Effect of Freeze-thaw Cycles on Quality Characteristics of Mutton
-
摘要: 通过测定冻融 0(对照)、1、2、3、4、5 次的羊肉的解冻损失、蒸煮损失、pH、剪切力、硫代巴比妥酸值(TBARS)、挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、菌落总数及水分状态的变化,探讨了反复冻融对羊肉品质的影响。结果表明:随着冻融次数的增加,羊肉的解冻损失、蒸煮损失、TBARS、TVB-N和菌落总数均显著增加(P<0.05),pH显著降低(P<0.05),剪切力呈现先升高后降低的趋势。低场核磁技术显示,随着反复冻融次数的增加,结合水(T21)比例没有显著性变化(P>0.05),不易流动水(T22)比例呈上升趋势,自由水(T23)比例呈下降趋势,不易流动水和自由水间发生转变。这些变化表明反复冻融显著降低了羊肉品质,且随着冻融次数的增加,羊肉品质破坏更加严重。Abstract: The effect of freeze-thaw cycles (0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 cycles) on the mutton food quality were investigated by measuring the thawing loss, cooking loss, pH, shear force, TBARS, TVB-N, total number of colonies and moisture condition.The results indicated that with the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, thawing loss, cooking loss, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N) and total bacterial colony of mutton increased significantly (P<0.05), pH value decreased significantly (P<0.05), and shear force first increased and then decreased. Low-field NMR T2 relaxation time analysis showed that with the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, the content of uneasily flowing water (T22) increased, the content of free water (T23) decreased, and the content of bound water (T21) remained almost unchanged (P>0.05). Repeated freezing and thawing significantly reduced the quality of mutton, and with the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, the quality damage was more serious.
-
Keywords:
- freeze-thaw cycles /
- mutton /
- quality characteristics
-
目前,中国肉类消费主要以鲜肉制品和冷冻肉制品为主,在运输和消费环节中,尤其是偏远地区冷冻肉的运输过程中,经常出现温度波动现象,造成肉制品的反复冻融,进而导致品质下降[1-4]。羊肉,肉质细嫩,营养全面,具有低脂肪高蛋白的特点,深受人们喜爱。但是羊肉作为受地域影响比较大的一种肉制品,在运输流通环节中,容易出现反复冻融的现象[5]。
反复冻融会使新鲜肉及冷冻肉制品中营养成分流失,蛋白质、脂肪、肌纤维等发生一系列生理生化反应,从而影响肉制品的品质,严重破坏了肉制品的品质特性,降低了肉制品的食用价值[6-9]。常海军等[10]分析了反复冻融对猪肉品质的影响,探讨了该过程中一系列参数如全蛋白和肌浆蛋白含量、脂肪氧化、全质构等食用品质的变化,结果显示猪肉在经过了反复的冻融处理之后,其品质将会显著下降。刘文营等[11]研究反复冻融牛肉品质和流失汁液分析,随着冻融次数的增加,牛肉的pH呈现下降、微生物菌落总数增加、汁液流失率和溶解性蛋白损失增加,以及溶解性蛋白的变性温度也有变化。反复冻融会使得肉品性质发生变化,影响牛肉的食用品质和安全性。邓思杨等[12]研究冻融次数对镜鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白功能和结构特性变化的影响,反复冻融破坏了镜鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白的完整结构,降低了蛋白质的功能特性。
冻融处理对羊肉品质影响的相关研究较少。戚军等[13]结合低场核磁技术研究了羊肉冻融过程中持水力的变化,结果表明羊肉冻融后持水力显著降低,应避免流通过程中出现的反复冻融现象。张宏博等[14]通过对色泽、剪切力、解冻损失等结果的测定,研究了反复冻融对巴美肉羊肉品质的影响,结果表明反复冻融过程中巴美羊肉品质下降明显。已有的研究主要针对反复冻融过程中羊肉的保水性、色泽和剪切力等的变化。因此,从食用品质特性、挥发性盐基氮、菌落总数等方面全面了解反复冻融对羊肉品质的影响具有重要意义。
本文从解冻损失、蒸煮损失、pH、剪切力、硫代巴比妥酸值(TBARS)、挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、菌落总数、水分状态等多方面研究反复冻融对羊肉制品品质的影响,以期为企业制定科学的生产规程和提高冷冻羊肉制品的食用品质提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
湖羊 购自临清润林牧业有限公司,本实验选用的原料为湖羊肉背最长肌肉,选择饲养管理和屠宰条件一致,12 月龄湖羊,成熟时间均为60 h的湖羊肉;氯化钾、三氯乙酸、硫代巴比妥酸、硼酸,甲基红等 均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司;实验中所用试剂 均为分析纯。
SW-CJ-2FB超净工作台 苏州净化设备有限公司;LDZX-50KBS蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;SHX 150 III生化培养箱 上海树立仪器仪表有限公司;低温培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;FSH-2可调高速匀浆机 常州市伟嘉仪器制造有限公司;紫外可见分光光度计 赛默飞世尔科技公司; pH计 梅特勒-托利多集团;食品质构仪 美国 FTC 公司;低场核磁共振分析仪 苏州纽迈分析仪器股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原料处理
取屠宰后,成熟时间为60 h的湖羊背最长肌肉,去除表面的结缔组织和脂肪,将处理好的背脊沿与肌纤维垂直的方向切成质量相近(100±5) g、形状相似的肉块,用塑料冷冻包装袋分别包装,除去包装袋中空气,随机分成6 组,每组8 份羊肉样,然后放入冰箱内冷冻,循环冻融处理肉样。具体如下:第1组为鲜肉对照组(不进行冷冻),第2组为冻融1次组,即湖羊背脊肉先放置于−18 ℃冷冻24 h,然后流水解冻至完全1次。第3组为冻融2次组,即重复第2组步骤2次;第4组为冻融3次组,即重复第2组步骤3次;第5组为冻融4次组,即重复第2组步骤4次;第6组为冻融5次组,即重复第2组步骤5次。
1.2.2 解冻损失率测定
对尚未进行解冻的肉样精确称重,所对应质量m1 (g),当样品已经解冻之后,将其外表面上的汁液全部擦干,然后进行称重得到m2 (g),根据式(1)计算解冻损失率。每组样品设置8个重复。
(1) 1.2.3 蒸煮损失率测定
解冻完成后选取羊肉背最长肌部分,切成大小、形状相近,重50 g左右的肉块。精确称量肉样m3 (g),将肉样放到蒸煮袋中,放于80 ℃水浴中,待中心温度达到75 ℃时计时20 min。然后将其取出,冷却至室温,然后进行称重得到m4 (g),根据式(2)分析蒸煮损失率。每组样品设置8个重复。
(2) 1.2.4 pH测定
在含有1 g肉样的试管中,加入9 mL 0.1 mol/L氯化钾溶液并用匀浆机混匀,然后用pH计测定。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.2.5 硫代巴比妥酸值(TBARS)的测定
根据常海军等[10]提出的方法进行测定。称取10 g湖羊肉,绞碎后加入25 mL蒸馏水和25 mL三氯乙酸(25%),均质后离心,在2 mL上清液中加入相同体积的硫代巴比妥酸(0.02 mol/L),沸水浴20 min,冷却后测定吸光度值。TBARS值以每千克脂质氧化样品溶液中丙二醛的毫克数表示。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.2.6 挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)的测定
参考国家标准《食品安全国家标准-食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》[15]方法进行测定。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.2.7 剪切力测定
参照张昕等[16]的方法对羊肉剪切力进行测定。每个样品测量5 次。取厚度为5 cm左右的肉块,去除表面结缔组织和脂肪,水浴加热至中心温度为70 ℃,0~4 ℃条件下放置24 h,冷却后,用取样器沿与肌纤维平行的方向取样,测定剪切力值。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.2.8 菌落总数测定
参照GB/T4789.2-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》[17]进行的测定。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.2.9 低电场核磁共振分析
参照戚军等[13]和Zhang等[18]的方法对羊肉中的水分状态进行测定。准确称取1 g湖羊肉,放入直径15 mm的核磁管中,进行核磁测定,采用CPMG序列进行测量。主要参数设定如下:测试温度为32 ℃;质子共振频率为22.6 MHz;每个样品重复采样20 次,τ值(90 °脉冲和180 °脉冲之间的时间)为200 μs;重复间隔时间为6.5 s得到3000个回波 ,得到的图为指数衰减图形。每组样品设置8个重复。
1.3 数据处理
使用SPSS 20.0软件进行数据处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 反复冻融对羊肉食用品质的影响
2.1.1 反复冻融对羊肉保水性的影响
由图1和图2可知,随着反复冻融次数的增加,羊肉的解冻损失率显著升高(P<0.05);解冻损失率和蒸煮损失率总体呈现升高趋势,冻融前3次,变化显著(P<0.05),冻融4次及5次时变化不显著(P>0.05)。引起上述现象的原因主要是肌肉被冷冻解冻后,细胞内水分变成冰晶,体积增大刺破了细胞膜,细胞整体出现了损坏,细胞液流失造成了较显著的解冻失水率,随着冻融次数的增加,细胞结构受到较大的破坏,发生了不可逆变化,肉的保水性能也达到了极限值,解冻损失率和蒸煮损失率趋于平稳[19]。
![]() 图 1 不同冻融次数对羊肉解冻损失率的影响注:小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。Figure 1. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the thawing loss of mutton
图 1 不同冻融次数对羊肉解冻损失率的影响注:小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。Figure 1. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the thawing loss of mutton2.1.2 反复冻融对羊肉pH的影响
羊肉中的pH是反应肉品质变化的重要指标[20]。图3为反复冻融状态下羊肉pH的变化趋势,由图3可知,随着反复冻融次数的增加,羊肉pH呈下降趋势。在前期0~4次反复冷冻解冻状态下,下降趋势显著(P<0.05)。第4次和第5次冻融次数下,下降趋势不显著(P>0.05)。原因可能是,随着反复冻融次数的增加,汁液流失增加,解冻时糖酵解不断产生乳酸,这是pH降低的主要原因,同时解冻过程激活磷酸化酶,也会导致pH降低,当pH下降到肌原纤维蛋白的等电点时,此时肌原纤维蛋白的持水力最低,引起水分的大量流失,下降趋势显著,随着水分流失达到饱和,pH下降速率变化不显著[20]。
2.1.3 反复冻融对羊肉硫代巴比妥酸值(TBARS)的影响
TBARS是脂肪氧化的最要参考指标。图4为不同冻融次数状态下羊肉硫代巴比妥酸值(TBARS)的变化,随着反复冻融次数的增加,TBARS呈显著升高趋势(P<0.05)。原因主要是随着冷冻解冻次数的增加,冰晶不断刺破细胞,细胞的完整组织结构不断被破坏,加速了脂肪的氧化[21-22]。
2.1.4 反复冻融对羊肉挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)的影响
由图5可知,在进行多次冻融处理之后,羊肉的TVB-N值显著升高(P<0.05)。新鲜羊肉的挥发性盐基氮值为1.06 mg/100 g,在进行了5次的冷冻解冻之后数值达到了7.77 mg/100 g。随着不断的冷冻解冻处理,冰晶破坏了肌纤维的结构,肌纤维结构的降解和水分的不断流失促使微生物的进一步增殖,产生大量的胺类及小分子物质,导致羊肉中TVB-N不断增加[2]。
2.1.5 不同冻融次数对羊肉剪切力的影响
肉的嫩度是消费者最重视的食用品质之一,是反映肉质地的指标,在实际生产中通常用剪切力值表示肉嫩度的高低[23]。根据图6可知,在进行多次反复冻融的处理后,羊肉的剪切力值呈先上升后下降的趋势,整体来讲仍然呈下降趋势。新鲜羊肉的剪切力为3.25 kg,在进行2次冻融后的剪切力提高到4.59 kg,与新鲜羊肉相比差异性显著(P<0.05),在进行4次冻融后剪切力下降到3.21 kg,和新鲜肉所需的力度大致一致(P>0.05)。剪切力在第1次冻融之后明显增加,可能是由于保水性的下降使得肌肉收缩,剪切力增加。随后剪切力下降,主要是由于多次的冷冻解冻操作使得肌纤维断裂,组织结构破坏[20]。
2.2 反复冻融过程中微生物菌落总数的变化
由图7可知,随着反复冻融次数的增加,菌落总数呈现显著增加的趋势(P<0.05)。经过2 次冻融时微生物菌落总数仍然保持在300 CFU/g左右,但是经过第3次冻融微生物达到 4000 CFU/g以后,微生物显著性增加(P<0.05),第4次冻融以后的冻融样品微生物菌落总数均接近或者超过6000 CFU/g。微生物菌落总数随着冻融次数增加而增加的可能原因为,经历冻融的肉样会有汁液流出,这提供了微生物所需的营养素。在解冻阶段,丰富的营养和适宜的温度使得微生物迅速增长[8]。
2.3 反复冻融对羊肉水分状态的影响
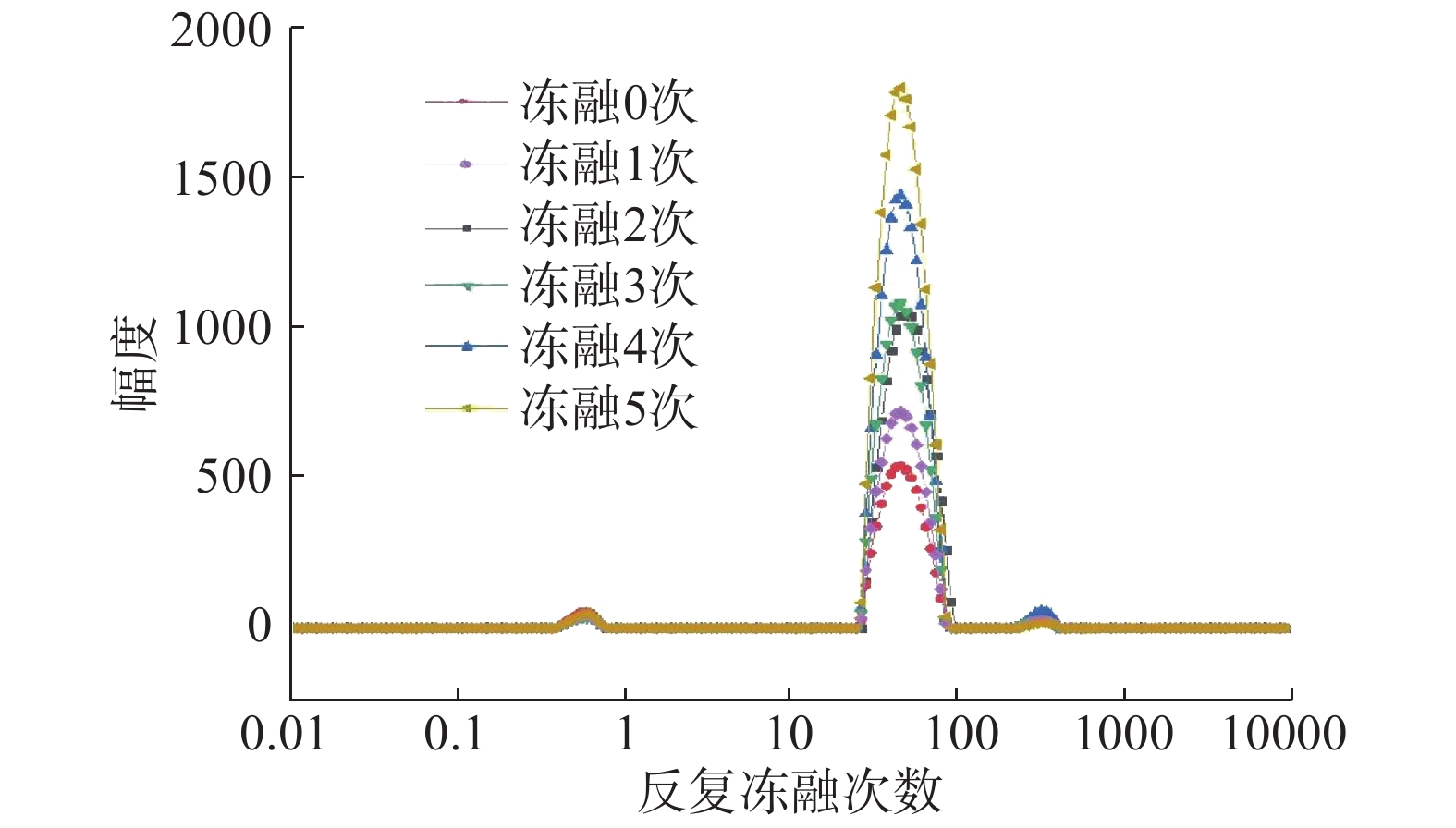
图8为不同冻融次数影响下羊肉横向豫驰时间分布,测量结果(表1)显示有3个明显峰。豫驰时间0~10 ms的峰代表结合水(T21),结合水为与蛋白质表面紧密结合的水;豫驰时间10~100 ms的峰代表不易流动水(T22),不易流动水为存在于肌纤维蛋白基质内部的水分,是羊肉中主要的水分存在形式;豫驰时间100 ms以上的峰代表自由水(T23),自由水为存在于细胞外能自由流动的水[24-25]。由表1可以看出,随着反复冻融次数的增加,结合水比例没有显著性变化(P>0.05);不易流动水比例呈上升趋势,冻融第5次比冻融前4次显著性升高(P<0.05);自由水比例呈下降趋势,冻融过的肉与鲜肉相比出现显著性下降(P<0.05)。原因主要是:因为结合水是与蛋白质紧密结合的水,所以结合水对羊肉的保水性基本没有影响。随着不断的冷冻解冻处理,肌细胞受到冰晶的不断破坏,自由水以解冻汁液的形式损失,比例呈现不断下降趋势。不易流动水的比例增加与损失汁液的一部分回吸有关[13]。
表 1 不同冻融次数羊肉中不同形态的水比例变化Table 1. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on different forms of water content of mutton冻融次数 T21(%) T22 (%) T23 (%) 0 2.94±0.15a 82.11±1.14b 14.95±0.38a 1 2.93±0.16a 83.45±1.24b 13.62±0.33b 2 2.91±0.15a 84.10±1.18b 12.99±0.44b 3 2.95±0.14a 85.28±1.16b 11.77±0.37b 4 2.96±0.15a 86.21±1.38b 10.83±0.34b 5 2.94±0.14a 91.32±1.52a 5.74±0.24c 注:同行小写字母不同,表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表2显示了在对羊肉进行不同次数的冻融操作之后水分横向弛豫时间的T2变化,由表可知羊肉T21(结合水)在不断地冷冻解冻当中无显著差异(P>0.05)。不过T22(不易流动水)随着冻融次数的增加时间发生位移。T22与反复冻融次数呈负相关,可能是因为冻融使肌原纤维蛋白分子空间结构发生变化,肌原纤维蛋白无法收集更多的水原子,持水力下降,也说明冻融后T22对应水分的移动性即自由度下降了。T22时间越短,水与底物之间的连接更加紧致。T23(自由水)先上升随后开始下降,意味着此部分的水分移动性并不稳定。
表 2 不同冻融次数羊肉中水分横向弛豫时间变化Table 2. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on transverse relaxation time of water of mutton冻融次数 T21(ms) T22(ms) T23 (ms) 0 0.63±0.04a 48.35±1.52a 332.15±20.09a 1 0.62±0.04a 45.32±1.64b 338.93±21.23a 2 0.64±0.04a 44.19±1.59b 344.20±19.51a 3 0.65±0.04a 44.08±1.73b 329.74±19.48a 4 0.62±0.04a 41.27±1.48c 293.47±19.32a 5 0.66±0.04a 39.23±1.39c 292.74±19.04a 3. 结论
羊肉经过反复冻融后,pH和保水性下降,硫代巴比妥酸值、挥发性盐基氮值和菌落总数均增加,嫩度呈总体下降趋势。低场核磁共振T2弛豫时间分析结果表明,随着反复冻融次数的增加,结合水比例基本没有变化;不易流动水比例上升;自由水比例下降。通过分析豫驰时间T2的变化,不易流动水和自由水两种水分状态发生转变。反复的冷冻解冻过程中,冰晶的长大和重结晶不断破坏了细胞结构,严重降低了羊肉食用品质。该研究为反复冻融引起羊肉品质下降提供了理论依据。因此,在实际生产过程及流通中应完善羊肉冷链管理以避免产生反复冻融现象。
-
图 1 不同冻融次数对羊肉解冻损失率的影响
注:小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05);图2~图7同。
Figure 1. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the thawing loss of mutton
表 1 不同冻融次数羊肉中不同形态的水比例变化
Table 1 Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on different forms of water content of mutton
冻融次数 T21(%) T22 (%) T23 (%) 0 2.94±0.15a 82.11±1.14b 14.95±0.38a 1 2.93±0.16a 83.45±1.24b 13.62±0.33b 2 2.91±0.15a 84.10±1.18b 12.99±0.44b 3 2.95±0.14a 85.28±1.16b 11.77±0.37b 4 2.96±0.15a 86.21±1.38b 10.83±0.34b 5 2.94±0.14a 91.32±1.52a 5.74±0.24c 注:同行小写字母不同,表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 不同冻融次数羊肉中水分横向弛豫时间变化
Table 2 Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on transverse relaxation time of water of mutton
冻融次数 T21(ms) T22(ms) T23 (ms) 0 0.63±0.04a 48.35±1.52a 332.15±20.09a 1 0.62±0.04a 45.32±1.64b 338.93±21.23a 2 0.64±0.04a 44.19±1.59b 344.20±19.51a 3 0.65±0.04a 44.08±1.73b 329.74±19.48a 4 0.62±0.04a 41.27±1.48c 293.47±19.32a 5 0.66±0.04a 39.23±1.39c 292.74±19.04a -
[1] 苏燕, 夏杨毅. 反复冻融对缠丝兔加工过程中脂肪酸含量变化的影响[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(12):260−263. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201512049 [2] 陈丽丽, 张树峰, 袁美兰, 等. 反复冻融对脆肉鲩鱼肉营养品质和质构特性的影响[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,40(1):72−78. [3] 韩敏义, 刘志勤, 刘岳, 等. 反复冻融对鸡肉品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报,2013,29(1):167−171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2013.01.029 [4] 王芳芳, 张一敏, 罗欣, 等. 冷冻解冻对生鲜肉品质的影响及其新技术研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,11(41):295−301. [5] Coombs C E O, Holman B W B, Friend M A, et al. Long-term red meat preservation using chilled and frozen storage combinations: A review[J]. Meat Science,2017,125:84−94. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.11.025
[6] Li F, Zhong Q, Kong B, et al. Deterioration in quality of quick-frozen pork patties induced by changes in protein structure and lipid and protein oxidation during frozen storage[J]. Food Research International,2020,133:109142. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109142
[7] 蔡勇, 阿依木古丽, 徐红伟, 等. 冻融对兰州大尾羊肉品质、营养成分及超微结构的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报,2014,2(45):243−248. [8] 李媛媛, 赵钜阳, 韩齐, 等. 反复冻融对肉制品品质影响的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2015,36(8):243−248. [9] 李伟明, 王鹏, 陈天浩, 等. 基于阻抗特性和神经网络的鸡胸肉冻融次数鉴别方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014(7):250−257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.07.030 [10] 常海军, 牛晓影, 周文斌. 不同冻融次数对猪肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(15):43−48. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201415009 [11] 刘文营, 田寒友, 邹昊. 反复冻融牛肉肉品质和流失汁液分析[J]. 肉类研究,2014,8(28):5−7. [12] 邓思杨, 王博, 李海静, 等. 冻融次数对镜鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白功能和结构特性变化的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(11):95−101. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180606-079 [13] 戚军, 高菲菲, 李春保, 等. 低场NMR研究冻融过程中羊肉持水力的变化[J]. 江苏农业学报,2010,26(3):617−622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2010.03.033 [14] 张宏博, 刘树军, 靳烨, 等. 反复冻融对巴美羊肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2014,39(5):116−119. [15] 农业部. GB5009.228—2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 1-10. [16] 张昕, 宋蕾, 高天, 等. 超声波解冻对鸡胸肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(5):135−140. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201805021 [17] 农业部. GB4789.2-2016食品安全国家标准食品微生物学检验菌落总数测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 1-5. [18] Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu Y, et al. Effects of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of frozen dough[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2018,95(4):499−507. doi: 10.1002/cche.10053
[19] Lagerstedt Å, Enfält L, Johansson L, et al. Effect of freezing on sensory quality, shear force and water loss in beef M. longissimus dorsi[J]. Meat Science,2008,80(2):457−461. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.01.009
[20] 李婉竹, 梁琪, 张炎, 等. 不同冻融次数下牦牛肉蛋白质氧化与保水性的关系[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(2):14−19. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201802003 [21] 李金平, 李春保, 徐幸莲, 等. 反复冻融对牛外脊肉品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报,2010,26(2):406−410. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2010.02.033 [22] Wu X, Song X, Qiu Z, et al. Mapping of TBARS distribution in frozen–thawed pork using NIR hyperspectral imaging[J]. Meat Science,2016,113:92−96. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.11.008
[23] 夏秀芳, 孔保华, 郭园园, 等. 反复冷冻-解冻对猪肉品质特性和微观结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2009,42(3):982−988. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.03.029 [24] 朱学伸, 黄雪方, 鲁小讯, 等. 结合低场核磁共振分析反复冻融处理对肉鸡不同部位肌肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(9):23−28. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201609005 [25] Tan M, Lin Z, Zu Y, et al. Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of instant sea cucumber: Emphatically on water status of by LF-NMR and MRI[J]. Food Research International,2018,109:65−71. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.029








 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
