Analysis of Different Proteins Affecting Water Holding Capacity of Pork Based on Microstructure and Proteomics
-
摘要: 为探究宰后初期生鲜猪肉肌细胞微观结构和蛋白质组变化对持水能力的影响,将猪背最长肌样品按照汁液流失的高低分为高汁液流失组(High drip loss group≥5.93%, H组, n=3)和低汁液流失组(Low drip loss group≤0.81%, L组, n=3),对两组样品的微观结构和蛋白质组进行比较。采用透射电镜(Transmission Electron Microscopy, TEM)观测细胞间隙,并用多肽体外标记技术(Tandem Mass Tag, TMT)鉴定高低汁液流失组间的差异蛋白。结果表明,宰后24 h时,H组的细胞外间隙极显著大于L组的细胞外间隙(P<0.01)。宰后肌肉中葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1、热休克蛋白70(Heat shock protein 70, Hsp70)、锚蛋白、硒蛋白W和层黏连蛋白的表达量越高,汁液流失越低,持水性越好,而磷酸甘油变位酶和转酮醇酶的表达量越高,汁液流失越高,持水性越差。Abstract: In order to investigate the effects of microstructural and proteomic changes of fresh pork on their water holding capacity in the early postmortem period, the longissimus dorsi samples of pigs were divided into high drip loss group (H-group≥5.93%, n=3) and low drip loss group (L-group≤0.81%, n=3) according to the level of drip loss. The microstructure and proteomics of the two groups were compared. The difference proteins between the two groups were identified using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) and intercellular spaces were observed using electron microscopy. The results showed that the extracellular space of H-group was significantly larger than that of L-group at 24 h after slaughter(P<0.01). The higher the expression level of glucose-phosphotransferase-1, heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), ankyrin, selenoprotein W and laminin in postmortem muscle, the lower the drip loss and the better the water holding capacity, while the higher the expression level of phosphoglycerate mutase and transketolase, the higher the drip loss and the worse the water holding capacity.
-
Keywords:
- pork /
- proteomics /
- drip loss /
- biological metabolism /
- transketolase
-
蛋白质组学是通过将基因表达的信息翻译为蛋白质,进而研究蛋白质的一门学科[1]。通过蛋白质组学实验可以对肉类在蛋白质水平进行定性、定量分析[2]。目前,被广泛用于肉及其制品研究的定量蛋白质组学鉴定技术主要有无标记定量(Label-free)测定技术和标记(Stable isotope labeling)定量测定技术[3-4]。无标记测定蛋白组学技术,具有通量大、线性范围广和检测价格低等优势,但对前期样品制备和质谱稳定性要求较高,在检测丰富度较低的蛋白时灵敏度低[5]。标记定量技术主要包括多肽体外标记技术(Tandem Mass Tag, TMT)和标记相对定量技术(isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification,iTRAQ)。标记定量技术在检测中灵敏度高,但在样品复杂的情况下,母离子共筛选和共碎裂会对其结果产生干扰[6]。
持水性(Water-holding capacity, WHC)是指宰后肌肉对其内部水分束缚的能力,常用汁液流失率(drip loss)的高低来衡量。研究发现,汁液流失率的高低受宰后温度、pH下降速率、细胞骨架蛋白降解程度、氧化应激反应程度和肌细胞微观结构的变化等因素影响[7-8]。目前有研究发现,宰后汁液流失现象与蛋白质变化有密切的联系[9-10]。已有研究人员利用蛋白质组学鉴定技术对宰后牛肉、鹅肉、鸡肉和猪肉进行持水性的研究,其中,Luca等[11]通过SDS-PAGE和质谱分析对贮藏期的猪肉渗出液进行蛋白质组学鉴定,发现高汁液流失组渗出液中Hsp70表达量显著高于低汁液渗出组;Gap-Don等[12]通过液相二级质谱对宰后猪最长肌的不同部位进行蛋白质组学分析,发现各段磷酸甘油变位酶的表达量不同可能导致不同段猪最长肌的持水性不同。国内外学者在研究宰后蛋白质组变化对肉品质的影响时多采用无标记蛋白组学和iTRAQ蛋白质组学进行分析,然而有研究表明iTRAQ蛋白质组学鉴定技术比TMT多肽体外标记技术灵敏度低,噪音信号干扰较大[13]。
本实验采用TMT多肽体外标记定量蛋白质组学技术,结合UniProt蛋白数据库对宰后初期不同持水能力的猪背最长肌样品进行蛋白质组比较,找到两组间存有差异的蛋白,探讨两组猪肉持水能力不同的原因,为提高肉的持水能力提供理论指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
三元杂交猪 在曲靖市东恒经贸集团食品有限公司屠宰场选择品种和饲养条件相同、体重相近(105 ± 5 kg)的三元杂交猪(大河乌猪 × 约克夏 × 长白猪)作为样品;蛋白酶抑制剂 Calbiochem公司;胰蛋白酶 Promega公司;碘代乙酰胺(分析纯)、二硫苏糖醇(分析纯)、尿素(分析纯)、三乙基碳酸氢铵(TEAB)(分析纯)、三氟乙酸(分析纯) 美国Sigma公司;BCA试剂盒 碧云天公司;TMT标记试剂盒、预染标记物 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;二甲苯(分析纯) 中国上海试剂厂;柠檬酸(分析纯) 湖北津乐达化工有限公司;醋酸铀(分析纯) 北京中科光析化工技术研究所。
Bio Rad通用迷你垂直电泳细胞电泳槽、电泳仪电源、IMARK酶标仪 伯乐生命医学有限公司;JY92-ⅡN高强度超声处理、Velocity 18R离心机 英国Dynamica Scientific Ltd.公司;HI9025C便携式pH计 意大利哈纳;1000纳米高效液相色谱、164568液相柱、Q-Exactive质谱仪 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;JEM-1011透射电子显微镜 日本电子株式会社(JEOL);Agilent 1260高pH反向液相色谱 美国安捷伦科技公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
依照生猪屠宰操作规程(GB / T17236-2008)进行屠宰,宰后进行四分体分割。依据Warner等[14]和Florowski等[15]的标准,选取10条苍白发软表面有汁液渗出的肉(pale, soft exudative,PSE)样品:L*>50, 汁液流失率≥5%,pH45 min≤5.8, pH24 h≤5.5;;10条正常肉(Reddish-pink, firm, nonexudative,RFN)样品:L*=42~50, 汁液流失率<5%, pH45 min>5.8, pH24 h=5.6~6.0。样品为左侧背最长肌第七腰椎段至最后腰椎段肌肉。样品用保鲜膜包裹,放在4 ℃的条件,在不同时间点取样用于基本指标测定、蛋白质组学检测和电镜拍摄。测定汁液流失率后,挑选汁液流失率最高的3个样品(汁液流失率分别为:5.66%、5.78%和6.36%)和汁液流失率最低的3个样品(汁液流失率分别为:0.57%、0.81%和1.06%)用于蛋白质组学分析和其他指标测定。
1.2.2 检测指标及其测定方法
1.2.2.1 基本肉质指标测定
在4 ℃的冷藏环境中,将矫正好的便携式pH计的pH探头和温度探头插入待检测猪背最长肌样品内部3 cm处,测定宰后9、24 h时样品背最长肌的温度和pH。
参照Honikel等[16]的方法测定汁液流失,具体如下:将之前准备好的样品切成2.5 cm的肉片,用精度为万分之一的天平称重,记做W1,称重后用细铁丝穿过肉片进行固定,使肌纤维始终保持垂直向下,放置在清洁干燥的聚乙烯薄膜袋中(肉片与袋壁要保持距离,不能接触袋壁),扎紧袋口后吊挂于4 ℃冷库中,24 h后取出肉片再次称重,记做W2,依据公式计算汁液流失率。
称取25 g样品,剔除外表脂肪和筋膜,剁成鲜肉肉糜,取10 g肉糜放在105 ℃的恒温干燥箱中干燥至恒重,将肉糜用滤纸包裹好放入萃取套管中,启动通风橱。将160 mL石油醚加入萃取杯中没过滤纸包,萃取循环设置在10 次/h,连续萃取6 h,取出抽提杯(包括滤纸包)并放置于硅胶干燥器中过夜,第二日将抽提杯放入真空干燥箱内(80 ℃,13 kPa)干燥1.5 h后取出称重记做B1,依据公式计算肌间脂肪含量。
1.2.2.2 肌肉微观结构观察
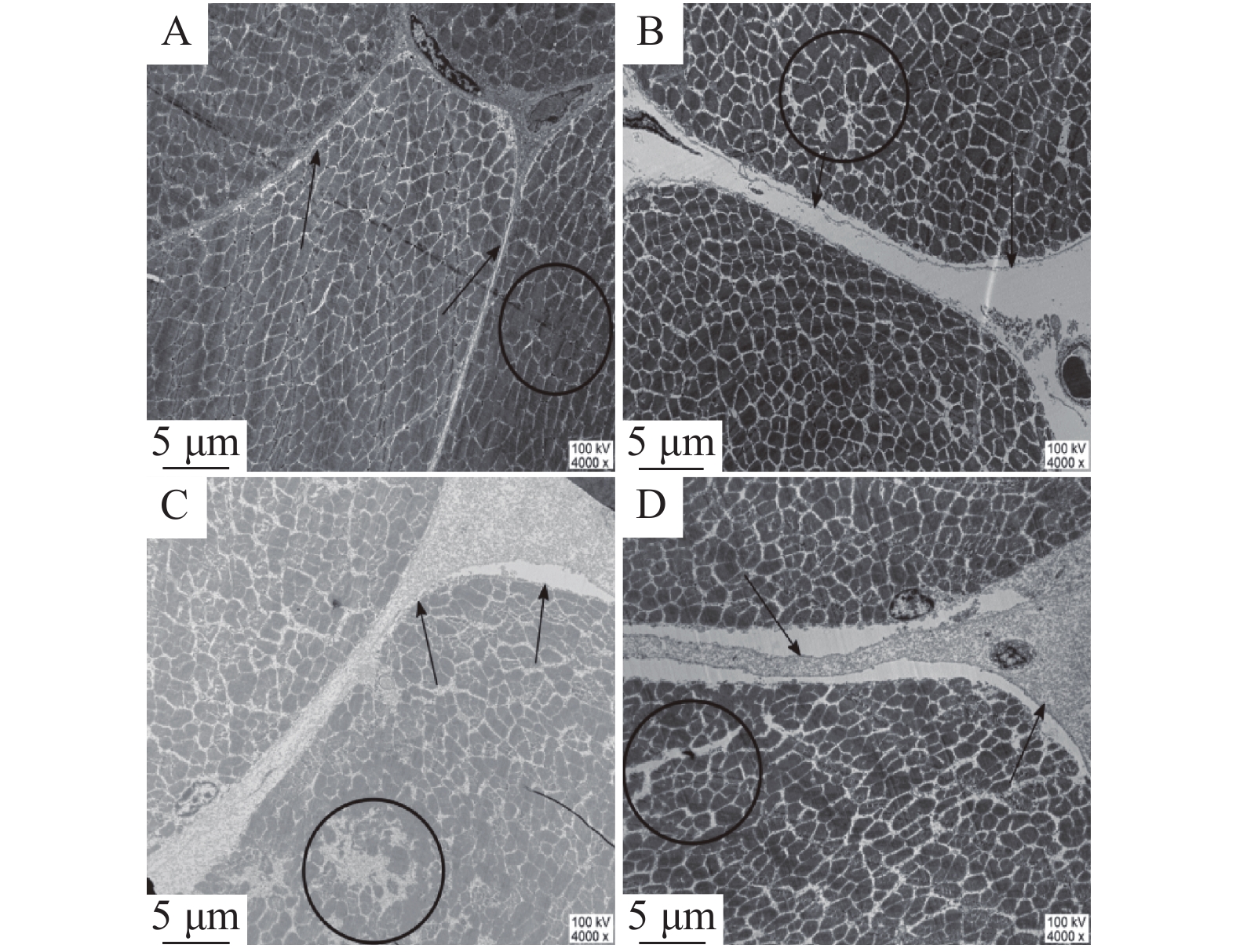
参照Luo等[17]的方法,将样品置入3.5%戊二醛试剂(pH 7.2)中进行2 h的前期固定,用0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液冲洗样品表面残留的前期固液,冲洗完成后,用2%的锇酸进行1.5 h的后期固定。两次固定完成后,将样品取出放入乙醇溶液中脱水,脱水完成后从乙醇溶液中移至室温下的丙酮溶液中,用Epon-618渗透包埋并切片。用柠檬酸铅-醋酸铀对切片进行染色,在4000倍的电子显微镜下得到细胞内外间隙图片。对每个样品的9和24 h分别进行8~10张数字照片的拍摄,用Image-Pro Plus 5.1(Image House, Denmark)软件测量肌细胞膜与细胞体之间的平均宽度(细胞内间隙)和肌细胞之间的平均宽度(细胞外间隙)。
1.2.3 TMT定量蛋白质组学检测
1.2.3.1 蛋白质提取
称取0.8 g组织样品放置于提前用液氮预冷的研钵中,添加液氮充分研磨至粉末状,加入1%的蛋白酶抑制剂裂解缓冲液,在高强度超声处理机中进行超声裂解后,放入离心机,调至4 ℃,12000×g离心10 min,去除细胞膜等碎片,将上清液吸取至干净的离心管内,利用BCA试剂盒在IMARK酶标仪中对蛋白浓度测定。
1.2.3.2 高速液相色谱分级
使用色谱柱(5 μm,4.6 mm×250 mm)对酶解后肽段进行多肽体外标记(Tandem mass tag,TMT),用pH反向高速液相色谱(High performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)分级,具体操作如下:肽段用pH=9、分级梯度为8%(8 min)、16%(35 min)、32%(25 min)的乙腈,流速均为1.0 mL/min,分离出60组分后将分离的肽段以9组分合并,合并完成后再次进行真空冷冻干燥处理以便后续操作。
1.2.3.3 液相色谱-质谱联用分析
使用液相色谱流动相A相溶解肽段后用超高效液相系统将肽段分离。流动相A、B均为甲酸乙腈混合而成的水溶液,流动相A[0.1(v/v)甲酸、0.2(v/v)乙腈];流动相B(0.1%甲酸、90%乙腈)。对液相进行梯度设置:0~38 min,6%~22% B;38~52 min,22%~32% B;52 ~56 min,32%~80% B;56~60 min,80% B, 维持流速75 nL/s。通过数据依赖型扫描(DDA)程序对数据进行采集汇总,将一级扫描中信号强度前20%的肽段用28%的能量碎裂,后用二级质谱逐个进行分析。
1.2.3.4 蛋白质鉴定
使用UniProt 数据库中Sus_scrofa_9823_PR_20190816库作为搜索数据库,利用Proteome Discoverer 2.2软件对检索数据过滤:认为可信度99%以上的肽段为可信肽段PSMs(peptide spectrum matches),含有单个肽段(特有肽段)的蛋白为可信蛋白,只保留可信的肽段和可信蛋白,使用FDR对其验证,舍弃FDR大于1%的肽段和蛋白。对鉴定到的蛋白进行GO蛋白注释。
1.2.3.5 差异蛋白的确定
根据谱图峰面积可得每个样品中各个可信肽段的相对定量值,将鉴定出的特有肽段中所包含所有肽段匹配定量信息校正后,得到特有肽段的相对定量值,最后将通过特有肽段在蛋白质中的含量对蛋白质进行相对定量。将高汁液组和低汁液组中多次重复实验得到的质谱峰面积的均值之比作为差异倍数(Fold Change,FC),对FC≥1.2倍的蛋白的质谱峰面积值进行t-检验,P值作为显著性指标,应用超几何检验计算P值,以P≤0.05为阈值,将FC≥1.2倍,且 P ≤ 0.05的蛋白定义为高汁液流失组和低汁液流失组中表达量存在显著差异的蛋白,最后针对筛选出来的差异蛋白进行GO功能富集分析。
1.3 数据分析
数据采用SPSS 23.0(SPSS程序,SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA)进行平均值、标准误差、聚类分析和相关性分析。使用image J测量软件对现有电镜图片进行细胞间距的测量。使用Inter Pro Scan v.5.14-53.0对差异蛋白进行GO注释,R package networkD3 v.0.4绘制差异蛋白互作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 肉样基本指标测定及微观结构观察
从采集到的样品中挑取汁液流失率最低的三个样品和汁液流失率最高的三个样品(每个样品重复5次),分为两组,即高汁液流失组(High Drip Loss Group,H组,n=3)和低汁液流失组(Low Drip Loss Group, L组, n=3)。将两组样品存放在4 ℃环境下,于9 和24 h后分别测量两组样品的pH、温度、肌细胞内间隙(Intracellular space)、肌细胞外间隙(Extracellular space)和肌间脂肪(instramusclar fat, IFM)含量(见表1)。
表 1 宰后存放在4 ℃下9 和24 h的H组与L组的样品的肉质指标Table 1. Meat quality indicators of samples in the H-group and L-group after slaughter at 4 ℃ for 9 and 24 h指标 汁液流失率 L组(n=3) H组(n=3) 汁液流失率(%) 0.81 ± 0.14 5.93 ± 0.22** 肌间脂肪(%) 3.26 ± 0.06 3.01 ± 0.05* pH9 h 5.74 ± 0.12 5.52 ± 0.01* pH24 h 5.78 ± 0.07 5.62 ± 0.03 温度9 h(℃) 7.03 ± 0.07 7.13 ± 0.86 温度24 h(℃) 6.03 ± 1.35 7.08 ± 0.56** 细胞内间隙9 h 0.32 ± 0.10 0.39 ± 0.11 细胞内间隙24 h 0.54 ± 0.26 0.66 ± 0.29 细胞外间隙9 h 2.39 ± 1.25 2.93 ± 0.65 细胞外间隙24 h 2.43 ± 0.74 5.21 ± 1.39** 注:*表示L组与H组组间差异显著,P<0.05;**表示L组与H组组间差异极显著,P<0.01;细胞内间隙和细胞外间隙单位为微米(μm)。 如表1所示,H组汁液流失率极显著高于L组(P<0.01)。宰后9 h时,H组pH显著低于L组(P<0.05),24 h时H组温度极显著高于L组(P<0.01)。宰后温度和pH的变化是由糖原代谢引发的,肌肉的pH下降主要是由肌糖原无氧糖酵解产生乳酸以及ATP分解产生的磷酸根离子造成的[18]。pH的下降加速了肌动球蛋白形成和肌肉收缩,从而加速汁液流出。
在电子显微镜下,观察到H组和L组样品的肌细胞微观结构如图1所示。宰后9 h的L组中(如图1A),肌原纤维的排布有序且紧凑,肌细胞膜紧密地贴合在肌细胞周边,肌细胞与肌细胞间几乎没有缝隙,而H组中(见图1C),肌原纤维排布松散,部分肌细胞膜脱离肌细胞,肌细胞间的间隙大于9 h的L的组。在宰后24 h的L组中(见图1B),大面积细胞膜脱离肌细胞,细胞内间隙和细胞外间隙对比9 h均增大。而H组中(见图1D),肌细胞膜与肌细胞间的间隙增大,与24 h时L组相比,肌细胞之间呈现出更大程度的分离。为了量化宰后肌细胞微观结构变化,使用Image-Pro Plus 5.1测量肌细胞内、外间隙。测量结果如表1所示,宰后9~24 h,H组和L组的肌细胞内外间隙值均增大,且L组细胞内外间隙小于H组,其中在24 h时,L组的细胞外间隙极显著小于H组(P<0.01)。肌细胞内外间隙的大小与汁液流失的相关性分析如表2所示。肌细胞内外间隙均与汁液流失率呈正相关。在24 h时,肌细胞外间隙同汁液流失呈显著正相关(P<0.05),这表明细胞内外间隙越大的样品汁液流失率越高,即保水性(WHC)越弱。Schäfer等[19]研究也发现宰后肌细胞间隙大,对肉的WHC有负面影响,与本实验结论相同。
表 2 宰后背最长肌中细胞内外间隙与汁液流失率的相关性Table 2. Correlation between intracellular and extracellular spaces and drip loss rate in the longissimus dorsi muscle细胞内间隙 细胞外间隙 时间(h) 9 24 9 24 汁液流失率(%) 0.536 0.804 0.598 0.882* 注:*表示在0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 2.2 蛋白质鉴定结果
对宰后9 、24 h时L组与H组的样品采用肽质量指纹法进行蛋白质组学鉴定,对所有鉴定到的酶解后肽段进行蛋白分析。成功识别出2299个蛋白质,可以进行定量的蛋白质为1476个。两组中有57个蛋白的表达量差异显著,如表3所示。
表 3 宰后9 h和24 h高低汁液流失组存在显著差异的57个蛋白Table 3. 57 proteins with significant differences in high and low drip loss groups were identified at 9 h and 24 h postmortem蛋白检索号a 蛋白质名称a 基因检索号a 物种a 蛋白得分/肽段 质谱得分(%) 差异倍数 9 h 24 h F1SRI8 肌球蛋白结合蛋白C MYBPC1 Sus scrofa 323.31/69 62.4 1.32b 1.22c F1RZM4 层粘连蛋白亚基α4 LAMA4 Sus scrofa 52.118/5 0.042 1.08c 1.21c B5KJG2 磷酸甘油酸酯变位酶 PGAM2 Sus scrofa 323.31/18 63.6 1.21b 1.24b F1S814 葡萄糖磷酸变位酶1 PGM1 Sus scrofa 323.31/30 56.6 1.34c 1.23c A0A287ARW1 肌钙蛋白T TNNT3 Sus scrofa 11.937/21 45.1 1.23c 1.35b A0A287BHG2 肌钙蛋白T TNNT3 Sus scrofa 323.31/21 47.3 1.61b 1.15b Q6S4N2 热休克蛋白70 HSPA1B Sus scrofa 323.31/23 44.3 1.21c 1.19c A0A287ANE3 LIM和衰老细胞含抗原样结构域蛋白 MYOM3 Sus scrofa 323.31/26 25.6 1.35c 1.01c I3LIE7 结合蛋白H MYBPH Sus scrofa 323.31/16 50.7 1.72c 1.10c F2Z5S8 微管蛋白α链 TUBA4A Sus scrofa 278.04/15 47 1.25c 1.11c P43368 钙蛋白酶-3 CAPN3 Sus scrofa 225.79/19 30.2 1.22c 1.21c K7GQ48 巨球蛋白α2 A2M Sus scrofa 170.36/17 15.1 1.22b 1.14b I3LN42 维生素D结合蛋白 GC Sus scrofa 267.86/11 28.5 1.24b 1.04b A0A287BTD0 LIM和衰老细胞含抗原样结构域蛋白 LIMS1 Sus scrofa 25.352/3 11.4 1.33c 1.03 P01846 链C区域 N/A Sus scrofa 141.98/5 73.3 1.58b 1.13b I3L9X0 冠蛋白 CORO6 Sus scrofa 80.9/5 14.3 1.29b 1.01c F1S431 丙氨酰 AARS Sus scrofa 25.266/4 4.9 1.21b 1.02b F2Z4Y0 小核核糖核蛋白 SNRPD3 Sus scrofa 25.11/2 23.8 1.20c 1.04c P36968 磷脂过氧化氢谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 GPX4 Sus scrofa 19.056/3 14.7 1.49c 1.66c Q29197 40号核糖体蛋白 RPS9 Sus scrofa 17.985/3 18.5 3.26b / I3L804 酪氨酸- tRNA连接酶 YARS Sus scrofa 17.626/3 7.2 1.20b 1.12b I3LB80 溶质载体家族3成员2 SLC3A2 Sus scrofa 39.458/3 7.8 1.53c 1.35b K7GRK7 腱生蛋白-X TNXB Sus scrofa 31.477/3 1.8 1.95b / Q07717 微球蛋白β2 B2M Sus scrofa 12.148/2 16.9 1.28b / F1RQC1 具有序列相似性的家族114成员A2 FAM114A2 Sus scrofa 15.059/2 6.4 1.35c 1.35b F2Z5N9 蛋白质回力球同族体 PELO Sus scrofa 14.704/2 6.8 1.22b 1.47b Q95KL4 硒蛋白W SELENOW Sus scrofa 11.99/2 24.1 3.55c 2.74c A0A287A781 中心体蛋白85 CEP85 Sus scrofa 6.7513/1 1 1.73b / A0A287A816 磷脂磷酸酶7(非活性) PLPP7 Sus scrofa 6.4318/1 6.3 1.90b 1.24b F1RN28 旁斑区域1 PSPC1 Sus scrofa 9.2318/1 5.9 1.46b 1.47b I3LPU8 异质核核糖核蛋白L HNRNPL Sus scrofa 6.4381/1 4 1.38b 1.08c F1SSL4 ATP结合区域 ABCF2 Sus scrofa 104.22/3 5.8 1.03b 1.37b A0A287BI36 PDZ和LIM区域5 PDLIM5 Sus scrofa 59.067/7 38.3 1.07b 1.37c F1SAW8 肌集钙蛋白 CASQ2 Sus scrofa 40.941/2 6.8 1.31b 1.35b F1RYZ1 跨膜四蛋白 CD151 Sus scrofa 91.064/1 3.2 1.04b 1.23c F2Z5N9 蛋白质回力球同族体 PELO Sus scrofa 74.392/2 5 1.22b 1.47b A0A286ZTL8 层粘连蛋白β2 LMNB2 Sus scrofa 56.139/5 9.1 1.02c 1.26c P62844 40S核糖体蛋白 RPS1 Sus scrofa 45.28/2 9 1.13b 1.78b A0A287B3D6 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 BCAT2 Sus scrofa 125.22/2 9.1 1.08b 1.30b A0A287ACR8 N(α)-乙酰转移酶50,NatE催化亚基 NAA50 Sus scrofa 34.773/2 14.3 1.02b 1.39b F1RJ93 转凝蛋白 TAGLN2 Sus scrofa 90.15/3 18.1 1.06b 1.06b D6QST6 2,4-dienoyl-CoA还原酶1 DECR1 Sus scrofa 58.699/2 5.18 1.25b 1.34b F1SKI0 肌球蛋白-11 MYH11 Sus scrofa 58.433/5 3.2 1.07c 1.49c A0A287AAD5 Alpha-1B-糖蛋白α1 A1BG Sus scrofa 59.067/4 9.2 1.36b 1.23c F1RLL9 IV型- 2型胶原链 COL4A2 Sus scrofa 49.715/4 3.1 1.05b 1.26b A0A287B1F9 溶质载体家族12名成员2 SLC12A2 Sus scrofa 110.08/1 1 1.05c 1.23b A0A286ZLW9 磷酸肌醇磷脂酶C PLCL2 Sus scrofa 29.58/1 1.6 1.14b 1.05c P43368 钙蛋白酶-3 CAPN3 Sus scrofa 96.299/9 14.3 1.22c 1.21b A5A8V7 热休克蛋白70 HSPA1L Sus scrofa 55.353/8 12.5 1.07c 4.70c D2ST34 富亮氨酸重复蛋白4 FBXL4 Sus scrofa 446.001/1 1.6 / 2.73b F1SJ30 6-磷酸甘露糖异构酶 MPI Sus scrofa 45.433/5 17.5 1.23b 1.23b A0A287BEP2 锚蛋白1 ANK1 Sus scrofa 79.809/1 0.6 / 1.32c I3LB80 溶质载体家族3成员2 SLC3A2 Sus scrofa 48.091/2 5.2 2.64b 3.30c A0A287A5C9 信号转换器和转录激活器 STAT1 Sus scrofa 46.88/2 4.3 2.59b 2.77c A8U4R4 转酮醇酶 TKT Sus scrofa 74.533/1 1.4 2.50b 1.60b 注:a: 从Uniprot数据库中提取蛋白序列、蛋白名称和基因;b: H组质谱峰面积度与L组质谱峰面积 的比值,即该蛋白在H组中的表达量高;c: L组质谱峰面积度与H组质谱峰面积的比值,即该蛋白在L组中的表达量高。 2.2.1 结构蛋白
结构蛋白变化对肉的持水性有重要影响,宰后结构蛋白降解会破坏肌纤维的稳定性[8]。实验结果发现,在宰后24 h两组间锚蛋白1(Ankyrin 1)和层粘连蛋白(Laminin)亚基表达量存在显著差异。锚蛋白1是结构蛋白家族中重要的一员,可将细胞骨架蛋白固定在细胞上,维持细胞形态稳定[20]。本实验发现,宰后24 h,L组中锚蛋白的表达量为H组1.32倍。这表明锚蛋白表达量高,有助于增强细胞稳定性,减少汁液流失。与Aslan等[21]研究的锚蛋白1基因表达量越多,肌肉的持水性越强一致。层粘连蛋白是位于细胞膜上的结构蛋白,与细胞外基质相连。本实验观察到宰后24 h时L组层粘连蛋白的亚基(Laminin α4)表达量为H组的1.21倍,且24 h的L组细胞外间隙明显小于H组(表1)。L组中鉴定到的层黏连蛋白亚基表达量越高,说明该蛋白在L组中存在越完整,细胞与细胞外基质的连接更加紧密,Schäfer等[19]等发现细胞与细胞外基质间间距小,有助于减小细胞间间隙,从而提高肌肉的持水能力。本文推测L组中汁液流失量低可能与其内laminin表达量大,细胞间间隙小有关。
2.2.2 糖酵解相关蛋白
宰后由肌肉向肉转化的过程中,无氧呼吸逐步代替有氧呼吸,肌细胞中与糖酵解相关的酶随即也发生变化,这些酶变化会影响糖酵解的速率,从而影响汁液流失率。宰后9、24 h时,L组中葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1的表达量均高于H组,而转酮醇酶和磷酸甘油变位酶的表达量均低于H组。
葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1(Phosphoglucomutase 1,PGM1)是肌间脂肪(intramuscular fat;IMF)合成的还原性辅因子[22]。有研究表明,在葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1基因表达量高的样品中IMF含量高,汁液流失率低[23]。Watanabe等[24]实验发现,在猪最长肌中,IMF含量高的组,汁液流失率低,持水能力强。本实验发现在宰后9、24 h时,L组的葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1表达量分别为H组的1.34倍和1.23倍,且L组的IFM含量(表1)显著高于H组(P<0.05)。L组肉具有较低的汁液流失率可能是因为葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1表达量高,IFM含量大,肌肉持水性强。
磷酸甘油变位酶(Phosphoglycerate mutase,PGAM2)是糖酵解途径中重要的酶,参与了糖酵解途径的最后一个步骤:丙酮酸在厌氧条件下转化为乳酸。肌细胞中磷酸甘油变位酶表达量高会导致3-磷酸甘油酸和磷酸烯醇丙酮酸表达量升高,进而能促进丙酮酸转化为乳酸[25],降低肌肉的pH,影响肉的持水性、肉色和肌间脂肪表达量[26]。有报道证明磷酸甘油变位酶基因表达量与肉的WHC呈负相关[27],即磷酸甘油变位酶表达量越高,汁液流失率越高。实验显示,在9、24 h时H组中磷酸甘油变位酶表达量分别为L组的1.21和1.24倍。导致H组肉样高汁液流失的原因可能是肌细胞中磷酸甘油变位酶表达量高,促使丙酮酸转化为乳酸,造成低pH和高汁液流失(表1)。
转酮醇酶(Transketolase,TKT)在磷酸戊糖途径的非氧化阶段起着关键作用。与戊糖磷酸途径中其他酶一样,它位于细胞质中[28],是碳水化合物在戊糖磷酸途径转化中非氧化阶段的关键限速酶,其表达量越高,糖酵解反应速率越快,产生乳酸量越多[29]。本实验发现在宰后9 、24 h时,H组的转酮醇酶表达量分别是L组的2.5倍和1.6倍。推测H组汁液流失率高的原因,可能是H组中转酮醇酶表达量高,糖酵解反应剧烈,乳酸产生速率加快,含量增多,导致pH下降快,汁液流失率高。因此,转酮醇酶有可能作为宰后预测宰后肉类持水性的蛋白质。前人的相关报道中未发现转酮醇酶与汁液流失有关。
2.2.3 氧化应激相关蛋白
猪肉汁液流失率的高低受到遗传、宰后蛋白质变化和氧化应激反应的剧烈程度等多种因素的影响[30]。从肌细胞中热休克蛋白70(Hsp70)的表达量可以看出宰前应激反应的剧烈程度[31]。宰前机体内应激反应越剧烈,宰后肌细胞内的Hsp70的表达量越低,样品的汁液流失率越高[32]。本试验发现24 h时,L组中Hsp70表达量是H组的4.70倍,与前人研究发现Hsp70表达量越高,汁液流失率越低,持水性越强[33],这一结论相符合。Traore等[34]学者证明氧化反应会使肌细胞结构和完整性遭到破坏。Liu等[35]通过电子显微镜观察到,被氧化试剂处理过的猪最长肌样本的细胞间隙大于对照组(未使用氧化剂处理的组),且汁液流失率高于对照组。Jeong等[36]学者证明硒蛋白W(Selenoprotein W;SELENOW),具有抗氧化活性。Li等[37]的研究发现,宰后肌肉中硒蛋白W的表达量越多,肌肉的抗氧化能力越强,汁液流失率越低,持水性越强。本实验发现宰后9和24 h,L组比H组细胞间隙小(表1),且L组的硒蛋白W表达量是H组的3.5倍和2.74倍。肉样出现高汁液流率的原因可能为肌细胞中硒蛋白W表达量低,抗氧化能力弱氧,使肌细胞结构被破坏,细胞间间隙增大造成的。
2.3 生物信息学分析
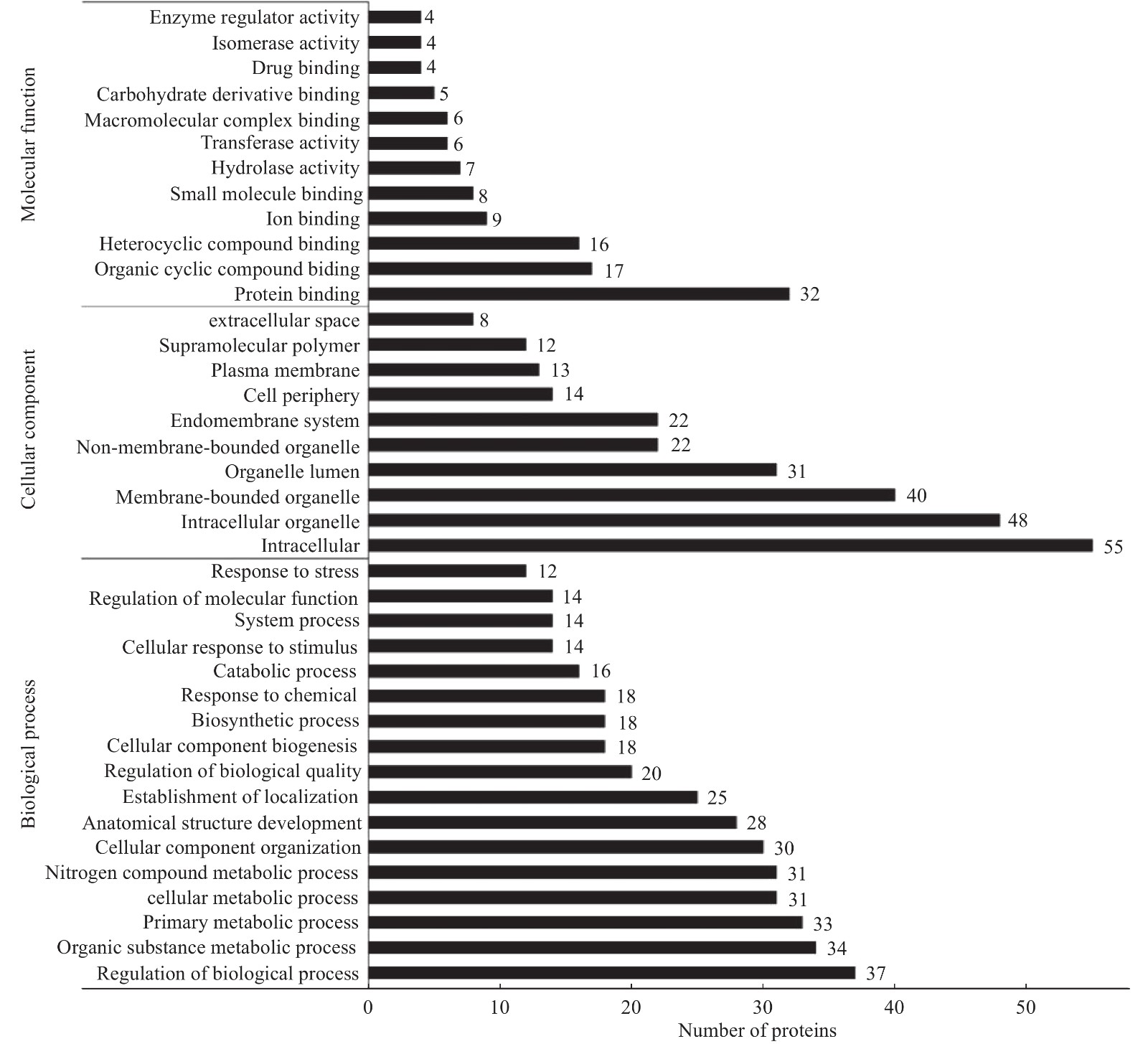
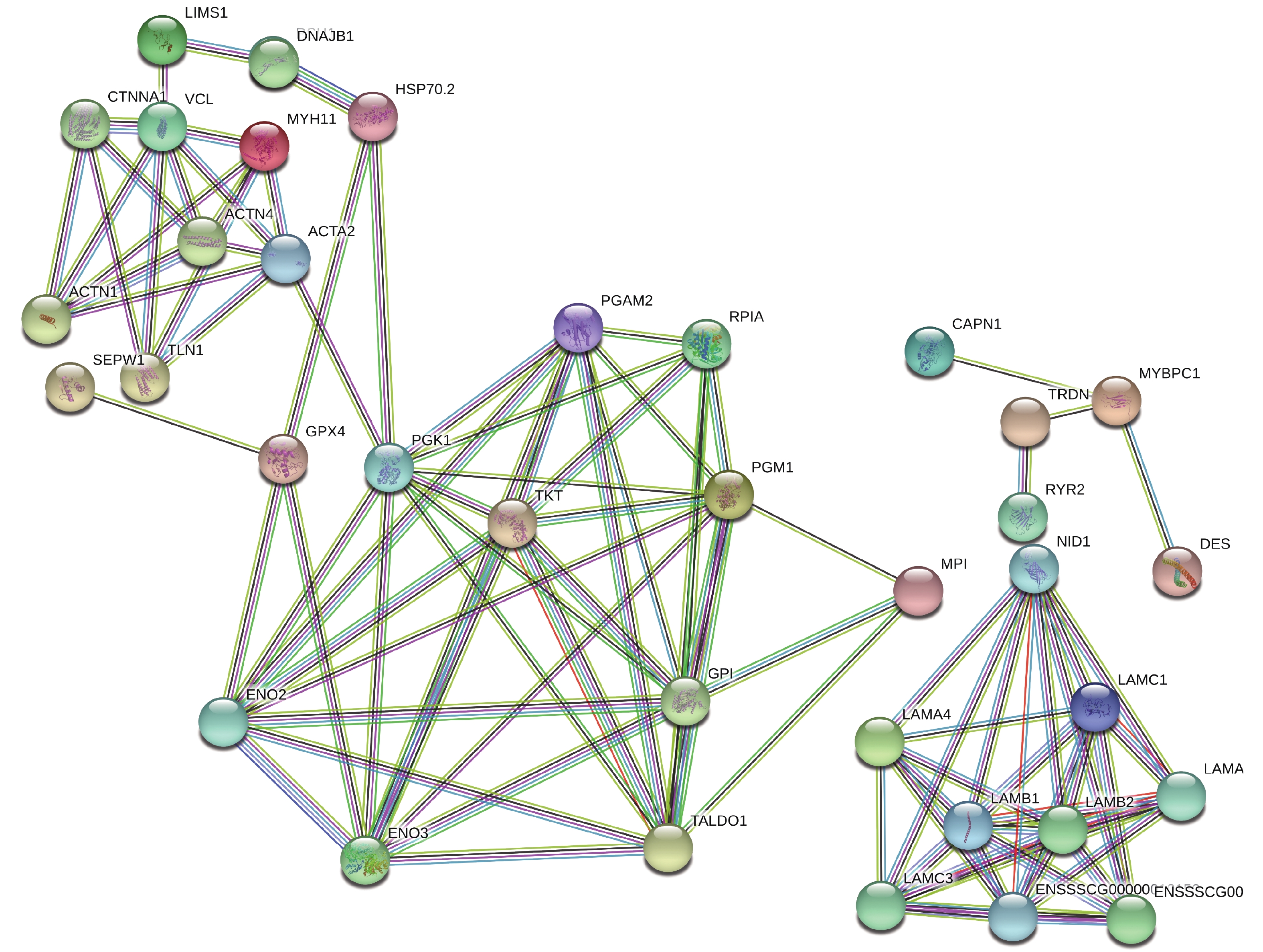
对鉴定到的差异蛋白,进行GO分类及KEGG富集,旨在寻找差异蛋白功能、涉及到的代谢途径。使用InterProScan5.14-53.0软件对差异蛋白进行聚类分析(见图2),发现H组和L组中的差异蛋白主要存在于细胞内(intracellar,GO:0005622)、细胞器(intracellar organelle,GO:0043229)、和膜系统(membrane-bounded organelle,GO:0012505)等。这些蛋白参与的生物过程(见图2)有:有机环化合物结合(organic cyclic compound binding,GO:0071704)和生物调节过程(regulation of biological process,GO:0009056)等。这些差异蛋白的分子功能(见图2)有:蛋白绑定(protein bounding, GO:0005515)等。京都基因和基因组百科全书的通路富集分析计数显示57个差异蛋白质所在的145通路(见图3),这些通路包含糖酵解途径(ssc00010)和戊醣酸途径(ssc00030)等。如图4,使用String 10.0对差异蛋白互作网络进行可视化展示(见图4)。鉴定到的差异蛋白在互作网络图中可以分为三个关键的蛋白簇,从左至右依次为氧化应激蛋白簇、糖酵解蛋白簇和细胞结构蛋白簇。前人的研究表明糖酵解蛋白簇是影响汁液流失的关键蛋白簇[38]。因糖酵解蛋白簇中的转酮醇酶(Transketolase, TKT)可以调节乳酸产生量,所以推测转酮醇酶与宰后肉的持水性有关。
3. 结论
本次TMT蛋白质组学实验分析和证实了一些蛋白质与汁液流失有关,葡萄糖磷酸变位酶-1、硒蛋白W、Hsp70和磷酸甘油变位酶在H组和L组中存有显著差异(P<0.05)。结合透射电镜和差异蛋白推测,laminin表达量越大,细胞间间隙可能小,肌肉持水性越好。本实验推测转酮醇酶与肉类持水性有关,转酮醇酶表达量高会加速磷酸戊糖途径中乳酸的形成,导致肉样持水性降低,所以转酮醇酶有可能作为宰后预测肉汁液流失的蛋白。对宰后初期蛋白质变化与持水性的关系还需进一步研究,以便更好地了解因蛋白质变化导致的持水性变化。
-
表 1 宰后存放在4 ℃下9 和24 h的H组与L组的样品的肉质指标
Table 1 Meat quality indicators of samples in the H-group and L-group after slaughter at 4 ℃ for 9 and 24 h
指标 汁液流失率 L组(n=3) H组(n=3) 汁液流失率(%) 0.81 ± 0.14 5.93 ± 0.22** 肌间脂肪(%) 3.26 ± 0.06 3.01 ± 0.05* pH9 h 5.74 ± 0.12 5.52 ± 0.01* pH24 h 5.78 ± 0.07 5.62 ± 0.03 温度9 h(℃) 7.03 ± 0.07 7.13 ± 0.86 温度24 h(℃) 6.03 ± 1.35 7.08 ± 0.56** 细胞内间隙9 h 0.32 ± 0.10 0.39 ± 0.11 细胞内间隙24 h 0.54 ± 0.26 0.66 ± 0.29 细胞外间隙9 h 2.39 ± 1.25 2.93 ± 0.65 细胞外间隙24 h 2.43 ± 0.74 5.21 ± 1.39** 注:*表示L组与H组组间差异显著,P<0.05;**表示L组与H组组间差异极显著,P<0.01;细胞内间隙和细胞外间隙单位为微米(μm)。 表 2 宰后背最长肌中细胞内外间隙与汁液流失率的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between intracellular and extracellular spaces and drip loss rate in the longissimus dorsi muscle
细胞内间隙 细胞外间隙 时间(h) 9 24 9 24 汁液流失率(%) 0.536 0.804 0.598 0.882* 注:*表示在0.05 水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 3 宰后9 h和24 h高低汁液流失组存在显著差异的57个蛋白
Table 3 57 proteins with significant differences in high and low drip loss groups were identified at 9 h and 24 h postmortem
蛋白检索号a 蛋白质名称a 基因检索号a 物种a 蛋白得分/肽段 质谱得分(%) 差异倍数 9 h 24 h F1SRI8 肌球蛋白结合蛋白C MYBPC1 Sus scrofa 323.31/69 62.4 1.32b 1.22c F1RZM4 层粘连蛋白亚基α4 LAMA4 Sus scrofa 52.118/5 0.042 1.08c 1.21c B5KJG2 磷酸甘油酸酯变位酶 PGAM2 Sus scrofa 323.31/18 63.6 1.21b 1.24b F1S814 葡萄糖磷酸变位酶1 PGM1 Sus scrofa 323.31/30 56.6 1.34c 1.23c A0A287ARW1 肌钙蛋白T TNNT3 Sus scrofa 11.937/21 45.1 1.23c 1.35b A0A287BHG2 肌钙蛋白T TNNT3 Sus scrofa 323.31/21 47.3 1.61b 1.15b Q6S4N2 热休克蛋白70 HSPA1B Sus scrofa 323.31/23 44.3 1.21c 1.19c A0A287ANE3 LIM和衰老细胞含抗原样结构域蛋白 MYOM3 Sus scrofa 323.31/26 25.6 1.35c 1.01c I3LIE7 结合蛋白H MYBPH Sus scrofa 323.31/16 50.7 1.72c 1.10c F2Z5S8 微管蛋白α链 TUBA4A Sus scrofa 278.04/15 47 1.25c 1.11c P43368 钙蛋白酶-3 CAPN3 Sus scrofa 225.79/19 30.2 1.22c 1.21c K7GQ48 巨球蛋白α2 A2M Sus scrofa 170.36/17 15.1 1.22b 1.14b I3LN42 维生素D结合蛋白 GC Sus scrofa 267.86/11 28.5 1.24b 1.04b A0A287BTD0 LIM和衰老细胞含抗原样结构域蛋白 LIMS1 Sus scrofa 25.352/3 11.4 1.33c 1.03 P01846 链C区域 N/A Sus scrofa 141.98/5 73.3 1.58b 1.13b I3L9X0 冠蛋白 CORO6 Sus scrofa 80.9/5 14.3 1.29b 1.01c F1S431 丙氨酰 AARS Sus scrofa 25.266/4 4.9 1.21b 1.02b F2Z4Y0 小核核糖核蛋白 SNRPD3 Sus scrofa 25.11/2 23.8 1.20c 1.04c P36968 磷脂过氧化氢谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 GPX4 Sus scrofa 19.056/3 14.7 1.49c 1.66c Q29197 40号核糖体蛋白 RPS9 Sus scrofa 17.985/3 18.5 3.26b / I3L804 酪氨酸- tRNA连接酶 YARS Sus scrofa 17.626/3 7.2 1.20b 1.12b I3LB80 溶质载体家族3成员2 SLC3A2 Sus scrofa 39.458/3 7.8 1.53c 1.35b K7GRK7 腱生蛋白-X TNXB Sus scrofa 31.477/3 1.8 1.95b / Q07717 微球蛋白β2 B2M Sus scrofa 12.148/2 16.9 1.28b / F1RQC1 具有序列相似性的家族114成员A2 FAM114A2 Sus scrofa 15.059/2 6.4 1.35c 1.35b F2Z5N9 蛋白质回力球同族体 PELO Sus scrofa 14.704/2 6.8 1.22b 1.47b Q95KL4 硒蛋白W SELENOW Sus scrofa 11.99/2 24.1 3.55c 2.74c A0A287A781 中心体蛋白85 CEP85 Sus scrofa 6.7513/1 1 1.73b / A0A287A816 磷脂磷酸酶7(非活性) PLPP7 Sus scrofa 6.4318/1 6.3 1.90b 1.24b F1RN28 旁斑区域1 PSPC1 Sus scrofa 9.2318/1 5.9 1.46b 1.47b I3LPU8 异质核核糖核蛋白L HNRNPL Sus scrofa 6.4381/1 4 1.38b 1.08c F1SSL4 ATP结合区域 ABCF2 Sus scrofa 104.22/3 5.8 1.03b 1.37b A0A287BI36 PDZ和LIM区域5 PDLIM5 Sus scrofa 59.067/7 38.3 1.07b 1.37c F1SAW8 肌集钙蛋白 CASQ2 Sus scrofa 40.941/2 6.8 1.31b 1.35b F1RYZ1 跨膜四蛋白 CD151 Sus scrofa 91.064/1 3.2 1.04b 1.23c F2Z5N9 蛋白质回力球同族体 PELO Sus scrofa 74.392/2 5 1.22b 1.47b A0A286ZTL8 层粘连蛋白β2 LMNB2 Sus scrofa 56.139/5 9.1 1.02c 1.26c P62844 40S核糖体蛋白 RPS1 Sus scrofa 45.28/2 9 1.13b 1.78b A0A287B3D6 支链氨基酸氨基转移酶 BCAT2 Sus scrofa 125.22/2 9.1 1.08b 1.30b A0A287ACR8 N(α)-乙酰转移酶50,NatE催化亚基 NAA50 Sus scrofa 34.773/2 14.3 1.02b 1.39b F1RJ93 转凝蛋白 TAGLN2 Sus scrofa 90.15/3 18.1 1.06b 1.06b D6QST6 2,4-dienoyl-CoA还原酶1 DECR1 Sus scrofa 58.699/2 5.18 1.25b 1.34b F1SKI0 肌球蛋白-11 MYH11 Sus scrofa 58.433/5 3.2 1.07c 1.49c A0A287AAD5 Alpha-1B-糖蛋白α1 A1BG Sus scrofa 59.067/4 9.2 1.36b 1.23c F1RLL9 IV型- 2型胶原链 COL4A2 Sus scrofa 49.715/4 3.1 1.05b 1.26b A0A287B1F9 溶质载体家族12名成员2 SLC12A2 Sus scrofa 110.08/1 1 1.05c 1.23b A0A286ZLW9 磷酸肌醇磷脂酶C PLCL2 Sus scrofa 29.58/1 1.6 1.14b 1.05c P43368 钙蛋白酶-3 CAPN3 Sus scrofa 96.299/9 14.3 1.22c 1.21b A5A8V7 热休克蛋白70 HSPA1L Sus scrofa 55.353/8 12.5 1.07c 4.70c D2ST34 富亮氨酸重复蛋白4 FBXL4 Sus scrofa 446.001/1 1.6 / 2.73b F1SJ30 6-磷酸甘露糖异构酶 MPI Sus scrofa 45.433/5 17.5 1.23b 1.23b A0A287BEP2 锚蛋白1 ANK1 Sus scrofa 79.809/1 0.6 / 1.32c I3LB80 溶质载体家族3成员2 SLC3A2 Sus scrofa 48.091/2 5.2 2.64b 3.30c A0A287A5C9 信号转换器和转录激活器 STAT1 Sus scrofa 46.88/2 4.3 2.59b 2.77c A8U4R4 转酮醇酶 TKT Sus scrofa 74.533/1 1.4 2.50b 1.60b 注:a: 从Uniprot数据库中提取蛋白序列、蛋白名称和基因;b: H组质谱峰面积度与L组质谱峰面积 的比值,即该蛋白在H组中的表达量高;c: L组质谱峰面积度与H组质谱峰面积的比值,即该蛋白在L组中的表达量高。 -
[1] Diniz W J, Banerjee P, Regitano L C, et al. Cross talk between mineral metabolism and meat quality: A systems biology overview[J]. Physiological Genomics,2019,51(11):529−538. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00072.2019
[2] 肖智超, 王桂瑛, 王雪峰, 等. 云南盐津乌骨鸡与武定鸡肌肉蛋白质组学差异研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(16):102−106, 117. [3] 马静, 武开乐, 库西塔别克·买买提依不拉音, 等. iTRAQ技术在动物生产中的应用[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2017,39(12):1599−1604. [4] 金绍明, 宁霄, 曹进, 等. 非标记蛋白定量方法在掺假肉鉴别中的应用[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(1):71−74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.01.012 [5] 牟永颖, 顾培明, 马博, 等. 基于质谱的定量蛋白质组学技术发展现状[J]. 生物技术通报,2017,33(9):73−84. [6] 赵雅娟, 苏琳, 尹丽卿, 等. 蛋白质组学技术在肉品质中的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(4):233−236. [7] Lee S H, Kim J M, Ryu Y C, et al. Effects of morphological characteristics of muscle fibers on porcine growth performance and pork quality[J]. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources,2016,36(5):583−593. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2016.36.5.583
[8] 杨汝男, 李燕清, 陈韬. 宰后猪最长肌踝蛋白降解与汁液流失的关系[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(20):12−17. [9] Wang Z, He F, Rao W, et al. Proteomic analysis of goat longissimus dorsi muscles with different drip loss values related to meat quality traits[J]. Food Science & Biotechnology,2016,25(2):425−431.
[10] Pas M F W T, Kruijt L, Pierzchala M, et al. Identification of proteomic biomarkers in longissimus dorsi as potential predictors of pork quality[J]. Meat Science,2013,95(3):679−687. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.12.015
[11] Luca A D, Mullen A M, Elia G, et al. Centrifugal drip is an accessible source for protein indicators of pork ageing and water-holding capacity[J]. Meat Science,2011,88(2):261−270. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.12.033
[12] Gap-Don, Kim, Jin-Yeon, et al. Differential abundance of proteome associated with intramuscular variation of meat quality in porcine longissimus thoracis et lumborum muscle[J]. Meat Science,2019:85−95.
[13] Sandberg A, Brance R M, Lehtio J, et al. Quantitative accuracy in mass spectrometry based proteomics of complex samples: The impact of labeling and precursor interference[J]. Journal of Proteomics,2014:133−144.
[14] Warner R D, Kaufman R G, Greaser M L. Muscle protein changes post mortem in relation to pork quality traits[J]. Meat Science,1997,45(3):339−352. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(96)00116-7
[15] Florowski T, Pisula A, Rola M, et al. Comparison of meatiness and the technological quality of pork from Polish Pulawy breed and its crosses with Polish Large White and Polish Landrace pigs[J]. Meat Science,2008,64(5):673−676.
[16] Honikel K O. Reference methods for the assessment of physical characteristics of meat[J]. Meat Science,1998,49(4):447−457. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(98)00034-5
[17] Luo X, Zhu Y, Zhou G. Electron microscopy of contractile bands in low voltage electrical stimulation beef[J]. Meat Science,2008,80(3):948−951. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.03.017
[18] 吴霜, 陈韬, 张冬怡, 等. 猪屠宰后正常肉与PSE肉中整联蛋白变化与持水性的相关性[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(21):64−67, 72. [19] Schäfer A, Rosenvold K, Purslow P. Physiological and structural events post mortem of importance for drip loss in pork[J]. Meat Science,2002,61(4):355−366. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(01)00205-4
[20] 雄安秀. 锚蛋白研究进展[J]. 国外医学(儿科分册),2003(3):159−161. [21] Aslan O, Hamill R M, Mullen A M, et al. Association between promoter polymorphisms in a key cytoskeletal gene (Ankyrin 1) and intramuscular fat and water-holding capacity in porcine muscle[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2012,39(4):3903−3914. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1169-4
[22] 王州. 基于重测序研究贵州地方住猪种基因组拷贝数变异[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019. [23] Ceasar A, Regitano L C, Koltes J E, et al. Putative regulatory factors associated with intramuscular fat content[J]. Plos One,2015,10(6):1−21.
[24] Watanabe G, Motoyama M, Nakajima I, et al. Relationship between water-holding capacity and intramuscular fat content in Japanese commercial pork loin[J]. Asian Journal of Animal Sciences,2017,31(6):914−918.
[25] 宋林霞, 徐振彪. 磷酸甘油酸变位酶[J]. 生命的化学,2011(1):90−93. [26] Koning D, Harlizius B, Rattink A P, et al. Detection and characterization of quantitative trait loci for meat quality traits in pigs[J]. Journal of Animal Science,2001,79(11):2812−2819. doi: 10.2527/2001.79112812x
[27] Yang H, He J, Wei W, et al. The c. −360 T>C mutation affects PGAM2 transcription activity and is linked with the water holding capacity of the longissimus lumborum muscle in pigs[J]. Meat Science,2016,122(12):139−144.
[28] Prejano M, Medinal F E, Fernandes P A, et al. The catalytic mechanism of human transketolase[J]. Chem Phys Chem,2019,20(21):2881−2886. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201900650
[29] Kochetov G A. et al. Structure and functioning mechanism of transketolase[J]. Proteins & Proteomics,2014,61(12):59−68.
[30] 谢华. 冷却猪肉汁液流失及控制研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2006. [31] Trocino A, Zomeno C, Birolo M, et al. Impact of pre-slaughter transport conditions on stress response, carcass traits, and meat quality in growing rabbits[J]. Meat Science,2018:68−74.
[32] Hu H, Chen L, Dai S, et al. Effect of glutamine on antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in the breast muscle of heat-stressed broilers via antioxidant genes and Hsp70 pathway[J]. Animals,2020,10(3):404. doi: 10.3390/ani10030404
[33] Wei Y, Li X, Zhang D, et al. Comparison of protein differences between high-and low-quality goat and bovine parts based on iTRAQ technology[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,289(AUG. 15):240−249.
[34] Traore S, Aubry L, Gatellier P, et al. Higher drip loss is associated with protein oxidation[J]. Meat Science,2011,90(4):917−924.
[35] Liu Z, Xiong Y L, Chen J. Protein oxidation enhances hydration but suppresses water-holding capacity in porcine longissimus muscle[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2010,58(19):10697−10704.
[36] Jeong D W, Kim E H, Kim T S, et al. Different distributions of selenoprotein W and thioredoxin during postnatal brain development and embryogenesis[J]. Molecules and Cells,2004,17(1):156−159.
[37] Li Jungang. Enhanced water-holding capacity of meat was associated with increased Sepw1 gene expression in pigs feed selenium-enriched yeast[J]. Meat Science,2011,13(1):101−112.
[38] Zhang M, Wang D, Xu X, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of proteins associated with water holding capacity in goose muscles[J]. Food Research International,2019:354−361.







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



