The Effect of Mercaptoethanol on the Interface Properties of Heat-Induced Aggregation of Soy Protein Isolate
-
摘要: 为探讨β-巯基乙醇对大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物界面性质的影响,以大豆分离蛋白为原料,在pH7.0、90 ℃加热添加和不添加β-巯基乙醇(2 mmol/L)浓度为10 mg/mL的大豆分离蛋白溶液0 h和10 h,制备不同大豆分离蛋白质热致聚合物。观察了大豆分离蛋白、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的微观形态、游离巯基含量的变化,同时比较了起泡能力、泡沫稳定性、乳化活性、乳化稳定性、表面疏水性和浊度的差异。结果表明,大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白呈现无规则状态,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物为有规则的球状颗粒,而β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物部分形成球状聚合物部分形成无规则聚合物。添加β-巯基乙醇改善了大豆分离蛋白的界面性质。与大豆分离蛋白相比较,添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的起泡能力分别提高了64.56%和95.77%,乳化活性提高的幅度分别为12.94%和14.61%。添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物在长时间储藏中表现出良好的乳化稳定性和泡沫稳定性。这种良好的界面性质源于β-巯基乙醇的加入赋予聚合物具有更高的游离巯基含量和表面疏水性。并且本实验建立了4种样品的泡沫稳定性和乳化稳定性随时间变化的Rational函数和Linear函数经验模型,为大豆分离蛋白质的实际应用奠定了理论基础。Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of β-mercaptoethanol on the interface properties of soy protein isolate(SPI), the samples (10 mg/mL) were prepared by heating with or without β-mercaptoethanol (2 mmol/L) at pH7.0 and 90 ℃ for 0 and 10 h. The micromorphology and free sulfhydryl group of the samples were observed. Meanwhile, the foaming ability, foam stability, emulsifying activity, emulsifying stability, surface hydrophobicity and turbidity were evaluated. The results showed that irregular aggregations were formed from SPI and SPI with β-mercaptoethanol. The regular spherical particles were formed from SPI by heating, while both regular spherical particles and irregular aggregations were formed from SPI with β-mercaptoethanol by heating. The interface properties of SPI were improved by adding β-mercaptoethanol. Compared with those of SPI, the foaming abilities of SPI with β-mercaptoethanol and the aggregations formed from SPI with β-mercaptoethanol increased by 64.56% and 95.77%, respectively. Moreover, their emulsifying activities increased by 12.94% and 14.61%, respectively. Good emulsifying stability and foam stability of SPI with β-mercaptoethanol and the aggregations formed from SPI with β-mercaptoethanol were found during long time storage. The reason for the good interfacial property was that the higher free sulfhydryl content and surface hydrophobicity of SPI and its aggregations were obtained by the addition of β-mercaptoethanol. The empirical models of Rational function and Linear function of foam stability and emulsion stability for the 4 samples with time were established, which laid a theoretical foundation for the practical application of SPI.
-
Keywords:
- soy protein isolate /
- β-mercaptoethanol /
- aggregations /
- foaming property /
- emulsifying property
-
蛋白质界面性质涉及蛋白质在极性不同的两相之间所产生的作用,主要包括起泡性、乳化性、表面张力等性质[1]。而且蛋白质的起泡性和乳化性等功能性质与蛋白质在食品工业中的用途息息相关,是开发和利用蛋白质资源的重要依据。所谓的乳化液是一种由两种互不相溶的液体,其中一种作为分散相分散至另一种连续相中组成的非均相体系(通常是油和水)[2]。但是大部分乳化液都易发生絮凝、相反转、聚集而具有热力学不稳定的性质[3]。泡沫指气体在连续相或者半固相中分散形成的分散体系,为了提高其稳定性需要泡沫表面活性剂的参与。蛋白质因具有两亲性而常被用作泡沫稳定剂,蛋白泡沫稳定性是指蛋白质溶液在机械剪应力的作用下可以快速分散在气液两相中形成的蛋白膜的稳定性[4-5]。蛋白质因具有快速吸附特性、空间斥力和良好的黏性而作为乳化剂或者泡沫表面活性剂应用于食品、化妆品、医药等领域[6]。
大豆分离蛋白是大豆深加工的重要副产物,属于重要的植物蛋白。与动物蛋白相比,植物蛋白来源更广、价格更低、可再生性更强。但是大豆分离蛋白的界面性质(如起泡性、乳化性)比动物蛋白质如乳清蛋白、酪蛋白酸钠的界面性质要差,其应用受到一定限制。维持蛋白质构象的二硫键、氢键、静电力、疏水作用力等均影响着蛋白质的界面性质。调控大豆蛋白质中二硫键的断开程度可以改善其乳化性、起泡性等特性[7]。李荫展等[8]利用过氧化氢断开大豆蛋白11S的二硫键提高了其乳化性和起泡性。β-巯基乙醇具有强还原剂,能够保护蛋白质中的巯基不被氧化。加热可以诱导大豆蛋白质形成聚合物。当90 ℃以上加热大豆蛋白时,蛋白质完全变性,二硫键参与到大豆蛋白质聚合物的形成[9]。一般认为,巯基或二硫键的交换反应导致分子间二硫键的形成。通过添加β-巯基乙醇可以抑制大豆蛋白热致聚合物中二硫键的形成[10]。但是β-巯基乙醇如何影响大豆蛋白热致聚合物的界面性质没有系统性的研究。
因此,本实验研究了在中性pH条件下90 ℃加热及添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白质热致聚合物界面性质(乳化性和起泡性)的变化,同时比较了制备的不同样品的微观形态、游离巯基、表面疏水性和浊度的差异,旨在探究β-巯基乙醇抑制二硫键的形成后,两种聚合物界面性质和形态的差异,为拓宽大豆分离蛋白质的应用奠定一定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆分离蛋白(蛋白质80.75%) 哈尔滨高科技有限公司;2,2'-二硝基-5,5'-二硫代二苯甲酸酯 Merck公司;8-苯氨基-1-奈磺酸 Sigma公司。
JEM-1200EX透射电子显微镜 日本日立公司;F-4500荧光分光光度计 日本岛津公司;T6紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;DK-98数显恒温水浴锅 天津泰斯特有限公司;YP202N电子天平 上海精密仪器科学有限公司;JJ-2B高速组织捣碎机 金坛市国旺实验仪器厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大豆分离蛋白质聚合物的制备
称取一定量大豆分离蛋白分散至去离子水中,然后在10000×g离心力下离心20 min(4 ℃),收集上清液。通过凯氏定氮法测定上清液蛋白含量,然后将上清液利用去离子水准确稀释至10 mg/mL,并精确调节pH至7.0。将该溶液平均分成4份,每份100 mL,一份不加热(大豆分离蛋白溶液),一份在90 ℃加热10 h,一份添加2 mmol/L[10]的β-巯基乙醇,一份添加2 mmol/L[10]的β-巯基乙醇然后在90 ℃加热10 h,加热后立即冷却。以上4份样品分别对应大豆分离蛋白(SPI)、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物。将这4种样品在4 ℃冰箱保存过夜用于后续试验。
1.2.2 透射电镜试验
利用去离子水将大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物溶液稀释浓度至3 mg/mL,取一滴稀释液滴于透射电镜专用铜网上吸附20 min,多余的部分用滤纸移除,室温下干燥20 min,采用80 kV电压下用透射电镜采集图片。
1.2.3 游离巯基含量的测定
采用Beveridge等[11]测定游离巯基含量的方法评估样品中游离巯基含量的变化。取1 mL浓度为10 mg/mL的样品溶液加入到5 mL的Tris-Gly缓冲溶液(0.086mol/L Tris,0.09 mol/L甘氨酸,0.004 mol/L乙二胺四乙酸,pH8.0和8 mol/L尿素)中,然后向其中加入20 μL的2,2'-二硝基-5,5'-二硫代二苯甲酸酯(DTNB)试剂,振混匀,在室温下静止15 min,利用紫外分光光度计在412 nm波长下测定吸光值,以不加DTNB的溶液做空白调零。每一个样品测定重复3次。
−SH(μmol/g)=(73.53×A412×D)/C
式中:A412:在412nm下的吸光值,计算时可用平均值;C:固形物含量(mg/mL);D:稀释系数。
1.2.4 起泡性的测定
利用pH=7.0的0.01 mol/L的磷酸缓冲液分别将上述4种样品按照1:10的比例稀释,最终蛋白浓度为1 mg/mL。取200 mL稀释溶液到入高速组织捣碎机中,在10000 r/min转速下搅打1 min,然后迅速转移至500 mL量筒中,测定泡沫的体积。然后分别测定放置10、20、30、60、90、120 min时泡沫体积,每个样品测定3个重复试验[12]。利用刚搅打后泡沫体积和原始溶液的比值评价起泡能力,利用静置后泡沫体积和刚搅打后泡沫体积的比值评价样品泡沫稳定性,具体公式如下:
起泡能力(%)=V0/Vi×100
泡沫稳定性(%)=Vt/V0×100
式中:V0:起泡0 h时的泡沫体积,Vt:起泡t h后的泡沫体积,Vi:起泡前最初液体的体积。
1.2.5 泡沫微观结构的观察
按照1.2.4方法制备的泡沫静置1 min和10 min,取部分泡沫置于载玻片上,轻轻盖上盖玻片,然后用显微镜观察其微观结构,利用数码相机从目镜观察泡沫微观结构[13]。所有照片放大倍数为40×40(物镜×目镜)。
1.2.6 乳化性的测定
采用Pearce等[14]测定乳化能力和乳化稳定性的方法。取3 mL、10 mg/mL的样品放在5 mL的测量杯中,然后加入1 mL大豆油,利用高速匀浆机在20000 r/min下均质2 min,分别在均质后0、10、20、30、60、90、120 min迅速地从距离测量杯底部0.5 cm处取10 μL乳状液加入到5 mL的十二烷基苯磺酸钠(SDS)溶液(c=1 mg/mL),然后在500 nm处测定吸光值,以1 mg/mL的SDS溶液空白调零。乳化活性(EAI)和乳化稳定性(ESI)计算公式如下:
EAI(m2/g)={(2×2.303)/[C×(1−φ)×104]}× A500×D
ESI(%)=100×At/A0
式中:A500:溶液在500 nm下的吸光值;C:蛋白质浓度(g/mL);φ:大豆油占乳化液的体积分数(φ=0.25);D:稀释倍数;At:乳化液静止时间为t min时的吸光值;A0:乳化液静止时间为0 min时的吸光值。
1.2.7 浊度的测定
参照Tang等[10]测定样品浊度的方法,将3种样品利用去离子水稀释一定的倍数,利用分光光度计在波长660 nm下测定OD值,用去离子水作为空白进行调零。OD值即为浊度值。
1.2.8 表面疏水性的测定
采用8-苯氨基-1-奈磺酸荧光探针法测定样品的表面疏水性[15],具体过程如下。利用pH=7.0的0.01 mol/L的磷酸缓冲液将样品稀释成浓度梯度为0.1、0.05、0.0025和0.00125 mg/mL的溶液,取稀释后溶液6 mL,加入20 μL的8 mmol/L ANS(8 mmol/L,溶于0.01 mol/L的磷酸缓冲液,pH7.0)荧光探针,漩涡振荡混合均匀,在避光储藏15 min(室温),然后在激发波长为390 nm、发射波长为470 nm和狭缝均为5 nm的条件下利用荧光分光光度计比色,测定荧光强度,以荧光强度值为纵坐标,蛋白质溶液浓度为横坐标作图,初始斜率即为样品表面疏水性值。
1.3 数据处理与统计分析
数据均以平均值±标准差表示(n=3)。试验数据采用Origin 8.0和Statisix 8.1软件对试验数据进行统计分析(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 聚合物微观形态
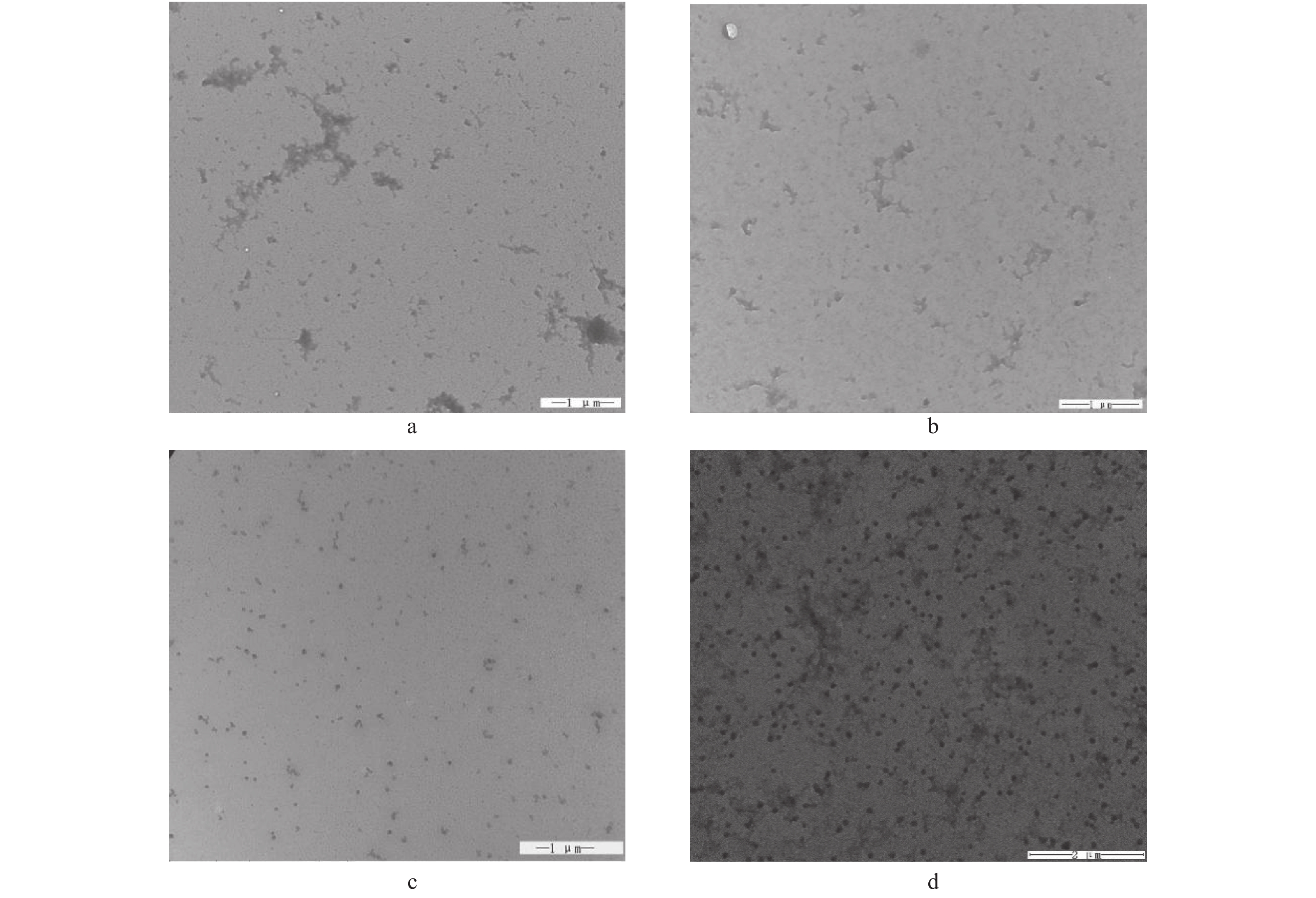
大豆分离蛋白(SPI)、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的微观结构具体见图1所示。大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白呈现无规则的聚集状态。热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物呈现有规则的颗粒状形态,但β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物除了形成规则颗粒聚合物还形成了无规则的絮状聚合物。这种无规则聚合物的形成可能是因为β-巯基乙醇的添加抑制了二硫键的形成,使得部分蛋白质无法形成这种有规则的颗粒状聚合物。
2.2 聚合物游离巯基含量的变化
加热和添加β-巯基乙醇对大豆分离蛋白聚合物游离巯基含量的影响如表1所示。天然大豆分离蛋白的游离巯基含量为21.38 μmol/g,热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物的游离巯基为6.04 μmol/g,降低的幅度为71.75%。在热诱导过程中,大豆分离蛋白中游离巯基含量降低可能是由于游离巯基转变为二硫键。添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白的游离巯基含量为50.87 μmol/g。在热诱导过程中,添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物游离巯基含量为51.23 μmol/g。添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白的游离巯基含量增大,这可能是因为在加热过程中抑制了大豆分离蛋白之间二硫键的生成,同时一定程度断开了大豆分离蛋白内部的二硫键,游离巯基含量略微增大,增加的幅度为0.71%。
表 1 4种样品游离巯基含量的变化Table 1. The change of free sulfhydryl group for the four samples样品 游离巯基含量(μmol/g) 大豆分离蛋白 21.38±0.77b β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白 50.87±1.01c 大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 6.04±0.45a β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 51.23±0.89c 注:小写字母相同表示差异不显著( P >0.05),不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 2.3 β-巯基乙醇对起泡性的影响
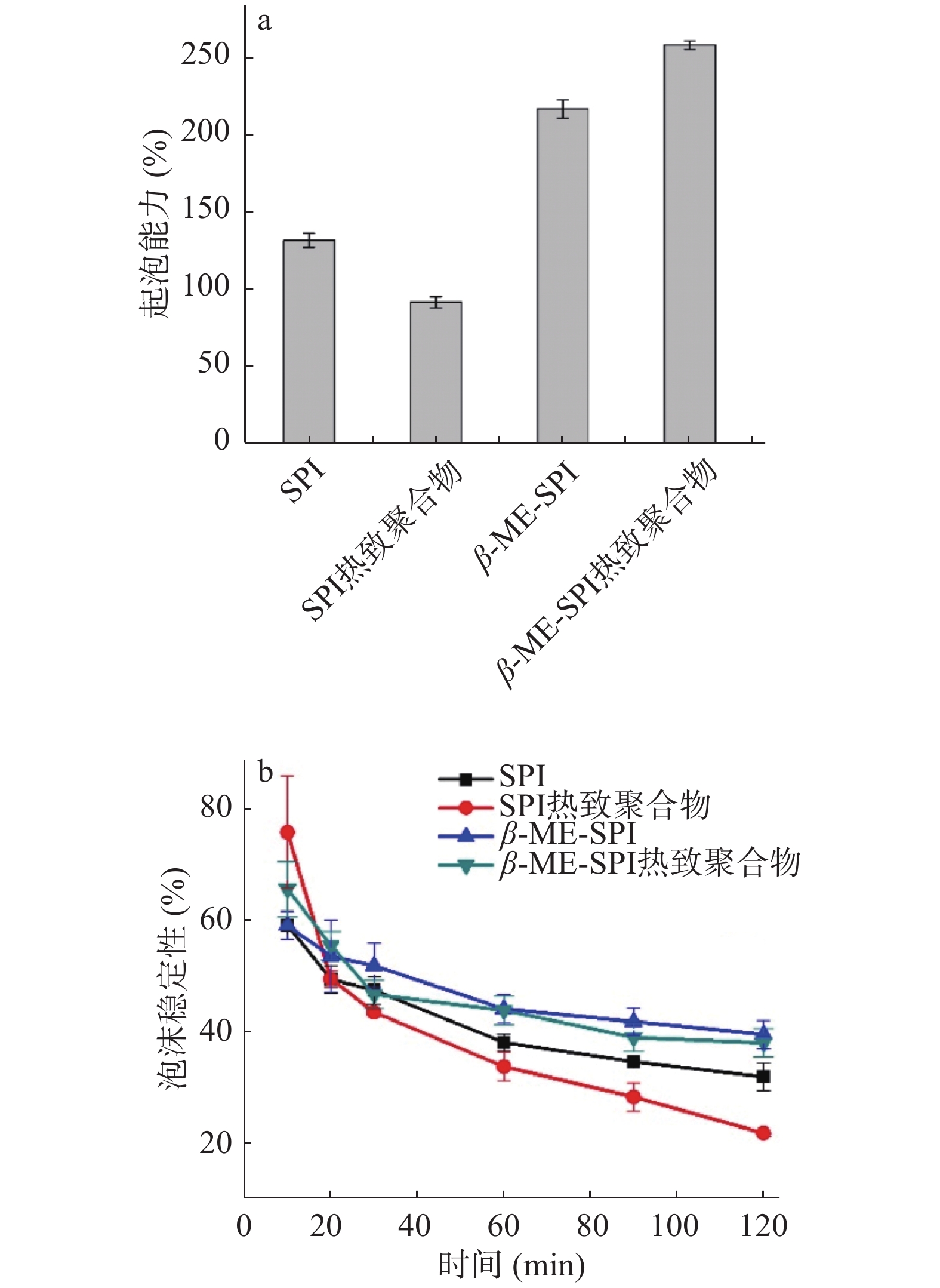
天然大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的起泡能力和泡沫稳定性的差异如图2。4种样品的起泡能力和泡沫稳定性均存在较大差异。从图2a可以得出,大豆分离蛋白的起泡能力为132.17%,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的起泡能力降低至92.10%,降低幅度为30.31%。添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白的起泡能力增加至217.5%,添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的起泡能力提高至258.75%。与大豆分离蛋白的起泡能力相比较,两者的提高幅度分别为64.56%和95.77%。说明单独的热修饰不利于大豆分离蛋白起泡能力的改善,但是添加β-巯基乙醇结合或者不结合热修饰均有利于大豆分离蛋白起泡能力的改善。
大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫稳定性均随着时间的延长呈现下降的趋势(图2b),但是下降的幅度不同。当泡沫静置10 min时,大豆分离蛋白的泡沫稳定性为58.19%,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫稳定性为76.66%,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白的泡沫稳定性为59.19%,β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物的泡沫稳定性为66.28%,热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物具有较好的泡沫稳定性。当泡沫静置20 min时,原始大豆分离蛋白的泡沫稳定性48.12%,热致大豆分离蛋白聚合物仍然表现出较好的泡沫稳定性(49.66%),β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物仍然表现出较好的泡沫稳定性,泡沫稳定性为54.78%。随着时间的延长,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫稳定性较差,而β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫稳定性维持较高程度。当静置120 min时,原始大豆分离蛋白的泡沫稳定性为30.91%,热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物的泡沫稳定性仅为21.34%,而β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物泡沫稳定性为37.15%。在短时间储藏过程中,单独加热有利于维持大豆分离蛋白泡沫稳定性,但延长储藏时间,单独加热不利于维持大豆分离蛋白泡沫的稳定性。然而,β-巯基乙醇或者β-巯基乙醇结合加热修饰大豆分离蛋白表现出较好的泡沫稳定性,而且在长时间储藏过程中均维持较好的泡沫稳定性。
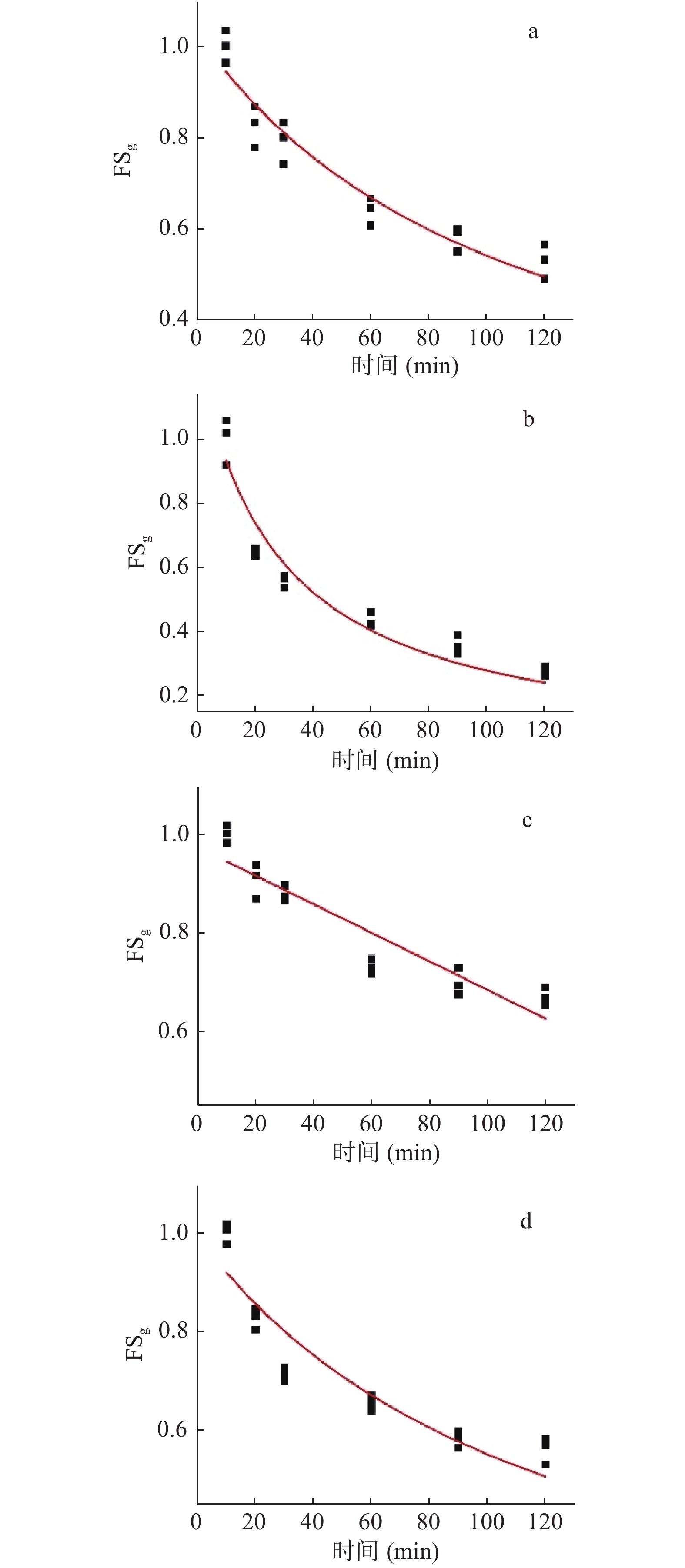
为定量反映大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫稳定性随时间的变化规律,本研究采用Rational函数和Linear函数拟合归一化的泡沫稳定性(FSg:不同时间下泡沫稳定性与泡沫静置10 min时平均泡沫稳定性的比值)(见图3)。大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的FSg最小二乘法回归分析方程分见公式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4),而且4个公式的决定系数均大于0.95。
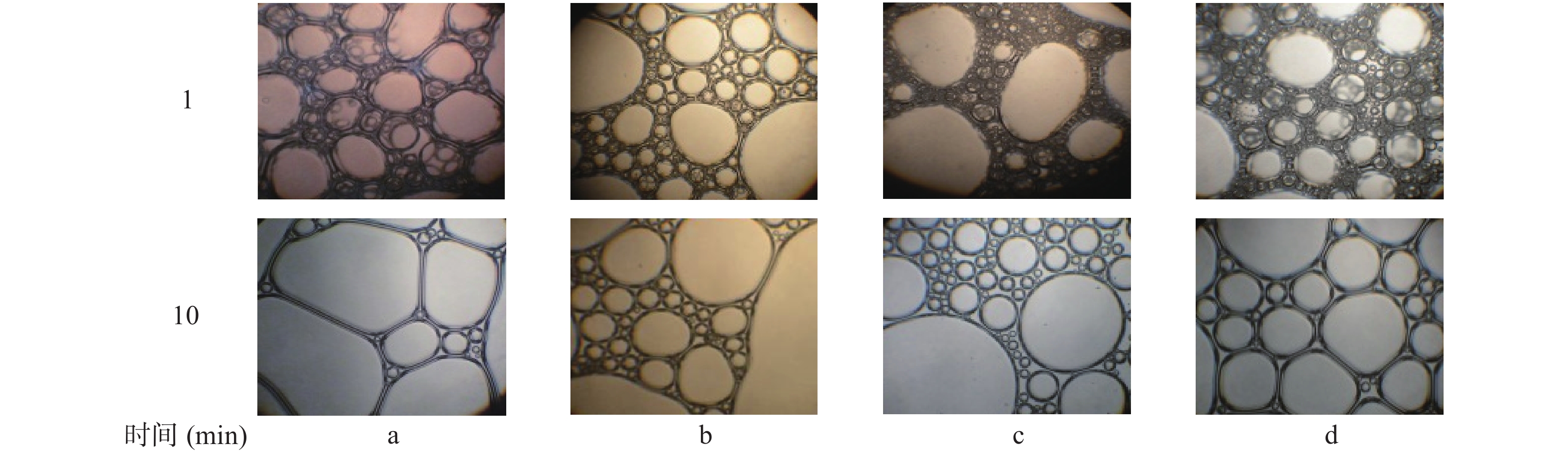
(1) (2) (3) (4) 泡沫稳定性也可以通过显微镜观察其微观形态图的变化表示,具体结果见图4。大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫在放置1 min时,均呈现良好的泡沫形状。在放置10 min后,大豆分离蛋白的泡沫孔隙度变大,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物有部分泡沫保持良好状态,但部分泡沫已经破碎。添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白的泡沫也保持较好的泡沫状态,但是泡沫大小不均匀。添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的泡沫保持均匀的泡沫状态。说明β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导方式对改善大豆分离蛋白的泡沫稳定性起到积极作用。
2.4 β-巯基乙醇对乳化性的影响
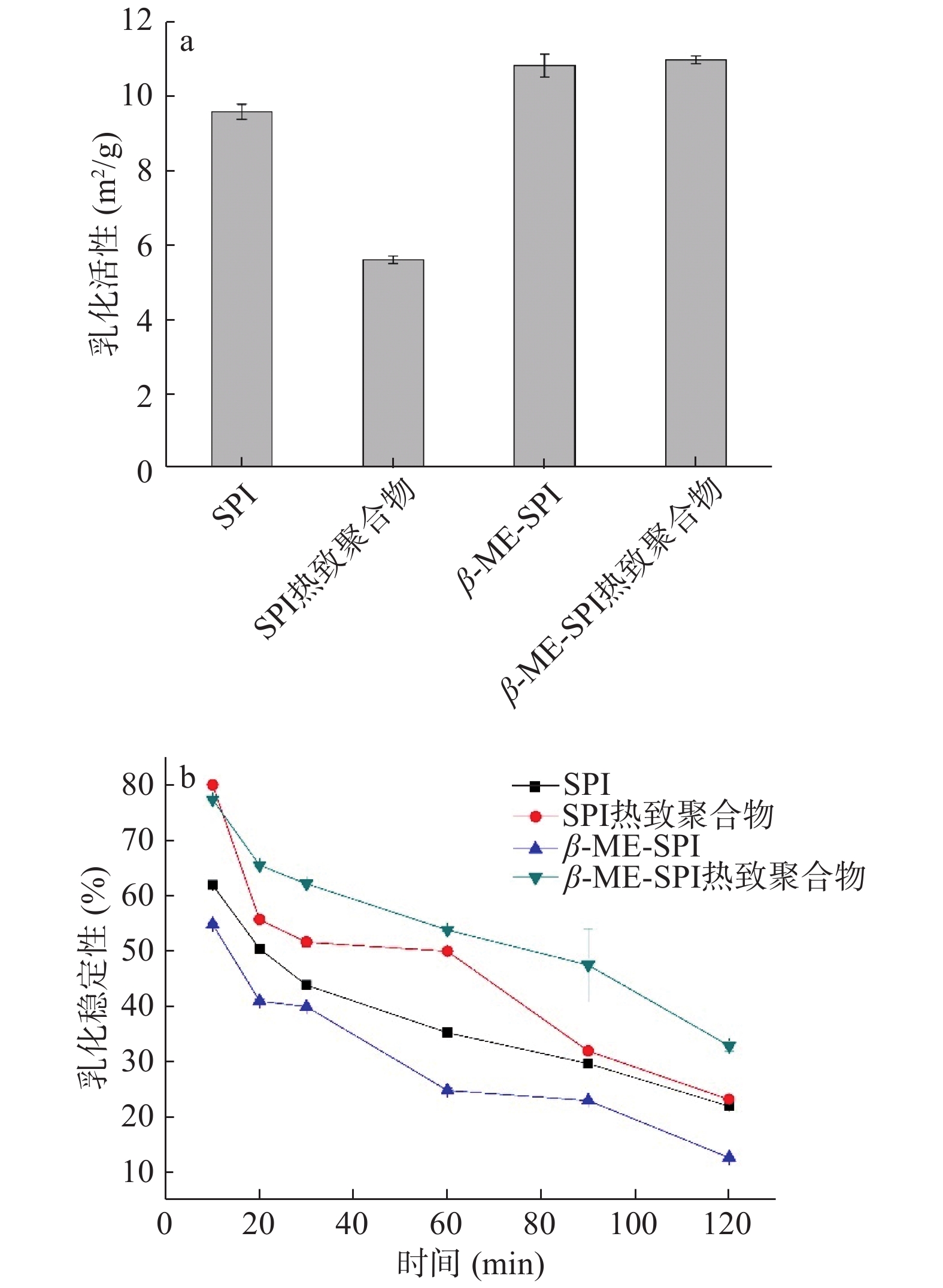
大豆分离蛋白、热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物、添加 β -巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物4种样品的乳化活性和乳化稳定性的结果见图5。从图5的结果可以得出,4种样品的乳化活性和乳化稳定性存在不同。大豆分离蛋白乳化活性为9.58 m2/g,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化活性降低至5.60 m2/g,添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白的乳化活性增加至10.82 m2/g,提高的幅度为12.94%,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化活性升高至10.98 m2/g,提高的幅度为14.61%。
4种样品乳化稳定性随着时间的延长均呈现下降的趋势,但是下降的幅度不同(图5b)。当乳化液静置10 min时,大豆分离蛋白的乳化稳定性为62.53%,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物表现出良好的乳化稳定性,乳化稳定性达到80.67%,添加β-巯基乙醇的大豆分离蛋白的乳化稳定性为54.75%,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化稳定性为77.01%。当泡沫静置20 min时,热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物的乳化稳定性(57.62%)仍优于大豆分离蛋白的乳化稳定性(52.32%),添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白的乳化稳定性为40.85%,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化稳定性保持在65.45%。但当静置120 min时,与大豆分离蛋白的乳化稳定性(21.13%)相比较,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化稳定性保持在22.34%,β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物的乳化稳定性为32.73%。结果表明β-巯基乙醇结合热诱导大豆分离蛋白聚合物在乳化液长时间储藏过程中均表现出较好的乳化稳定性。β-巯基乙醇的加入断开二硫键或者抑制了聚合物二硫键的生成,使得蛋白质分子展开程度增加,蛋白质在溶液状态下亲水或疏水基团比例接近平衡,蛋白质分子在溶液表面的定向排列更加有序[16],因此增加了乳化活性和乳化稳定性。β-巯基乙醇的加入断开蛋白质的二硫键或者抑制蛋白质聚合物二硫键的生成,可以增加蛋白质分子的表面活性,有利于蛋白质分子在油水/气水界面的吸附[17],进而改善了大豆分离蛋白的乳化活性或者起泡能力。
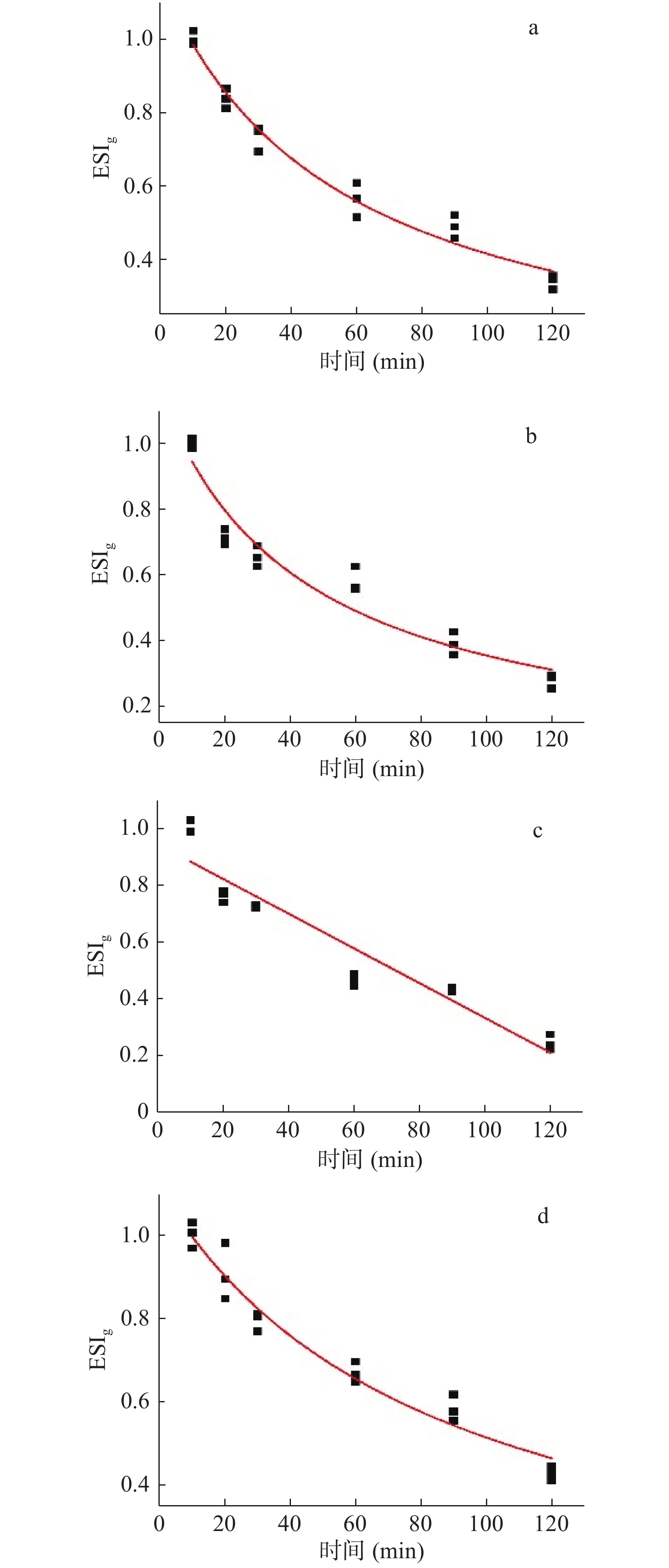
为定量反映大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的乳化稳定性随时间的变化规律,本研究采用Rational函数和Linear函数拟合归一化的泡沫稳定性(ESIg:不同时间下乳化稳定性与泡沫静置10 min时平均泡沫稳定性的比值)(见图6),大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的ESIg最小二乘法回归分析方程分别见公式(5)、(6)、(7)和(8),其决定系数均大于0.95。
(5) (6) (7) (8) 2.5 β-巯基乙醇对浊度的影响
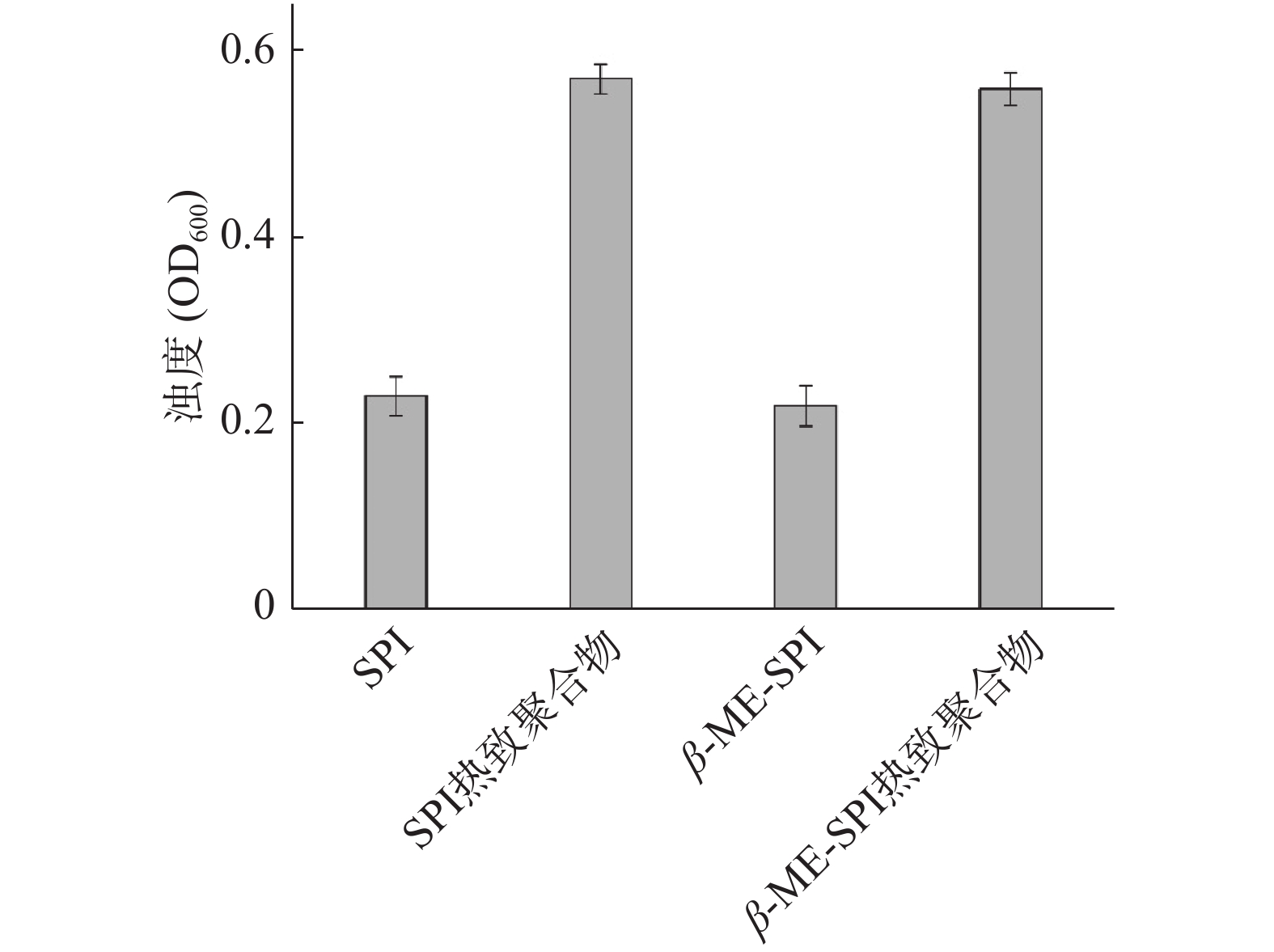
大豆分离蛋白、大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白、β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物4种样品的浊度存在较大差异,结果见图7。从图7的结果可以看出,大豆分离蛋白的浊度值为0.23,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的浊度值为0.57,添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白的浊度值为0.22,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的浊度值为0.56。β-巯基乙醇断开了蛋白质间的二硫键或者抑制了聚合物二硫键的形成,这种作用可能使得蛋白质的聚集形态存在一定差异。结合电镜的结果可以发现,4种聚合物的聚集形态存在一定差异。不同聚集方式表现出不同的界面性质(乳化性和起泡性)。
2.6 β-巯基乙醇对表面疏水性的影响
4种样品表面疏水性的变化见表2。大豆分离蛋白的表面疏水性为276.96,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的表面疏水性为853.48。与天然大豆分离蛋白表面疏水性含量相比较,热修饰后的大豆分离蛋白的表面疏水性增加了208.16%。添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白的表面疏水性为950.87,β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的表面疏水性为1012.23。表面疏水性的增加与乳化性和起泡性的改善有一定的关系,有相关报道适宜的表面疏水性区域有利于改善蛋白质的起泡性和乳化性[18-20]。添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白具有较高的表面疏水性,进而表现出较好的界面性质。而且添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋加热形成的无规则聚合物具有较高的表面疏水性,这种无规则聚合物结果有利于改善蛋白质的起泡能力、泡沫稳定性、乳化活性和乳化稳定性。
表 2 4种样品表面疏水性的变化Table 2. The change of surface hydrophobicity for the four samples样品 表面疏水性(So) 大豆分离蛋白 276.96±5.64a β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白 950.87±8.01c 大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 853.48±9.87b β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 1012.23±11.28d 3. 结论
大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白呈现无规则状态,大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物为有规则的球状颗粒,而β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物部分形成球状聚合物部分形成无规则聚合物。添加β-巯基乙醇可以改善大豆分离蛋白的起泡能力、泡沫稳定性、乳化活性和乳化稳定性。与大豆分离蛋白相比较,添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物的起泡能力分别提高了64.56%和95.77%,乳化活性提高的幅度分别为12.94%和14.61%。添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白和添加β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物在长时间储藏中表现出良好的乳化稳定性和泡沫稳定性。这种良好的界面性质源于β-巯基乙醇的加入赋予聚合物具有更高的游离巯基含量和更高的表面疏水性。本研究的结果可以为拓宽大豆分离蛋白的应用范围提供一定的理论指导。
-
表 1 4种样品游离巯基含量的变化
Table 1 The change of free sulfhydryl group for the four samples
样品 游离巯基含量(μmol/g) 大豆分离蛋白 21.38±0.77b β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白 50.87±1.01c 大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 6.04±0.45a β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 51.23±0.89c 注:小写字母相同表示差异不显著( P >0.05),不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 4种样品表面疏水性的变化
Table 2 The change of surface hydrophobicity for the four samples
样品 表面疏水性(So) 大豆分离蛋白 276.96±5.64a β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白 950.87±8.01c 大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 853.48±9.87b β-巯基乙醇大豆分离蛋白热致聚合物 1012.23±11.28d -
[1] 赵新淮, 徐红华, 姜毓君. 食品蛋白质结构、性质与功能[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 321-323. [2] Dickinson E. Hydrocolloids at interfaces and the influence on the properties of dispersed systems[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2003,17(1):25−39. doi: 10.1016/S0268-005X(01)00120-5
[3] Juttulapa M, Piryaprasarth S, Takeuchi H, et al. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on stability of emulsions containing zein and pectin[J]. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2017,12(1):21−27. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2016.09.004
[4] Halling P J. Protein-stabilized foams and emulsions[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1981, 15(2): 155-203.
[5] 曹荣锟, 李佳泰, 王金晶, 等. 大米辅料啤酒中蛋白质疏水性与蛋白质泡沫稳定性的分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2018,44(9):66−70. [6] Evans M, Ratclifee I, Williams P A. Emulsion stabilisation using polysaccharide-protein complexes[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science,2013,18(4):272−282. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2013.04.004
[7] 李军生, 李丽娜, 程海涛. 通过打开蛋白质二硫键制备蛋白质基表面活性剂的方法: 中国, 200810166640.4[P]. 2012-02-18. [8] 李荫展, 李军生, 王靖婷. 过氧化氢氧化二硫键对大豆11S蛋白表面活性的影响[J]. 中国饲料,2020(5):27−33. [9] 牛祥臣, 王洪彩, 马军, 等. 食盐浓度和热处理条件对大豆蛋白凝胶特性影响的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(6):19−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.06.004 [10] Tang C H, Wang X Y, Yang X Q, et al. Formation of soluble aggregates from insoluble commercial soy protein isolate by means of ultrasonic treatment and their gelling properties[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2009,92(4):432−437. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.12.017
[11] Bevridge T, Toma S, Nakai S. Determination of SH- and SS-groups in some food proteins using Ellman'sreagent[J]. Journal of Food Science,1974,39(1):49−51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1974.tb00984.x
[12] 耿军凤, 张丽芬, 陈复生. 超声波辅助提取对花生蛋白结构与功能特性的影响[J], 食品研究与开发, 2020, 41(9): 61-69. [13] Martinez M J, Ruiz-Henestrosa V M P, Sanchez C C, et al. Foaming and surface properties of casein glycomacropeptide-gelatin mixtures as affected by their interactions in the aqueous phase[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,33(1):48−57. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.02.016
[14] Pearce K N, Kinsella J E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1978,26(3):716−723. doi: 10.1021/jf60217a041
[15] Hayakawa S, Nakai S. Relationships of hydrophobicity and net charge to the solubility of milk and soy proteins[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,50(2):486−491.
[16] 王碧璇, 李军生, 钟新, 等. 控制性打开二硫键-葡聚糖修饰对大豆分离蛋白表面活性性能及结构的影响[J]. 中国饲料,2019(11):22−27. [17] 董振, 李军生, 阎柳娟, 等. 分子动力学模拟二硫键对大豆11S球蛋白结构及表面活性的影响[J]. 山东化工,2016,45(16):1−4, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.16.001 [18] Foegeding E A, Luck P, Davis J. Factors determining the physical properties ofprotein foams[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2006,20(2):284−292.
[19] Nakai S, Ho L, Helbig N, et al. Relationship between hydrophobicity and emulsifying properties of some plant proteins[J]. Canadian Institute of Food and Science and Technology Journal,1980,1(13):23−27.
[20] Townsend A, Nakai S. Relationships between hydrophobicity and foaming characteristics of food proteins[J]. Journal of Food Science,2006,48(2):588−594.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 吴广武,白蓉,方虎,赵成,陈佩圆. 维生素C调控合成纯球霰石及其形成机理. 硅酸盐通报. 2025(01): 195-201+242 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 范旭,朱迎澳,朱嘉敏,陈倩,王辉. 明胶改善海藻酸钠水凝胶膜的物理性能研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(15): 108-115 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:



