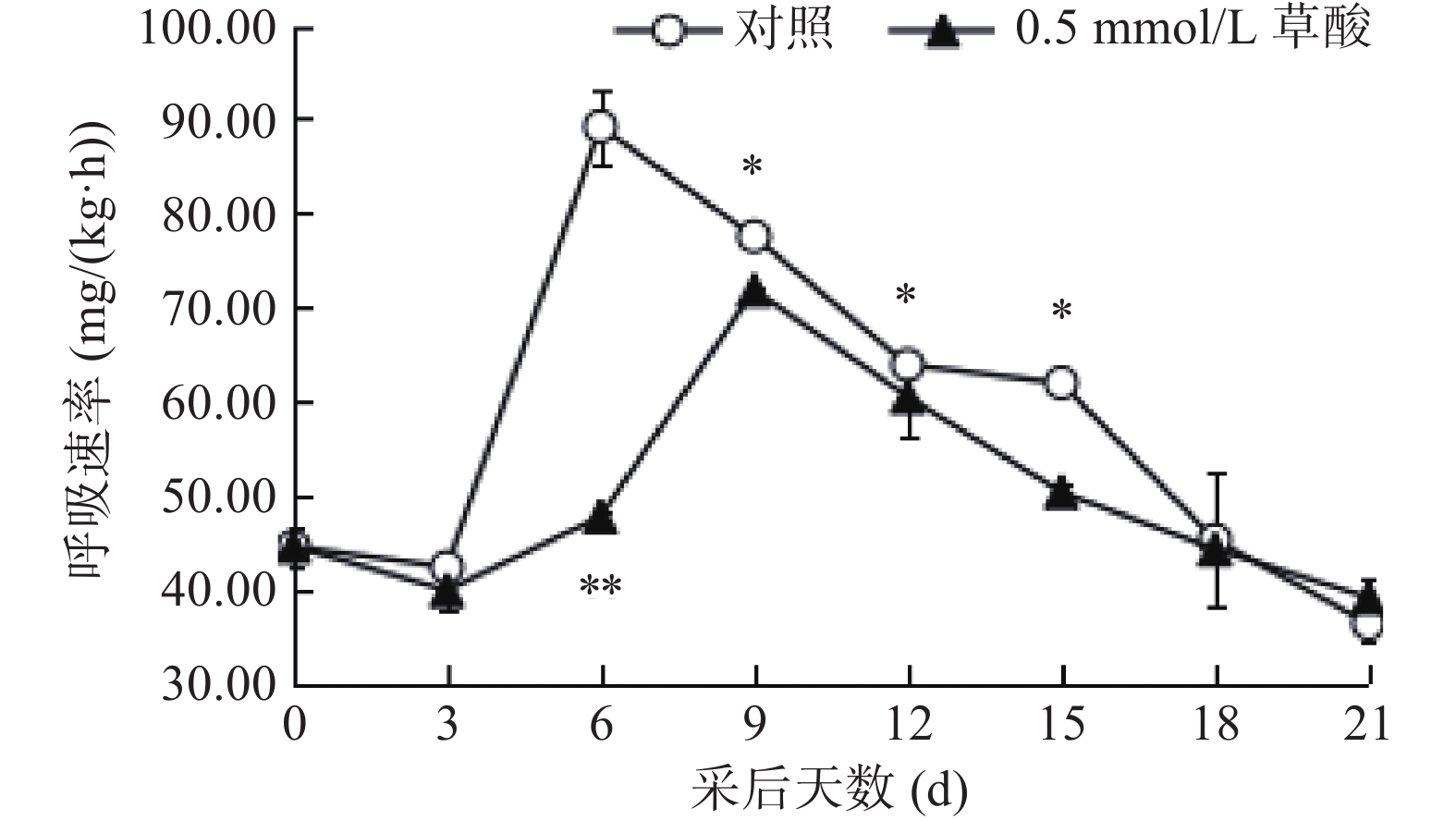
2.2 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实呼吸速率的影响
蜂糖李为呼吸跃变型果实,在其成熟衰老的过程中会产生呼吸跃变,果实呼吸速率突然升高,出现明显的呼吸高峰。如图2所示,对照组果实呼吸高峰出现在采后第6 d,处理组果实呼吸高峰则出现在采后第9 d,二者呼吸强度峰值分别为89.20、71.85 mg/(kg·h),处理组比对照组低19.45%。两组果实呼吸速率都呈现先下降再上升最后下降的趋势。相比于对照组,处理组果实呼吸高峰的出现往后推迟了3 d。在采后6~15 d期间,处理组果实的呼吸速率显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。
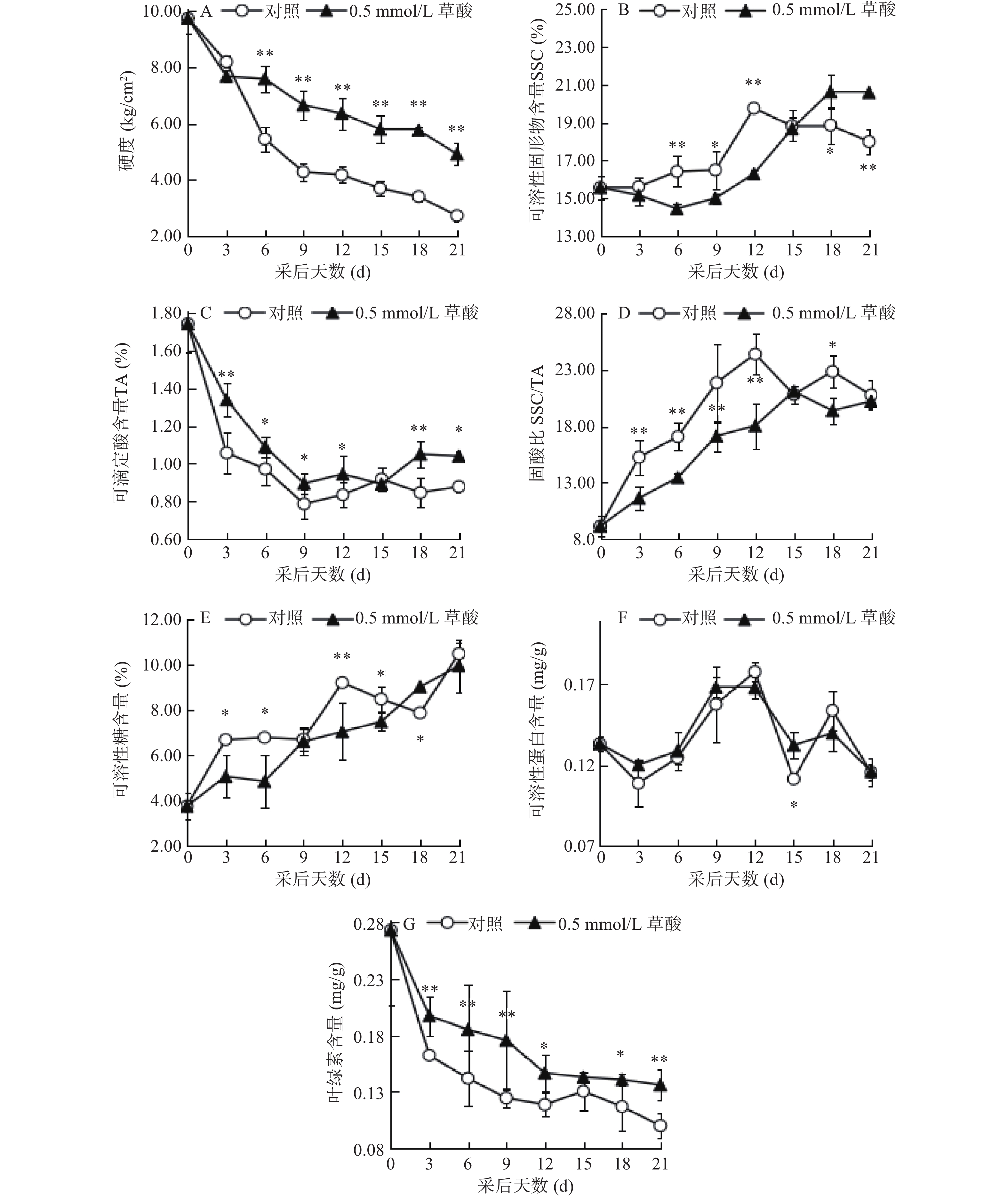
2.3 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实硬度、SSC、TA、固酸比、可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白以及叶绿素含量的影响
果实硬度、叶绿素、可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白、SSC、TA等的含量以及固酸比与果实成熟衰老和果实品质息息相关。果实可溶性糖含量的增加及果实硬度、TA含量、叶绿素含量等的下降是果实成熟衰老的体现。固酸比会影响果实风味,而可溶性固形物、可溶性蛋白含量则是评价果实品质和营养的重要指标。
在贮藏过程中,随着果实成熟度的增加,果实软化,硬度降低。Wu等[10]研究发现草酸可降低多聚半乳糖醛酸酶(PG)和果胶酯酶(PE)的活性,抑制李果实软化。从图3-A可以看出,蜂糖李果实硬度随着贮藏期的延长都呈下降趋势,但在处理3 d后,草酸处理的蜂糖李果实相比较于对照其硬度下降幅度明显减缓。到21 d时,处理组硬度为4.91 kg/cm2,而对照组则为2.73 kg/cm2。在6~21 d期间草酸处理组的硬度都大于对照组,且处理组和对照组之间差异极显著(P<0.01)。可见,草酸处理可抑制贮藏期间蜂糖李果实硬度的下降,这可能是由于草酸降低了果实PG和PE的活性,从而抑制了果实硬度的下降。
SSC能反映果实品质和成熟度。如图3-B所示,采后贮藏期间蜂糖李果实SSC大致呈上升而后开始下降的趋势。对照组果实SSC自第0 d开始上升,在第12 d后开始下降,而处理组果实SSC则是在采后6~18 d阶段呈现逐渐上升的趋势。对照组果实SSC在第12 d达到最高值19.75%,而处理组则是在采后第18 d达到最高值20.62%。在采后6~12 d期间,处理组和对照组之间SSC差异显著(P<0.05)。
TA含量是影响果实风味及口感的重要因素。从图3-C可看出,在贮藏期间,蜂糖李果实TA含量大体上呈下降趋势,但在采后9~21 d期间,草酸处理组果实TA含量相比于对照组有略微上升的趋势,这可能是由于草酸处理抑制了果实有机酸代谢相关酶活性的原因[23]。在果实处理后除第15 d对照组可滴定酸含量为0.92%高于处理组0.89%外,对照组果实TA含量均低于处理组,草酸处理果实与对照组果实之间TA含量存在显著差异(P<0.05),在采后3 d和18 d二者差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。这表明草酸处理可延缓蜂糖李果实采后贮藏期间其可滴定酸含量的下降。
如图3-D所示,采后贮藏期间,蜂糖李果实固酸比整体呈上升趋势。草酸处理后蜂糖李果实固酸比除第15 d值为21.08略高于对照组20.81外,其固酸比均低于对照组,在采后3~12 d期间,处理组果实和对照组果实固酸比差异达到了极显著水平(P<0.01)。在采后第12 d,对照组果实固酸比达到最高值,为24.39,处理组果实固酸比则是在采后第15 d达到最高值21.08。
果实中可溶性糖含量的高低与其品质、成熟度和贮藏性密切相关。从图3-E可以看出,采后蜂糖李果实可溶性糖含量呈上升趋势。贮藏期间,除第18 d外,草酸处理的蜂糖李果实可溶性糖含量均低于对照组。到第21 d时,处理组果实可溶性糖含量为9.96%,对照组为10.49%,略高于处理组。经草酸处理的蜂糖李果实与对照组果实之间可溶性糖含量在第3、6、15、21 d差异显著(P<0.05),第12 d时,处理组与对照组果实可溶性糖含量差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。
从图3-F可以看出,采后贮藏期间,蜂糖李果实可溶性蛋白含量大致呈先上升后下降的趋势。对照组果实可溶性蛋白含量在采后第12 d达到了最高值0.18 mg/g,处理组果实可溶性蛋白含量则是在采后第9 d达到最高值0.17 mg/g。统计分析结果表明,处理组果实与对照组果实之间可溶性蛋白含量差异不显著(P>0.05)。
随着采后果实的成熟衰老,其组织中的叶绿素含量不断下降。如图3-G所示,在采后贮藏过程中,蜂糖李果实叶绿素含量呈现不断下降的趋势。贮藏期间第3、6、9 d以及第21 d,处理组果实叶绿素含量极显著高于对照组(P<0.01)。经草酸处理的果实叶绿素含量由第0 d的0.27 mg/g下降到第21 d的0.14 mg/g,对照组则是下降到0.10 mg/g,至第21 d时,两组果实叶绿素含量间相差值为0.04 mg/g,这说明草酸处理可有效抑制采后蜂糖李果实组织中叶绿素的降解,延缓果实新鲜度的降低。
本试验中,蜂糖李果实硬度的变化与刘锴栋等[7]在番荔枝上的研究结果一致,可溶性蛋白及可溶性固形物含量的变化与其研究结果不一致,这可能是由于试验材料、草酸浓度以及果实处理方式不同所引起的。果实叶绿素含量变化与程春梅等[24]在西兰花上的研究结果一致,而果实可溶性糖以及TA含量的变化与喻最新等[25]在血橙和梁春强等[26]在猕猴桃上的研究结果相似。
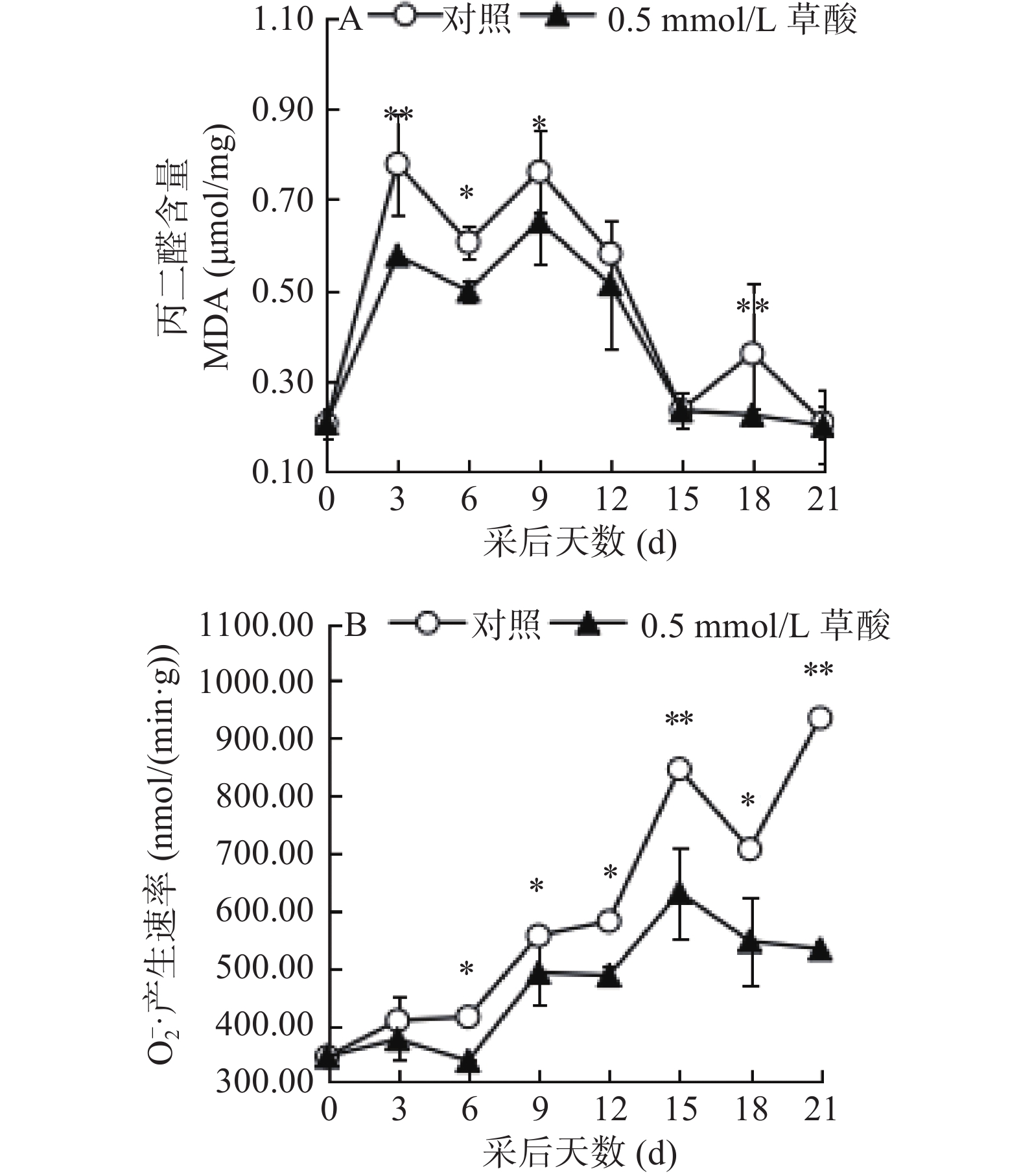
2.4 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实MDA含量、
从图4-A可以看出,在采后贮藏期间,经过草酸处理的蜂糖李果实MDA含量低于未经草酸处理的蜂糖李果实。处理组果实MDA含量最高时为0.65 µmol/mg,而对照组MDA含量最高时为0.78 µmol/mg。经草酸处理后3~9 d期间,处理组果实和对照组果实之间MDA含量差异显著(P<0.05),在第3 d和第18 d二者差异可达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。
生物膜过氧化是引起细胞膜结构和功能丧失的重要原因,MDA则是膜脂过氧化的主要产物之一,其水平是检测有机体膜脂过氧化程度的一个公认的指标,可反映植物细胞膜过氧化的程度[27]。本试验中,相比于对照组,草酸处理可在一定程度上降低蜂糖李果实采后贮藏期间的MDA含量。这与草酸处理在番茄[15]、桃[16]和荔枝[19]等果实上的研究结果相似。贮藏后期,MDA含量下降到较低水平,这可能是由于在贮藏后期蜂糖李果实糖含量的上升,从而影响了后期的试验结果。
在果蔬成熟衰老的过程中,大量积累的活性氧会打破代谢平衡,对植物细胞造成伤害[28]。而活性氧中的
2.5 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实VC和GSH含量的影响
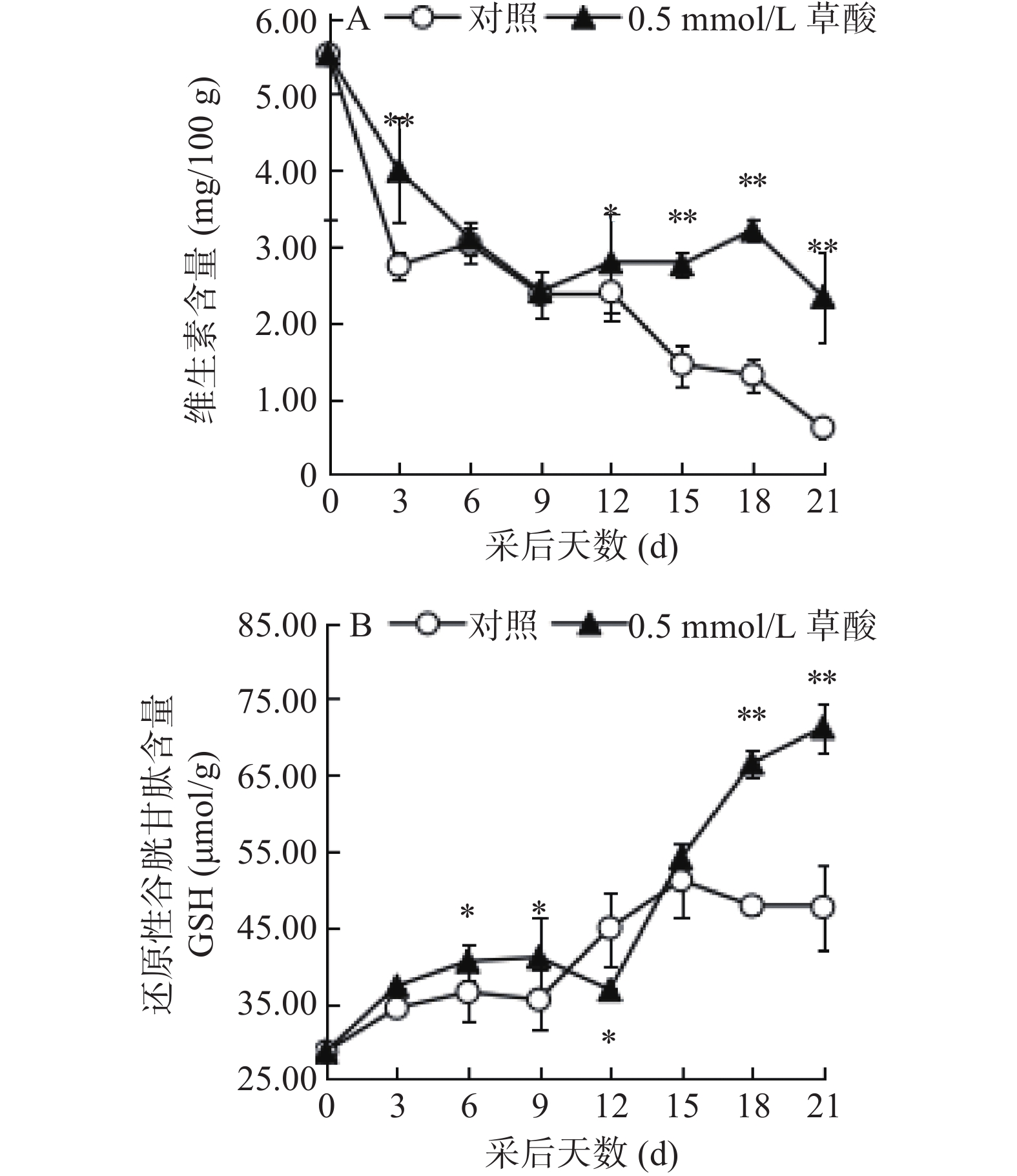
如图5-A所示,采后蜂糖李果实的VC含量大体呈下降趋势。贮藏期间,经草酸处理的蜂糖李果实的VC含量整体上高于对照组。在第21 d时,对照组果实的VC含量为0.62 mg/100 g,处理组VC含量则为2.34 mg/100 g,此时处理组果实的VC含量接近于对照组的4倍。在采后第3 d以及15~21 d期间,草酸处理极显著抑制了采后蜂糖李果实中VC的降解(P<0.01)。如图5-B所示,贮藏期间,除第12 d外,草酸处理的蜂糖李果实GSH含量均高于对照组,采后6~21 d期间,除第15 d外,二者GSH含量差异显著(P<0.05)。
VC是人类营养中最重要的维生素之一,是可在植物体内合成的一类抗氧化物质[31],具有很强的还原性,是衡量果实抗氧化衰老能力的因素之一,通过转变为半脱氢型和脱氢型,VC可清除植物组织中的多种活性氧自由基[32]。GSH则可协助VC清除活性氧自由基,从而限制脂类过氧化,提高活性氧自由基的清除水平,增强植物机体的抗逆性,应对氧化胁迫[33],对维持蛋白质或酶的正常功能、维持细胞内较高的还原势具有重大意义。相比于对照组果实,草酸处理可有效减缓采后蜂糖李果实VC含量的降低,并将其GSH含量保持在较高的水平,本试验中VC的含量变化与在番荔枝[7]和猕猴桃[26]的研究上得到的结果一致,而GSH的含量变化与郑小林等[34]在杧果的研究上得到的结论相似。
2.6 草酸处理对蜂糖李果实SOD、POD、CAT、APX等酶活性的影响
SOD可清除
如图6-B所示,采后蜂糖李果实POD活性大致呈上升趋势。到第21 d时,对照组果实的POD活性为0.79 U/g,处理组为0.90 U/g。贮藏期间,除第18 d外,处理组与对照组果实之间POD活性差异不显著(P>0.05)。
CAT可催化植物体中的H2O2分解为水和氧气,降低H2O2对植物有机体造成的氧化伤害。由图6-C可以看出,采后蜂糖李果实的CAT活性大致呈现先升高后降低的趋势。处理3 d后,草酸处理的蜂糖李果实CAT活性明显高于对照组。草酸处理6 d后,处理组果实与对照组果实之间CAT活性差异极显著(P<0.01),草酸处理可抑制蜂糖李果实CAT活性的下降。
APX具有抗衰老的作用,在植物体物质代谢的过程中具有重要意义。如图6-D所示,采后蜂糖李果实APX活性呈下降趋势。在处理9~21 d时,除第12 d外,处理组果实APX活性极显著高于对照组果实(P<0.01)。第21 d时,对照组果实APX活性为8.53(0.01ΔOD290/min·g),处理组则为17.60(0.01ΔOD290/min·g),其APX活性约为对照组的2倍。由以上分析可得出,草酸处理可有效延缓采后蜂糖李果实APX活性的降低。
果蔬组织中存在包括酶促保护系统和非酶促保护系统的两类活性氧清除机制。SOD、CAT、POD、APX等是植物组织中重要的活性氧清除酶。SOD是一种重要的抗氧化酶,可与CAT、POD等酶协同作用来防御活性氧及其它过氧化物自由基对有机体的伤害,对植物组织中自由基、活性氧的代谢平衡具有重要意义[35]。CAT可分解植物组织中的H2O2,将H2O2歧化为无害化合物,保护植物细胞膜免受自由基伤害[36]。POD与果实抗病性、抗氧化性等密切相关,具有清除H2O2以及胺类、醛类、苯类毒性的作用[37]。APX可催化VC与H2O2发生氧化还原反应,是植物体中VC-GSH氧化还原途径中的重要组成部分,对清除植物组织中的H2O2具有重要意义[38]。本试验结果表明,草酸处理能有效抑制蜂糖李果实中包括SOD、CAT、APX等酶活性的降低。但在试验中草酸处理对蜂糖李果实POD活性的影响并不明显。草酸处理对蜂糖李果实SOD活性变化的影响与沈玫等[39]在绿竹笋上的研究结果相一致,对CAT活性的影响结果与草酸在辣椒[40]上的研究结果一致。此外,草酸处理抑制蜂糖李果实APX活性的降低与在哈密瓜[33]上的研究结果相似,而对POD活性的影响与陈维维等[41]在梨果实上的研究结果相反,这可能是由于材料不同以及草酸处理浓度不同所造成的。草酸处理抑制了采后蜂糖李果实SOD、CAT、APX等酶活性的降低,这说明草酸处理有助于增强采后蜂糖李果实抗氧化能力。
3. 结论
草酸处理能有效延缓蜂糖李果实失重率、腐烂率、呼吸速率、固酸比、可溶性糖含量、MDA含量以及
本研究结果表明,草酸处理能够延缓采后蜂糖李果实的成熟衰老进程,提升其抗氧化能力,抑制采后贮藏期间其果实品质的降低,对蜂糖李果实具有良好的保鲜效果。因此,作为一种安全无毒的有机酸,草酸处理可作为采后蜂糖李果实保鲜的一种新方法。
-
-
[1] 张毅, 李用奇, 肖祎, 等. 中熟李新品种蜂糖李[J]. 北方果树,2018(5):56−56. [2] 董晓庆, 石其宇, 卢梅, 等. 草酸处理对采后蜂糖李果实贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(10):53−59. [3] 冯雪立, 董晓庆, 朱守亮, 等. 褪黑素处理对蜂糖李果实的保鲜效应[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(6):265−271. [4] 王静. 草酸在果实采后贮藏保鲜中的应用研究[J]. 现代农业科技,2014(12):273−276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2014.12.174 [5] 梁春强, 吕茳, 饶景萍. 草酸处理对采后‘华优’猕猴桃果实耐冷性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(19):230−235. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201719037 [6] Huang H, Jing G X, Guo L F, et al. Effect of oxalic acid on ripening attributes of banana fruit during storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2013,84:22−27. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.04.002
[7] 刘锴栋, 袁长春, 敬国兴, 等. 外源草酸对采后番荔枝后熟及耐藏性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(14):329−334. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201314069 [8] 周道志. 草酸处理对采后木瓜成熟及其品质的影响[J]. 现代食品,2016(5):106−110. [9] Kawaljit K, Gill P P S, Jawandha S K. Enzymatic and physico-chemical changes in pear fruits in response to post-harvest application of oxalic acid[J]. Indian Journal of Horticulture,2017,74(2):303−305. doi: 10.5958/0974-0112.2017.00062.7
[10] Wu F W, Zhang D D, Zhang H Y, et al. Physiological and biochemical response of harvested plum fruit to oxalic acid during ripening or shelf-life[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(5):1299−1305. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.027
[11] Kasshif R, Ahmad S K, Aman U M, et al. Effect of oxalic acid application on Samar Bahisht Chaunsa mango during ripening and postharvest[J]. LWT- Food Science and Technology,2015,63(1):152−160. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.069
[12] 郑小林, 田世平, 李博强, 等. 外源草酸延缓采后芒果成熟及其生理基础的研究[J]. 中国农业科学,2007,40(8):1767−1773. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2007.08.024 [13] Zhu Y Y, Yu J, Brecht J K, et al. Pre-harvest application of oxalic acid increases quality and resistance toPenicillium expansum in kiwifruit during postharvest storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,190:537−543. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.06.001
[14] Deng J J, Bi Y, Zhang Z K, et al. Postharvest oxalic acid treatment induces resistance against pink rot by priming in muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2015,106:53−61. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.04.005
[15] Li P Y, Yin F, Song L J, et al. Alleviation of chilling injury in tomato fruit by exogenous application of oxalic acid[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,202:125−132. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.142
[16] Jin P, Zhu H, Wang L, et al. Oxalic acid alleviates chilling injury in peach fruit by regulating energy metabolism and fatty acid contents[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,161:87−93. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.103
[17] Wang Z, Cao J K, Jiang W B. Changes in sugar metabolism caused by exogenous oxalic acid related to chilling tolerance of apricot fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2016,114:10−16. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.11.015
[18] 王静, 茅林春, 李学文, 等. 草酸处理对哈密瓜采后冷害及品质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(16):167−172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.16.037 [19] Zheng X L, Tian S P. Effect of oxalic acid on control of postharvest browning of litchi fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2005,96(4):519−523.
[20] Sajid A, Ahmad S K, Muhammad A A, et al. Effect of postharvest oxalic acid application on enzymatic browning and quality of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) root slices[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,32:1−8.
[21] 董晓庆, 饶景萍, 朱守亮, 等. 气调包装和1-MCP抑制苹果蜡质成分降低[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(16):269−277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.16.034 [22] 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2007. [23] 赵永红, 李宪利. 设施油桃果实发育过程中糖酸代谢的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2009,37(19):8959−8962. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.19.065 [24] 程春梅, 郭衍银. 采前草酸处理对西兰花贮藏品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2020,34(6):1213−1220. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.06.1213 [25] 喻最新, 王日葵, 王晶, 等. 草酸处理对塔罗科血橙采后花色苷积累和糖酸含量的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(8):63−70. [26] 梁春强, 吕茳, 靳蜜静, 等. 草酸处理对采后猕猴桃冷害、抗氧化能力及能荷的影响[J]. 园艺学报,2017,44(2):279−287. [27] Wan C P, Chen J Y, Chen C Y, et al. Effects of hot air treatments on postharvest storage of newhall navel orange[J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland),2020,9(2):170−184.
[28] 张瑞杰, 张杼润, 金鹏, 等. 24-表油菜素内酯减轻杏果实冷害及与活性氧的代谢关系[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(4):39−44. [29] 蔺经. 渗透胁迫对杏叶片膜脂过氧化及保护酶的影响[J]. 北方果树,2001(3):9−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5698.2001.03.004 [30] Wang J, Mao L C, Li X W, et al. Oxalic acid pretreatment reduces chilling injury in Hami melons (Cucumis melo var. reticulatus Naud.) by regulating enzymes involved in antioxidative pathways[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2018,241:201−208. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.06.084
[31] 张晓宇, 王春生, 赵桂芳, 等. 桃果实采后生理研究及贮藏保鲜技术应用进展[J]. 中国农学通报,2008(5):117−120. [32] 邵远志, 孙思胜, 贾志伟, 等. 1-MCP和外源乙烯处理对番木瓜果实贮藏品质的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2011,11(2):3−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2011.02.003 [33] 季作梁, 戴宏芬, 张昭其. 芒果果实冷害过程中谷胱甘肽和抗坏血酸含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报,1998(4):13−17. [34] 郑小林, 陈燕, 敬国兴, 等. 草酸处理对 杧果采后果实AsA-GSH循环系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报,2011,38(9):1633−1640. [35] Shafa N, Kashif R, Sami U, et al. Genotypes and harvest maturity influence the nutritional fruit quality of mulberry[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2020,266:1−7.
[36] 周开兵, 李世军, 袁孟玲, 等. 杧果成年树在增强UV-B辐射处理下的损伤与抗氧化响应[J]. 园艺学报,2019,46(7):1279−1289. [37] 张一冉, 王雅楠, 杨杨, 等. 脱落酸与水杨酸处理调节李果实抗冷性及氧化酶活性[J]. 江苏农业学报,2020,36(2):471−476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2020.02.030 [38] 凌晨, 谢兵, 洪羽婕, 等. 外源钙和钙调素拮抗剂对冷藏桃果实耐冷性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(1):240−248. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180521-296 [39] 沈玫, 王琪, 赵宇瑛, 等. 外源草酸对冷藏绿竹笋的保鲜效果及其生理基础[J]. 园艺学报,2013,40(2):355−362. [40] 朱丽琴, 张伟, 汪伟, 等. 外源草酸对辣椒保鲜效果和抗氧化防御系统的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2013,35(3):521−524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2286.2013.03.016 [41] 陈维维, 赵晓梅, 叶凯, 等. 草酸处理对库尔勒香梨黑斑病抑制效果的研究[J]. 保鲜与加工,2016,16(2):38−43. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 何兰兰,马四补,姜特,梁文娟,晋海军,张丽艳. 固态发酵刺梨果渣改性膳食纤维工艺优化及结构特性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(02): 183-191 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 武思齐,苟长秀,赵杰. 酸碱法提取葛根粉膳食纤维素的工艺优化. 绿色科技. 2023(12): 271-275 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李悦,张钰,张玉萍,曾庆华,郭兴峰,孔峰. 汽爆对麦麸可溶性膳食纤维功能性质的影响. 粮食与油脂. 2022(11): 48-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)










 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载:





