Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Deer Bone Polypeptide by Response Surface Method and Its Antioxidant Activity in Vitro
-
摘要: 目的:筛选鹿骨蛋白最适提取温度和最佳酶解工艺并检测其抗氧化活性。方法:根据鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度筛选出最适提取温度,根据水解度(DH)通过单因素及响应面实验设计筛选鹿骨多肽的最佳酶解工艺,并通过测定鹿骨多肽对DPPH自由基、羟自由基的清除能力来评价鹿骨多肽的抗氧化活性。结果:最佳提取温度为95 ℃,通过响应面法优化及实际验证确定了胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶最佳酶解工艺分别为胃蛋白酶酶用量6200 U/g,温度37.3 ℃,pH2.0,时间3.2 h,此时的水解度为11.23%;胰蛋白酶酶用量6300 U/g,温度37.2 ℃,pH8.1,时间4.0 h,此时的水解度为23.09%。鹿骨多肽对DPPH自由基、羟自由基具有清除能力,其IC50值分别为:3.72、2.24 mg/mL。结论:本实验得到了鹿骨蛋白最佳提取温度并确定鹿骨多肽最佳酶解工艺,且鹿骨多肽对DPPH自由基、羟自由基具有良好的清除能力,说明鹿骨多肽具有良好的抗氧化活性。Abstract: Objective: To screen the optimal extraction temperature and optimal enzymatic hydrolysis process of deer bone protein and detect its antioxidant activity. Method: According to the protein concentration of deer bone protein, the optimal extraction temperature was selected. According to the degree of hydrolysis (DH), the optimal enzymatic hydrolysis process of deer bone polypeptide was screened through single factor and response surface experiment design, and the antioxidant activity of deer bone polypeptide was evaluated by measuring DPPH· and ·OH scavenging ability of deer bone polypeptide. Results: The optimal extraction temperature was 95 ℃. The optimal digestion process for pepsin and trypsin was determined by response surface method optimization and actual verification as the amount of pepsin enzyme 6200 U/g, temperature 37.3 ℃, pH2.0, and time 3.2 h, the degree of hydrolysis at this time was 11.23%; the amount of trypsin was 6300 U/g, the temperature was 37.2 ℃, the pH was 8.1, and the time was 4.0 h, the degree of hydrolysis at this time was 23.09%. Deer bone polypeptide had scavenging ability to DPPH· and ·OH free radicals, and its IC50 values were 3.72 and 2.24 mg/mL, respectively. Conclusion: The best extraction temperature and optimal enzymatic hydrolysis process of deer bone protein are obtained. Deer bone protein has a good scavenging ability on DPPH· and ·OH free radicals, indicating that deer bone polypeptide has good antioxidant activity.
-
Keywords:
- deer bone /
- peptide /
- enzymatic hydrolysis /
- antioxidant activity
-
近年来,生物活性肽由于在代谢调节中具有非常重要的作用而倍受关注,并且也越来越多的被用作功能性食品成分、保健食品和药物,以改善人体健康并预防疾病[1]。鹿骨是鹿科动物梅花鹿(Cervus hortulorum)或马鹿(Cervus elaphus)的骨骼,含有大量的优质蛋白,对人体无毒副作用,具有广泛的药理活性和医用保健功能,能补肾壮阳,祛风除湿,对体弱、精髓不足、风湿、四肢疼痛有较好的疗效,可作为天然活性蛋白多肽的可靠来源[2-5]。有研究表明,多肽在抗氧化方面具有优异的活性,是天然的抗氧化剂,能预防或减轻人体氧化应激引发的衰老、免疫疾病及其他各类疾病[6-10]。鹿骨多肽是鹿骨蛋白经过酶解得到的产物,因其比鹿骨蛋白水溶性更好,更易被人体吸收一直备受关注[11]。张鹤等[12-16]发现梅花鹿胶原蛋白、鹿骨胶原蛋白、猪骨多肽、鳕鱼骨蛋白肽、马面鱼骨胶原混合肽均具有良好的抗氧化活性。本文选用对鹿骨蛋白进行双酶酶解的方式得到鹿骨多肽,并基于鹿骨多肽的水解度,通过响应面法筛选出胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶的最佳酶解工艺,验证其抗氧化活性,为今后鹿骨多肽的开发与利用提供了理论依据。
本文首先利用热水抽提法提取鹿骨胶,然后采用硫酸铵盐析法提取出提取液中的蛋白,并根据在不同提取温度条件下蛋白浓度的多少筛选出最优的提取温度。然后将蛋白依次用胃、胰蛋白酶水解,通过单因素及响应面实验设计,根据水解度(DH)筛选鹿骨多肽的最佳酶解工艺,并检测双酶酶解后的多肽的体外抗氧化功能,以期为鹿骨多肽的应用提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鹿骨 吉林市向阳鹿厂;抗坏血酸(VC)、硫酸铵、水杨酸 天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;BCA试剂盒、Folin-酚试剂盒、胃蛋白酶(1:3000)、胰蛋白酶(1:250) 北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH) 东京化成工业株式会社;硫酸亚铁 辽宁泉瑞试剂公司。
Eppendorf台式离心机冷冻干燥机 美国SP Scientific-Vritis BenchTop Pro;Infinite M200型酶标仪 瑞士TECAN集团公司;Five Easy plus型pH计 瑞士Mettler Toledo;5430R低温高速离心机 美国Eppendorf公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鹿骨蛋白制备及酶解工艺
除去鹿骨上肉、筋膜等非骨物质,在石油醚中脱脂后挥干,在0.5 mol/L的HCl中脱钙并采用EDTA滴定法测定酸液中的钙含量[17]。确定完成脱钙后用水洗至中性,室温干燥处理后将脱脂脱钙骨在一定温度下,料液比为1:10条件下提取3 h,提取三次,合并提取液,在4 ℃的温度条件下缓慢加入硫酸铵粉末至终浓度达到80%,在4.0×103 r/min的条件下离心15 min后将沉淀复溶,用透析袋透析除盐24 h,冷冻干燥得到鹿骨蛋白粉末。在底物浓度(蛋白质量与溶液体积的比)为4%,酶用量、温度、pH和时间一定时进行胃蛋白酶酶解,冷冻干燥得到的蛋白粉末再进行胰蛋白酶酶解,底物浓度为4%,酶用量、温度、pH一定,酶解一定时间后将样品放入沸水中煮15 min,终止酶解,并进行冷冻干燥得到鹿骨多肽粉末。
1.2.2 鹿骨蛋白提取温度的筛选
在上述条件下,设置提取温度分别为65、95、121 ℃,其中65 ℃为鹿骨胶原蛋白变性的临界温度[18],95 ℃下提取的鹿骨蛋白具有良好的抗氧化活性,121 ℃为药典中鹿骨成药鹿骨多肽的提取温度,以提取所得鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度为指标筛选最佳提取温度。鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度测定方法:利用BCA试剂盒对鹿骨蛋白含量进行检测。蛋白标准曲线为Y=0.00056X+0.02607(R2=0.99549),并比较三种温度提取鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度,筛选出最佳提取温度。
1.2.3 胃蛋白酶酶解鹿骨蛋白工艺的响应面优化
前期进行了单因素实验,在底物浓度为4%的条件下,依次改变酶用量、酶解温度、pH、酶解时间根据水解度变化得到单因素实验结果。在单因素实验基础上,以水解度为衡量标准,如表1所示,设计4因素3水平响应面分析实验。
表 1 响应面分析法优化胃蛋白酶解工艺Table 1. Optimization of pepsin hydrolysis process by response surface methodology因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 酶用量(U/g) X1 4000 5500 7000 温度(℃) X2 34 37 40 pH X3 1.5 2.0 2.5 时间(h) X4 2 3 4 1.2.4 胰蛋白酶酶解鹿骨蛋白工艺的响应面优化
取胃蛋白酶酶解后的蛋白冻干粉末,用胰蛋白酶继续水解。前期进行了单因素实验,在底物浓度为4%的条件下,依次改变酶用量、酶解温度、pH、酶解时间根据水解度变化得到单因素实验结果。在单因素实验基础上,以水解度为衡量标准,如表2所示,设计4因素3水平响应面分析实验。
表 2 响应面分析法优化胰蛋白酶解工艺Table 2. Optimization of trypsin hydrolysis process by response surface methodology因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 酶用量(U/g) X1 4500 6000 7500 温度(℃) X2 34 37 40 pH X3 7.0 8.0 9.0 时间(h) X4 3 4 5 1.2.5 水解度的测定
取鹿骨蛋白酶解液3 mL加入等体积的10%三氯乙酸(TCA)溶液,充分混匀,切断蛋白的肽链,静置30 min,在4.0×103 r/ min的条件下离心15 min,取上清液,用BCA试剂盒对游离态氮的含量进行测定[19]。
DH(%)=N1−N0N2−N0×100 式中:DH:水解过程中被裂解的肽键数与给定蛋白质的总肽键数之比;N0:蛋白质水解前上清液中TCA可溶性氮含量(mol/L);N1:蛋白水解后上清液TCA可溶性氮含量(mol/L);N2:蛋白总氮含量(mol/L)。
1.2.6 鹿骨多肽抗氧化性的测定
1.2.6.1 DPPH自由基清除率的测定
吸取不同浓度样品100 μL于96孔板中,加入100 μL 0.2 mmol/L DPPH溶液,充分摇匀并避光处理,于25 ℃的条件下孵育30 min,在517 nm处测定吸光度值抗坏血酸为阳性对照药,每组各做3个平行样,避光操作[20-22]。
清除率(%)=(1−Ai−AjA0−A空白)×100 式中:Ai:加入样品和DPPH的吸光度值;Aj:加入样品和无水乙醇的吸光度值;A0:加入水和DPPH的吸光度值;A空白:加入水和无水乙醇的吸光度值。
1.2.6.2 羟自由基清除率的测定
在96孔板中加入50 μL不同浓度样品,并依次吸取H2O2溶液、FeSO4溶液均50 μL于96孔板中,避光摇匀10 min,再加入50 μL水杨酸启动反应,于37 ℃的条件下孵育30 min,510 nm处测定吸光度值,抗坏血酸为阳性对照药;每组各做3个平行样[23-24]。
清除率(%)=(1−Ai−AjA0)×100 式中:Ai:加入样品+FeSO4+H2O2+水杨酸的吸光度值;Aj:加入样品+FeSO4+水+水杨酸的吸光度值;A0:水+FeSO4+ H2O2+水杨酸吸光度值。
1.3 数据处理
各组数据均采用Graphpad Prism 7.0进行分析处理,Design Experts 8.0.6进行分析,结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 提取温度对鹿骨蛋白提取效果的影响
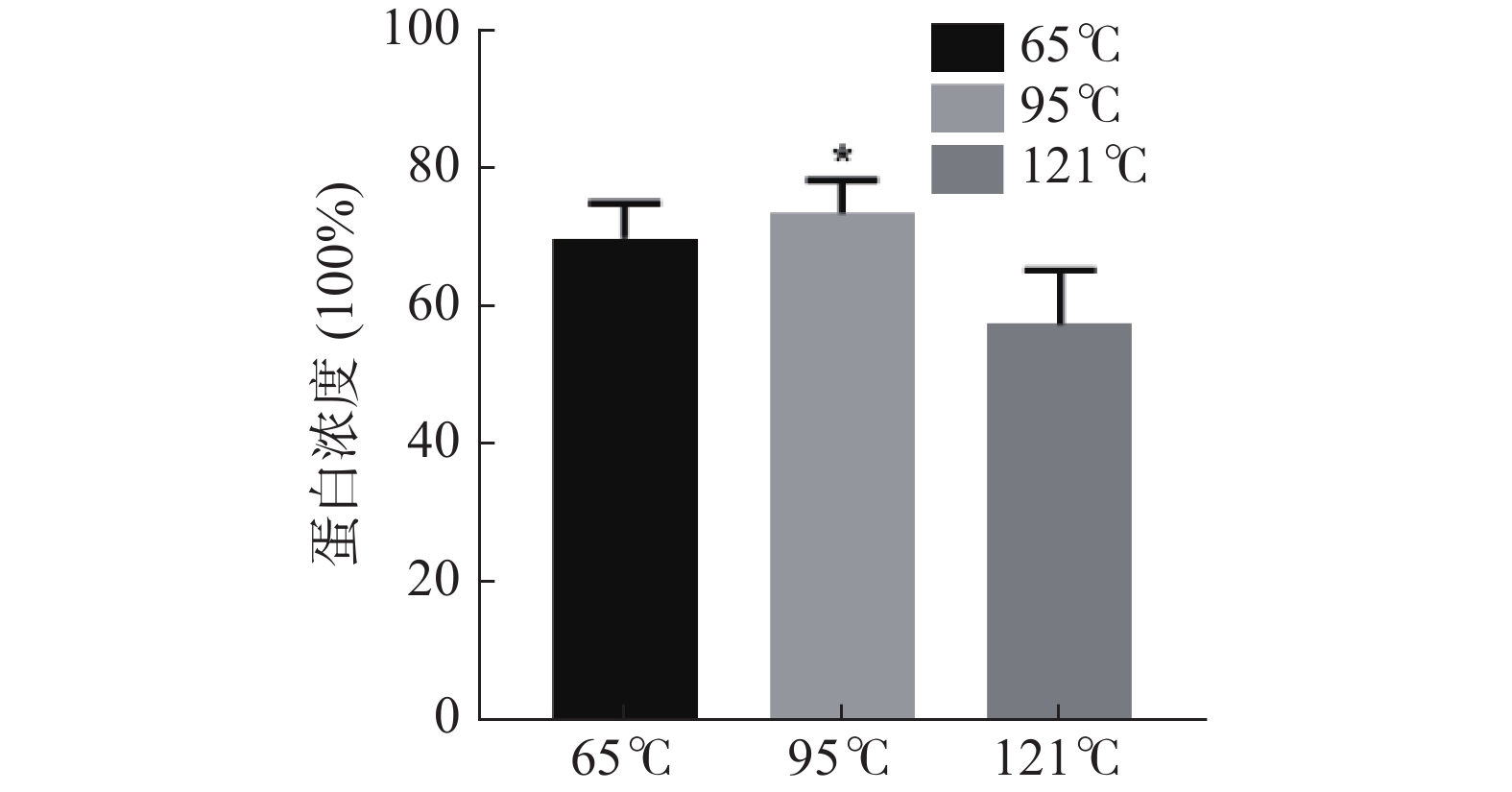
提取温度在蛋白提取过程中具有很重要的影响,提取温度过高时蛋白可能失去分子活性,提取温度过低,则提取不完全,因此选择最适的蛋白提取温度至关重要[25]。三种温度提取鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度结果如图1所示,最佳提取温度为95 ℃,此时鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度最高,达到73.43%,高于121 ℃和65 ℃时提取出的鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度57.53%和69.87%,且此条件下提取所得的蛋白浓度高于郭冰洁等[26]121 ℃提取的鹿骨蛋白的蛋白浓度(51.2%),所以确定95 ℃为最佳提取温度。
2.2 胃蛋白酶水解工艺优化结果
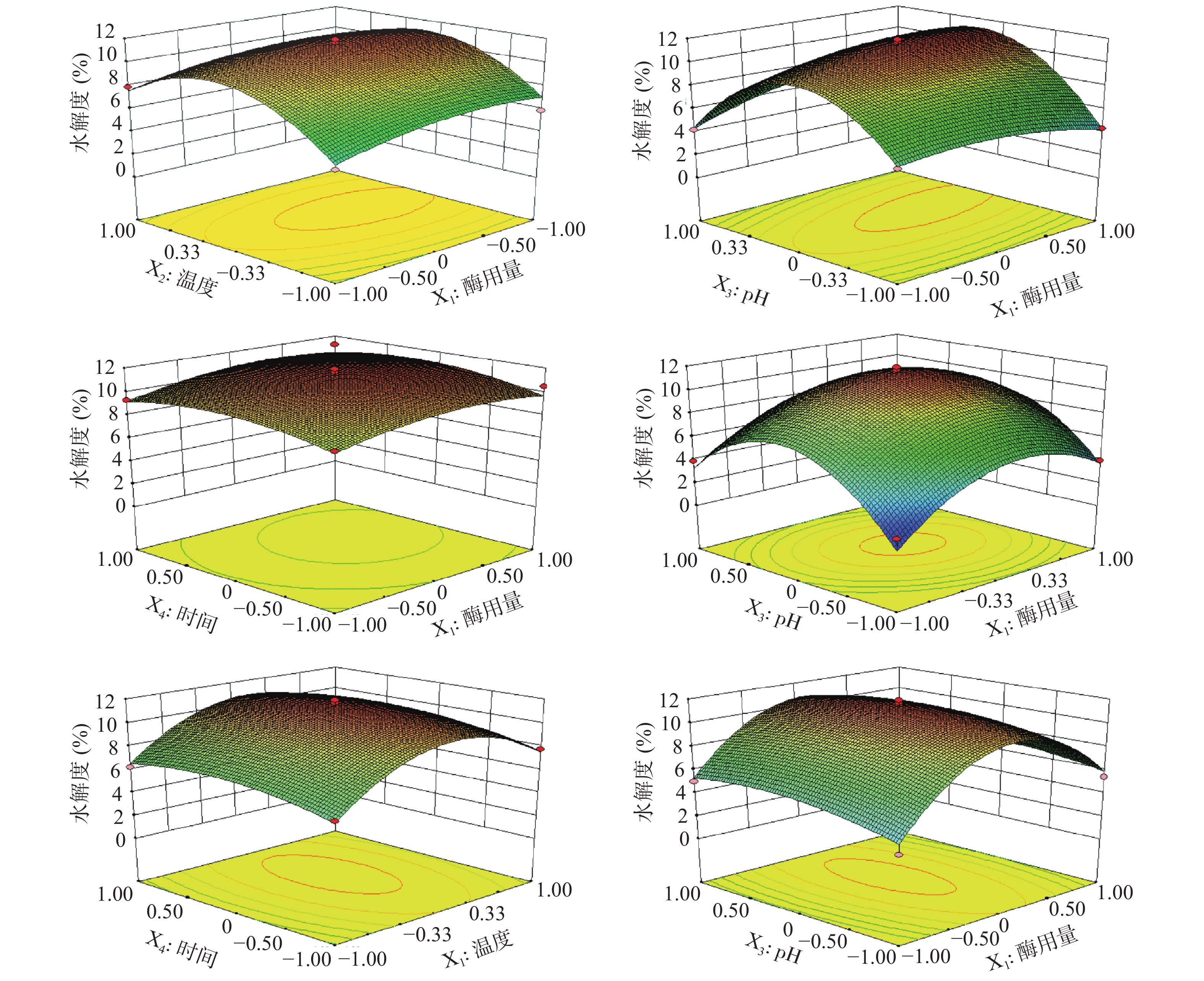
本研究在单因素实验结果基础上,利用多元二次回归方程拟合因素与响应值之间的函数关系,通过对回归方程的分析解决多变量问题,寻求最佳酶解工艺[27-29],前期实验得到胃蛋白酶水解单因素最佳条件为:酶用量5500 U/g,温度37 ℃,pH2.0,时间3 h。根据响应面结果表3及方差分析结果表4可知,模型P<0.0001,F=34.93,且失拟项P=0.1759>0.05,说明模型高度显著,拟合度较高,理论值与实际值呈一定的相关性(R2=0.9722),模型调整系数RAdj2=0.9443,说明该模型可以解释94.43%的响应值变化,所得实验结果真实可靠。同时,X1对响应面值有显著的影响(P<0.05),X2、X3、X1X3、X12、X22、X32和X42对响应面值都有极显著的影响(P<0.01)。各因素影响程度依次为:温度>pH>酶用量>时间。建立了二次多项回归模型:
表 3 响应面设计方案及结果Table 3. Design and results of response surface experiment试验号 X1 X2 X3 X4 水解度(%) 1 0 1 0 1 7.89 2 1 0 0 −1 10.46 3 0 1 0 −1 7.79 4 0 1 1 0 3.78 5 −1 0 1 0 4.23 6 1 0 0 1 11.23 7 0 −1 0 −1 5.98 8 0 0 0 0 10.89 9 0 0 1 1 6.09 10 0 0 −1 1 5.03 11 1 0 −1 0 4.34 12 1 0 1 0 7.92 13 −1 1 0 0 7.89 14 0 0 0 0 11.12 15 1 −1 0 0 5.89 16 0 −1 0 1 6.28 17 0 0 −1 −1 3.39 18 0 0 0 0 11.89 19 0 1 −1 0 3.96 20 0 0 0 0 11.69 21 0 0 1 −1 5.43 22 1 1 0 0 7.89 23 −1 0 −1 0 5.34 24 0 0 0 0 10.93 25 −1 0 0 −1 8.88 26 −1 0 0 1 9.28 27 0 −1 −1 0 2.03 28 0 −1 1 0 3.92 29 −1 −1 0 0 5.23 表 4 响应面回归方程方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of response surface regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 模型 226.39 14 16.17 34.93 < 0.0001 ** X1 3.94 1 3.94 8.52 0.0112 * X2 8.12 1 8.12 17.54 0.0009 ** X3 4.42 1 4.42 9.54 0.0080 ** X4 1.25 1 1.25 2.70 0.1229 X1X2 0.11 1 0.11 0.24 0.6352 X1X3 5.50 1 5.50 11.88 0.0039 ** X1X4 0.03 1 0.03 0.07 0.7897 X2X3 1.07 1 1.07 2.31 0.1505 X2X4 1.00E-02 1 1.00E-02 0.02 0.8852 X3X4 0.24 1 0.24 0.52 0.4833 X12 4.53 1 4.53 9.79 0.0074 ** X22 72.45 1 72.45 156.49 < 0.0001 ** X32 160.59 1 160.59 346.89 < 0.0001 ** X42 5.76 1 5.76 12.43 0.0034 ** 残差 6.48 14 0.46 2.70 0.1759 失拟检验 5.64 10 0.56 纯误差 0.84 4 0.21 总误差 232.87 28 R2=0.9722 RAdj2=0.9443 Y=−631.58558+2.51311E−003X1+28.69450X2+86.46200X3+7.23200X4−3.66667E−005X1X2+1.56333E−003X1X3+6.16667E−005X1X4−0.34500X2X3−0.016667X2X4−0.49000X3X4−3.71444E−007X12−0.37133X22−19.90300X32−0.94200X42。
响应面的坡度可以直观地呈现出反应条件对响应值的敏感度。由图2可知,酶用量、温度、pH对水解度均有显著的影响,在各因素水平范围内,酶用量与pH具有极显著的交互作用(P<0.01),与酶用量相比,pH对水解度影响程度更大,酶用量与时间对水解度影响较小,且二者交互作用不明显。温度与pH对水解度影响较大,酶解时间对水解度的影响较小。
通过对回归模型分析,得出最大水解度为11.52%,胃蛋白酶最佳工艺为:酶用量6121.05 U/g,温度37.31 ℃,pH2.05,时间3.18 h。为进一步确定鹿骨多肽酶解工艺的最佳条件,对各试验参数进行优化,得到胃蛋白酶最佳工艺为:6200 U/g,温度37.3 ℃,pH2.0,时间3.2 h,重复3次进行验证,实际水解度值为11.23%。与理论值非常接近,证明应用响应面法优化胃蛋白酶酶解工艺方法可行、可靠。
2.3 胰蛋白酶水解工艺优化结果
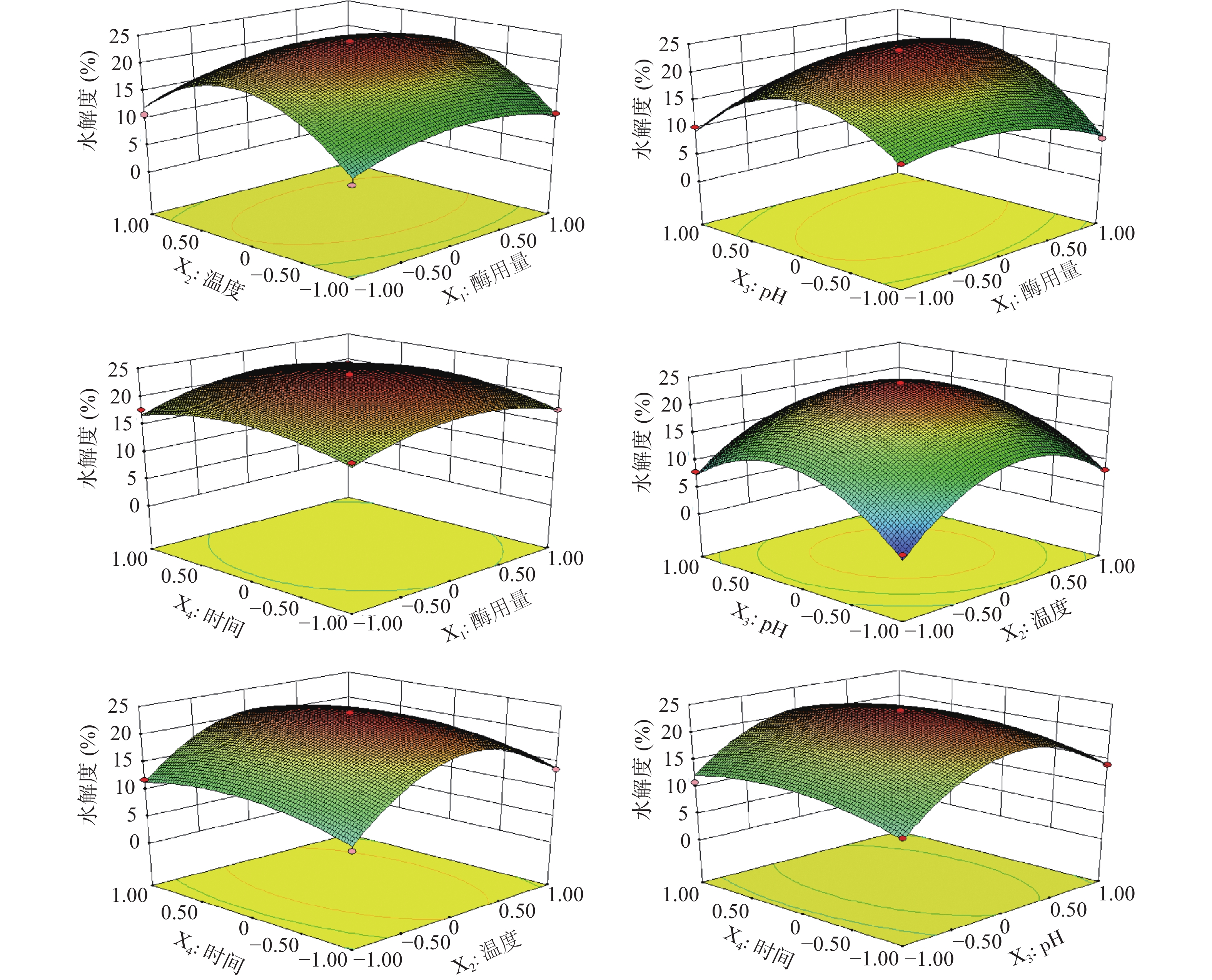
前期实验得到胰蛋白酶水解单因素最佳条件为:酶用量6000 U/g,温度37 ℃,pH8.0,时间4 h。由响应面结果表5及方差分析结果表6可知,模型P<0.0001,F=60.75,且失拟度P=0.1192 > 0.05,说明该模型高度显著,且拟合度较高,理论值与实际值呈一定的相关性(R2=0.9838),模型调整系数RAdj2=0.9676,说明该模型可以解释96.76%的响应值变化,所得实验结果真实可靠。同时,X1和X2X3对响应面值有显著的影响(P<0.05),X2、X3、X1X3、X12、X22、X32和X42对响应面值都有极显著的影响(P<0.01)。各因素影响程度依次为:温度>pH>酶用量>时间。建立了二次多项回归模型:
表 5 响应面设计方案及结果Table 5. Design proposal and experiment result of response surface试验号 X1 X2 X3 X4 水解度(%) 1 0 0 0 0 23.92 2 −1 −1 0 0 7.89 3 1 0 0 1 19.23 4 0 0 −1 −1 10.43 5 0 0 1 −1 13.98 6 1 0 0 −1 17.62 7 0 −1 0 −1 8.79 8 1 0 1 0 16.98 9 0 0 0 0 22.67 10 −1 0 0 1 17.72 11 0 0 −1 1 10.93 12 0 1 −1 0 8.23 13 0 1 1 0 8.12 14 0 1 0 1 14.72 15 0 −1 −1 0 3.32 16 0 −1 1 0 7.98 17 0 0 0 0 22.68 18 0 −1 0 1 11.86 19 −1 1 0 0 10.76 20 0 0 0 0 23.72 21 −1 0 −1 0 12.98 22 −1 0 1 0 10.18 23 0 0 1 1 12.09 24 0 1 0 −1 13.62 25 1 1 0 0 13.93 26 −1 0 0 −1 17.09 27 1 −1 0 0 10.75 28 0 0 0 0 23.69 29 1 0 −1 0 7.99 表 6 响应面回归方程方差分析Table 6. Response surface regression equation analysis of variance方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 模型 881.87 14 62.99 60.75 < 0.0001 ** X1 8.13 1 8.13 7.85 0.0142 * X2 29.42 1 29.42 28.38 0.0001 ** X3 19.89 1 19.89 19.19 0.0006 ** X4 2.10 1 2.10 2.03 0.1766 X1X2 0.02 1 0.02 0.02 0.8812 X1X3 34.75 1 34.75 33.52 < 0.0001 ** X1X4 0.24 1 0.24 0.23 0.6378 X2X3 5.69 1 5.69 5.49 0.0345 * X2X4 0.97 1 0.97 0.94 0.3498 X3X4 1.43 1 1.43 1.38 0.2601 X12 68.27 1 68.27 65.85 < 0.0001 ** X22 483.99 1 483.99 466.79 < 0.0001 ** X32 439.67 1 439.67 424.05 < 0.0001 ** X42 44.67 1 44.67 43.08 < 0.0001 ** 残差 14.52 14 1.04 3.50 0.1192 失拟检验 13.03 10 1.30 纯误差 1.49 4 0.37 总误差 896.38 28 R2=0.9838 RAdj2=0.9676 Y= −2004.99972+8.41000E−004X1 +75.27883X2+138.32300X3+31.28650X4+1.72222E−005X1X2+1.96500E−003X1X3+1.63333E−004X1X4−0.39750X2X3−0.16417X2X4−0.59750X3X4−1.44189E−006X12−0.95978X22−8.23300X32−2.62425X42。
由图3可知,因素水平范围内,酶用量、温度、pH对水解度均有显著的影响,酶用量与pH具有显著的交互作用(P<0.01),温度与pH具有显著的交互作用(P<0.05),酶用量与时间交互作用很小。与酶用量相比,pH对水解度影响程度更大。总之,酶解时间与酶用量对水解度影响较小,温度和pH对水解度影响较大。
通过对回归模型分析,得出最大水解度为23.55%,胰蛋白酶最佳工艺为:酶用量6263.47 U/g,温度37.25 ℃,pH8.10,时间4.07 h。为进一步确定鹿骨多肽酶解工艺的最佳条件,对各试验参数进行优化,得到胰蛋白酶实际最佳工艺为:酶用量6300 U/g,温度37.2 ℃,pH8.1,时间4.0 h,重复3次进行验证,实际水解度值为23.09%,与理论值接近,说明该模型可获得胰蛋白酶水解工艺的最优条件。
2.4 鹿骨多肽体外抗氧化结果
2.4.1 鹿骨多肽对DPPH自由基的清除能力
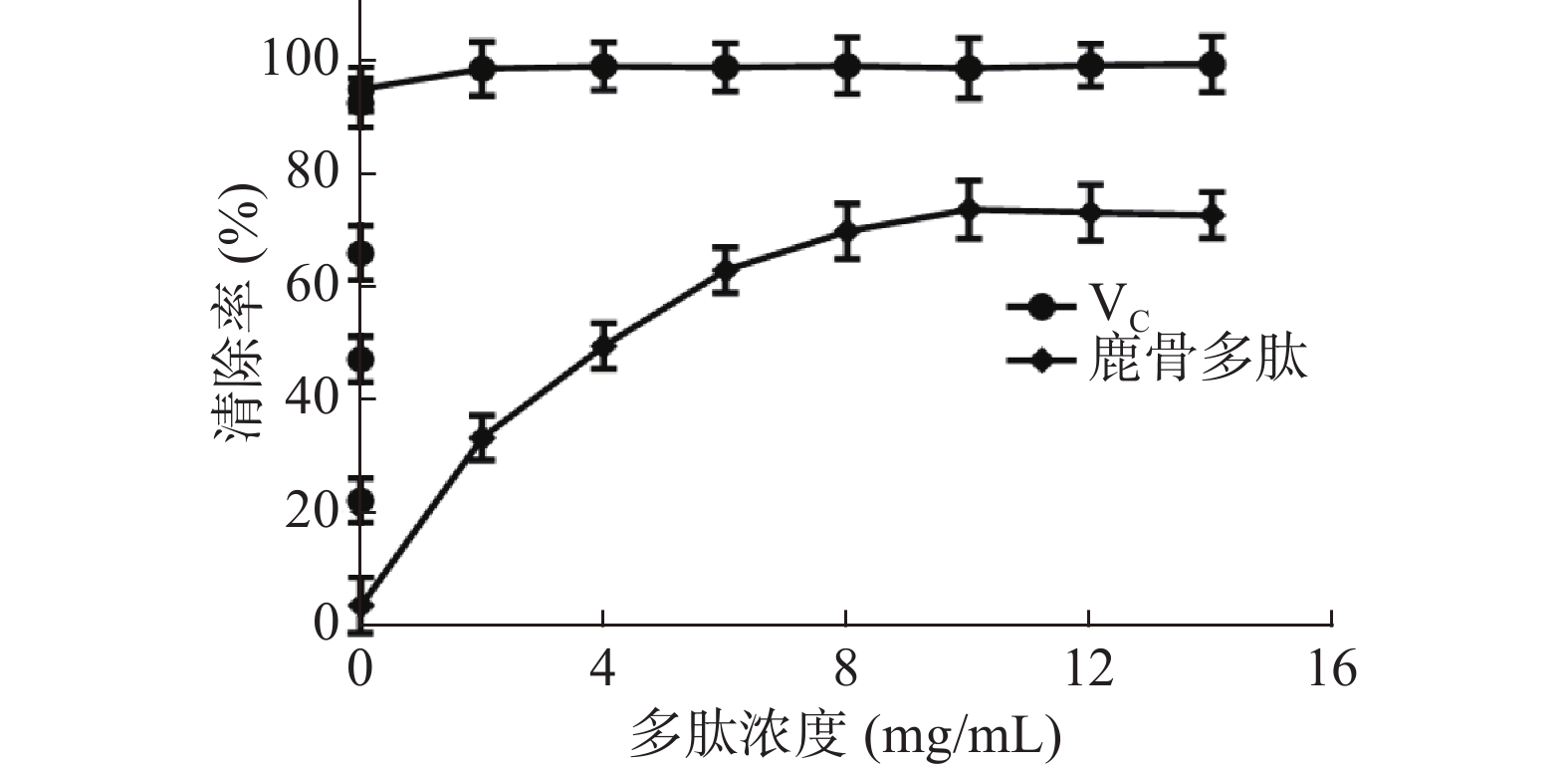
鹿骨多肽可有效的清除试验体系中的DPPH自由基,VC水溶液对DPPH的清除效果非常显著,如图4,与VC相比,鹿骨多肽在0~6 mg/mL清除率与鹿骨多肽浓度呈剂量依赖关系,随鹿骨多肽浓度增加,清除率迅速升高,6~10 mg/mL时,清除率增加趋于平缓,鹿骨多肽浓度为10 mg/mL时,最大清除率为74.63%,其IC50=3.72 mg/mL。
2.4.2 鹿骨多肽对羟自由基的清除能力
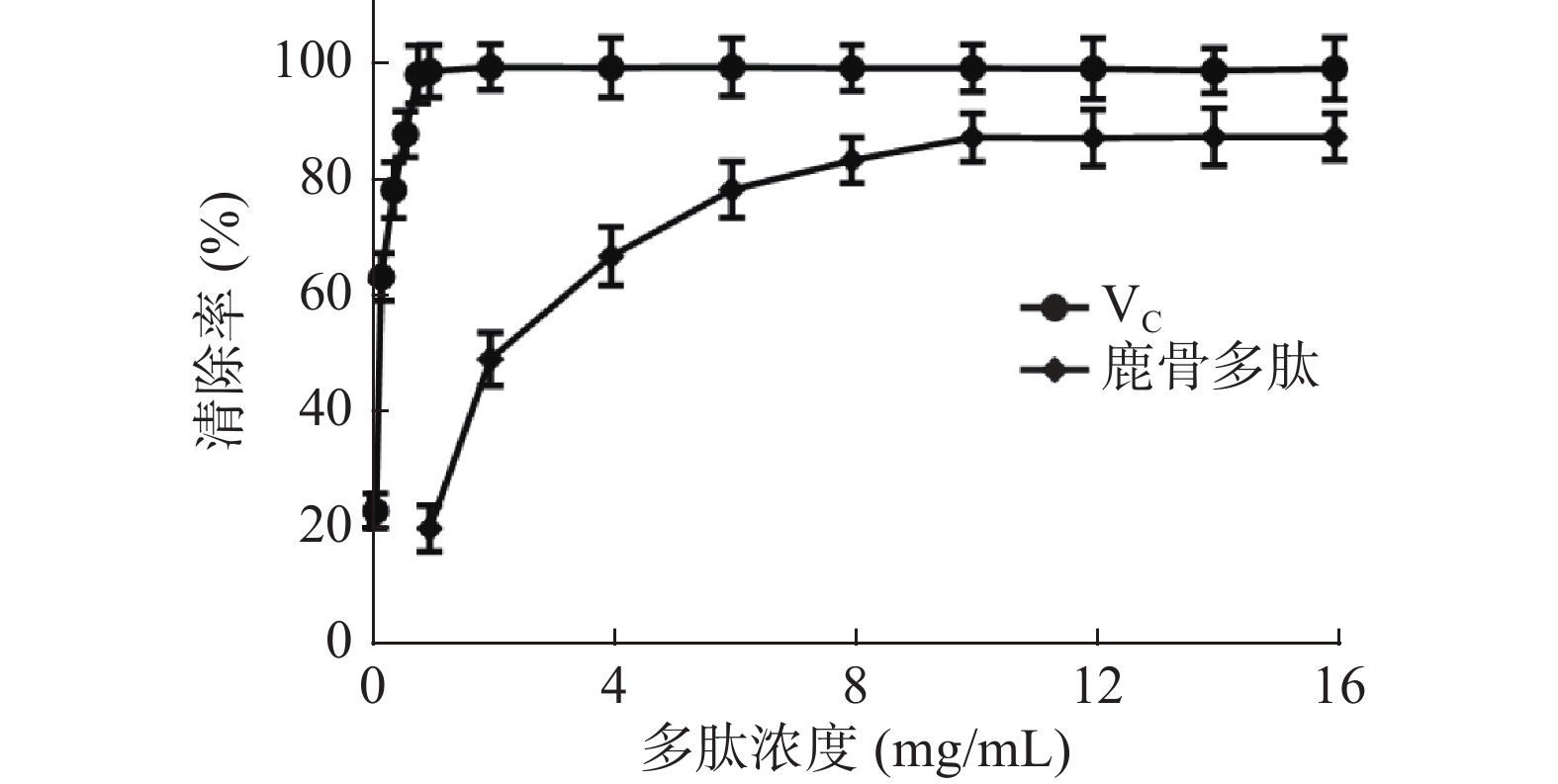
鹿骨多肽对试验体系中的羟自由基有显著的清除作用(P<0.05),如图5所示,VC水溶液对DPPH的清除效果非常显著,与VC相比,当鹿骨多肽质量浓度小于4 mg/mL时,随着鹿骨多肽浓度增加,羟自由基的清除率迅速升高;当浓度大于4 mg/mL时,清除率平缓升高,在10 mg/mL时达最大清除率87.02%,其IC50=2.24 mg/mL。
3. 结论
在本研究中,在提取温度为95 ℃时,鹿骨蛋白中的蛋白浓度最高,达到73.43%。通过对胃蛋白酶水解工艺进行响应面优化及实际验证确定了胃蛋白酶酶解最佳工艺为:6200 U/g,温度37.3 ℃,pH2.0,时间3.2 h,此时的实际水解度值为11.23%。同法优化胰蛋白酶最佳工艺及实际验证确定了在酶用量6300 U/g,温度37.2 ℃,pH8.1,时间4.0 h的条件下胰蛋白酶酶解最佳,其实际水解度值为23.09%。并通过体外抗氧化实验表明,鹿骨多肽对DPPH自由基、羟自由基具有良好的清除能力,在一定范围内,对自由基的清除能力呈剂量依赖关系,其IC50值依次为:3.72、2.24 mg/mL,说明鹿骨多肽具有良好的抗氧化活性。
-
表 1 响应面分析法优化胃蛋白酶解工艺
Table 1 Optimization of pepsin hydrolysis process by response surface methodology
因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 酶用量(U/g) X1 4000 5500 7000 温度(℃) X2 34 37 40 pH X3 1.5 2.0 2.5 时间(h) X4 2 3 4 表 2 响应面分析法优化胰蛋白酶解工艺
Table 2 Optimization of trypsin hydrolysis process by response surface methodology
因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 酶用量(U/g) X1 4500 6000 7500 温度(℃) X2 34 37 40 pH X3 7.0 8.0 9.0 时间(h) X4 3 4 5 表 3 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 3 Design and results of response surface experiment
试验号 X1 X2 X3 X4 水解度(%) 1 0 1 0 1 7.89 2 1 0 0 −1 10.46 3 0 1 0 −1 7.79 4 0 1 1 0 3.78 5 −1 0 1 0 4.23 6 1 0 0 1 11.23 7 0 −1 0 −1 5.98 8 0 0 0 0 10.89 9 0 0 1 1 6.09 10 0 0 −1 1 5.03 11 1 0 −1 0 4.34 12 1 0 1 0 7.92 13 −1 1 0 0 7.89 14 0 0 0 0 11.12 15 1 −1 0 0 5.89 16 0 −1 0 1 6.28 17 0 0 −1 −1 3.39 18 0 0 0 0 11.89 19 0 1 −1 0 3.96 20 0 0 0 0 11.69 21 0 0 1 −1 5.43 22 1 1 0 0 7.89 23 −1 0 −1 0 5.34 24 0 0 0 0 10.93 25 −1 0 0 −1 8.88 26 −1 0 0 1 9.28 27 0 −1 −1 0 2.03 28 0 −1 1 0 3.92 29 −1 −1 0 0 5.23 表 4 响应面回归方程方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of response surface regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 模型 226.39 14 16.17 34.93 < 0.0001 ** X1 3.94 1 3.94 8.52 0.0112 * X2 8.12 1 8.12 17.54 0.0009 ** X3 4.42 1 4.42 9.54 0.0080 ** X4 1.25 1 1.25 2.70 0.1229 X1X2 0.11 1 0.11 0.24 0.6352 X1X3 5.50 1 5.50 11.88 0.0039 ** X1X4 0.03 1 0.03 0.07 0.7897 X2X3 1.07 1 1.07 2.31 0.1505 X2X4 1.00E-02 1 1.00E-02 0.02 0.8852 X3X4 0.24 1 0.24 0.52 0.4833 X12 4.53 1 4.53 9.79 0.0074 ** X22 72.45 1 72.45 156.49 < 0.0001 ** X32 160.59 1 160.59 346.89 < 0.0001 ** X42 5.76 1 5.76 12.43 0.0034 ** 残差 6.48 14 0.46 2.70 0.1759 失拟检验 5.64 10 0.56 纯误差 0.84 4 0.21 总误差 232.87 28 R2=0.9722 RAdj2=0.9443 表 5 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 5 Design proposal and experiment result of response surface
试验号 X1 X2 X3 X4 水解度(%) 1 0 0 0 0 23.92 2 −1 −1 0 0 7.89 3 1 0 0 1 19.23 4 0 0 −1 −1 10.43 5 0 0 1 −1 13.98 6 1 0 0 −1 17.62 7 0 −1 0 −1 8.79 8 1 0 1 0 16.98 9 0 0 0 0 22.67 10 −1 0 0 1 17.72 11 0 0 −1 1 10.93 12 0 1 −1 0 8.23 13 0 1 1 0 8.12 14 0 1 0 1 14.72 15 0 −1 −1 0 3.32 16 0 −1 1 0 7.98 17 0 0 0 0 22.68 18 0 −1 0 1 11.86 19 −1 1 0 0 10.76 20 0 0 0 0 23.72 21 −1 0 −1 0 12.98 22 −1 0 1 0 10.18 23 0 0 1 1 12.09 24 0 1 0 −1 13.62 25 1 1 0 0 13.93 26 −1 0 0 −1 17.09 27 1 −1 0 0 10.75 28 0 0 0 0 23.69 29 1 0 −1 0 7.99 表 6 响应面回归方程方差分析
Table 6 Response surface regression equation analysis of variance
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 模型 881.87 14 62.99 60.75 < 0.0001 ** X1 8.13 1 8.13 7.85 0.0142 * X2 29.42 1 29.42 28.38 0.0001 ** X3 19.89 1 19.89 19.19 0.0006 ** X4 2.10 1 2.10 2.03 0.1766 X1X2 0.02 1 0.02 0.02 0.8812 X1X3 34.75 1 34.75 33.52 < 0.0001 ** X1X4 0.24 1 0.24 0.23 0.6378 X2X3 5.69 1 5.69 5.49 0.0345 * X2X4 0.97 1 0.97 0.94 0.3498 X3X4 1.43 1 1.43 1.38 0.2601 X12 68.27 1 68.27 65.85 < 0.0001 ** X22 483.99 1 483.99 466.79 < 0.0001 ** X32 439.67 1 439.67 424.05 < 0.0001 ** X42 44.67 1 44.67 43.08 < 0.0001 ** 残差 14.52 14 1.04 3.50 0.1192 失拟检验 13.03 10 1.30 纯误差 1.49 4 0.37 总误差 896.38 28 R2=0.9838 RAdj2=0.9676 -
[1] 王晨. 牛骨胶原多肽的制备及其清除自由基活性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2010. [2] 张磊, 刘松鑫, 刘畅, 等. 鹿骨胶原多肽螯合钙的制备[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(11):1−6. [3] 张敏, 陈晓燕. 鹿骨粉制作工艺及营养成分分析[J]. 食品科技,2004(1):95−97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2004.01.033 [4] Karami Z, Akbari-Adergani B. Bioactive food derived peptides: A review on correlation between structure of bioactive peptides and their functional properties[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,56(2):535−547. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3549-4
[5] 刘春雷, 于妍, 尤丽新. 鹿骨胶原肽粉的制备工艺研究[J]. 吉林农业,2015(21):111. [6] Finkel Toren. Radical medicine: treating ageing to cure disease[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2005,6:971−976. doi: 10.1038/nrm1763
[7] Dickinson Bryan C, Chang Christopher J, Chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species in signaling or stress responses[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2011, 7(8): 504.
[8] Finkel T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species[J]. Cell Biol,2011,194(1):7−15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102095
[9] 陈冲, 赵谋明, 孙为正. 含酪氨酸二肽在脂质体体系中的抗氧化活性与其供电子能力[J]. 食品科学: 1-10[2020-09-25]. [10] Najafian L, Babji A S. A review of fish-derived antioxidant and antimicrobial peptides: Their production, assessment, and applications[J]. Peptides,2012,33(1):178−185. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.11.013
[11] 刘彦明, 陈志勇, 韩金土, 等. 微波消解/电感耦合等离子体质谱测定鹿骨粉中微量元素[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2006,26(5):947−949. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2006.05.041 [12] 张鹤. 梅花鹿胶原蛋白制备及治疗骨质疏松症作用研究[D]. 长春: 长春中医药大学, 2011. [13] 高天. 鹿骨胶原蛋白的制备及其水解物抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2007. [14] 付刚. 猪骨胶原多肽的制备及其抗氧化性研究[D]. 成都: 四川农业大学, 2006. [15] 赵玲, 李亚, 刘淇, 等. 鳕鱼骨胶原蛋白肽的抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2013,32(4):425−429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2013.04.015 [16] 杨露, 丁利君, 蓝德安. 马面鱼骨胶原多肽的理化特性及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(11):109−112. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201311024 [17] 陆健. 蛋白纯化技术及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 6. [18] 王沥浩, 王文慧, 张雪, 等. 胶原蛋白功能概述[A]. 中国药学会. 2013年中国药学大会暨第十三届中国药师周论文集[C]. 中国药学会: 中国药学会, 2013: 10. [19] 郭冰洁, 苑广信, 安丽萍, 等. 酶法制备鹿骨多肽的工艺研究[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版),2019,20(1):47−50. [20] 蒋海萍. 蓝圆鲹蛋白制备抗氧化肽的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014. [21] Kim S Y, Je J Y, Kim S K, et al. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from hoki(Johnius belengerii) frame protein by gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2007(18):31−38.
[22] Tai A, Iomori A, Ito H. Structural evidence for the DPPH radical-scavenging mechanism of 2-O-α-d-glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2017, 25(20): 5303-5310.
[23] 成兰英, 梁书凤, 张治强. DPPH法研究麦冬提取物抗氧化活性[J]. 精细化工,2012,29(9):870−874. [24] Tong H, Zheng X, Song J, et al. Radical scavenging activity of sulfated Bupleurum chinense polysaccharides and their effects against oxidative stress-induced senescence[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2018, 192,143-149.
[25] 郅慧, 于慧, 张辉, 等. 动物源胶原蛋白提取及应用研究进展[J]. 吉林中医药,2019,39(2):225−227. [26] 郭冰洁, 苑广信, 张静, 等. 鹿骨胶水解物抗氧化活性及对H2O2损伤PC12细胞保护作用的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2019,47(7):193−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2019.07.058 [27] 郝颖, 东方, 金莉娜, 等. 响应面法优化黄芪多糖提取工艺[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版),2013,29(1):22−26. [28] 张妙妙. 薄荷素油微胶囊的制备及包埋率测定[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016. [29] 叶琴, 杨洋, 袁经权. 正交实验设计法优化超声复合酶提取甜茶苷工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(20):216−220, 239. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 熊思瑞,金铁岩. 青楷槭茎皮乙醇提取工艺优化和抗氧化性研究. 食品工业. 2023(04): 122-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈伟玲,陈邦栋,廖惠青,覃海桑,梁文静. 皮蛋清抗氧化肽制备工艺优化及体外抗氧化性. 食品工业科技. 2022(09): 148-155 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 黄雨,刘魏红,王洪阳,朱倩儿,郎晓晓,王唯,陈生龙,于慧. 裙带菜孢子叶仿生酶解工艺优化及酶解肽的抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2022(13): 180-189 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 郭鑫,陈美华,何旭,夏广清,臧皓. 梅花鹿角多肽的制备工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究. 时珍国医国药. 2021(08): 1911-1915 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:
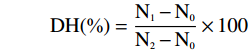
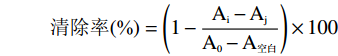
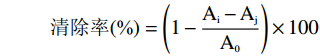
 下载:
下载:



