Protective Effect of Wuzhiyin against Acetaminophen-induced Hepatic Injury in Mice
-
摘要: 目的:探讨五汁饮(Wuzhiyin,WZY)对对乙酰氨基酚(acetaminophen,AP)致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用。方法:将小鼠随机分为空白组,模型组及五汁饮低、中、高剂量组,灌胃给药100、200、400 mg/kg,空白组和模型组灌胃等体积生理盐水。通过计算脏器指数,检测血清中的ALT、AST及肝组织匀浆中的MDA、GSH、TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β水平,结合肝组织切片来观察病理学变化。结果:五汁饮低、中、高剂量组小鼠肝脏指数较模型组降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与模型组相比,五汁饮中、高剂量明显抑制血清中的AST、ALT活力(P<0.05或P<0.01),显著性降低TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β的水平(P<0.05或P<0.01),使肝组织匀浆中MDA水平降低,同时缓解肝组织匀浆中GSH水平的升高;组织病理学HE和Tunel染色显示五汁饮可改善肝组织的坏死与凋亡,并减轻细胞炎性浸润。结论:五汁饮对对乙酰氨基酚诱导的急性肝损伤有一定的保护作用,其机制可能与其抗氧化作用、减少炎症反应及抑制细胞凋亡有关。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the protective effect of Wuzhiyin (WZY) against acetaminophen (AP) induced hepatic injury in mice. Methods: Male KM mice were randomly divided into blank group, model group, low, medium and high dose WZY groups (100, 200, 400 mg/kg). The normal saline of equal volume was used in the blank group and model group. In addition to the blank group, the other groups were given AP (300 mg/kg) on the 6th day to establish the model of liver injury in mice. Calculate the organ index to detect alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in serum and malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β level, combined with liver tissue sections to observe pathological changes. Results: The liver index of the mice in the low, medium and high dose group were significantly lower than that in the model group (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the serum AST, ALT, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β in the medium-, high- dose group significantly decreased (P<0.05 or P<0.01). The content of GSH in the medium-, high- dose group significantly increased, while the content of MDA significantly decreased. Histopathological HE and Tunel staining showed that WZY could improve the necrosis and apoptosis of liver tissue, and reduce the inflammatory infiltration of cells. Conclusion: WZY had certain protective effect on acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury, and its mechanism might be related to its antioxidant effect, reduction of inflammation and inhibition of cell apoptosis.
-
Keywords:
- Wuzhiyin /
- acetaminophen /
- hepatic injury /
- apoptosis
-
对乙酰氨基酚(N-acetyl-para-aminophenol,APAP)是一般用于治疗普通感冒的一类非甾体解热镇痛药,属于乙酰水杨酸类,由于其解热作用较好副作用小被广泛用于临床,故常发生不规范性使用的现象。短期低剂量使用不会对肝脏造成影响,而对乙酰氨基酚大剂量摄入会使肝脏积累代谢有毒物质,进而引发药物性肝损伤和肝炎[1-2]。药物性肝损伤是指药物本身毒性或其活性代谢产物毒性所导致的肝脏损伤,严重时可发展为肝功能衰竭甚至导致患者死亡[3]。对乙酰氨基酚超剂量导致葡萄糖醛酸化和硫酸化不充足以及肝脏中过量的N-乙酰苯醌亚胺消耗谷胱甘肽,一旦肝脏谷胱甘肽储备耗尽,未结合的乙酰苯醌亚胺可与其他细胞蛋白自由组合,从而加剧肝细胞氧化应激和细胞凋亡[4-5]。
五汁饮出自清朝吴瑭《温病条辨》一书,处方由鲜藕汁、鲜梨汁、鲜荸荠汁、芦根水煎液、鲜麦冬汁组成,具有清热养阴、生津止渴的功效[6]。组成是由常见食品与使用安全的中药组成,具有很好的养身保健作用。现代药理研究表明:梨作为常见水果,有清心、润肺、养肝、解疮毒和酒毒的功效[7];荸荠富含硒、黄酮、多酚等抗氧化物质,具有抗氧化、抗癌的作用[8];芦根中的多糖成分具有抗氧化[9]、抗自由基作用,并可通过抗氧化作用保护肝细胞、抑制胶原沉积等途径来抑制肝纤维化,改善肝功能,降低肝脂肪化[10];麦冬是我国临床常用的中药之一,具有养阴生津、润肺清心的功效。麦冬的主要成分有皂苷、黄酮、多糖等[11],具有抗炎、抗氧化、增强免疫、改善肝损伤等药理作用[12];莲藕是常见的蔬菜,莲藕中的多糖、多酚物质具有降血糖作用[13],可提升体内超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)的活性,减少丙二醛(MDA)的生成。五汁饮的所有组成成分具有良好的保肝、抗氧化、抗自由基作用,由常见食品和使用安全的中药组成,具有很好的使用安全性。
本文采用高剂量对乙酰氨基酚诱导小鼠急性肝脏损伤模型[14],但目前对五汁饮的营养和保健作用的机制研究较少,本文探讨了五汁饮(WZY)对对乙酰氨基酚AP所致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用及可能机制,为五汁饮的研究与开发新型保健饮品提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
SPF级雄性KM小鼠 40只,5~6周龄,体重18~22 g,由动物实验中心提供,合格证号SCXK(鄂)2019-0017,小鼠每天给予充足的水和饲料,3 d后开始实验;新鲜的梨、荸荠、藕 1000 g,均购买于本地市场;芦根和麦冬 1000 g,本地药房;HE染液、谷草转氨酶(AST)试剂盒、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)试剂盒、谷胱甘肽(GSH)试剂盒、丙二醛(MDA)试剂盒、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)试剂盒、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)试剂盒、白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)试剂盒 上海碧云天生物科技有限公司;对乙酰氨基酚 纯度99%,上海源叶生物有限公司。
RE-5203旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;SHZ-Ш型循环水真空泵 上海知信实验仪器有限公司;AR224CN分析天平 奥豪斯上海有限公司。Leica DMI6000B荧光显微镜 德国徕卡显微系统(上海)有限公司;GL-12C高速冷冻离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 五汁饮样品制备
梨(去心皮)、荸荠、藕洗净榨汁合并,芦根和麦冬(各500 g)放入大砂锅内,加入2 L水,浸泡30 min后置大火上煮沸30 min后,改小火煮30 min,过滤,合并梨、荸荠、藕汁,小火煎煮10 min,反复三次,纱布挤压过滤,滤液减压浓缩为2.0 g生药/mL浓缩液,密封,放入4 ℃冷藏。
1.2.2 动物分组及造模给药处理
参考文献[15],40只昆明小鼠适应性饲养1周后随机分为5组:空白组、模型组、五汁饮低剂量组(100 mg/kg)、五汁饮中剂量组(200 mg/kg)和五汁饮高剂量组(400 mg/kg),每组8只。五汁饮(低、中、高)组小鼠持续灌胃给药7 d,每日1次,空白组和模型组小鼠灌胃给予等量的生理盐水。最后一次给药2 h后,除空白组外,其余各组小鼠腹腔注射AP(300 mg/kg)建立肝损伤模型。24 h后,对小鼠进行眼球取血,静置离心后留取上清检测相关指标;取小鼠肝脏和脾脏称重记录,后取一部分肝组织固定于福尔马林溶液中,用于肝组织切片染色观察病理变化,另一部分肝组织冻存,用于后续相关指标检测。
1.2.3 免疫器官指数检测
称小鼠体质量及肝脏和脾脏质量,计算脏器指数。肝脏(脾脏)指数=肝脏(脾脏)质量/体质量。
1.2.4 血清指标检测
小鼠进行眼球取血,静置离心(2000 r/min,4 ℃,离心5 min)后留取上清液用试剂盒检测ALT、AST酶活力。
1.2.5 氧化应激指标检测
取−80 ℃冻存的小鼠肝组织,置于冰上解冻后,加入生理盐水,匀浆,离心(5000 r/min,常温,离心5 min),留取上清液,按照GSH和MDA试剂盒的操作说明书测定相关指标。
1.2.6 炎症因子的检测
取血清,按照试剂盒说明书,测定TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β含量。
1.2.7 HE染色
按照HE染色步骤进行染色,封片,在显微镜下观察拍照。将H&E染色后的肝组织切片置于显微镜下观察,根据AP肝损伤评价标准对其进行评分统计。肝损伤评价标准为:0级(0~1分):无明确肝损伤的形态学特征;1级(1~2分):肝小叶Ⅲ区,静脉周围散在的片状坏死病灶;2级(2~3分):静脉周围散在的片状坏死病灶,一直延续到Ⅱ区;3级(3~4分):静脉片状坏死病灶,一直延续到Ⅰ区。
1.2.8 Tunel染色
将待染色的片子置于脱水框中,脱蜡水化步骤同HE染色,接着用3%H2O2灭活内源性过氧化物酶,再滴加0.01 mol/L TBS新鲜稀释的Proteinase K(1:200),37 ℃条件下消化12 min,接着在37 ℃条件下,依次用标记缓冲液孵育2 h、封闭液孵育30 min、抗体稀释液稀释的生物素化抗地高辛抗体(1:100)孵育30 min,抗体稀释液稀释的SABC(1:100)孵育30 min,最后置于新鲜配制的DAB发色液中,至镜检出现阳性信号出现,再置于苏木素中,之后同HE染色脱水、树脂封片步骤,待片子风干,置于显微镜下观察肝组织细胞炎症与凋亡情况。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据采用GraphPad Prism 5.01科学统计绘图软件进行分析,以Mean±SD表示,组间和组内采用双向方差分析,当P<0.05时,表示数据之间具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 五汁饮对小鼠脏器指数的影响
给药7 d后,五汁饮对小鼠脏器指数[16]的影响结果见表1。观察可见模型组小鼠肝组织出现肿大,说明造模成功,肝脏指数的降低说明给药组对于肝脏肿大有缓解作用。与空白组相比,模型组小鼠的肝脏指数下降高度显著(P<0.001);与模型组比,除低剂量组外,五汁饮可显著(P<0.05或P<0.01)降低小鼠的肝脏指数,其中以高剂量组的五汁饮降低效果最为显著(P<0.01)。结果表明,适宜剂量的五汁饮能够改善APAP致急性肝损伤小鼠的肝肿胀情况。
表 1 五汁饮对AP致急性肝损伤小鼠脏器指数的影响($\bar {\rm{x}} \pm {\rm{s}}$ , n=8)Table 1. Effects of WZY on organ indices in acute liver-injury mice induced by AP ($\bar {\rm{x}} \pm {\rm{s}}$ , n=8)组别 剂量(g/kg) 肝脏指数(mg/g) 脾脏指数(mg/g) 空白组 / 52.30±1.45 4.28±0.07 模型组 / 60.50±2.24*** 3.97±0.10*** 五汁饮组 100 58.10±1.37# 4.04±0.07 200 56.80±2.50# 4.14±0.07## 400 55.40±1.99## 4.23±0.06### 注:与空白组相比,*表示数据差异显著,P<0.05;**表示数据差异极显著,P <0.01;***表示数据差异高度显著,P<0.001;与模型组相比,#表示数据差异显著,P<0.05;##表示数据差异极显著,P<0.01;###表示数据差异高度显著,P<0.001;表2、图1~图3同。 2.2 五汁饮对小鼠血清指标的影响
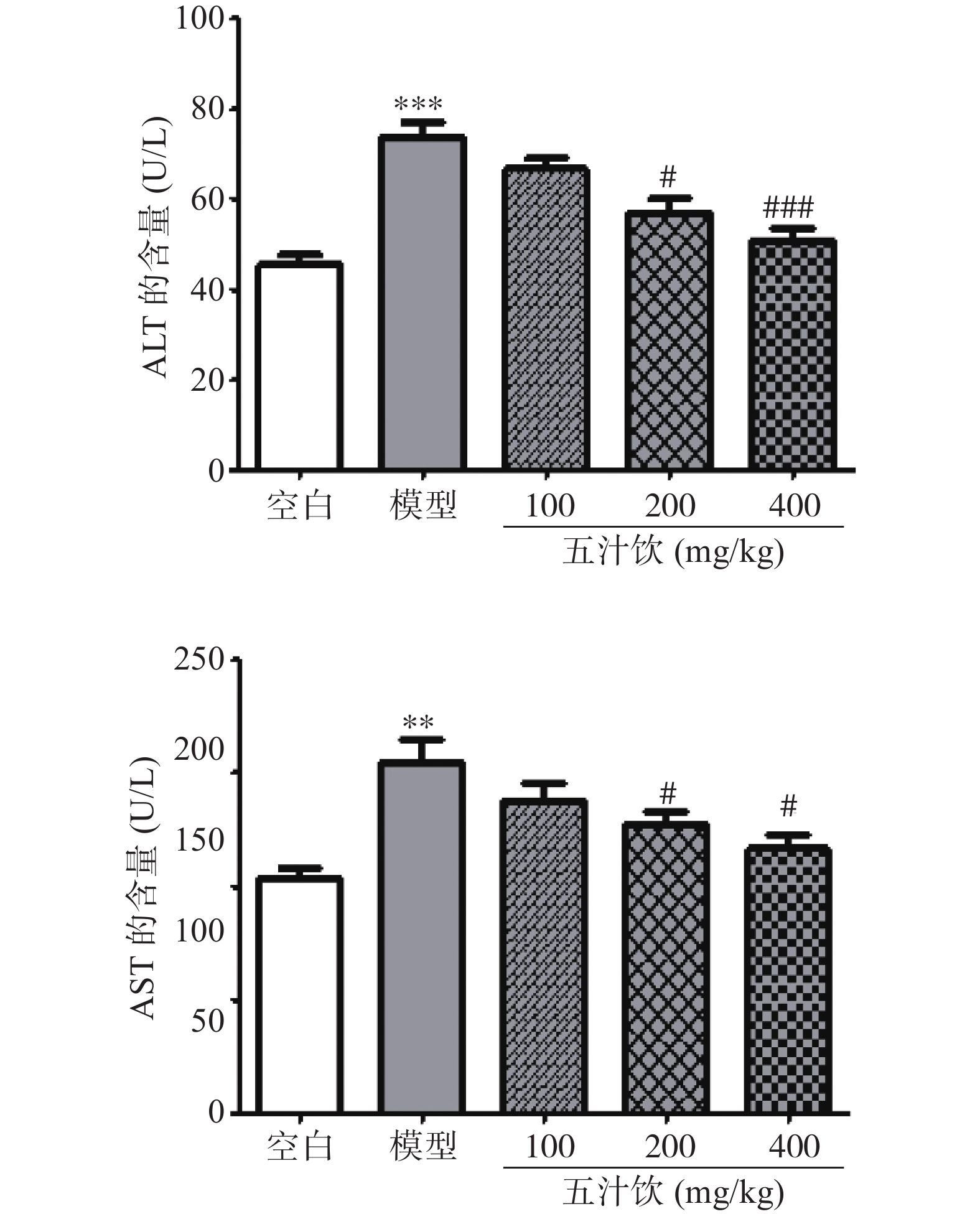
ALT和AST是肝损伤的主要指标参数,当肝脏受到损伤时,这些生理指标会在血液中发生变化,二者在血清中的指数会有所升高[17-18]。如图1所示,与空白组相比,模型组小鼠血清中ALT(P<0.001)和AST(P<0.01)活力均显著升高;给予五汁饮后,与模型组相比,小鼠血清中ALT和AST活力均有不同程度的减少,其中,高剂量的五汁饮给药组引起小鼠机体变化,其显著降低了AP作用于小鼠机体血清中ALT(P<0.001)和AST(P<0.05)的水平。结果表明五汁饮对对乙酰氨基酚所致的急性肝损伤有一定的保护作用。
2.3 五汁饮对小鼠肝脏中GSH和MDA的影响
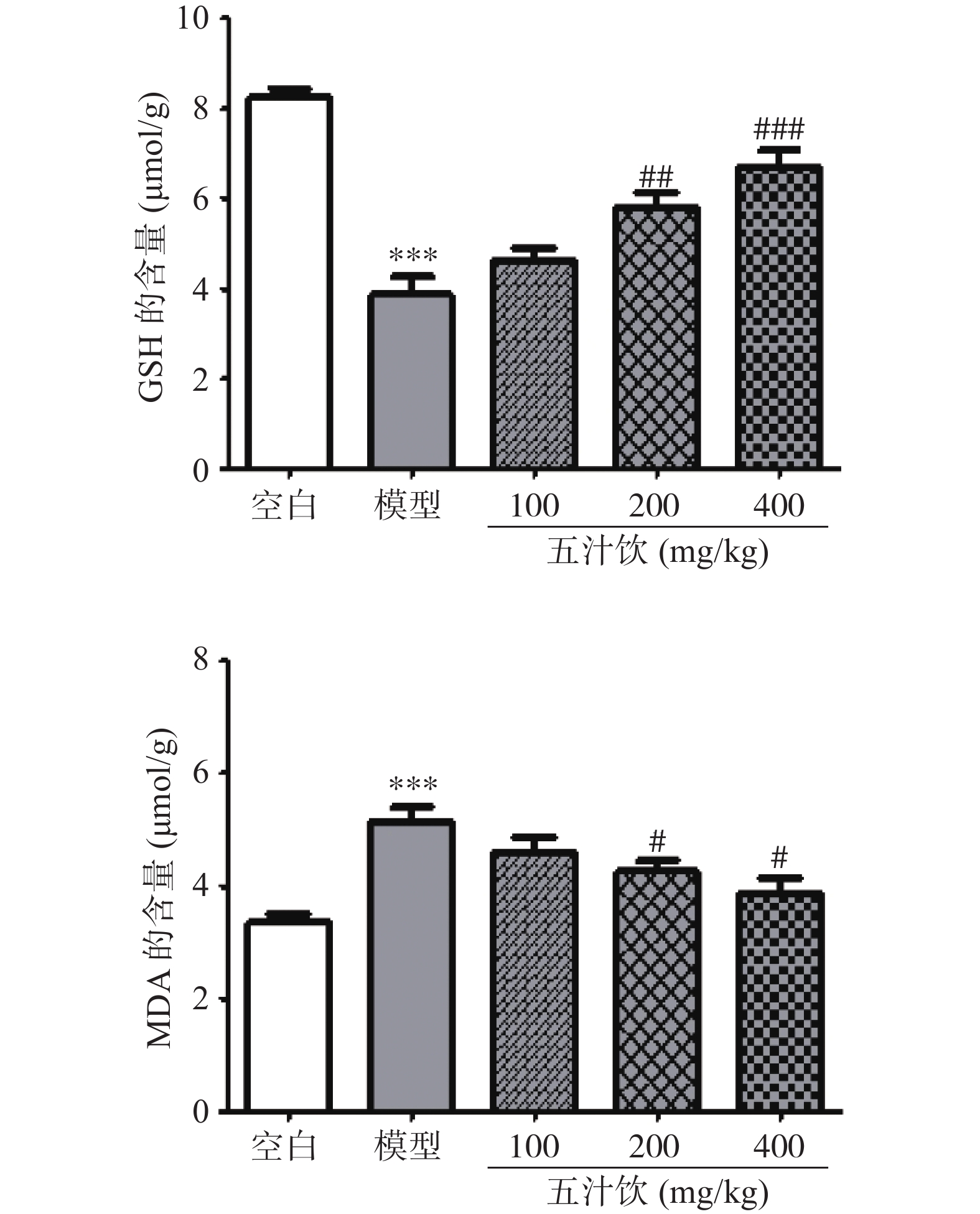
如图2所示,与空白组相比,模型组小鼠肝组织中GSH(还原型谷胱甘肽)含量显著降低(P<0.001),而五汁饮的中(P<0.01)、高剂量组(P<0.001)不同程度地改善了AP引起的小鼠肝组织中GSH含量的减少。MDA水平显示组织的脂质过氧化物的多少,含量与细胞的受损程度有关[19-20]。与空白组小鼠相比,模型组小鼠肝组织中MDA水平显著升高(P<0.001);与模型组比,中、高剂量的五汁饮显著降低了小鼠肝组织中MDA的含量(P<0.05)。结果表明五汁饮能够提高肝组织抗氧化能力并缓解AP对肝细胞产生的脂质过氧化作用。
2.4 五汁饮对小鼠肝组织中炎症因子的影响
肝组织中炎症因子水平反映炎症反应的强弱[21-23]。由表2可知,与空白组相比,模型组的炎症因子含量明显升高;与模型组相比,五汁饮低、中、高剂量组显著抑制了组织中炎症因子的升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。
表 2 五汁饮对小鼠肝脏中炎症因子的影响Table 2. Effects of WZY on inflammatory factors in liver of mice分组 剂量
(mg/kg)炎症因子(pg/mg protein) TNF-α IL-6 IL-1β 空白组 − 15.1±1.1 17.3±3.2 13.3±4.8 模型组 − 248.3±18.8** 328.2±14.8** 173.3±18.1** 五汁饮 100 155.8±17.8## 172.4±12.4## 112.3±11.3# 200 117.7±16.5## 126.4±13.6## 83.2±10.2## 400 97.8±16.3## 102.7±13.1## 51.2±8.7## 2.5 五汁饮对小鼠肝组织病理变化的影响
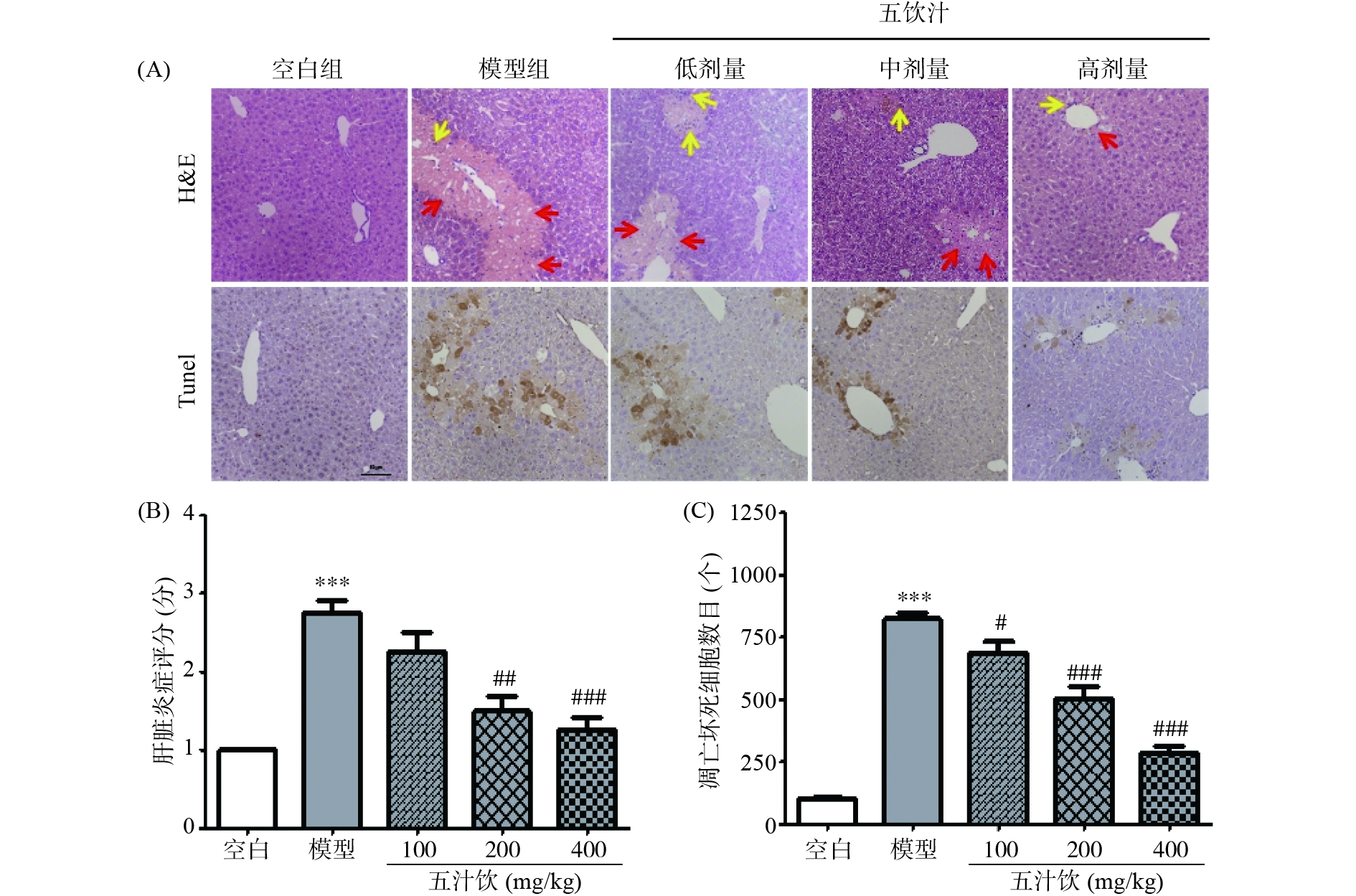
如图3所示,空白组小鼠的肝组织细胞排列整齐,肝小叶结构清晰;HE染色结果显示,模型组小鼠肝组织中央静脉周围多数融合坏死,且部分坏死面积从III区扩张至II区,并伴混合性炎细胞浸润,Tunel凋亡染色图片可看出模型组小鼠肝脏中央静脉周围细胞变性肿胀,大部分肝细胞凋亡,呈现灶状坏死[24-25];经过五汁饮的干预,小鼠肝组织细胞的凋亡坏死情况得到不同程度的改善,五汁饮高剂量组细胞完整,排列整齐,肝组织炎症浸润现象轻微,显著减轻了AP引起的小鼠肝细胞凋亡坏死症状,并改善了肝组织的炎症浸润程度,从而改善肝组织的损伤情况。
3. 结论
本实验中通过对小鼠腹腔注射高剂量对乙酰氨基酚溶液,导致小鼠出现肝脏损伤现象,探讨五汁饮对对乙酰氨基酚致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用。结果表明,五汁饮高、中剂量组小鼠血清中ALT和AST的水平均有明显下降,GSH活性提高,MDA水平降低,肝组织切片显示肝组织变性及坏死等病理症状明显改善。说明五汁饮具有清除自由基、抑制脂质过氧化反应、防止细胞膜受损、减轻细胞肿胀坏死的效果,对药物所致肝损伤具有显著保护作用。五汁饮对对乙酰氨基酚所致肝损伤具有一定的保护作用,其保护机制与提高抗氧化酶体系活力、抑制脂质过氧化、维持肝细胞膜正常形态有关。综上所述,五汁饮能保护AP所致的小鼠急性肝损伤,其机制与抑制氧化应激、缓解炎症反应有关,这为五汁饮的研究与开发提供了理论依据。
-
表 1 五汁饮对AP致急性肝损伤小鼠脏器指数的影响(
ˉx±s , n=8)Table 1 Effects of WZY on organ indices in acute liver-injury mice induced by AP (
ˉx±s , n=8)组别 剂量(g/kg) 肝脏指数(mg/g) 脾脏指数(mg/g) 空白组 / 52.30±1.45 4.28±0.07 模型组 / 60.50±2.24*** 3.97±0.10*** 五汁饮组 100 58.10±1.37# 4.04±0.07 200 56.80±2.50# 4.14±0.07## 400 55.40±1.99## 4.23±0.06### 注:与空白组相比,*表示数据差异显著,P<0.05;**表示数据差异极显著,P <0.01;***表示数据差异高度显著,P<0.001;与模型组相比,#表示数据差异显著,P<0.05;##表示数据差异极显著,P<0.01;###表示数据差异高度显著,P<0.001;表2、图1~图3同。 表 2 五汁饮对小鼠肝脏中炎症因子的影响
Table 2 Effects of WZY on inflammatory factors in liver of mice
分组 剂量
(mg/kg)炎症因子(pg/mg protein) TNF-α IL-6 IL-1β 空白组 − 15.1±1.1 17.3±3.2 13.3±4.8 模型组 − 248.3±18.8** 328.2±14.8** 173.3±18.1** 五汁饮 100 155.8±17.8## 172.4±12.4## 112.3±11.3# 200 117.7±16.5## 126.4±13.6## 83.2±10.2## 400 97.8±16.3## 102.7±13.1## 51.2±8.7## -
[1] 潘家琪, 宋丹军, 李鹏旭, 等. 对乙酰氨基酚肝毒性机制与防治研究新进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2014,28(4):618−624. doi: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2014.04.023 [2] Bhushan B, Apte U. Liver regeneration after acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities[J]. American Journal of Pathology,2019,189(4):719−729. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.12.006
[3] Bessone F, Robles-Diaz M, Hernandez N. Assessment of serious acute and chronic idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury in clinical practice[J]. Seminars in Liver Disease,2019,39(3):381−394. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685519
[4] Mukherjee S, Ghosh S, Choudhury S, et al. Pomegranate reverses methotrexate-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in hepatocytes by modulating Nrf2-NF-κB pathways[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2013,24(12):2040−2050. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.07.005
[5] Krishnan N, Perazella M A. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis: Pathology, pathogenesis, and treatment[J]. Iranian Journal of Kidney Diseases,2015,9(1):3−13.
[6] 游宇, 张玉蝶, 罗林, 等. 采用星点设计-效应面优化五汁饮的制备工艺[J]. 食品工业,2019(7):24−28. [7] 李丽梅, 赵哲, 何近刚, 等. 不同品种梨果实酚类物质和抗氧化性能分析[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(17):83−88. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201417017 [8] 赵广河, 陈振林. 荸荠活性成分与功能作用研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2011,32(9):235−237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2011.09.068 [9] 沈蔚, 任晓婷, 张建, 等. 芦根多糖的提取及其抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2010(5):1078−1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2010.05.023 [10] 李立华, 张国升. 芦根多糖保肝作用及抗肝纤维化的研究[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2007,26(5):32−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2219.2007.05.015 [11] 袁春丽, 孙立, 袁胜涛, 等. 麦冬有效成分的药理活性及作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志,2013(21):2496−2502. [12] 彭婉, 马骁, 王建, 等. 麦冬化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药,2018,49(2):477−488. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.02.032 [13] 罗登宏, 周桃英, 袁仲, 等. 莲藕多糖的降血糖活性及对体内抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(6):3334−3335, 3385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.06.072 [14] J C Mossanen, F Tacke. A cetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Laboratory animals,2015,49(1 Suppl):30−36.
[15] 舒广文, 邱韵涵, 付千, 等. 桑葚总多糖对对乙酰氨基酚诱导小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2019,38(3):377−382. [16] 伍智慧, 冉喆, 张睛睛, 等. 枸杞多糖对四氯化碳致急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报,2021,43(4):364−370. [17] Susilo R J K, Hayaza S, Ansori A N M, et al. The effect of Garcinia mangostana extract on ALT and AST levels and liver structure in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Annals of Biology,2020,36(2):149−153.
[18] 李飞, 陆伦根. 肝功能异常的评估及临床意义[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2015,31(9):1543−1546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.09.046 [19] 杨宽, 钱卫东, 秦蓓. 茶多酚对高脂血症大鼠血脂代谢和肝组织MDA、T-SOD含量的影响[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(1):77−80, 103. [20] 翟晓虎, 杨海锋, 陈慧英, 等. 丙二醛的毒性作用及检测技术研究进展[J]. 上海农业学报,2018,34(1):144−148. [21] 艾国, 雒真龙, 张志成, 等. 炎症相关细胞因子及趋化因子在小鼠自身免疫性肝损伤不同 时期的表达及作用[J]. 医学研究杂志,2020,49(2):20−24. [22] Sun C, Kono H, Furuya S, et al. Interleukin-17A plays a pivotal role in chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice[J]. Digestive Diseases & Sciences,2016,61(2):474−488.
[23] Kong L Z, Chandimali N, Han Y H, et al. Pathogenesis, early diagnosis, and therapeutic management of alcoholic liver disease[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20:2712. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112712
[24] 张俊逸, 罗光明, 柴华文, 等. 栀子油对对乙酰氨基酚致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(11):127−130. [25] 黄小强, 丁辉, 刘顺和, 等. 马齿苋多糖对四氯化碳诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):315−319, 324. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 周昀璐,李荣群. 五汁饮临床应用及现代研究进展. 新中医. 2023(23): 30-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)







 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



