Effects of NaCl Stress on Lutein Accumulation and Antioxidant Capacity of Broccoli Sprouts
-
摘要: 为探究NaCl胁迫对西兰花芽苗叶黄素富集及抗氧化能力的影响,本实验以“青峰”西兰花种子为实验原材料,研究了不同浓度NaCl溶液处理对西兰花芽苗的芽长、鲜重、干重、含水率、可溶性蛋白、还原糖、丙二醛、脯氨酸、叶黄素含量及抗氧化酶[超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)]活性的影响。结果表明,不同NaCl浓度对西兰花芽苗生长影响较大,随NaCl浓度由0~300 mmol/L变化,叶黄素含量先升高后下降。经100 mmol/L NaCl胁迫处理至第4 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量为546.25 μg/g,比对照组增加了37.54%,该条件下芽苗的芽长、鲜重、干重、含水率、可溶性蛋白、还原糖含量也均明显提高,较对照组分别增加了20.88%、161.16%、68.65%、2.86%、54.90%和40.0%,SOD、POD、CAT抗氧化酶活性与对照组相比分别增加了36.26%、14.62%、32.34%。本研究为通过NaCl胁迫西兰花种子萌发来提高叶黄素含量提供了新的方式,为开发功能性西兰花芽苗食品提供参考。Abstract: To explore the effect of NaCl stress on the lutein enrichment and antioxidant capacity of broccoli sprouts, the "Qingfeng" broccoli seeds were used as the experimental raw material. The sprouts length, fresh weight, dry weight, moisture content, soluble protein, reducing sugar, malondialdehyde, proline, lutein content and antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and peroxidase catalase activity were studied in this experiment. Results showed that different NaCl concentrations had a greater impact on the growth of broccoli sprouts. As NaCl concentration increased from 0 to 300 mmol/L, the content of lutein in the sprouts first increased and then decreased. Under 100 mmol/L NaCl stress, the lutein content in 4-day old sprouts was 546.25 g/g, which was 37.54% higher than that in the control group. The sprouts length, fresh weight, dry weight, moisture content, soluble protein and reducing sugar content also increased by 20.88%, 161.16%, 68.65%, 2.86%, 54.90% and 40.0%, respectively. At the same time, the antioxidant enzyme activities of SOD, POD and CAT increased by 36.26%, 14.62%, and 32.34% respectively. The results of this study provided a new way to improve lutein content through NaCl stress on the germination of broccoli seeds, thus providing a reference for the development of functional food of broccoli sprouts.
-
Keywords:
- NaCl stress /
- broccoli sprouts /
- germination /
- lutein /
- antioxidant capacity
-
西兰花(Brassica oleracea L.var.italica Plenck)又名西蓝花、青花菜、绿花菜等,作为十字花科芸薹属类甘蓝种的一个变种,富含蛋白质、脂肪、矿物质等营养物质以及抗坏血酸、总酚、类胡萝卜素、硫代葡萄糖苷等生物活性物质,其在预防癌症方面具有积极的作用[1],被誉为“蔬菜皇后”[2],因而近年来被广泛开发研究。叶黄素隶属于类胡萝卜素,是一种天然的色素,人类无法自身合成,需通过食物供给满足机体需要。它是一种重要的膳食抗氧化剂,具有保护眼睛、预防疾病、抗癌等多种生理功能,也可作为着色剂应用于医疗及生产行业[3-4]。
绿色蔬菜是叶黄素的一大重要来源,有研究报道西兰花中主要类胡萝卜素有叶黄素、β-胡萝卜素、新黄质和紫黄质[5],其中叶黄素含量占总类胡萝卜素的50%以上[6]。此外叶黄素与高等植物的抗氧化系统也存在着联系,李诺等[7]从黄秋葵叶中提取的叶黄素具有较好的DPPH自由基和ABTS自由基清除能力。同时,种子发芽是一种有效积累植物体内活性物质和次生代谢产物的重要手段,发芽不仅会改变种子的形态,还会在其内部不断合成新的物质,这在豆类、谷物、蔬果、花卉中均被得到证实[8-9]。研究发现NaCl胁迫作为最常见的非生物胁迫方式,可以有效促进植物发芽过程中化合物的合成和积累[10]。逆境下种子的生长会首先受到延缓或抑制,进而产生应激效应,导致其内部营养物质含量发生变化,田璐等[11]发现160 mmol/L NaCl处理会显著抑制西兰花芽苗生长,但其硫苷和异硫氰酸盐含量均显著提高,在甘蓝芽苗中160 mmol/L NaCl也有效促进了抗坏血酸和类胡萝卜素的积累[12],据Ariviani等[13]报道,NaCl浓度越大对豇豆芽苗生长的抑制作用越强,然而其总酚含量、DPPH自由基清除力及铁还原能力呈逐渐升高的趋势。荞麦芽苗虽在50 mmol/L的低盐胁迫下被延缓生长,但其内部类胡萝卜素和酚类物质含量得到显著提高[14]。以上研究说明适宜浓度的NaCl胁迫处理有助于芽苗中营养物质的富集和抗氧化活性的提高。
随着生活水平的提高,人们对叶黄素等类胡萝卜素的需求明显增加,而西兰花芽苗中含有丰富的叶黄素等生物活性物质。因此探索一种可以提高西兰花芽苗中叶黄素含量的新途径变得至关重要。目前有关西兰花的研究多集中于硫苷及萝卜硫素的积累鉴定与功能分析,但鲜有关于其芽苗期叶黄素的富集研究,因此本研究通过向西兰花种子外源施用不同浓度的NaCl溶液,以探究盐胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗的生长状况、重量、含水率、可溶性蛋白、还原糖、丙二醛、脯氨酸、叶黄素含量及抗氧化能力的影响,为通过NaCl胁迫西兰花种子萌发来提高叶黄素含量提供了新的方式,为开发功能性西兰花芽苗食品提供参考。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
西兰花种子 品种为“青峰”,2018年10月由江苏省农业科学院蔬菜研究所提供,并已经过西兰花育种专家严继勇研究员监定,种子用锡箔袋包装并储藏于4 ℃备用;叶黄素标准品 生化试剂,Sigma公司;黄嘌呤氧化酶 生化试剂,南京建成生物研究所;甲醇、甲基叔丁基醚 色谱纯,Tedia公司;6-羟基-2,5,7,8-四甲基色烷-2-羧酸、亮氨酸 分析纯,梯希爱(上海)化成工业发展有限公司;2,2-偶氮二(2-甲基丙基咪)二盐酸盐 分析纯,阿拉丁(上海)有限公司;正己烷、丙酮、甲苯、愈创木酚、无水乙醇、氢氧化钾、盐酸羟胺、氯化亚锡 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
LBI-150生化培养箱 上海龙跃仪器设备有限公司;Agilent 1200高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;微孔板分光光度计Epoch BioTek Instruments;BS-224-S电子分析天平 北京赛多利斯科学仪器公司;UV-6300紫外可见分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;FD-1A-50冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;RE52CS旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;B-220恒温水浴锅 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;D10氮气吹扫仪 杭州奥盛仪器有限公司;FW100高速万能粉碎机 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 发芽试验设计
选择颗粒饱满、大小均匀、具有发芽能力的西兰花种子为原料。除杂、筛选后用蒸馏水冲洗后,置于0.5% NaClO溶液中浸泡15 min,用蒸馏水冲洗5次至溶液pH呈中性,最后浸泡于蒸馏水中,在30 ℃下放置4 h。将浸泡后的西兰花种子滤干后均匀散落在铺有蛭石的发芽盘上,置于25 ℃恒温培养箱,在光周期为16 h光照/ 8 h黑暗条件下发芽。用蒸馏水喷施催芽1 d后开始计时,样品组每隔12 h喷施20 mL不同浓度的NaCl溶液(50、100、150、200、250、300 mmol/L),对照组每隔12 h喷施20 mL蒸馏水,分别于第2、4 d收获芽苗(预实验测得第6 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量较第4 d差异不大,为了短时高效提高芽苗产量及叶黄素含量,故选择发芽2、4 d继续进行实验),冲洗干净并用滤纸吸干水分,一部分样品保存于−80 ℃冰箱中用于测定干重、鲜重、含水率、丙二醛含量及抗氧化活性,另一部分样品经真空冷冻干燥,研磨成粉末并过60目筛后干燥保存,用于测定脯氨酸、可溶性蛋白、还原糖及叶黄素含量。
1.2.2 芽长测定
随机选取30株西兰花芽苗,用游标卡尺测量其芽长,取平均值。
1.2.3 鲜重测定
随机选取30株西兰花芽苗,准确测定其鲜重并取平均值。
1.2.4 干重测定
采用烘干恒重法[15]测定。随机选取10株西兰花芽苗,在105 ℃烘箱干燥30 min后,于80 ℃烘干至恒重,测定重量并取平均值。
1.2.5 含水率测定
含水率测定参照GB 5009.3-2016《食品中水分的测定》。
1.2.6 叶黄素含量测定
叶黄素的提取方法参考Luo等[16]方法并稍加修改。称取3.0 g冻干西兰花粉末,加入35 mL混合萃取液(正己烷-乙醇-丙酮-甲苯,10:6:7:7,v/v)暗处静置4 h,加入2 mL 40% 氢氧化钾-甲醇溶液充分摇匀,移至室温环境避光皂化16~18 h。将皂化液倒入分液漏斗中,依次加入30 mL正己烷、38 mL 10%硫酸钠溶液,摇匀后静置片刻,收集上层溶液,重复上述操作两次并合并所有上层溶液,于25 ℃旋转蒸发至溶液全干,加入2 mL正己烷溶解、氮气吹干,最后用1 mL甲醇复溶过膜后待液相色谱测定。
HPLC分析条件:YMC-C30色谱柱(4.6 mmol/L×250 mmol/L,5 μm);柱温:25 ℃;检测器:DAD;检测波长:450 nm;流速:0.6 mL/min;进样量:20 μL。流动相A由水:MTBE:甲醇=5:25:70(v/v/v)配比混合;流动相B由水:MTBE:甲醇=5:85:10(v/v/v)配比混合。梯度洗脱时间为0 min(95% A)~4.5 min(80% A)~12.5 min(50% A)~18 min(25% A)~24 min(5% A)~30 min(5% A)。
1.2.7 丙二醛含量测定
取5株西兰花芽苗,加入5 mL 5%三氯乙酸冰浴研磨,于10000 r/min离心20 min。取2 mL上清液加入2 mL 0.67%硫代巴比妥酸,混匀后于沸水浴加热30 min,冷却后于5000×g离心10 min,取上清液分别于450、532、600 nm 处测定吸光值。计算公式如下,式中W为样品鲜重(g)。
MDA含量(nmol/g FW)=5×[6.45×(A532 nm−A600 nm)−0.56×A450 nm] / W
1.2.8 脯氨酸含量测定
称取0.1 g冻干西兰花粉末,加入5 mL 3%磺基水杨酸,混匀后置于沸水浴10 min,取出后冷却至室温,10000×g离心10 min。吸取2 mL上清液,依次加入2 mL冰醋酸、2 mL 2.5%酸性茚三酮,振荡摇匀,再置于沸水中加热30 min,取出后冷却至室温,加入4 mL甲苯充分涡旋混匀,取出上清液于8000×g离心5 min,取上层红色溶液于520 nm处测定吸光值。
1.2.9 可溶性蛋白含量测定
称取2.0 g冻干西兰花粉末,加少量水在室温下振荡浸提1 h,8000×g离心20 min后取上清液,沉淀再次水提,操作同上,合并两次滤液,定容到50 mL。吸取3 mL滤液于具塞试管中,加入15 mL考马斯亮蓝G-250试剂摇匀,静置10 min后在595 nm处测定吸光值。
1.2.10 还原糖含量测定
称取3.0 g冻干西兰花粉末,加入50 mL蒸馏水搅拌均匀,于50 ℃恒温水浴中放置20 min,离心取出上清液,再向沉淀中加入20 mL蒸馏水,摇匀离心取出上清液并合并所有上清液,定容于100 mL容量瓶,此溶液即为待测液。将待测液适度稀释,吸取1 mL待测液于试管中,依次加入1 mL 50%乙醇、1.5 mL DNS试剂,摇匀后置于沸水中加热5 min,取出立即冷却,加蒸馏水至10 mL,静置20 min后在496 nm处测定吸光值。
1.2.11 抗氧化酶活性测定
取5株西兰花芽苗,加入预冷的5 mL 0.05 mol/L pH 7.0 磷酸盐缓冲液于冰浴中研磨。在4 ℃条件下10000×g离心10 min,上清液即为粗酶提取液。
SOD活性:参考徐东等[17]方法并加以修改。取粗酶提取液50 μL于试管中,依次加入1 mL 66.7 mmol/L pH7.8磷酸缓冲液,100 μL mmol/L盐酸羟胺、200 μL 7.5 mol/L黄嘌呤、200 μL 0.2 mg/mL黄嘌呤氧化酶、490 μL双蒸水,充分混匀后在37 °C下静置反应30 min,再加入2 mL 0.33%对氨基苯磺酸、2 mL 0.1%甲萘胺,在25 °C下静置反应10 min,于550 nm处测定吸光值。以抑制 NBT 光还原50%所需的酶量为1个酶活性单位(U),最终酶活性以U/g FW表示。
POD活性:采用愈创木酚氧化法[18]。取75 μL粗酶提取液于试管中,加10 mL 1%愈创木酚、10 mL 0.3% H2O2和100 mL 50 mmol/L pH6.5的磷酸缓冲液配制的混合液3 mL,随后每隔1 min记录470 nm处的吸光值。以每分钟吸光度增加0.01为1个酶活性单位(U),最终酶活性以U/g FW表示。
CAT:参考Bai等方法并加以修改[19]。取粗酶提取液50 μL,加入2 mL 由100 mmol/L pH7.0的磷酸缓冲液配制的0.1 mmol/L EDTA溶液,混匀后在25 ℃恒温水浴锅中放置5 min,随后加入1 mL 20 mmol/L H2O2溶液,每隔30 s记录470 nm处的吸光值。以每分钟吸光度减少0.01为1个酶活性单位(U),最终酶活性以U/g FW表示。
1.3 统计分析
试验各指标的测定设置3次重复,结果以平均值±标准差表示。试验数据的方差分析采用SPSS 25.0软件进行Duncan多重比较分析,在0.05水平上进行显著性检验。图表采用 Origin Pro 8.5软件绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗形态和重量的影响
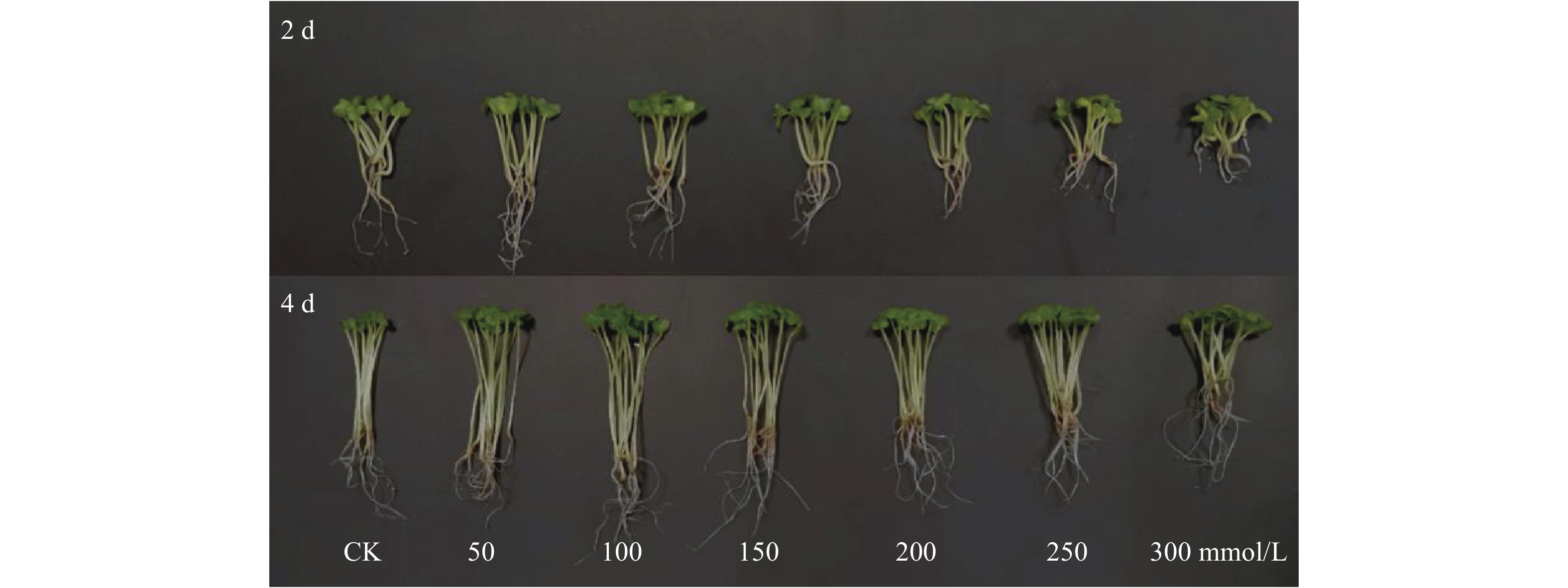
逆境胁迫下,芽苗的生长情况是反映其对胁迫响应最直观的指标。图1为不同浓度NaCl胁迫处理下西兰花芽苗的生长情况,数据详见表1。与对照组相比,低浓度NaCl处理对芽苗生长具有一定的促进作用,NaCl浓度为50和100 mmol/L时芽长较长且显著(P<0.05)长于对照组,增长最为显著,100 mmol/L处理第2、4 d收获的芽苗长度分别较对照组高20.24%和20.89%。随着NaCl浓度进一步增大,芽长逐渐降低,芽苗生长受到抑制。在西兰花芽苗生长期间,鲜重随NaCl浓度增大呈现先上升后下降的趋势,尤其在50~150 mmol/L NaCl处理下鲜重增长最多,尽管300 mmol/L NaCl抑制了芽苗根茎的伸长,但其根茎和子叶均发育明显,因此芽苗鲜重仍显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。第4 d收获的芽苗干重均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),第2 d收获的芽苗在200、250 mmol/L NaCl胁迫下其干重并无明显变化。综上所述,50、100 mmol/L NaCl可有效促进西兰花芽苗的生长,NaCl胁迫浓度大于200 mmol/L处理时虽然抑制了芽苗的伸长,但鲜重和干重仍有显著增加(P<0.05)。
表 1 不同NaCl浓度胁迫处理下西兰花芽苗芽长、鲜重、干重变化Table 1. Changes in sprouts length, fresh weight and dry weight of broccoli under different NaCl concentration stress发芽天数(d) NaCl浓度(mmol/L) 芽长(mm/株) 鲜重(mg/株) 干重(mg/株) 2 CK 12.73±1.26d 13.12±2.87b 1.78±0.17a 50 15.31±0.84f 17.74±2.56e 2.32±0.12d 100 13.47±1.13e 18.11±3.16e 2.36±0.09d 150 12.13±1.42cd 15.43±2.06d 2.03±0.15c 200 11.33±1.06c 12.15±1.83a 1.91±0.03ab 250 10.13±1.22b 13.10±2.32b 1.84±0.10a 300 8.80±0.72a 14.92±1.11c 2.01±0.13c 4 CK 36.07±2.87i 22.46±1.97e 1.85±0.05a 50 41.73±2.35j 47.95±3.22i 2.89±0.09g 100 43.60±3.15k 55.34±3.71k 3.12±0.16i 150 33.07±3.56h 53.31±3.50j 3.07±0.10h 200 30.73±1.52h 45.44±2.15h 2.62±0.18e 250 26.47±2.03g 44.52±3.20g 2.77±0.14f 300 22.94±2.27f 36.11±2.83f 2.64±0.06e 注:不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著。 2.2 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗含水率的影响
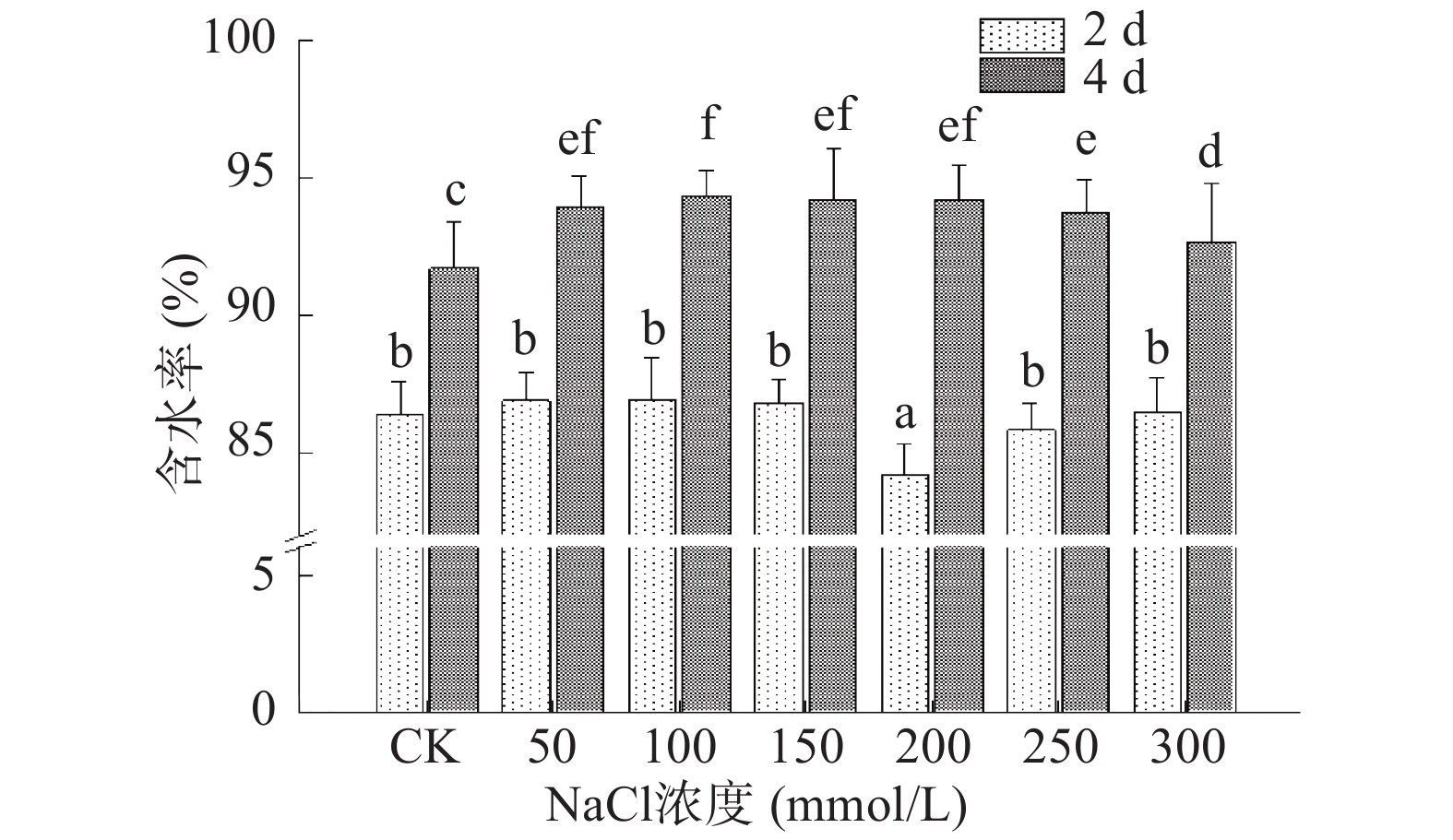
水分是保障芽苗自身生长及新陈代谢的基础物质,西兰花种子吸收水分开始萌发生长。图2显示,第2 d收获的芽苗含水率在200 mmol/L NaCl处理下显著下降,而其他处理组中芽苗含水率与对照组相比无显著性变化(P>0.05),含水率总体在86%左右浮动。相比之下第4 d收获的芽苗含水率与对照组相比上升明显,100 mmol/L NaCl处理下含水率最高,为94.36%,而后随NaCl浓度增大至300 mmol/L时,含水率又下降至92.69%,这可能是高浓度盐对芽苗产生渗透胁迫所致。
2.3 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗叶黄素含量的影响
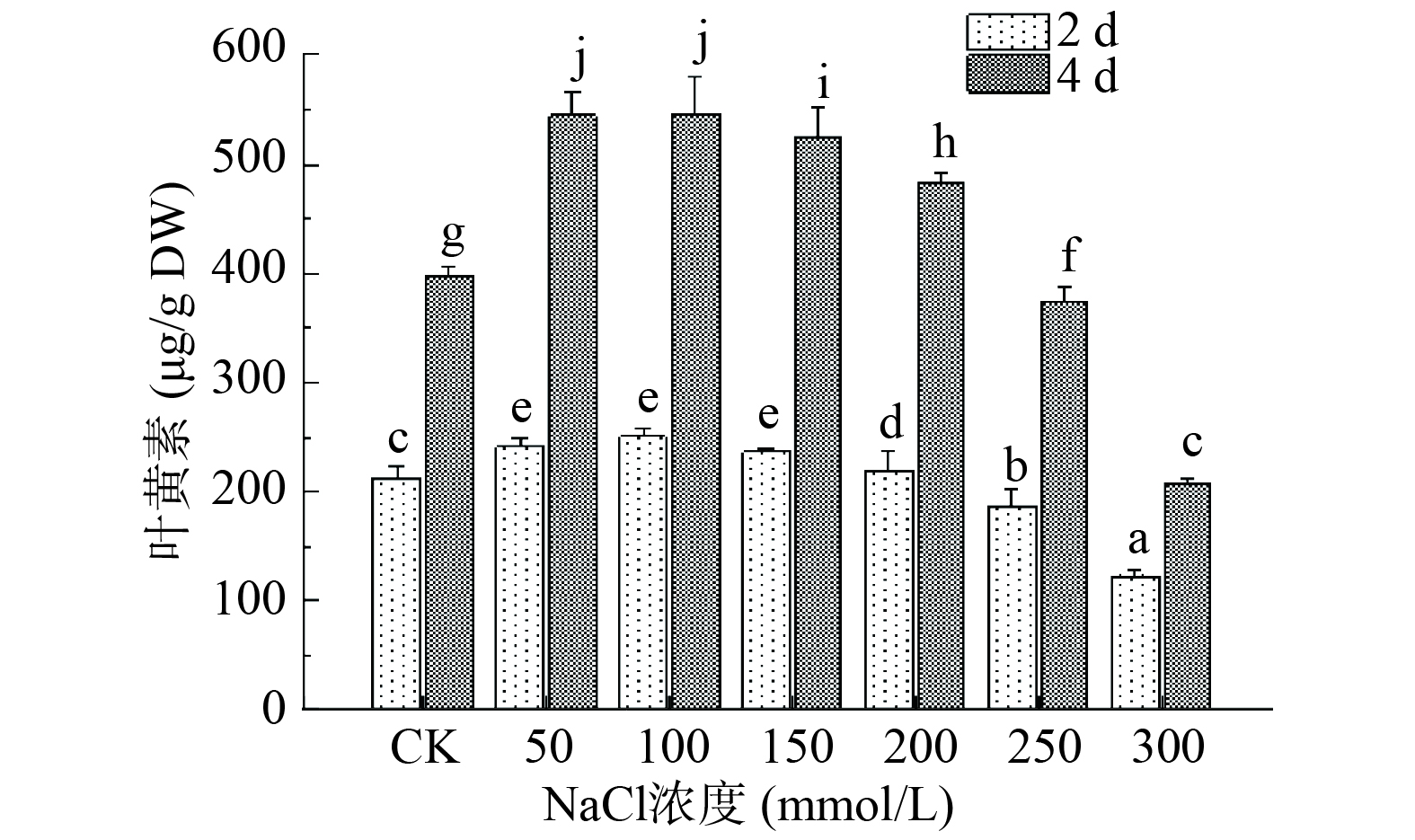
非生物胁迫通常会对植株造成不同程度的迫害作用,为抵御外界环境的影响,植株内通常会诱导释放一些次生代谢物质,叶黄素是绿叶蔬菜中一类丰富的次生代谢产物。由图3可知,随着NaCl浓度增大,第2、4 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量均呈现先升高后下降的趋势,可见中低浓度盐胁迫对西兰花芽苗中叶黄素的积累具有促进作用,以50和100 mmol/L NaCl处理的效果最好,在第2 d收获的芽苗中分别比对照组高13.53%、17.49%。第4 d收获的芽苗在100 mmol/L NaCl处理下测得叶黄素含量达546.25 μg/g,较对照组提高了37.54%。Guo等[20]对西兰花种子喷施NaCl后测得芽苗中酚类物质的含量显著升高,Wang等[21]在发芽的玉米籽粒中测得叶黄素含量随NaCl胁迫浓度增大呈现先增大后减小的趋势,并在300 mmol/L处理下得到最大值,这与本文研究结果趋为一致。NaCl胁迫浓度不变时,第4 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量与第2 d相比有明显增加(P>0.05),不同处理组两天间叶黄素含量积累了85.20~302.73 μg/g ,随着NaCl浓度由50 mmol/L增大至300 mmol/L,第4 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量分别是第2 d的2.25、2.18、2.21、2.21、1.99和1.72倍。以上结果说明在西兰花发芽初期其体内叶黄素含量是逐渐增加的,且适宜浓度的盐胁迫能够有效促进叶黄素含量的积累。
2.4 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗生理指标的影响
2.4.1 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗可溶性蛋白和还原糖含量的影响
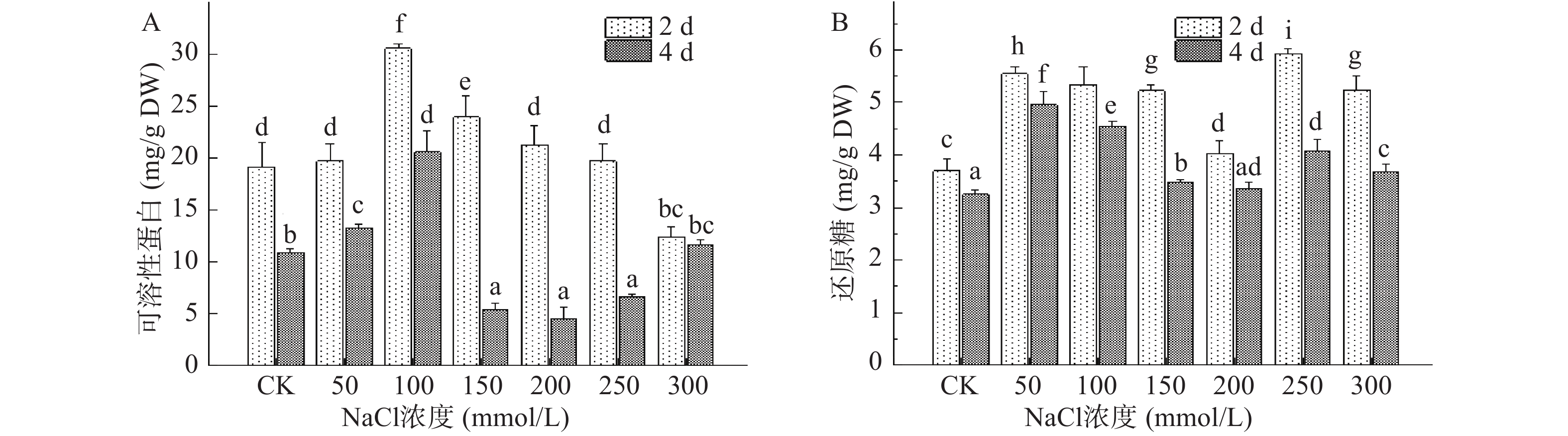
盐胁迫对植株造成最直接的迫害作用即为渗透胁迫,此时植株内的渗透调节物质在抵御逆境的过程中起到至关重要的作用。可溶性蛋白是植物体内重要的渗透调节物质之一,它能够有效贮存细胞水分,保护生物膜的完整性[22],同时它也是重要的营养物质,能够合成大分子蛋白质[23]。由图4A可知,在第2 d收获的芽苗中,可溶性蛋白含量随NaCl浓度增加呈现先上升后下降的趋势,与对照组相比,100 mmol/L NaCl处理下可溶性蛋白含量显著增加了59.37%,而300 mmol/L NaCl对可溶性蛋白的合成具有显著抑制作用(P<0.05)。随着芽苗继续生长,第4 d收获的芽苗在100 mmol/L NaCl处理下可溶性蛋白含量最高,比对照组高约65.00%,此时芽苗细胞具有较高的保水性,有效提高了芽苗细胞抵御盐胁迫的能力。当NaCl浓度为200 mmol/L时,可溶性蛋白含量降至为对照组的58.45%,随后芽苗中可溶性蛋白含量随NaCl浓度增大再次逐渐积累。以上表明,芽苗组织在盐胁迫下会通过释放和积累可溶性蛋白提高自身的代谢,此外其含量变化与植株内部物质的生成转化也有重要的联系,种子萌发时内部的淀粉、蛋白质等成分会在内源酶的作用下降解促进其他营养成分的积累[24-25]。
还原糖作为植物体内主要的渗透调节剂,它能够调节植物细胞的渗透势,保持胞内水分,保护膜的完整性以维持细胞正常的生理代谢。图4B为NaCl胁迫处理下西兰花芽苗中还原糖含量的变化,第2、4 d收获的芽苗均在50 mmol/L NaCl处理下出现首个峰值,分别达到5.54、4.96 mg/g DW,此结果与卞紫秀等[26]对荞麦芽苗的研究相一致。第2 d收获的芽苗在250 mmol/L NaCl处理下出现第二个峰值,较对照组增加了59.90%,许寅生等[27]研究干旱胁迫金莲花幼苗生长时也发现相似变化,高浓度盐胁迫促使还原糖积累以缓解芽苗细胞受到的损伤,此前杨涓等[28]研究发现NaCl胁迫还会影响植株体内糖代谢过程,本实验中高浓度NaCl胁迫延缓了芽苗的生长,此时还原糖消耗量相对减少,可能也是还原糖积累的原因之一。随着NaCl的浓度继增加,还原糖含量出现下降,可能是由于盐胁迫浓度过高使细胞膜受损严重,导致还原糖被分解消耗[29]。此外,第4 d收获的芽苗还原糖含量均高于对照组,50~300 mmol/L NaCl处理后分别提高了52.45%、40.05%、7.26%、3.38%、25.25%和13.01%,随胁迫天数的延长,还原糖含量出现下降,这可能是种子发芽初期对胁迫做出应激反应时被消耗过多,以及随芽苗生长需消耗还原糖等物质维持正常的光合作用和呼吸作用[26],因此导致还原糖含量有所减少。
2.4.2 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗丙二醛和脯氨酸含量的影响
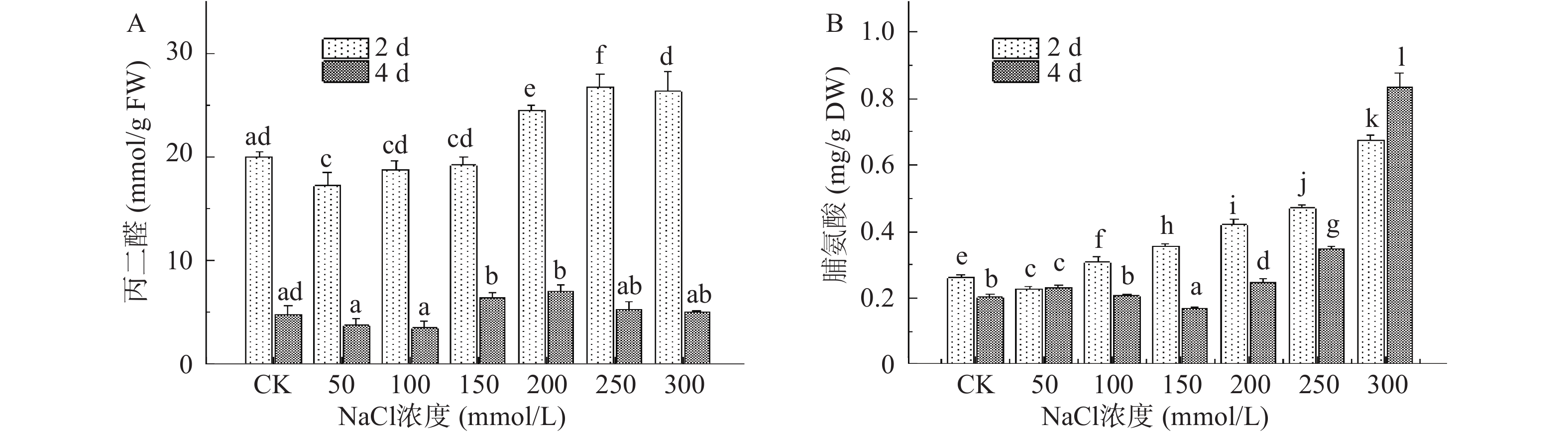
植物细胞在正常环境中生长时,其体内活性氧的代谢处于相对平衡的状态,然而在盐胁迫下活性氧的产生速度快于清除速度,过度积累的活性氧最终导致细胞膜系统受到损伤,MDA即为膜脂过氧化反应的终产物之一,因此常用作判定细胞膜氧化受损程度和植株耐盐性的重要指标[30]。图5A结果显示,MDA含量随NaCl胁迫程度加剧先升高后下降。100、150 mmol/L中低盐浓度下,第2 d收获的芽苗MDA含量与对照组间无显著性差异(P>0.05),当浓度增至200 mmol/L时MDA出现大量积累,并在250 mmol/L处理下达到峰值,较对照组增加了33.76%。MDA含量还与组织的自我保护能力存在负相关的关系[31],第4 d收获的芽苗MDA含量变化与第2 d基本一致,在低盐浓度处理下MDA含量从4.79 nmol/g下降至3.50 nmol/g,较对照组显著降低了36.86%(P<0.05),此时芽苗中产生大量的可溶性蛋白、还原糖及脯氨酸等物质,它们可作为渗透调节物质来调节细胞的渗透势,有效保护芽苗细胞免受盐胁迫的损害。NaCl浓度为200 mmol/L时,MDA含量达对照组的1.46倍,此时芽苗损伤严重,表现出相对较弱的抗逆性。随后MDA含量出现下降,相似的变化趋势在白杨幼苗中也被观察到[32],这可能由于盐浓度过高加剧细胞过氧化反应,导致膜结构损坏严重,也有学者将这种现象归因于高浓度NaCl胁迫致使植株细胞死亡,进而导致MDA被分解[33]。在相同的NaCl浓度下,第4 d收获的芽苗较第2 d的MDA含量有所下降,这可能是由于随着胁迫时间延长植株内部产生了相应的适应机制[34]。以上结果表明,芽苗在萌发初期对胁迫处理最为敏感,这一时期芽苗细胞膜脂过氧化程度最高,随盐胁迫程度加剧细胞膜损伤逐渐加重,过高盐浓度下丙二醛含量出现下降可能与细胞膜的稳定性和产生的渗透调节物质有关。
脯氨酸是植物体内存在的一种可以自身合成的小分子物质,通常情况其含量很低,但在逆境条件下会被迅速激活,具有稳定蛋白质和膜结构的作用[35],其含量变化可作为芽苗响应盐胁迫程度的一项指标[36]。图5B结果显示,NaCl胁迫处理能够显著促进芽苗中脯氨酸积累(P<0.05) ,尤其以高浓度盐处理最显著,200~300 mmol/L NaCl处理下,第4 d收获的芽苗中脯氨酸含量分别是对照组的1.22、1.71和4.11倍,第2 d收获的芽苗中脯氨酸含量分别是对照组的1.61、1.80和2.59倍,此外100 mmol/L和150 mmol/L NaCl处理也使2 d收获的芽苗中脯氨酸含量有显著提高(P<0.05)。此前Bai等[37]在马铃薯幼苗中发现脯氨酸的含量与NaCl胁迫程度呈正相关分布,穆旦等[22]也在研究中发现随盐胁迫浓度的增加溪荪和黄菖蒲叶片中脯氨酸含量总体呈上升的趋势,本研究中脯氨酸含量也呈现随NaCl胁迫浓度增加逐渐升高的趋势,说明芽苗受到渗透胁迫作用逐渐加剧,因此芽苗大量合成脯氨酸来增加植株对渗透胁迫的耐受性,进而调节机体细胞恢复到正常水平。
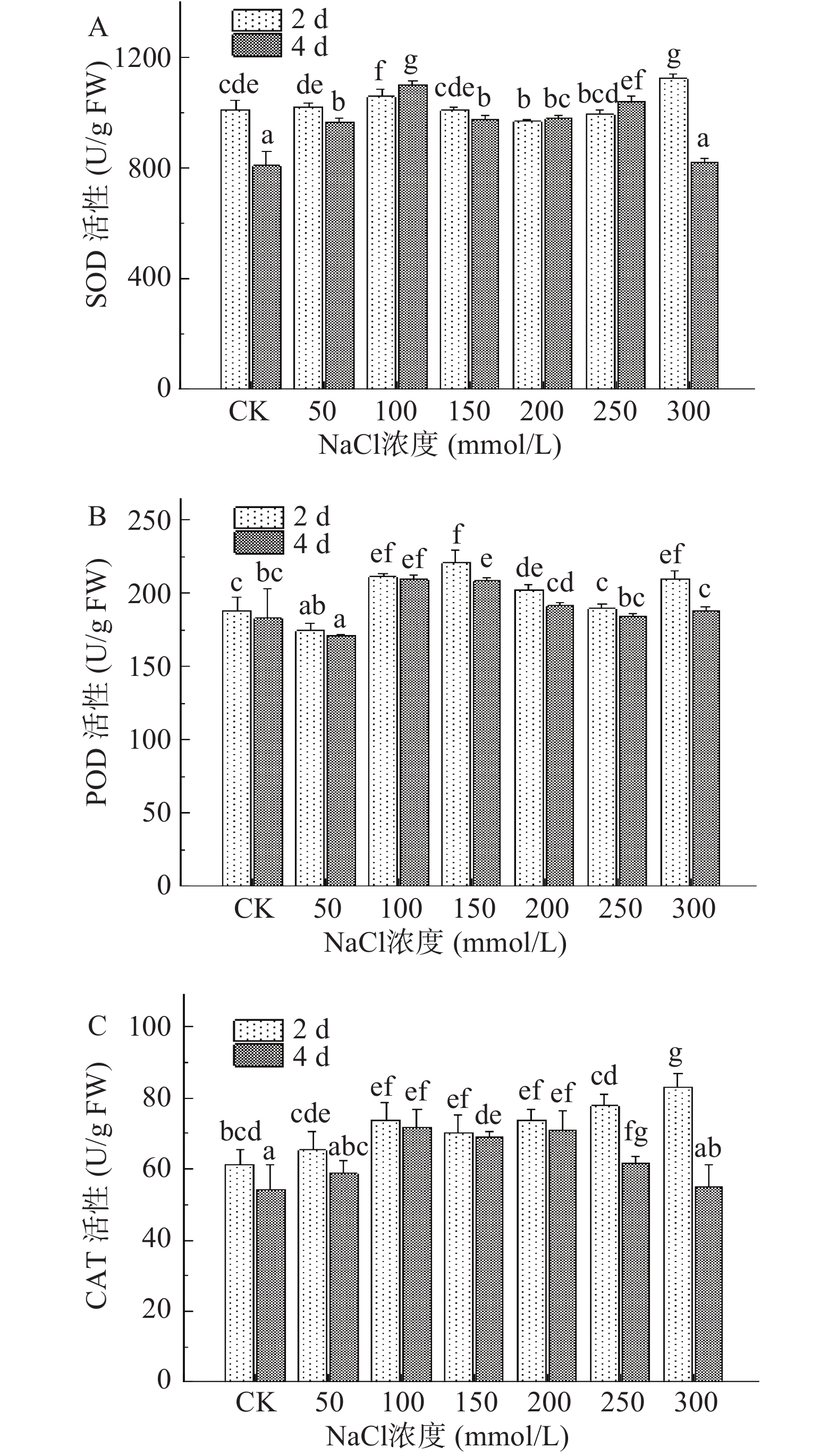
2.4.3 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗抗氧化酶活性的影响
盐胁迫下Na+和Cl−在植物体内大量积累,进而产生过量的活性氧,对细胞造成损害,为此芽苗细胞内会形成一种酶促保护系统以保护自身免受伤害[38]。SOD是其中重要的金属酶,它能够将超氧化物阴离子自由基分解成为过氧化氢和分子氧,修复由活性氧引起的氧化损伤[39],此外作为植物抗氧化的第一道防线,SOD被认为是维持细胞正常生理条件和应对氧化应激的关键酶。图6A结果显示,第2 d收获的芽苗SOD活性受盐胁迫浓度影响较小,仅在NaCl浓度为100 mmol/L较对照组显著增加了4.72%%(P<0.05) ,随后SOD活性逐渐增强,在300 mmol/L高浓度盐处理下达到最大值。第4 d收获的芽苗SOD活性随NaCl浓度增加总体呈先升高后降低的趋势,并且依次在100、250 mmol/L NaCl处理下表现出较强的活性,与对照组相比分别显著增加了36.14%和28.72%(P<0.05),300 mmol/L处理下SOD活性又再次降至与对照组相当。
POD和CAT进一步催化细胞内过氧化氢分解以防止氧化,维持细胞内活性氧的动态平衡[40]。由图6B可知,POD活性与SOD活性变化趋势相似,在100、150 mmol/L NaCl处理下,第2 d收获的芽苗POD活性分别是对照组的1.12和1.17倍,第4 d收获的芽苗POD活性分别是对照组的1.15和1.14倍。随着NaCl浓度由200 mmol/L增大至300 mmol/L,第4 d收获的芽苗POD活性略微减弱但并无显著性差异(P>0.05)。西兰花芽苗中CAT活性在不同处理条件下也存在差异(图6C),第2d收获的芽苗CAT活性随NaCl浓度增加逐渐增强,50~300 mmol/L NaCl处理下分别比对照组显著增加6.53%、20.11%、14.44%、20.19%、26.91%和35.39%(P<0.05) ,而在第4 d收获的芽苗中,CAT活性则随NaCl胁迫程度加剧先升高后降低,100 mmol/L NaCl处理下CAT活性最强,是对照组的1.32倍,此外150 mmol/L和200 mmol/L NaCl处理下CAT活性也显著高于对照组(P<0.05) ,但100、150和200 mmol/L这三组间差异并不明显(P>0.05)。
由此可见,NaCl胁迫处理有效提高了抗氧化酶的活性,SOD与CAT、POD相互协作,提升了西兰花芽苗细胞氧化防御能力,尤其在中度盐胁迫下,抗氧化酶活性均显著增强(P<0.05) ,芽苗中MDA含量显著降低(P<0.05) ,缓解了盐胁迫对芽苗细胞造成的损害。但同时高盐浓度下观察到抗氧化酶活性减弱,可能是其结构被破坏而导致防御能力下降,也有学者认为植物细胞在盐胁迫下的耐受性存在一个阈值,在一定范围内提高抗氧化酶活性能够有效缓解盐胁迫下细胞受损程度,但当超过该临界时抗氧化酶活性会受到抑制,无法发挥清除作用[32]。综合本研究各项指标,尽管盐胁迫增加了抗氧化酶活性和具有渗透调节功能的小分子物质的含量,但MDA含量仍处于较高水平,说明高浓度盐胁迫给西兰花芽苗细胞带来的损伤较为严重且难以恢复,在提高抗性方面,应结合多种氧化清除剂的功效,相互协同作用以增强芽苗细胞的抗逆性。
2.5 NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗叶黄素含量与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析
通过对NaCl胁迫处理下西兰花芽苗叶黄素含量与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析,如表2和表3所示,第2 d收获的芽苗叶黄素含量与可溶性蛋白含量和CAT活性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与脯氨酸含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与SOD活性呈显著负相关(P<0.05),同时POD和CAT两种抗氧化酶之间也呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。在第4 d收获的芽苗中,叶黄素含量与SOD、CAT活性呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与脯氨酸含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),此外,丙二醛含量与还原糖和可溶性蛋白含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与POD活性呈显著正相关(P<0.05),脯氨酸含量分别与SOD、POD活性呈极显著负相关和极显著正相关(P<0.01),综上,叶黄素含量与抗氧化酶活性及氧化损伤程度之间有密切的联系,可以推断,芽苗通过脯氨酸的释放与积累调节抗氧化酶活性增强,进而保护盐胁迫下芽苗细胞生理生化正常代谢进程。
表 2 NaCl胁迫处理2 d的西兰花芽苗叶黄素积累与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析Table 2. Correlation analysis of lutein accumulation, related physiological indexes and antioxidant enzyme activity of broccoli sprouts harvested 2 d after NaCl stress treatment指标 叶黄素 还原糖 可溶性蛋白 丙二醛 脯氨酸 SOD POD CAT 叶黄素 1 还原糖 −0.081 1 可溶性蛋白 0.781** 0.089 1 丙二醛 −0.297 −0.015 −0.153 1 脯氨酸 −0.882** 0.209 −0.557** 0.381 1 SOD −0.526* 0.287 −0.288 −0.361 0.502* 1 POD −0.093 −0.005 0.271 −0.020 0.394 0.269 1 CAT 0.554** 0.400 −0.244 0.346 0.802** 0.431 0.469* 1 注:*表示相关性在0. 05水平达到显著,**表示相关性在0. 01水平达到极显著;表3同。 表 3 NaCl胁迫处理4 d的西兰花芽苗叶黄素积累与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of lutein accumulation, related physiological indexes and antioxidant enzyme activity of broccoli sprouts harvested 4 d after NaCl stress treatment指标 叶黄素 还原糖 可溶性蛋白 丙二醛 脯氨酸 SOD POD CAT 叶黄素 1 还原糖 0.425 1 可溶性蛋白 0.205 0.626** 1 丙二醛 −0.149 −0.686** −0.808** 1 脯氨酸 −0.865** −0.109 0.037 −0.026 1 SOD 0.626** 0.543* 0.192 0.120 −0.462* 1 POD 0.253 −0.195 0.104 0.165 −0.178 0.407 1 CAT 0.566** 0.093 −0.014 0.260 −0.408 0.674** 0.508* 1 3. 结论
本文研究了不同浓度NaCl胁迫处理对西兰花芽苗生理生化指标、叶黄素含量及抗氧化能力的影响,结果表明,随着NaCl处理浓度的增大,芽苗的芽长、重量先增大后减小,高浓度盐胁迫下芽苗生长受到显著抑制作用。芽苗中渗透调节物质可溶性蛋白、还原糖、脯氨酸等均随NaCl胁迫浓度变化而变化,以维持芽苗细胞正常的代谢功能。研究发现中低浓度的NaCl是西兰花芽苗富集叶黄素的最佳胁迫条件,当浓度为100 mmol/L时,第4 d收获的芽苗中叶黄素含量最高,达到546.25 μg/g,比对照组增加了37.54%,该条件下SOD、POD、CAT抗氧化酶活性较对照组分别增加了36.26%、14.62%、32.34%。此外芽苗的鲜重、可溶性蛋白、还原糖含量较对照组也均显著提高。同时发现叶黄素与脯氨酸共同协作能够有效应对盐胁迫环境,主要是通过调节脯氨酸含量可以提高芽苗在盐分胁迫下的适应程度。综上所述,通过100 mmol/L NaCl胁迫处理西兰花种子发芽4 d可作为提高西兰花芽苗叶黄素含量的一种方式,并为开发功能性西兰花芽苗食品提供理论参考。
-
表 1 不同NaCl浓度胁迫处理下西兰花芽苗芽长、鲜重、干重变化
Table 1 Changes in sprouts length, fresh weight and dry weight of broccoli under different NaCl concentration stress
发芽天数(d) NaCl浓度(mmol/L) 芽长(mm/株) 鲜重(mg/株) 干重(mg/株) 2 CK 12.73±1.26d 13.12±2.87b 1.78±0.17a 50 15.31±0.84f 17.74±2.56e 2.32±0.12d 100 13.47±1.13e 18.11±3.16e 2.36±0.09d 150 12.13±1.42cd 15.43±2.06d 2.03±0.15c 200 11.33±1.06c 12.15±1.83a 1.91±0.03ab 250 10.13±1.22b 13.10±2.32b 1.84±0.10a 300 8.80±0.72a 14.92±1.11c 2.01±0.13c 4 CK 36.07±2.87i 22.46±1.97e 1.85±0.05a 50 41.73±2.35j 47.95±3.22i 2.89±0.09g 100 43.60±3.15k 55.34±3.71k 3.12±0.16i 150 33.07±3.56h 53.31±3.50j 3.07±0.10h 200 30.73±1.52h 45.44±2.15h 2.62±0.18e 250 26.47±2.03g 44.52±3.20g 2.77±0.14f 300 22.94±2.27f 36.11±2.83f 2.64±0.06e 注:不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上差异显著。 表 2 NaCl胁迫处理2 d的西兰花芽苗叶黄素积累与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of lutein accumulation, related physiological indexes and antioxidant enzyme activity of broccoli sprouts harvested 2 d after NaCl stress treatment
指标 叶黄素 还原糖 可溶性蛋白 丙二醛 脯氨酸 SOD POD CAT 叶黄素 1 还原糖 −0.081 1 可溶性蛋白 0.781** 0.089 1 丙二醛 −0.297 −0.015 −0.153 1 脯氨酸 −0.882** 0.209 −0.557** 0.381 1 SOD −0.526* 0.287 −0.288 −0.361 0.502* 1 POD −0.093 −0.005 0.271 −0.020 0.394 0.269 1 CAT 0.554** 0.400 −0.244 0.346 0.802** 0.431 0.469* 1 注:*表示相关性在0. 05水平达到显著,**表示相关性在0. 01水平达到极显著;表3同。 表 3 NaCl胁迫处理4 d的西兰花芽苗叶黄素积累与相关生理指标、抗氧化酶活性的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of lutein accumulation, related physiological indexes and antioxidant enzyme activity of broccoli sprouts harvested 4 d after NaCl stress treatment
指标 叶黄素 还原糖 可溶性蛋白 丙二醛 脯氨酸 SOD POD CAT 叶黄素 1 还原糖 0.425 1 可溶性蛋白 0.205 0.626** 1 丙二醛 −0.149 −0.686** −0.808** 1 脯氨酸 −0.865** −0.109 0.037 −0.026 1 SOD 0.626** 0.543* 0.192 0.120 −0.462* 1 POD 0.253 −0.195 0.104 0.165 −0.178 0.407 1 CAT 0.566** 0.093 −0.014 0.260 −0.408 0.674** 0.508* 1 -
[1] Sakr M T, Ibrahim H M, Elawady A E, et al. Growth, yield and biochemical constituents as well as post-harvest quality of water-stressed broccoli (Brassica oleraceae L. var. italica) as affected by certain biomodulators[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2021,275:109605. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109605
[2] 王慧倩, 郑聪, 王华东, 等. 乙醇熏蒸处理对鲜切西兰花活性成分和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(16):250−254. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201416048 [3] Maia M, Furlani B A, Souza-Lima A A, et al. Lutein: A new dye for chromovitrectomy[J]. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa.),2014,34(2):262−272. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3182a0b7f4
[4] 郭俊杰, 季绍东, 邹世杰, 等. 不同类型叶黄素对高温条件下黄羽肉鸡生长性能及着色效果的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2020:1−8. [5] Yuan H, Zhang J, Nageswaran D, et al. Carotenoid metabolism and regulation in horticultural crops[J]. Horticulture Research,2015,2(1):15036. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2015.36
[6] Farnham M W, Kopsell D A. Importance of genotype on carotenoid and chlorophyll levels in broccoli heads[J]. HortScience,2009,44(5):1248−1253. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.44.5.1248
[7] 李诺, 钟秋平, 陈文学, 等. 乙醇-硫酸铵双水相萃取黄秋葵叶中的叶黄素[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(17):167−172. [8] Bartalné-Berceli M, Izsó E, Gergely S, et al. Sprouting of soybean: A natural process to produce unique quality food products and additives[J]. Quality Assurance and Safety of Crops & Foods,2016,8(4):519−538.
[9] Gan R, Lui W, Wu K, et al. Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of germinated edible seeds and sprouts: An updated review[J]. Trends in food science & technology,2017,59:1−14.
[10] Linić, I Šamec, D Grúz, et al. Involvement of phenolic acids in short-term adaptation to salinity stress is species-specific among brassicaceae[J]. Plants (Basel),2019,8(6):155.
[11] 田璐, 吴嘉琪, 李昕悦, 等. NaCl与CaCl2处理对西兰花芽苗硫苷和异硫氰酸盐含量的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报,2017,40(2):352−358. doi: 10.7685/jnau.201610002 [12] Wang M, Cai C, Lin J, et al. Combined treatment of epi-brassinolide and NaCl enhances the main phytochemicals in Chinese kale sprouts[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,315:126275. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126275
[13] Ariviani S, Fiyan M R, Ishartani D, et al. Antioxidant capacity and germination power of NaCl-elicited cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) sprouts with various NaCl concentrations and elicitation durations[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2020,518(1):012020 (7pp).
[14] Lim J, Park K, Kim B, et al. Effect of salinity stress on phenolic compounds and carotenoids in buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum M.) sprout[J]. Food Chemistry, 2012, 135(3): 1065-1070.
[15] 谷娇娇, 胡博文, 贾琰, 等. 盐胁迫对水稻根系相关性状及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志,2019(4):176−182. [16] Luo H, He W, Li D, et al. Effect of methyl jasmonate on carotenoids biosynthesis in germinated maize kernels[J]. Food Chem,2020,307:125525. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125525
[17] 徐东, 赵建, 黄汉昌, 等. 改良的黄嘌呤氧化酶法测定动植物组织中SOD比活力[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(6):237−241. [18] Hammerschmidt R, Nuckles E M, Kuć J. Association of enhanced peroxidase activity with induced systemic resistance of cucumber to Colletotrichum lagenarium[J]. Physiological Plant Pathology,1982,20(1):73−82. doi: 10.1016/0048-4059(82)90025-X
[19] Bai Q, Chai M, Gu Z, et al. Effects of components in culture medium on glutamate decarboxylase activity and γ-aminobutyric acid accumulation in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) during germination[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,116(1):152−157. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.022
[20] Guo L, Yang R, Wang Z, et al. Effect of NaCl stress on health-promoting compounds and antioxidant activity in the sprouts of three broccoli cultivars[J]. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition,2013,65(4):476−481.
[21] Wang Y, He W, Li D, et al. Response surface optimization of culture conditions for improving lutein content in NaCl-stressed germinated corn kernels[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2019,43(10):523−531.
[22] 穆丹, 梁英辉, 姚丹丹, 等. 龙凤湿地2种湿生花卉对盐胁迫的生理响应[J]. 西部林业科学,2020,49(3):49−55. [23] 王泳超, 郑博元, 顾万荣, 等. γ-氨基丁酸对盐胁迫下玉米幼苗根系氧化损伤及内源激素的调控[J]. 农药学学报,2018,20(5):607−617. [24] Martinez-Villaluenga C, Peñas E, Ciska E, et al. Time dependence of bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity during germination of different cultivars of broccoli and radish seeds[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,120(3):710−716. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.067
[25] Kuo Y, Rozan P, Lambein F, et al. Effects of different germination conditions on the contents of free protein and non-protein amino acids of commercial legumes[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,86(4):537−545. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.09.042
[26] 卞紫秀, 马辉, 汪建飞, 等. 超声结合NaCl处理对苦荞麦萌发及芽苗主要成分的影响[J]. 安徽工程大学学报,2019,34(5):8−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0977.2019.05.002 [27] 许寅生, 孟文秀, 郭亚丽. 金莲花幼苗对不同强度干旱胁迫的生理响应[J]. 农业科技通讯,2018(6):171−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6400.2018.06.058 [28] 杨涓, 许兴, 魏玉清, 等. 盐胁迫对枸杞果实糖代谢及相关酶的影响[J]. 宁夏农学院学报,2004(3):28−31. [29] 白晓霞, 龚晔. 水稻幼苗对渗透胁迫的响应[J]. 陕西农业科学,2020,66(7):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2020.07.004 [30] Abouelsaad I, Renault S. Enhanced oxidative stress in the jasmonic acid-deficient tomato mutant def-1 exposed to NaCl stress[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology,2018,226:136−144. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2018.04.009
[31] 米永伟, 王国祥, 龚成文, 等. 盐胁迫对菘蓝幼苗生长和抗性生理的影响[J]. 草业学报,2018,27(6):43−51. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017282 [32] Ji J, Shi Z, Xie T, et al. Responses of GABA shunt coupled with carbon and nitrogen metabolism in poplar under NaCl and CdCl2 stresses[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2020,193:110322. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110322
[33] 杨佳鑫, 李庆卫, 郭子燕, 等. 3个梅花品种幼苗耐盐性综合评价[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(8):65−74. [34] 孙伟泽, 韩博, 胡晓宁, 等. 不同浓度盐胁迫下苜蓿丙二醛含量变化[J]. 安徽农业科学,2009,37(5):1905−1906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.05.020 [35] Verbruggen N, Hermans C. Proline accumulation in plants: A review[J]. Amino Acids,2008,35(4):753−759. doi: 10.1007/s00726-008-0061-6
[36] 王宁, 袁美丽. 入侵植物节节麦种子萌发及幼苗生长对盐碱胁迫的响应[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,44(5):167−173. [37] Bai J, Gao H, Yang H, et al. Comparison of ultrastructural and physiological changes of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plantlets subjected to salt and modeling drought stresses[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2016,38(7):1−9.
[38] Qiu Z, Li J, Zhang M, et al. He-Ne laser pretreatment protects wheat seedlings against cadmium-induced oxidative stress[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2013,88:135−141. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.11.001
[39] Lang D, Yu X, Jia X, et al. Methyl jasmonate improves metabolism and growth of NaCl-stressed Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2020,266:109287. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109287
[40] Türkan İ, Bor M, Özdemir F, et al. Differential responses of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaves of drought-tolerant P. acutifolius Gray and drought-sensitive P. vulgaris L. subjected to polyethylene glycol mediated water stress[J]. Plant Science (Limerick),2005,168(1):223−231. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.07.032
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 马雪莹,刘璐璐,陆佩瑶,张思佳,白心怡,冯永巍,黄晓东. 基于血糖管理的特殊食品开发进展分析. 现代食品. 2024(02): 116-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张素敏,崔艳,陈振家,王晓闻. 压热改性对黄米淀粉多尺度结构及理化性质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(18): 80-87 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 马天琛,张津铭,张诺,张竞文,常丹妮,曹炜. 糜子抗性淀粉的制备及其在食品中的应用研究进展. 食品研究与开发. 2024(22): 212-217 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郭硕,刘景圣,郑明珠. 热处理过程中食品组分与淀粉相互作用研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(01): 17-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邵颖,刘晓媛,魏宗烽,李坤. 板栗RS_3型抗性淀粉的制备方法筛选及其压热法制备工艺优化. 粮食与油脂. 2023(11): 100-104+114 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
